



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1147-1153. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020166 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020166
所属专题: 数据论文
范宗骥1,2, 欧阳学军1,2, 万雅琼3,*( ), 肖文宏4, 谢文贵5, 欧世坤5, 邓锡杰5, 黄忠良1,2, 肖治术4,*(
), 肖文宏4, 谢文贵5, 欧世坤5, 邓锡杰5, 黄忠良1,2, 肖治术4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-24
接受日期:2020-07-13
出版日期:2020-09-20
发布日期:2020-09-13
通讯作者:
万雅琼,肖治术
作者简介:wanyaqiong0229@163.com基金资助:
Zongji Fan1,2, Xuejun Ouyang1,2, Yaqiong Wan3,*( ), Wenhong Xiao4, Wengui Xie5, Shikun Ou5, Xijie Deng5, Zhongliang Huang1,2, Zhishu Xiao4,*(
), Wenhong Xiao4, Wengui Xie5, Shikun Ou5, Xijie Deng5, Zhongliang Huang1,2, Zhishu Xiao4,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-24
Accepted:2020-07-13
Online:2020-09-20
Published:2020-09-13
Contact:
Yaqiong Wan,Zhishu Xiao
摘要:
本研究采用公里网格抽样方案, 在广东鼎湖山国家级自然保护区及其周边林地(烂柯山省级自然保护区和小湘林区)选取3个监测样地, 共设置60个红外相机监测位点, 对区域内大中型兽类和地面活动鸟类开展物种编目清查与评估。2017年1月至2018年12月, 红外相机累计工作34,212个相机日, 共获得独立有效照片11,725份。共记录到75种野生动物, 隶属于13目32科63属, 包括兽类12种、鸟类63种, 其中国家一级重点保护动物有1种, 即中华穿山甲(Manis pentadactyla), 国家二级重点保护动物有9种。兽类中相对多度指数排前三的依次为野猪(Sus scrofa)、鼬獾(Melogale moschata)和赤麂(Muntiacus vaginalis); 鸟类依次为白鹇(Lophura nycthemera)、橙头地鸫(Geokichla citrina)和紫啸鸫(Myophonus caeruleus)。三个监测样地的相对多度指数排前三的物种基本一致, 其中鼎湖山的白鹇相对多度指数最高; 小湘的豹猫(Prionailurus bengalensis)相对多度指数位列第三, 仅次于野猪和鼬獾; 烂柯山相对多度指数排前三的鸟类则依次为画眉(Garrulax canorus)、灰胸竹鸡(Bambusicola thoracicus)和红嘴相思鸟(Leiothrix lutea)。本研究为广东鼎湖山及其周边林地生物多样性监测与评估提供了数据参考。
范宗骥, 欧阳学军, 万雅琼, 肖文宏, 谢文贵, 欧世坤, 邓锡杰, 黄忠良, 肖治术 (2020) 基于红外相机技术对广东鼎湖山及其周边林地的鸟兽调查. 生物多样性, 28, 1147-1153. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020166.
Zongji Fan, Xuejun Ouyang, Yaqiong Wan, Wenhong Xiao, Wengui Xie, Shikun Ou, Xijie Deng, Zhongliang Huang, Zhishu Xiao (2020) Mammals and birds survey using camera trapping in Dinghushan and its surrounding forests, Guangdong Province. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1147-1153. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020166.
| 行政区域 Geographical location | 面积 Area (km2) | 植被 Vegetation | 林地类型 Forest land types | 保护级别 Protection level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鼎湖山 Dinghushan | 鼎湖区 Dinghu District | 11.33 | 自然 Nature | 保护区 Reserve | 国家级 National |
| 烂柯山 Lankeshan | 鼎湖区、高要区 Dinghu District, Gaoyao District | 79.61 | 自然 Nature | 保护区 Reserve | 省级 Provincial |
| 小湘 Xiaoxiang | 高要区 Gaoyao District | 133.33 | 人工 Artificial | 集体林地 Collective woodland | - |
表1 广东鼎湖山及其周边林地的调查区域概况
Table 1 Overview of three study forest sites in the Dinghushan and its surrounding forests of Guangdong Province
| 行政区域 Geographical location | 面积 Area (km2) | 植被 Vegetation | 林地类型 Forest land types | 保护级别 Protection level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鼎湖山 Dinghushan | 鼎湖区 Dinghu District | 11.33 | 自然 Nature | 保护区 Reserve | 国家级 National |
| 烂柯山 Lankeshan | 鼎湖区、高要区 Dinghu District, Gaoyao District | 79.61 | 自然 Nature | 保护区 Reserve | 省级 Provincial |
| 小湘 Xiaoxiang | 高要区 Gaoyao District | 133.33 | 人工 Artificial | 集体林地 Collective woodland | - |
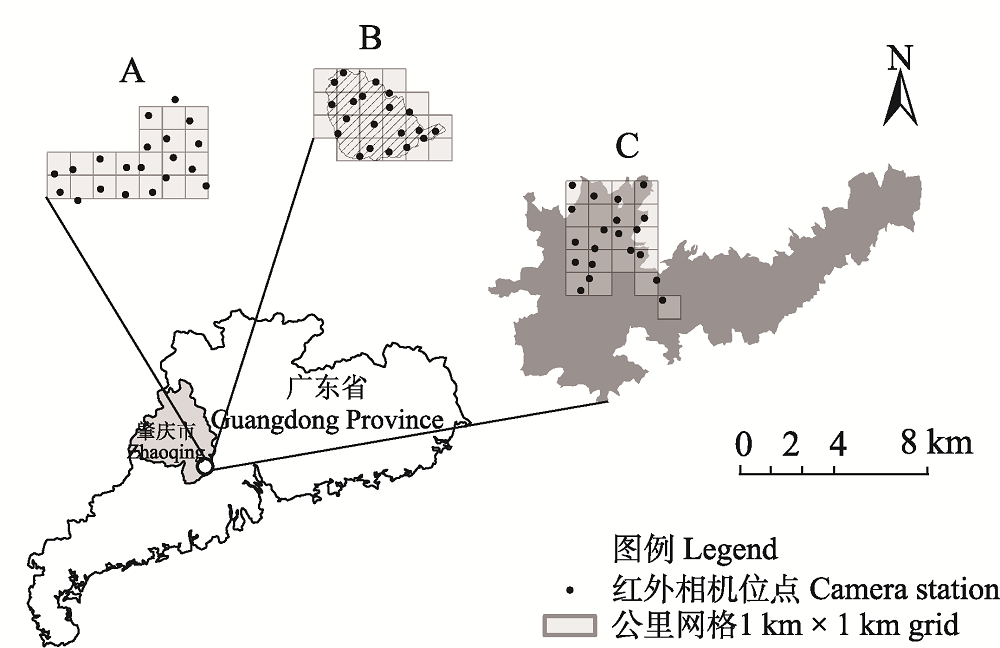
图1 广东鼎湖山及其周边林地红外相机监测位点分布图。A: 小湘林区; B: 鼎湖山国家级自然保护区; C: 烂柯山省级自然保护区。
Fig. 1 The distribution of camera trapping sites in the Dinghushan and its surrounding forests of Guangdong Province. A, Xiaoxiang forest region; B, Dinghushan National Nature Reserve; C, Lankeshan Provincial Nature Reserve.
| 内容 Item | 鼎湖山 Dinghushan | 烂柯山 Lankeshan | 小湘 Xiaoxiang | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 网格数 Grids | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| 相机工作有效时长(相机日) Camera-trapping effort (d) | 11,553 | 11,370 | 11,289 | 34,212 |
| 相机丢失时长(相机日) Missing camera-trapping effort (d) | 3,496 | 1,350 | 1,159 | 6,005 |
| 有效照片数 Number of valid photograph | 28,217 | 15,671 | 24,489 | 68,377 |
| 独立有效照片数 Number of independent photograph | 5,242 | 2,500 | 3,983 | 11,725 |
| 记录兽类物种数 Number of mammal species | 12 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| 记录鸟类物种数 Number of bird species | 43 | 37 | 53 | 63 |
| 记录总物种数 Total species | 55 | 45 | 63 | 75 |
表2 广东鼎湖山及其周边林地红外相机编目清查结果汇总(2017-2018年)
Table 2 Summary of species inventory based on camera trapping data in Dinghushan and its surrounding forests of Guangdong Province (2017-2018)
| 内容 Item | 鼎湖山 Dinghushan | 烂柯山 Lankeshan | 小湘 Xiaoxiang | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 网格数 Grids | 20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| 相机工作有效时长(相机日) Camera-trapping effort (d) | 11,553 | 11,370 | 11,289 | 34,212 |
| 相机丢失时长(相机日) Missing camera-trapping effort (d) | 3,496 | 1,350 | 1,159 | 6,005 |
| 有效照片数 Number of valid photograph | 28,217 | 15,671 | 24,489 | 68,377 |
| 独立有效照片数 Number of independent photograph | 5,242 | 2,500 | 3,983 | 11,725 |
| 记录兽类物种数 Number of mammal species | 12 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| 记录鸟类物种数 Number of bird species | 43 | 37 | 53 | 63 |
| 记录总物种数 Total species | 55 | 45 | 63 | 75 |
| [1] | Andrew TS, Xie Y (2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China, Hunan Education Press. Changsha.(in Chinese) |
| [ Andrew TS, 解焱 (2009) 中国兽类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [2] | Fan ZJ, Ouyang XJ, Bai WK, Huang ZL, Cheng DH, Li JQ, Xiao ZS (2019a) Rediscovery of Chinese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla) in the Zhaoqing Region, Guangdong Province. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 40, 811-813.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范宗骥, 欧阳学军, 白文科, 黄忠良, 程德洪, 李佳琦, 肖治术 (2019a) 广东肇庆地区再现中华穿山甲. 野生动物学报, 40, 811-813.] | |
| [3] | Fan ZJ, Ouyang XJ, Huang ZL, Zhang Q (2019b) Photographic Guide to Common Birds of Dinghushan, Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou.(in Chinese) |
| [ 范宗骥, 欧阳学军, 黄忠良, 张强 (2019b) 鼎湖山常见鸟类图鉴, 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [4] | He JS, Ma KP (2000) Advances in biodiversity inventory and monitoring. In: China’s Biodiversity Conservation Toward the 21st Century: Proceedings of the Third National Symposium on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biological Diversity (eds Biodiversity Committee, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Department of Natural Conservation, State Environmental Protection Administration, Department for Wildlife and Forest Plants Protection, the National Forestry Administration), pp. 316-330, China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贺金生, 马克平 (2000) 生物多样性编目与监测进展. 见: 面向21世纪的中国生物多样性保护: 第三届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集(主编: 中国科学院生物多样性委员会, 国家环境保护总局自然生态保护司, 国家林业局野生动植物保护司), 316-330页, 中国林业出版社: 北京.] | |
| [5] | Heywood VH (1995) 鼎湖山常见鸟类图鉴, Global Biodiversity Assessment. Cambridge University Press, New York. |
| [6] | Huang ZL (2015) Report of Comprehensive Scientific Investigation in Dinghushan National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province, Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou.(in Chinese) |
| [ 黄忠良 (2015) 广东鼎湖山国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告, 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [7] |
Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English)
DOI URL |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| [8] |
Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Feng ZJ, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Luo ZH, Li CW (2015) China’s mammalian diversity. Biodiversity Science, 23, 351-364.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 冯祚建, 周开亚, 刘少英, 罗振华, 李春旺 (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 351-364.] | |
| [9] | Kong GH, Liang C, Wu HM, Huang ZL (1993) Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve: Ecological Research History and Perspective. Science Press: Beijing. |
| [10] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.] | |
| [11] | Liu ZH (1982) Survey of mammals in Dinghushan. Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem, 1, 201-208.(in Chinese) |
| [ 刘振河 (1982) 鼎湖山兽类调查. 热带亚热带森林生态系统研究, 1, 201-208.] | |
| [12] |
Ma KP (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science, 19, 125-126.(in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 马克平 (2011) 监测是评估生物多样性保护进展的有效途径. 生物多样性, 19, 125-126.] | |
| [13] | MacKinnon J, Phillipps K, He FQ (2000) A Field Guide to the Birds of China, Hunan Education Press. Changsha.(in Chinese) |
| [ 约翰·马敬能, 卡伦·菲利普斯, 何芬奇 (2000) 中国鸟类野外手册, 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [14] |
O’Brien TG, Kinnaird MF, Wibisono HT (2003) Crouching tigers, hidden prey: Sumatran tiger and prey populations in a tropical forest landscape. Animal Conservation, 6, 131-139.
DOI URL |
| [15] | O’Connell AF, Nichols JD, Karanth KU (2011) Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses. Springer, New York. |
| [16] |
Vaughan RE, Jones KH (1913) The Birds of Hong Kong, Macao, and the West River or Si Kiang in South-East China, with special reference to their nidification and seasonal movements. IBIS, 55, 17-384.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Wallace P (2016) Managing human disturbance of wildlife in coastal areas. New Zealand Geographer, 72, 133-143.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Wu Y, Peng HY (2005) Two new records of Chiroptera in Guangdong Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 24, 176-177.(in Chinese) |
| [ 吴毅, 彭洪源 (2005) 广东省蝙蝠 (Chiroptera)二新记录. 四川动物, 24, 176-177.] | |
| [19] |
Xiao ZS (2019) Application of camera trapping to species inventory and assessment of wild animals across China’s protected areas. Biodiversity Science, 27, 235-236.(in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 肖治术 (2019) 红外相机技术在我国自然保护地野生动物清查与评估中的应用. 生物多样性, 27, 235-236.] | |
| [20] |
Xiao ZS, Chen LJ, Song XJ, Shu ZF, Xiao RG, Huang XQ (2019) Species inventory and assessment of large- and medium-size mammals and pheasants using camera trapping in the Chebaling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province. Biodiversity Science, 27, 237-242.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 肖治术, 陈立军, 宋相金, 束祖飞, 肖荣高, 黄小群 (2019) 基于红外相机技术对广东车八岭国家级自然保护区大中型兽类与雉类的编目清查与评估. 生物多样性, 27, 237-242.] | |
| [21] |
Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang XZ, Zhou QH, Quan RC, Shen XL, Li S (2014a) Developing camera-trapping protocols for wildlife monitoring in Chinese forests. Biodiversity Science, 22, 704-711.(in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 肖治术, 李欣海, 王学志, 周岐海, 权锐昌, 申小莉, 李晟 (2014a) 探讨我国森林野生动物红外相机监测规范. 生物多样性, 22, 704-711.] | |
| [22] |
Xiao ZS, Wu LF, Tang LF, Lu XL, Huang ZL, Ye WH, Huang XQ (2014b) Camera trap survey of mammals and birds in Dinghushan forest dynamics plot, Southern China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 823-825.(in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 肖治术, 吴林芳, 唐林芳, 卢学理, 黄忠良, 叶万辉, 黄小群 (2014b) 运用红外相机对鼎湖山森林动态监测样地鸟兽的初步调查. 生物多样性, 22, 823-825.] | |
| [23] | Zhang YH, Dai RK, Ou SK (2004) An investigation of the wild ornamental plants in Lankeshan Nature Reserve, Guangdong. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 31(2), 93-96.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张运宏, 戴瑞坤, 欧世坤 (2004) 广东省烂柯山自然保护区野生观赏植物资源调查. 福建林业科技, 31(2), 93-96.] | |
| [24] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn, Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版), 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Zheng YL (1981) New record of ferret-badger in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 1, 158.(in Chinese) |
| [ 郑永烈 (1981) 我国兽类新纪录——缅甸鼬獾. 兽类学报, 1, 158.] | |
| [26] | Zhou YY, Qin YL, Wang YP, Yu SM (1981) Terrestrial vertebrates in the Dinghushan Region. In: Colloquium for Animal Science in Guangdong Province (ed. Zhou YY), pp. 48-60, Guangdong Zoological Association: Guangzhou(in Chinese) |
| [ 周宇垣, 秦耀亮, 王耀培, 余斯绵 (1981) 鼎湖山地区的陆栖脊椎动物. 见: 广东省动物学论文集(周宇垣主编), 48-60页, 广东省动物学会: 广州.] |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 王大伟, 程帅, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北地区张广才岭2015-2020年野生动物红外相机监测数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [3] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [4] | 冉辉, 杨天友, 米小其. 贵州省爬行动物更新名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23348-. |
| [5] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [6] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [7] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [10] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [11] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [12] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [13] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [14] | 杜诚, 汪远, 闫小玲, 严靖, 李惠茹, 张庆费, 胡永红. 上海市植物物种多样性组成和历史变化暨上海维管植物名录更新(2022版)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23093-. |
| [15] | 楼晨阳, 任海保, 陈小南, 米湘成, 童冉, 朱念福, 陈磊, 吴统贵, 申小莉. 钱江源国家公园森林群落的物种多样性、结构多样性及其对黑麂出现概率的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22518-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()