



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1558-1569. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020023 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020023
Special Issue: 物种形成与系统进化
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rui Hu1, Ruxiao Wang1, Shiyu Du1, Meng Li1, Yuhui Xing1, Da Pan1, Haigen Xu2,*( ), Hongying Sun1,*(
), Hongying Sun1,*( )
)
Received:2020-01-17
Accepted:2020-04-30
Online:2020-12-20
Published:2020-09-12
Contact:
Haigen Xu,Hongying Sun
Rui Hu, Ruxiao Wang, Shiyu Du, Meng Li, Yuhui Xing, Da Pan, Haigen Xu, Hongying Sun. Biodiversity and spatiotemporal variations of benthic macroinvertebrates in the Baoying Lake, Yangzhou, Jiangsu[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569.
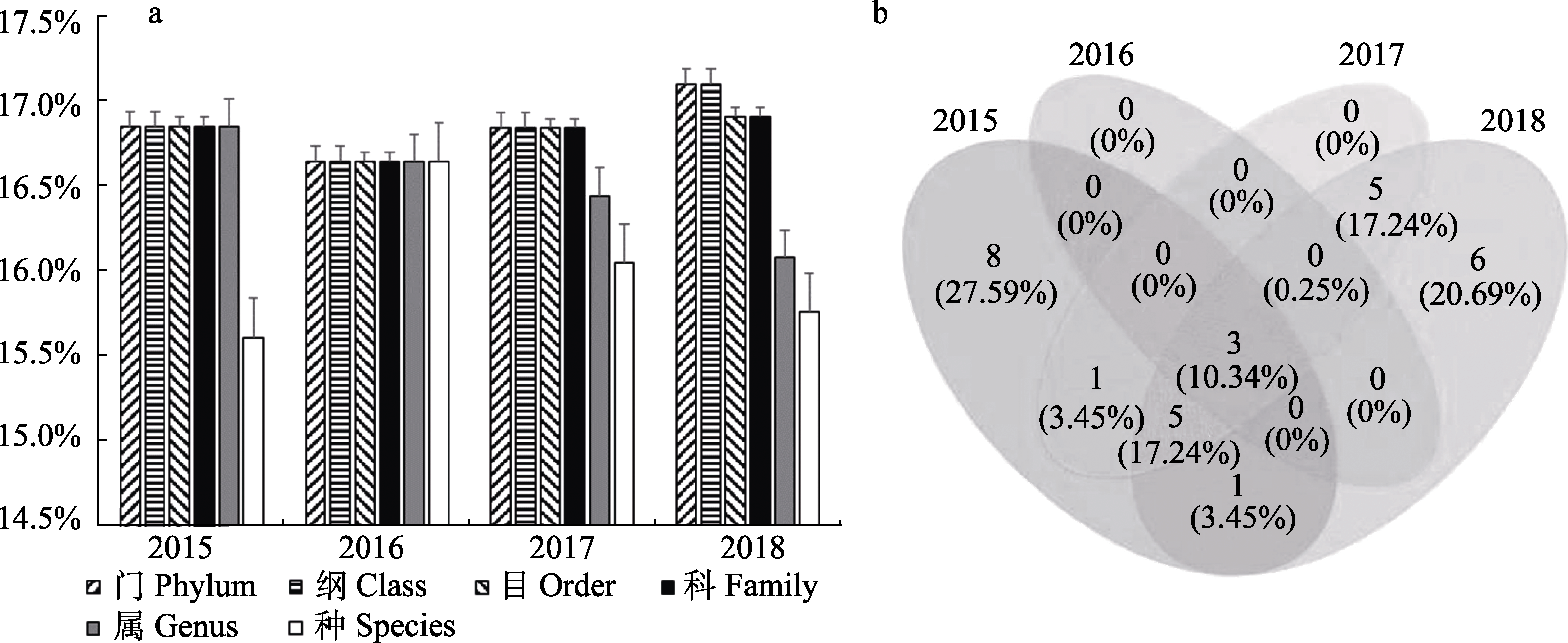
Fig. 3 Results of DNA barcoding identification of Oligochaeta and Insecta in the Baoying Lake. a, Proportion of OTUs at different classification levels and their annual change; b, Percentage of endemic or common species of Oligochaeta and Insecta.
| 物种 Species | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | |
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 472 | 0.0702 | 1,488 | 0.6889 | 694 | 0.1474 | 125 | 0.1045 | 330 | 0.2123 |
| 赤豆螺 Bithynia fuchsiana | 2,062 | 1.1788 | 1,101 | 0.3818 | 1,262 | 0.4509 | 108 | 0.0824 | 1,018 | 1.4705 |
| 檞豆螺 Bithynia misella | 708 | 0.1350 | 886 | 0.2314 | 710 | 0.1447 | 93 | 0.0659 | 110 | 0.0247 |
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 335 | 0.0287 | 408 | 0.0473 | 110 | 0.0030 | 44 | 0.0122 | 129 | 0.0281 |
| 梨形环棱螺 Bellamya purificata | 820 | 0.1752 | 301 | 0.0252 | 102 | 0.0032 | 12 | 0.0020 | 113 | 0.0327 |
| 凸旋螺 Gyraulus convexiusculu | 137 | 0.0033 | 297 | 0.0235 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 103 | 0.0153 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantor | 0 | 0 | 37 | 0.0008 | 360 | 0.0358 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 5 | 0.0001 | 202 | 0.0124 | 162 | 0.0077 | 47 | 0.0234 | 231 | 0.1236 |
| 方形环棱螺 Bellamya quadrata | 88 | 0.0021 | 215 | 0.0142 | 113 | 0.0040 | 24 | 0.0054 | 123 | 0.0318 |
Table 1 The dominant species and their dominant values (Y) of 2015-2019 in the Baoying Lake
| 物种 Species | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | 个体数 No. of individuals | 优势度 Dominant values | |
| 长角涵螺 Alocinma longicornis | 472 | 0.0702 | 1,488 | 0.6889 | 694 | 0.1474 | 125 | 0.1045 | 330 | 0.2123 |
| 赤豆螺 Bithynia fuchsiana | 2,062 | 1.1788 | 1,101 | 0.3818 | 1,262 | 0.4509 | 108 | 0.0824 | 1,018 | 1.4705 |
| 檞豆螺 Bithynia misella | 708 | 0.1350 | 886 | 0.2314 | 710 | 0.1447 | 93 | 0.0659 | 110 | 0.0247 |
| 纹沼螺 Parafossarulus striatulus | 335 | 0.0287 | 408 | 0.0473 | 110 | 0.0030 | 44 | 0.0122 | 129 | 0.0281 |
| 梨形环棱螺 Bellamya purificata | 820 | 0.1752 | 301 | 0.0252 | 102 | 0.0032 | 12 | 0.0020 | 113 | 0.0327 |
| 凸旋螺 Gyraulus convexiusculu | 137 | 0.0033 | 297 | 0.0235 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 103 | 0.0153 |
| 尖口圆扁螺 Hippeutis cantor | 0 | 0 | 37 | 0.0008 | 360 | 0.0358 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 铜锈环棱螺 Bellamya aeruginosa | 5 | 0.0001 | 202 | 0.0124 | 162 | 0.0077 | 47 | 0.0234 | 231 | 0.1236 |
| 方形环棱螺 Bellamya quadrata | 88 | 0.0021 | 215 | 0.0142 | 113 | 0.0040 | 24 | 0.0054 | 123 | 0.0318 |
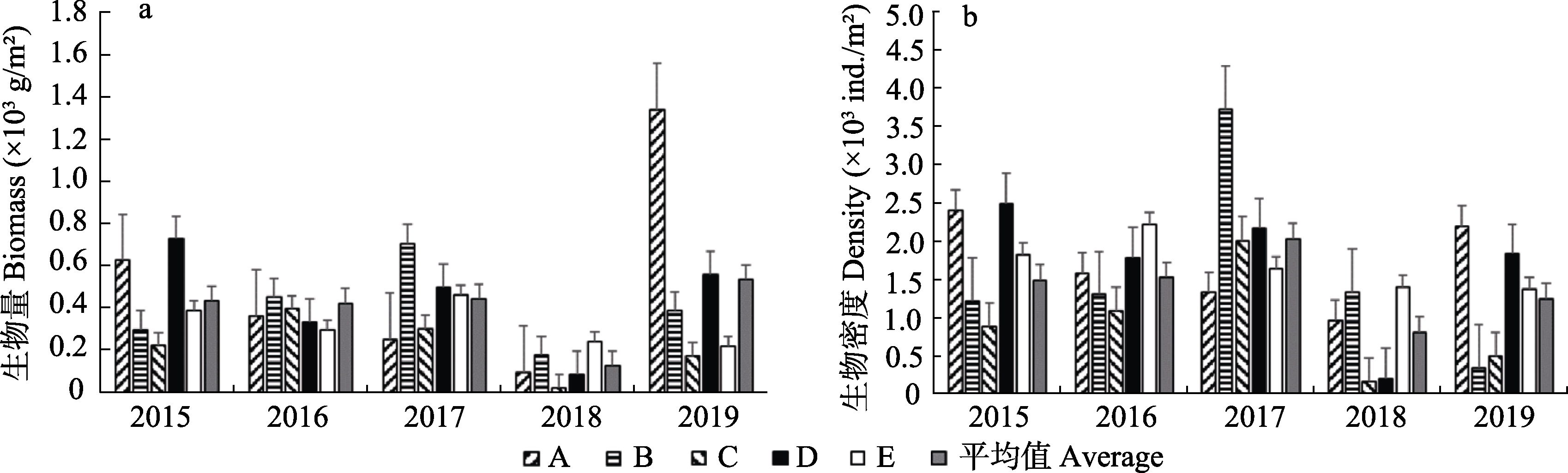
Fig. 4 The changes of the annual average biomass (a) and annual average density (b) of the benthic macroinvertebrate groups at A-E transect in the Baoying Lake
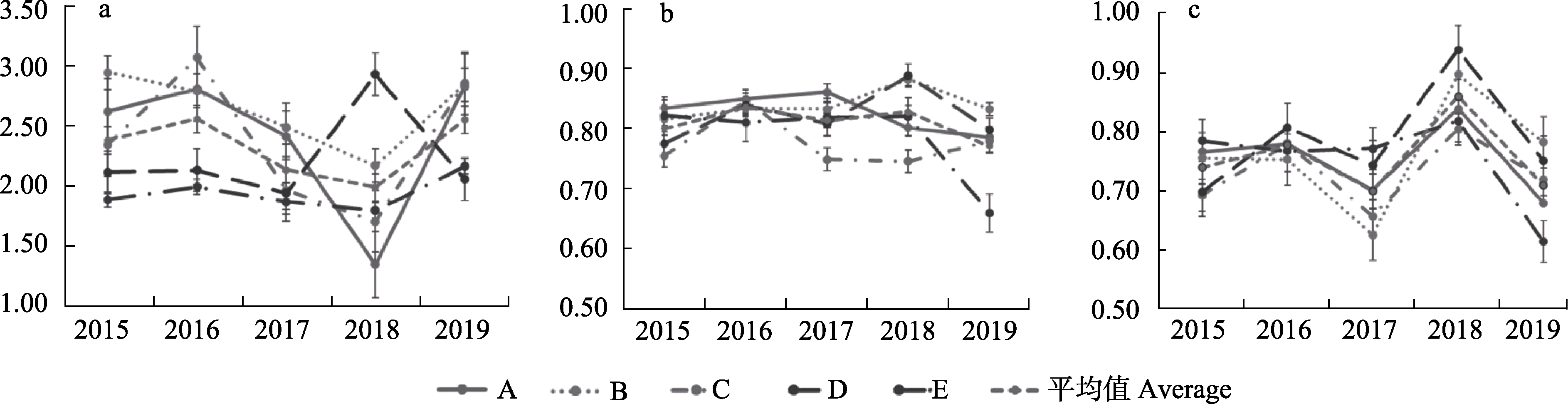
Fig. 5 Margalef abundance index (a), Simpson dominance index (b), and Pielou evenness index (c) of the benthic macroinvertebrate groups in the Baoying Lake
| 调查年份 Investigating year | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | BI指数 Biotic index |
|---|---|---|
| (H') | (BI) | |
| 2015 | 2.15 | 5.98 |
| 2016 | 2.14 | 5.78 |
| 2017 | 2.56 | 6.77 |
| 2018 | 2.32 | 6.94 |
| 2019 | 1.89 | 5.77 |
Table 2 Annual Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') and biotic index (BI) values of benthic macroinvertebrates in the Baoying Lake
| 调查年份 Investigating year | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | BI指数 Biotic index |
|---|---|---|
| (H') | (BI) | |
| 2015 | 2.15 | 5.98 |
| 2016 | 2.14 | 5.78 |
| 2017 | 2.56 | 6.77 |
| 2018 | 2.32 | 6.94 |
| 2019 | 1.89 | 5.77 |
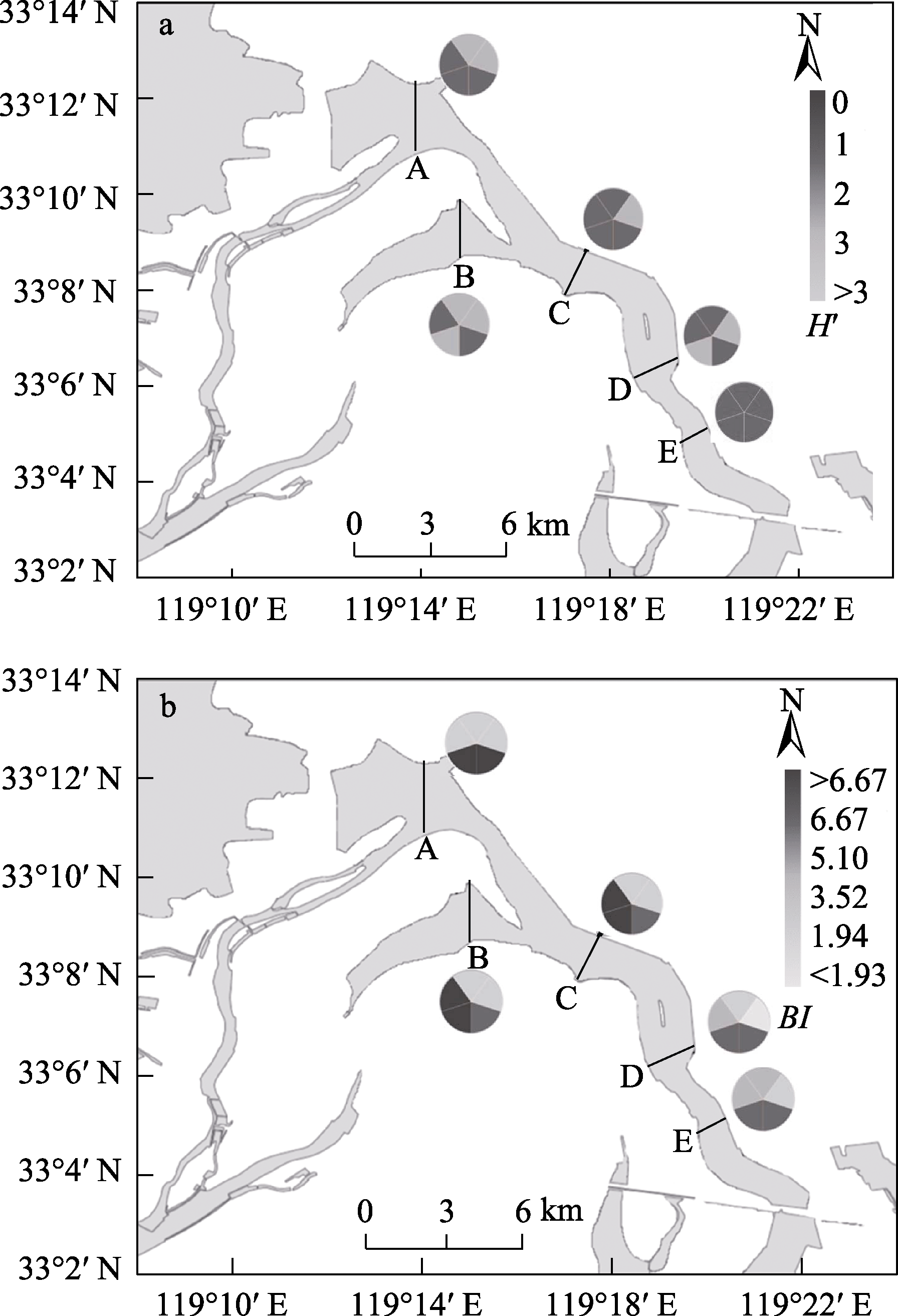
Fig. 6 The bioassessments of water qulity based on Shannon-Wiener diversity index (a) and BI index (b). The first fan-shaped section in the 12 o’clock direction represents 2015, followed by 2016 to 2019 in a clockwise direction.
| [1] | Ackefors H, Enell M ( 1994) The release of nutrients and organic matter from aquaculture systems in Nordic countries. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 10, 225-241. |
| [2] | Balderas ECS, Grac C, Berti-Equille L, Hernandez MAA ( 2016) Potential application of macroinvertebrates indices in bioassessment of Mexican streams. Ecological Indicators, 61, 558-567. |
| [3] | Bao CH, Xin YT, Hua Y, Li K ( 2018) Ecological environment quality of Baoying Lake and its countermeasures. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 46(21), 85-89(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 鲍春晖, 辛玉婷, 花月, 李科 ( 2018) 宝应湖生态环境质量状况及对策. 安徽农业科学, 46(21), 85-89.] | |
| [4] | Barbour MT( ( 1999) Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Wadeable Streams and Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish. The Offiec of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency. |
| [ 郑丙辉, 刘录三, 李黎(译) (2011) 溪流及浅河快速生物评价方案: 着生藻类、大型底栖动物及鱼类. 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG ( 2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nature Methods, 10, 57-59. |
| [6] | Brodin Y, Ejdung G, Strandberg J, Lyrholm T ( 2013) Improving environmental and biodiversity monitoring in the Baltic Sea using DNA barcoding of Chironomidae (Diptera). Molecular Ecology Resources, 13, 996-1004. |
| [7] | Cai YJ, Jiang JH, Zhang L, Chen YW, Gong ZJ ( 2012) Simplification of macrozoobenthic assemblages related to anthropogenic eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms in two large shallow subtropical lakes in China. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 15, 81-91. |
| [8] | Cai YJ, Liu JS, Dai XL, Xu H, Xue QJ, Gong ZJ ( 2014) Community structure of macrozoobenthos and bioassessment of water quality in Lake Changdang, Jiangsu Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 1224-1232(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 蔡永久, 刘劲松, 戴小琳, 许浩, 薛庆举, 龚志军 ( 2014) 长荡湖大型底栖动物群落结构及水质生物学评价. 生态学杂志, 33, 1224-1232.] | |
| [9] | Cao Y, Shen WJ, Chen L, Hu FL, Zhou L, Xu HG ( 2016) Application of metabarcoding technology in studies of fungal diversity. Biodiversity Science, 24, 932-939(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 曹云, 沈文静, 陈炼, 胡飞龙, 周蕾, 徐海根 ( 2016) Metabarcoding技术在真菌多样性研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 24, 932-939.] | |
| [10] |
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R ( 2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7, 335-336.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Chen YQ, Xu ZL, Wang YL, Hu FX, Hu H, Gu GC ( 1995) An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) River estuarine area. I. Biomass distribution of dominant species. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2, 49-58(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 陈亚瞿, 徐兆礼, 王云龙, 胡方西, 胡辉, 谷国传 ( 1995) 长江口河口锋区浮游动物生态研究.I. 生物量及优势种的平面分布. 中国水产科学, 2, 49-58.] | |
| [12] | Covich AP, Palmer MA, Crowl TA ( 1999) The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems. BioScience, 49, 119-127. |
| [13] | Dai AY ( 1999) Fauna Sinica · Arthropoda · Crustacea · Malacostraca · Decapoda · Parathelphusidae · Potamidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 戴爱云 ( 1999) 中国动物志 · 节肢动物门 · 甲壳动物亚门 · 软甲纲 · 十足目 · 束腹蟹科 · 溪蟹科. 科学出版社,北京.] | |
| [14] | Dai JH, Sun HY, Wu J ( 2016) Study on fish composition and dominant species in the Baoying Lake, Jiangsu Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 44(3), 74-76(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 戴建华, 孙红英, 吴军 ( 2016) 江苏省宝应湖鱼类组成和优势种研究. 安徽农业科学, 44(3), 74-76.] | |
| [15] | Duan XH, Wang ZY, Xu MH ( 2010) Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Application in the Assessment of Stream Ecology. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 段学花, 王兆印, 徐梦花 ( 2010) 底栖动物与河流生态评价. 清华大学出版社,北京.] | |
| [16] |
Edgar RC ( 2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Geller J, Meyer C, Parker M, Hawk H ( 2013) Redesign of PCR primers for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I for marine invertebrates and application in all-taxa biotic surveys. Molecular Ecology Resources, 13, 851-861.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Gong ZJ, Xie P, Tang HJ, Wang SD ( 2001) The influence of eutrophication upon community structure and biodiversity of macrozoobenthos. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 25, 210-216(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 龚志军, 谢平, 唐汇涓, 王士达 ( 2001) 水体富营养化对大型底栖动物群落结构及多样性的影响. 水生生物学报, 25, 210-216.] | |
| [19] | Han MS, Shu YF ( 1995) Atlas of Freshwater Species in China. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 韩茂森, 束蕴芳 ( 1995) 中国淡水生物图谱. 海洋出版社,北京.] | |
| [20] | Hebert PD, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR ( 2003) Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I divergences among closely related species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 270(Suppl. 1), S96-S99. |
| [21] | James RT, David DH, Donald FC, Timothy LN, Winter DM ( 2005) Effects of removal of a small dam on downstream macroinvertebrate and algal assemblages in a Pennsylvania stream. The North American Benthological Society, 24, 192-207. |
| [22] | Jin Q, Chen F, Luo GJ, Cai WJ, Liu X, Wang H, Yang CQ, Hao MD, Zhang AB ( 2016) Estimation of species richness of moths (Insecta: Lepidoptera) based on DNA barcoding in Suqian, China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1296-1305(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 金倩, 陈芬, 罗桂杰, 蔡卫佳, 刘旭, 王昊, 杨采青, 郝梦迪, 张爱兵 ( 2016) 基于DNA条形码的物种丰富度估计: 以宿迁地区鳞翅目蛾类为例. 生物多样性, 24, 1296-1305.] | |
| [23] | Kutti T, Hansen PK, Ervik A, Høisæter T, Johannessen P ( 2007) Effects of organic effluents from a salmon farm on a fjord system. II. Temporal and spatial patterns in infauna community composition. Aquaculture, 262, 355-366. |
| [24] |
Leray M, Yang JY, Meyer CP, Mills SC, Agudelo N, Ranwez V, Boehm JT, Machida RJ ( 2013) A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Frontiers in Zoology, 10, 34.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Li CL, Wang MX, Cheng FP, Sun S ( 2011) DNA barcoding and its application to marine zooplankton ecology. Biodiversity Science, 19, 805-814(in Chinese with English abstract).
DOI URL |
| [ 李超伦, 王敏晓, 程方平, 孙松 ( 2011) DNA条形码及其在海洋浮游动物生态学研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 19, 805-814.] | |
| [26] | Li J, Yang J, Huang Y ( 2016) Characterizing the aquatic biodiversity of the Qinling Mountains using DNA metabarcoding approach. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 6103-6112(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 李杰, 杨婧, 黄原 ( 2016) 应用DNA复合条形码技术研究秦岭水生动物多样性. 生态学报, 36, 6103-6112.] | |
| [27] |
Li M, Wei TT, Shi BY, Hao XY, Xu HG, Sun HY ( 2019) Biodiversity monitoring of freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates using environmental DNA. Biodiversity Science, 27, 480-490(in Chinese with English abstract).
