



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 41-49. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014100 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014100
李乃成1, 刘晓收1,*( ), 徐兆东1, 赵瑞1, 石洪华2,*(
), 徐兆东1, 赵瑞1, 石洪华2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-05-20
接受日期:2014-09-16
出版日期:2015-01-20
发布日期:2015-05-04
通讯作者:
刘晓收,石洪华
作者简介:E-mail: shihonghua@fio.org.cn基金资助:
Naicheng Li1, Xiaoshou Liu1,*( ), Zhaodong Xu1, Rui Zhao1, Honghua Shi2,*(
), Zhaodong Xu1, Rui Zhao1, Honghua Shi2,*( )
)
Received:2014-05-20
Accepted:2014-09-16
Online:2015-01-20
Published:2015-05-04
Contact:
Xiaoshou Liu,Honghua Shi
摘要:
为了解庙岛群岛南部海域大型底栖动物群落多样性变化, 我们在该海域设置了11个站位, 于2012年11月、2013年2月、5月、8月共进行了4个航次的调查, 对该海域大型底栖动物的生物多样性变化、种类组成以及优势种等进行了分析。在研究海域共采集到大型底栖动物164种, 包括环节动物多毛类82种, 节肢动物甲壳类38种, 软体动物30种, 棘皮动物9种, 其他类群5种。各站位种类数在6-42种之间。物种数冬夏较多、春季较少。各站位Shannon-Wiener多样性指数未呈现明显的季节性变化; 均匀度指数春夏最高; 而丰富度指数春夏两季最低。沉积物中有机质与叶绿素含量是影响大型底栖动物多样性的主要因素。丰度-生物量比较曲线(ABC曲线)结果表明, 位于庙岛与北长山岛之间的C13站、毗邻庙岛的C17站和C28站的底栖动物群落受到了中等程度的扰动, 其余站位未受到明显扰动。
李乃成, 刘晓收, 徐兆东, 赵瑞, 石洪华 (2015) 庙岛群岛南部海域大型底栖动物多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 41-49. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014100.
Naicheng Li, Xiaoshou Liu, Zhaodong Xu, Rui Zhao, Honghua Shi (2015) Biodiversity of macrofauna in the southern waters of Miaodao Archipelago, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 41-49. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014100.
| 种类 Species | 相对重要性指数 Indices of relative importance (IRI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2月Feb. | 5月May | 8月Aug. | 11月Nov. | |
| 梳鳃虫 Terebellides stroemii | 1,092 | 435 | 215 | 1,324 |
| 短叶索沙蚕 Lumbrineris latreilli | 711 | 260 | 468 | |
| 拟特须虫 Paralacydonia paradoza | 647 | 270 | 499 | |
| 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys oligobranchia | 437 | |||
| 深钩毛虫 Sigambra bassi | 343 | |||
| 日本角吻沙蚕 Goniada japonica | 348 | |||
| 不倒翁虫 Sternaspis sculata | 291 | 643 | ||
| 岩虫 Marphysa sanguinea | 215 | 308 | 1,283 | |
| 甲虫螺 Cantharus cecillei | 507 | |||
| 异足索沙蚕 Lumbrineris heteropoda | 437 | |||
| 锥毛似帚毛虫 Lygdamis giardi | 384 | |||
| 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | 252 | |||
| 西方似蛰虫 Amaeana occidentalis | 393 | |||
| 温哥华真旋虫 Eudistylis vancouveri | 239 | |||
| 刚鳃虫 Chaetozone setosa | 542 | |||
| 头吻沙蚕 Glycera capitata | ||||
| 苍白亮樱蛤 Nitidotellina pallidula | 266 | 746 | ||
| 路氏肋海星 Ctenopleufa ludwigc | 376 | |||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 Moerella iridescens | 4,280 | |||
| 孟加拉海扇虫 Pherusa cf. bengalensis | 2,160 | |||
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | 447 | |||
| 短角双眼钩虾 Ampelisca brevicornis | 335 | |||
| 日本拟背尾水虱 Paranthura japonica | 332 | |||
| 中华异稚虫 Heterospio sinica | 275 | |||
| 背蚓虫 Notomastus latericeus | 290 | |||
表1 庙岛群岛南部海域大型底栖动物优势种
Table 1 Dominant species of macrofauna in the southern waters of Miaodao Archipelago
| 种类 Species | 相对重要性指数 Indices of relative importance (IRI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2月Feb. | 5月May | 8月Aug. | 11月Nov. | |
| 梳鳃虫 Terebellides stroemii | 1,092 | 435 | 215 | 1,324 |
| 短叶索沙蚕 Lumbrineris latreilli | 711 | 260 | 468 | |
| 拟特须虫 Paralacydonia paradoza | 647 | 270 | 499 | |
| 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys oligobranchia | 437 | |||
| 深钩毛虫 Sigambra bassi | 343 | |||
| 日本角吻沙蚕 Goniada japonica | 348 | |||
| 不倒翁虫 Sternaspis sculata | 291 | 643 | ||
| 岩虫 Marphysa sanguinea | 215 | 308 | 1,283 | |
| 甲虫螺 Cantharus cecillei | 507 | |||
| 异足索沙蚕 Lumbrineris heteropoda | 437 | |||
| 锥毛似帚毛虫 Lygdamis giardi | 384 | |||
| 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | 252 | |||
| 西方似蛰虫 Amaeana occidentalis | 393 | |||
| 温哥华真旋虫 Eudistylis vancouveri | 239 | |||
| 刚鳃虫 Chaetozone setosa | 542 | |||
| 头吻沙蚕 Glycera capitata | ||||
| 苍白亮樱蛤 Nitidotellina pallidula | 266 | 746 | ||
| 路氏肋海星 Ctenopleufa ludwigc | 376 | |||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 Moerella iridescens | 4,280 | |||
| 孟加拉海扇虫 Pherusa cf. bengalensis | 2,160 | |||
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | 447 | |||
| 短角双眼钩虾 Ampelisca brevicornis | 335 | |||
| 日本拟背尾水虱 Paranthura japonica | 332 | |||
| 中华异稚虫 Heterospio sinica | 275 | |||
| 背蚓虫 Notomastus latericeus | 290 | |||
| 站位 Stations | 物种数 Species | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity indices | 物种均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | 物种丰富度指数 Species richness index | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | |
| C6 | 27 | - | 23 | 4.09 | - | 4.38 | - | 0.86 | - | 0.97 | - | 3.96 | - | 3.50 | - | |
| C7 | 17 | - | - | - | 3.54 | - | - | - | 0.87 | - | - | - | 2.54 | - | - | - |
| C10 | 10 | - | 15 | - | 3.16 | - | 2.43 | - | 0.95 | - | 0.94 | - | 1.72 | - | 2.43 | - |
| C11 | 23 | 24 | 7 | 42 | 3.95 | 3.43 | 2.46 | 4.24 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 3.15 | 3.43 | 1.13 | 5.33 |
| C12 | 22 | 12 | 19 | - | 4.06 | 3.41 | 3.84 | - | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.92 | - | 3.00 | 1.99 | 2.64 | - |
| C13 | 22 | 16 | 25 | - | 4.44 | 3.48 | 3.33 | - | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.72 | - | 4.49 | 2.26 | 2.93 | - |
| C17 | 19 | 21 | 22 | - | 2.48 | 3.14 | 3.49 | - | 0.58 | 0.71 | 0.78 | - | 2.27 | 2.60 | 2.85 | - |
| C24 | 32 | 20 | 25 | - | 4.47 | 3.91 | 4.09 | - | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.89 | - | 4.88 | 2.93 | 3.40 | - |
| C28 | 33 | 26 | 19 | - | 4.11 | 4.12 | 3.92 | - | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.91 | - | 4.54 | 3.64 | 2.90 | - |
| C30 | 7 | 7 | 21 | - | 2.75 | 1.23 | 4.04 | - | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.92 | - | 1.37 | 1.23 | 2.99 | - |
| C31 | 6 | 29 | 23 | - | 2.21 | 4.34 | 4.29 | - | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.95 | - | 0.97 | 3.91 | 3.25 | - |
表2 庙岛群岛南部海域各站位底栖动物生物多样性指数 (2012-2013)
Table 2 Diversity indices of macrofauna at each station in the southern waters of Miaodao Archipelago (2012-2013)
| 站位 Stations | 物种数 Species | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity indices | 物种均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | 物种丰富度指数 Species richness index | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | 2月 Feb. | 5月 May | 8月 Aug. | 11月 Nov. | |
| C6 | 27 | - | 23 | 4.09 | - | 4.38 | - | 0.86 | - | 0.97 | - | 3.96 | - | 3.50 | - | |
| C7 | 17 | - | - | - | 3.54 | - | - | - | 0.87 | - | - | - | 2.54 | - | - | - |
| C10 | 10 | - | 15 | - | 3.16 | - | 2.43 | - | 0.95 | - | 0.94 | - | 1.72 | - | 2.43 | - |
| C11 | 23 | 24 | 7 | 42 | 3.95 | 3.43 | 2.46 | 4.24 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 3.15 | 3.43 | 1.13 | 5.33 |
| C12 | 22 | 12 | 19 | - | 4.06 | 3.41 | 3.84 | - | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.92 | - | 3.00 | 1.99 | 2.64 | - |
| C13 | 22 | 16 | 25 | - | 4.44 | 3.48 | 3.33 | - | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.72 | - | 4.49 | 2.26 | 2.93 | - |
| C17 | 19 | 21 | 22 | - | 2.48 | 3.14 | 3.49 | - | 0.58 | 0.71 | 0.78 | - | 2.27 | 2.60 | 2.85 | - |
| C24 | 32 | 20 | 25 | - | 4.47 | 3.91 | 4.09 | - | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.89 | - | 4.88 | 2.93 | 3.40 | - |
| C28 | 33 | 26 | 19 | - | 4.11 | 4.12 | 3.92 | - | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.91 | - | 4.54 | 3.64 | 2.90 | - |
| C30 | 7 | 7 | 21 | - | 2.75 | 1.23 | 4.04 | - | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.92 | - | 1.37 | 1.23 | 2.99 | - |
| C31 | 6 | 29 | 23 | - | 2.21 | 4.34 | 4.29 | - | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.95 | - | 0.97 | 3.91 | 3.25 | - |
| 有机质含量 Content of organic matter | 叶绿素 Content of chlorophyll | 水深 Water depth | 水温 Water temperature | 粉砂-粘土含量 Silt-clay fraction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener indices | 0.184 | -0.052 | 0.291 | -0.094 | 0.324 |
| 物种均匀度 Species evenness indices | -0.487* | -0.408* | 0.110 | 0.009 | -0.397* |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness indices | 0.410* | 0.027 | 0.354 | -0.245 | 0.412* |
| 物种数 Species number | 0.389* | 0.130 | 0.373* | -0.107 | 0.467* |
表3 庙岛群岛南部海域大型底栖动物群落多样性指数与环境因子的相关性分析(2012-2013)
Table 3 Correlation coefficients among biodiversity indices of macrofauna and environmental factors in southern waters of the Miaodao Archipelago (2012-2013)
| 有机质含量 Content of organic matter | 叶绿素 Content of chlorophyll | 水深 Water depth | 水温 Water temperature | 粉砂-粘土含量 Silt-clay fraction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener indices | 0.184 | -0.052 | 0.291 | -0.094 | 0.324 |
| 物种均匀度 Species evenness indices | -0.487* | -0.408* | 0.110 | 0.009 | -0.397* |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness indices | 0.410* | 0.027 | 0.354 | -0.245 | 0.412* |
| 物种数 Species number | 0.389* | 0.130 | 0.373* | -0.107 | 0.467* |
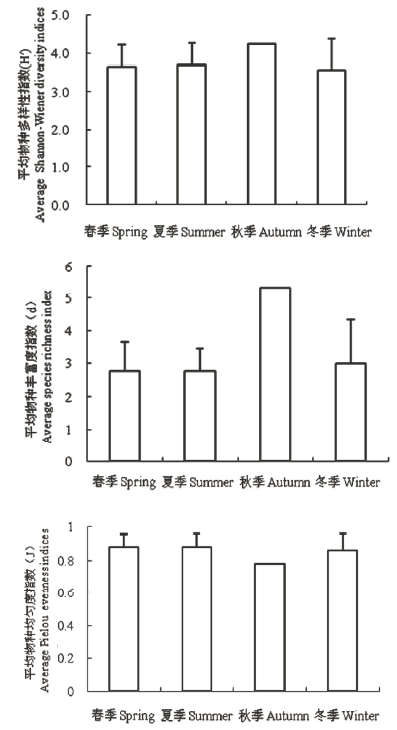
图2 庙岛群岛南部海域各季节大型底栖动物多样性指数 (2012-2013)
Fig. 2 Biodiversity indices of macrofauna at each season in the southern waters of Miaodao Archipelago (2012-2013)
| 1 | Cai LZ ( 蔡立哲 ) ( 2006) Progress on marine benthic ecology and biodiversity. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 45(S2), 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Cai WQ ( 蔡文倩), Meng W ( 孟伟), Liu LS ( 刘录三), Zhu YZ ( 朱延忠), Zhou J ( 周娟 ) ( 2013) Long-term trends of the dominant macrozoobenthos in Bohai Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (环境科学学报), 33, 2332-2340. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 |
Carvalho S, Pereira P, Pereira F, Pablo H, Vale C, Miguel B ( 2011) Factors structuring temporal and spatial dynamics of macrobenthic communities in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Óbidos lagoon, Portugal). Marine Environmental Research, 71, 97-110.
DOI URL PMID |
| 4 | Clarke KR, Warwick RM ( 2001) Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation (2nd ed.). Plymouth: PRIMER-E. |
| 5 |
Dowd M, Grant J, Lu L ( 2014) Predictive modeling of marine benthic macrofauna and its use to inform spatial monitoring design. Ecological Applications, 24, 862-876.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 | Fang EJ ( 房恩军), Li J ( 李军), Ma WL ( 马维林), Chen W ( 陈卫), Wang QL ( 王麒麟 ) ( 2006) A primary study on bottom marcofauna in the coastal waters of Bohai Bay. Modern Fisheries Information (现代渔业信息), 21, 11-15. (in Chinese) |
| 7 | Han J ( 韩洁), Zhang ZN ( 张志南), Yu ZS ( 于子山 ) ( 2003) Macrobenthic species diversity in southern and central Bohai Sea, China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 11, 20-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 8 | Han J ( 韩洁), Zhang ZN ( 张志南), Yu ZS ( 于子山 ) ( 2004) Macrobenthic community structure in the southern and central Bohai Sea, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 24, 532-536. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 9 | Holme NA, McIntyre AD ( 1984) Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. |
| 10 |
Kronckei TM, Fiege D ( 2003) Macrofauna communities in the eastern Mediterranean. Marine Ecology, 24, 193-216.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Li BQ ( 李宝泉), Li XZ ( 李新正), Wang HF ( 王洪法), Zhang BL ( 张宝琳 ) ( 2006) Species diversity of macrobenthic mollusk fauna in Jiaozhou Bay. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14, 136-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 12 | Li XZ ( 李新正), Yu HY ( 于海燕), Wang YQ ( 王永强), Shuai LM ( 帅莲梅), Zhang BL ( 张宝琳), Liu RY ( 刘瑞玉 ) ( 2001) Study on species diversity of macrobenthic fauna in Jiaozhou Bay. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9, 80-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 13 |
Li XZ ( 李新正 ) ( 2011) An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: principally from the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 676-684. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 14 | Liu LS ( 刘录三), Li XZ ( 李新正 ) ( 2003) Distribution of macrobenthos in spring and autumn in the southern Yellow Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 34, 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Liu XS ( 刘晓收), Zhao R ( 赵瑞), Hua E ( 华尔), Lu L ( 路璐), Zhang ZN ( 张志南 ) ( 2014) Macrofaunal community structure in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea in summer and comparison with historical data. Marine Science Bulletin (海洋通报), 33, 282-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Liu ZY ( 刘仲雨 ) ( 2009) The theory of long island tourism sustainable development and environmental protection. Financial Management (财经管理), 16, 190-191. (in Chinese) |
| 17 | Margalef R ( 1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 18 | Muniz P, Pires AMS ( 2000) Polychaete associations in a subtropical environment (Sao Sebastiao Channel, Brazil): a structural analysis. Marine Ecology, 21, 145-160. |
| 19 | Pielou EC ( 1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley, New York. |
| 20 | Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson ILK ( 1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. California Department of Fish and Game Fish Bulletin, 152, 1-105. |
| 21 |
Qu FY ( 曲方圆), Yu ZS ( 于子山 ) ( 2010) The application of taxonomic diversity in macrobenthic ecology: taking Yellow Sea for example. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 155-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 22 | Shannon CE, Weaver W ( 1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbanna. |
| 23 | Shen GY ( 沈国英), Shi BZ ( 施并章 ) ( 1996) Marine Ecology (海洋生态学). Xiamen University Press, Xiamen. (in Chinese) |
| 24 |
Shields M, Blanco-Perez R ( 2013) Polychaete abundance, biomass and diversity patterns at the mid-Atlantic Ridge, North Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 98, 315-325.
DOI URL |
| 25 | Tian SY ( 田胜艳), Zhang WL ( 张文亮), Zhang R ( 张锐 ) ( 2009) Role of macrobenthos in marine ecosystem. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry (盐业与化工), 38(2), 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 26 |
Wang XC, Li XZ ( 2009) Summertime community structure of intertidal macrobenthos in Changdao Archipelago, Shandong Province, China. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27, 425-434.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Warwick RM ( 1986) A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Marine Biology, 92, 557-562.
DOI URL |
| 28 | Xu QZ ( 徐勤增), Li RX ( 李瑞香), Wang ZL ( 王宗灵), Fan SL ( 范士亮 ) ( 2009) Macrobenthos distribution of the south Yellow Sea in summer. Advances in Marine Science (海洋科学进展), 27, 393-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 29 |
Yemane D, Field JG, Leslie RW ( 2005) Exploring the effect of fishing on fish assemblages using abundance biomass comparison (ABC) curves. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 62, 374-379.
DOI URL |
| 30 | Yu HY ( 于海燕), Li XZ ( 李新正), Li BQ ( 李宝泉 ) ( 2006) The species diversity of macrobenthic fauna in Jiaozhou Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26, 417-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 31 |
Yuan W ( 袁伟), Zhang ZN ( 张志南), Yu ZS ( 于子山 ) ( 2007) Macrofaunal diversity in the western Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15, 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 32 | Zhang Y ( 张莹), Lv ZB ( 吕振波), Xu ZF ( 徐宗法), Chen W ( 陈玮 ) ( 2012) Impacts of environmental pollution on macrobenthos diversity in Xiaoqing Estuary. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 31, 381-387. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 33 | Zhou R ( 周然), Qin XB ( 覃雪波), Peng ST ( 彭士涛), Shi HH ( 石洪华), Deng SH ( 邓仕槐 ) ( 2014) Macroinvertebrate investigation and their relation to environment factors in Bohai Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 34, 50-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()