



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 200-210. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019012 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019012
杨陆飞1,2,陈琳琳2,李晓静2,周政权2,刘博1,2,宋博1,2,李秉钧1,*( ),李宝泉2,*(
),李宝泉2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-01-16
接受日期:2019-02-26
出版日期:2019-02-20
发布日期:2019-04-16
通讯作者:
李秉钧,李宝泉
基金资助:
Yang Lufei1,2,Chen Linlin2,Li Xiaojing2,Zhou Zhengquan2,Liu Bo1,2,Song Bo1,2,Li Bingjun1,*( ),Li Baoquan2,*(
),Li Baoquan2,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-16
Accepted:2019-02-26
Online:2019-02-20
Published:2019-04-16
Contact:
Li Bingjun,Li Baoquan
摘要:
由于气候变化和人类活动的影响, 世界许多海区尤其是近岸海区发生了不同程度的低氧现象, 导致海洋动物大量死亡, 对海洋生态系统产生了不同程度的影响。为明确烟台牟平海洋牧场低氧对大型底栖动物的生态效应, 我们于2016年夏季(6月、8月、9月共3个航次)在该海域进行现场调查, 分析低氧对大型底栖动物群落时空变化的影响。结果表明: 牟平海洋牧场8月低氧事件发生时, 大型底栖动物群落的优势种为短叶索沙蚕(Lumbrinereis latreilli)、不倒翁虫(Sternaspis scutata)和内肋蛤(Endopleura lubrica)。低氧在一定程度上改变了大型底栖动物的群落结构, 表现为物种组成和优势种变化上。例如, 耐受低氧的机会种数量增加, 如短叶索沙蚕; 敏感种数量减少, 如微小海螂(Leptomya minuta)、长吻沙蚕(Glycera chirori)、大蝼蛄虾(Upogebia major)、极地蚤钩虾(Pontocrates altamarimus)、塞切尔泥钩虾(Eriopisella sechellensis)等。同时, 低氧也导致了物种多样性的降低, 但丰度和生物量受其影响不明显, 这主要是由于机会种短叶索沙蚕丰度和生物量的剧增所致。大型底栖动物不同物种耐受低氧的阈值不同。例如, 短叶索沙蚕在溶解氧(DO) < 1.0 mg/L受影响最大, 在DO = 2.0 mg/L时受到的影响不明显, 而其他敏感种如微小海螂、大蝼蛄虾、极地蚤钩虾、塞切尔泥钩虾等在DO < 2.5 mg/L时, 已表现出明显的不适。低氧事件之后, 大型底栖动物群落得到一定程度的恢复, 其恢复程度和需要的时间长短与低氧发生的程度有关。
杨陆飞, 陈琳琳, 李晓静, 周政权, 刘博, 宋博, 李秉钧, 李宝泉 (2019) 烟台牟平海洋牧场季节性低氧对大型底栖动物群落的生态效应. 生物多样性, 27, 200-210. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019012.
Yang Lufei, Chen Linlin, Li Xiaojing, Zhou Zhengquan, Liu Bo, Song Bo, Li Bingjun, Li Baoquan (2019) Effect of seasonal hypoxia on macrobenthic communities in the Muping Marine Ranch, Yantai, China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 200-210. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019012.
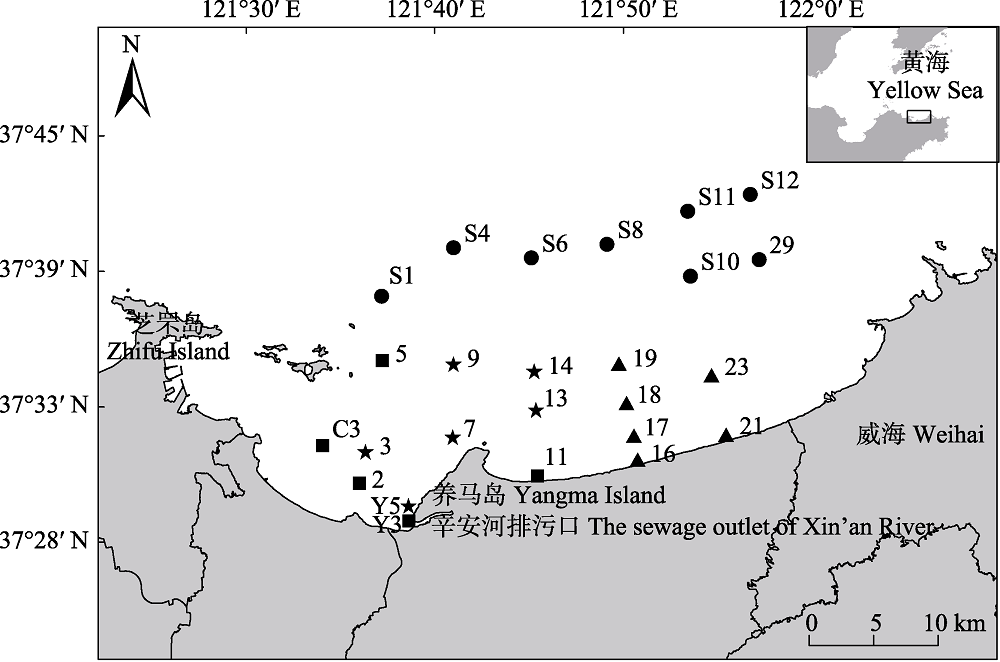
图1 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年夏季大型底栖动物调查站位及低氧分区。★ 低氧区; ■ 低氧边缘区;▲ 养殖区; ● 外海区。
Fig. 1 Sampling stations of macrobenthos in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016. ★ Hypoxic zone; ■ Marginal area of hypoxic zone; ▲ Aquaculture zone; ● Offshore zone.
| 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.20 | 4.25 | 4.24 | 17 | 6.68 | 2.54 | 3.78 | S1 | 7.77 | 2.73 | 3.62 |
| 3 | 6.44 | 2.00 | 4.23 | 18 | 6.96 | 2.96 | 4.04 | S4 | 7.13 | 3.39 | 3.53 |
| 5 | 7.43 | 3.30 | 4.38 | 19 | 6.96 | 3.23 | 4.74 | S6 | 7.08 | 3.26 | - |
| 7 | 4.43 | 1.02 | 4.15 | 21 | 7.26 | 3.59 | 7.79 | S8 | 7.71 | 3.56 | - |
| 9 | 6.36 | 2.50 | 8.28 | 23 | 7.11 | 2.71 | 7.33 | S10 | 7.05 | 3.18 | - |
| 11 | 6.41 | 5.99 | 4.22 | 29 | 7.45 | 3.04 | 4.42 | S11 | 7.15 | 3.74 | 3.65 |
| 13 | 4.93 | 2.03 | 3.94 | C3 | 5.93 | 3.54 | 4.51 | S12 | 6.72 | 2.63 | 5.10 |
| 14 | 5.28 | 2.25 | 4.19 | Y3 | 5.68 | 3.84 | 4.04 | 平均值 Average | 6.56 | 3.25 | 4.78 |
| 16 | 7.53 | 8.02 | 6.97 | Y5 | 5.29 | 1.95 | 3.93 |
表1 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年夏季底层水溶解氧值(mg/L)
Table 1 Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) of bottom water in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016
| 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | 站位 Station | 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.20 | 4.25 | 4.24 | 17 | 6.68 | 2.54 | 3.78 | S1 | 7.77 | 2.73 | 3.62 |
| 3 | 6.44 | 2.00 | 4.23 | 18 | 6.96 | 2.96 | 4.04 | S4 | 7.13 | 3.39 | 3.53 |
| 5 | 7.43 | 3.30 | 4.38 | 19 | 6.96 | 3.23 | 4.74 | S6 | 7.08 | 3.26 | - |
| 7 | 4.43 | 1.02 | 4.15 | 21 | 7.26 | 3.59 | 7.79 | S8 | 7.71 | 3.56 | - |
| 9 | 6.36 | 2.50 | 8.28 | 23 | 7.11 | 2.71 | 7.33 | S10 | 7.05 | 3.18 | - |
| 11 | 6.41 | 5.99 | 4.22 | 29 | 7.45 | 3.04 | 4.42 | S11 | 7.15 | 3.74 | 3.65 |
| 13 | 4.93 | 2.03 | 3.94 | C3 | 5.93 | 3.54 | 4.51 | S12 | 6.72 | 2.63 | 5.10 |
| 14 | 5.28 | 2.25 | 4.19 | Y3 | 5.68 | 3.84 | 4.04 | 平均值 Average | 6.56 | 3.25 | 4.78 |
| 16 | 7.53 | 8.02 | 6.97 | Y5 | 5.29 | 1.95 | 3.93 |
| 物种数 Species number (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | |
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 23(67.6) | 21(63.6) | 25(62.5) |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 5(14.7) | 4(12.1) | 6(15) |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 4(11.8) | 6(18.2) | 6(15) |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | 1(2.9) | - | 2(5) |
| 其他 Others | 1(2.9) | 2(6.1) | 1(2.5) |
| 总计 Total | 34(100) | 33(100) | 40(100) |
表2 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年夏季低氧区大型底栖动物群落组成
Table 2 Composition of macrobenthic community in hypoxic zone in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016
| 物种数 Species number (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6月 June | 8月 August | 9月 September | |
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 23(67.6) | 21(63.6) | 25(62.5) |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 5(14.7) | 4(12.1) | 6(15) |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 4(11.8) | 6(18.2) | 6(15) |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | 1(2.9) | - | 2(5) |
| 其他 Others | 1(2.9) | 2(6.1) | 1(2.5) |
| 总计 Total | 34(100) | 33(100) | 40(100) |
| 物种数 Species number (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | ||
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 21(63.6) | 20(52.6) | 31(55.4) | 18(50) | |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 4(12.1) | 7(18.4) | 11(19.6) | 8(22.2) | |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 6(18.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(17.9) | 8(22.2) | |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | - | 2(5.3) | 3(5.4) | 1(2.8) | |
| 其他 Others | 2(6.1) | 1(2.6) | 1(1.8) | 1(2.8) | |
| 总计 Total | 33(100) | 38(100) | 56(100) | 36(100) | |
表3 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年8月不同海区大型底栖动物群落组成
Table 3 Composition of macrobenthic community in different zones in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during August 2016
| 物种数 Species number (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | ||
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 21(63.6) | 20(52.6) | 31(55.4) | 18(50) | |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 4(12.1) | 7(18.4) | 11(19.6) | 8(22.2) | |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 6(18.2) | 8(21.1) | 10(17.9) | 8(22.2) | |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | - | 2(5.3) | 3(5.4) | 1(2.8) | |
| 其他 Others | 2(6.1) | 1(2.6) | 1(1.8) | 1(2.8) | |
| 总计 Total | 33(100) | 38(100) | 56(100) | 36(100) | |
| 月份 Month | 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | 总计 Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |
| 6 | 2,183.33 | 5.84 | 2,573.33 | 10.31 | 853.33 | 9.69 | 855.83 | 5.71 | 1,500.3 | 7.41 |
| 8 | 2,102.22 | 12.16 | 1,645.33 | 5.01 | 496.67 | 5.02 | 444.17 | 2.92 | 1,094.9 | 6.06 |
| 9 | 1,216.67 | 7.96 | 1,972 | 4.79 | 595 | 2.16 | 533.33 | 13.62 | 999.97 | 7.75 |
表4 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年夏季不同海区大型底栖动物丰度和生物量
Table 4 The macrobenthic abundance and biomass in different zones in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016
| 月份 Month | 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | 总计 Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |
| 6 | 2,183.33 | 5.84 | 2,573.33 | 10.31 | 853.33 | 9.69 | 855.83 | 5.71 | 1,500.3 | 7.41 |
| 8 | 2,102.22 | 12.16 | 1,645.33 | 5.01 | 496.67 | 5.02 | 444.17 | 2.92 | 1,094.9 | 6.06 |
| 9 | 1,216.67 | 7.96 | 1,972 | 4.79 | 595 | 2.16 | 533.33 | 13.62 | 999.97 | 7.75 |
| 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 1,933.33 | 6.96 | 1,048 | 3.45 | 397.78 | 3.66 | 270.83 | 1.56 |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 16.67 | 2.31 | 44 | 0.33 | 24.44 | 0.61 | 17.50 | 0.085 |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 147.78 | 0.55 | 542.67 | 1.02 | 68.89 | 0.27 | 153.33 | 1.20 |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | - | - | 5.33 | 0.06 | 4.44 | 0.39 | 1.67 | 0.049 |
| 其他 Others | 4.45 | 2.34 | 5.33 | 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 0.018 |
表5 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年8月不同海区丰度和生物量组成
Table 5 Composition of macrobenthic abundance and biomass in different zones in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during August 2016
| 低氧区 Hypoxic zone | 低氧边缘区 Marginal area of hypoxic zone | 养殖区 Aquaculture zone | 外海区 Offshore zone | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 丰度 Abundance (ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | 1,933.33 | 6.96 | 1,048 | 3.45 | 397.78 | 3.66 | 270.83 | 1.56 |
| 甲壳类 Crustacea | 16.67 | 2.31 | 44 | 0.33 | 24.44 | 0.61 | 17.50 | 0.085 |
| 软体动物 Mollusca | 147.78 | 0.55 | 542.67 | 1.02 | 68.89 | 0.27 | 153.33 | 1.20 |
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | - | - | 5.33 | 0.06 | 4.44 | 0.39 | 1.67 | 0.049 |
| 其他 Others | 4.45 | 2.34 | 5.33 | 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 0.018 |
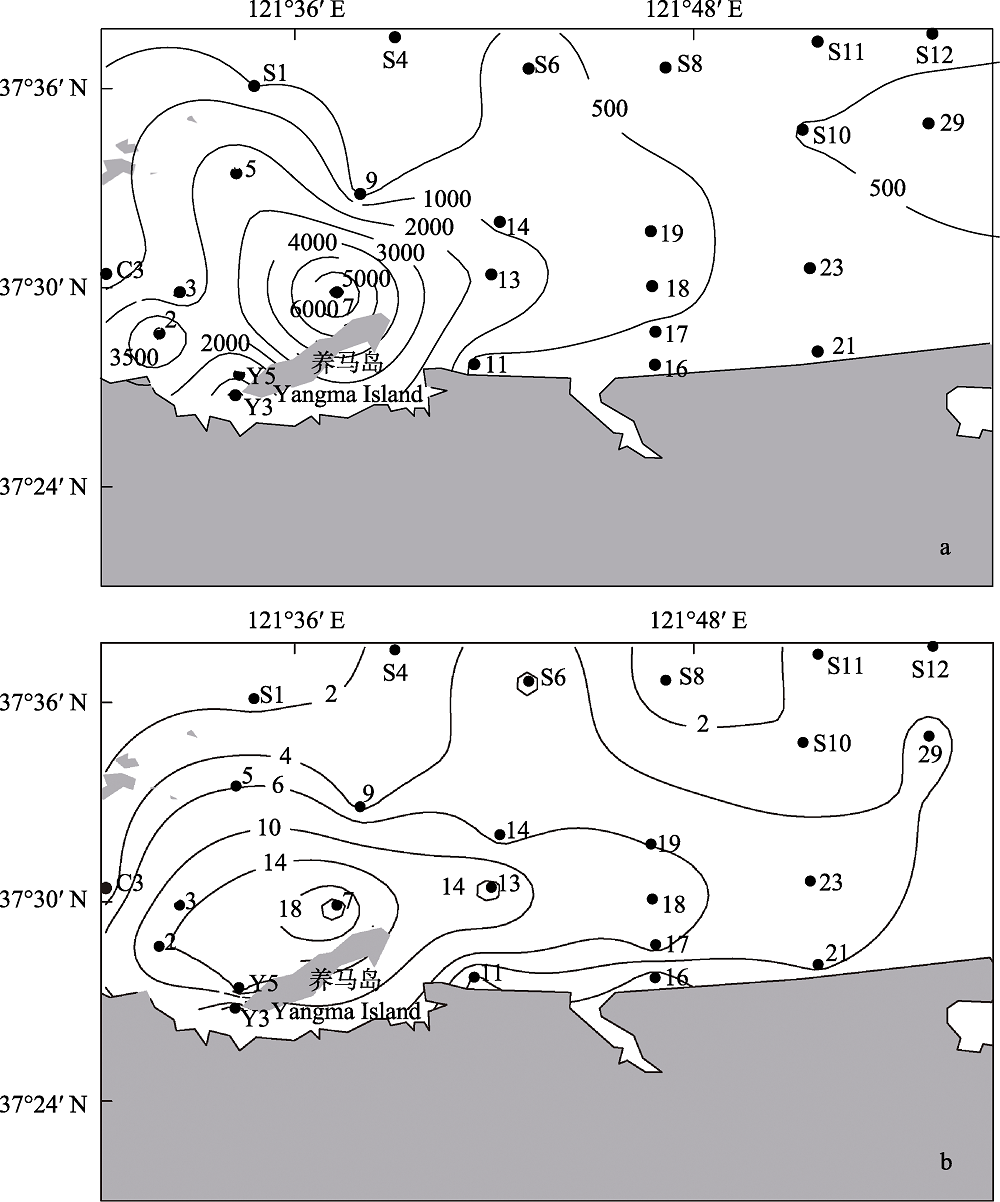
图2 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年8月大型底栖动物丰度(a, ind./m2)和生物量(b, g/m2)空间分布
Fig. 2 Spatial distribution of macrobenthic abundance (a, ind./m2) and biomass (b, g/m2) in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during August 2016
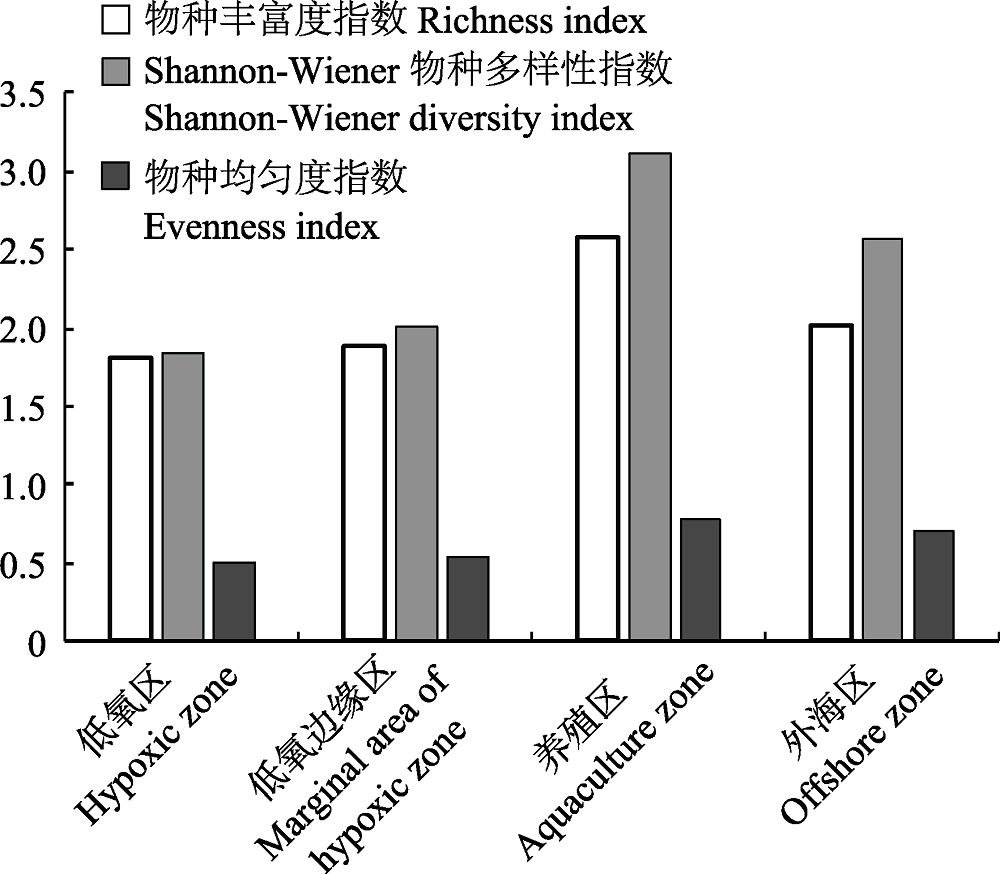
图3 烟台牟平海洋牧场2016年8月不同海区大型底栖动物群落多样性指数
Fig. 3 Diversity indices of macrobenthic community in different zones in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during August 2016
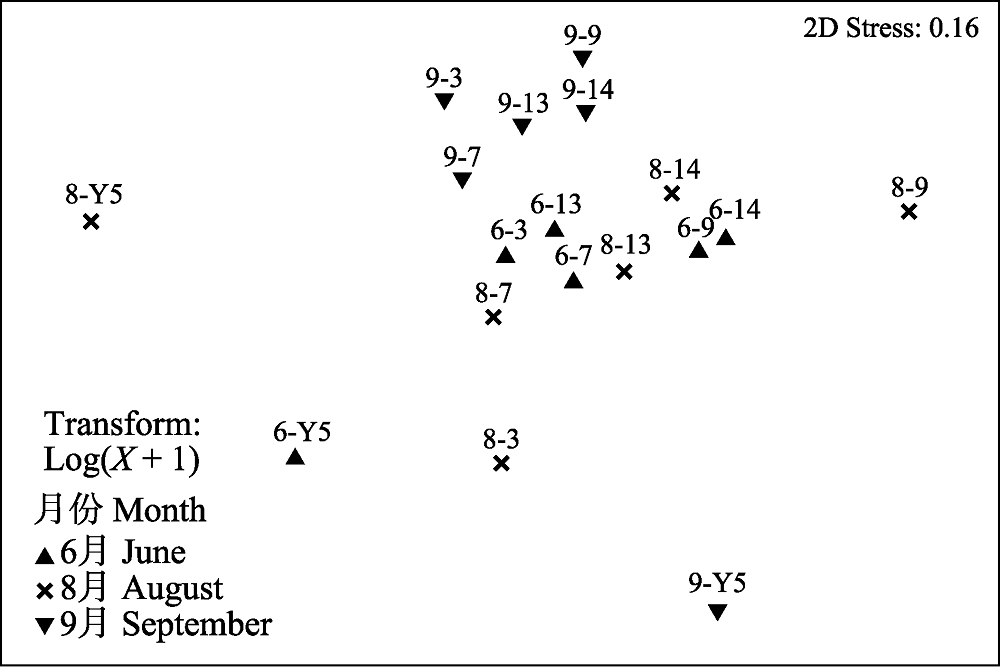
图4 烟台牟平海洋牧场低氧区大型底栖动物非度量多维尺度分析。“6-3”表示6月份的3号站位, 以此类推。
Fig. 4 Analysis of NMDS on macrobenthos in hypoxic zone in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016. “6-3” represents for the third sampling station in June, the others are likewise.
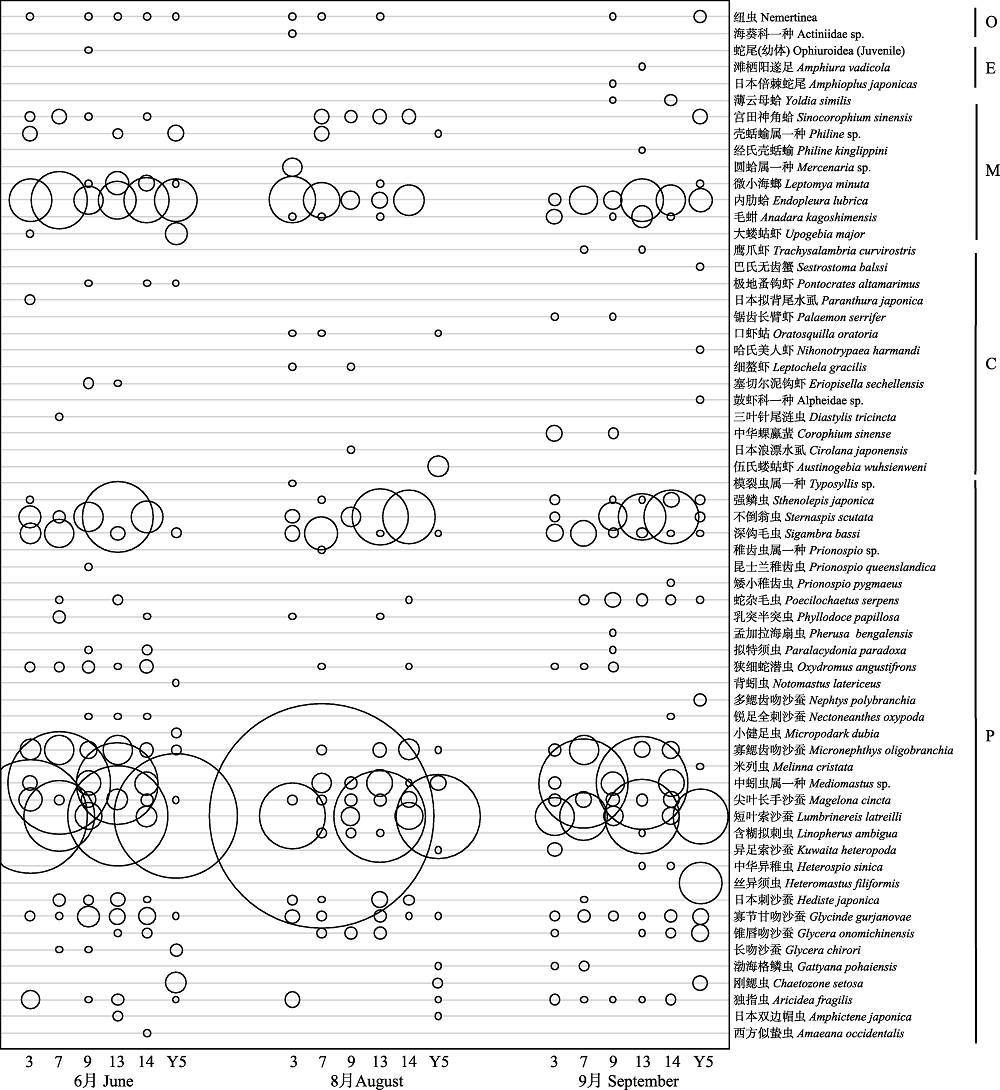
图5 烟台牟平海洋牧场夏季低氧区大型底栖动物丰度(丰度与圆圈直径成正比)。P: 多毛类; C: 甲壳类; M: 软体动物; E: 棘皮动物; O: 其他动物。
Fig. 5 The macrobenthic abundance in hypoxic zone in the Muping Marine Ranch (Yantai) during summer 2016. Abundance value increases linearly with the circle diameter. P, Polychaeta; C, Crustacea; M, Mollusca; E, Echinodermata; O, Others.
| [1] |
Baustian MM, Rabalais NN ( 2009) Seasonal composition of benthic macroinfauna exposed to hypoxia in the northern gulf of Mexico. Estuaries and Coasts, 32, 975-983.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Briggs KB, Cartwright G, Friedrichs CT, Shivarudruppa S ( 2015) Biogenic effects on cohesive sediment erodibility resulting from recurring seasonal hypoxia on the Louisiana shelf. Continental Shelf Research, 93, 17-26.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chen YQ, Xu ZL, Wang YL ( 1995) An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) River estuarine area. I. Biomass distribution of dominant species. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2, 49-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈亚瞿, 徐兆礼, 王云龙 ( 1995) 长江口河口锋区浮游动物生态研究. I. 生物量及优势种的平面分布. 中国水产科学, 2, 49-58.] | |
| [4] |
Chi LB, Song XX, Yuan YQ, Wang WT, Zhou P, Fan X, Cao XH, Yu ZM ( 2017) Distribution and key influential factors of dissolved oxygen off the Changjiang River Estuary (CRE) and its adjacent waters in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 125, 440-450.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Chu JWF, Tunnicliffe V ( 2015) Oxygen limitations on marine animal distributions and the collapse of epibenthic community structure during shoaling hypoxia. Global Change Biology, 21, 2989-3004.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Conley DJ, Humborg C, Rahm L, Savchuk OP, Wulff F ( 2002) Hypoxia in the Baltic Sea and basin-scale changes in phosphorus biogeochemistry. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 5315-5320.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Dauer DM ( 1993) Biological criteria, environmental health and estuarine macrobenthic community structure. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 26, 249-257.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Diaz RJ ( 2001) Overview of hypoxia around the world. Journal of Environment Quality, 30, 275-281.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R ( 1995) Marine benthic hypoxia: A review of its ecological effects and the behavioural response of benthic macrofauna. Oceanography and Marine Biology, 33, 245-303. |
| [10] |
Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R ( 2008) Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science, 321, 926-929.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Gong SB, Gao AG, Ni GT, Zhu XX, Zhang YP, Hou YT ( 2017) Progress in research of hypoxia in estuaries and coastal areas in China. Water Resources Protection, 33(4), 62-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 龚松柏, 高爱国, 倪冠韬, 朱旭旭, 张延颇, 侯昱廷 ( 2017) 中国部分河口及其近海水域缺氧现象研究. 水资源保护, 33(4), 62-69.]
DOI URL |
|
| [12] | Gooday AJ, Levin LA, Silva AAD, Bett BJ, Cowie GL ( 2009) Faunal responses to oxygen gradients on the Pakistan margin: A comparison of foraminiferans, macrofauna and megafauna. Deep-Sea Research II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 56, 488-502. |
| [13] |
Gray JS, Wu RSS, Ying Y ( 2002) Effects of hypoxia and organic enrichment on the marine environment. Marine Ecology Progress, 238, 249-279.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Gu XL, Xu ZL ( 2009) A review on the effects of hypoxia on aquatic animals in estuaries. Marine Fisheries, 31, 426-437. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 顾孝连, 徐兆礼 ( 2009) 河口及近岸海域低氧环境对水生动物的影响. 海洋渔业, 31, 426-437.]
DOI URL |
|
| [15] |
Li DJ, Zhang J, Wu Y, Liang J, Huang DJ ( 2002) Loss of oxygen outside the Changjiang Estuary. Science in China, 32, 686-694. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李道季, 张经, 吴莹, 梁俊, 黄大吉 ( 2002) 长江口外氧的亏损. 中国科学, 32, 686-694.]
DOI URL |
|
| [16] | Li XZ, Liu LS, Li BQ ( 2010) The Macrobenthic Assemblages in China: Research and Practice. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李新正, 刘录三, 李宝泉 ( 2010) 中国海洋大型底栖生物: 研究与实践. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] |
Li YY, Wang ZM ( 2006) The relation among dissolution oxygen (DO) to COD, inorganic nitrogen, reactive phosphate and primary yield-power in the Liaodong Gulf and seaport of Daliaohe. Environmental Monitoring in China, 22(3), 70-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李艳云, 王作敏 ( 2006) 大辽河口和辽东湾海域水质溶解氧与COD、无机氮、磷及初级生产力的关系. 中国环境监测, 22(3), 70-72.]
DOI URL |
|
| [18] |
Liu HX ( 2012) Study on main influencing factors of formation and deterioration of summer hypoxia off the Yangtze River Estuary. Advance in Marine Science, 30, 186-197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 刘海霞 ( 2012) 长江口夏季低氧区形成及加剧的成因分析. 海洋科学进展, 30, 186-197.]
DOI URL |
|
| [19] | Luo L, Li SY, Wang DX ( 2008) Modelling of hypoxia in the Pearl River Estuary in summer. Advances in Water Science, 19, 729-735. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗琳, 李适宇, 王东晓 ( 2008) 珠江河口夏季缺氧现象的模拟. 水科学进展, 19, 729-735.] | |
| [20] | Margalef R ( 1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [21] |
Meng CX, Deng CM, Yao P, Zhang XQ, Mi TZ, Chen HT, Yu ZG ( 2005) Dissolved oxygen in the Xiaoqinghe Estuary and adjacent waters. Marine Environmental Science, 24(3), 25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 孟春霞, 邓春梅, 姚鹏, 张欣泉, 米铁柱, 陈洪涛, 于志刚 ( 2005) 小清河口及邻近海域的溶解氧. 海洋环境科学, 24(3), 25-28.]
DOI URL |
|
| [22] |
Nilsson HC, Rosenberg R ( 1994) Hypoxic response of two marine benthic communities. Marine Ecology Progress, 115, 209-217.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Pielou EC ( 1975) Ecology Diversity. Wiley-Inters, New York. |
| [24] |
Ran XB, Zang JY, Wei QS, Guo JS, Yin XF, Liu W, Liu J ( 2012) Hypoxia and its cause of formation in the adjacent waters of Rushan Bay. Advances in Marine Science, 30, 347-356. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 冉祥滨, 臧家业, 韦钦胜, 郭景松, 尹晓斐, 刘玮, 刘军 ( 2012) 乳山湾邻近海域低氧现象及成因浅析. 海洋科学进展, 30, 347-356.]
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | Shannon CE, Weaver W ( 1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbanna. |
| [26] |
Stachowitsch M ( 1991) Anoxia in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Rapid death, slow recovery. Modern & Ancient Continental Shelf Anoxia, 58, 119-129.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Steckbauer A, Duarte CM, Carstensen J, Vaquer-Sunyer R, Conley DJ ( 2011) Ecosystem impacts of hypoxia: Thresholds of hypoxia and pathways to recovery. Environmental Research Letters, 6, 025003.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Sturdivant SK, Seitz RD, Diaz RJ ( 2013) Effects of seasonal hypoxia on macrobenthic production and function in the Rappahannock River, Virginia, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 490, 53-68.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Vaquer-Sunyer R, Duarte CM ( 2008) Thresholds of hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 15452-15457.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Wang QC, Li BQ ( 2013) Community structure of macrobenthos in coastal water off Yantai, East China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 44, 1667-1680. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 王全超, 李宝泉 ( 2013) 烟台近海大型底栖动物群落特征. 海洋与湖沼, 44, 1667-1680.]
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | Wang QN, Yan T, Zhou MJ ( 2012) Research progress on cause of hypoxia and its influence in coastal and estuary region. Marine Environmental Science, 31, 775-778. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王巧宁, 颜天, 周名江 ( 2012) 近岸和河口低氧成因及其影响的研究进展. 海洋环境科学, 31, 775-778.] | |
| [32] |
Wang YM, Li DJ, Fang T, Liu ZG, He SQ ( 2008) Study on relation of distribution of benthos and hypoxia in Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent sea. Marine Environmental Science, 27(2), 41-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 王延明, 李道季, 方涛, 刘志刚, 何松琴 ( 2008) 长江口及邻近海域底栖生物分布及与低氧区的关系研究. 海洋环境科学, 27(2), 41-66.]
DOI URL |
|
| [33] |
Wu RSS ( 2002) Hypoxia: From molecular responses to ecosystem responses. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 45, 35-45.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Yang D, Zhou ZQ, Zhang JS, Liu TT, Li XJ, Ai BH, Li BQ, Chen LL ( 2017) Characteristics of macrobenthic communities at the Muping Marine Ranch of Yantai in summer. Marine Sciences, 41(5), 136-145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 杨东, 周政权, 张建设, 刘甜甜, 李晓静, 艾冰花, 李宝泉, 陈琳琳 ( 2017) 烟台牟平海洋牧场夏季大型底栖动物群落特征. 海洋科学, 41(5), 136-145.]
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | Ye F, Huang XP ( 2010) The status, causes, and ecological effects of coastal hypoxia. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, ( 3), 91-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 叶丰, 黄小平 ( 2010) 近岸海域缺氧现状、成因及其生态效应. 海洋湖沼通报, ( 3), 91-99.] | |
| [36] | Zhang YY, Zhang J, Wu Y, Zhu ZY ( 2007) Characteristics of dissolved oxygen and its affecting factors in the Yangtze Estuary. Environmental Science, 28, 1649-1654. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张莹莹, 张经, 吴莹, 朱卓毅 ( 2007) 长江口溶解氧的分布特征及影响因素研究. 环境科学, 28, 1649-1654.] |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [11] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [12] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [13] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [14] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [15] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn