



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 557-566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019021 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019021
Special Issue: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhang Xue1,Li Xing’an2,Su Qinzhi1,Cao Qina1,Li Chenyi1,Niu Qingsheng2,*( ),Zheng Hao1,*(
),Zheng Hao1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-25
Accepted:2019-05-07
Online:2019-05-20
Published:2019-05-20
Contact:
Niu Qingsheng,Zheng Hao
Zhang Xue, Li Xing’an, Su Qinzhi, Cao Qina, Li Chenyi, Niu Qingsheng, Zheng Hao. A curated 16S rRNA reference database for the classification of honeybee and bumblebee gut microbiota[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(5): 557-566.
| 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 其他名 Other names | BGM-Db数据库聚类名 BGM-Db names | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snodgrassella | Snodgrassella alvi | Beta | Snodgrassella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Gilliamella | Gilliamella apicola | Gamma-1 | Gilliamella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Frischella | Frischella perrara | Gamma-2 | Frischella | Engel et al, 2013 |
| Schmidhempelia | ‘Candidatus Schmidhempelia bombi’ | Schmidhempelia | Martinson et al, 2014 | |
| Bartonella | Bartonella apis | Alpha-1 | Bartonella apis | Moran, 2015 |
| Commensalibacter | Commensalibacter intestini | Alpha-2.1 | Commensalibacter Alpha2.1 | Kwong et al, 2014b |
| Bombella | Bombella apis | Alpha-2.2 | Bombella Alpha2.2 | Yun et al, 2017 |
| Bombella intestini | Yun et al, 2017 | |||
| Parasaccharibacter | Parasaccharibacter apium | Moran, 2015 | ||
| Lactobacillus | Lactobacillus mellis | Firm-4 | Lactobacillus Firm-4 | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 |
| Lactobacillus mellifer | ||||
| Lactobacillus apis | Firm-5 | Lactobacillus Firm-5 | Kwong et al, 2014b | |
| Lactobacillus helsingborgensis | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 | |||
| Lactobacillus melliventris | ||||
| Lactobacillus kimbladii | ||||
| Lactobacillus kullabergensis | ||||
| Lactobacillus apinorum | ||||
| Lactobacillus kunkeei | / | Lactobacillus kunkeei | Moran, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium | Bifidobacterium asteroides | / | Bifidobacterium asteroides | Bottacini et al, 2012 |
| Bifidobacterium coryneforme | / | Bifidobacterium coryneforme/indicum | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium indicum | / | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bombi | / | Bifidobacterium bombi/commune/bohemicum | Killer et al, 2009 | |
| Bifidobacterium commune | / | Praet et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bohemicum | / | Killer et al, 2011 | ||
| Bombiscardovia | Bombiscardovia coagulans | / | Bombiscardovia | Killer et al, 2010 |
| Apibacter | Apibacter adventoris | / | Apibacter | Kwong & Moran, 2016 |
| Apibacter mensalis | / | Praet et al, 2016 |
Table 1 List of the nomenclature of the curated bacterial species from bee gut
| 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 其他名 Other names | BGM-Db数据库聚类名 BGM-Db names | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snodgrassella | Snodgrassella alvi | Beta | Snodgrassella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Gilliamella | Gilliamella apicola | Gamma-1 | Gilliamella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Frischella | Frischella perrara | Gamma-2 | Frischella | Engel et al, 2013 |
| Schmidhempelia | ‘Candidatus Schmidhempelia bombi’ | Schmidhempelia | Martinson et al, 2014 | |
| Bartonella | Bartonella apis | Alpha-1 | Bartonella apis | Moran, 2015 |
| Commensalibacter | Commensalibacter intestini | Alpha-2.1 | Commensalibacter Alpha2.1 | Kwong et al, 2014b |
| Bombella | Bombella apis | Alpha-2.2 | Bombella Alpha2.2 | Yun et al, 2017 |
| Bombella intestini | Yun et al, 2017 | |||
| Parasaccharibacter | Parasaccharibacter apium | Moran, 2015 | ||
| Lactobacillus | Lactobacillus mellis | Firm-4 | Lactobacillus Firm-4 | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 |
| Lactobacillus mellifer | ||||
| Lactobacillus apis | Firm-5 | Lactobacillus Firm-5 | Kwong et al, 2014b | |
| Lactobacillus helsingborgensis | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 | |||
| Lactobacillus melliventris | ||||
| Lactobacillus kimbladii | ||||
| Lactobacillus kullabergensis | ||||
| Lactobacillus apinorum | ||||
| Lactobacillus kunkeei | / | Lactobacillus kunkeei | Moran, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium | Bifidobacterium asteroides | / | Bifidobacterium asteroides | Bottacini et al, 2012 |
| Bifidobacterium coryneforme | / | Bifidobacterium coryneforme/indicum | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium indicum | / | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bombi | / | Bifidobacterium bombi/commune/bohemicum | Killer et al, 2009 | |
| Bifidobacterium commune | / | Praet et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bohemicum | / | Killer et al, 2011 | ||
| Bombiscardovia | Bombiscardovia coagulans | / | Bombiscardovia | Killer et al, 2010 |
| Apibacter | Apibacter adventoris | / | Apibacter | Kwong & Moran, 2016 |
| Apibacter mensalis | / | Praet et al, 2016 |
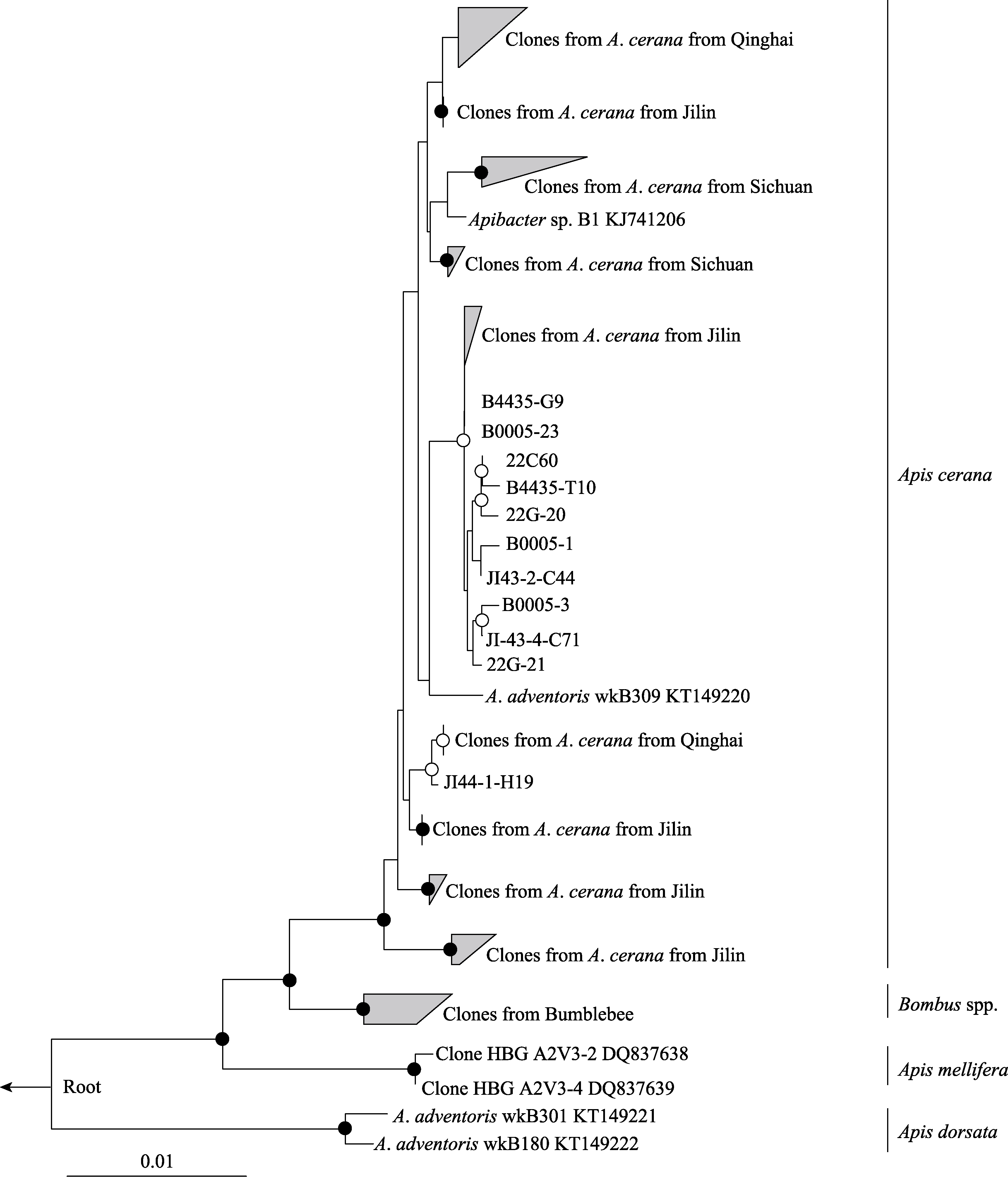
Fig. 1 A maximum-likelihood tree of the Apibacter genus from A. cerana based on the near full-length 16S rRNA sequences (1,168 bp). Bootstrap values are indicated at the branching nodes (· > 95%, 〇 > 75%).
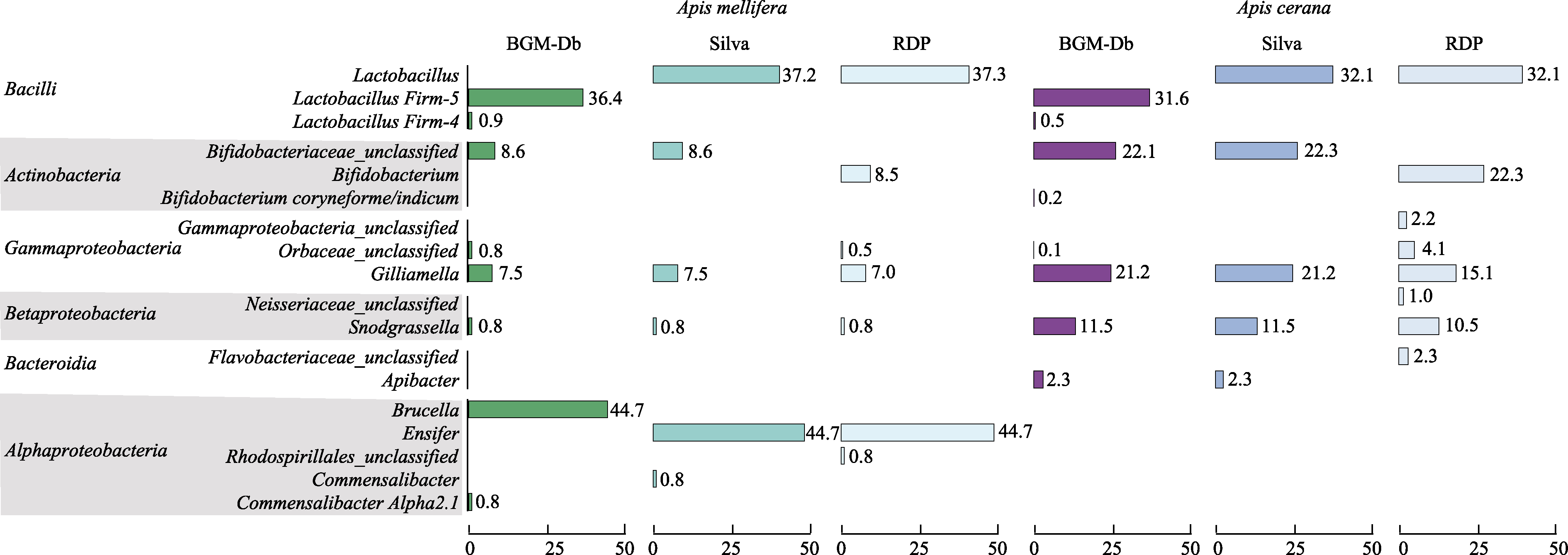
Fig. 2 Comparison of the behaviors of the BGM-Db, SILVA, and Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) databases when they are used in the classification of the gut microbiota of Apis cerana and Apis mellifera
| [1] |
Asama T, Arima TH, Gomi T, Keishi T, Tani H, Kimura Y, Tatefuji T, Hashimoto K ( 2015) Lactobacillus kunkeei YB38 from honeybee products enhances IgA production in healthy adults. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 119, 818-826.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bottacini F, Milani C, Turroni F, Sánchez B, Foroni E, Duranti S, Serafini F, Viappiani A, Strati F, Ferrarini A, Delledonne M, Henrissat B, Coutinho P, Fitzgerald GF, Margolles A, van Sinderen D, Ventura M ( 2012) Bifidobacterium asteroides PRL2011 genome analysis reveals clues for colonization of the insect gut. PLoS ONE, 7, e44229.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM ( 2014) Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D633-D642.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Corby-Harris V, Snyder L, Meador CAD, Naldo R, Mott B, Anderson KE ( 2016) Parasaccharibacter apium, gen. nov., sp. nov., improves honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) resistance to Nosema. Journal of Economic Entomology, 109, 537-543.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Corby-Harris V, Snyder LA, Schwan MR, Maes P, McFrederick QS, Anderson KE ( 2014) Origin and effect of Alpha 2.2 Acetobacteraceae in honey bee larvae and description of Parasaccharibacter apium gen. nov., sp. nov. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 7460-7472.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Cox-Foster DL, Conlan S, Holmes EC, Palacios G, Evans JD, Moran NA, Quan PL, Briese T, Hornig M, Geiser DM, Martinson V, vanEngelsdorp D, Kalkstein AL, Drysdale A, Hui J, Zhai J, Cui L, Hutchison SK, Simons JF, Egholm M, Pettis JS, Lipkin WI ( 2007) A metagenomic survey of microbes in honey bee colony collapse disorder. Science, 318, 283-287.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Ellegaard KM, Tamarit D, Javelind E, Olofsson TC, Andersson SGE, Vásquez A ( 2015) Extensive intra-phylotype diversity in Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria from the honeybee gut. BMC Genomics, 16, 284.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Engel P, Bartlett KD, Moran NA ( 2015) The bacterium Frischella perrara causes scab formation in the gut of its honeybee host. mBio, 6, e00193-15. |
| [9] | Engel P, Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2013) Frischella perrara gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gammaproteobacterium isolated from the gut of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63, 3646-3651. |
| [10] |
Engel P, Martinson VG, Moran NA ( 2012) Functional diversity within the simple gut microbiota of the honey bee. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 11002-11007.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Engel P, Stepanauskas R, Moran NA ( 2014) Hidden diversity in honey bee gut symbionts detected by single-cell genomics. PLoS Genetics, 10, e1004596.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Killer J, Kopečný J, Mrázek J, Havlík J, Koppová I, Benada O, Rada V, Kofroňová O ( 2010) Bombiscardovia coagulans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Bifidobacteriaceae isolated from the digestive tract of bumblebees. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 33, 359-366.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Killer J, Kopecny J, Mrazek J, Koppova I, Havlik J, Benada O, Kott T ( 2011) Bifidobacterium actinocoloniiforme sp. nov. and Bifidobacterium bohemicum sp. nov., from the bumblebee digestive tract. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 61, 1315-1321.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Killer J, Kopecny J, Mrazek J, Rada V, Benada O, Koppova I, Havlik J, Straka J ( 2009) Bifidobacterium bombi sp. nov., from the bumblebee digestive tract. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, 2020-2024.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kim EK, Kim SH, Nam HJ, Choi MK, Lee KA, Choi SH, Seo YY, You H, Kim B, Lee WJ ( 2012) Draft genome sequence of Commensalibacter intestini A911T, a symbiotic bacterium isolated from Drosophila melanogaster intestine. Journal of Bacteriology, 194, 1246.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Klein AM, Vaissière BE, Cane JH, Steffan-Dewenter I, Cunningham SA, Kremen C, Tscharntke T ( 2007) Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274, 303-313.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Kwong WK, Engel P, Koch H, Moran NA ( 2014 a) Genomics and host specialization of honey bee and bumble bee gut symbionts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 11509-11514.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Kwong WK, Mancenido AL, Moran NA ( 2014 b) Genome sequences of Lactobacillus sp. strains wkB8 and wkB10, members of the Firm-5 clade, from honey bee guts. Genome Announcements, 2, e01176-14. |
| [19] | Kwong WK, Medina LA, Koch H, Sing KW, Soh EJY, Ascher JS, Jaffé R, Moran NA ( 2017) Dynamic microbiome evolution in social bees. Science Advances, 3, 1-16. |
| [20] |
Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2013) Cultivation and characterization of the gut symbionts of honey bees and bumble bees: Description of Snodgrassella alvi gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Neisseriaceae of the betaproteobacteria, and Gilliamella apicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of Orbaceae fam. nov., Orbales ord. nov., a sister taxon to the order 'Enterobacteriales' of the Gammaproteobacteria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63, 2008-2018.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2016) Apibacter adventoris gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from honey bees. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 1323-1329.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lane DJ ( 1991) 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In: Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic (eds Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M), pp. 115-175. John Wiley and Sons, New York |
| [23] |
Li L, Praet J, Borremans W, Nunes OC, Manaia CM, Cleenwerck I, Meeus I, Smagghe G, De Vuyst L, Vandamme P ( 2015) Bombella intestini gen. nov., sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium isolated from bumble bee crop. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 65, 267-273.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Martinson VG, Danforth BN, Minckley RL, Rueppell O, Tingek S, Moran NA ( 2011) A simple and distinctive microbiota associated with honey bees and bumble bees. Molecular Ecology, 20, 619-628.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Martinson VG, Mago T, Koch H, Salzberg SL, Moran NA ( 2014) Genomic features of a bumble bee symbiont reflect its host environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 3793-3803.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Martinson VG, Moy J, Moran NA ( 2012) Establishment of characteristic gut bacteria during development of the honeybee worker. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 2830-2840.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Mikaelyan A, Köhler T, Lampert N, Rohland J, Boga H, Meuser K, Brune A ( 2015) Classifying the bacterial gut microbiota of termites and cockroaches: A curated phylogenetic reference database (DictDb). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 38, 472-482.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Moran NA ( 2015) Genomics of the honey bee microbiome. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 10, 22-28.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Newton IL, Roeselers G ( 2012) The effect of training set on the classification of honey bee gut microbiota using the Naïve Bayesian Classifier. BMC Microbiology, 12, 221.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Olofsson TC, Alsterfjord M, Nilson B, Butler E, Vásquez A ( 2014) Lactobacillus apinorum sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellifer sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellis sp. nov., Lactobacillus melliventris sp. nov., Lactobacillus kimbladii sp. nov., Lactobacillus helsingborgensis sp. nov. and Lactobacillus kullabergensis sp. nov., isolated from the honey stomach of the honeybee Apis mellifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64, 3109-3119.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Praet J, Aerts M, Brandt ED, Meeus I, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2016) Apibacter mensalis sp. nov.: A rare member of the bumblebee gut microbiota. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 1645-1651.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Praet J, Meeus I, Cnockaert M, Aerts M, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2015) Bifidobacterium commune sp. nov. isolated from the bumble bee gut. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 107, 1307-1313.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Praet J, Parmentier A, Schmid-Hempel R, Meeus I, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2018) Large-scale cultivation of the bumblebee gut microbiota reveals an underestimated bacterial species diversity capable of pathogen inhibition. Environmental Microbiology, 20, 214-227.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO ( 2007) SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, 7188-7196.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Raymann K, Shaffer Z, Moran NA ( 2017) Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biology, 15, e2001861.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Segers FH, Kešnerová L, Kosoy M, Engel P ( 2017) Genomic changes associated with the evolutionary transition of an insect gut symbiont into a blood-borne pathogen. The ISME Journal, 11, 1232-1244.
DOI |
| [37] | Steele MI, Kwong WK, Whiteley M, Moranb NA ( 2017) Diversification of type VI secretion system toxins reveals ancient antagonism among bee gut microbes. mBio, 8, e01630-17. |
| [38] |
Tarpy DR, Mattila HR, Newton ILG ( 2015) Development of the honey bee gut microbiome throughout the Queen- Rearing Process. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81, 3182-3191.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
vanEngelsdorp D, Evans JD, Saegerman C, Mullin C, Haubruge E, Nguyen BK, Frazier M, Frazier J, Cox-Foster D, Chen Y, Underwood R, Tarpy DR, Pettis JS ( 2009) Colony collapse disorder: A descriptive study. PLoS ONE, 4, e6481.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR ( 2007) Naïve Bayesian Classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5261-5267.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Yilmaz P, Parfrey LW, Yarza P, Gerken J, Pruesse E, Quast C, Schweer T, Peplies J, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO ( 2014) The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D643-D648.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Yun JH, Lee JY, Hyun DW, Jung MJ, Bae JW ( 2017) Bombella apis sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium isolated from the midgut of a honey bee. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67, 2184-2188.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Zheng H, Nishida A, Kwong WK, Koch H, Engel P, Steele MI, Moran NA ( 2016) Metabolism of toxic sugars by strains of the bee gut symbiont Gilliamella apicola. mBio, 7, e01326-16. |
| [44] |
Zheng H, Powell JE, Steele MI, Dietrich C, Moran NA ( 2017) Honeybee gut microbiota promotes host weight gain via bacterial metabolism and hormonal signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 4775-4780.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Yaqing Liao, Zefeng Huang, Xiaoyun Wang, Libiao Zhang, Yi Wu, Wenhua Yu. An updated checklist of Chiroptera in Guangdong Province and a molecular barcode database [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [2] | Jing Chen, Bingchang Zhang, Yanjin Liu, Jie Wu, Kang Zhao, Jiao Ming. Diversity of Leptolyngbya-like cyanobacteria in biocrusts in desert area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24186-. |
| [3] | Cao Hao, Donghui Wu, Lingzi Mo, Guoliang Xu. A review on gut microbial diversity and function of overwintering animals [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23407-. |
| [4] | Kaiying He, Xinhui Xu, Chengyun Zhang, Zezhou Hao, Zhishu Xiao, Yingying Guo. Bioacoustics data archives management standards and management technology progress [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24266-. |
| [5] | Zhengming Luo, Jinxian Liu, Bianhua Zhang, Yanying Zhou, Aihua Hao, Kai Yang, Baofeng Chai. Diversity characteristics and driving factors of soil protist communities in subalpine meadow at different degradation stages [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [6] | Chao Xing, Yi Lin, Zhiqiang Zhou, Lianjun Zhao, Shiwei Jiang, Zhenzhen Lin, Jiliang Xu, Xiangjiang Zhan. The establishment of terrestrial vertebrate genetic resource bank and species identification based on DNA barcoding in Wanglang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [7] | Yinger Mao, Xiumei Zhou, Nan Wang, Xiuxiu Li, Yuke You, Shangbin Bai. Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [8] | Wen Zhao, Dandan Wang, Mumin Reyila, Kaichuan Huang, Shun Liu, Baokai Cui. Soil microbial community structure of Larix gmelinii forest in the Aershan area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [9] | Fan Xia, Jing Yang, Jian Li, Yang Shi, Lixin Gai, Wenhua Huang, Jingwei Zhang, Nan Yang, Fuli Gao, Yingying Han, Weidong Bao. Gut bacterial composition of four leopard cat subpopulations in Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(9): 22103-. |
| [10] | Yixin Sun, Yingbin Li, Yuhui Li, Bing Li, Xiaofang Du, Qi Li. Application of high-throughput sequencing technique in the study of nematode diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [11] | Cheng Gao, Liang-Dong Guo. Progress on microbial species diversity, community assembly and functional traits [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [12] | Yichao Li, Yongsheng Chen, Denis Sandanov, Ao Luo, Tong Lü, Xiangyan Su, Yunpeng Liu, Qinggang Wang, Viktor Chepinoga, Sergey Dudov, Wei Wang, Zhiheng Wang. Patterns and environmental drivers of Ranunculaceae species richness and phylogenetic diversity across eastern Eurasia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 561-574. |
| [13] | Qifeng Lu, Zhihuan Huang, Wenhua Luo. Characterization of complete chloroplast genome in Firmiana kwangsiensis and F. danxiaensis with extremely small populations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 586-595. |
| [14] | Nan Wang, Jinghua Huang, Na Huo, Panpan Yang, Xinyue Zhang, Shiwei Zhao. Characteristics of soil nematode community under different vegetation restoration approaches in the mountainous region of southern Ningxia: A comparative study based on morphological identification and high-throughput sequencing methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| [15] | Xuehua Liu, Yuke Zhang, Xiangyu Zhao, Xiangbo He, Qiong Cai, Yun Zhu, Baisuo He, Qiang Jiu. Introduction to the wildlife camera-trapping database of the middle Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()