



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 419-432. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018316 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018316
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能; 生物安全
马燕婕1, 何浩鹏1, 沈文静2, 刘标2,*( ), 薛堃1,2,*(
), 薛堃1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-11-23
接受日期:2019-02-28
出版日期:2019-04-20
发布日期:2019-06-05
通讯作者:
刘标,薛堃
基金资助:
Yanjie Ma1, Haopeng He1, Wenjing Shen2, Biao Liu2,*( ), Kun Xue1,2,*(
), Kun Xue1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-11-23
Accepted:2019-02-28
Online:2019-04-20
Published:2019-06-05
Contact:
Biao Liu, Kun Xue
摘要:
通过对转基因耐除草剂(EPSPS)抗虫(Cry1Ab)玉米转化体‘DBN9936’、受体玉米‘DBN318’、常规玉米‘先玉335’和喷施除草剂的转化体‘DBN9936’玉米田中节肢动物种类及数量的调查, 评价转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响。2015年和2017年我们采用直接观察法、陷阱调查法和剖秆法对田间节肢动物进行调查, 采用聚类分析、物种累积曲线等方法对数据进行分析, 并比较了4个处理玉米田节肢动物群落的Margalef丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson多样性指数、Pielou均匀度指数、优势集中性指数和群落相似性指数的差异及其随时间变化的规律。调查期间共记录节肢动物20目80科; 转化体玉米‘DBN9936’ (2015: 10.3 ± 2.6头, 2017: 3.3 ± 1.7头)和喷施除草剂的转化体玉米‘DBN9936’ (2015: 6.0 ± 1.5头, 2017: 17.0 ± 0.6头)上鳞翅目昆虫的数量明显低于受体‘DBN318’ (2015: 20.0 ± 3.2头, 2017: 24.0 ± 6.0头)和‘先玉335’ (2015: 21.0 ± 8.9头, 2017: 26.7 ± 2.0头); 物种累积曲线呈典型的抛物线, 各类玉米田间总体物种丰富度差异较小; 玉米生育期节肢动物调查结果累计数量的功能团组成及其丰富度、多样性、均匀度、优势集中性间均无明显的差异, 各类指数随时间变化的动态趋于一致, 群落间相似性程度较高。转基因玉米‘DBN9936’对鳞翅目害虫有明显的抗性, 对非靶标节肢动物无显著的影响, 对田间节肢动物的群落多样性、均匀度、丰富度、优势集中性等没有明显的影响。
马燕婕, 何浩鹏, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃 (2019) 转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 27, 419-432. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018316.
Yanjie Ma, Haopeng He, Wenjing Shen, Biao Liu, Kun Xue (2019) Effects of transgenic maize on arthropod diversity. Biodiversity Science, 27, 419-432. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018316.
| 功能群 Functional groups | 主要类群 Major groups | ‘DBN9936’ | ‘DBN318’ | ‘先玉335’ Xianyu 335 | ‘DBN9936’喷除草剂 DBN9936 + herbicide | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ||||||
| 主要害虫 Main pest | 鳞翅目 Lepidopteron | 10.3 ± 2.6a | 20.0 ± 3.2a | 21.0 ± 8.9a | 6.0 ± 1.5a | 0.166 |
| 长角䖴科 Entomobryidae | 112.3 ± 25.5a | 105.7 ± 9.9a | 128.3 ± 11.3a | 113.7 ± 8.1a | 0.765 | |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 834.0 ± 206.6a | 763.3 ± 118.3a | 515.7 ± 62.1a | 590.0 ± 84.3a | 0.341 | |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 1,194.0 ± 94.4b | 1,308.7 ± 32.9b | 1,009.7 ± 56.4a | 1,217.3 ± 42.9b | 0.047 | |
| 总和 Total | 2,212.3 ± 266.9a | 2,258.0 ± 154.5a | 1,736.0 ± 37.8a | 1,985.7 ± 109.9a | 0.176 | |
| 捕食性天敌 Predatory natural enemy | 蜘蛛目 Araneida | 43.7 ± 4.6a | 52.3 ± 2.2a | 59.3 ± 3.8a | 54.3 ± 7.7a | 0.246 |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | 113.7 ± 6.1a | 106.3 ± 11.2a | 104.3 ± 7.9a | 120.0 ± 15.1a | 0.720 | |
| 草蛉科 Chrysopidae | 36.3 ± 6.2a | 32.3 ± 2.8a | 25.3 ± 4.1a | 25.3 ± 4.1a | 0.288 | |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 12.7 ± 2.9a | 15.0 ± 3.2a | 20.7 ± 9.9a | 20.0 ± 6.5a | 0.808 | |
| 总和 Total | 214.7 ± 8.6a | 213.3 ± 10.3a | 219.7 ± 3.8a | 231.0 ± 5.5a | 0.386 | |
| 寄生性天敌 Parasitic natural enemy | 总和 Total | 8.7 ± 3.3a | 6.7 ± 1.9a | 5.7 ± 0.9a | 7.7 ± 0.9a | 0.742 |
| 中性节肢动物 Neutral arthropod | 总和 Total | 206.7 ± 31.5a | 177.7 ± 9.0a | 152.0 ± 28.6a | 147.0 ± 20.4a | 0.339 |
| 2017 | ||||||
| 主要害虫 Main pest | 鳞翅目 Lepidopteron | 3.3 ± 1.7a | 24.0 ± 6.0b | 26.7 ± 2.0b | 17.0 ± 0.6a | 0.005 |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 5,357.0 ± 148.5a | 5,408.3 ± 324.9a | 5,444.0 ± 607.7a | 4,751.7 ± 171.3a | 0.520 | |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 42.3 ± 3.8a | 51.0 ± 4.6a | 40.0 ± 3.5a | 46.7 ± 1.5a | 0.213 | |
| 长角䖴科 Entomobryidae | 86.3 ± 9.8a | 95.0 ± 12.5a | 93.4 ± 6.6a | 97.0 ± 10.0a | 0.882 | |
| 总和 Total | 5,880.7 ± 133.5a | 5,974.7 ± 334.9a | 6,011.7 ± 592.7a | 5,321.7 ± 185.8a | 0.526 | |
| 捕食性天敌 Predatory natural enemy | 蜘蛛目 Araneida | 87.0 ± 8.5a | 97.7 ± 12.1a | 88.0 ± 3.5a | 86.3 ± 5.2a | 0.732 |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | 235.7 ± 8.7a | 211.3 ± 34.0a | 221.3 ± 21.9a | 250.7 ± 10.4a | 0.607 | |
| 草蛉科 Chrysopidae | 51.0 ± 6.5a | 41.0 ± 7.0a | 39.0 ± 3.5a | 54.0 ± 6.7a | 0.295 | |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 36.7 ± 4.5a | 49.7 ± 7.5a | 39.0 ± 5.6a | 45.7 ± 7.1a | 0.481 | |
| 小花蝽 Orius sauteri | 57.3 ± 2.3b | 36.7 ± 4.3a | 39.7 ± 0.9a | 39.7 ± 6.8a | 0.029 | |
| 总和 Total | 510.7 ± 22.0a | 481.3 ± 15.2a | 476.7 ± 23.7a | 522.0 ± 11.8a | 0.298 | |
| 寄生性天敌 Parasitic natural enemy | 总和 Total | 7.3 ± 1.8a | 9.0 ± 3.8a | 8.0 ± 0.6a | 7.0 ± 2.0a | 0.933 |
| 中性节肢动物 Neutral arthropod | 总和 Total | 166.7 ± 22.0a | 181.0 ± 8.6a | 150.7 ± 5.5a | 153.3 ± 25.2a | 0.613 |
表1 2015年和2017年4个玉米处理上节肢动物各功能群中主要类群的累积数量(头/50株)
Table 1 The cumulative number of main arthropods in the functional groups of four maize treatments in 2015 and 2017 (number of arthropods every 50 plants)
| 功能群 Functional groups | 主要类群 Major groups | ‘DBN9936’ | ‘DBN318’ | ‘先玉335’ Xianyu 335 | ‘DBN9936’喷除草剂 DBN9936 + herbicide | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ||||||
| 主要害虫 Main pest | 鳞翅目 Lepidopteron | 10.3 ± 2.6a | 20.0 ± 3.2a | 21.0 ± 8.9a | 6.0 ± 1.5a | 0.166 |
| 长角䖴科 Entomobryidae | 112.3 ± 25.5a | 105.7 ± 9.9a | 128.3 ± 11.3a | 113.7 ± 8.1a | 0.765 | |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 834.0 ± 206.6a | 763.3 ± 118.3a | 515.7 ± 62.1a | 590.0 ± 84.3a | 0.341 | |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 1,194.0 ± 94.4b | 1,308.7 ± 32.9b | 1,009.7 ± 56.4a | 1,217.3 ± 42.9b | 0.047 | |
| 总和 Total | 2,212.3 ± 266.9a | 2,258.0 ± 154.5a | 1,736.0 ± 37.8a | 1,985.7 ± 109.9a | 0.176 | |
| 捕食性天敌 Predatory natural enemy | 蜘蛛目 Araneida | 43.7 ± 4.6a | 52.3 ± 2.2a | 59.3 ± 3.8a | 54.3 ± 7.7a | 0.246 |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | 113.7 ± 6.1a | 106.3 ± 11.2a | 104.3 ± 7.9a | 120.0 ± 15.1a | 0.720 | |
| 草蛉科 Chrysopidae | 36.3 ± 6.2a | 32.3 ± 2.8a | 25.3 ± 4.1a | 25.3 ± 4.1a | 0.288 | |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 12.7 ± 2.9a | 15.0 ± 3.2a | 20.7 ± 9.9a | 20.0 ± 6.5a | 0.808 | |
| 总和 Total | 214.7 ± 8.6a | 213.3 ± 10.3a | 219.7 ± 3.8a | 231.0 ± 5.5a | 0.386 | |
| 寄生性天敌 Parasitic natural enemy | 总和 Total | 8.7 ± 3.3a | 6.7 ± 1.9a | 5.7 ± 0.9a | 7.7 ± 0.9a | 0.742 |
| 中性节肢动物 Neutral arthropod | 总和 Total | 206.7 ± 31.5a | 177.7 ± 9.0a | 152.0 ± 28.6a | 147.0 ± 20.4a | 0.339 |
| 2017 | ||||||
| 主要害虫 Main pest | 鳞翅目 Lepidopteron | 3.3 ± 1.7a | 24.0 ± 6.0b | 26.7 ± 2.0b | 17.0 ± 0.6a | 0.005 |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 5,357.0 ± 148.5a | 5,408.3 ± 324.9a | 5,444.0 ± 607.7a | 4,751.7 ± 171.3a | 0.520 | |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 42.3 ± 3.8a | 51.0 ± 4.6a | 40.0 ± 3.5a | 46.7 ± 1.5a | 0.213 | |
| 长角䖴科 Entomobryidae | 86.3 ± 9.8a | 95.0 ± 12.5a | 93.4 ± 6.6a | 97.0 ± 10.0a | 0.882 | |
| 总和 Total | 5,880.7 ± 133.5a | 5,974.7 ± 334.9a | 6,011.7 ± 592.7a | 5,321.7 ± 185.8a | 0.526 | |
| 捕食性天敌 Predatory natural enemy | 蜘蛛目 Araneida | 87.0 ± 8.5a | 97.7 ± 12.1a | 88.0 ± 3.5a | 86.3 ± 5.2a | 0.732 |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | 235.7 ± 8.7a | 211.3 ± 34.0a | 221.3 ± 21.9a | 250.7 ± 10.4a | 0.607 | |
| 草蛉科 Chrysopidae | 51.0 ± 6.5a | 41.0 ± 7.0a | 39.0 ± 3.5a | 54.0 ± 6.7a | 0.295 | |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 36.7 ± 4.5a | 49.7 ± 7.5a | 39.0 ± 5.6a | 45.7 ± 7.1a | 0.481 | |
| 小花蝽 Orius sauteri | 57.3 ± 2.3b | 36.7 ± 4.3a | 39.7 ± 0.9a | 39.7 ± 6.8a | 0.029 | |
| 总和 Total | 510.7 ± 22.0a | 481.3 ± 15.2a | 476.7 ± 23.7a | 522.0 ± 11.8a | 0.298 | |
| 寄生性天敌 Parasitic natural enemy | 总和 Total | 7.3 ± 1.8a | 9.0 ± 3.8a | 8.0 ± 0.6a | 7.0 ± 2.0a | 0.933 |
| 中性节肢动物 Neutral arthropod | 总和 Total | 166.7 ± 22.0a | 181.0 ± 8.6a | 150.7 ± 5.5a | 153.3 ± 25.2a | 0.613 |
| ACE 指数 ACE Index | Bootstrap 指数 Bootstrap Index | Jackknife 1 指数 Jackknife 1 Index | 实际物 种数 Number of species | 比例 Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | |||||
| 植株 Maize plant | 51.49 | 54.25 | 58.88 | 48 | 88.87 |
| 地表 Land surface | 58.26 | 51.41 | 54.96 | 49 | 88.25 |
| 总体 Total | 66.61 | 65.33 | 70.96 | 61 | 90.56 |
| 2017 | |||||
| 植株 Maize plant | 71.07 | 71.32 | 72.97 | 68 | 95.11 |
| 地表 Land surface | 78.65 | 64.66 | 72.81 | 59 | 80.98 |
| 总体 Total | 93.36 | 88.45 | 93.95 | 83 | 89.92 |
表2 2015年和2017年不同玉米处理上节肢动物物种丰富度
Table 2 Species richness index of arthropods of different maize treatments in 2015 and 2017
| ACE 指数 ACE Index | Bootstrap 指数 Bootstrap Index | Jackknife 1 指数 Jackknife 1 Index | 实际物 种数 Number of species | 比例 Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | |||||
| 植株 Maize plant | 51.49 | 54.25 | 58.88 | 48 | 88.87 |
| 地表 Land surface | 58.26 | 51.41 | 54.96 | 49 | 88.25 |
| 总体 Total | 66.61 | 65.33 | 70.96 | 61 | 90.56 |
| 2017 | |||||
| 植株 Maize plant | 71.07 | 71.32 | 72.97 | 68 | 95.11 |
| 地表 Land surface | 78.65 | 64.66 | 72.81 | 59 | 80.98 |
| 总体 Total | 93.36 | 88.45 | 93.95 | 83 | 89.92 |
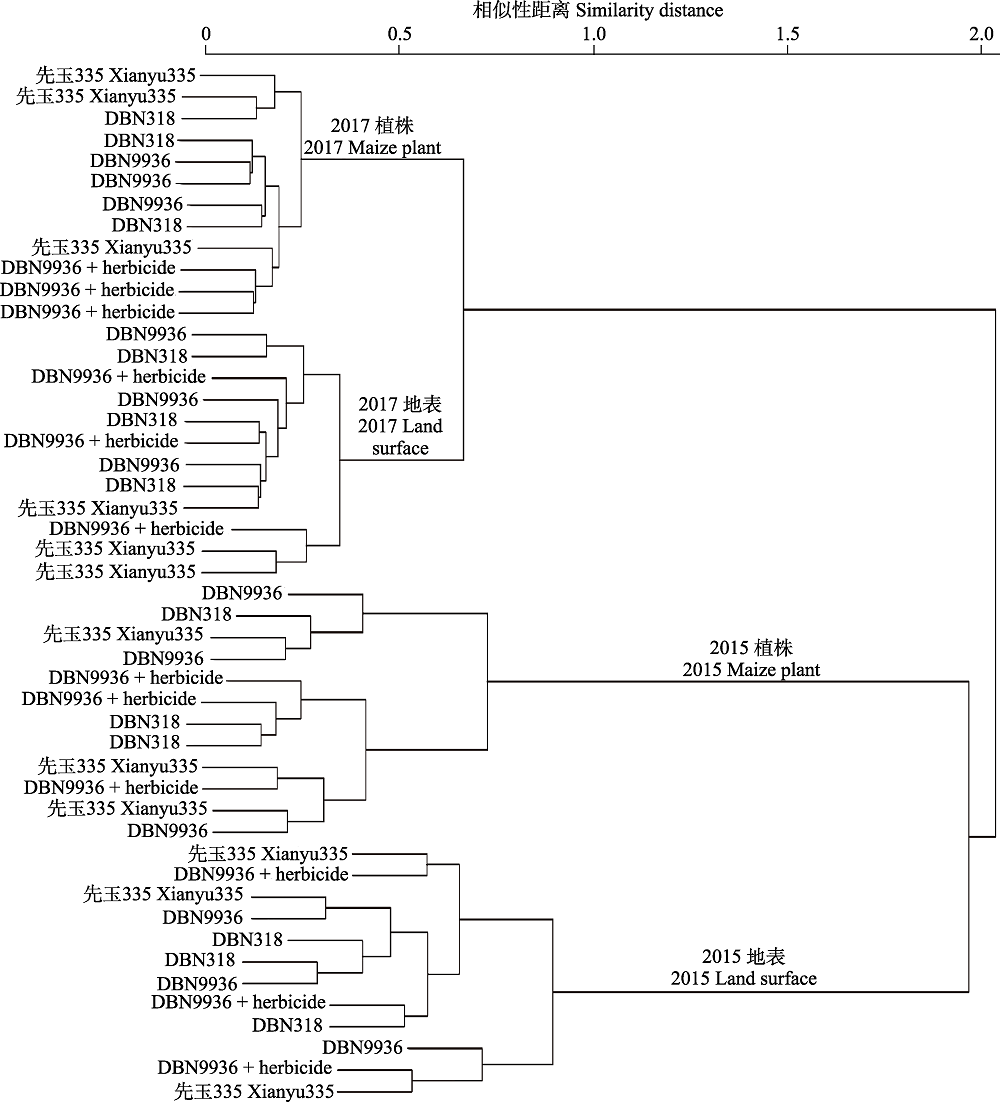
图4 2015年和2017年4个玉米处理上节肢动物群落聚类结果。每个玉米处理具有3个重复试验, 节肢动物种类和数量的相似度越高的样地, 其聚类支靠的越近。
Fig. 4 The clustering results of the arthropod communities of four maize treatments in 2015 and 2017. Each maize treatment has 3 replicates. The higher the similarity of arthropod species and quantity is, the closer the clustering branches is.
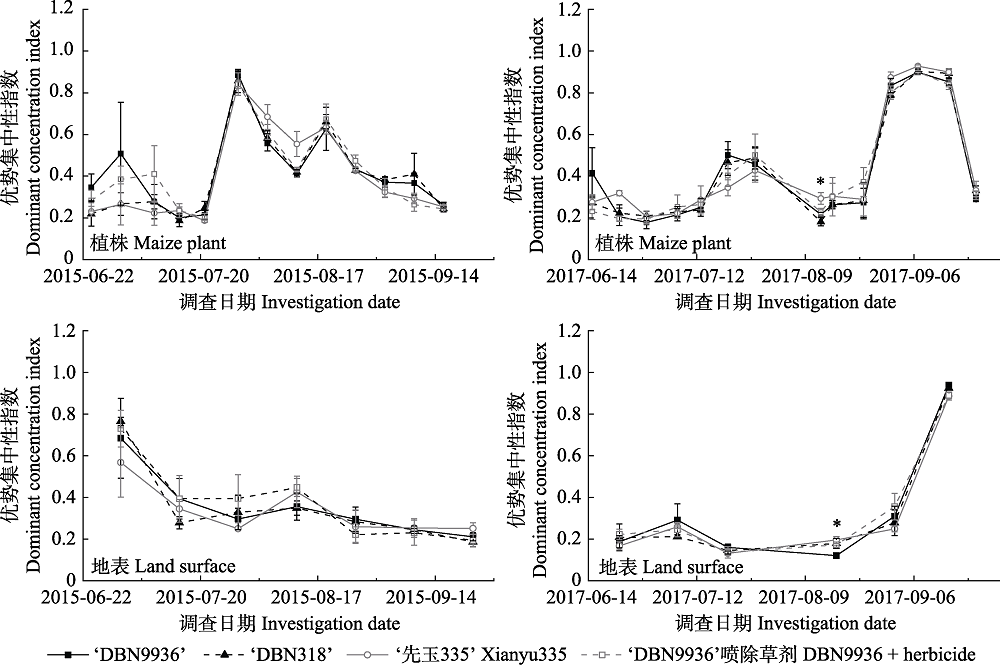
图7 2015年和2017年4个玉米处理上田间节肢动物群落优势集中性指数动态
Fig. 7 The dominant concentration index dynamics of arthropod community of four maize treatments in 2015 and 2017
| 为害指标 Damage parameter and degree | ‘DBN9936’ | ‘DBN318’ | ‘先玉335’ Xianyu 335 | ‘DBN9936’喷除草剂 DBN9936 + herbicide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ||||
| 蛀孔数(个/50株) Number of apertures every 50 plants | 0.0 ± 0.0b | 14.3 ± 1.2a | 22.0 ± 4.0a | 0.0 ± 0.0b |
| 活虫数(头/50株) Number of alive borers every 50 plants | 0.3 ± 0.3b | 10.3 ± 1.0a | 12.5 ± 1.9a | 0.3 ± 0.3b |
| 最长隧道长度 Maximum tunnel length (cm) | 0.0 | 16.5 | 13.0 | 0.0 |
| 平均隧道长度 Average tunnel length (cm) | - | 6.50 ± 0.56b | 4.97 ± 0.40a | - |
| 最长穗尖被害长度 Maximum damage length of spike tip (cm) | 5.5 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 |
| 平均穗尖被害长度 Average damage length of spike tip (cm) | 2.33 ± 1.59a | 3.01 ± 0.21a | 2.98 ± 0.20a | 1.94 ± 0.39a |
| 2017 | ||||
| 蛀孔数(个/50株) Number of apertures every 50 plants | 8.0 ± 7.9a | 16.0 ± 8.1a | 8.7 ± 2.4a | 5.3 ± 1.8a |
| 活虫数(头/50株) Number of alive borers every 50 plants | 3.3 ± 0.3a | 10.7 ± 0.5a | 6.0 ± 0.1a | 2.7 ± 0.2a |
| 最长隧道长度 Maximum tunnel length (cm) | 13.5 | 20.0 | 20.8 | 7.0 |
| 平均隧道长度 Average tunnel length (cm) | 2.97 ± 2.97a | 5.92 ± 2.87a | 3.68 ± 4.06a | 0.87 ± 0.49a |
| 最长穗尖被害长度 Maximum damage length of spike tip (cm) | 9.0 | 27.4 | 22.8 | 16.8 |
| 平均穗尖被害长度 Average damage length of spike tip (cm) | 2.39 ± 1.74a | 6.24 ± 1.23a | 8.18 ± 2.36a | 3.76 ± 3.42a |
表3 2015年和2017年4个处理玉米的亚洲玉米螟和棉铃虫为害情况
Table 3 Damage degree of four maize treatment by Ostrinia furnacalis and Helicoverpa armigera in 2015 and 2017
| 为害指标 Damage parameter and degree | ‘DBN9936’ | ‘DBN318’ | ‘先玉335’ Xianyu 335 | ‘DBN9936’喷除草剂 DBN9936 + herbicide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ||||
| 蛀孔数(个/50株) Number of apertures every 50 plants | 0.0 ± 0.0b | 14.3 ± 1.2a | 22.0 ± 4.0a | 0.0 ± 0.0b |
| 活虫数(头/50株) Number of alive borers every 50 plants | 0.3 ± 0.3b | 10.3 ± 1.0a | 12.5 ± 1.9a | 0.3 ± 0.3b |
| 最长隧道长度 Maximum tunnel length (cm) | 0.0 | 16.5 | 13.0 | 0.0 |
| 平均隧道长度 Average tunnel length (cm) | - | 6.50 ± 0.56b | 4.97 ± 0.40a | - |
| 最长穗尖被害长度 Maximum damage length of spike tip (cm) | 5.5 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 4.0 |
| 平均穗尖被害长度 Average damage length of spike tip (cm) | 2.33 ± 1.59a | 3.01 ± 0.21a | 2.98 ± 0.20a | 1.94 ± 0.39a |
| 2017 | ||||
| 蛀孔数(个/50株) Number of apertures every 50 plants | 8.0 ± 7.9a | 16.0 ± 8.1a | 8.7 ± 2.4a | 5.3 ± 1.8a |
| 活虫数(头/50株) Number of alive borers every 50 plants | 3.3 ± 0.3a | 10.7 ± 0.5a | 6.0 ± 0.1a | 2.7 ± 0.2a |
| 最长隧道长度 Maximum tunnel length (cm) | 13.5 | 20.0 | 20.8 | 7.0 |
| 平均隧道长度 Average tunnel length (cm) | 2.97 ± 2.97a | 5.92 ± 2.87a | 3.68 ± 4.06a | 0.87 ± 0.49a |
| 最长穗尖被害长度 Maximum damage length of spike tip (cm) | 9.0 | 27.4 | 22.8 | 16.8 |
| 平均穗尖被害长度 Average damage length of spike tip (cm) | 2.39 ± 1.74a | 6.24 ± 1.23a | 8.18 ± 2.36a | 3.76 ± 3.42a |
| [1] | Arias-Martín M, García M, Castañera P, Ortego F, Farinós GP (2016) Farm-scale evaluation of the impact of Cry1Ab Bt maize on canopy nontarget arthropods: A 3-year study. Insect Science, 25, 87-98. |
| [2] |
Bhatti MA, Duan J, Head GP, Jiang CJ, Mckee MJ, Nickson TE, Pilcher CL, Pilcher CD (2005) Field evaluation of the impact of corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)-protected Bt corn on foliage-dwelling arthropods. Environmental Entomology, 34, 1336-1345.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bitzer RJ, Rice ME, Pilcher CD, Pilcher CL, Lam WF (2005) Biodiversity and community structure of epedaphic and euedaphic springtails (Collembola) in transgenic rootworm Bt corn. Environmental Entomology, 34, 1346-1376.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Cai BH (2015) Insect Taxonomy. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蔡邦华 (2015) 昆虫分类学. 化学工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] |
Carrière Y, Williams JL, Crowder DW, Tabashnik BE (2018) Genotype-specific fitness cost of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in pink bollworm. Pest Management Science, 74, 2496-2503.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Farinos GP, Mdela P, Hernándezcrespo P, Ortego F, Castanera P (2008) Diversity and seasonal phenology of aboveground arthropods in conventional and transgenic maize crops in central Spain. Biological Control, 44, 362-371.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Guo JF, He KL, Hellmich RL, Bai SX, Zhang TT, Liu YJ, Ahmed T, Wang ZY (2016) Field trials to evaluate the effects of transgenic Cry1Ie maize on the community characteristics of arthropod natural enemies. Scientific Reports, 6, 22102.
DOI |
| [8] | Guo JH, Ji GZ, Li G, Zhao JN, Yang DL, Zhang GL, Yan FM, Xiu WM (2016) The impact of non-Bt genetically modified cotton on the community diversity and food-web structure of arthropods. Cotton Science, 28, 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭佳惠, 冀国桢, 李刚, 赵建宁, 杨殿林, 张贵龙, 闫凤鸣, 修伟明 (2016) 3种转非抗虫基因棉花田间节肢动物群落的多样性和食物网结构. 棉花学报, 28, 81-86.] | |
| [9] | Guo JY, Zhou HX, Wan FH, Han ZJ (2007) Structure and seasonal dynamics of arthropods in transgenic cotton fields. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 22(6), 183-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 郭建英, 周洪旭, 万方浩, 韩召军 (2007) 转基因棉田节肢动物群落结构与动态. 华北农学报, 22(6), 183-189.]
DOI |
|
| [10] | He HP, Ren ZT, Shen WJ, Liu B, Xue K (2018) Effects of transgenic herbicide-tolerate maize on biodiversity of arthropod communities in the fields. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34, 333-341. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何浩鹏, 任振涛, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃 (2018) 耐除草剂转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响. 生态与农村环境学报, 34, 333-341.] | |
| [11] |
Hilbeck A, Baumgartner M, Fried PM, Bigler F (1998) Effects of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis corn-fed prey on mortality and development time of immature Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Environmental Entomology, 27, 480-487.
DOI URL |
| [12] | International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications ( ISAAA) (2017) Global biotechnology / GM crop commercial development trend in 2016. China Biotechnology, 37(4), 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国际农业生物技术应用服务组织 (2017) 2016年全球生物技术/转基因作物商业化发展态势. 中国生物工程杂志, 37(4), 1-8.] | |
| [13] | Kang L, Chen M (2013) GMO biosafety management, suggestions and biotech public acceptance in China. Plant Physiology Journal, 49, 637-644. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 康乐, 陈明 (2013) 我国转基因作物安全管理体系介绍、发展建议及生物技术舆论导向. 植物生理学报, 49, 637-644.] | |
| [14] | Li BP, Meng L, Wan FH (2002) The impact of insect resistant transgenic crops on natural enemies. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 18, 97-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李保平, 孟玲, 万方浩 (2002) 转基因抗虫植物对天敌昆虫的影响. 中国生物防治学报, 18, 97-105.] | |
| [15] | Li F, Sun HW, Zhao W, Yang SK, Lu XB (2013) Effects of herbicide-tolerant transgenic soybean on biodiversity of arthropod community in field. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 45(7), 83-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李凡, 孙红炜, 赵维, 杨淑珂, 路兴波 (2013) 抗除草剂转基因大豆对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响. 山东农业科学, 45(7), 83-86.] | |
| [16] | Li LL, Wang ZY, He KL, Peng YF, Hua L (2004) Impact of the insect-resistant transgenic crops on non-target insects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 1793-1802. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李丽莉, 王振营, 何康来, 彭于发, 花蕾 (2004) 转基因抗虫作物对非靶标昆虫的影响. 生态学报, 24, 1793-1802.] | |
| [17] | Li Q (2011) Species accumulation curves and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 1882-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李巧 (2011) 物种累积曲线及其应用. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 1882-1888.] | |
| [18] |
Li YH, Zhang XJ, Chen XP, Romeis J, Yin XM, Peng YF (2015) Consumption of Bt rice pollen containing Cry1C or Cry2A does not pose a risk to Propylea japonica (Thunberg) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Scientific Reports, 5, 7679.
DOI |
| [19] | Liu QS, Li YH, Chen XP, Peng YF (2014) Research progress in chemical communication among insect-resistant genetically modified plants, insect pests and natural enemies. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 2431-2439. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘清松, 李云河, 陈秀萍, 彭于发 (2014) 转基因抗虫植物-植食性昆虫-天敌间化学通讯的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 25, 2431-2439.] | |
| [20] |
Lu YH, Wu KM, Jiang YY, Xia B, Li P, Feng HQ, Kris AG, Guo YY (2010) Mirid bug outbreaks in multiple crops correlated with wide-scale adoption of Bt cotton in China. Science, 328, 1151-1154.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Magurran AE (2013) Measuring Biological Diversity. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford. |
| [22] |
Marques LH, Santos AC, Castro BA, Storer NP, Babcock JM, Lepping MD, Fernandes OA (2018) Impact of transgenic soybean expressing Cry1Ac and Cry1F proteins on the non-target arthropod community associated with soybean in Brazil. PLoS ONE, 13, e0191567.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Marvier M, Mccreedy C, Regetz J, Kareiva P (2007) A meta-analysis of effects of Bt cotton and maize on nontarget invertebrates. Science, 316, 1475-1477.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Naranjo SE, Head G, Dively GP (2005) Field studies assessing arthropod nontarget effects in Bt transgenic crops: Introduction. Environmental Entomology, 34, 1178-1180. |
| [25] | Ren ZT, Shen WJ, Liu B, Xue K (2017) Effects of transgenic maize on biodiversity of arthropod communities in the fields. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50, 2315-2325. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任振涛, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃 (2017) 转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响. 中国农业科学, 50, 2315-2325.] | |
| [26] | Shen P, Zhang QY, Lin YH, Li WL, Li A, Song GW (2016) Thinking to promote the industrialization of genetically modified corn of our country. China Biotechnology, 36(4), 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 沈平, 章秋艳, 林友华, 李文龙, 李昂, 宋贵文 (2016) 推进我国转基因玉米产业化的思考. 中国生物工程杂志, 36(4), 24-29.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Shetty MJ, Chandan K, Krishna HC, Aparna GS (2018) Genetically modified crops: An overview. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 7, 2405-2410. |
| [28] |
Skoková HO, Svobodová Z, Spitzer L, Doležal P, Hussein HM, Sehnal F (2015) Communities of ground-dwelling arthropods in conventional and transgenic maize: Background data for the post-market environmental monitoring. Journal of Applied Entomology, 139, 31-45.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Storer NP, Babcock JM, Schlenz M, Meade T, Huckaba RM (2010) Discovery and characterization of field resistance to Bt maize: Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Puerto Rico. Journal of Economic Entomology, 103, 1031-1038.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Tabashnik BE, Gassmann AJ, Crowder DW, Carrière Y (2008) Insect resistance to Bt crops: Evidence versus theory. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 199-202.
DOI |
| [31] | Wu L, Zhao QZ, Li DQ, Wang JR, Liu MF, Yang ZL (2016) Application of species accumulation curves in study on fruit flies in Nanting River basin. China Plant Protection, 36(8), 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴岚, 赵琴植, 李德强, 汪金蓉, 刘梅芳, 杨子林 (2016) 物种累积曲线在南汀河流域实蝇调查研究中的应用. 中国植保导刊, 36(8), 46-49.] | |
| [32] | Xue K, Zhang WG (2008) Non-target effects of transgenic plant: Transgenic Bt cotton. Journal of the Central University of Nationalities (Natural Sciences Edition), 17(Suppl.), 40-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛堃, 张文国 (2008) 转基因植物的非靶标效应——以转Bt基因棉为例. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 17(Suppl.), 40-50.] | |
| [33] | Yang Y, Li YH, Cao FQ, Cheng LS, Peng YF (2014) Progress in the assessment of ecological effects of insect-resistant Bt crops on non-target of Lepidopteran insects. Journal of Biosafety, 23, 224-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨艳, 李云河, 曹凤勤, 程立生, 彭于发 (2014) 转Bt基因抗虫作物对鳞翅目非靶标昆虫生态影响的研究进展. 生物安全学报, 23, 224-237.] | |
| [34] | Yin JQ, Wu FC, Zhou L, Song XY (2017) Impacts of a transgenic insect-resistant maize (Bt-799) containing a Cry1Ac gene on arthropod biodiversity. Journal of Biosafety, 26, 159-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尹俊琦, 武奉慈, 周琳, 宋新元 (2017) 转Cry1Ac基因抗虫玉米Bt-799对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响. 生物安全学报, 26, 159-167.] | |
| [35] |
Zhang XJ, Li YH, Romeis J, Yin XM, Wu KM, Peng YF (2014) Use of a pollen-based diet to expose the ladybird beetle Propylea japonica to insecticidal proteins. PLoS ONE, 9, e85395.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Zhu Y, Jiang T, Yang YZ (2017) Research advances in arthropod community in corn fields. Plant Protection, 43(6), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱莹, 姜韬, 杨益众 (2017) 玉米田节肢动物群落研究进展. 植物保护, 43(6), 1-5.] | |
| [37] | Zou Y, Sang WG, Wang SZ, Thomas EW, Liu YH, Yu ZR, Wang CL, Axmacher JC (2015) Diversity patterns of ground beetles and understory vegetation in mature, secondary, and plantation forest regions of temperate northern China. Ecology & Evolution, 5, 531-542. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn