



Biodiv Sci ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 192-201. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014157 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014157
• Original Papers: Community Structure and Patterns of Tropical and Subtropical Forest in China • Previous Articles Next Articles
Han Xu1, Yide Li1,*( ), Mingxian Lin2, Jianhui Wu1, Tushou Luo1, Zhang Zhou1, Dexiang Chen1, Huai Yang2, Guangjian Li3, Shirong Liu4
), Mingxian Lin2, Jianhui Wu1, Tushou Luo1, Zhang Zhou1, Dexiang Chen1, Huai Yang2, Guangjian Li3, Shirong Liu4
Received:2014-08-01
Accepted:2014-12-03
Online:2015-03-20
Published:2015-04-09
Contact:
Li Yide
Han Xu, Yide Li, Mingxian Lin, Jianhui Wu, Tushou Luo, Zhang Zhou, Dexiang Chen, Huai Yang, Guangjian Li, Shirong Liu. Community characteristics of a 60 ha dynamics plot in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(2): 192-201.
| 区系类型 Area types | 属数目 Number of genera | 这些属包含的物种数目 Number of species |
|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 1 | 1 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 32 | 88 |
| 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and tropical America disjuncted | 8 | 16 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old world tropics | 21 | 34 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia | 18 | 26 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Africa | 8 | 10 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia (Indo-Malaysia) | 49 | 86 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North temperate | 3 | 4 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 9 | 16 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 | 3 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia | 3 | 4 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 1 | 1 |
| 总计 Total | 154 | 289 |
Table 1 Statistics of area types of woody plants in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 区系类型 Area types | 属数目 Number of genera | 这些属包含的物种数目 Number of species |
|---|---|---|
| 1. 世界分布 Cosmopolitan | 1 | 1 |
| 2. 泛热带分布 Pantropic | 32 | 88 |
| 3. 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 Tropical Asia and tropical America disjuncted | 8 | 16 |
| 4. 旧世界热带分布 Old world tropics | 21 | 34 |
| 5. 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Australasia | 18 | 26 |
| 6. 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 Tropical Asia to tropical Africa | 8 | 10 |
| 7. 热带亚洲分布 Tropical Asia (Indo-Malaysia) | 49 | 86 |
| 8. 北温带分布 North temperate | 3 | 4 |
| 9. 东亚和北美洲间断分布 East Asia and North America disjuncted | 9 | 16 |
| 12. 地中海区、西亚至中亚分布 Mediterranean, West Asia to Central Asia | 1 | 3 |
| 14. 东亚分布 East Asia | 3 | 4 |
| 15. 中国特有分布 Endemic to China | 1 | 1 |
| 总计 Total | 154 | 289 |
| 物种名 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area at the breast height | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大叶蒲葵 Livistona saribus | 3.57 | 8.95 | 0.76 | 0.99 |
| 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 3.01 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 1.24 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2.62 | 2.80 | 3.82 | 1.22 |
| 油丹 Alseodaphne hainanensis | 2.23 | 4.35 | 1.21 | 1.14 |
| 四蕊三角瓣花 Prismatomeris tetrandra | 2.14 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 1.24 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 2.10 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 1.23 |
| 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 1.99 | 4.89 | 0.40 | 0.69 |
| 香果新木姜子 Neolitsea ellipsoidea | 1.92 | 1.00 | 3.58 | 1.19 |
| 东方琼楠 Beilschmiedia tungfangensis | 1.83 | 1.98 | 2.42 | 1.10 |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 1.77 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 1.22 |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 1.70 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 1.13 |
| 变色山槟榔 Pinanga baviensis | 1.41 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 0.75 |
| 杏叶柯 Lithocarpus amygdalifolius | 1.29 | 2.89 | 0.31 | 0.67 |
| 东方肖榄 Platea parvifolia | 1.27 | 1.21 | 1.46 | 1.14 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 1.26 | 2.36 | 0.58 | 0.86 |
| 钮子果 Ardisia virens | 1.25 | 0.12 | 2.46 | 1.16 |
| 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 1.23 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 0.86 |
| 卵叶桂 Cinnamomum rigidissimum | 1.17 | 1.30 | 1.18 | 1.03 |
| 海岛冬青 Ilex goshiensis | 1.14 | 1.44 | 1.03 | 0.95 |
| 托盘青冈 Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis | 1.14 | 2.51 | 0.27 | 0.63 |
| 海南蕈树 Altingia obovata | 1.10 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 1.05 | 0.13 | 1.90 | 1.13 |
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 1.04 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 0.38 |
| 海南紫荆木 Madhuca hainanensis | 1.01 | 2.20 | 0.35 | 0.48 |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 1.00 | 1.49 | 0.58 | 0.93 |
| 合计 Total | 41.24 | 56.02 | 44.03 | 23.66 |
Table 2 Dominant species of woody plants in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 物种名 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area at the breast height | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大叶蒲葵 Livistona saribus | 3.57 | 8.95 | 0.76 | 0.99 |
| 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 3.01 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 1.24 |
| 厚壳桂 Cryptocarya chinensis | 2.62 | 2.80 | 3.82 | 1.22 |
| 油丹 Alseodaphne hainanensis | 2.23 | 4.35 | 1.21 | 1.14 |
| 四蕊三角瓣花 Prismatomeris tetrandra | 2.14 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 1.24 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 2.10 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 1.23 |
| 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 1.99 | 4.89 | 0.40 | 0.69 |
| 香果新木姜子 Neolitsea ellipsoidea | 1.92 | 1.00 | 3.58 | 1.19 |
| 东方琼楠 Beilschmiedia tungfangensis | 1.83 | 1.98 | 2.42 | 1.10 |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 1.77 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 1.22 |
| 黄叶树 Xanthophyllum hainanense | 1.70 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 1.13 |
| 变色山槟榔 Pinanga baviensis | 1.41 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 0.75 |
| 杏叶柯 Lithocarpus amygdalifolius | 1.29 | 2.89 | 0.31 | 0.67 |
| 东方肖榄 Platea parvifolia | 1.27 | 1.21 | 1.46 | 1.14 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 1.26 | 2.36 | 0.58 | 0.86 |
| 钮子果 Ardisia virens | 1.25 | 0.12 | 2.46 | 1.16 |
| 盆架树 Alstonia rostrata | 1.23 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 0.86 |
| 卵叶桂 Cinnamomum rigidissimum | 1.17 | 1.30 | 1.18 | 1.03 |
| 海岛冬青 Ilex goshiensis | 1.14 | 1.44 | 1.03 | 0.95 |
| 托盘青冈 Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis | 1.14 | 2.51 | 0.27 | 0.63 |
| 海南蕈树 Altingia obovata | 1.10 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| 罗伞树 Ardisia quinquegona | 1.05 | 0.13 | 1.90 | 1.13 |
| 柏拉木 Blastus cochinchinensis | 1.04 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 0.38 |
| 海南紫荆木 Madhuca hainanensis | 1.01 | 2.20 | 0.35 | 0.48 |
| 橄榄 Canarium album | 1.00 | 1.49 | 0.58 | 0.93 |
| 合计 Total | 41.24 | 56.02 | 44.03 | 23.66 |
| 起测胸径 Minimum DBH | 植株数目 Number of stems | 物种数目 Number of species | 属数目 Number of genera | 科数目 Number of families |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 1.0 cm | 439,676 | 290 | 155 | 62 |
| ≥ 5.0 cm | 103,496 | 262 | 145 | 60 |
| ≥ 10.0 cm | 54,733 | 236 | 131 | 58 |
| ≥ 15.0 cm | 35,368 | 223 | 124 | 58 |
| ≥ 20.0 cm | 24,104 | 206 | 116 | 57 |
| ≥ 40.0 cm | 5,589 | 130 | 78 | 46 |
| ≥ 60.0 cm | 1,419 | 69 | 47 | 27 |
Table 3 Number of species, genera, families and stems with different minimum diameter at breast height in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 起测胸径 Minimum DBH | 植株数目 Number of stems | 物种数目 Number of species | 属数目 Number of genera | 科数目 Number of families |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 1.0 cm | 439,676 | 290 | 155 | 62 |
| ≥ 5.0 cm | 103,496 | 262 | 145 | 60 |
| ≥ 10.0 cm | 54,733 | 236 | 131 | 58 |
| ≥ 15.0 cm | 35,368 | 223 | 124 | 58 |
| ≥ 20.0 cm | 24,104 | 206 | 116 | 57 |
| ≥ 40.0 cm | 5,589 | 130 | 78 | 46 |
| ≥ 60.0 cm | 1,419 | 69 | 47 | 27 |
| 植物科名 Family name | 重要值 Importance value | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 樟科Lauraceae | 13.78 | 16.53 | 21.85 | 2.95 |
| 壳斗科Fagaceae | 9.02 | 18.44 | 5.68 | 2.94 |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 6.37 | 2.05 | 14.10 | 2.95 |
| 棕榈科Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5.31 | 9.07 | 4.13 | 2.74 |
| 榆科Ulmaceae | 3.56 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 2.91 |
| 山矾科Symplocaceae | 3.32 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 2.94 |
| 山茶科Theaceae | 3.12 | 4.02 | 2.47 | 2.87 |
| 大戟科Euphorbiaceae | 2.81 | 2.04 | 3.46 | 2.91 |
| 木兰科Magnoliaceae | 2.69 | 4.30 | 1.13 | 2.62 |
| 无患子科Sapindaceae | 2.65 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 2.90 |
| 紫金牛科Myrsinaceae | 2.55 | 0.31 | 4.44 | 2.90 |
| 桃金娘科Myrtaceae | 2.47 | 1.97 | 2.58 | 2.87 |
| 野牡丹科Melastomataceae | 2.37 | 0.17 | 4.08 | 2.84 |
| 远志科Polygalaceae | 2.21 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 2.65 |
| 冬青科Aquifoliaceae | 2.17 | 1.88 | 1.86 | 2.78 |
| 山榄科Sapotaceae | 2.14 | 3.41 | 0.74 | 2.28 |
| 茶茱萸科Icacinaceae | 2.12 | 1.39 | 2.11 | 2.85 |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 2.11 | 1.08 | 2.47 | 2.78 |
| 夹竹桃科Apocynaceae | 2.11 | 2.41 | 1.21 | 2.71 |
| 木犀科Oleaceae | 1.98 | 1.13 | 1.94 | 2.87 |
| 杜英科Elaeocarpaceae | 1.66 | 1.28 | 1.10 | 2.60 |
| 桑科Moraceae | 1.65 | 1.38 | 1.02 | 2.57 |
| 芸香科Rutaceae | 1.59 | 0.92 | 1.20 | 2.64 |
| 虎耳草科Saxifragaceae | 1.48 | 0.92 | 1.08 | 2.45 |
| 橄榄科Burseraceae | 1.45 | 1.55 | 0.58 | 2.22 |
| 梧桐科Sterculiaceae | 1.40 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 2.52 |
| 番荔枝科Annonaceae | 1.34 | 0.11 | 1.35 | 2.55 |
| 罗汉松科Podocarpaceae | 1.32 | 1.83 | 0.41 | 1.72 |
| 金缕梅科Hamamelidaceae | 1.30 | 2.69 | 0.46 | 0.73 |
| 藤黄科Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 1.13 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 2.29 |
| 合计 Total | 89.18 | 93.93 | 95.05 | 78.57 |
Table S1 The dominant families composition of woody plants in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 植物科名 Family name | 重要值 Importance value | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 樟科Lauraceae | 13.78 | 16.53 | 21.85 | 2.95 |
| 壳斗科Fagaceae | 9.02 | 18.44 | 5.68 | 2.94 |
| 茜草科Rubiaceae | 6.37 | 2.05 | 14.10 | 2.95 |
| 棕榈科Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5.31 | 9.07 | 4.13 | 2.74 |
| 榆科Ulmaceae | 3.56 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 2.91 |
| 山矾科Symplocaceae | 3.32 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 2.94 |
| 山茶科Theaceae | 3.12 | 4.02 | 2.47 | 2.87 |
| 大戟科Euphorbiaceae | 2.81 | 2.04 | 3.46 | 2.91 |
| 木兰科Magnoliaceae | 2.69 | 4.30 | 1.13 | 2.62 |
| 无患子科Sapindaceae | 2.65 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 2.90 |
| 紫金牛科Myrsinaceae | 2.55 | 0.31 | 4.44 | 2.90 |
| 桃金娘科Myrtaceae | 2.47 | 1.97 | 2.58 | 2.87 |
| 野牡丹科Melastomataceae | 2.37 | 0.17 | 4.08 | 2.84 |
| 远志科Polygalaceae | 2.21 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 2.65 |
| 冬青科Aquifoliaceae | 2.17 | 1.88 | 1.86 | 2.78 |
| 山榄科Sapotaceae | 2.14 | 3.41 | 0.74 | 2.28 |
| 茶茱萸科Icacinaceae | 2.12 | 1.39 | 2.11 | 2.85 |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 2.11 | 1.08 | 2.47 | 2.78 |
| 夹竹桃科Apocynaceae | 2.11 | 2.41 | 1.21 | 2.71 |
| 木犀科Oleaceae | 1.98 | 1.13 | 1.94 | 2.87 |
| 杜英科Elaeocarpaceae | 1.66 | 1.28 | 1.10 | 2.60 |
| 桑科Moraceae | 1.65 | 1.38 | 1.02 | 2.57 |
| 芸香科Rutaceae | 1.59 | 0.92 | 1.20 | 2.64 |
| 虎耳草科Saxifragaceae | 1.48 | 0.92 | 1.08 | 2.45 |
| 橄榄科Burseraceae | 1.45 | 1.55 | 0.58 | 2.22 |
| 梧桐科Sterculiaceae | 1.40 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 2.52 |
| 番荔枝科Annonaceae | 1.34 | 0.11 | 1.35 | 2.55 |
| 罗汉松科Podocarpaceae | 1.32 | 1.83 | 0.41 | 1.72 |
| 金缕梅科Hamamelidaceae | 1.30 | 2.69 | 0.46 | 0.73 |
| 藤黄科Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 1.13 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 2.29 |
| 合计 Total | 89.18 | 93.93 | 95.05 | 78.57 |
| 植物属 Genus name | 重要值 Importance value | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area at the breast height | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石栎属Lithocarpus | 4.44 | 9.39 | 2.26 | 1.65 |
| 蒲葵属Livistona | 3.68 | 8.95 | 0.76 | 1.34 |
| 厚壳桂属Cryptocarya | 3.35 | 3.40 | 4.98 | 1.67 |
| 白颜树属Gironniera | 3.15 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 1.68 |
| 新木姜子属Neolitsea | 3.15 | 1.43 | 6.36 | 1.66 |
| 山矾属Symplocos | 2.91 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 1.70 |
| 琼楠属Beilschmiedia | 2.86 | 3.39 | 3.51 | 1.68 |
| 栲属Castanopsis | 2.66 | 4.29 | 2.23 | 1.47 |
| 青冈属Cyclobalanopsis | 2.50 | 4.76 | 1.18 | 1.56 |
| 油丹属Alseodaphne | 2.36 | 4.35 | 1.21 | 1.54 |
| 南山花属Prismatomeris | 2.29 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 1.69 |
| 韶子属Nephelium | 2.24 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 1.68 |
| 紫金牛属Ardisia | 2.12 | 0.30 | 4.40 | 1.67 |
| 蒲桃属Syzygium | 2.00 | 1.89 | 2.47 | 1.65 |
| 樟属Cinnamomum | 1.98 | 1.98 | 2.39 | 1.57 |
| 九节属Psychotria | 1.92 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 1.66 |
| 青兰属Xanthophyllum | 1.84 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 1.53 |
| 冬青属Ilex | 1.78 | 1.88 | 1.86 | 1.60 |
| 红豆属Ormosia | 1.62 | 1.02 | 2.26 | 1.57 |
| 山槟榔属Pinanga | 1.49 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 1.01 |
| 肖榄属Platea | 1.45 | 1.26 | 1.53 | 1.56 |
| 木荷属Schima | 1.37 | 2.36 | 0.58 | 1.18 |
| 盆架树属Alstonia | 1.33 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 1.17 |
| 粗叶木属Lasianthus | 1.33 | 0.22 | 2.14 | 1.62 |
| 润楠属Machilus | 1.31 | 1.09 | 1.38 | 1.46 |
| 橄榄属Canarium | 1.14 | 1.55 | 0.58 | 1.28 |
| 阿丁枫属Altingia | 1.14 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 0.39 |
| 木姜子属Litsea | 1.12 | 0.41 | 1.36 | 1.59 |
| 多香木属Polyosma | 1.11 | 0.89 | 1.02 | 1.41 |
| 柏拉木属Blastus | 1.09 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 0.52 |
| 紫荆木属Madhuca | 1.07 | 2.20 | 0.35 | 0.65 |
| 杜英属Elaeocarpus | 1.04 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 1.41 |
| 木兰属Michelia | 1.02 | 1.59 | 0.44 | 1.05 |
| 合计 Total | 65.87 | 77.36 | 73.39 | 46.87 |
Table S2 The genera composition of woody plants in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 植物属 Genus name | 重要值 Importance value | 相对胸高断面积 Relative basal area at the breast height | 相对密度 Relative density | 相对频度 Relative frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 石栎属Lithocarpus | 4.44 | 9.39 | 2.26 | 1.65 |
| 蒲葵属Livistona | 3.68 | 8.95 | 0.76 | 1.34 |
| 厚壳桂属Cryptocarya | 3.35 | 3.40 | 4.98 | 1.67 |
| 白颜树属Gironniera | 3.15 | 5.50 | 2.28 | 1.68 |
| 新木姜子属Neolitsea | 3.15 | 1.43 | 6.36 | 1.66 |
| 山矾属Symplocos | 2.91 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 1.70 |
| 琼楠属Beilschmiedia | 2.86 | 3.39 | 3.51 | 1.68 |
| 栲属Castanopsis | 2.66 | 4.29 | 2.23 | 1.47 |
| 青冈属Cyclobalanopsis | 2.50 | 4.76 | 1.18 | 1.56 |
| 油丹属Alseodaphne | 2.36 | 4.35 | 1.21 | 1.54 |
| 南山花属Prismatomeris | 2.29 | 0.25 | 4.93 | 1.69 |
| 韶子属Nephelium | 2.24 | 2.35 | 2.70 | 1.68 |
| 紫金牛属Ardisia | 2.12 | 0.30 | 4.40 | 1.67 |
| 蒲桃属Syzygium | 2.00 | 1.89 | 2.47 | 1.65 |
| 樟属Cinnamomum | 1.98 | 1.98 | 2.39 | 1.57 |
| 九节属Psychotria | 1.92 | 0.66 | 3.44 | 1.66 |
| 青兰属Xanthophyllum | 1.84 | 2.47 | 1.51 | 1.53 |
| 冬青属Ilex | 1.78 | 1.88 | 1.86 | 1.60 |
| 红豆属Ormosia | 1.62 | 1.02 | 2.26 | 1.57 |
| 山槟榔属Pinanga | 1.49 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 1.01 |
| 肖榄属Platea | 1.45 | 1.26 | 1.53 | 1.56 |
| 木荷属Schima | 1.37 | 2.36 | 0.58 | 1.18 |
| 盆架树属Alstonia | 1.33 | 2.38 | 0.44 | 1.17 |
| 粗叶木属Lasianthus | 1.33 | 0.22 | 2.14 | 1.62 |
| 润楠属Machilus | 1.31 | 1.09 | 1.38 | 1.46 |
| 橄榄属Canarium | 1.14 | 1.55 | 0.58 | 1.28 |
| 阿丁枫属Altingia | 1.14 | 2.61 | 0.41 | 0.39 |
| 木姜子属Litsea | 1.12 | 0.41 | 1.36 | 1.59 |
| 多香木属Polyosma | 1.11 | 0.89 | 1.02 | 1.41 |
| 柏拉木属Blastus | 1.09 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 0.52 |
| 紫荆木属Madhuca | 1.07 | 2.20 | 0.35 | 0.65 |
| 杜英属Elaeocarpus | 1.04 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 1.41 |
| 木兰属Michelia | 1.02 | 1.59 | 0.44 | 1.05 |
| 合计 Total | 65.87 | 77.36 | 73.39 | 46.87 |
| 中文种名 Chinese species name | 拉丁种名 Latin species name | 中文科名 Chinese family name | 拉丁科名 Latin family name | 属区系类型* Area type of genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白花含笑 | Michelia mediocris Dandy | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 白肉榕 | Ficus vasculosa Wallich ex Miquel | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 白颜树 | Gironniera subaequalis Planchon | 榆科 | Ulmaceae | 7 |
| 百日青 | Podocarpus neriifolius D. Don in Lambert | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 2.1 |
| 柏拉木 | Blastus cochinchinensis Loureiro | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 棒花蒲桃 | Syzygium claviflorum (Roxburgh) Wallich ex Steudel | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 薄叶红厚壳 | Calophyllum membranaceum Gardner & Champion | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 2 |
| 薄叶猴耳环 | Archidendron utile (Chun & F. C. How) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 薄叶壳斗(暂拟) | Lithocarpus sp.2 | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 薄叶山矾 | Symplocos anomala Brand | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 保亭柿 | Diospyros potingensis Merrill & Chun | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 笔管榕 | Ficus subpisocarpa Gagnepain | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 笔罗子 | Meliosma rigida Siebold & Zuccarini | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 变色山槟榔 | Pinanga baviensis Beccari | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 7 |
| 滨木犀榄 | Olea brachiata (Loureiro) Merrill | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 柄果柯 | Lithocarpus longipedicellatus (Hickel & A. Camus) A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 柴龙树 | Apodytes dimidiata E. Meyer ex Arnott | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 4.1 |
| 齿叶冬青 | Ilex crenata Thunberg | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 赤楠 | Syzygium buxifolium Hooker & Arnott | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 赤杨叶 | Alniphyllum fortunei (Hemsley) Makino | 安息香科 | Styracaceae | 7.4 |
| 丛花山矾 | Symplocos poilanei Guillaumin | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 粗毛野桐 | Hancea hookeriana Seemann | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 粗丝木 | Gomphandra tetrandra (Wallich) Sleumer | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 粗叶榕 | Ficus hirta Vahl | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 粗壮润楠 | Machilus robusta W. W. Smith | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 大萼木姜子 | Litsea baviensis Lecomte | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 大花五桠果 | Dillenia turbinata Finet & Gagnepain | 五桠果科 | Dilleniaceae | 5 |
| 大叶蒲葵 | Livistona saribus (Loureiro) Merrill ex Chevalier | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5 |
| 大叶鼠刺 | Itea macrophylla Wallich | 虎耳草科 | Saxifragaceae | 9 |
| 大叶鱼骨木 | Canthium simile Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 滇越杜英 | Elaeocarpus poilanei Gagnepain | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 东方琼楠 | Beilschmiedia tungfangensis S. K. Lee & L. F. Lau | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 东方肖榄 | Platea parvifolia Merrill & Chun | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 短柄紫珠 | Callicarpa brevipes (Bentham) Hance | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 短药蒲桃 | Syzygium globiflorum (Craib) P. Chantanaranothai & J. Parnell | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 多萼核果茶 | Pyrenaria jonquieriana Pierre ex Lanessan subsp. multisepala (Merrill & Chun) S. X. Yang | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7 |
| 多花五月茶 | Antidesma maclurei Merrill | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 多香木 | Polyosma cambodiana Gagnepain | 虎耳草科 | Saxifragaceae | 5 |
| 鹅掌柴 | Schefflera heptaphylla (Linnaeus) Frodin | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 二色波罗蜜 | Artocarpus styracifolius Pierre | 桑科 | Moraceae | 7 |
| 饭甑青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis fleuryi (Hickel & A. Camus) Chun ex Q. F. Zheng | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 方枝蒲桃 | Syzygium tephrodes (Hance) Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 肥荚红豆 | Ormosia fordiana Oliver | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 粉背琼楠 | Beilschmiedia glauca S. K. Lee & L. F. Lau | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 缝线海桐 | Pittosporum perryanum Gowda | 海桐花科 | Pittosporaceae | 4 |
| 橄榄 | Canarium album (Loureiro) Raeuschel | 橄榄科 | Burseraceae | 4 |
| 高山榕 | Ficus altissima Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 公孙锥 | Castanopsis tonkinensis Seemen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 贡甲 | Maclurodendron oligophlebium (Merrill) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 狗骨柴 | Diplospora dubia (Lindley) Masamune | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 谷木 | Memecylon ligustrifolium Champion ex Bentham | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 4 |
| 灌丛泡花树 | Meliosma dumicola W. W. Smith | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 灌木土密树 | Bridelia harmandii Gagnepain | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 6 |
| 光叶山矾 | Symplocos lancifolia Siebold & Zuccarini | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 光叶山小橘 | Glycosmis craibii var. glabra (Craib) Tanaka | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 广东粗叶木 | Lasianthus curtisii King & Gamble | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 广东大青 | Clerodendrum kwangtungense Handel-Mazzetti | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 广东冬青 | Ilex kwangtungensis Merrill | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 广东假木荷 | Craibiodendron scleranthum (Dop) Judd var. kwang-tungense (S. Y. Hu) Judd | 杜鹃花科 | Ericaceae | 7.4 |
| 广东山胡椒 | Lindera kwangtungensis (H. Liu) C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 广南天料木 | Homalium paniculiflorum How & Ko | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 过布柿 | Diospyros susarticulata Lecomte | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 海岛冬青 | Ilex goshiensis Hayata | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 海南暗罗 | Polyalthia laui Merrill | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 4 |
| 海南槽裂木 | Pertusadina metcalfii (Merrill ex H. L. Li) Y. F. Deng & C. M. Hu | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 海南草珊瑚 | Sarcandra glabra subsp. brachystachys (Blume) Verdcourt | 金粟兰科 | Chloranthaceae | 7 |
| 海南大头茶 | Polyspora hainanensis (Hung T. Chang) C. X. Ye ex B. M. Bartholomew & T. L. Ming | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 9 |
| 海南冬青 | Ilex hainanensis Merrill | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 海南鹅耳枥 | Carpinus londoniana var. lanceolata (Handel-Mazzetti) P. C. Li in P. C. Li & S. H. Cheng | 桦木科 | Betulaceae | 8 |
| 海南鹅掌柴 | Schefflera hainanensis Merrill & Chun | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 海南玫瑰木 | Rhodamnia dumetorum var. hainanensis Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 5 |
| 海南蜜茱萸 | Melicope chunii (Merrill) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 海南木莲 | Manglietia fordiana var. hainanensis (Dandy) N. H. Xia | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 海南木犀榄 | Olea hainanensis H. L. Li | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 海南破布叶 | Microcos chungii (Merrill) Chun | 椴树科 | Tiliaceae | 7 |
| 海南雀舌木 | Leptopus hainanensis (Merrill & Chun) Pojarkova | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 5 |
| 海南山矾 | Symplocos hainanensis Merrill & Chun ex H. L. Li | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 海南山胡椒 | Lindera robusta (C. K. Allen) H. P. Tsui | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 海南山龙眼 | Helicia hainanensis Hayata | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 海南韶子 | Nephelium topengii (Merrill) H. S. Lo | 无患子科 | Sapindaceae | 7 |
| 海南树参 | Dendropanax hainanensis (Merrill & Chun) Chun | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 海南腺萼木 | Mycetia hainanensis H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 海南蕈树 | Altingia obovata Merrill & Chun | 金缕梅科 | Hamamelidaceae | 7.1 |
| 海南杨桐 | Adinandra hainanensis Hayata | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 6.2 |
| 海南栀子 | Gardenia hainanensis Merrill | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 海南轴榈 | Licuala hainanensis A. J. Henderson | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5 |
| 海南紫荆木 | Madhuca hainanensis Chun & How | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 5 |
| 禾串树 | Bridelia balansae Tutcher | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 6 |
| 黑桫椤 | Alsophila podophylla (Hook.) Cop. | 桫椤科 | Cyatheaceae | 蕨类植物 |
| 红果坚木 | Dysoxylum gotadhora (Buchanan-Hamilton) Mabberley | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 7 |
| 红柯 | Lithocarpus fenzelianus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 红鳞蒲桃 | Syzygium hancei Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 红毛山楠 | Phoebe hungmoensis S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 红木荷 | Schima wallichii (Candolle) Korthals | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7.1 |
| 红算盘子 | Glochidion coccineum (Buchanan-Hamilton) Müller Argoviensis | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 2 |
| 红枝蒲桃 | Syzygium rehderianum Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 红枝琼楠 | Beilschmiedia laevis C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 红锥 | Castanopsis hystrix J. D. Hooker & Thomson ex A. de Candolle | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 猴耳环 | Archidendron clypearia (Jack) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 猴欢喜 | Sloanea sinensis (Hance) Hemsley | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 3 |
| 厚边木犀 | Osmanthus marginatus (Champion ex Bentham) Hemsley | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 厚梗染木树 | Saprosma crassipes H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 厚壳桂 | Cryptocarya chinensis (Hance) Hemsley | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 厚皮香 | Ternstroemia gymnanthera (Wight & Arnott) Beddome | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 2 |
| 厚皮香八角 | Illicium ternstroemioides A. C. Smith | 八角科 | Illiciaceae | 9 |
| 华南毛柃 | Eurya ciliata Merrill | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 华南青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis edithiae (Skan) Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 华润楠 | Machilus chinensis (Bentham) Hemsley | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 黄丹木姜子 | Litsea elongata (Nees) J. D. Hooker | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 黄果粗叶木 | Lasianthus calycinus Dunn | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 黄脉九节 | Psychotria straminea Hutchinson | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 黄毛粗叶木 | Lasianthus rhinocerotis Blume | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 黄杞 | Engelhardia roxburghiana Wallich | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 黄桐 | Endospermum chinense Bentham | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 7 |
| 黄叶树 | Xanthophyllum hainanense Hu | 远志科 | Polygalaceae | 5 |
| 黄樟 | Cinnamomum parthenoxylon (Jack) Meisner | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 灰毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus limitaneus Handel-Mazzetti | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 喙果黑面神 | Breynia rostrata Merrill | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 5 |
| 喙果皂帽花 | Dasymaschalon rostratum Merrill & Chun | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 7 |
| 鸡毛松 | Dacrycarpus imbricatus (Blume) de Laubenfels var. patulus de Laubenfels | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 5.1 |
| 鸡屎树 | Lasianthus hirsutus (Roxburgh) Merrill | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 鲫鱼胆 | Maesa perlarius (Loureiro) Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 4 |
| 假黄皮 | Clausena excavata N. L. Burman | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 4 |
| 假苹婆 | Sterculia lanceolata Cavanilles | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 2 |
| 假鹊肾树 | Streblus indicus (Bureau) Corner | 桑科 | Moraceae | 7 |
| 假鱼骨木 | Psydrax dicocca Gaertner | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 尖峰岭锥 | Castanopsis jianfenglingensis Duanmu | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 尖峰蒲桃 | Syzygium jienfunicum Hung T. Chang & R. H. Miao | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 尖峰润楠 | Machilus monticola S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 尖蕾狗牙花 | Tabernaemontana bufalina Loureiro | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 2 |
| 尖叶弯管花 | Chassalia curviflora var. longifolia J. D. Hooker | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 柬埔寨子楝树 | Decaspermum montanum Ridley | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 7 |
| 剑叶梭罗 | Reevesia lancifolia H. L. Li | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 7.1 |
| 金叶树 | Chrysophyllum lanceolatum (Blume) A. de Candolle var. stellatocarpon P. Royen | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 3 |
| 九节 | Psychotria asiatica Linnaeus | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 绢毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus nitentifolius Merrill & Chun | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 刻节润楠 | Machilus cicatricosa S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 苦梓含笑 | Michelia balansae (Aug. Candolle) Dandy | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 阔叶肖榄 | Platea latifolia Blume | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 乐东拟单性木兰 | Parakmeria lotungensis (Chun & C. H. Tsoong) Y. W. Law | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 15 |
| 乐东锥 | Castanopsis ledongensis C. C. Huang & Y. T. Chang | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 簕党花椒 | Zanthoxylum avicennae (Lamarck) Candolle | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 2 |
| 雷公青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis hui (Chun) Chun ex Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 梨果柯 | Lithocarpus howii Chun | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 黧蒴锥 | Castanopsis fissa (Champion ex Bentham) Rehder & E. H. Wilson | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 栎子青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis blakei (Skan) Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 楝叶吴萸 | Tetradium glabrifolium (Champion ex Bentham) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 14 |
| 两广梭罗 | Reevesia thyrsoidea Lindley | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 7.1 |
| 两叶黄杞 | Engelhardia unijuga Chun ex P. Y. Chen | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 亮叶猴耳环 | Archidendron lucidum (Bentham) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 亮叶青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis phanera (Chun) Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 鳞斑荚蒾 | Viburnum punctatum Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don | 五福花科 | Adoxaceae | 8 |
| 岭罗麦 | Tarennoidea wallichii (J. D. Hooker) Tirvengadum & Sastre | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 岭南山竹子 | Garcinia oblongifolia Champion ex Bentham | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 6 |
| 瘤果柯 | Lithocarpus handelianus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 陆均松 | Dacrydium pectinatum de Laubenfels | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 2.1 |
| 卵叶桂 | Cinnamomum rigidissimum Hung T. Chang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 卵叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea ovatifolia Yen C. Yang & P. H. Huang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 轮叶木姜子 | Litsea verticillata Hance | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 罗浮枫 | Acer fabri Hance | 槭树科 | Aceraceae | 8 |
| 罗浮柿 | Diospyros morrisiana Hance | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 罗浮锥 | Castanopsis fabri Hance | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 罗伞树 | Ardisia quinquegona Blume | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 萝芙木 | Rauvolfia verticillata (Loureiro) Baillon | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 3 |
| 绿枝山矾 | Symplocos viridissima Brand | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 毛冬青 | Ilex pubescens Hooker & Arnott | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 毛果柯 | Lithocarpus pseudovestitus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 毛菍 | Melastoma sanguineum Sims | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
| 毛叶脚骨脆 | Casearia velutina Blume | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 美丽新木姜子 | Neolitsea pulchella (Meisner) Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 美脉粗叶木 | Lasianthus lancifolius J. D. Hooker | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 米锥 | Castanopsis carlesii (Hemsley) Hayata | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 密花山矾 | Symplocos congesta Bentham | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 密花树 | Myrsine seguinii H. Léveillé | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 6 |
| 密鳞紫金牛 | Ardisia densilepidotula Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 木荷 | Schima superba Gardner & Champion | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7.1 |
| 木荚红豆 | Ormosia xylocarpa Chun ex Merrill & L. Chen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 木竹子 | Garcinia multiflora Champion ex Bentham | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 6 |
| 南亚柏拉木 | Blastus borneensis Cogniaux ex Boerlage | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 泥柯 | Lithocarpus fenestratus (Roxburgh) Rehder | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 拟杜茎山 | Maesa consanguinea Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 4 |
| 拟榕叶冬青 | Ilex subficoidea S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 牛耳枫 | Daphniphyllum calycinum Bentham | 交让木科 | Daphniphyllaceae | 7 |
| 钮子果 | Ardisia virens Kurz | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 泡叶龙船花 | Ixora nienkui Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 盆架树 | Alstonia rostrata C. E. C. Fischer | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 7 |
| 披针叶乌口树 | Tarenna lancilimba W. C. Chen | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 枇杷叶山龙眼 | Helicia obovatifolia var. mixta (H. L. Li) Sleumer | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 平塘榕 | Ficus tuphapensis Drake | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 坡垒 | Hopea hainanensis Merrill & Chun | 龙脑香科 | Dipterocarpaceae | 7 |
| 漆树 | Toxicodendron vernicifluum (Stokes) F. A. Barkley | 漆树科 | Anacardiaceae | 9 |
| 千里香 | Murraya paniculata (Linnaeus) Jack | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 青梅 | Vatica mangachapoi Blanco | 龙脑香科 | Dipterocarpaceae | 7 |
| 琼岛染木树 | Saprosma merrillii H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 琼楠 | Beilschmiedia intermedia C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 绒毛山胡椒 | Lindera nacusua (D. Don) Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 榕叶冬青 | Ilex ficoidea Hemsley | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 肉实树 | Sarcosperma laurinum (Bentham) J. D. Hooker | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 7 |
| 软荚红豆 | Ormosia semicastrata Hance | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 山地五月茶 | Antidesma montanum Blume | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 山杜英 | Elaeocarpus sylvestris (Loureiro) Poiret | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 山矾 | Symplocos sumuntia Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 山橘树 | Glycosmis cochinchinensis (Loureiro) Pierre | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 山牡荆 | Vitex quinata (Loureiro) Williams | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 山榕 | Ficus heterophylla Linnaeus f. | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 山乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis Loureiro | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 2 |
| 山香圆 | Turpinia montana (Blume) Kurz | 省沽油科 | Staphyleaceae | 3 |
| 山油柑 | Acronychia pedunculata (Linnaeus) Miquel | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 十蕊枫 | Acer laurinum Hasskarl | 槭树科 | Aceraceae | 8 |
| 石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis indica (Linnaeus) Lindley | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 疏花卫矛 | Euonymus laxiflorus Champion ex Bentham | 卫矛科 | Celastraceae | 2 |
| 双瓣木犀 | Osmanthus didymopetalus P. S. Green | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 水锦树 | Wendlandia uvariifolia Hance | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 5 |
| 水同木 | Ficus fistulosa Reinwardt ex Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 四蕊三角瓣花 | Prismatomeris tetrandra (Roxburgh) K. Schumann | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 台湾枇杷 | Eriobotrya deflexa (Hemsley) Nakai | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 台湾榕 | Ficus formosana Maximowicz | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 桃榄 | Pouteria annamensis (Pierre) Baehni | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 2 |
| 桃叶石楠 | Photinia prunifolia (Hooker & Arnott) Lindley | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 9 |
| 调羹树 | Heliciopsis lobata (Merrill) Sleumer | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 7 |
| 铁山矾 | Symplocos pseudobarberina Gontscharow | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 铜盆花 | Ardisia obtusa Mez | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 凸脉冬青 | Ilex kobuskiana S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 土沉香 | Aquilaria sinensis (Loureiro) Sprengel | 瑞香科 | Thymelaeaceae | 7 |
| 臀果木 | Pygeum topengii Merrill | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 7 |
| 托盘青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis (Chun) Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 洼皮冬青 | Ilex nuculicava S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 弯管花 | Chassalia curviflora (Wallich) Thwaites | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 网脉琼楠 | Beilschmiedia tsangii Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 微毛柃 | Eurya hebeclados Y. Ling | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 微毛山矾 | Symplocos wikstroemiifolia Hayata | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 蚊母树 | Distylium racemosum Siebold & Zuccarini | 金缕梅科 | Hamamelidaceae | 7 |
| 乌材 | Diospyros eriantha Champion ex Bentham | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 乌榄 | Canarium pimela K. D. Koenig | 橄榄科 | Burseraceae | 4 |
| 乌檀 | Nauclea officinalis (Pierre ex Pitard) Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 五列木 | Pentaphylax euryoides Gardner & Champion | 五列木科 | Pentaphylacaceae | 7 |
| 细齿叶柃 | Eurya nitida Korthals | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 细轴荛花 | Wikstroemia nutans Champion ex Bentham | 瑞香科 | Thymelaeaceae | 5 |
| 狭叶泡花树 | Meliosma angustifolia Merrill | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 显脉杜英 | Elaeocarpus dubius A. Candolle | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 显脉虎皮楠 | Daphniphyllum paxianum K. Rosenthal | 交让木科 | Daphniphyllaceae | 7 |
| 显脉天料木 | Homalium phanerophlebium How & Ko | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 线枝蒲桃 | Syzygium araiocladum Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 腺叶山矾 | Symplocos adenophylla Wallich ex G. Don | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 香港大沙叶 | Pavetta hongkongensis Bremekamp | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 香港坚木 | Dysoxylum hongkongense (Tutcher) Merrill | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 7 |
| 香港木兰 | Lirianthe championii (Bentham) N. H. Xia & C. Y. Wu, | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 9 |
| 香桂 | Cinnamomum subavenium Miquel | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 香果新木姜子 | Neolitsea ellipsoidea C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 香楠 | Aidia canthioides (Champion ex Bentham) Masamune | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 肖蒲桃 | Syzygium acuminatissimum (Blume) Candolle | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 小果山龙眼 | Helicia cochinchinensis Loureiro | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 斜脉异萼花 | Disepalum plagioneurum (Diels) D. M. Johnson | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 4 |
| 杏叶柯 | Lithocarpus amygdalifolius (Skan) Hayata | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 雄鸡树 | Litsea variabilis f. chinensis (C. K. Allen) Yen C. Yang & P. H. Huang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 锈毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus howii Merrill & Chun | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 锈毛石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis ferruginea F. P. Metcalf | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 锈叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea cambodiana Lecomte | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 羊舌树 | Symplocos glauca (Thunberg) Koidzumi | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 药用狗牙花 | Tabernaemontana bovina Loureiro | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 2 |
| 野牡丹 | Melastoma malabathricum Linnaeus | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
| 异形木 | Allomorphia balansae Cogniaux | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 阴香 | Cinnamomum burmannii (Nees & T. Nees) Blume | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 隐脉红淡比 | Cleyera obscurinervia (Merrill & Chun) Hung T. Chang | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 2 |
| 硬核 | Scleropyrum wallichianum (Wight & Arnott) Arnott | 檀香科 | Santalaceae | 7 |
| 硬壳桂 | Cryptocarya chingii W. C. Cheng | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 硬壳柯 | Lithocarpus hancei (Benth.) Rehd. | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 油丹 | Alseodaphne hainanensis Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 越南冬青 | Ilex cochinchinensis (Loureiro) Loesener | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 云南黄杞 | Engelhardia spicata Leschenault ex Blume | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 云南木犀榄 | Olea tsoongii (Merrill) P. S. Green | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 杂色榕 | Ficus variegata Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 粘木 | Ixonanthes reticulata Jack | 古柯科 | Erythroxylaceae | 7 |
| 樟叶泡花树 | Meliosma squamulata Hance | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 长柄山龙眼 | Helicia longipetiolata Merrill & Chun | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 长柄鼠李 | Rhamnus longipes Merrill & Chun | 鼠李科 | Rhamnaceae | 1 |
| 长萼粗叶木 | Lasianthus chevalieri Pitard | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 长花厚壳树 | Ehretia longiflora Champion ex Bentham | 紫草科 | Boraginaceae | 4 |
| 长脐红豆 | Ormosia balansae Drake | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 长尾毛蕊茶 | Camellia caudata Wallich | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7 |
| 长叶粗丝木(暂拟) | Gomphandra sp.1 | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 长圆叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea oblongifolia Merrill & Chun | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 鹧鸪花 | Heynea trijuga Roxburgh | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 2.2 |
| 枝花流苏树 | Chionanthus ramiflorus Roxburgh | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 中华耳草 | Hedyotis cathayana W. C. Ko | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 钟萼粗叶木 | Lasianthus trichophlebus Hemsley | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 竹节树 | Carallia brachiata (Loureiro) Merrill | 红树科 | Rhizophoraceae | 4 |
| 竹叶青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis neglecta Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 子凌蒲桃 | Syzygium championii (Bentham) Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 紫毛野牡丹 | Melastoma penicillatum Naud. | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
Table S3 The species checklist of woody plants and their genus area types in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island
| 中文种名 Chinese species name | 拉丁种名 Latin species name | 中文科名 Chinese family name | 拉丁科名 Latin family name | 属区系类型* Area type of genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白花含笑 | Michelia mediocris Dandy | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 白肉榕 | Ficus vasculosa Wallich ex Miquel | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 白颜树 | Gironniera subaequalis Planchon | 榆科 | Ulmaceae | 7 |
| 百日青 | Podocarpus neriifolius D. Don in Lambert | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 2.1 |
| 柏拉木 | Blastus cochinchinensis Loureiro | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 棒花蒲桃 | Syzygium claviflorum (Roxburgh) Wallich ex Steudel | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 薄叶红厚壳 | Calophyllum membranaceum Gardner & Champion | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 2 |
| 薄叶猴耳环 | Archidendron utile (Chun & F. C. How) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 薄叶壳斗(暂拟) | Lithocarpus sp.2 | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 薄叶山矾 | Symplocos anomala Brand | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 保亭柿 | Diospyros potingensis Merrill & Chun | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 笔管榕 | Ficus subpisocarpa Gagnepain | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 笔罗子 | Meliosma rigida Siebold & Zuccarini | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 变色山槟榔 | Pinanga baviensis Beccari | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 7 |
| 滨木犀榄 | Olea brachiata (Loureiro) Merrill | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 柄果柯 | Lithocarpus longipedicellatus (Hickel & A. Camus) A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 柴龙树 | Apodytes dimidiata E. Meyer ex Arnott | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 4.1 |
| 齿叶冬青 | Ilex crenata Thunberg | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 赤楠 | Syzygium buxifolium Hooker & Arnott | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 赤杨叶 | Alniphyllum fortunei (Hemsley) Makino | 安息香科 | Styracaceae | 7.4 |
| 丛花山矾 | Symplocos poilanei Guillaumin | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 粗毛野桐 | Hancea hookeriana Seemann | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 粗丝木 | Gomphandra tetrandra (Wallich) Sleumer | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 粗叶榕 | Ficus hirta Vahl | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 粗壮润楠 | Machilus robusta W. W. Smith | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 大萼木姜子 | Litsea baviensis Lecomte | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 大花五桠果 | Dillenia turbinata Finet & Gagnepain | 五桠果科 | Dilleniaceae | 5 |
| 大叶蒲葵 | Livistona saribus (Loureiro) Merrill ex Chevalier | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5 |
| 大叶鼠刺 | Itea macrophylla Wallich | 虎耳草科 | Saxifragaceae | 9 |
| 大叶鱼骨木 | Canthium simile Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 滇越杜英 | Elaeocarpus poilanei Gagnepain | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 东方琼楠 | Beilschmiedia tungfangensis S. K. Lee & L. F. Lau | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 东方肖榄 | Platea parvifolia Merrill & Chun | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 短柄紫珠 | Callicarpa brevipes (Bentham) Hance | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 短药蒲桃 | Syzygium globiflorum (Craib) P. Chantanaranothai & J. Parnell | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 多萼核果茶 | Pyrenaria jonquieriana Pierre ex Lanessan subsp. multisepala (Merrill & Chun) S. X. Yang | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7 |
| 多花五月茶 | Antidesma maclurei Merrill | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 多香木 | Polyosma cambodiana Gagnepain | 虎耳草科 | Saxifragaceae | 5 |
| 鹅掌柴 | Schefflera heptaphylla (Linnaeus) Frodin | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 二色波罗蜜 | Artocarpus styracifolius Pierre | 桑科 | Moraceae | 7 |
| 饭甑青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis fleuryi (Hickel & A. Camus) Chun ex Q. F. Zheng | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 方枝蒲桃 | Syzygium tephrodes (Hance) Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 肥荚红豆 | Ormosia fordiana Oliver | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 粉背琼楠 | Beilschmiedia glauca S. K. Lee & L. F. Lau | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 缝线海桐 | Pittosporum perryanum Gowda | 海桐花科 | Pittosporaceae | 4 |
| 橄榄 | Canarium album (Loureiro) Raeuschel | 橄榄科 | Burseraceae | 4 |
| 高山榕 | Ficus altissima Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 公孙锥 | Castanopsis tonkinensis Seemen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 贡甲 | Maclurodendron oligophlebium (Merrill) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 狗骨柴 | Diplospora dubia (Lindley) Masamune | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 谷木 | Memecylon ligustrifolium Champion ex Bentham | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 4 |
| 灌丛泡花树 | Meliosma dumicola W. W. Smith | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 灌木土密树 | Bridelia harmandii Gagnepain | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 6 |
| 光叶山矾 | Symplocos lancifolia Siebold & Zuccarini | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 光叶山小橘 | Glycosmis craibii var. glabra (Craib) Tanaka | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 广东粗叶木 | Lasianthus curtisii King & Gamble | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 广东大青 | Clerodendrum kwangtungense Handel-Mazzetti | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 广东冬青 | Ilex kwangtungensis Merrill | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 广东假木荷 | Craibiodendron scleranthum (Dop) Judd var. kwang-tungense (S. Y. Hu) Judd | 杜鹃花科 | Ericaceae | 7.4 |
| 广东山胡椒 | Lindera kwangtungensis (H. Liu) C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 广南天料木 | Homalium paniculiflorum How & Ko | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 过布柿 | Diospyros susarticulata Lecomte | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 海岛冬青 | Ilex goshiensis Hayata | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 海南暗罗 | Polyalthia laui Merrill | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 4 |
| 海南槽裂木 | Pertusadina metcalfii (Merrill ex H. L. Li) Y. F. Deng & C. M. Hu | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 海南草珊瑚 | Sarcandra glabra subsp. brachystachys (Blume) Verdcourt | 金粟兰科 | Chloranthaceae | 7 |
| 海南大头茶 | Polyspora hainanensis (Hung T. Chang) C. X. Ye ex B. M. Bartholomew & T. L. Ming | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 9 |
| 海南冬青 | Ilex hainanensis Merrill | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 海南鹅耳枥 | Carpinus londoniana var. lanceolata (Handel-Mazzetti) P. C. Li in P. C. Li & S. H. Cheng | 桦木科 | Betulaceae | 8 |
| 海南鹅掌柴 | Schefflera hainanensis Merrill & Chun | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 海南玫瑰木 | Rhodamnia dumetorum var. hainanensis Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 5 |
| 海南蜜茱萸 | Melicope chunii (Merrill) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 海南木莲 | Manglietia fordiana var. hainanensis (Dandy) N. H. Xia | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 海南木犀榄 | Olea hainanensis H. L. Li | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 海南破布叶 | Microcos chungii (Merrill) Chun | 椴树科 | Tiliaceae | 7 |
| 海南雀舌木 | Leptopus hainanensis (Merrill & Chun) Pojarkova | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 5 |
| 海南山矾 | Symplocos hainanensis Merrill & Chun ex H. L. Li | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 海南山胡椒 | Lindera robusta (C. K. Allen) H. P. Tsui | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 海南山龙眼 | Helicia hainanensis Hayata | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 海南韶子 | Nephelium topengii (Merrill) H. S. Lo | 无患子科 | Sapindaceae | 7 |
| 海南树参 | Dendropanax hainanensis (Merrill & Chun) Chun | 五加科 | Araliaceae | 2 |
| 海南腺萼木 | Mycetia hainanensis H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 海南蕈树 | Altingia obovata Merrill & Chun | 金缕梅科 | Hamamelidaceae | 7.1 |
| 海南杨桐 | Adinandra hainanensis Hayata | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 6.2 |
| 海南栀子 | Gardenia hainanensis Merrill | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 海南轴榈 | Licuala hainanensis A. J. Henderson | 棕榈科 | Arecaceae (Palmae) | 5 |
| 海南紫荆木 | Madhuca hainanensis Chun & How | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 5 |
| 禾串树 | Bridelia balansae Tutcher | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 6 |
| 黑桫椤 | Alsophila podophylla (Hook.) Cop. | 桫椤科 | Cyatheaceae | 蕨类植物 |
| 红果坚木 | Dysoxylum gotadhora (Buchanan-Hamilton) Mabberley | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 7 |
| 红柯 | Lithocarpus fenzelianus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 红鳞蒲桃 | Syzygium hancei Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 红毛山楠 | Phoebe hungmoensis S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 红木荷 | Schima wallichii (Candolle) Korthals | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7.1 |
| 红算盘子 | Glochidion coccineum (Buchanan-Hamilton) Müller Argoviensis | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 2 |
| 红枝蒲桃 | Syzygium rehderianum Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 红枝琼楠 | Beilschmiedia laevis C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 红锥 | Castanopsis hystrix J. D. Hooker & Thomson ex A. de Candolle | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 猴耳环 | Archidendron clypearia (Jack) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 猴欢喜 | Sloanea sinensis (Hance) Hemsley | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 3 |
| 厚边木犀 | Osmanthus marginatus (Champion ex Bentham) Hemsley | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 厚梗染木树 | Saprosma crassipes H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 厚壳桂 | Cryptocarya chinensis (Hance) Hemsley | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 厚皮香 | Ternstroemia gymnanthera (Wight & Arnott) Beddome | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 2 |
| 厚皮香八角 | Illicium ternstroemioides A. C. Smith | 八角科 | Illiciaceae | 9 |
| 华南毛柃 | Eurya ciliata Merrill | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 华南青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis edithiae (Skan) Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 华润楠 | Machilus chinensis (Bentham) Hemsley | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 黄丹木姜子 | Litsea elongata (Nees) J. D. Hooker | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 黄果粗叶木 | Lasianthus calycinus Dunn | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 黄脉九节 | Psychotria straminea Hutchinson | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 黄毛粗叶木 | Lasianthus rhinocerotis Blume | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 黄杞 | Engelhardia roxburghiana Wallich | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 黄桐 | Endospermum chinense Bentham | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 7 |
| 黄叶树 | Xanthophyllum hainanense Hu | 远志科 | Polygalaceae | 5 |
| 黄樟 | Cinnamomum parthenoxylon (Jack) Meisner | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 灰毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus limitaneus Handel-Mazzetti | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 喙果黑面神 | Breynia rostrata Merrill | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 5 |
| 喙果皂帽花 | Dasymaschalon rostratum Merrill & Chun | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 7 |
| 鸡毛松 | Dacrycarpus imbricatus (Blume) de Laubenfels var. patulus de Laubenfels | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 5.1 |
| 鸡屎树 | Lasianthus hirsutus (Roxburgh) Merrill | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 鲫鱼胆 | Maesa perlarius (Loureiro) Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 4 |
| 假黄皮 | Clausena excavata N. L. Burman | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 4 |
| 假苹婆 | Sterculia lanceolata Cavanilles | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 2 |
| 假鹊肾树 | Streblus indicus (Bureau) Corner | 桑科 | Moraceae | 7 |
| 假鱼骨木 | Psydrax dicocca Gaertner | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 尖峰岭锥 | Castanopsis jianfenglingensis Duanmu | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 尖峰蒲桃 | Syzygium jienfunicum Hung T. Chang & R. H. Miao | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 尖峰润楠 | Machilus monticola S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 尖蕾狗牙花 | Tabernaemontana bufalina Loureiro | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 2 |
| 尖叶弯管花 | Chassalia curviflora var. longifolia J. D. Hooker | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 柬埔寨子楝树 | Decaspermum montanum Ridley | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 7 |
| 剑叶梭罗 | Reevesia lancifolia H. L. Li | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 7.1 |
| 金叶树 | Chrysophyllum lanceolatum (Blume) A. de Candolle var. stellatocarpon P. Royen | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 3 |
| 九节 | Psychotria asiatica Linnaeus | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 绢毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus nitentifolius Merrill & Chun | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 刻节润楠 | Machilus cicatricosa S. K. Lee | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 苦梓含笑 | Michelia balansae (Aug. Candolle) Dandy | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 7 |
| 阔叶肖榄 | Platea latifolia Blume | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 乐东拟单性木兰 | Parakmeria lotungensis (Chun & C. H. Tsoong) Y. W. Law | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 15 |
| 乐东锥 | Castanopsis ledongensis C. C. Huang & Y. T. Chang | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 簕党花椒 | Zanthoxylum avicennae (Lamarck) Candolle | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 2 |
| 雷公青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis hui (Chun) Chun ex Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 梨果柯 | Lithocarpus howii Chun | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 黧蒴锥 | Castanopsis fissa (Champion ex Bentham) Rehder & E. H. Wilson | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 栎子青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis blakei (Skan) Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 楝叶吴萸 | Tetradium glabrifolium (Champion ex Bentham) T. G. Hartley | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 14 |
| 两广梭罗 | Reevesia thyrsoidea Lindley | 梧桐科 | Sterculiaceae | 7.1 |
| 两叶黄杞 | Engelhardia unijuga Chun ex P. Y. Chen | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 亮叶猴耳环 | Archidendron lucidum (Bentham) I. C. Nielsen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 7 |
| 亮叶青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis phanera (Chun) Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 鳞斑荚蒾 | Viburnum punctatum Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don | 五福花科 | Adoxaceae | 8 |
| 岭罗麦 | Tarennoidea wallichii (J. D. Hooker) Tirvengadum & Sastre | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 岭南山竹子 | Garcinia oblongifolia Champion ex Bentham | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 6 |
| 瘤果柯 | Lithocarpus handelianus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 陆均松 | Dacrydium pectinatum de Laubenfels | 罗汉松科 | Podocarpaceae | 2.1 |
| 卵叶桂 | Cinnamomum rigidissimum Hung T. Chang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 卵叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea ovatifolia Yen C. Yang & P. H. Huang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 轮叶木姜子 | Litsea verticillata Hance | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 罗浮枫 | Acer fabri Hance | 槭树科 | Aceraceae | 8 |
| 罗浮柿 | Diospyros morrisiana Hance | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 罗浮锥 | Castanopsis fabri Hance | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 罗伞树 | Ardisia quinquegona Blume | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 萝芙木 | Rauvolfia verticillata (Loureiro) Baillon | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 3 |
| 绿枝山矾 | Symplocos viridissima Brand | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 毛冬青 | Ilex pubescens Hooker & Arnott | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 毛果柯 | Lithocarpus pseudovestitus A. Camus | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 毛菍 | Melastoma sanguineum Sims | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
| 毛叶脚骨脆 | Casearia velutina Blume | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 美丽新木姜子 | Neolitsea pulchella (Meisner) Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 美脉粗叶木 | Lasianthus lancifolius J. D. Hooker | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 米锥 | Castanopsis carlesii (Hemsley) Hayata | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 9 |
| 密花山矾 | Symplocos congesta Bentham | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 密花树 | Myrsine seguinii H. Léveillé | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 6 |
| 密鳞紫金牛 | Ardisia densilepidotula Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 木荷 | Schima superba Gardner & Champion | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7.1 |
| 木荚红豆 | Ormosia xylocarpa Chun ex Merrill & L. Chen | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 木竹子 | Garcinia multiflora Champion ex Bentham | 藤黄科 | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) | 6 |
| 南亚柏拉木 | Blastus borneensis Cogniaux ex Boerlage | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 泥柯 | Lithocarpus fenestratus (Roxburgh) Rehder | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 拟杜茎山 | Maesa consanguinea Merrill | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 4 |
| 拟榕叶冬青 | Ilex subficoidea S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 牛耳枫 | Daphniphyllum calycinum Bentham | 交让木科 | Daphniphyllaceae | 7 |
| 钮子果 | Ardisia virens Kurz | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 泡叶龙船花 | Ixora nienkui Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 盆架树 | Alstonia rostrata C. E. C. Fischer | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 7 |
| 披针叶乌口树 | Tarenna lancilimba W. C. Chen | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 枇杷叶山龙眼 | Helicia obovatifolia var. mixta (H. L. Li) Sleumer | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 平塘榕 | Ficus tuphapensis Drake | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 坡垒 | Hopea hainanensis Merrill & Chun | 龙脑香科 | Dipterocarpaceae | 7 |
| 漆树 | Toxicodendron vernicifluum (Stokes) F. A. Barkley | 漆树科 | Anacardiaceae | 9 |
| 千里香 | Murraya paniculata (Linnaeus) Jack | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 青梅 | Vatica mangachapoi Blanco | 龙脑香科 | Dipterocarpaceae | 7 |
| 琼岛染木树 | Saprosma merrillii H. S. Lo | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 琼楠 | Beilschmiedia intermedia C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 绒毛山胡椒 | Lindera nacusua (D. Don) Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 榕叶冬青 | Ilex ficoidea Hemsley | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 肉实树 | Sarcosperma laurinum (Bentham) J. D. Hooker | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 7 |
| 软荚红豆 | Ormosia semicastrata Hance | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 山地五月茶 | Antidesma montanum Blume | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 4 |
| 山杜英 | Elaeocarpus sylvestris (Loureiro) Poiret | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 山矾 | Symplocos sumuntia Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 山橘树 | Glycosmis cochinchinensis (Loureiro) Pierre | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 7 |
| 山牡荆 | Vitex quinata (Loureiro) Williams | 马鞭草科 | Verbenaceae | 2 |
| 山榕 | Ficus heterophylla Linnaeus f. | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 山乌桕 | Triadica cochinchinensis Loureiro | 大戟科 | Euphorbiaceae | 2 |
| 山香圆 | Turpinia montana (Blume) Kurz | 省沽油科 | Staphyleaceae | 3 |
| 山油柑 | Acronychia pedunculata (Linnaeus) Miquel | 芸香科 | Rutaceae | 5 |
| 十蕊枫 | Acer laurinum Hasskarl | 槭树科 | Aceraceae | 8 |
| 石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis indica (Linnaeus) Lindley | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 疏花卫矛 | Euonymus laxiflorus Champion ex Bentham | 卫矛科 | Celastraceae | 2 |
| 双瓣木犀 | Osmanthus didymopetalus P. S. Green | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 水锦树 | Wendlandia uvariifolia Hance | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 5 |
| 水同木 | Ficus fistulosa Reinwardt ex Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 四蕊三角瓣花 | Prismatomeris tetrandra (Roxburgh) K. Schumann | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 7 |
| 台湾枇杷 | Eriobotrya deflexa (Hemsley) Nakai | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 台湾榕 | Ficus formosana Maximowicz | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 桃榄 | Pouteria annamensis (Pierre) Baehni | 山榄科 | Sapotaceae | 2 |
| 桃叶石楠 | Photinia prunifolia (Hooker & Arnott) Lindley | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 9 |
| 调羹树 | Heliciopsis lobata (Merrill) Sleumer | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 7 |
| 铁山矾 | Symplocos pseudobarberina Gontscharow | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 铜盆花 | Ardisia obtusa Mez | 紫金牛科 | Myrsinaceae | 2 |
| 凸脉冬青 | Ilex kobuskiana S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 土沉香 | Aquilaria sinensis (Loureiro) Sprengel | 瑞香科 | Thymelaeaceae | 7 |
| 臀果木 | Pygeum topengii Merrill | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 7 |
| 托盘青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis (Chun) Y. C. Hsu & H. W. Jen | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 洼皮冬青 | Ilex nuculicava S. Y. Hu | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 弯管花 | Chassalia curviflora (Wallich) Thwaites | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 网脉琼楠 | Beilschmiedia tsangii Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 微毛柃 | Eurya hebeclados Y. Ling | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 微毛山矾 | Symplocos wikstroemiifolia Hayata | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 蚊母树 | Distylium racemosum Siebold & Zuccarini | 金缕梅科 | Hamamelidaceae | 7 |
| 乌材 | Diospyros eriantha Champion ex Bentham | 柿科 | Ebenaceae | 2 |
| 乌榄 | Canarium pimela K. D. Koenig | 橄榄科 | Burseraceae | 4 |
| 乌檀 | Nauclea officinalis (Pierre ex Pitard) Merrill & Chun | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 6 |
| 五列木 | Pentaphylax euryoides Gardner & Champion | 五列木科 | Pentaphylacaceae | 7 |
| 细齿叶柃 | Eurya nitida Korthals | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 3 |
| 细轴荛花 | Wikstroemia nutans Champion ex Bentham | 瑞香科 | Thymelaeaceae | 5 |
| 狭叶泡花树 | Meliosma angustifolia Merrill | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 显脉杜英 | Elaeocarpus dubius A. Candolle | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 显脉虎皮楠 | Daphniphyllum paxianum K. Rosenthal | 交让木科 | Daphniphyllaceae | 7 |
| 显脉天料木 | Homalium phanerophlebium How & Ko | 大风子科 | Flacourtiaceae | 2 |
| 线枝蒲桃 | Syzygium araiocladum Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 腺叶山矾 | Symplocos adenophylla Wallich ex G. Don | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 香港大沙叶 | Pavetta hongkongensis Bremekamp | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4 |
| 香港坚木 | Dysoxylum hongkongense (Tutcher) Merrill | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 7 |
| 香港木兰 | Lirianthe championii (Bentham) N. H. Xia & C. Y. Wu, | 木兰科 | Magnoliaceae | 9 |
| 香桂 | Cinnamomum subavenium Miquel | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 香果新木姜子 | Neolitsea ellipsoidea C. K. Allen | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 香楠 | Aidia canthioides (Champion ex Bentham) Masamune | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 4.1 |
| 肖蒲桃 | Syzygium acuminatissimum (Blume) Candolle | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 小果山龙眼 | Helicia cochinchinensis Loureiro | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 斜脉异萼花 | Disepalum plagioneurum (Diels) D. M. Johnson | 番荔枝科 | Annonaceae | 4 |
| 杏叶柯 | Lithocarpus amygdalifolius (Skan) Hayata | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 雄鸡树 | Litsea variabilis f. chinensis (C. K. Allen) Yen C. Yang & P. H. Huang | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 3 |
| 锈毛杜英 | Elaeocarpus howii Merrill & Chun | 杜英科 | Elaeocarpaceae | 2 |
| 锈毛石斑木 | Rhaphiolepis ferruginea F. P. Metcalf | 蔷薇科 | Rosaceae | 14 |
| 锈叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea cambodiana Lecomte | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 羊舌树 | Symplocos glauca (Thunberg) Koidzumi | 山矾科 | Symplocaceae | 2 |
| 药用狗牙花 | Tabernaemontana bovina Loureiro | 夹竹桃科 | Apocynaceae | 2 |
| 野牡丹 | Melastoma malabathricum Linnaeus | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
| 异形木 | Allomorphia balansae Cogniaux | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 7 |
| 阴香 | Cinnamomum burmannii (Nees & T. Nees) Blume | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 5 |
| 隐脉红淡比 | Cleyera obscurinervia (Merrill & Chun) Hung T. Chang | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 2 |
| 硬核 | Scleropyrum wallichianum (Wight & Arnott) Arnott | 檀香科 | Santalaceae | 7 |
| 硬壳桂 | Cryptocarya chingii W. C. Cheng | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 2 |
| 硬壳柯 | Lithocarpus hancei (Benth.) Rehd. | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 油丹 | Alseodaphne hainanensis Merrill | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 越南冬青 | Ilex cochinchinensis (Loureiro) Loesener | 冬青科 | Aquifoliaceae | 2 |
| 云南黄杞 | Engelhardia spicata Leschenault ex Blume | 胡桃科 | Juglandaceae | 7 |
| 云南木犀榄 | Olea tsoongii (Merrill) P. S. Green | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 12.3 |
| 杂色榕 | Ficus variegata Blume | 桑科 | Moraceae | 2 |
| 粘木 | Ixonanthes reticulata Jack | 古柯科 | Erythroxylaceae | 7 |
| 樟叶泡花树 | Meliosma squamulata Hance | 清风藤科 | Sabiaceae | 3 |
| 长柄山龙眼 | Helicia longipetiolata Merrill & Chun | 山龙眼科 | Proteaceae | 5 |
| 长柄鼠李 | Rhamnus longipes Merrill & Chun | 鼠李科 | Rhamnaceae | 1 |
| 长萼粗叶木 | Lasianthus chevalieri Pitard | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 长花厚壳树 | Ehretia longiflora Champion ex Bentham | 紫草科 | Boraginaceae | 4 |
| 长脐红豆 | Ormosia balansae Drake | 豆科 | Fabaceae | 2 |
| 长尾毛蕊茶 | Camellia caudata Wallich | 山茶科 | Theaceae | 7 |
| 长叶粗丝木(暂拟) | Gomphandra sp.1 | 茶茱萸科 | Icacinaceae | 7 |
| 长圆叶新木姜子 | Neolitsea oblongifolia Merrill & Chun | 樟科 | Lauraceae | 7 |
| 鹧鸪花 | Heynea trijuga Roxburgh | 楝科 | Meliaceae | 2.2 |
| 枝花流苏树 | Chionanthus ramiflorus Roxburgh | 木犀科 | Oleaceae | 9 |
| 中华耳草 | Hedyotis cathayana W. C. Ko | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2 |
| 钟萼粗叶木 | Lasianthus trichophlebus Hemsley | 茜草科 | Rubiaceae | 2.2 |
| 竹节树 | Carallia brachiata (Loureiro) Merrill | 红树科 | Rhizophoraceae | 4 |
| 竹叶青冈 | Cyclobalanopsis neglecta Schottky | 壳斗科 | Fagaceae | 7 |
| 子凌蒲桃 | Syzygium championii (Bentham) Merrill & L. M. Perry | 桃金娘科 | Myrtaceae | 4 |
| 紫毛野牡丹 | Melastoma penicillatum Naud. | 野牡丹科 | Melastomataceae | 5 |
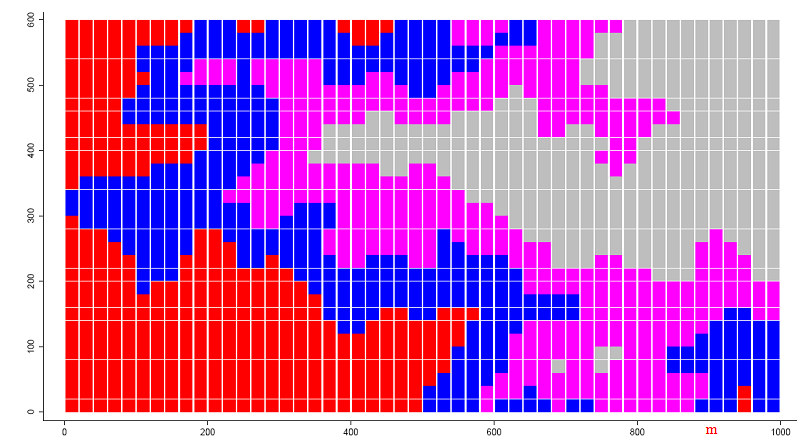
Fig. S2 Clustering analysis of three topographical parameters of the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island. Red, Flat ground, Blue, Gentle slope, Purple, Mesoslope, Grey, Ridge.
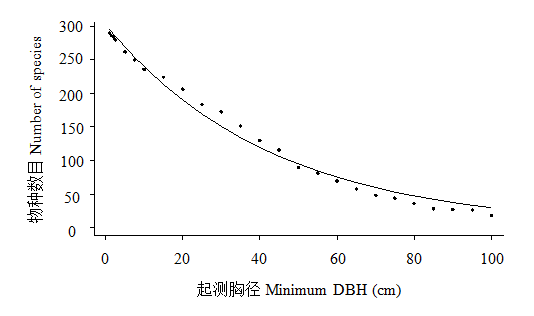
Fig. S3 Number of species increased with the minimum diameter at breast height of the woody plants in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island.
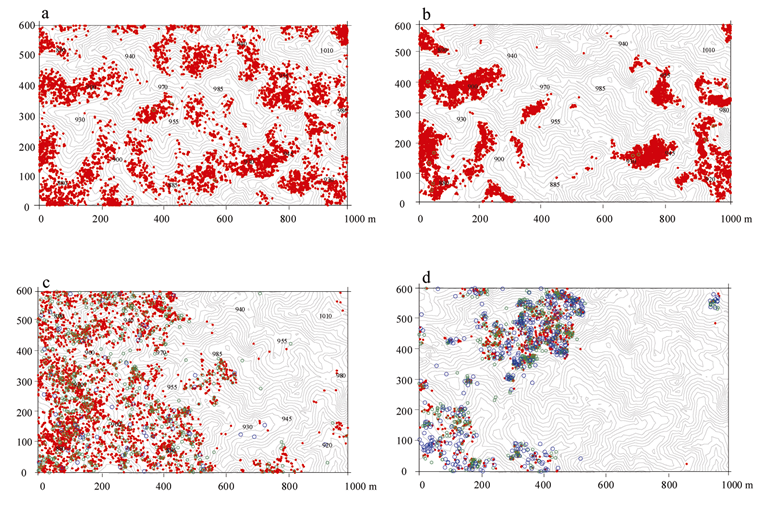
Fig. S4 Spatial distribution map of four species in the 60-ha Jianfengling Forest Dynamics Plot on Hainan Island. (a) Pinanga baviensis; (b) Blastus cochinchinensis; (c) Ormosia balansae; (d) Altingia obovata. Red, 1 cm ≤ DBH < 5 cm; Green, 5 cm ≤ DBH < 20 cm; Blue, DBH ≥ 20 cm.
| 1 | Cao HL (曹洪麟), Wu LF (吴林芳), Wang ZG (王志高), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Lian JY (练琚愉), Ye WH (叶万辉) (2013) Dinghushan Lower Subtropical Forest Dynamics Plot: Tree Species and Their Distribution Patterns (鼎湖山南亚热带森林: 树种及其分布格局). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 2 | Cao M, Zhu H, Wang H, Lan GY, Hu YH, Zhou SS, Deng XB, Cui JY (2008) Xishuangbanna Tropical Seasonal Rainforest Dynamics Plot: Tree Distribution Maps, Diameter Tables and Species Documentation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. |
| 3 | Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18-22. |
| 4 | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| 5 | Condit R, Ashton P, Bunyavejchewin S, Dattaraja HS, Davies S, Esufali S, Ewango C, Foster R, Gunatilleke IAUN, Gunatilleke CVS, Hall P, Harms KE, Hart T, Hernandez C, Hubbell S, Itoh A, Kiratiprayoon S, LaFrankie J, Lao SL, Makana JR, Noor MNS, Kassim AR, Russo S, Sukumar R, Samper C, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas S, Valencia R, Vallejo M, Villa G, Zillio T (2006) The importance of demographic niches to tree diversity.Science, 313, 98-101. |
| 6 | Fang JY (方精云), Li YD (李意德), Zhu B (朱彪), Liu GH (刘国华), Zhou GY (周光益) (2004) Community structures and species richness in the montane rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 12, 29-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008) Broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan (CBS) of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 238-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 8 | Huang Q (黄全), Li YD (李意德), Zheng DZ (郑德璋) (1986) Study of tropical vegetation series in Jianfengling region, Hainan Island.Acta Phytoecologica et Geototanica Sinica(植物生态学和地植物学学报), 10, 90-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 9 | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a Neotropical forest: implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: the Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soule ME), pp. 205-231. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA. |
| 10 | Jiang HS (江海声) (2006) Biodiversity and Protection in Diaoluoshan, Hainan Island (海南吊罗山生物多样性及其保护). Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| 11 | Jiang YX (蒋有绪), Lu JP (卢俊培) (1991) Forest Ecosystem of Tropical Forest of Jianfengling Mountain, Hainan Island, China (中国海南岛尖峰岭热带林生态系统). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 12 | Lan GY (兰国玉), Hu YH (胡跃华), Cao M (曹敏), Zhu H (朱华), Wang H (王洪), Zhou SS (周仕顺), Deng XB (邓晓保), Cui JY (崔景云), Huang JG (黄建国), Liu LY (刘林云), Xu HL (许海龙), Song JP (宋军平), He YC (何有才) (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamics plot: species composition and spatial distribution patterns. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 287-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 13 | Li YD (李意德) (1997) Community characteristics of tropical mountain rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island.Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 5, 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Li YD (李意德), Chen BF (陈步峰), Zhou GY (周光益), Wu ZM (吴仲民), Zeng QB (曾庆波), Luo TS (骆土寿), Huang SN (黄世能), Xie MD (谢明东), Huang Q (黄全) (2002) Research and Conservation of Tropical Forest and the Biodiversity: A Special Reference to Hainan Island, China (中国海南岛热带森林及其生物多样性保护研究). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 15 | Li YD (李意德), Fang H (方洪), Luo W (罗文), Chen HQ (陈焕强), Jiang ZL (蒋忠亮) (2006) The resource and community characteristics of Vatica mangachapoi forest in Jianfengling National Nature Reserve, Hainan Island.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 42(1), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Li YD (李意德), Xu H (许涵), Chen DX (陈德祥), Luo TS (骆土寿), Mo JH (莫锦华), Luo W (罗文), Chen HQ (陈焕强), Jiang ZL (蒋忠亮) (2007) Discussing on the ecological species groups and functional groups division based on the interspecific association—a case study on the arbor layer data in tropical lowland rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 43(4), 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Li YD (李意德), Xu H (许涵), Luo TS (骆土寿), Chen DX (陈德祥), Lin MX (林明献) (2012) Permanent Monitoring and Research Dataset of Chinese Ecosystem: Forest Ecosystem: Jianfengling Station (Bio-species Checklist) (中国生态系统定位观测与研究数据集: 森林生态系统卷:海南尖峰岭站(生物物种数据集)). Chinese Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 18 | Long WX (龙文兴), Zang RG (臧润国), Ding Y (丁易) (2011) Community characteristics of tropical montane evergreen forest and tropical montane dwarf forest in Bawangling National Nature Reserve on Hainan Island, South China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 558-566. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Wang BS (王伯荪), Yu SX (余世孝), Peng SL (彭少麟) (1996) Experimental Manual for Plant Community (植物群落学实验手册). Guangdong Higher Education Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| 20 | Xu H (许涵), Li YD (李意德), Luo TS (骆土寿), Lin MX (林明献), Chen DX (陈德祥), Mo JH (莫锦华), Luo W (罗文), Hong XJ (洪小江), Jiang ZL (蒋忠亮) (2009) Community structure characteristics of tropical montane rain forests with different regeneration types in Jianfengling.Scientia Silvae Sinicae(林业科学), 45(1), 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Yang QS (杨庆松), Ma ZP (马遵平), Xie YB (谢玉彬), Zhang ZG (张志国), Wang ZH (王樟华), Liu HM (刘何铭), Li P (李萍), Zhang N (张娜), Wang DL (王达力), Yang HB (杨海波), Fang XF (方晓峰), Yan ER (阎恩荣), Wang XH (王希华) (2011) Community structure and species composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong’s 20 ha dynamic plot, Zhejiang Province, eastern China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evegreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 23 | Yu SX (余世孝), Zang RG (臧润国), Jiang YX (蒋有绪) (2001) Species richness-abundance relationship in four tropical forests on altitudinal gradient in Bawangling Nature Reserve, Hainan.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 25, 291-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Zang RG (臧润国), Yang YC (杨彦承), Jiang YX (蒋有绪) (2001) Community structure and tree species diversity characteristics in a tropical montane rain forest in Bawangling Nature Reserve, Hainan Island.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 25, 270-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 25 | Zeng QB (曾庆波), Li YD (李意德), Chen BF (陈步峰), Wu ZM (吴仲民), Zhou GY (周光益) (1997) Research and Management of Tropical Forest Ecosystem (热带森林生态系统研究与管理). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 26 | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, east China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [13] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [14] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [15] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn