



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 21484. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021484 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021484
胡远芳1, 李斌强1,2, 梁丹3, 李兴权4, 刘兰香4, 杨家伟4, 罗旭1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-25
接受日期:2022-06-06
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
罗旭
作者简介:* E-mail: luoxu@swfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yuanfang Hu1, Binqiang Li1,2, Dan Liang3, Xingquan Li4, Lanxiang Liu4, Jiawei Yang4, Xu Luo1,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-25
Accepted:2022-06-06
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-08-31
Contact:
Xu Luo
摘要:
人类足迹的扩张增加了人与野生动物的相互作用。理解自然保护地的濒危物种对人为干扰的响应有助于更好地保护濒危物种和指导保护管理。以往的研究表明野生动物在时空维度会对人类的干扰进行规避, 然而这类研究在野生雉类中还较少, 尤其是分布在人为干扰相对较强的中低海拔区域的雉类, 如白腹锦鸡(Chrysolophus amherstiae)。2017年11月至2018年10月, 我们在中国西南部的一个亚热带森林保护区中使用红外相机陷阱技术对白腹锦鸡和人为干扰进行调查, 并研究了白腹锦鸡在时空维度对3种不同类型人为干扰(人类活动、放牧和家养动物活动)的响应及其季节变化。结果表明, 白腹锦鸡在空间维度并未对人为干扰进行规避, 而在非繁殖季节的活动节律上对人为干扰在时间维度上进行了规避。具体而言, 白腹锦鸡在全年和非繁殖季节的活动高峰集中在17:30-18:30, 明显避开中午的人类活动高峰; 而在繁殖季节, 白腹锦鸡活动水平明显提高, 和人为干扰的重叠度很高, 可能是由于求偶、占区等繁殖行为使得白腹锦鸡无法规避人为干扰。此外, 在人为干扰强度较高的位点, 白腹锦鸡倾向于通过改变其日活动节律, 将活动高峰期推迟至傍晚以降低与人为干扰的重叠度, 进一步说明白腹锦鸡可通过调节其自身的日活动节律从而避开高强度的人为干扰。由于白腹锦鸡地面营巢和春夏季繁殖, 自然保护区管理部门可通过管理人为活动, 尤其在繁殖季节通过控制放牧和猫狗的活动来帮助白腹锦鸡及其他地面营巢鸟类维持繁殖成功率。
胡远芳, 李斌强, 梁丹, 李兴权, 刘兰香, 杨家伟, 罗旭 (2022) 人为干扰对白腹锦鸡活动节律的影响. 生物多样性, 30, 21484. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021484.
Yuanfang Hu, Binqiang Li, Dan Liang, Xingquan Li, Lanxiang Liu, Jiawei Yang, Xu Luo (2022) Effect of anthropogenic disturbance on Lady Amherst’s pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae) activity. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21484. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021484.
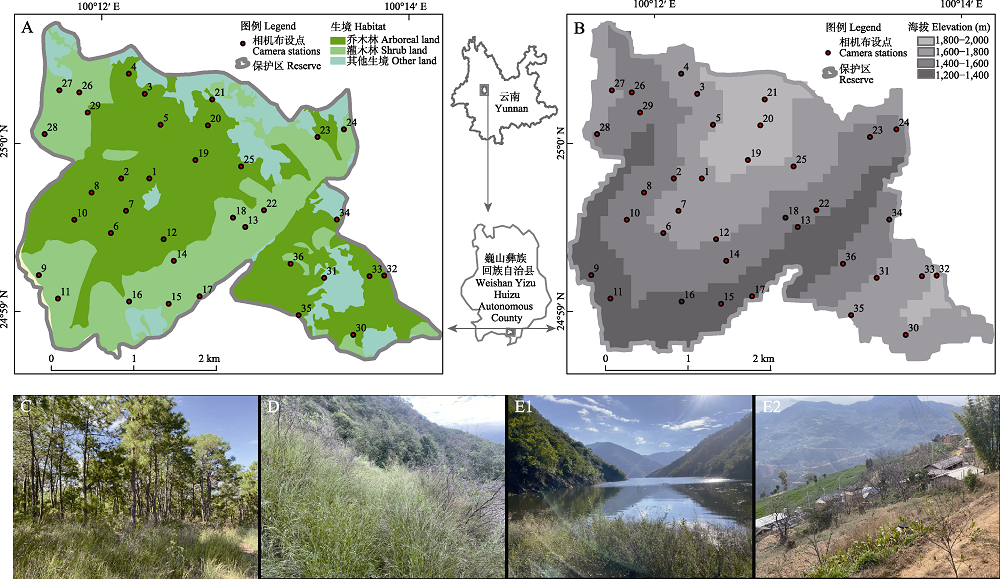
图1 巍山青华绿孔雀省级自然保护区红外相机布设位点图(A: 不同生境; B: 不同海拔)及3种生境类型图(C: 乔木林; D: 灌木林; E1, E2: 其他生境)
Fig. 1 Maps of infrared camera locations and the three habitat types in the Weishan Qinghua Green Peafowl Nature Reserve. A, Different habitats; B, Different altitudes; C, Arboreal land; D, Shrub land; E1 and E2, Other habitats.
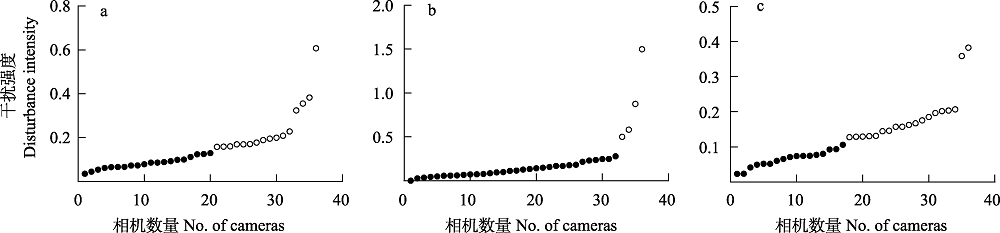
图2 全年(a)、繁殖季(b)和非繁殖季(c)的不同人为干扰强度位点划分。 表示低人为干扰强度位点; 表示高人为干扰强度位点。
Fig. 2 Classification of camera sites with different levels (high and low) of anthropogenic disturbance during the entire year (a), the breeding (b) and non-breeding (c) seasons. indicates sites with low anthropogenic disturbance; indicates sites with high anthropogenic disturbance.
| 季节 Season/变量 Variable | Beta系数 Beta coefficient | 标准误 SE | T | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体人为干扰 All anthropogenic disturbance | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.095 | 0.280 | 0.339 | 0.737 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.071 | 0.191 | 0.371 | 0.713 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.098 | 0.225 | -0.437 | 0.665 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.179 | 0.415 | -0.432 | 0.669 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.059 | 0.272 | 0.216 | 0.830 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.197 | 0.182 | -1.082 | 0.288 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.135 | 0.215 | -0.630 | 0.533 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.111 | 0.405 | -0.275 | 0.785 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.024 | 0.262 | 0.092 | 0.928 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.340 | 0.170 | 2.003 | 0.054 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.025 | 0.200 | 0.123 | 0.903 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.045 | 0.387 | -0.117 | 0.907 | ||||
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.105 | 0.277 | 0.381 | 0.706 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.158 | 0.189 | 0.834 | 0.411 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.137 | 0.223 | -0.614 | 0.544 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.200 | 0.410 | -0.487 | 0.630 | ||||
| 季节 Season/变量 Variable | Beta系数 Beta coefficient | 标准误 SE | T | P | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.073 | 0.275 | 0.267 | 0.791 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.128 | 0.186 | -0.689 | 0.496 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.159 | 0.220 | -0.722 | 0.475 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.139 | 0.409 | -0.340 | 0.736 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.025 | 0.238 | 0.104 | 0.918 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.525 | 0.154 | 3.402 | 0.002* | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.018 | 0.182 | -0.100 | 0.921 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.047 | 0.352 | -0.133 | 0.895 | ||||
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.075 | 0.278 | 0.272 | 0.788 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.082 | 0.181 | -0.453 | 0.653 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.045 | 0.213 | -0.210 | 0.835 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.143 | 0.411 | -0.348 | 0.730 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.090 | 0.271 | 0.331 | 0.743 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.167 | 0.181 | -0.923 | 0.363 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.157 | 0.212 | -0.740 | 0.465 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.170 | 0.401 | -0.424 | 0.674 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | -0.003 | 0.277 | -0.011 | 0.991 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.022 | 0.178 | -0.122 | 0.904 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.114 | 0.210 | 0.544 | 0.590 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | 0.006 | 0.410 | 0.014 | 0.989 | ||||
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.085 | 0.279 | 0.307 | 0.761 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.033 | 0.178 | -0.185 | 0.854 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.072 | 0.210 | -0.342 | 0.734 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.162 | 0.412 | -0.392 | 0.697 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.097 | 0.273 | 0.354 | 0.725 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.077 | 0.176 | -0.436 | 0.666 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.229 | 0.207 | -1.105 | 0.277 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.184 | 0.404 | -0.454 | 0.653 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | -0.019 | 0.278 | -0.070 | 0.945 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.095 | 0.177 | 0.536 | 0.596 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.121 | 0.208 | 0.581 | 0.566 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | 0.037 | 0.413 | 0.089 | 0.929 | ||||
表1 全年和不同季节白腹锦鸡活动强度与总体人为干扰强度以及3种人为干扰类型强度间的关系
Table 1 The relationship between the activity intensity of Lady Amherst’s pheasant and the intensity of anthropogenic disturbance (overall and three types of disturbance) throughout the year and in different seasons (breeding and non-breeding).
| 季节 Season/变量 Variable | Beta系数 Beta coefficient | 标准误 SE | T | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体人为干扰 All anthropogenic disturbance | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.095 | 0.280 | 0.339 | 0.737 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.071 | 0.191 | 0.371 | 0.713 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.098 | 0.225 | -0.437 | 0.665 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.179 | 0.415 | -0.432 | 0.669 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.059 | 0.272 | 0.216 | 0.830 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.197 | 0.182 | -1.082 | 0.288 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.135 | 0.215 | -0.630 | 0.533 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.111 | 0.405 | -0.275 | 0.785 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.024 | 0.262 | 0.092 | 0.928 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.340 | 0.170 | 2.003 | 0.054 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.025 | 0.200 | 0.123 | 0.903 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.045 | 0.387 | -0.117 | 0.907 | ||||
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.105 | 0.277 | 0.381 | 0.706 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.158 | 0.189 | 0.834 | 0.411 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.137 | 0.223 | -0.614 | 0.544 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.200 | 0.410 | -0.487 | 0.630 | ||||
| 季节 Season/变量 Variable | Beta系数 Beta coefficient | 标准误 SE | T | P | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.073 | 0.275 | 0.267 | 0.791 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.128 | 0.186 | -0.689 | 0.496 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.159 | 0.220 | -0.722 | 0.475 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.139 | 0.409 | -0.340 | 0.736 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.025 | 0.238 | 0.104 | 0.918 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.525 | 0.154 | 3.402 | 0.002* | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.018 | 0.182 | -0.100 | 0.921 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.047 | 0.352 | -0.133 | 0.895 | ||||
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.075 | 0.278 | 0.272 | 0.788 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.082 | 0.181 | -0.453 | 0.653 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.045 | 0.213 | -0.210 | 0.835 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.143 | 0.411 | -0.348 | 0.730 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.090 | 0.271 | 0.331 | 0.743 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.167 | 0.181 | -0.923 | 0.363 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.157 | 0.212 | -0.740 | 0.465 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.170 | 0.401 | -0.424 | 0.674 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | -0.003 | 0.277 | -0.011 | 0.991 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.022 | 0.178 | -0.122 | 0.904 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.114 | 0.210 | 0.544 | 0.590 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | 0.006 | 0.410 | 0.014 | 0.989 | ||||
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | ||||||||
| 全年 Whole year | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.085 | 0.279 | 0.307 | 0.761 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.033 | 0.178 | -0.185 | 0.854 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.072 | 0.210 | -0.342 | 0.734 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.162 | 0.412 | -0.392 | 0.697 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 Breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | 0.097 | 0.273 | 0.354 | 0.725 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | -0.077 | 0.176 | -0.436 | 0.666 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | -0.229 | 0.207 | -1.105 | 0.277 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | -0.184 | 0.404 | -0.454 | 0.653 | ||||
| 非繁殖季节 Non-breeding season | ||||||||
| 截距 Intercept | -0.019 | 0.278 | -0.070 | 0.945 | ||||
| 干扰强度 Disturbance intensity | 0.095 | 0.177 | 0.536 | 0.596 | ||||
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.121 | 0.208 | 0.581 | 0.566 | ||||
| 生境 Habitat | 0.037 | 0.413 | 0.089 | 0.929 | ||||
| 繁殖季节 In breeding seasons | 非繁殖季节 In non-breeding seasons | 差异 Differences in activity levels | Wald值 Wald value | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白腹锦鸡 Lady Amherst’s pheasants | 0.503 ± 0.019 | 0.314 ± 0.019 | 0.188 ± 0.028 | 45.542 | < 0.001 |
| 总体人为干扰 Overall anthropogenic disturbance | 0.326 ± 0.015 | 0.320 ± 0.015 | 0.006 ± 0.022 | 0.089 | 0.756 |
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | 0.374 ± 0.020 | 0.352 ± 0.020 | 0.022 ± 0.028 | 0.633 | 0.426 |
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | 0.222 ± 0.018 | 0.239 ± 0.019 | -0.018 ± 0.026 | 0.455 | 0.500 |
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | 0.267 ± 0.063 | 0.250 ± 0.053 | 0.018 ± 0.083 | 0.045 | 0.832 |
表2 不同季节白腹锦鸡和人为干扰的活动水平比较
Table 2 Activity levels differences of Lady Amherst’s pheasant and anthropogenic disturbance between breeding and non-breeding seasons
| 繁殖季节 In breeding seasons | 非繁殖季节 In non-breeding seasons | 差异 Differences in activity levels | Wald值 Wald value | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白腹锦鸡 Lady Amherst’s pheasants | 0.503 ± 0.019 | 0.314 ± 0.019 | 0.188 ± 0.028 | 45.542 | < 0.001 |
| 总体人为干扰 Overall anthropogenic disturbance | 0.326 ± 0.015 | 0.320 ± 0.015 | 0.006 ± 0.022 | 0.089 | 0.756 |
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | 0.374 ± 0.020 | 0.352 ± 0.020 | 0.022 ± 0.028 | 0.633 | 0.426 |
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | 0.222 ± 0.018 | 0.239 ± 0.019 | -0.018 ± 0.026 | 0.455 | 0.500 |
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | 0.267 ± 0.063 | 0.250 ± 0.053 | 0.018 ± 0.083 | 0.045 | 0.832 |
| 平均重叠系数 Mean overlap coefficient (△) | 平均零重叠度指数 Mean null overlap index | 零重叠度标准误 Standard error of the null distribution | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体人为干扰 Overall anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.826 | 0.968 | 0.008 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.879 | 0.956 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.786 | 0.958 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.860 | 0.964 | 0.009 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.835 | 0.960 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.788 | 0.950 | 0.013 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.660 | 0.951 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.630 | 0.937 | 0.017 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.684 | 0.938 | 0.016 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.749 | 0.896 | 0.025 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.757 | 0.868 | 0.035 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.679 | 0.858 | 0.036 | <0.001 |
表3 不同季节白腹锦鸡和3种类型人为干扰的重叠度
Table 3 Overlap coefficient between Lady Amherst’s pheasant and anthropogenic disturbance annually and in each season
| 平均重叠系数 Mean overlap coefficient (△) | 平均零重叠度指数 Mean null overlap index | 零重叠度标准误 Standard error of the null distribution | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体人为干扰 Overall anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.826 | 0.968 | 0.008 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.879 | 0.956 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.786 | 0.958 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(人类活动) Anthropogenic disturbance: human activities | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.860 | 0.964 | 0.009 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.835 | 0.960 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.788 | 0.950 | 0.013 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(放牧) Anthropogenic disturbance: grazing | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.660 | 0.951 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.630 | 0.937 | 0.017 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.684 | 0.938 | 0.016 | <0.001 |
| 人为干扰(家养动物) Anthropogenic disturbance: domestic animals | ||||
| 全年 Whole year | 0.749 | 0.896 | 0.025 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season | 0.757 | 0.868 | 0.035 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season | 0.679 | 0.858 | 0.036 | <0.001 |
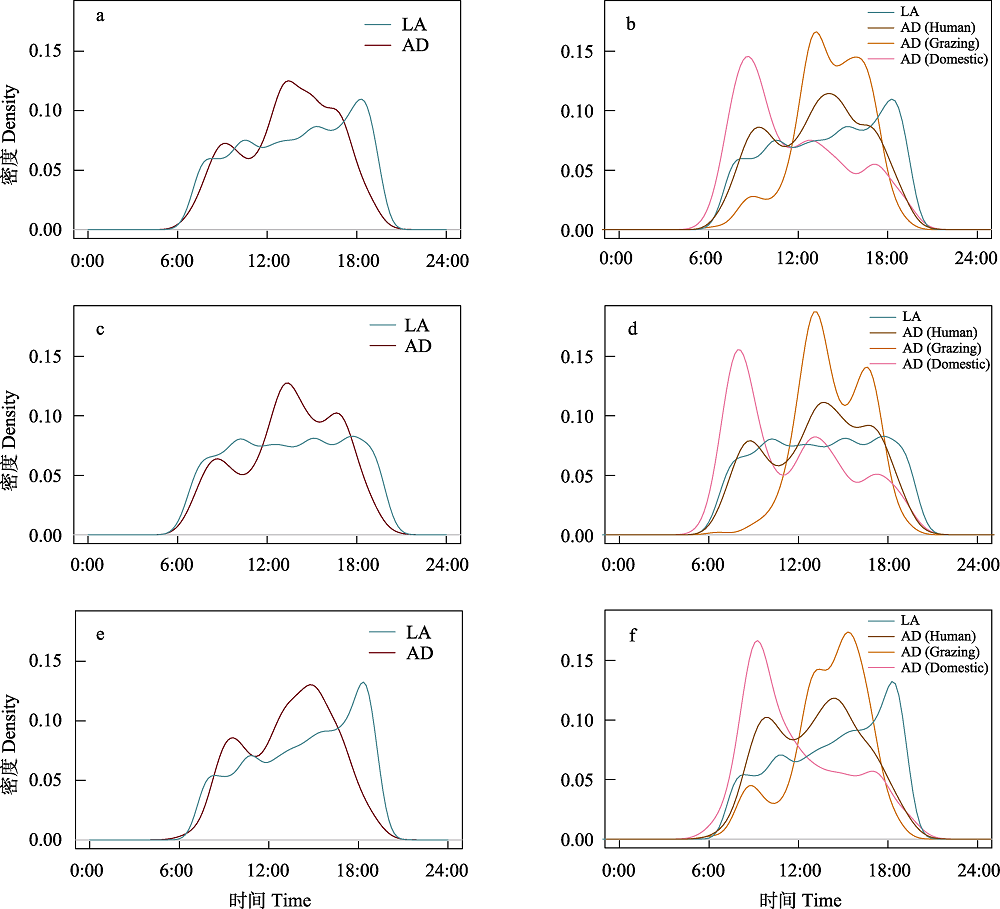
图3 人为干扰和白腹锦鸡的日活动节律比较和两者间重叠度。 a-b: 全年总体人为干扰和各个类型的人为干扰与白腹锦鸡日活动节律比较; c-d: 繁殖季节总体人为干扰和各个类型的人为干扰与白腹锦鸡的日活动节律比较; e-f: 非繁殖季节总体人为干扰和各个类型人为干扰与白腹锦鸡的日活动节律比较。LA表示白腹锦鸡; AD表示总人为干扰; AD (Human)表示人类活动; AD (Grazing)表示放牧活动; AD (Domestic)表示家养动物活动。详细活动水平和重叠度见表2和表3。
Fig. 3 The activity patterns and overlaps of anthropogenic disturbance and Lady Amherst’s pheasants. The comparisons of daily activities between the Lady Amherst’s pheasant (LA) and the overall anthropogenic disturbance and the three types of anthropogenic disturbance throughout the year (a and b), as well as in the breeding (c and d) and non-breeding (e and f) seasons. Anthropogenic disturbance were classified into human activities (AD (Human)), grazing (AD (Grazing)), and domestic animals (AD (domestic)). See Table 2 and 3 for details.
| 位点 Sites/季节 Season | 平均重叠系数 Mean overlap coefficient (△) | 平均零重叠度指数 Mean null overlap index | 零重叠度标准误 Standard error of the null distribution | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低人为干扰位点Camera sites with low anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year (N = 20 sites) | 0.858 | 0.957 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season (N = 32 sites) | 0.842 | 0.954 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season (N = 18 sites) | 0.855 | 0.941 | 0.018 | <0.001 |
| 高人为干扰位点 Camera sites with high anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year (N = 16 sites) | 0.741 | 0.956 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season (N = 4 sites) | 0.647 | 0.809 | 0.074 | 0.024 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season (N = 18 sites) | 0.783 | 0.951 | 0.013 | <0.001 |
表4 繁殖季节和非繁殖季节高低人为干扰强度间白腹锦鸡和总体人为干扰的重叠度
Table 4 Coefficient of overlap between Lady Amherst’s pheasant and anthropogenic disturbance between low and high anthropogenic disturbance in the whole year and in both breeding and non-breeding seasons
| 位点 Sites/季节 Season | 平均重叠系数 Mean overlap coefficient (△) | 平均零重叠度指数 Mean null overlap index | 零重叠度标准误 Standard error of the null distribution | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低人为干扰位点Camera sites with low anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year (N = 20 sites) | 0.858 | 0.957 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season (N = 32 sites) | 0.842 | 0.954 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season (N = 18 sites) | 0.855 | 0.941 | 0.018 | <0.001 |
| 高人为干扰位点 Camera sites with high anthropogenic disturbance | ||||
| 全年 Whole year (N = 16 sites) | 0.741 | 0.956 | 0.011 | <0.001 |
| 繁殖季 Breeding season (N = 4 sites) | 0.647 | 0.809 | 0.074 | 0.024 |
| 非繁殖季 Non-breeding season (N = 18 sites) | 0.783 | 0.951 | 0.013 | <0.001 |
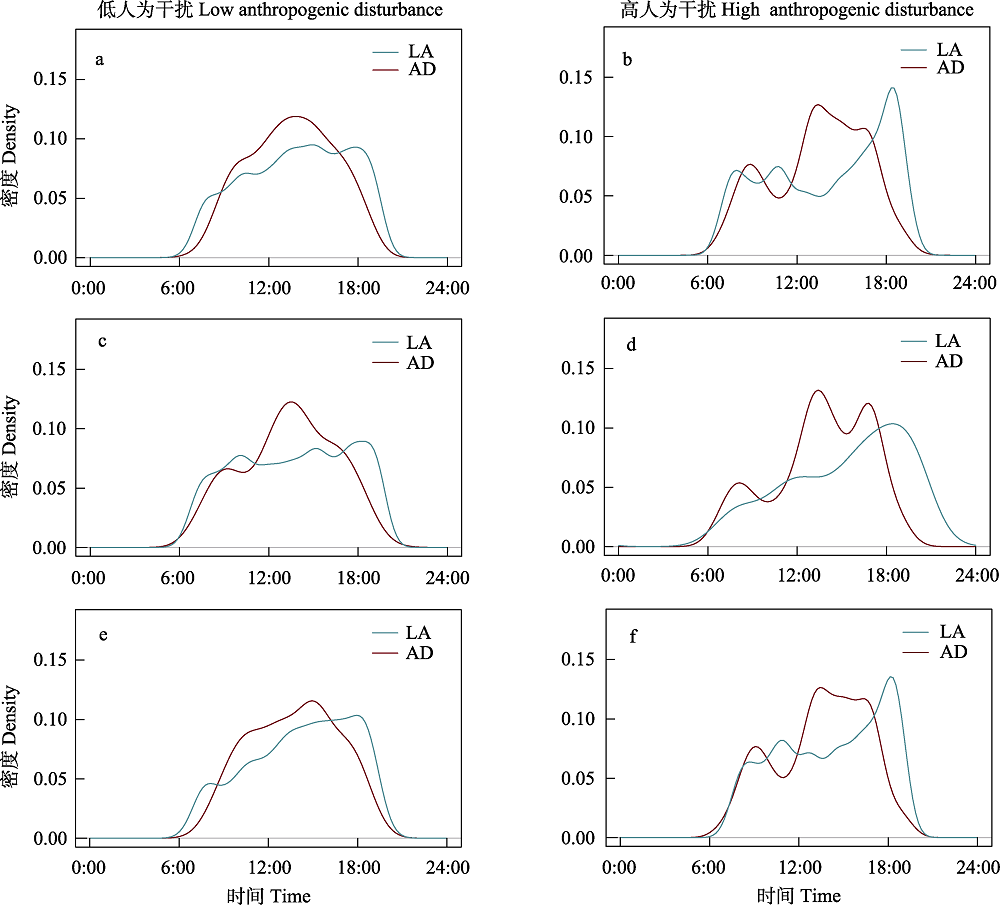
图4 白腹锦鸡活动节律在不同人为干扰强度下的变化。 a-b: 全年总体人为干扰与白腹锦鸡日活动节律重叠; c-d: 繁殖季节总体人为干扰与白腹锦鸡的日活动节律重叠; e-f: 非繁殖季节总体人为干扰与白腹锦鸡的日活动节律重叠。LA表示白腹锦鸡; AD表示总体人为干扰; 高低划分标准见图2。
Fig. 4 The activity patterns and overlaps of anthropogenic disturbance and Lady Amherst’s pheasants. The comparisons of daily activities between the Lady Amherst’s pheasant (LA) and the overall anthropogenic disturbance (AD) throughout the year (a and b), as well as in the breeding (c and d), and non-breeding (e and f) seasons. See Fig. 2 for the classifications of sites.
| [1] |
Benítez-López A, Alkemade R, Verweij PA (2010) The impacts of roads and other infrastructure on mammal and bird populations: A meta-analysis. Biological Conservation, 143, 1307-1316.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Chen LJ, Shu ZF, Xiao ZS (2019) Application of camera-trapping data to study daily activity patterns of Galliformes in Guangdong Chebaling National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 27, 266-272. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[陈立军, 束祖飞, 肖治术 (2019) 应用红外相机数据研究动物活动节律——以广东车八岭保护区鸡形目鸟类为例. 生物多样性, 27, 266-272.]
DOI |
|
| [3] |
Dormann CF, Elith J, Bacher S, Buchmann C, Carl G, Carré G, Marquéz JRG, Gruber B, Lafourcade B, Leitão PJ, Münkemüller T, McClean C, Osborne PE, Reineking B, Schröder B, Skidmore AK, Zurell D, Lautenbach S (2013) Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography, 36, 27-46.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Gaynor KM, Brown JS, Middleton AD, Power ME, Brashares JS (2019) Landscapes of fear: Spatial patterns of risk perception and response. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 34, 355-368.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Gaynor KM, Hojnowski CE, Carter NH, Brashares JS (2018) The influence of human disturbance on wildlife nocturnality. Science, 360, 1232-1235.
DOI |
| [6] | Han LX, Shun Y (2017) Tracking the Lady Amherst’s pheasant. Forest & Humankind, (2), 98-105. (in Chinese) |
| [韩联宪, 舜尧 (2017) 追踪白腹锦鸡. 森林与人类, (2), 98-105.] | |
| [7] | Han LX, Yang L, Zheng BL (1988) The sound spectrogrhic analyses on the calls of Lady Amherst’s pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae). Zoological Research, 9, 127-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩联宪, 杨岚, 郑宝赉 (1988) 白腹锦鸡鸣声的声谱分析. 动物学研究, 9, 127-132.] | |
| [8] | Han LX, Yang L, Zheng BL (1989) Observation on breeding ecology of Lady Amherst’s pheasant. Zoological Research, 10, 285-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩联宪, 杨岚, 郑宝赉 (1989) 白腹锦鸡繁殖生态观察. 动物学研究, 10, 285-294.] | |
| [9] | Kang MJ (2007) Studies on Ecology of Lady Amherst’s Pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae). PhD dissertation, Beijing Normal University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [康明江 (2007) 白腹锦鸡(Chrysolophus amherstiae)生态学研究. 博士学位论文, 北京师范大学, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Kang MJ, Zheng GM (2007a) Roost-site selection of Lady Amherst’s pheasant. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 2929-2934. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [康明江, 郑光美 (2007a) 白腹锦鸡(Chrysolophus amherstiae)的夜栖地选择. 生态学报, 27, 2929-2934.] | |
| [11] | Kang MJ, Zheng GM (2007b) Home range and habitat selection of female Lady Amherst’s pheasant during breeding period. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 43, 558-562. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [康明江, 郑光美 (2007b) 白腹锦鸡雌鸟繁殖期的活动区和栖息地选择. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43, 558-562.] | |
| [12] |
Kitchen AM, Gese EM, Schauster ER (2000) Changes in coyote activity patterns due to reduced exposure to human persecution. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 78, 853-857.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Li BQ, Li PY, Yang JW, Zi HJ, Li XQ, Duan XH, Luo X (2018) Wildlife monitoring in Weishan Qinghua Green Peafowl Nature Reserve using infrared cameras, Yunnan Province. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1343-1347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李斌强, 李鹏映, 杨家伟, 字红军, 李兴权, 段锡焕, 罗旭 (2018) 运用红外相机调查云南巍山青华绿孔雀自然保护区的鸟兽多样性. 生物多样性, 26, 1343-1347.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Li BV, Jiang BK (2021) Responses of forest structure, functions, and biodiversity to livestock disturbances: A global meta-analysis. Global Change Biology, 27, 4745-4757.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Li XY, Hu WQ, Bleisch WV, Li Q, Wang HJ, Lu W, Sun J, Zhang FY, Ti B, Jiang XL (2021) Functional diversity loss and change in nocturnal behavior of mammals under anthropogenic disturbance. Conservation Biology, 36, e13839. |
| [16] |
Li YH, Wan Y, Shen H, Loss SR, Marra PP, Li ZQ (2021) Estimates of wildlife killed by free-ranging cats in China. Biological Conservation, 253, 108929.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Liang D, Pan XY, Luo X, Cheng WD, Zhao YY, Hu YM, Robinson SK, Liu Y (2021) Seasonal variation in community composition and distributional ranges of birds along a subtropical elevation gradient in China. Diversity and Distributions, 27, 2527-2541.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Liu XB, Wei W, Zheng XG, Zhao KH, He SW, Zhou WL (2017) Activity rhythms of golden pheasant (Chrysolophus pictus) and Satyr Tragopan (Tragopan temminckii) revealed by infrared-triggered cameras. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 52, 194-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘小斌, 韦伟, 郑筱光, 赵凯辉, 何少文, 周文良 (2017) 红腹锦鸡和红腹角雉活动节律——基于红外相机监测数据. 动物学杂志, 52, 194-202.] | |
| [19] | Long S, Zhou CQ, Wang WK, Pan L, Hu JC (2009) Diurnal behavioral rhythm, time budgets and group behavior of dwarf blue sheep in summer. Zoological Research, 30, 687-693. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龙帅, 周材权, 王维奎, 潘立, 胡锦矗 (2009) 矮岩羊夏季活动节律、时间分配和集群行为. 动物学研究, 30, 687-693.] | |
| [20] |
Maeda T, Nakashita R, Shionosaki K, Yamada F, Watari Y (2019) Predation on endangered species by human-subsidized domestic cats on Tokunoshima Island. Scientific Reports, 9, 16200.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Norris D, Michalski F, Peres CA (2010) Habitat patch size modulates terrestrial mammal activity patterns in Amazonian forest fragments. Journal of Mammalogy, 91, 551-560.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
O’Brien TG, Kinnaird MF, Wibisono HT (2003) Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape. Animal Conservation, 6, 131-139.
DOI URL |
| [23] | R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2022-01-22) |
| [24] |
Ridout MS, Linkie M (2009) Estimating overlap of daily activity patterns from camera trap data. Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 14, 322-337.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Rowcliffe JM, Kays R, Kranstauber B, Carbone C, Jansen PA (2014) Quantifying levels of animal activity using camera trap data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1170-1179.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Shi JB, Dunbar RIM, Buckland D, Miller D (2003) Daytime activity budgets of feral goats (Capra hircus) on the Isle of Rum: Influence of season, age, and sex. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 81, 803-815.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Shi JY, Yang H, Hua JQ, Zhao YZ, Li JQ, Xu JL (2020) The relationship between the diurnal activity rhythm of Reeves’s pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) and human disturbance revealed by camera trapping. Biodiversity Science, 28, 796-805. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[石江艳, 杨海, 华俊钦, 赵玉泽, 李建强, 徐基良 (2020) 利用红外相机研究白冠长尾雉日活动节律与人为干扰的关系. 生物多样性, 28, 796-805.]
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Stillfried M, Belant JL, Svoboda NJ, Beyer DE, Kramer-Schadt S (2015) When top predators become prey: Black bears alter movement behaviour in response to hunting pressure. Behavioural Processes, 120, 30-39.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Wang KF, Zhang JR, Lei FM (2010) Geographical distribution pattern and its temporal and spatial variation of birds breeding in zoogeographical subregion of China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 35, 145-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王开锋, 张继荣, 雷富民 (2010) 中国动物地理亚区繁殖鸟类地理分布格局与时空变化. 动物分类学报, 35, 145-157.] | |
| [30] |
Xiao ZS, Li XH, Jiang GS (2014) Applications of camera trapping to wildlife surveys in China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 683-684. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[肖治术, 李欣海, 姜广顺 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物监测研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 22, 683-684.]
DOI |
|
| [31] |
Xu JL, Zhang ZW, Liu WJ, McGowan PJK (2012) A review and assessment of nature reserve policy in China: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Oryx, 46, 554-562.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Xu WY, Gong Y, Wang HT (2021) Alert time reflects the negative impacts of human disturbance on an endangered bird species in Changbai Mountain, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 28, e01709. |
| [33] | Xue L (1993) Weishan Yi and Hui Autonomous County Annals. Yunnan People’s Publishing House, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [薛琳 (1993) 巍山彝族回族自治县志. 云南人民出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [34] | Yang JL, Wu ZK, Lin QW (1981) Preliminary remarks on the breeding behaviour and feeding habits of the Chinese copper pheasant. Zoological Research, 2, 243-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨炯蠡, 吴至康, 林齐维 (1981) 白腹锦鸡繁殖及食性的初步观察. 动物学研究, 2, 243-246.] | |
| [35] | Yang L (1992) Pheasants in China:Lady Amherst’s Pheasant. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨岚 (1992) 中国雉类: 白腹锦鸡. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [36] | Yang XJ, Wen XJ, Yang L (1994) Feeding activity of Lady Amherst’s pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae) in captivity. Zoological Research, 15, 49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨晓君, 文贤继, 杨岚 (1994) 笼养白腹锦鸡觅食活动的观察. 动物学研究, 15, 49-54.] | |
| [37] | Yang XJ, Wen XJ, Yang L (1995) Time budgets of captive Lady Amherst’s pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae) in breeding season. Zoological Research, 16, 178-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨晓君, 文贤继, 杨岚 (1995) 笼养白腹锦鸡繁殖季节的时间分配. 动物学研究, 16, 178-184.] | |
| [38] | Zhang SS, Bao YX, Wang YN, Fang PF, Ye B (2012) Comparisons of different camera trap placement patterns in monitoring mammal resources in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31, 2016-2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [章书声, 鲍毅新, 王艳妮, 方平福, 叶彬 (2012) 不同相机布放模式在古田山兽类资源监测中的比较. 生态学杂志, 31, 2016-2022.] | |
| [39] | Zhang YY, Zheng GM (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity•Vertebrates (Volume Ⅱ): Bird. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张雁云, 郑光美 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录•脊椎动物(第二卷):鸟类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] |
Zhang ZW, Ding CQ, Ding P, Zheng GM (2003) The current status and a conservation strategy for species of Galliformes in China. Biodiversity Science, 11, 414-421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[张正旺, 丁长青, 丁平, 郑光美 (2003) 中国鸡形目鸟类的现状与保护对策. 生物多样性, 11, 414-421.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Zhao CG, Chen F, Yan ZK, Liu XY, Liu LM, Li WW, Duan YB (2021) Behaviors and interspecific association of sympatric Lady Amherst’s pheasant and Temminck’s tragopan in the Yaoshan Mountains. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 4008-4014. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵晨光, 陈飞, 颜再奎, 刘兴元, 刘鲁明, 李维薇, 段玉宝 (2021) 同域分布的白腹锦鸡和红腹角雉的活动节律及种间联结关系. 生态学杂志, 40, 4008-4014.] | |
| [42] | Zhao YL, Wang SY, Duan CC, Jiang WX, Xu ZG (2018) Behavioral rhythm of captive Chrysolophus amherstiae in summer and autumn. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 2995-3000. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵运林, 王双业, 段酬苍, 姜卫星, 徐正刚 (2018) 笼养白腹锦鸡(Chrysolophus amherstiae)夏、秋季行为节律. 生态学杂志, 37, 2995-3000.] | |
| [43] |
Zhao YZ, Wang ZC, Xu JL, Luo X, An LD (2013) Activity rhythm and behavioral time budgets of wild Reeves’s Pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) using infrared camera. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 6021-6027. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [赵玉泽, 王志臣, 徐基良, 罗旭, 安丽丹 (2013) 利用红外照相技术分析野生白冠长尾雉活动节律及时间分配. 生态学报, 33, 6021-6027.] | |
| [44] | Zheng GM (2015) Pheasants in China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2015) 中国雉类. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 刘咏华, 童光蓉, 余航远, 王宁宁, 任海保, 陈磊, 马克平, 米湘成. 钱江源-百山祖国家公园候选区钱江源园区冠层三维结构及光谱特征对人为干扰的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [3] | 王凤琼, 张心怡, 王鑫厅, 姜超, 侯亚丽, 包道日娜. 羊草草原原生群落羊草种群点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [4] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [5] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [6] | 高翔, 潘淑芳, 孙争争, 李霁筱, 高天雨, 董路, 王宁. 广东珠海凤凰山和淇澳岛小灵猫的分布与活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24045-. |
| [7] | 张明军, 王合升, 颜文博, 符运南, 王琦, 曾治高. 海南大田国家级自然保护区小灵猫的活动节律与栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [8] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [9] | 麦晓烔, 康佳, 李梓琛, 王天明. 东北虎豹国家公园梅花鹿活动节律及其对道路的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24178-. |
| [10] | 赵坤明, 陈圣宾, 杨锡福. 基于红外相机技术调查四川都江堰破碎化森林鸟兽多样性及优势种活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [11] | 赵秋杰, 郭辉军, 孟广涛, 钟明川, 尹俊, 刘倬橙, 李品荣, 陈力, 陶毅, 秋生, 王红, 赵延会. 放牧对蜜蜂的影响及其生态修复建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23037-. |
| [12] | 王怡涵, 赵倩倩, 刁奕欣, 顾伯健, 翁悦, 张卓锦, 陈泳滨, 王放. 基于红外相机调查上海市区小灵猫的活动节律、栖息地利用及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22294-. |
| [13] | 唐楚飞, 葛成, 曹烨, 曹弘毅, 宋晓晓, 廖怀建. 城市森林不同林分类型的昆虫多样性: 以南京紫金山南麓为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22357-. |
| [14] | 杨瑾谕, 朱万龙. 生境差异和人类活动对云南剑川甸南镇小型哺乳动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23246-. |
| [15] | 杨剑焕, 李敬华, 杨浩炫, 欧梓键, 郑玺, Anthony J. Giordano, 陈辈乐. 基于红外相机数据评估华南地区豹猫的种群密度和活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21357-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn