



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 81-97. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020359 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020359
李治霖1,2( ), 多立安1,2, 李晟3,*(
), 多立安1,2, 李晟3,*( )(
)( ), 王天明4,5,6,*(
), 王天明4,5,6,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-09
接受日期:2020-12-29
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-11
通讯作者:
李晟,王天明
基金资助:
Zhilin Li1,2( ), Li’an Duo1,2, Sheng Li3,*(
), Li’an Duo1,2, Sheng Li3,*( )(
)( ), Tianming Wang4,5,6,*(
), Tianming Wang4,5,6,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2020-09-09
Accepted:2020-12-29
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-11
Contact:
Sheng Li, Tianming Wang
摘要:
陆生食肉动物(食肉目哺乳动物, 以下简称食肉动物)作为食物链与营养级的高位物种对维持生态系统结构与功能稳定性起到重要作用。过度人类干扰已在全球范围内造成食肉动物种群数量剧烈下降和栖息地质量显著退化, 探究食肉动物的区域共存机制对理解生物群落构建、濒危物种保护与管理具有重要意义。本文通过梳理100余篇有关食肉动物在空间、时间和营养3个生态位维度上相互作用的研究, 分析了体型大小、猎物组成、种群结构、环境差异、人类干扰和气候变化等因素对食肉动物种间关系和区域共存的影响, 并对今后食肉动物区域共存研究中亟需解决的问题进行了展望。食肉动物通过生态位分离达到共存并没有单一的理论解释, 猎物、栖息地和人类干扰等因素可以调节食肉动物相互作用关系并直接或间接地影响共存, 共同适应在食肉动物区域共存中具重要作用。食肉动物区域共存是经过长期演化形成的相对稳定状态, 需要以动态的眼光去审视。要明晰生态位重叠与区域共存机制的区别与联系, 在理解生态位分离的基础上, 结合生活史、家域和行为等对食肉动物共存进行综合分析。
李治霖, 多立安, 李晟, 王天明 (2021) 陆生食肉动物竞争与共存研究概述. 生物多样性, 29, 81-97. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020359.
Zhilin Li, Li’an Duo, Sheng Li, Tianming Wang (2021) Competition and coexistence among terrestrial mammalian carnivores. Biodiversity Science, 29, 81-97. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020359.
| 分类 Classification | 体重 Body weight | 种群调节方式 Population regulation | 生态作用 Ecological function | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大型食肉动物 Large carnivore | ≥ 15 kg | 种群内部调节 Intra-population regulation | 控制草食类动物过度繁殖、维护植被结构、防止外来物种入侵及疾病传播、降低碳排放 Control over-reproduction of herbivores, maintain vegetation structure, prevent exotic species invasion and diseases spread, and reduce carbon emissions | |
| 小型食肉动物 Small carnivore | < 15 kg | 外部环境调节 Environmental regulation | 控制物质循环、塑造猎物群落构成、促进植被群落更新、调控疾病传播 Control material circulation, shape the composition of prey communities, promote the regeneration of vegetation communities, and regulate the diseases spread |
表1 依据体重的食肉动物分类及其种群调控方式与生态作用
Table 1 Carnivore classification based on body weight, corresponding with population regulation mode and their ecological function
| 分类 Classification | 体重 Body weight | 种群调节方式 Population regulation | 生态作用 Ecological function | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大型食肉动物 Large carnivore | ≥ 15 kg | 种群内部调节 Intra-population regulation | 控制草食类动物过度繁殖、维护植被结构、防止外来物种入侵及疾病传播、降低碳排放 Control over-reproduction of herbivores, maintain vegetation structure, prevent exotic species invasion and diseases spread, and reduce carbon emissions | |
| 小型食肉动物 Small carnivore | < 15 kg | 外部环境调节 Environmental regulation | 控制物质循环、塑造猎物群落构成、促进植被群落更新、调控疾病传播 Control material circulation, shape the composition of prey communities, promote the regeneration of vegetation communities, and regulate the diseases spread |
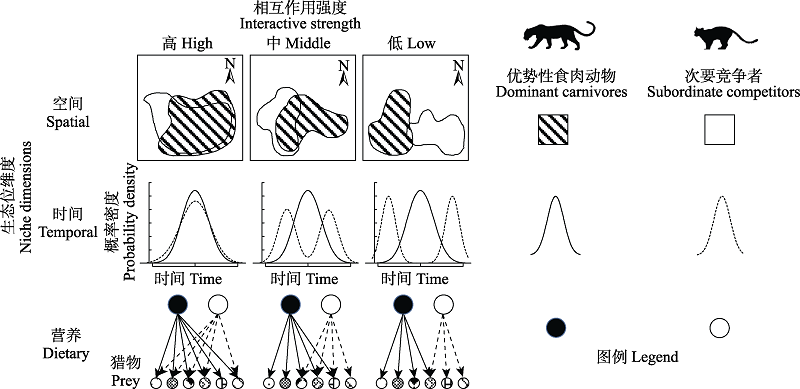
图1 优势性食肉动物和次要竞争者需要在空间、时间和营养等生态位维度分化以促进共存
Fig. 1 Dominant carnivores and subordinate competitors need to segregate among spatial, temporal and dietary niche dimensions to promote coexistence
| [1] | Ait Kaci Azzou S, Aebischer T, Singer L, Wolf B, Wegmann D (2019) A sparse occupancy model to quantify species interactions in time and space. BioRxiv, 815027. |
| [2] | Allen ML, Peterson B, Krofel M (2018) No respect for apex carnivores: Distribution and activity patterns of honey badgers in the Serengeti. Mammalian Biology, 89, 90-94. |
| [3] | Andersen GE, Johnson CN, Jones ME (2020) Space use and temporal partitioning of sympatric Tasmanian devils and spotted-tailed quolls. Austral Ecology, 45, 355-365. |
| [4] | Andheria AP, Karanth KU, Kumar NS (2007) Diet and prey profiles of three sympatric large carnivores in Bandipur Tiger Reserve, India. Journal of Zoology, 273, 169-175. |
| [5] | Balme GA, Miller JRB, Pitman RT, Hunter LTB (2017) Caching reduces kleptoparasitism in a solitary, large felid. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 634-644. |
| [6] | Bhattarai BP, Kindlmann P (2012) Interactions between Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris) and leopard (Panthera pardus): Implications for their conservation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 2075-2094. |
| [7] | Bischof R, Ali H, Kabir M, Hameed S, Nawaz MA (2014) Being the underdog: An elusive small carnivore uses space with prey and time without enemies. Journal of Zoology, 293, 40-48. |
| [8] | Bohmann K, Evans A, Gilbert MTP, Carvalho GR, Creer S, Knapp M, Yu DW, de Bruyn M (2014) Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 29, 358-367. |
| [9] | Brashares JS, Prugh LR, Stoner CJ, Epps CW (2010) Ecological and conservation implications of mesopredator release. In: Trophic Cascades: Predators, Prey, and the Changing Dynamics of Nature (ed. Zdilla KM), pp. 221‒240. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [10] | Broekhuis F, Grunewalder S, McNutt JW, MacDonald DW (2014) Optimal hunting conditions drive circalunar behavior of a diurnal carnivore. Behavioral Ecology, 25, 1268-1275. |
| [11] | Brook LA, Johnson CN, Ritchie EG (2012) Effects of predator control on behaviour of an apex predator and indirect consequences for mesopredator suppression. Journal of Applied Ecology, 49, 1278-1286. |
| [12] | Bruno JF, Stachowicz JJ, Bertness MD (2003) Inclusion of facilitation into ecological theory. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 119-125. |
| [13] | Bu HL, Wang F, McShea WJ, Lü Z, Wang DJ, Li S (2016) Spatial co-occurrence and activity patterns of mesocarnivores in the temperate forests of Southwest China. PLoS ONE, 11, e0164271. |
| [14] | Carothers JH, Jaksić FM (1984) Time as a niche difference: The role of interference competition. Oikos, 42, 403-406. |
| [15] |
Carroll C (2007) Interacting effects of climate change, landscape conversion, and harvest on carnivore populations at the range margin: Marten and lynx in the northern Appalachians. Conservation Biology, 21, 1092-1104.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Carter NH, Linnell JDC (2016) Co-adaptation is key to coexisting with large carnivores. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 575-578.
URL PMID |
| [17] | Carter N, Jasny M, Gurung B, Liu J (2015) Impacts of people and tigers on leopard spatiotemporal activity patterns in a global biodiversity hotspot. Global Ecology and Conservation, 3, 149-162. |
| [18] | Choi MB, Woo D, Choi TY (2015) Composition of the insect diet in feces of yellow-throated marten, Martes flavigula, in Jirisan National Park, South Korea. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 38, 389-395. |
| [19] | Chutipong W, Steinmetz R, Savini T, Gale GA (2017) Assessing resource and predator effects on habitat use of tropical small carnivores. Mammal Research, 62, 21-36. |
| [20] | Crooks KR, Burdett ChL, Theobald DM, King SRB, di Marco M, Rondinini C, Boitani L (2017) Quantification of habitat fragmentation reveals extinction risk in terrestrial mammals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 7635-7640. |
| [21] | Cusack JJ, Dickman AJ, Kalyahe M, Rowcliffe JM, Carbone C, MacDonald DW, Coulson T (2017) Revealing kleptoparasitic and predatory tendencies in an African mammal community using camera traps: A comparison of spatiotemporal approaches. Oikos, 126, 812-822. |
| [22] | Davis CL, Rich LN, Farris ZJ, Kelly MJ, Di Bitetti MS, Blanco YD, Albanesi S, Farhadinia MS, Gholikhani N, Hamel S, Harmsen BJ, Wultsch C, Kane MD, Martins Q, Murphy AJ, Steenweg R, Sunarto S, Taktehrani A, Thapa K, Tucker JM, Whittington J, Widodo FA, Yoccoz NG, Miller DAW (2018) Ecological correlates of the spatial co-occurrence of sympatric mammalian carnivores worldwide. Ecology Letters, 21, 1401-1412. |
| [23] | de Satgé J, Teichman K, Cristescu B (2017) Competition and coexistence in a small carnivore guild. Oecologia, 184, 873-884. |
| [24] | Di Bitetti MS, de Angelo CD, Di Blanco YE, Paviolo A (2010) Niche partitioning and species coexistence in a Neotropical felid assemblage. Acta Oecologica, 36, 403-412. |
| [25] | Ditchkoff SS, Saalfeld ST, Gibson CJ (2006) Animal behavior in urban ecosystems: Modifications due to human-induced stress. Urban Ecosystems, 9, 5-12. |
| [26] |
Donadio E, Buskirk SW (2006) Diet, morphology, and interspecific killing in Carnivora. The American Naturalist, 167, 524-536.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Elmeros M, Mikkelsen DMG, Nørgaard LS, Pertoldi C, Jensen TH, Chriél M (2018) The diet of feral raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and native badger (Meles meles) and red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark. Mammal Research, 63, 405-413. |
| [28] |
Farhadinia MS, Heit DR, Montgomery RA, Johnson PJ, Hobeali K, Hunter LTB, MacDonald DW (2019) Vertical relief facilitates spatial segregation of a high density large carnivore population. Oikos, 129, 346-355.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Farrington JD, Tsering D (2019) Human-snow leopard conflict in the Chang Tang region of Tibet, China. Biological Conservation, 237, 504-513. |
| [30] | Farris ZJ, Gerber BD, Karpanty S, Murphy A, Wampole E, Ratelolahy F, Kelly MJ (2020) Exploring and interpreting spatiotemporal interactions between native and invasive carnivores across a gradient of rainforest degradation. Biological Invasions, 22, 2033-2047. |
| [31] | Farris ZJ, Kelly MJ, Karpanty S, Ratelolahy F (2016) Patterns of spatial co-occurrence among native and exotic carnivores in north-eastern Madagascar. Animal Conservation, 19, 189-198. |
| [32] | Fedriani JM, Palomares F, Delibes M (1999) Niche relations among three sympatric Mediterranean carnivores. Oecologia, 121, 138-148. |
| [33] |
Filazzola A, Brown C, Dettlaff MA, Batbaatar A, Grenke J, Bao T, Peetoom Heida I, Cahill JF Jr (2020) The effects of livestock grazing on biodiversity are multi-trophic: A meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 23, 1298-1309.
URL PMID |
| [34] |
Finke DL, Denno RF (2006) Spatial refuge from intraguild predation: Implications for prey suppression and trophic cascades. Oecologia, 149, 265-275.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] | Frey S, Fisher JT, Burton AC, Volpe JP (2017) Investigating animal activity patterns and temporal niche partitioning using camera-trap data: Challenges and opportunities. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation, 3, 123-132. |
| [36] | Gómez-Ortiz Y, Monroy-Vilchis O, Castro-Arellano I (2019) Temporal coexistence in a carnivore assemblage from central Mexico: Temporal-domain dependence. Mammal Research, 64, 333-342. |
| [37] | Gómez-Ortiz Y, Monroy-Vilchis O, Mendoza-Martínez GD (2015) Feeding interactions in an assemblage of terrestrial carnivores in central Mexico. Zoological Studies, 54, 16. |
| [38] |
Gallo T, Fidino M, Lehrer EW, Magle SB (2017) Mammal diversity and metacommunity dynamics in urban green spaces: Implications for urban wildlife conservation. Ecological Applications, 27, 2330-2341.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Gaynor KM, Hojnowski CE, Carter NH, Brashares JS (2018) The influence of human disturbance on wildlife nocturnality. Science, 360, 1232-1235.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
Geldmann J, Joppa LN, Burgess ND (2014) Mapping change in human pressure globally on land and within protected areas. Conservation Biology, 28, 1604-1616.
URL PMID |
| [41] | Gerber BD, Karpanty SM, Randrianantenaina J (2012) Activity patterns of carnivores in the rain forests of Madagascar: Implications for species coexistence. Journal of Mammalogy, 93, 667-676. |
| [42] | Ghoshal A (2011) Impact of Urbanization on Winter Resource Use and Relative Abundance of a Commensal Carnivore, the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes). PhD dissertation, Forest Research Institute University, Dehradun. |
| [43] |
Gittleman JL (1985) Carnivore body size: Ecological and taxonomic correlates. Oecologia, 67, 540-554.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] | Gosselink TE, Van Deelen TR, Warner RE, Joselyn MG (2003) Temporal habitat partitioning and spatial use of coyotes and red foxes in east-central Illinois. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 67, 90-103. |
| [45] | Grassel SM, Rachlow JL, Williams CJ (2015) Spatial interactions between sympatric carnivores: Asymmetric avoidance of an intraguild predator. Ecology and Evolution, 5, 2762-2773. |
| [46] | Grinnell J (1917) The niche-relationships of the California thrasher. Auk, 34, 427-433. |
| [47] | Halle S (2000) Ecological relevance of daily activity patterns. In: Activity Patterns in Small Mammals (eds. Halle S, Stenseth NC), pp. 67‒90. Springer, Berlin. |
| [48] | Harihar A, Pandav B, Goyal SP (2011) Responses of leopard Panthera pardus to the recovery of a tiger Panthera tigris population. Journal of Applied Ecology, 48, 806-814. |
| [49] |
Haswell PM, Jones KA, Kusak J, Hayward MW (2018) Fear, foraging and olfaction: How mesopredators avoid costly interactions with apex predators. Oecologia, 187, 573-583.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] | Hayward MW, Slotow R (2009) Temporal partitioning of activity in large African carnivores: Tests of multiple hypotheses. South African Journal of Wildlife Research, 39, 109-125. |
| [51] | Holt RD, Polis GA (1997) A theoretical framework for intraguild predation. The American Naturalist, 149, 745-764. |
| [52] | Hua Y, Vitekere K, Wang J, Zhu MY, Zaman M, Jiang GS (2020) Coexistence of sympatric carnivores in a relatively homogenous landscape and the effects of environmental factors on site occupation. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 57, 47-58. |
| [53] | Hunter L (2020) Field Guide to Carnivores of the World. Bloomsbury Publishing, London. |
| [54] | Hutchinson GE (1959) Homage to Santa Rosalia or why are there so many kinds of animals? The American Naturalist, 93, 145-159. |
| [55] | Hutchinson GE (1957) Concluding remarks Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 53, 193-213. |
| [56] | Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY (2017) China’s mammal diversity (2nd edition). Biodiversity Science, 25, 886-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 (2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性(第2版). 生物多样性, 25, 886-895.] | |
| [57] | Karanth KU, Srivathsa A, Vasudev D, Puri M, Parameshwaran R, Kumar NS (2017) Spatio-temporal interactions facilitate large carnivore sympatry across a resource gradient. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284, 20161860. |
| [58] | Karanth KU, Sunquist ME (1995) Prey selection by tiger, leopard and dhole in tropical forests. Journal of Animal Ecology, 64, 439-450. |
| [59] | Karanth KU, Sunquist ME (2000) Behavioural correlates of predation by tiger (Panthera tigris), leopard (Panthera pardus) and dhole (Cuon alpinus) in Nagarahole, India. Journal of Zoology, 250, 255-265. |
| [60] | Kauhala K, Laukkanen P, von Rége I (1998) Summer food composition and food niche overlap of the raccoon dog, red fox and badger in Finland. Ecography, 21, 457-463. |
| [61] |
Kerley LL, Mukhacheva AS, Matyukhina DS, Salmanova E, Salkina GP, Miquelle DG (2015) A comparison of food habits and prey preference of Amur tiger (Panthera tigris altaica) at three sites in the Russian Far East. Integrative Zoology, 10, 354-364.
URL PMID |
| [62] | Kitchen AM, Gese EM, Schauster ER (2000) Changes in coyote activity patterns due to reduced exposure to human persecution. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 78, 853-857. |
| [63] |
Kronfeld-Schor N, Dayan T (2003) Partitioning of time as an ecological resource. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34, 153-181.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Lanszki J, Heltai M, Kövér G, Zalewski A (2019) Non-linear relationship between body size of terrestrial carnivores and their trophic niche breadth and overlap. Basic and Applied Ecology, 38, 36-46. |
| [65] |
Lashley MA, Cove MV, Chitwood MC, Penido G, Gardner B, DePerno CS, Moorman CE (2018) Estimating wildlife activity curves: Comparison of methods and sample size. Scientific Reports, 8, 4173.
DOI URL PMID |
| [66] |
Li S (2020) Development progress and outlook of the wildlife camera-trapping networks in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1045-1048. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 李晟 (2020) 中国野生动物红外相机监测网络建设进展与展望. 生物多样性, 28, 1045-1048.] | |
| [67] |
Li S, William JM, Wang DJ, Gu XD, Zhang XF, Zhang L, Shen XL (2020) Retreat of large carnivores across the giant panda distribution range. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 1327-1331.
DOI URL PMID |
| [68] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook . Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云(2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.] | |
| [69] |
Li ZL, Kang AL, Gu JY, Xue YG, Ren Y, Zhu ZW, Liu PQ, Ma JZ, Jiang GS (2017) Effects of human disturbance on vegetation, prey and Amur tigers in Hunchun Nature Reserve, China. Ecological Modelling, 353, 28-36.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Li ZL, Wang TM, Smith JLD, Feng RN, Feng LM, Mou P, Ge JP (2019) Coexistence of two sympatric flagship carnivores in the human-dominated forest landscapes of Northeast Asia. Landscape Ecology, 34, 291-305.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Li ZL, Kang AL, Lang JM, Xue YG, Ren Y, Zhu ZW, Ma JZ, Liu PQ, Jiang GS (2014) On the assessment of big cats and their prey populations based on camera trap data . Biodiversity Science, 22, 725-732.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 李治霖, 康霭黎, 郎建民, 薛延刚, 任毅, 朱志文, 马建章, 刘培琦, 姜广顺 (2014) 探讨基于红外相机技术对大型猫科动物及其猎物的种群评估方法. 生物多样性, 22, 725-732.] | |
| [72] | Liu SY, Wu Y (2019) Handbook of the Mammals of China. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou, (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘少英, 吴毅 (2019) 中国兽类图鉴. 海峡书局, 福州.] | |
| [73] | Lonsinger RC, Gese EM, Waits LP (2015) Evaluating the reliability of field identification and morphometric classifications for carnivore scats confirmed with genetic analysis. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 39, 593-602. |
| [74] |
López-Bao JV, Mattisson J, Persson J, Aronsson M, Andrén H (2016) Tracking neighbours promotes the coexistence of large carnivores. Scientific Reports, 6, 23198.
DOI URL PMID |
| [75] | Lovari S, Ventimiglia M, Minder I (2013) Food habits of two leopard species, competition, climate change and upper treeline: A way to the decrease of an endangered species? Ethology Ecology & Evolution, 25, 305-318. |
| [76] | Lovari S, Pokheral CP, Jnawali SR, Fusani L, Ferretti F (2015) Coexistence of the tiger and the common leopard in a prey-rich area: The role of prey partitioning. Journal of Zoology, 295, 122-131. |
| [77] |
Marinho PH, Fonseca CR, Sarmento P, Fonseca C, Venticinque EM (2020) Temporal niche overlap among mesocarnivores in a Caatinga dry forest. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 66, 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [78] | McGee BK, Ballard WB, Nicholson KL, Cypher BL, Lemons PR, Kamler JF (2006) Effects of artificial escape dens on swift fox populations in northwest Texas. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 34, 821-827. |
| [79] | Mella-Méndez I, Flores-Peredo R, Bolívar-Cimé B, Vázquez-Domínguez G (2019a) Effect of free-ranging dogs and cats on medium-sized wild mammal assemblages in urban protected areas of a Mexican city. Wildlife Research, 46, 669-678. |
| [80] | Mella-Méndez I, Flores-Peredo R, Pérez-Torres J, Hernández-González S, González-Uribe DU, Socorro Bolívar-Cimé B (2019b) Activity patterns and temporal niche partitioning of dogs and medium-sized wild mammals in urban parks of Xalapa, Mexico. Urban Ecosystems, 22, 1061-1070. |
| [81] | Miller JRB, Schmitz OJ (2019) Landscape of fear and human-predator coexistence: Applying spatial predator-prey interaction theory to understand and reduce carnivore-livestock conflict. Biological Conservation, 236, 464-473. |
| [82] | Mondal K, Gupta S, Bhattacharjee S, Qureshi Q, Sankar K (2012) Response of leopards to re-introduced tigers in Sariska Tiger Reserve, Western India. International Journal of Biodiversity and Conservation, 4, 228-236. |
| [83] | Monterroso P, Alves PC, Ferreras P (2014) Plasticity in circadian activity patterns of mesocarnivores in Southwestern Europe: Implications for species coexistence. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 68, 1403-1417. |
| [84] | Monterroso P, Godinho R, Oliveira T, Ferreras P, Kelly MJ, Morin DJ, Waits LP, Alves PC, Mills LS (2019) Feeding ecological knowledge: The underutilised power of faecal DNA approaches for carnivore diet analysis. Mammal Review, 49, 97-112. |
| [85] |
Mueller MA, Drake D, Allen ML (2018) Coexistence of coyotes (Canis latrans) and red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in an urban landscape. PLoS ONE, 13, e0190971.
URL PMID |
| [86] | Mumma MA, Adams JR, Zieminski C, Fuller TK, Mahoney SP, Waits LP (2016) A comparison of morphological and molecular diet analyses of predator scats. Journal of Mammalogy, 97, 112-120. |
| [87] | Ngoprasert D, Lynam AJ, Gale GA (2017) Effects of temporary closure of a national park on leopard movement and behaviour in tropical Asia. Mammalian Biology, 82, 65-73. |
| [88] | Nickel BA, Suraci JP, Allen ML, Wilmers CC (2020) Human presence and human footprint have non-equivalent effects on wildlife spatiotemporal habitat use. Biological Conservation, 241, 108383. |
| [89] | Nishimura K (2010) Kleptoparasitism and cannibalism. In: Encyclopedia of Animal Behavior (eds Breed MD, Moore J), pp. 667-675. Academic Press, Oxford. |
| [90] | Norouzzadeh MS, Nguyen A, Kosmala M, Swanson A, Palmer MS, Packer C, Clune J (2018) Automatically identifying, counting, and describing wild animals in camera-trap images with deep learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, E5716-E5725. |
| [91] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2010) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin. |
| [92] |
O’Malley C, Elbroch LM, Lendrum PE, Quigley H (2018) Motion-triggered video cameras reveal spatial and temporal patterns of red fox foraging on carrion provided by mountain lions. PeerJ, 6, e5324.
DOI URL PMID |
| [93] | Odden M, Wegge P, Fredriksen T (2010) Do tigers displace leopards? If so, why? Ecological Research, 25, 875-881. |
| [94] | Oriol-Cotterill A, Valeix M, Frank LG, Riginos C, Macdonald DW (2015) Landscapes of coexistence for terrestrial carnivores: The ecological consequences of being downgraded from ultimate to penultimate predator by humans. Oikos, 124, 1263-1273. |
| [95] |
Palomares F, Caro TM (1999) Interspecific killing among mammalian carnivores. The American Naturalist, 153, 492-508.
DOI URL PMID |
| [96] | Palomares F, Ferreras P, Fedriani JM, Delibes M (1996) Spatial relationships between Iberian lynx and other carnivores in an area of south-western Spain. Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 5-13. |
| [97] | Parsons AW, Rota CT, Forrester T, Baker-Whatton MC, McShea WJ, Schuttler SG, Millspaugh JJ, Kays R (2019) Urbanization focuses carnivore activity in remaining natural habitats, increasing species interactions. Journal of Applied Ecology, 56, 1894-1904. |
| [98] | Petersen WJ, Savini T, Steinmetz R, Ngoprasert D (2019) Periodic resource scarcity and potential for interspecific competition influences distribution of small carnivores in a seasonally dry tropical forest fragment. Mammalian Biology, 95, 112-122. |
| [99] | Pokheral CP, Wegge P (2019) Coexisting large carnivores: Spatial relationships of tigers and leopards and their prey in a prey-rich area in lowland Nepal. Ecoscience, 26, 1-9. |
| [100] |
Polis GA, Holt RD (1992) Intraguild predation: The dynamics of complex trophic interactions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 7, 151-154.
DOI URL PMID |
| [101] | du Preez B, Purdon J, Trethowan P, MacDonald DW, Loveridge AJ (2017) Dietary niche differentiation facilitates coexistence of two large carnivores. Journal of Zoology, 302, 149-156. |
| [102] |
Prugh LR, Sivy KJ (2020) Enemies with benefits: Integrating positive and negative interactions among terrestrial carnivores. Ecology Letters, 23, 902-918.
URL PMID |
| [103] | Radloff FGT, Du Toit JT (2004) Large predators and their prey in a southern African savanna: A predator’s size determines its prey size range. Journal of Animal Ecology, 73, 410-423. |
| [104] | Ralls K, White PJ (1995) Predation on San Joaquin kit foxes by larger canids. Journal of Mammalogy, 76, 723-729. |
| [105] | Ramakrishnan U, Coss RG, Pelkey NW (1999) Tiger decline caused by the reduction of large ungulate prey: Evidence from a study of leopard diets in southern India. Biological Conservation, 89, 113-120. |
| [106] | Ramesh T, Kalle R, Sankar K, Qureshi Q (2012) Spatio-temporal partitioning among large carnivores in relation to major prey species in Western Ghats. Journal of Zoology, 287, 269-275. |
| [107] |
Richmond OMW, Hines JE, Beissinger SR (2010) Two-species occupancy models: A new parameterization applied to co-occurrence of secretive rails. Ecological Applications, 20, 2036-2046.
DOI URL PMID |
| [108] |
Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG, Hebblewhite M, Berger J, Elmhagen B, Letnic M, Nelson MP, Schmitz OJ, Smith DW, Wallach AD, Wirsing AJ (2014) Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science, 343,1241484.
DOI URL PMID |
| [109] |
Ritchie EG, Johnson CN (2009) Predator interactions, mesopredator release and biodiversity conservation. Ecology Letters, 12, 982-998.
DOI URL PMID |
| [110] | Roper TJ (1992) Badger Meles meles setts—Architecture, internal environment and function. Mammal Review, 22, 43-53. |
| [111] | Šálek M, Drahníková L, Tkadlec E (2015) Changes in home range sizes and population densities of carnivore species along the natural to urban habitat gradient. Mammal Review, 45, 1-14. |
| [112] | Salo P, Nordstrom M, Thomson RL, Korpimaki E (2008) Risk induced by a native top predator reduces alien mink movements. Journal of Animal Ecology, 77, 1092-1098. |
| [113] | Sæbø JS (2016) Spatial and Temporal Distributions and Interactions in a Neotropical Ground-Dwelling Animal Community. Master dissertation, Norwegian University, Ås. |
| [114] |
Santini L, González-Suárez M, Russo D, Gonzalez-Voyer A, von Hardenberg A, Ancillotto L (2019) One strategy does not fit all: Determinants of urban adaptation in mammals. Ecology Letters, 22, 365-376.
DOI URL PMID |
| [115] |
Santos F, Carbone C, Wearn OR, Rowcliffe JM, Espinosa S, Lima MGM, Ahumada JA, Gonçalves ALS, Trevelin LC, Alvarez-Loayza P, Spironello WR, Jansen PA, Juen L, Peres C (2019) Prey availability and temporal partitioning modulate felid coexistence in Neotropical forests. PLoS ONE, 14, e0213671.
DOI URL PMID |
| [116] |
Sévêque A, Gentle LK, López-Bao JV, Yarnell RW, Uzal A (2020) Human disturbance has contrasting effects on niche partitioning within carnivore communities. Biological Reviews, 95, 1689-1705.
DOI URL PMID |
| [117] | Scharf FS, Juanes F, Rountree RA (2000) Predator size‒prey size relationships of marine fish predators: Interspecific variation and effects of ontogeny and body size on trophic-niche breadth. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 208, 229-248. |
| [118] | Schieltz JM, Rubenstein DI (2016) Evidence based review: Positive versus negative effects of livestock grazing on wildlife. What do we really know? Environmental Research Letters, 11, 113003. |
| [119] |
Schoener TW (1974) Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science, 185, 27-39.
URL PMID |
| [120] | Schoener TW (1982) The controversy over interspecific competition: Despite spirited criticism, competition continues to occupy a major domain in ecological thought. American Scientist, 70, 586-595. |
| [121] | Scully AE, Fisher S, Miller DAW, Thornton DH (2018) Influence of biotic interactions on the distribution of Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis) at the southern edge of their range. Journal of Mammalogy, 99, 760-772. |
| [122] | Seidensticker J (1976) On the ecological separation between tigers and leopards. Biotropica, 8, 225-234. |
| [123] | Shamoon H, Saltz D, Dayan T (2017) Fine-scale temporal and spatial population fluctuations of medium sized carnivores in a Mediterranean agricultural matrix. Landscape Ecology, 32, 1243-1256. |
| [124] | Shao XN, Song DZ, Huang QW, Li S, Yao M (2019) Fast surveys and molecular diet analysis of carnivores based on fecal DNA and metabarcoding. Biodiversity Science, 27, 543-543‒556. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙 (2019) 基于粪便DNA及宏条形码技术的食肉动物快速调查及食性分析. 生物多样性, 27, 543-556.] | |
| [125] |
Shen XL, Li S, McShea WJ, Wang DJ, Yu JP, Shi XG, Dong W, Mi XC, Ma KP (2020) Effectiveness of management zoning designed for flagship species in protecting sympatric species. Conservation Biology, 34, 158-167.
DOI URL PMID |
| [126] | Silva-Rodríguez EA, Sieving KE (2012) Domestic dogs shape the landscape-scale distribution of a threatened forest ungulate. Biological Conservation, 150, 103-110. |
| [127] | Simcharoen A, Simcharoen S, Duangchantrasiri S, Bump J, Smith JLD (2018) Tiger and leopard diets in western Thailand: Evidence for overlap and potential consequences. Food Webs, 15, e00085. |
| [128] | Soh YH, Carrasco LR, Miquelle DG, Jiang JS, Yang J, Stokes EJ, Tang JR, Kang AL, Liu PQ, Rao M (2014) Spatial correlates of livestock depredation by Amur tigers in Hunchun, China: Relevance of prey density and implications for protected area management. Biological Conservation, 169, 117-127. |
| [129] | Spencer K, Sambrook M, Bremner-Harrison S, Cilliers D, Yarnell RW, Brummer R, Whitehouse-Tedd K (2020) Livestock guarding dogs enable human-carnivore coexistence: First evidence of equivalent carnivore occupancy on guarded and unguarded farms. Biological Conservation, 241, 108256. |
| [130] | St-Pierre C, Ouellet JP, Crête M (2006) Do competitive intraguild interactions affect space and habitat use by small carnivores in a forested landscape? Ecography, 29, 487-496. |
| [131] | Steenweg R, Hebblewhite M, Kays R, Ahumada J, Fisher JT, Burton C, Townsend SE, Carbone C, Rowcliffe JM, Whittington J, Brodie J, Royle JA, Switalski A, Clevenger AP, Heim N, Rich LN (2017) Scaling-up camera traps: Monitoring the planet’s biodiversity with networks of remote sensors. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 15, 26-34. |
| [132] | Steinmetz R, Seuaturien N, Chutipong W (2013) Tigers, leopards, and dholes in a half-empty forest: Assessing species interactions in a guild of threatened carnivores. Biological Conservation, 163, 68-78. |
| [133] |
Steinmetz R, Seuaturien N, Intanajitjuy P, Inrueang P, Prempree K (2020) The effects of prey depletion on dietary niches of sympatric apex predators in Southeast Asia. Integrative Zoology, 16, 19-32.
DOI URL PMID |
| [134] |
Støen OG, Ordiz A, Evans AL, Laske TG, Kindberg J, Frobert O, Swenson JE, Arnemo JM (2015) Physiological evidence for a human-induced landscape of fear in brown bears (Ursus arctos). Physiology & Behavior, 152, 244-248.
DOI URL PMID |
| [135] | Sunarto S, Kelly MJ, Parakkasi K, Hutajulu MB (2015) Cat coexistence in central Sumatra: Ecological characteristics, spatial and temporal overlap, and implications for management. Journal of Zoology, 296, 104-115. |
| [136] | Tabak MA, Norouzzadeh MS, Wolfson DW, Sweeney SJ, VerCauteren KC, Snow NP, Halseth JM, Di Salvo PA, Lewis JS, White MD, Teton B, Beasley JC, Schlichting PE, Boughton RK, Wight B, Newkirk ES, Ivan JS, Odell EA, Brook RK, Lukacs PM, Moeller AK, Mandeville EG, Clune J, Miller RS (2019) Machine learning to classify animal species in camera trap images: Applications in ecology. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 585-590. |
| [137] |
Tobler MW, Kéry M, Hui FKC, Guillera-Arroita G, Knaus P, Sattler T (2019) Joint species distribution models with species correlations and imperfect detection. Ecology, 100, e02754.
DOI URL PMID |
| [138] | Torretta E, Serafini M, Puopolo F, Schenone L (2016) Spatial and temporal adjustments allowing the coexistence among carnivores in Liguria (N-W Italy). Acta Ethologica, 19, 123-132. |
| [139] |
Vanak AT, Fortin D, Thaker M, Ogden M, Owen C, Greatwood S, Slotow R (2013) Moving to stay in place: Behavioral mechanisms for coexistence of African large carnivores. Ecology, 94, 2619-2631.
DOI URL PMID |
| [140] | Vanak AT, Gompper ME (2009) Dogs Canis familiaris as carnivores: Their role and function in intraguild competition. Mammal Review, 39, 265-283. |
| [141] | Vilella M, Ferrandiz-Rovira M, Sayol F (2020) Coexistence of predators in time: Effects of season and prey availability on species activity within a Mediterranean carnivore guild. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 11408-11422. |
| [142] | Wallach AD, Izhaki I, Toms JD, Ripple WJ, Shanas U (2015) What is an apex predator? Oikos, 124, 1453-1461. |
| [143] | Wang F, McShea WJ, Li S, Wang DJ (2018) Does one size fit all? A multispecies approach to regional landscape corridor planning. Diversity and Distributions, 24, 415-425. |
| [144] | Wang SW, Macdonald DW (2009) Feeding habits and niche partitioning in a predator guild composed of tigers, leopards and dholes in a temperate ecosystem in central Bhutan. Journal of Zoology, 277, 275-283. |
| [145] | Wang TM, Feng LM, Mou P, Wu JG, Smith JLD, Xiao WH, Yang HT, Dou HL, Zhao XD, Cheng YC, Zhou B, Wu HY, Zhang L, Tian Y, Guo QX, Kou XJ, Han XM, Miquelle DG, Oliver CD, Xu RM, Ge JP (2016) Amur tigers and leopards returning to China: Direct evidence and a landscape conservation plan. Landscape Ecology, 31, 491-503. |
| [146] | Wang TM, Feng LM, Yang HT, Han BY, Zhao YH, Juan L, Lü X, Zou L, Li T, Xiao WH, Mou P, Smith JLD, Ge JP (2017) A science-based approach to guide Amur leopard recovery in China. Biological Conservation, 210, 47-55. |
| [147] | Wang YW, Allen ML, Wilmers CC (2015) Mesopredator spatial and temporal responses to large predators and human development in the Santa Cruz Mountains of California. Biological Conservation, 190, 23-33. |
| [148] |
Wilmers CC, Wang YW, Nickel B, Houghtaling P, Shakeri Y, Allen ML, Kermish-Wells J, Yovovich V, Williams T (2013) Scale dependent behavioral responses to human development by a large predator, the puma. PLoS ONE, 8, e60590.
DOI URL PMID |
| [149] | Wootton JT, Emmerson M (2005) Measurement of interaction strength in nature. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution & Systematics, 36, 419-444. |
| [150] |
Yan CC, Stenseth NC, Krebs CJ, Zhang ZB (2013) Linking climate change to population cycles of hares and lynx. Global Change Biology, 19, 3263-3271.
DOI URL PMID |
| [151] | Yen SC, Ju YT, Shaner PL, Chen HL (2019) Spatial and temporal relationship between native mammals and free-roaming dogs in a protected area surrounded by a metropolis. Scientific Reports, 9, 8161. |
| [152] | Zapata- Ríos G, Branch LC (2016) Altered activity patterns and reduced abundance of native mammals in sites with feral dogs in the high Andes. Biological Conservation, 193, 9-16. |
| [153] | Zhao GJ, Yang HT, Xie B, Gong YN, Ge JP, Feng LM (2020) Spatio-temporal coexistence of sympatric mesocarnivores with a single apex carnivore in a fine-scale landscape. Global Ecology and Conservation, 21, e00897. |
| [154] | Zhang LJ, Wang AM, Yuan L, Bao WD, Yang YX, Ba TE (2011) Preliminary comparison of diet composition of four small sized carnivores at Saihanwula Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 31, 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张逦嘉, 王安梦, 袁梨, 鲍伟东, 杨永昕, 巴特尔 (2011) 内蒙古赛罕乌拉自然保护区4种小型食肉目动物的食性构成的初步分析. 兽类学报, 31, 55-61.] |
| [1] | 陈楠, 张全国. 实验进化研究途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [2] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [3] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [4] | 吕晓波, 李东海, 杨小波, 张孟文. 红树林群落通过淹水时间及海水盐度的生态位分化实现物种共存[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [5] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [6] | 公欣桐, 陈飞, 高欢欢, 习新强. 两种果蝇成虫与幼虫期的竞争及其对二者共存的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22603-. |
| [7] | 刘向, 刘木, 肖瑶. 叶片病原真菌对植物物种共存的影响: 进展与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22525-. |
| [8] | 王一晴, 马子驭, 王刚, 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 李露, 范新国, 黄巧雯, 李晟. 太行山华北豹袭击家畜的时空特点与管理建议: 以山西省和顺县为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21510-. |
| [9] | 朱逸晓, 王大伟, 李治霖, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 亚洲虎种群恢复的机遇与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22421-. |
| [10] | 马子驭, 何再新, 王一晴, 宋大昭, 夏凡, 崔士明, 苏红信, 邓建林, 李平, 李晟. 中国云豹种群分布现状与关键栖息地信息更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22349-. |
| [11] | 李治霖, 王天明. 亚洲同域分布虎和豹竞争与共存关系概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22271-. |
| [12] | 罗恬, 俞方圆, 练琚愉, 王俊杰, 申健, 吴志峰, 叶万辉. 冠层垂直高度对植物叶片功能性状的影响: 以鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21414-. |
| [13] | 王少鹏, 罗明宇, 冯彦皓, 储诚进, 张大勇. 生物多样性理论最新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22410-. |
| [14] | 田佳, 朱淑怡, 张晓峰, 何礼文, 古晓东, 官天培, 李晟. 大熊猫国家公园的地栖大中型鸟兽多样性现状: 基于红外相机数据的分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1490-1504. |
| [15] | 宋础良. 结构稳定性: 概念、方法和应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(11): 1345-1361. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn