



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 355-365. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019016 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019016
• 研究报告: 植物多样性 • 下一篇
张亚红1, 贾会霞1, 王志彬2, 孙佩1, 曹德美1, 胡建军1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-01-21
接受日期:2019-04-18
出版日期:2019-04-20
发布日期:2019-06-05
通讯作者:
胡建军
基金资助:
Yahong Zhang1, Huixia Jia1, Zhibin Wang2, Pei Sun1, Demei Cao1, Jianjun Hu1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-21
Accepted:2019-04-18
Online:2019-04-20
Published:2019-06-05
Contact:
Jianjun Hu
摘要:
滇杨(Populus yunnanensis)是我国西南地区的特有树种, 具有速生、易无性繁殖、适应性强等优良特性, 是典型的南方型杨属树种。研究滇杨遗传多样性及种群结构对其种质资源的收集、保存和利用具有重要的意义。本研究从我国滇杨主要分布区云南和四川共采集了6个种群, 包括云南的昭通(ZT)、会泽(HZ)、嵩明(SM)、洱源(EY)、拉市海(LS)以及四川的美姑(MG), 共64个个体, 利用34对SSR分子标记和3对cpDNA叶绿体标记开展遗传多样性与遗传结构研究。SSR引物共检测到154个等位基因, 平均等位基因数为4.529, 观测杂合度(Ho)与期望杂合度(He)分别为0.552和0.472, 遗传分化系数(Fst)平均值为0.238, 多态性信息含量指数(PIC)平均值为0.421, 基因流(Nm)为0.806。滇杨的遗传结构分析(DAPC)与遗传距离的主坐标分析(PCoA)、UPGMA聚类分析均将6个种群划分为3个亚类: 第І亚类包括昭通种群、会泽种群和嵩明种群的4个个体, 第ІІ亚类包括嵩明种群的6个个体以及洱源种群和拉市海种群, 第III亚类为美姑种群; 嵩明种群包含第І和第ІІ两个亚类的混合遗传成分。3个cpDNA联合序列中共检测到35个变异位点, 分为13个单倍型, 其中单倍型H5在种群中分布最为广泛, 其余的单倍型均为种群特有的单倍型。分子方差分析(AMOVA)表明种群内的遗传变异大于种群间变异。研究表明滇杨不同种群的遗传分化具有地域性, 可选择就地保护; 昭通种群遗传多样性最高, 且包含7种叶绿体单倍型, 单倍型类型最多, 应优先保护。
张亚红, 贾会霞, 王志彬, 孙佩, 曹德美, 胡建军 (2019) 滇杨种群遗传多样性与遗传结构. 生物多样性, 27, 355-365. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019016.
Yahong Zhang, Huixia Jia, Zhibin Wang, Pei Sun, Demei Cao, Jianjun Hu (2019) Genetic diversity and population structure of Populus yunnanensis. Biodiversity Science, 27, 355-365. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019016.
| 种群 Population | 代号 Code | 样本量 Sample size | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 昭通 Zhaotong | ZT | 12 | 27°33°52″-27°38°29″ N | 103°45°05″-103°46°43″ E | 1,802-1,914 |
| 会泽 Huize | HZ | 12 | 26°12°07″-26°23°42″ N | 103°15°19″-103°24°09″ E | 2,118-2,303 |
| 嵩明 Songming | SM | 10 | 25°12°07″-25°17°42″ N | 103°02°42″-103°03°43″ E | 1,900-1,930 |
| 洱源 Eryuan | EY | 12 | 26°05°56″-26°08°17″ N | 99°58°13″-100°00°08″ E | 2,056-2,060 |
| 拉市海 Lashihai | LS | 12 | 26°51°03″-27°00°28″ N | 100°08°58″-100°15°24″ E | 2,418-2,657 |
| 美姑 Meigu | MG | 6 | 28°19°40″-28°20°09″ N | 103°08°22″-103°08°44″ E | 1,944-2,027 |
表1 滇杨各种群采样地地理信息及采样数
Table 1 Geographic information and sample size of Populus yunnanensis
| 种群 Population | 代号 Code | 样本量 Sample size | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 昭通 Zhaotong | ZT | 12 | 27°33°52″-27°38°29″ N | 103°45°05″-103°46°43″ E | 1,802-1,914 |
| 会泽 Huize | HZ | 12 | 26°12°07″-26°23°42″ N | 103°15°19″-103°24°09″ E | 2,118-2,303 |
| 嵩明 Songming | SM | 10 | 25°12°07″-25°17°42″ N | 103°02°42″-103°03°43″ E | 1,900-1,930 |
| 洱源 Eryuan | EY | 12 | 26°05°56″-26°08°17″ N | 99°58°13″-100°00°08″ E | 2,056-2,060 |
| 拉市海 Lashihai | LS | 12 | 26°51°03″-27°00°28″ N | 100°08°58″-100°15°24″ E | 2,418-2,657 |
| 美姑 Meigu | MG | 6 | 28°19°40″-28°20°09″ N | 103°08°22″-103°08°44″ E | 1,944-2,027 |
| 名称 Name | 区域 Primer area | 正向序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | trnK | AGATGGAAAAAAGAGAGGATAGAGG | CAAATAATATCCAAATACCAAACCC |
| CO5 | rpoC1 | CGAATGGAAGACATAGACAAGT | AAGTGACCTTCGGGAGCTTCTC |
| CO9 | atpF | TTGAAGTCCAGACAGAGCAGGTTAC | GGTCAAACAACTATTCAAAGTCCCT |
表3 用于滇杨PCR扩增的3个cpDNA引物序列信息
Table 3 Three chloroplast DNA primers sequence information of Populus yunnanensis
| 名称 Name | 区域 Primer area | 正向序列 Forward primer sequence (5’-3’) | 反向序列 Reverse primer sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | trnK | AGATGGAAAAAAGAGAGGATAGAGG | CAAATAATATCCAAATACCAAACCC |
| CO5 | rpoC1 | CGAATGGAAGACATAGACAAGT | AAGTGACCTTCGGGAGCTTCTC |
| CO9 | atpF | TTGAAGTCCAGACAGAGCAGGTTAC | GGTCAAACAACTATTCAAAGTCCCT |
| 种群 Popula-tion | 等位基因Number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位 基因 Number of effective alleles (Ne) | 观测杂合度Observed heterozygosity (Ho) | 期望杂合度Expected heterozygosity (He) | Shannon’s 信息指数Shannon’s information content (I) | 近交系数Inbreeding coefficient (F) | 单倍型多态性 Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸 多样性Nucleotide diversity (π) | 单倍型组成(个体数) Haplotype composition (No. of individuals) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | 2.000 | 1.695 | 0.537 | 0.345 | 0.514 | -0.439 | 0.864 | 0.00055 | H1(3); H2(1); H3(1); H4(1); H5(4); H6(1); H7(1) |
| HZ | 2.000 | 1.759 | 0.522 | 0.345 | 0.528 | -0.432 | - | - | H5(12) |
| SM | 2.265 | 1.806 | 0.532 | 0.368 | 0.585 | -0.313 | - | - | H5(10) |
| EY | 2.559 | 1.904 | 0.520 | 0.385 | 0.639 | -0.190 | 0.455 | 0.00013 | H5(9); H10(1); H11(1); H12(1) |
| LS | 2.441 | 1.862 | 0.559 | 0.390 | 0.627 | -0.260 | 0.378 | 0.00025 | H5(10); H8(1); H9(1) |
| MG | 1.794 | 1.623 | 0.495 | 0.324 | 0.473 | -0.454 | 0.333 | 0.00017 | H5(5); H13(1) |
| 平均Mean | 2.177 | 1.775 | 0.528 | 0.360 | 0.561 | -0.341 | 0.402 | 0.00020 |
表4 基于SSR和cpDNA所得的滇杨遗传多样性信息表。种群代号同表1。
Table 4 Genetic diversity of Populus yunnanensis based on SSR and cpDNA. Population codes see Table 1.
| 种群 Popula-tion | 等位基因Number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位 基因 Number of effective alleles (Ne) | 观测杂合度Observed heterozygosity (Ho) | 期望杂合度Expected heterozygosity (He) | Shannon’s 信息指数Shannon’s information content (I) | 近交系数Inbreeding coefficient (F) | 单倍型多态性 Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸 多样性Nucleotide diversity (π) | 单倍型组成(个体数) Haplotype composition (No. of individuals) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | 2.000 | 1.695 | 0.537 | 0.345 | 0.514 | -0.439 | 0.864 | 0.00055 | H1(3); H2(1); H3(1); H4(1); H5(4); H6(1); H7(1) |
| HZ | 2.000 | 1.759 | 0.522 | 0.345 | 0.528 | -0.432 | - | - | H5(12) |
| SM | 2.265 | 1.806 | 0.532 | 0.368 | 0.585 | -0.313 | - | - | H5(10) |
| EY | 2.559 | 1.904 | 0.520 | 0.385 | 0.639 | -0.190 | 0.455 | 0.00013 | H5(9); H10(1); H11(1); H12(1) |
| LS | 2.441 | 1.862 | 0.559 | 0.390 | 0.627 | -0.260 | 0.378 | 0.00025 | H5(10); H8(1); H9(1) |
| MG | 1.794 | 1.623 | 0.495 | 0.324 | 0.473 | -0.454 | 0.333 | 0.00017 | H5(5); H13(1) |
| 平均Mean | 2.177 | 1.775 | 0.528 | 0.360 | 0.561 | -0.341 | 0.402 | 0.00020 |
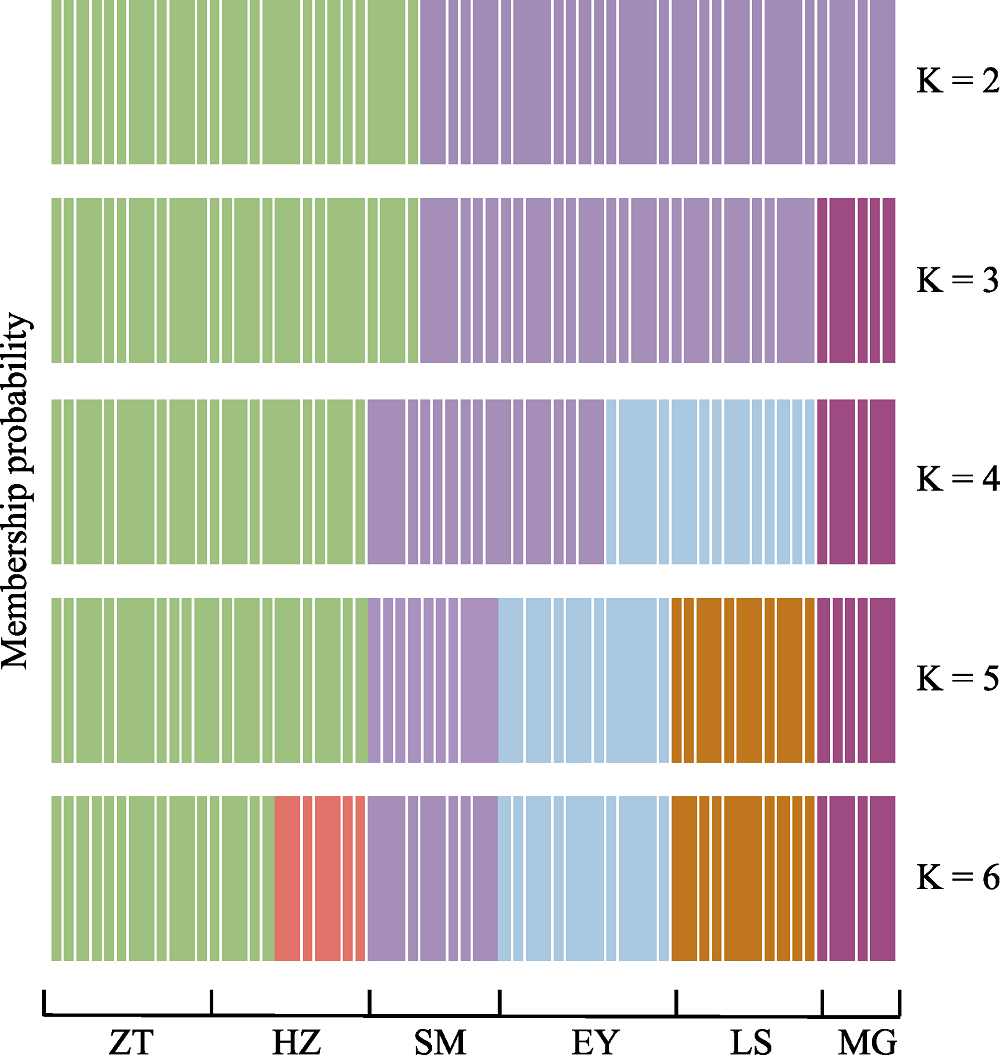
图1 基于DAPC的滇杨个体分布图(K = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)。种群代号同表1。
Fig. 1 Cluster membership probabilities of each genet based on the discriminant functions of DAPC (K = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). Population codes see Table 1.
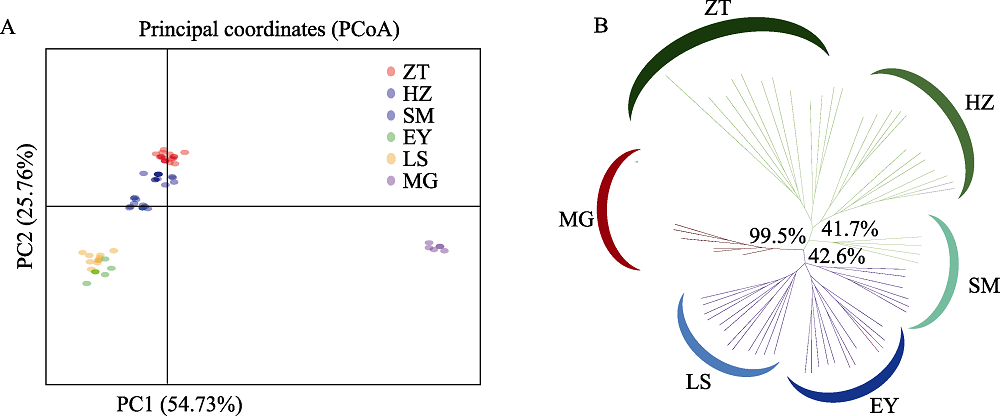
图2 滇杨主坐标分析图及聚类图。(A)个体主坐标分析(PCoA); (B)依据SSR标记基于遗传距离的UPGMA聚类分析, 百分比表示1,000次bootstrap值的比例。种群代号同表1。
Fig. 2 Principal coordinates analysis and clustering dendrogram of Populus yunnanensis. (A) Principal coordinates analysis; (B) UPGMA dendrogram based on genetic distance with SSR data. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. Population codes see Table 1.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异值 Estimated variance of components | 变异来源占比 Percentage of variation (%) | 遗传分化系数 Genetic differentiation coefficient (Fst) | 基因流 Gene flow (Nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR | cpDNA | SSR | cpDNA | SSR | cpDNA | |||
| 种群间 Among population | 5 | 1.966 | 9.663 | 18 | 15 | |||
| 种群内 Within populations | 59 | 9.016 | 39.047 | 82 | 85 | |||
| 总计 Total | 64 | 10.982 | 48.710 | 100 | 100 | 0.237 | 0.148 | 0.806 |
表5 基于SSR和cpDNA对种群内和种群间分子变异的方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of molecular variation (AMOVA) within and among populations based on the SSR and cpDNA
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异值 Estimated variance of components | 变异来源占比 Percentage of variation (%) | 遗传分化系数 Genetic differentiation coefficient (Fst) | 基因流 Gene flow (Nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR | cpDNA | SSR | cpDNA | SSR | cpDNA | |||
| 种群间 Among population | 5 | 1.966 | 9.663 | 18 | 15 | |||
| 种群内 Within populations | 59 | 9.016 | 39.047 | 82 | 85 | |||
| 总计 Total | 64 | 10.982 | 48.710 | 100 | 100 | 0.237 | 0.148 | 0.806 |
| ZT | HZ | SM | EY | LS | MG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | - | 0.081 | 0.182 | 0.227 | 0.266 | 0.434 |
| HZ | 2.837 | - | 0.171 | 0.217 | 0.228 | 0.424 |
| SM | 1.124 | 1.214 | - | 0.174 | 0.124 | 0.409 |
| EY | 0.849 | 0.904 | 1.186 | - | 0.101 | 0.340 |
| LS | 0.689 | 0.844 | 1.763 | 2.216 | - | 0.372 |
| MG | 0.327 | 0.339 | 0.362 | 0.486 | 0.422 | - |
表6 种群间遗传分化系数(Fst, 对角线上方)和基因流(Nm, 对角线下方)。种群代号同表1。
Table 6 Genetic differention (Fst, above diagonal) and gene flow (Nm, below diagonal) among populations. Population codes see Table 1.
| ZT | HZ | SM | EY | LS | MG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | - | 0.081 | 0.182 | 0.227 | 0.266 | 0.434 |
| HZ | 2.837 | - | 0.171 | 0.217 | 0.228 | 0.424 |
| SM | 1.124 | 1.214 | - | 0.174 | 0.124 | 0.409 |
| EY | 0.849 | 0.904 | 1.186 | - | 0.101 | 0.340 |
| LS | 0.689 | 0.844 | 1.763 | 2.216 | - | 0.372 |
| MG | 0.327 | 0.339 | 0.362 | 0.486 | 0.422 | - |
| 单倍型 Hap- lotype | 变异位点 Mutation sites | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CO5 | CO9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
| 6 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 7 | |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| H1 | - | - | - | G | A | - | - | - | A | A | - | C | - | G | - | G | C | - | C | A | C | T | - | C | T | A | C | C | C | - | - | T | G | G | - |
| H2 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H3 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H4 | . | . | . | A | G | A | T | A | . | . | . | G | . | A | T | . | . | . | . | . | - | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H5 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H6 | . | . | T | . | . | . | . | . | T | . | . | G | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . | . |
| H7 | . | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | T | . | T | . | T | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . | . | . | . | . |
| H8 | . | . | . | . | . | . | T | C | T | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | T | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H9 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | T | G | . | . | . |
| H10 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | A | - | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H11 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . |
| H12 | G | . | . | - | G | A | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H13 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | - | - | T | - | A | - | . | . | . | . | . | A |
表7 滇杨叶绿体片段13个单倍型间的序列变异位点表
Table 7 Mutation sites of 13 haplotypes in chloroplast DNA fragments of Populus yunnanensis
| 单倍型 Hap- lotype | 变异位点 Mutation sites | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CO5 | CO9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
| 6 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 7 | |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| H1 | - | - | - | G | A | - | - | - | A | A | - | C | - | G | - | G | C | - | C | A | C | T | - | C | T | A | C | C | C | - | - | T | G | G | - |
| H2 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H3 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H4 | . | . | . | A | G | A | T | A | . | . | . | G | . | A | T | . | . | . | . | . | - | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H5 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H6 | . | . | T | . | . | . | . | . | T | . | . | G | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . | . |
| H7 | . | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | T | . | T | . | T | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . | . | . | . | . |
| H8 | . | . | . | . | . | . | T | C | T | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | T | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H9 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | T | G | . | . | . |
| H10 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | A | - | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H11 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | A | . |
| H12 | G | . | . | - | G | A | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| H13 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | - | - | T | - | A | - | . | . | . | . | . | A |
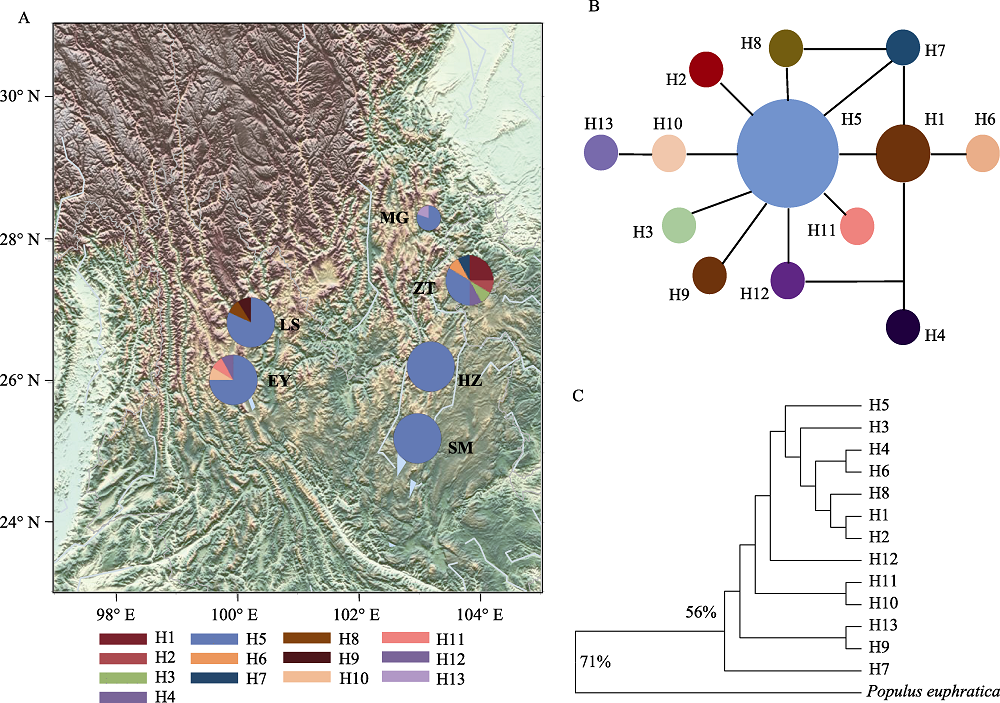
图3 滇杨基于cpDNA的单倍型网络图。(A)单倍型地理分布图, 圆大小代表种群个体数多少, 饼状图为各单倍型占比; (B)中央网络连接图; (C)最大简约法树(MP), 百分比表示1,000次bootstrap值的比例, 小于50%的不予显示。种群代号同表1。
Fig. 3 Haplotype network of Populus yunnanensis based on cpDNA. (A) Haplotype geographical distribution map. The circle size represents the number of individuals in the population. Size of pie charts is proportional to the numbers of individuals sequenced in each population. (B) Median-joining network; (C) The maximum parsimony consensus tree (MP). The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. Population codes see Table 1.
| [1] | Allen G, Flores-Vergara M, Krasynanski S, Kumar S, Thompson WF (2006) A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nature Protocols, 1, 2320-2325. |
| [2] | Bai WN, Zhang DY (2014) Current status and future directions in plant phylogeography. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 26, 125-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 白伟宁, 张大勇 (2014) 植物亲缘地理学的研究现状与发展趋势. 生命科学, 26, 125-137.] | |
| [3] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Burland TG (2000) DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods in Molecular Biology, 132, 71-91.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Chen K (2007) Genetic Relationships among Poplar Species in Section Tacamahaca Spach from Western Sichuan of China. PhD dissertation, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈珂 (2007) 川西青杨组(Section Tacamahaca Spach)不同种的亲缘关系分析. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院成都生物研究所, 成都.] | |
| [6] | Chen XM, He ZH, Shi JR, Xia LQ, Rick W, Zhou Y, Jiang GL (2003) Genetic diversity of high quality winter wheat varieties (lines) based on SSR markers. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 29, 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈新民, 何中虎, 史建荣, 夏兰芹, Ward Rick, 周阳, 蒋国梁 (2003) 利用SSR标记进行优质冬小麦品种(系)的遗传多样性研究. 作物学报, 29, 13-19.] | |
| [7] | Chen XY (2000) Effects of habitat fragmentation on genetic structure of plant populations and implications for the biodiversity conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20, 884-892. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈小勇 (2000) 生境片断化对植物种群遗传结构的影响及植物遗传多样性保护. 生态学报, 20, 884-892.] | |
| [8] | Crandall KA, Templeton AR (1993) Empirical tests of some predictions from coalescent theory with applications to intraspecific phylogeny reconstruction. Genetics, 134, 959-969. |
| [9] | DiFazio S, Slavov G, Rodgers-Melnick E, Martin J, Schackwitz W, Priya R, Tuskan G (2011) Inferring the evolutionary history of Populus trichocarpa from whole genome resequencing data. BMC Proceedings, 5, O1. |
| [10] |
Du QZ, Wang B, Wei ZZ, Zhang DQ, Li BL (2012) Genetic diversity and population structure of Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa) revealed by SSR markers. Journal of Heredity, 103, 853-862.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Ferradini N, Lancioni H, Torricelli R, Russi L, Ragione ID, Cardinali I, Marconi G, Gramaccia M, Concezzi L, Achilli A, Veronesi F, Albertini E (2017) Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of ancient Italian landraces of pear. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 751.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Golding GB (1987) The detection of deleterious selection using ancestors inferred from a phylogenetic history. Genetics Research, 49, 71-82.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Gong GT (2004) The geographic distribution and origin of Populus L. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 25(2), 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龚固堂 (2004) 杨属地理分布与起源初探. 四川林业科技, 25(2), 25-30.] | |
| [14] |
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW, Sherman-Broyles SL (1992) Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant species. New Forests, 6, 95-124.
DOI URL |
| [15] | He CZ, Che PY, Peng CY, Zhou XT, Duan AA, Wang DX, Xin PY (2010) A survey of research progress on gene resources of Populus yunnanensis. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 30(1), 83-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何承忠, 车鹏燕, 周修涛, 段安安, 王德新, 辛培尧 (2010) 滇杨基因资源及其研究概况. 西南林业大学学报, 30(1), 83-88.] | |
| [16] | He CZ, Zhang ZY, Duan AA, Feng XL (2009) Genetic Diversity Analysis of Populus yunnanensis by AFLP Markers. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 何承忠, 张志毅, 段安安, 冯夏莲 (2009) 滇杨基因资源遗传多样性的AFLP分析. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Jia HX, Ji HJ, Hu JJ, Lu MZ (2015) Fingerprints of SSR markers and ploidy detection for new Populus varieties. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51(2), 69-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 贾会霞, 姬慧娟, 胡建军, 卢孟柱 (2015) 杨树新品种的SSR指纹图谱构建和倍性检测. 林业科学, 51(2), 69-79.]
DOI |
|
| [18] |
Jiang DC, Wu GL, Mao KS, Feng JJ (2015) Structure of genetic diversity in marginal populations of black poplar (Populus nigra L.). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 61, 297-302.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F (2010) Discriminant analysis of principal components: A new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genetics, 11, 94. |
| [20] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Molecular Ecology Notes, 6, 288-295.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Peng YH (2006) Population Genetic Survey of Populus cathayana Rehd. Originating from eastern edge of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. PhD dissertation, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭幼红 (2006) 青藏高原东缘青杨(Populus cathayana Rehd.)遗传多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院研究生院成都生物研究所, 成都.] | |
| [23] |
Polzin T, Daneshmand SV (2003) On Steiner trees and minimum spanning trees in hypergraphs. Operations Research Letters, 31, 12-20.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Posada D, Crandall KA (2001) Intraspecific gene genealogies: Trees grafting into networks. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16 , 37-45. |
| [25] |
Qiu YX, Fu CX, Comes HP (2011) Plant molecular phylogeography in China and adjacent regions: Tracing the genetic imprints of Quaternary climate and environmental change in the world’s most diverse temperate flora. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 59, 225-244.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Retief JD (1999) Phylogenetic analysis using PHYLIP. Methods in Molecular Biology, 132, 243-258. |
| [27] |
Roy JK, Lakshmikumaran MS, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2004) AFLP-based genetic diversity and its comparison with diversity based on SSR, SAMPL, and phenotypic traits in bread wheat. Biochemical Genetics, 42, 43-59.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19, 2496-2497.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nature Biotechnology, 18, 233-234. |
| [30] | Semerikova SA, Semerikov VL (2014) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the genus Abies (Pinaceae) based on the nucleotide sequence of chloroplast DNA. Genetika, 50, 12-25. |
| [31] | Shang ZH, Yao AX (2002) Biological genetic diversity research methods and their protective measures. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 23(1), 66-69. (in Chinese) |
| [ 尚占环, 姚爱兴 (2002) 生物遗传多样性研究方法及其保护措施. 宁夏农学院学报, 23(1), 66-69.] | |
| [32] |
Shen XF, Wu ML, Liao BS, Liu ZX, Bai R, Xiao SM, Li XW, Zhang BL, Xu J, Chen SL (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the medicinal plant Artemisia annua. Molecules, 22, 1330.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Tippmann HF (2004) Analysis for free: Comparing programs for sequence analysis. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 5, 82-87.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Wan XQ, Zhang F, Zhong Y, Wang CL, Ding YH, Hu TX, Zhai MP, Qian ZL (2009) Conservation and application of the genetic resource of native poplars in Southwest China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45(4), 139-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 万雪琴, 张帆, 钟宇, 王长亮, 丁云海, 胡庭兴, 翟明普, 钱宗亮 (2009) 中国西南地区乡土杨树基因资源的保护与利用. 林业科学, 45(4), 139-144.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Wang J, Li ZJ, Guo QH, Ren GP, Wu YX (2011) Genetic variation within and between populations of a desert poplar (Populus euphratica) revealed by SSR markers. Annals of Forest Science, 68, 1143-1149.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Wang JL, Gao QB, Fu PC, Gulzar K, Chen SL, Zhang FQ (2014) Phylogeography of Spiraea mongolica (Rosaceae) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent highlands. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 10, 1981-1991. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王久利, 高庆波, 付鹏程, Gulzar K, 陈世龙, 张发起 (2014) 青藏高原及其毗邻山区蒙古绣线菊谱系地理学研究. 西北植物学报, 34, 1981-1991.] | |
| [37] | Xu WY (1988) Poplar. Heilongjiang People’s Publishing House. Harbin. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐纬英 (1988) 杨树. 黑龙江人民出版社, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [38] | Yan LQ, Li JM, Yuan T, Zhou AP, Zong D, Li D, Xin PY, He CZ (2016) Genetic diversity analysis of Populus yunnanensis by SRAP markers. Biotechnology Bulletin, 32, 159-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 颜璐茜, 李佳蔓, 员涛, 周安佩, 纵丹, 李旦, 辛培尧, 何承忠 (2016) 滇杨遗传多样性的SRAP分析. 生物技术通报, 32, 159-167.] | |
| [39] | Yu SQ, Liu J, Fu DR, Liu DJ, Liu YQ (2003) Characteristics of Tacamahaca genes in the Western Sichuan Plateau. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 20, 27-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余树全, 刘军, 付达荣, 刘大健, 刘友全 (2003) 川西高原青杨派基因资源特点. 浙江林学院学报, 20(1), 27-31.] | |
| [40] |
Závada T, Malik RJ, Kesseli RV (2017) Population structure in chicory (Cichorium intybus): A successful U. S. weed since the American revolutionary war. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 4209-4219.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Zeng YF, Zhang JG, Abuduhamiti B, Wang WT, Jia ZQ (2018) Phylogeographic patterns of the desert poplar in Northwest China shaped by both geology and climatic oscillations. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 18, 75.
DOI |
| [42] | Zhao N, Liu J (1994) Taxonomic studies on Populus L. in Southwestern China (II). Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 9, 225-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵能, 刘军 (1994) 中国西南地区杨属的分类学研究(II). 武汉植物科学学报, 9, 225-232.] | |
| [43] | Zheng HL, Fan LQ, Milne RI, Zhang L, Wang YL, Mao KS (2017) Species delimitation and lineage separation history of a species complex of aspens in China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 375. |
| [44] | Zong D, Yuan T, Zhou AP, Liu DY, Zheng Y, Duan AA, He CZ (2014) Analysis of genetic background of 52 Populus yunnanensis superior trees by AFLP markers. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29, 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 纵丹, 员涛, 周安佩, 刘东玉, 郑元, 段安安, 何承忠 (2014) 滇杨优树遗传多样性的AFLP分析. 西北林学院学报, 29, 103-108.] |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [5] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [6] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [9] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [10] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [11] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [12] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [13] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [14] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [15] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()