DOI URL |
| [ 李萌, 尉婷婷, 史博洋, 郝希阳, 徐海根, 孙红英 ( 2019) 环境DNA技术在淡水底栖大型无脊椎动物多样性监测中的应用. 生物多样性, 27, 480-490.] | |
| [28] | Liang YL, Wang HZ ( 1999) Zoobenthos. In: Advanced Hydrobiology (ed. Liu JK), pp. 241-259. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 梁彦龄, 王洪铸 ( 1999) 底栖动物(第十章). 见: 高级水生生物学(刘建康主编), 241-259页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Liu YY, Zhang WZ, Wang YX, Wang EY ( 1979) Economic Fauna of China: Freshwater Mollusk. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘月英, 张文珍, 王跃先, 王恩义 ( 1979) 中国经济动物: 淡水软体动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Ma DG, Wu W, Chen ZF, Yin H, Chen YJ ( 2017) Composition and diversity analysis of macroinvertebrate in water body of Baoying Lake. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 45(15), 14-17(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 马德高, 吴蔚, 陈志芳, 殷慧, 陈宇洁 ( 2017) 宝应湖水体大型底栖无脊椎动物组成和多样性分析. 安徽农业科学, 45(15), 14-17.] | |
| [31] |
Magoc T, Salzberg SL ( 2011) FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27, 2957-2963.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] | Markert B, Wappelhorst O, Weckert V, Herpin U, Siewers U, Friese K, Breulmann G ( 1999) The use of bioindicators for monitoring the heavy-metal status of the environment. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 240, 425-429. |
| [33] | Morse JC, Yang LF, Tian LX ( 1994) Aquatic Insects of China Useful for Monitoring Water Quality. Hohai University Press, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ Morse JC, 杨莲芳, 田立新 (1994) 中国水生昆虫及其水质监测应用. 河海大学出版社, 南京.] | |
| [34] | Mu YL, Shi HT, Zhao BW, Sun CX, Gao YS, Zhang ZJ, Li CJ ( 2018) Pollution load of nitrogen and phosphorus from cage aquaculture in Yangcheng Lake. China Water & Wastewater, 34(21), 86-91(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 穆玉林, 石鸿韬, 赵博文, 孙承兴, 高月淑, 张振家, 李春杰 ( 2018) 阳澄湖围网养殖氮磷污染负荷分析. 中国给水排水, 34(21), 86-91.] | |
| [35] | Niu ZH, Hu TX, He GJ, Yang ZJ ( 2008) Function analysis and scientific utilization for the Baoying Lake wetlands. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (20), 321-322, 324. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钮兆花, 胡天新, 何国俊, 杨正俊 ( 2008) 宝应湖湿地功能分析及其科学利用. 现代农业科技,(20), 321-322, 324. ] | |
| [36] | Ouyang ZY (2010) Review of 40-year Development of Chinese Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 欧阳志云 ( 2010) 中国生态学学科40年发展回顾. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] |
Quan WM, Shen XQ, Yan LJ ( 2003) Advances in research of biological purification of eutrophic water body. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14, 2057-2061(in Chinese with English abstract).
URL PMID |
|
[ 全为民, 沈新强, 严力蛟 ( 2003) 富营养化水体生物净化效应的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 14, 2057-2061.]
PMID |
|
| [38] | Reavell P (1980) A study of the diets of some British freshwater gastropods. Journal of Conchology, 30, 253-271. |
| [39] |
Resh VH ( 2007) Multinational, freshwater biomonitoring programs in the developing world: Lessons learned from African and Southeast Asian river surveys. Environmental Management, 39, 737-748.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] | Sahu BC, Adhikari S, Dey L ( 2013) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus budget in shrimp (Penaeus monodon) culture ponds in eastern India. Aquaculture International, 21, 453-466. |
| [41] | Shannon CE ( 1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illiois Press, Urbana. |
| [42] |
Silva FL, Wiedenbrug S ( 2014) Integrating DNA barcodes and morphology for species delimitation in the Corynoneura group (Diptera: Chironomidae: Orthocladiinae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 104, 65-78.
URL PMID |
| [43] | Song Y, Huang Y ( 2016) The application of DNA metabarcoding in the study of soil animal diversity in Taibai Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 4531-4539(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 宋飏, 黄原 ( 2016) DNA复合条形码在太白山土壤动物多样性研究中的应用. 生态学报, 36, 4531-4539.] | |
| [44] | Sun HY, Li P, Yin JW, Ji YK ( 2013) Monitoring freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. In: Generality to Biological Species Resource Monitoring (ed. Xu HG), pp. 233-261. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 孙红英, 李鹏, 殷稼雯, 纪永坤 ( 2013) 淡水底栖大型无脊椎动物监测(第十一章). 见: 生物物种资源监测概论(徐海根主编), 233-261页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [45] |
Tang BP, Zhou KY, Song DX, Yang G, Dai AY ( 2003) Molecular systematics of the Asian mitten crabs, genus Eriocheir (Crustacea : Brachyura). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 29, 309-316.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] | Wang BX ( 2003) Water Quality Bioassessment Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates. PhD dissertation, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王备新 ( 2003) 大型底栖无脊椎动物水质生物评价研究. 博士学位论文, 南京农业大学, 南京.] | |
| [47] | Wu DH, Wang BX, Zhang Y, Yang LF ( 2011) Advances in the use of biotic index for water quality bioassessment with benthic macroinvertebrate and its perspective in China. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 34, 132-137(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 吴东浩, 王备新, 张咏, 杨莲芳 ( 2011) 底栖动物生物指数水质评价进展及在中国的应用前景. 南京农业大学学报, 34, 132-137.] | |
| [48] | Wu ZN ( 2013) Analysis and scientific utilization of function in the Baoying Lake wetlands. Modern Horticulture, ( 8), 107. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴兆年 ( 2013) 宝应湖湿地功能的分析与利用. 现代园艺,( 8), 107.] | |
| [49] |
Xing Y, Wu XP, Ouyang S, Zhang JQ, Xu J, Yin SL, Xie ZC ( 2019) Assessment of macrobenthos biodiversity and potential human-induced stressors in the Ganjiang River system. Biodiversity Science, 27, 648-657(in Chinese with English abstract).
DOI URL |
| [ 邢圆, 吴小平, 欧阳珊, 张君倩, 徐靖, 银森录, 谢志才 ( 2019) 赣江水系大型底栖动物多样性与受胁因子初探. 生物多样性, 27, 648-657.] | |
| [50] | Xiong JL, Mei XG, Hu CL ( 2003) Comparasion of community structure and biodiversity of zoobenthos in lakes of different pollution states. Journal of Lake Sciences, 15(2), 66-74. (in Chinese) |
| [ 熊金林, 梅兴国, 胡传林 ( 2003) 不同污染程度湖泊底栖动物群落结构及多样性比较. 湖泊科学, 15(2), 66-74.] | |
| [51] | Yang M, Kou Q, Li XZ ( 2018) Advances in DNA barcoding of macrozoobenthos in coastal waters of China. Marine Sciences, 42, 163-173(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 杨梅, 寇琦, 李新正 ( 2018) 中国近海大型底栖动物DNA条形码的研究进展. 海洋科学, 42, 163-173.] | |
| [52] | Zhang X, Zhang XW, Yang JH, Zhou GD ( 2016) Applying DNA barcoding for identification of some invertebrate macrozoobenthos at Taihu Lake Basin. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 8(6), 18-21, 25(in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [ 张翔, 张效伟, 杨江华, 周国栋 ( 2016) 应用物种DNA条形码识别太湖流域部分底栖无脊椎动物种类. 环境监控与预警, 8(6), 18-21, 25.] | |
| [53] | Zhou KY, Gui H, Sun HY, Su CR, Zhao Q, Chang Q ( 2005) Jiangsu Local Chronicles, Zoography. Phoenix Publishing House, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周开亚, 归鸿, 孙红英, 苏翠荣, 赵强, 常青 ( 2005) 江苏省志 · 生物志 · 动物篇. 凤凰出版社, 南京.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()