



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 24243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024243 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024243
赵榕江1, 吴纪华1( ), 何维明2, 赵彩云3(
), 何维明2, 赵彩云3( ), 周波1, 李博4, 杨强1,*(
), 周波1, 李博4, 杨强1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-18
接受日期:2024-08-28
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-12-27
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Rongjiang Zhao1, Jihua Wu1( ), Weiming He2, Caiyun Zhao3(
), Weiming He2, Caiyun Zhao3( ), Bo Zhou1, Bo Li4, Qiang Yang1,*(
), Bo Zhou1, Bo Li4, Qiang Yang1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-06-18
Accepted:2024-08-28
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-27
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
外来植物入侵对本土生物多样性和生态安全构成严重威胁。尽管已有诸多研究探讨外来植物入侵的机制, 但土壤生物在这一过程中所起的关键作用尚未得到系统总结。本文首先综述了土壤生物驱动外来植物成功入侵的5种途径: (1)土壤微生物(病原微生物、共生微生物、腐生微生物、微生物多样性)驱动的外来植物入侵; (2)土壤动物(植食性昆虫、线虫和原生动物、螨虫和跳虫、蚯蚓)驱动的外来植物入侵; (3)土壤食物网(微食物网、整个食物网)驱动的外来植物入侵; (4)植物-土壤反馈与外来植物入侵的联系; (5)植物地上-地下生物互作对外来植物入侵的影响。其次, 基于上述研究进展, 本文提出该领域未来发展的4大趋势: (1)原产地和入侵地的生物地理学比较; (2)多样性-可入侵性假说的验证; (3)植物群落水平上的扩展; (4)多组学技术的应用。本文通过解析外来植物入侵的土壤生物学机制, 为防控外来入侵植物和保护生物多样性提供了重要依据。
赵榕江, 吴纪华, 何维明, 赵彩云, 周波, 李博, 杨强 (2024) 土壤生物多样性与外来植物入侵: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 32, 24243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024243.
Rongjiang Zhao, Jihua Wu, Weiming He, Caiyun Zhao, Bo Zhou, Bo Li, Qiang Yang (2024) Soil biodiversity and exotic plant invasions: Progress and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024243.
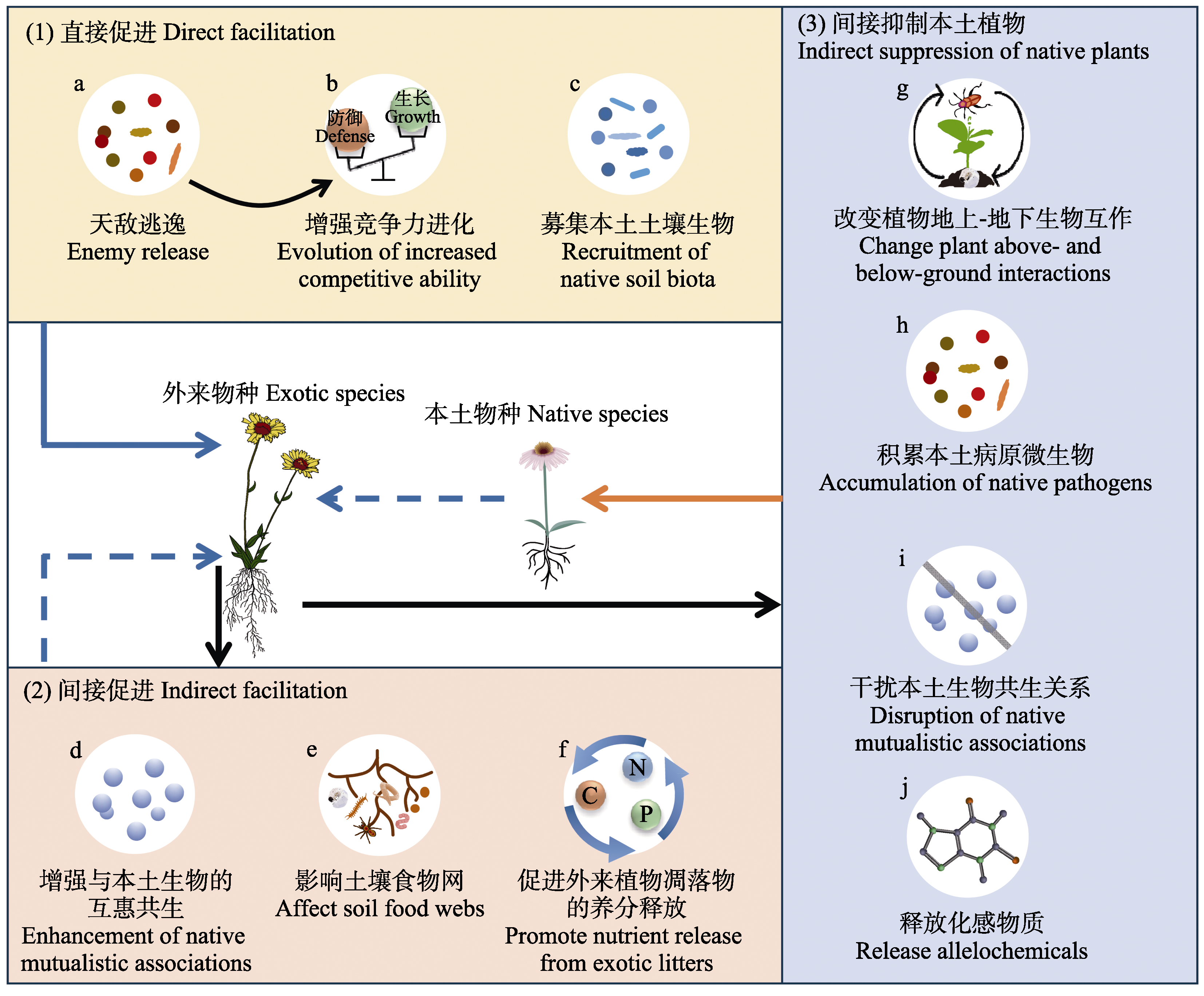
图1 土壤生物驱动的外来植物入侵。土壤生物驱动外来植物成功入侵的方式主要分为3类。(1)直接促进: 天敌逃逸(a)和本土土壤生物募集(c)可直接促进外来植物入侵; 外来植物逃离原产地天敌后, 可通过适应性进化(b)增强其对本土植物的竞争力, 进一步加速入侵。(2)间接促进: 外来植物也可通过增强与本土生物的互惠共生(d)、影响土壤食物网(e)、促进自身凋落物的养分释放(f)等间接方式来成功入侵。(3)间接抑制本土植物: 外来植物通过改变植物地上-地下生物互作(g)、积累本土病原微生物(h)、干扰本土生物共生关系(i)、释放化感物质(j)等方式抑制本土植物生长, 间接有利于自身入侵。蓝色箭头表示积极影响, 橙色箭头表示消极影响, 黑色箭头仅表示连接关系。实线箭头表示直接影响, 虚线箭头表示间接影响。
Fig. 1 Soil biota-driven exotic plant invasions. The successful invasion of exotic plants driven by soil biota can be categorized into three main pathways: (1) Direct facilitation: enemy release (a) and recruitment of native soil biota (c) could directly promote exotic plant invasions. Exotic plants could invade through the adaptive evolution of increased competitive ability (b). (2) Indirect facilitation: exotic plants could also benefit in indirect ways, including enhancing native mutualistic associations (d), affecting soil food webs (e), and promoting nutrient release from exotic litters (f). (3) Indirect suppression of native plants: exotic plants could suppress native plants by changing plant above- and below-ground interactions (g), accumulating native pathogens (h), disrupting native mutualistic associations (i), and releasing allelochemicals (j), which are indirectly beneficial to successful invasions. Blue arrows indicate positive effects, orange arrows indicate negative effects, and black arrows indicate connection relationships only; solid arrows indicate direct effects and dashed arrows indicate indirect effects.
| [1] | Abgrall C, Forey E, Chauvat M (2019) Soil fauna responses to invasive alien plants are determined by trophic groups and habitat structure: A global meta-analysis. Oikos, 128, 1390-1401. |
| [2] | Agrawal AA, Kotanen PM, Mitchell CE, Power AG, Godsoe W, Klironomos J (2005) Enemy release? An experiment with congeneric plant pairs and diverse above- and belowground enemies. Ecology, 86, 2979-2989. |
| [3] | Alexander JM, Diez JM, Levine JM (2015) Novel competitors shape species’ responses to climate change. Nature, 525, 515-518. |
| [4] |
Allen WJ, Waller LP, Barratt BIP, Dickie IA, Tylianakis JM (2021) Exotic plants accumulate and share herbivores yet dominate communities via rapid growth. Nature Communications, 12, 2696.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Averill C, Waring BG, Hawkes CV (2016) Historical precipitation predictably alters the shape and magnitude of microbial functional response to soil moisture. Global Change Biology, 22, 1957-1964.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Ayres E, Steltzer H, Simmons BL, Simpson RT, Steinweg JM, Wallenstein MD, Mellor N, Parton WJ, Moore JC, Wall DH (2009) Home-field advantage accelerates leaf litter decomposition in forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 606-610. |
| [7] |
Bais HP, Vepachedu R, Gilroy S, Callaway RM, Vivanco JM (2003) Allelopathy and exotic plant invasion: From molecules and genes to species interactions. Science, 301, 1377-1380.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bennett JA, Klironomos J (2019) Mechanisms of plant-soil feedback: Interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers. New Phytologist, 222, 91-96.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Bennion LD, Ward D (2022) Plant-soil feedback from eastern redcedar (Juniperus virginiana) inhibits the growth of grasses in encroaching range. Ecology and Evolution, 12, e9400. |
| [10] | Bhattarai GP, Meyerson LA, Anderson J, Cummings D, Allen WJ, Cronin JT (2017) Biogeography of a plant invasion: Genetic variation and plasticity in latitudinal clines for traits related to herbivory. Ecological Monographs, 87, 57-75. |
| [11] | Biederman LA, Boutton TW (2009) Biodiversity and trophic structure of soil nematode communities are altered following woody plant invasion of grassland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 1943-1950. |
| [12] | Blossey B, Nötzold R (1995) Evolution of increased competitive ability in invasive nonindigenous plants: A hypothesis. Journal of Ecology, 83, 887-889. |
| [13] | Bunn RA, Ramsey PW, Lekberg Y (2015) Do native and invasive plants differ in their interactions with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? A meta-analysis. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1547-1556. |
| [14] | Buzhdygan OY, Meyer ST, Weisser WW, Eisenhauer N, Ebeling A, Borrett SR, Buchmann N, Cortois R, de Deyn GB, de Kroon H, Gleixner G, Hertzog LR, Hines J, Lange M, Mommer L, Ravenek J, Scherber C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Scheu S, Schmid B, Steinauer K, Strecker T, Tietjen B, Vogel A, Weigelt A, Petermann JS (2020) Biodiversity increases multitrophic energy use efficiency, flow and storage in grasslands. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 393-405. |
| [15] |
Callaway RM, Aschehoug ET (2000) Invasive plants versus their new and old neighbors: A mechanism for exotic invasion. Science, 290, 521-523.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Callaway RM, Bedmar EJ, Reinhart KO, Gómez Silvan C, Klironomos J (2011) Effects of soil biota from different ranges on Robinia invasion: Acquiring mutualists and escaping pathogens. Ecology, 92, 1027-1035.
PMID |
| [17] | Callaway RM, Ridenour WM (2004) Novel weapons: Invasive success and the evolution of increased competitive ability. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2, 436-443. |
| [18] | Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Barth S, Ramsey PW, Gannon JE (2004a) Soil fungi alter interactions between the invader Centaurea maculosa and North American natives. Ecology, 85, 1062-1071. |
| [19] | Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Rodriguez A, Holben WE (2004b) Soil biota and exotic plant invasion. Nature, 427, 731-733. |
| [20] | Cameron EK, Proctor HC, Bayne EM (2013) Effects of an ecosystem engineer on belowground movement of microarthropods. PLoS ONE, 8, e62796. |
| [21] |
Catford JA, Bode M, Tilman D (2018) Introduced species that overcome life history tradeoffs can cause native extinctions. Nature Communications, 9, 2131.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Catford JA, Jansson R, Nilsson C (2009) Reducing redundancy in invasion ecology by integrating hypotheses into a single theoretical framework. Diversity and Distributions, 15, 22-40. |
| [23] | Chen D, van Kleunen M (2022) Invasional meltdown mediated by plant-soil feedbacks may depend on community diversity. New Phytologist, 235, 1589-1598. |
| [24] |
Chen EJ, Liao HX, Chen BM, Peng SL (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are a double-edged sword in plant invasion controlled by phosphorus concentration. New Phytologist, 226, 295-300.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Chen HL, Li B, Fang CM, Chen JK, Wu JH (2007) Exotic plant influences soil nematode communities through litter input. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 1782-1793. |
| [26] |
Chen HL, Li YJ, Li B, Chen JK, Wu JH (2005) Impacts of exotic plant invasions on soil biodiversity and ecosystem processes. Biodiversity Science, 13, 555-565. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈慧丽, 李玉娟, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华 (2005) 外来植物入侵对土壤生物多样性和生态系统过程的影响. 生物多样性, 13, 555-565.]
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Chen J, Sinsabaugh RL (2021) Linking microbial functional gene abundance and soil extracellular enzyme activity: Implications for soil carbon dynamics. Global Change Biology, 27, 1322-1325.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Chen YF, Tang Z, Li H, Han XM, Li YF, Hu C (2014) Research progress on ecosystem complexity-stability relationships based on soil food web. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 2173-2186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈云峰, 唐政, 李慧, 韩雪梅, 李钰飞, 胡诚 (2014) 基于土壤食物网的生态系统复杂性-稳定性关系研究进展. 生态学报, 34, 2173-2186.] | |
| [29] | Cheng C, Liu ZK, Zhang Q, Tian X, Ju RT, Li B, van Kleunen M, Chase JM, Wu JH (2024) Genotype diversity enhances invasion resistance of native plants via soil biotic feedbacks. Ecology Letters, 27, e14384. |
| [30] | Clavel J, Lembrechts J, Alexander J, Haider S, Lenoir J, Milbau A, Nuñez MA, Pauchard A, Nijs I, Verbruggen E (2021) The role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in nonnative plant invasion along mountain roads. New Phytologist, 230, 1156-1168. |
| [31] | Courchamp F, Fournier A, Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Bonnaud E, Jeschke JM, Russell JC (2017) Invasion biology: Specific problems and possible solutions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 32, 13-22. |
| [32] |
Craven D, Thakur MP, Cameron EK, Frelich LE, Beauséjour R, Blair RB, Blossey B, Burtis J, Choi A, Dávalos A, Fahey TJ, Fisichelli NA, Gibson K, Handa IT, Hopfensperger K, Loss SR, Nuzzo V, Maerz JC, Sackett T, Scharenbroch BC, Smith SM, Vellend M, Umek LG, Eisenhauer N (2017) The unseen invaders: Introduced earthworms as drivers of change in plant communities in North American forests (a meta-analysis). Global Change Biology, 23, 1065-1074.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Cripps MG, Schwarzländer M, McKenney JL, Hinz HL, Price WJ (2006) Biogeographical comparison of the arthropod herbivore communities associated with Lepidium draba in its native, expanded and introduced ranges. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 2107-2119. |
| [34] | Darwin C (1859) The Origin of Species. John Murray, London. |
| [35] |
Dawson W (2015) Release from belowground enemies and shifts in root traits as interrelated drivers of alien plant invasion success: A hypothesis. Ecology and Evolution, 5, 4505-4516.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Dawson W, Schrama M (2016) Identifying the role of soil microbes in plant invasions. Journal of Ecology, 104, 1211-1218. |
| [37] | De Almeida T, Forey E, Chauvat M (2022) Alien invasive plant effect on soil fauna is habitat dependent. Diversity, 14, 61. |
| [38] | Diagne C, Leroy B, Vaissière AC, Gozlan RE, Roiz D, Jarić I, Salles JM, Bradshaw CJA, Courchamp F (2021) High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature, 592, 571-576. |
| [39] |
Dickie IA, Bolstridge N, Cooper JA, Peltzer DA (2010) Co-invasion by Pinus and its mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 187, 475-484.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Dickie IA, Yeates GW, St John MG, Stevenson BA, Scott JT, Rillig MC, Peltzer DA, Orwin KH, Kirschbaum MUF, Hunt JE, Burrows LE, Barbour MM, Aislabie J (2011) Ecosystem service and biodiversity trade-offs in two woody successions. Journal of Applied Ecology, 48, 926-934. |
| [41] |
Divíšek J, Chytrý M, Beckage B, Gotelli NJ, Lososová Z, Pyšek P, Richardson DM, Molofsky J (2018) Similarity of introduced plant species to native ones facilitates naturalization, but differences enhance invasion success. Nature Communications, 9, 4631.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | Du SJ, Guo JY, Zhao HX, Wan FH, Liu WX (2023) Research progresses on management of invasive alien species in China. Plant Protection, 49, 410-418. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜素洁, 郭建洋, 赵浩翔, 万方浩, 刘万学 (2023) 近十年我国入侵生物预防与监控研究. 植物保护, 49, 410-418.] | |
| [43] | Du XF, Li YB, Liu F, Su XL, Li Q (2018) Structure and ecological functions of soil micro-food web. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 403-411. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[杜晓芳, 李英滨, 刘芳, 宿晓琳, 李琪 (2018) 土壤微食物网结构与生态功能. 应用生态学报, 29, 403-411.]
DOI |
|
| [44] |
Elliott BT (2020) Top-down and bottom-up controls limit woody encroachment into persistent temperate rainforest meadows. Journal of Vegetation Science, 31, 830-840.
DOI |
| [45] | Elton CS (1958) The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [46] | Eppinga MB, Rietkerk M, Dekker SC, de Ruiter PC, van der Putten WH (2006) Accumulation of local pathogens: A new hypothesis to explain exotic plant invasions. Oikos, 114, 168-176. |
| [47] | Feng YH, Fouqueray TD, van Kleunen M (2019) Linking Darwin’s naturalisation hypothesis and Elton’s diversity-invasibility hypothesis in experimental grassland communities. Journal of Ecology, 107, 794-805. |
| [48] | Franco ALC, Gherardi LA, de Tomasel CM, Andriuzzi WS, Ankrom KE, Shaw EA, Bach EM, Sala OE, Wall DH (2019) Drought suppresses soil predators and promotes root herbivores in mesic, but not in xeric grasslands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 12883-12888. |
| [49] |
Fu W, Wang N, Pang F, Huang YL, Wu J, Qi SS, Dai ZC, Du DL (2017) Soil microbiota and plant invasions: Current and future. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1295-1302. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[付伟, 王宁, 庞芳, 黄玉龙, 吴俊, 祁珊珊, 戴志聪, 杜道林 (2017) 土壤微生物与植物入侵: 研究现状与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 1295-1302.]
DOI |
|
| [50] | Gange A (2000) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Collembola and plant growth. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15, 369-372. |
| [51] | Gao LL, Wei CQ, He YF, Tang XF, Chen W, Xu H, Wu YQ, Wilschut RA, Lu XM (2023) Aboveground herbivory can promote exotic plant invasion through intra- and interspecific aboveground-belowground interactions. New Phytologist, 237, 2347-2359. |
| [52] |
Gao MX, Lin L, Chang L, Sun X, Liu D, Wu DH (2018) Spatial patterns and assembly rules in soil fauna communities: A review. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1034-1050. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[高梅香, 林琳, 常亮, 孙新, 刘冬, 吴东辉 (2018) 土壤动物群落空间格局和构建机制研究进展. 生物多样性, 26, 1034-1050.]
DOI |
|
| [53] |
Gao ZL, Karlsson I, Geisen S, Kowalchuk G, Jousset A (2019) Protists: Puppet masters of the rhizosphere microbiome. Trends in Plant Science, 24, 165-176.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Geisen S, Mitchell EAD, Adl S, Bonkowski M, Dunthorn M, Ekelund F, Fernández LD, Jousset A, Krashevska V, Singer D, Spiegel FW, Walochnik J, Lara E (2018) Soil protists: A fertile frontier in soil biology research. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 42, 293-323.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Gerber E, Hinz HL, Blossey B (2007) Impact of the belowground herbivore and potential biological control agent, Ceutorhynchus scrobicollis, on Alliaria petiolata performance. Biological Control, 42, 355-364. |
| [56] | Groffman PM, Fahey TJ, Fisk MC, Yavitt JB, Sherman RE, Bohlen PJ, Maerz JC (2015) Earthworms increase soil microbial biomass carrying capacity and nitrogen retention in northern hardwood forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 87, 51-58. |
| [57] | Grove S, Haubensak KA, Gehring C, Parker IM (2017) Mycorrhizae, invasions, and the temporal dynamics of mutualism disruption. Journal of Ecology, 105, 1496-1508. |
| [58] |
Gundale MJ, Kardol P, Nilsson MC, Nilsson U, Lucas RW, Wardle DA (2014) Interactions with soil biota shift from negative to positive when a tree species is moved outside its native range. New Phytologist, 202, 415-421.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Guo S, Tao CY, Jousset A, Xiong W, Wang Z, Shen ZZ, Wang BB, Xu ZH, Gao ZL, Liu SS, Li R, Ruan YZ, Shen QR, Kowalchuk GA, Geisen S (2022) Trophic interactions between predatory protists and pathogen-suppressive bacteria impact plant health. The ISME Journal, 16, 1932-1943. |
| [60] |
Hagedorn F, Gavazov K, Alexander JM (2019) Above- and belowground linkages shape responses of mountain vegetation to climate change. Science, 365, 1119-1123.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Han LX, Wang YJ, Liu X (2024) Comparisons between non-native species invasion and native species range expansion. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣 (2024) 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同. 生物多样性, 32, 23396.]
DOI |
|
| [62] | Hawkes CV, Waring BG, Rocca JD, Kivlin SN (2017) Historical climate controls soil respiration responses to current soil moisture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 6322-6327. |
| [63] |
Hayward J, Horton TR, Pauchard A, Nuñez MA (2015) A single ectomycorrhizal fungal species can enable a Pinus invasion. Ecology, 96, 1438-1444.
PMID |
| [64] | Helsen K, Smith SW, Brunet J, Cousins SAO, de Frenne P, Kimberley A, Kolb A, Lenoir J, Ma SY, Michaelis J, Plue J, Verheyen K, Speed JDM, Graae BJ (2018) Impact of an invasive alien plant on litter decomposition along a latitudinal gradient. Ecosphere, 9, e02097. |
| [65] | Hu CC, Lei YB, Tan YH, Sun XC, Xu H, Liu CQ, Liu XY (2019) Plant nitrogen and phosphorus utilization under invasive pressure in a montane ecosystem of tropical China. Journal of Ecology, 107, 372-386. |
| [66] | Hua FY, Bruijnzeel LA, Meli P, Martin PA, Zhang J, Nakagawa S, Miao XR, Wang WY, McEvoy C, Peña-Arancibia JL, Brancalion PHS, Smith P, Edwards DP, Balmford A (2022) The biodiversity and ecosystem service contributions and trade-offs of forest restoration approaches. Science, 376, 839-844. |
| [67] |
Huang W, Carrillo J, Ding JQ, Siemann E (2012) Invader partitions ecological and evolutionary responses to above- and belowground herbivory. Ecology, 93, 2343-2352.
PMID |
| [68] | Huang W, Siemann E, Ding JQ (2018) Eco-evolutionary dynamics of above- and belowground herbivores and invasive plants. In: Aboveground-Belowground Community Ecology (eds Ohgushi T, Wurst S, Johnson SN), pp. 271-291. Springer, Cham. |
| [69] |
Huang W, Siemann E, Xiao L, Yang XF, Ding JQ (2014) Species-specific defence responses facilitate conspecifics and inhibit heterospecifics in above-belowground herbivore interactions. Nature Communications, 5, 4851.
DOI PMID |
| [70] | Huang W, Wheeler GS, Purcell MF, Ding JQ (2011) The host range and impact of Bikasha collaris (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), a promising candidate agent for biological control of Chinese tallow, Triadica sebifera (Euphorbiaceae) in the United States. Biological Control, 56, 230-238. |
| [71] | Hynson NA, Merckx VSFT, Perry BA, Treseder KK (2013) Identities and distributions of the co-invading ectomycorrhizal fungal symbionts of exotic pines in the Hawaiian Islands. Biological Invasions, 15, 2373-2385. |
| [72] | Inderjit, Simberloff D, Kaur H, Kalisz S, Bezemer TM(2021) Novel chemicals engender myriad invasion mechanisms. New Phytologist, 232, 1184-1200. |
| [73] | Inderjit, van der Putten WH (2010) Impacts of soil microbial communities on exotic plant invasions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 512-519. |
| [74] |
Jing ZW, Wang J, Bai Y, Ge Y (2022) Faunal communities mediate the effects of plant richness, drought, and invasion on ecosystem multifunctional stability. Communications Biology, 5, 527.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Kalisz S, Kivlin SN, Bialic-Murphy L (2021) Allelopathy is pervasive in invasive plants. Biological Invasions, 23, 367-371. |
| [76] | Kamczyc J, Dyderski MK, Horodecki P, Jagodziński AM (2019) Mite communities (Acari, Mesostigmata) in the initially decomposed ‘litter islands’ of 11 tree species in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) forest. Forests, 10, 403. |
| [77] | Kamutando CN, Vikram S, Kamgan-Nkuekam G, Makhalanyane TP, Greve M, Le Roux JJ, Richardson DM, Cowan D, Valverde A (2017) Soil nutritional status and biogeography influence rhizosphere microbial communities associated with the invasive tree Acacia dealbata. Scientific Reports, 7, 6472. |
| [78] | Keane RM, Crawley MJ (2002) Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 17, 164-170. |
| [79] | Klironomos JN (2002) Feedback with soil biota contributes to plant rarity and invasiveness in communities. Nature, 417, 67-70. |
| [80] |
Koorem K, Snoek BL, Bloem J, Geisen S, Kostenko O, Manrubia M, Ramirez KS, Weser C, Wilschut RA, van der Putten WH (2020) Community-level interactions between plants and soil biota during range expansion. Journal of Ecology, 108, 1860-1873.
DOI PMID |
| [81] | Korell L, Schädler M, Brandl R, Schreiter S, Auge H (2019) Release from above- and belowground insect herbivory mediates invasion dynamics and impact of an exotic plant. Plants, 8, 544. |
| [82] | Kourtev PS, Ehrenfeld JG, Häggblom M (2002) Exotic plant species alter the microbial community structure and function in the soil. Ecology, 83, 3152-3166. |
| [83] |
La Pierre KJ, Simms EL, Tariq M, Zafar M, Porter SS (2017) Invasive legumes can associate with many mutualists of native legumes, but usually do not. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 8599-8611.
DOI PMID |
| [84] |
Lau JA, Schultheis EH (2015) When two invasion hypotheses are better than one. New Phytologist, 205, 958-960.
DOI PMID |
| [85] | Lazzaro L, Mazza G, D’Errico G, Fabiani A, Giuliani C, Inghilesi AF, Lagomarsino A, Landi S, Lastrucci L, Pastorelli R, Roversi PF, Torrini G, Tricarico E, Foggi B (2018) How ecosystems change following invasion by Robinia pseudoacacia: Insights from soil chemical properties and soil microbial, nematode, microarthropod and plant communities. Science of the Total Environment, 622, 1509-1518. |
| [86] | Lee MR, Bernhardt ES, van Bodegom PM, Cornelissen JHC, Kattge J, Laughlin DC, Niinemets Ü, Peñuelas J, Reich PB, Yguel B, Wright JP (2017) Invasive species’ leaf traits and dissimilarity from natives shape their impact on nitrogen cycling: A meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 213, 128-139. |
| [87] |
Lei YB, Xiao HF, Feng YL (2010) Impacts of alien plant invasions on biodiversity and evolutionary responses of native species. Biodiversity Science, 18, 622-630. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[类延宝, 肖海峰, 冯玉龙 (2010) 外来植物入侵对生物多样性的影响及本地生物的进化响应. 生物多样性, 18, 622-630.]
DOI |
|
| [88] | Lekberg Y, Gibbons SM, Rosendahl S, Ramsey PW (2013) Severe plant invasions can increase mycorrhizal fungal abundance and diversity. The ISME Journal, 7, 1424-1433. |
| [89] | Levine JM, Adler PB, Yelenik SG (2004) A meta-analysis of biotic resistance to exotic plant invasions. Ecology Letters, 7, 975-989. |
| [90] | Li G, Liu T, Whalen JK, Wei Z (2024) Nematodes: An overlooked tiny engineer of plant health. Trends in Plant Science, 29, 52-63. |
| [91] | Li KL, Veen GFC ten Hooven FC, Harvey JA, van der Putten WH (2023) Soil legacy effects of plants and drought on aboveground insects in native and range-expanding plant communities. Ecology Letters, 26, 37-52. |
| [92] |
Li XQ, Guo WF, Siemann E, Wen YG, Huang W, Ding JQ (2016) Plant genotypes affect aboveground and belowground herbivore interactions by changing chemical defense. Oecologia, 182, 1107-1115.
PMID |
| [93] |
Liao CZ, Peng RH, Luo YQ, Zhou XH, Wu XW, Fang CM, Chen JK, Li B (2008) Altered ecosystem carbon and nitrogen cycles by plant invasion: A meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 177, 706-714.
DOI PMID |
| [94] | Lindsay EA, French K (2006) The impact of the weed Chrysanthemoides monilifera ssp. rotundata on coastal leaf litter invertebrates. Biological Invasions, 8, 177-192. |
| [95] |
Liu HW, Brettell LE, Qiu ZG, Singh BK (2020) Microbiome-mediated stress resistance in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 25, 733-743.
DOI PMID |
| [96] |
Liu T, Chen XY, Gong X, Lubbers IM, Jiang YY, Feng W, Li XP, Whalen JK, Bonkowski M, Griffiths BS, Hu F, Liu MQ (2019) Earthworms coordinate soil biota to improve multiple ecosystem functions. Current Biology, 29, 3420-3429.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | Liu XY, Wei S, Wang F, James EK, Guo XY, Zagar C, Xia LG, Dong X, Wang YP (2012) Burkholderia and Cupriavidus spp. are the preferred symbionts of Mimosa spp. in Southern China. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 80, 417-426. |
| [98] | Liu Y, Zheng YL, Jahn LV, Burns JH (2023) Invaders responded more positively to soil biota than native or noninvasive introduced species, consistent with enemy escape. Biological Invasions, 25, 351-364. |
| [99] | Liu YJ, Huang W, Yang Q, Zheng YL, Li SP, Wu H, Ju RT, Sun Y, Ding JQ (2022) Research advances of plant invasion ecology over past the 10 years. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22438. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清 (2022) 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22438.]
DOI |
|
| [100] | Louca S, Polz MF, Mazel F, Albright MBN, Huber JA, O’Connor MI, Ackermann M, Hahn AS, Srivastava DS, Crowe SA, Doebeli M, Parfrey LW (2018) Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 936-943. |
| [101] | Lu XM, He MY, Ding JQ, Siemann E (2018) Latitudinal variation in soil biota: Testing the biotic interaction hypothesis with an invasive plant and a native congener. The ISME Journal, 12, 2811-2822. |
| [102] |
Lucero JE, Arab NM, Meyer ST, Pal RW, Fletcher RA, Nagy DU, Callaway RM, Weisser WW (2020) Escape from natural enemies depends on the enemies, the invader, and competition. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 10818-10828.
DOI PMID |
| [103] | Maaß S, Caruso T, Rillig MC (2015) Functional role of microarthropods in soil aggregation. Pedobiologia, 58, 59-63. |
| [104] |
Madrigal J, Kelt DA, Meserve PL, Gutierrez JR, Squeo FA (2011) Bottom-up control of consumers leads to top-down indirect facilitation of invasive annual herbs in semiarid Chile. Ecology, 92, 282-288.
PMID |
| [105] | Mangla S, Callaway RM (2008) Exotic invasive plant accumulates native soil pathogens which inhibit native plants. Journal of Ecology, 96, 58-67. |
| [106] | Maraun M, Thomas T, Fast E, Treibert N, Caruso T, Schaefer I, Lu JZ, Scheu S (2023) New perspectives on soil animal trophic ecology through the lens of C and N stable isotope ratios of oribatid mites. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 177, 108890. |
| [107] | Mariotte P, Mehrabi Z, Bezemer TM, de Deyn GB, Kulmatiski A, Drigo B, Veen GFC, van der Heijden MGA, Kardol P (2018) Plant-soil feedback: Bridging natural and agricultural sciences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 129-142. |
| [108] | Maron JL, Klironomos J, Waller L, Callaway RM (2014) Invasive plants escape from suppressive soil biota at regional scales. Journal of Ecology, 102, 19-27. |
| [109] | Mawarda PC, Le Roux X, Acosta MU, van Elsas JD, Salles JF (2022) The impact of protozoa addition on the survivability of Bacillus inoculants and soil microbiome dynamics. ISME Communications, 2, 82. |
| [110] | McCary MA, Mores R, Farfan MA, Wise DH (2016) Invasive plants have different effects on trophic structure of green and brown food webs in terrestrial ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 19, 328-335. |
| [111] | McCue MD, Javal M, Clusella-Trullas S, Le Roux JJ, Jackson MC, Ellis AG, Richardson DM, Valentine AJ, Terblanche JS (2020) Using stable isotope analysis to answer fundamental questions in invasion ecology: Progress and prospects. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 196-214. |
| [112] | McLeod ML, Cleveland CC, Lekberg Y, Maron JL, Philippot L, Bru D, Callaway RM (2016) Exotic invasive plants increase productivity, abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrogen availability in intermountain grasslands. Journal of Ecology, 104, 994-1002. |
| [113] | Meisner A, Gera Hol WH, de Boer W, Krumins JA, Wardle DA, van der Putten WH (2014) Plant-soil feedbacks of exotic plant species across life forms: A meta-analysis. Biological Invasions, 16, 2551-2561. |
| [114] | Memmott J, Fowler SV, Paynter Q, Sheppard AW, Syrett P (2000) The invertebrate fauna on broom, Cytisus scoparius, in two native and two exotic habitats. Acta Oecologica, 21, 213-222. |
| [115] |
Menzel A, Hempel S, Klotz S, Moora M, Pyšek P, Rillig MC, Zobel M, Kühn I (2017) Mycorrhizal status helps explain invasion success of alien plant species. Ecology, 98, 92-102.
DOI PMID |
| [116] |
Mitchell CE, Blumenthal D, Jarošik V, Puckett EE, Pyšek P (2010) Controls on pathogen species richness in plants’ introduced and native ranges: Roles of residence time, range size and host traits. Ecology Letters, 13, 1525-1535.
DOI PMID |
| [117] | Montesinos D, Callaway RM (2020) Soil origin corresponds with variation in growth of an invasive Centaurea, but not of non-invasive congeners. Ecology, 101, e03141. |
| [118] | Morriën E, Duyts H, van der Putten WH, (2012) Effects of native and exotic range-expanding plant species on taxonomic and functional composition of nematodes in the soil food web. Oikos, 121, 181-190. |
| [119] | Motard E, Dusz S, Geslin B, Akpa-Vinceslas M, Hignard C, Babiar O, Clair-Maczulajtys D, Michel-Salzat A (2015) How invasion by Ailanthus altissima transforms soil and litter communities in a temperate forest ecosystem. Biological Invasions, 17, 1817-1832. |
| [120] | Mounger J, Ainouche ML, Bossdorf O, Cavé-Radet A, Li B, Parepa M, Salmon A, Yang J, Richards CL (2021) Epigenetics and the success of invasive plants. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 376, 20200117. |
| [121] | Nakamura N, Toju H, Kitajima K (2023) Leaf, root, and soil microbiomes of an invasive plant, Ardisia crenata, differ between its native and exotic ranges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1302167. |
| [122] | Ndlovu J, Richardson DM, Wilson JRU, Le Roux JJ (2013) Co-invasion of South African ecosystems by an Australian legume and its rhizobial symbionts. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1240-1251. |
| [123] | Nijjer S, Rogers WE, Siemann E (2007) Negative plant-soil feedbacks may limit persistence of an invasive tree due to rapid accumulation of soil pathogens. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274, 2621-2627. |
| [124] | Nuñez MA, Dickie IA (2014) Invasive belowground mutualists of woody plants. Biological Invasions, 16, 645-661. |
| [125] | Parker IM, Saunders M, Bontrager M, Weitz AP, Hendricks R, Magarey R, Suiter K, Gilbert GS (2015) Phylogenetic structure and host abundance drive disease pressure in communities. Nature, 520, 542-544. |
| [126] |
Parker JD, Burkepile DE, Hay ME (2006) Opposing effects of native and exotic herbivores on plant invasions. Science, 311, 1459-1461.
PMID |
| [127] |
Peralta G, Schon NL, Dickie IA, St John MG, Orwin KH, Yeates GW, Peltzer DA (2019) Contrasting responses of soil nematode communities to native and non-native woody plant expansion. Oecologia, 190, 891-899.
DOI PMID |
| [128] | Pérez Castro S, Cleland EE, Wagner R, Sawad RA, Lipson DA (2019) Soil microbial responses to drought and exotic plants shift carbon metabolism. The ISME Journal, 13, 1776-1787. |
| [129] |
Phillips HRP, Guerra CA, Bartz MLC, Briones MJI, Brown G, Crowther TW, Ferlian O, Gongalsky KB, van den Hoogen J, Krebs J, Orgiazzi A, Routh D, Schwarz B, Bach EM, Bennett JM, Brose U, Decaëns T, König-Ries B, Loreau M, Mathieu J, Mulder C, van der Putten WH, Ramirez KS, Rillig MC, Russell D, Rutgers M, Thakur MP, de Vries FT, Wall DH, Wardle DA, Arai M, Ayuke FO, Baker GH, Beauséjour R, Bedano JC, Birkhofer K, Blanchart E, Blossey B, Bolger T, Bradley RL, Callaham MA, Capowiez Y, Caulfield ME, Choi A, Crotty FV, Crumsey JM, Dávalos A, Diaz Cosin DJ, Dominguez A, Duhour AE, van Eekeren N, Emmerling C, Falco LB, Fernández R, Fonte SJ, Fragoso C, Franco ALC, Fugère M, Fusilero AT, Gholami S, Gundale MJ, López MG, Hackenberger DK, Hernández LM, Hishi T, Holdsworth AR, Holmstrup M, Hopfensperger KN, Lwanga EH, Huhta V, Hurisso TT, Iannone BV, Iordache M, Joschko M, Kaneko N, Kanianska R, Keith AM, Kelly CA, Kernecker ML, Klaminder J, Koné AW, Kooch Y, Kukkonen ST, Lalthanzara H, Lammel DR, Lebedev IM, Li Y, Jesus Lidon JB, Lincoln NK, Loss SR, Marichal R, Matula R, Moos JH, Moreno G, Morón-Ríos A, Muys B, Neirynck J, Norgrove L, Novo M, Nuutinen V, Nuzzo V, Mujeeb R, Pansu J, Paudel S, Pérès G, Pérez-Camacho L, Piñeiro R, Ponge JF, Rashid MI, Rebollo S, Rodeiro-Iglesias J, Rodríguez MÁ, Roth AM, Rousseau GX, Rozen A, Sayad E, van Schaik L, Scharenbroch BC, Schirrmann M, Schmidt O, Schröder B, Seeber J, Shashkov MP, Singh J, Smith SM, Steinwandter M, Talavera JA, Trigo D, Tsukamoto J, de Valença AW, Vanek SJ, Virto I, Wackett AA, Warren MW, Wehr NH, Whalen JK, Wironen MB, Wolters V, Zenkova IV, Zhang WX, Cameron EK, Eisenhauer N (2019) Global distribution of earthworm diversity. Science, 366, 480-485.
DOI PMID |
| [130] | Pizano C, Kitajima K, Graham JH, Mangan SA (2019) Negative plant-soil feedbacks are stronger in agricultural habitats than in forest fragments in the tropical Andes. Ecology, 100, e02850. |
| [131] | Potapov A, Bellini B, Chown S, Deharveng L, Janssens F, Kováč L, Kuznetsova N, Ponge JF, Potapov M, Querner P, Russell D, Sun X, Zhang F, Berg M (2020) Towards a global synthesis of Collembola knowledge: Challenges and potential solutions. Soil Organisms, 92, 161-188. |
| [132] | Quail MA, Kozarewa I, Smith F, Scally A, Stephens PJ, Durbin R, Swerdlow H, Turner DJ (2008) A large genome center’s improvements to the Illumina sequencing system. Nature Methods, 5, 1005-1010. |
| [133] | Quist CW, van der Putten WH, Thakur MP (2020) Soil predator loss alters aboveground stoichiometry in a native but not in a related range-expanding plant when exposed to periodic heat waves. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 150, 107999. |
| [134] | Reinhart KO, Callaway RM (2004) Soil biota facilitate exotic Acer invasions in Europe and North America. Ecological Applications, 14, 1737-1745. |
| [135] |
Reinhart KO, Callaway RM (2006) Soil biota and invasive plants. New Phytologist, 170, 445-457.
DOI PMID |
| [136] |
Reinhart KO, Lekberg Y, Klironomos J, Maherali H (2017) Does responsiveness to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi depend on plant invasive status? Ecology and Evolution, 7, 6482-6492.
DOI PMID |
| [137] | Reinhart KO, Packer A, van der Putten WH, Clay K (2003) Plant-soil biota interactions and spatial distribution of black cherry in its native and invasive ranges. Ecology Letters, 6, 1046-1050. |
| [138] |
Reinhart KO, Tytgat T, van der Putten WH, Clay K (2010) Virulence of soil-borne pathogens and invasion by Prunus serotina. New Phytologist, 186, 484-495.
DOI PMID |
| [139] | Renčo M, Jurová J, Gömöryová E, Čerevková A (2021) Long-term giant hogweed invasion contributes to the structural changes of soil nematofauna. Plants, 10, 2103. |
| [140] |
Richardson DM, Allsopp N, D’Antonio CM, Milton SJ, Rejmánek M (2000) Plant invasions—The role of mutualisms. Biological Reviews, 75, 65-93.
PMID |
| [141] | Ridenour WM, Vivanco JM, Feng YL, Horiuchi J, Callaway RM (2008) No evidence for trade-offs: Centaurea plants from America are better competitors and defenders. Ecological Monographs, 78, 369-386. |
| [142] | Rillig MC, Muller LAH, Lehmann A (2017) Soil aggregates as massively concurrent evolutionary incubators. The ISME Journal, 11, 1943-1948. |
| [143] | Robson TC, Baker AC, Murray BR (2009) Differences in leaf-litter invertebrate assemblages between radiata pine plantations and neighbouring native eucalypt woodland. Austral Ecology, 34, 368-376. |
| [144] | Roesch LFW, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AKM, Kent AD, Daroub SH, Camargo FAO, Farmerie WG, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. The ISME Journal, 1, 283-290. |
| [145] | Rosenberg K, Bertaux J, Krome K, Hartmann A, Scheu S, Bonkowski M (2009) Soil amoebae rapidly change bacterial community composition in the rhizosphere of Arabidopsis thaliana. The ISME Journal, 3, 675-684. |
| [146] | Rotter MC, Holeski LM (2018) A meta-analysis of the evolution of increased competitive ability hypothesis: Genetic-based trait variation and herbivory resistance trade-offs. Biological Invasions, 20, 2647-2660. |
| [147] | Rusterholz HP, Salamon JA, Ruckli R, Baur B (2014) Effects of the annual invasive plant Impatiens glandulifera on the Collembola and Acari communities in a deciduous forest. Pedobiologia, 57, 285-291. |
| [148] | Sabatini MA, Innocenti G (2001) Effects of Collembola on plant-pathogenic fungus interactions in simple experimental systems. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 33, 62-66. |
| [149] | Sax DF, Brown JH (2000) The paradox of invasion. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 9, 363-371. |
| [150] | Shao YH, Zhang WX, Liu SJ, Wang XL, Fu SL (2015) Diversity and function of soil fauna. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 6614-6625. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邵元虎, 张卫信, 刘胜杰, 王晓丽, 傅声雷 (2015) 土壤动物多样性及其生态功能. 生态学报, 35, 6614-6625.] | |
| [151] | Shen HY, Shiratori Y, Ohta S, Masuda Y, Isobe K, Senoo K (2021) Mitigating N2O emissions from agricultural soils with fungivorous mites. The ISME Journal, 15, 2427-2439. |
| [152] | Sheng M, Rosche C, Al-Gharaibeh M, Bullington LS, Callaway RM, Clark T, Cleveland CC, Duan WY, Flory SL, Khasa DP, Klironomos JN, McLeod M, Okada M, Pal RW, Shah MA, Lekberg Y (2022) Acquisition and evolution of enhanced mutualism—An underappreciated mechanism for invasive success? The ISME Journal, 16, 2467-2478. |
| [153] | Shi N, Ma SL, Chen WL, Huang QY, Zhu YG, Hao XL (2023) Protozoa-pathogen interactions and soil health: A review. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 42, 481-489. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [石妮, 马斯琳, 陈雯莉, 黄巧云, 朱永官, 郝秀丽 (2023) 原生动物-病原菌互作与土壤健康综述. 农业环境科学学报, 42, 481-489.] | |
| [154] | Shu LF, He ZZ, Guan XT, Yang XQ, Tian YH, Zhang SY, Wu CY, He ZL, Yan QY, Wang C, Shi YJ (2021) A dormant amoeba species can selectively sense and predate on different soil bacteria. Functional Ecology, 35, 1708-1721. |
| [155] | Simberloff D, Martin JL, Genovesi P, Maris V, Wardle DA, Aronson J, Courchamp F, Galil B, García-Berthou E, Pascal M, Pyšek P, Sousa R, Tabacchi E, Vilà M (2013) Impacts of biological invasions: What’s what and the way forward. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 58-66. |
| [156] |
Simon C, Daniel R (2011) Metagenomic analyses: Past and future trends. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 1153-1161.
DOI PMID |
| [157] | Skubała P (2012) Invasive giant knotweed (Fallopia sachalinensis) alters the composition of oribatid mite communities. Biological Letters, 49, 143-155. |
| [158] | Soliveres S, van der Plas F, Manning P, Prati D, Gossner MM, Renner SC, Alt F, Arndt H, Baumgartner V, Binkenstein J, Birkhofer K, Blaser S, Blüthgen N, Boch S, Böhm S, Börschig C, Buscot F, Diekötter T, Heinze J, Hölzel N, Jung K, Klaus VH, Kleinebecker T, Klemmer S, Krauss J, Lange M, Morris EK, Müller J, Oelmann Y, Overmann J, Pašalić E, Rillig MC, Schaefer HM, Schloter M, Schmitt B, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Sikorski J, Socher SA, Solly EF, Sonnemann I, Sorkau E, Steckel J, Steffan-Dewenter I, Stempfhuber B, Tschapka M, Türke M, Venter PC, Weiner CN, Weisser WW, Werner M, Westphal C, Wilcke W, Wolters V, Wubet T, Wurst S, Fischer M, Allan E (2016) Biodiversity at multiple trophic levels is needed for ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature, 536, 456-459. |
| [159] | Stinson KA, Campbell SA, Powell JR, Wolfe BE, Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Hallett SG, Prati D, Klironomos JN (2006) Invasive plant suppresses the growth of native tree seedlings by disrupting belowground mutualisms. PLoS Biology, 4, e140. |
| [160] | Sun F, Zeng LD, Cai ML, Chauvat M, Forey E, Tariq A, Graciano C, Zhang ZH, Gu YF, Zeng FJ, Gong Y, Wang FM, Wang M (2022) An invasive and native plant differ in their effects on the soil food-web and plant-soil phosphorus cycle. Geoderma, 410, 115672. |
| [161] |
Sun X, Sun YM, Cao XY, Zhai XC, Callaway RM, Wan JL, Flory SL, Huang W, Ding JQ (2023) Trade-offs in non-native plant herbivore defences enhance performance. Ecology Letters, 26, 1584-1596.
DOI PMID |
| [162] | Sun ZK, He WM (2010) Evidence for enhanced mutualism hypothesis: Solidago canadensis plants from regular soils perform better. PLoS ONE, 5, e15418. |
| [163] |
Tedersoo L, Suvi T, Beaver K, Kõljalg U (2007) Ectomycorrhizal fungi of the Seychelles: Diversity patterns and host shifts from the native Vateriopsis seychellarum (Dipterocarpaceae) and Intsia bijuga (Caesalpiniaceae) to the introduced Eucalyptus robusta (Myrtaceae), but not Pinus caribea (Pinaceae). New Phytologist, 175, 321-333.
DOI PMID |
| [164] |
Thakur MP, Geisen S (2019) Trophic regulations of the soil microbiome. Trends in Microbiology, 27, 771-780.
DOI PMID |
| [165] | Tian BL, Pei YC, Huang W, Ding JQ, Siemann E (2021) Increasing flavonoid concentrations in root exudates enhance associations between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and an invasive plant. The ISME Journal, 15, 1919-1930. |
| [166] |
Trouvé R, Drapela T, Frank T, Hadacek F, Zaller JG (2014) Herbivory of an invasive slug in a model grassland community can be affected by earthworms and mycorrhizal fungi. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 50, 13-23.
PMID |
| [167] | van den Hoogen J, Geisen S, Routh D, Ferris H, Traunspurger W, Wardle DA, de Goede RGM, Adams BJ, Ahmad W, Andriuzzi WS, Bardgett RD, Bonkowski M, Campos-Herrera R, Cares JE, Caruso T, de Brito Caixeta L, Chen X, Costa SR, Creamer R, da Cunha Castro JM, Dam M, Djigal D, Escuer M, Griffiths BS, Gutiérrez C, Hohberg K, Kalinkina D, Kardol P, Kergunteuil A, Korthals G, Krashevska V, Kudrin AA, Li Q, Liang W, Magilton M, Marais M, Rodriguez Martín JA, Matveeva E, Mayad EH, Mulder C, Mullin P, Neilson R, Duong Nguyen TA, Nielsen UN, Okada H, Palomares Rius JE, Pan K, Peneva V, Pellissier L, Pereira da Silva JC, Pitteloud C, Powers TO, Powers K, Quist CW, Rasmann S, Sanchez Moreno S, Scheu S, Setälä H, Sushchuk A, Tiunov AV, Trap J, van der Putten WH, Vestergärd M, Villenave C, Waeyenberge L, Wall DH, Wilschut R, Wright DG, Yang J, Crowther TW(2019) Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature, 572, 194-198. |
| [168] | van der Putten WH, Bardgett RD, Bever JD, Bezemer TM, Casper BB, Fukami T, Kardol P, Klironomos JN, Kulmatiski A, Schweitzer JA, Suding KN, van de Voorde TFJ, Wardle DA (2013) Plant-soil feedbacks: The past, the present and future challenges. Journal of Ecology, 101, 265-276. |
| [169] | van der Putten WH, Klironomos JN, Wardle DA (2007a) Microbial ecology of biological invasions. The ISME Journal, 1, 28-37. |
| [170] | van der Putten WH, Kowalchuk GA, Brinkman EP, Doodeman GT, van der Kaaij RM, Kamp AF, Menting FB, Veenendaal EM (2007b) Soil feedback of exotic savanna grass relates to pathogen absence and mycorrhizal selectivity. Ecology, 88, 978-988. |
| [171] | van der Putten WH, van Dijk C, Peters BAM (1993) Plant-specific soil-borne diseases contribute to succession in foredune vegetation. Nature, 362, 53-56. |
| [172] | van der Putten WH, Yeates GW, Duyts H, Reis CS, Karssen G (2005) Invasive plants and their escape from root herbivory: A worldwide comparison of the root-feeding nematode communities of the dune grass Ammophila arenaria in natural and introduced ranges. Biological Invasions, 7, 733-746. |
| [173] | van Kleunen M, Dawson W, Essl F, Pergl J, Winter M, Weber E, Kreft H, Weigelt P, Kartesz J, Nishino M, Antonova LA, Barcelona JF, Cabezas FJ, Cárdenas D, Cárdenas-Toro J, Castaño N, Chacón E, Chatelain C, Ebel AL, Figueiredo E, Fuentes N, Groom QJ, Henderson L, Inderjit, Kupriyanov A, Masciadri S, Meerman J, Morozova O, Moser D, Nickrent DL, Patzelt A, Pelser PB, Baptiste MP, Poopath M, Schulze M, Seebens H, Shu WS, Thomas J, Velayos M, Wieringa JJ, Pyšek P (2015) Global exchange and accumulation of non-native plants. Nature, 525, 100-103. |
| [174] |
van Kleunen M, Weber E, Fischer M (2010) A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species. Ecology Letters, 13, 235-245.
DOI PMID |
| [175] | Veen GFC, Freschet GT, Ordonez A, Wardle DA (2015) Litter quality and environmental controls of home-field advantage effects on litter decomposition. Oikos, 124, 187-195. |
| [176] |
Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: A meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702-708.
DOI PMID |
| [177] |
Vogelsang KM, Bever JD (2009) Mycorrhizal densities decline in association with nonnative plants and contribute to plant invasion. Ecology, 90, 399-407.
PMID |
| [178] |
Waller LP, Allen WJ, Barratt BIP, Condron LM, França FM, Hunt JE, Koele N, Orwin KH, Steel GS, Tylianakis JM, Wakelin SA, Dickie IA (2020) Biotic interactions drive ecosystem responses to exotic plant invaders. Science, 368, 967-972.
DOI PMID |
| [179] | Walter D, Proctor H (2010) Mites as modern models: Acarology in the 21st century. Acarologia, 50, 131-141. |
| [180] | Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH (2002) Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 1, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 (2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 1, 119-125.] | |
| [181] | Wan JL, Yi JH, Tao ZB, Ren ZK, Otieno EO, Tian BL, Ding JQ, Siemann E, Erb M, Huang W (2022) Species-specific plant-mediated effects between herbivores converge at high damage intensity. Ecology, 103, e3647. |
| [182] |
Wang SK, Sheng Q, Chu TJ, Li B, Chen JK, Wu JH (2013) Impact of invasive plants on food webs and pathways. Biodiversity Science, 21, 249-259. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王思凯, 盛强, 储忝江, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华 (2013) 植物入侵对食物网的影响及其途径. 生物多样性, 21, 249-259.]
DOI |
|
| [183] |
Wang X, Liang SW, Tian YJ, Liu XT, Liang WJ, Zhang XK (2023) Application of stable isotope techniques in soil food web research. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 2861-2870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王骁, 梁思维, 田艺佳, 刘笑彤, 梁文举, 张晓珂 (2023) 稳定同位素技术在土壤食物网研究中的应用. 应用生态学报, 34, 2861-2870.]
DOI |
|
| [184] |
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science, 304, 1629-1633.
DOI PMID |
| [185] | Weir BS, Turner SJ, Silvester WB, Park DC, Young JM (2004) Unexpectedly diverse Mesorhizobium strains and Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulate native legume genera of New Zealand, while introduced legume weeds are nodulated by Bradyrhizobium species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 5980-5987. |
| [186] |
Wertz S, Degrange V, Prosser JI, Poly F, Commeaux C, Freitag T, Guillaumaud N, Le Roux X (2006) Maintenance of soil functioning following erosion of microbial diversity. Environmental Microbiology, 8, 2162-2169.
PMID |
| [187] |
Wilschut RA, Geisen S (2021) Nematodes as drivers of plant performance in natural systems. Trends in Plant Science, 26, 237-247.
DOI PMID |
| [188] | Wilschut RA, Geisen S, Martens H, Kostenko O, de Hollander M, ten Hooven FC, Weser C, Snoek LB, Bloem J, Caković D, Čelik T, Koorem K, Krigas N, Manrubia M, Ramirez KS, Tsiafouli MA, Vreš B, van der Putten WH (2019a) Latitudinal variation in soil nematode communities under climate warming-related range-expanding and native plants. Global Change Biology, 25, 2714-2726. |
| [189] | Wilschut RA, Geisen S, ten Hooven FC, van der Putten WH (2016) Interspecific differences in nematode control between range-expanding plant species and their congeneric natives. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 100, 233-241. |
| [190] |
Wilschut RA, Silva JCP, Garbeva P, van der Putten WH (2017) Belowground plant-herbivore interactions vary among climate-driven range-expanding plant species with different degrees of novel chemistry. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1861.
DOI PMID |
| [191] | Wilschut RA, van der Putten WH, Garbeva P, Harkes P, Konings W, Kulkarni P, Martens H, Geisen S (2019b) Root traits and belowground herbivores relate to plant-soil feedback variation among congeners. Nature Communications, 10, 1564. |
| [192] | Wilsey B, Martin L, Xu X, Isbell F, Polley HW (2024) Biodiversity: Net primary productivity relationships are eliminated by invasive species dominance. Ecology Letters, 27, e14342. |
| [193] |
Wolkovich EM (2010) Nonnative grass litter enhances grazing arthropod assemblages by increasing native shrub growth. Ecology, 91, 756-766.
PMID |
| [194] | Wu H, Ding JQ (2014) Recent progress in invasion ecology. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 438-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴昊, 丁建清 (2014) 入侵生态学最新研究动态. 科学通报, 59, 438-448.] | |
| [195] | Wu SQ, Cheng JL, Xu XY, Zhang Y, Zhao YX, Li HX, Qiang S (2019) Polyploidy in invasive Solidago canadensis increased plant nitrogen uptake, and abundance and activity of microbes and nematodes in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 138, 107594. |
| [196] | Xiao ZG, Wang X, Koricheva J, Kergunteuil A, Le Bayon RC, Liu MQ, Hu F, Rasmann S (2018) Earthworms affect plant growth and resistance against herbivores: A meta-analysis. Functional Ecology, 32, 150-160. |
| [197] | Yang Q, Carrillo J, Jin HY, Shang L, Hovick SM, Nijjer S, Gabler CA, Li B, Siemann E (2013) Plant-soil biota interactions of an invasive species in its native and introduced ranges: Implications for invasion success. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 65, 78-85. |
| [198] | Yang Q, Siemann E, Harvey JA, Ding JQ, Biere A (2021) Effects of soil biota on growth, resistance and tolerance to herbivory in Triadica sebifera plants. Geoderma, 402, 115191. |
| [199] | Yang Q, Veen GFC, Wagenaar R, Manrubia M, ten Hooven FC, van der Putten WH (2022) Temporal dynamics of range expander and congeneric native plant responses during and after extreme drought events. Ecological Monographs, 92, e1529. |
| [200] | Yang Q, Wei SJ, Shang L, Carrillo J, Gabler CA, Nijjer S, Li B, Siemann E (2015) Mycorrhizal associations of an invasive tree are enhanced by both genetic and environmental mechanisms. Ecography, 38, 1112-1118. |
| [201] | Yang W, Cai AD, Wang JS, Luo YQ, Cheng XL, An SQ (2020) Exotic Spartina alterniflora Loisel. invasion significantly shifts soil bacterial communities with the successional gradient of saltmarsh in Eastern China. Plant and Soil, 449, 97-115. |
| [202] |
Yang W, Jeelani N, Xia L, Zhu ZH, Luo YQ, Cheng XL, An SQ (2019) Soil fungal communities vary with invasion by the exotic Spartina alternifolia Loisel. in coastal salt marshes of Eastern China. Plant and Soil, 442, 215-232.
DOI |
| [203] |
Yao BM, Zeng Q, Zhang LM (2022) Research progress on the biodiversity and ecological function of soil protists. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22353. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[姚保民, 曾青, 张丽梅 (2022) 土壤原生生物多样性及其生态功能研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22353.]
DOI |
|
| [204] |
Yeates GW, Bongers T, De Goede RG, Freckman DW, Georgieva SS (1993) Feeding habits in nematode families and genera—An outline for soil ecologists. Journal of Nematology, 25, 315-331.
PMID |
| [205] |
Yin WD, Zhou LF, Yang KW, Fang JY, Biere A, Callaway RM, Wu MK, Yu HW, Shi Y, Ding JQ (2023) Rapid evolutionary trade-offs between resistance to herbivory and tolerance to abiotic stress in an invasive plant. Ecology Letters, 26, 942-954.
DOI PMID |
| [206] | Young HS, Miller-ter Kuile A, McCauley DJ, Dirzo R (2017) Cascading community and ecosystem consequences of introduced coconut palms (Cocos nucifera) in tropical islands. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 95, 139-148. |
| [207] | Yu HW, He YY, Zhang W, Chen L, Zhang JL, Zhang XB, Dawson W, Ding JQ (2022) Greater chemical signaling in root exudates enhances soil mutualistic associations in invasive plants compared to natives. New Phytologist, 236, 1140-1153. |
| [208] | Yu HX, Le Roux JJ, Jiang ZY, Sun F, Peng CL, Li WH (2021) Soil nitrogen dynamics and competition during plant invasion: Insights from Mikania micrantha invasions in China. New Phytologist, 229, 3440-3452. |
| [209] | Yu WB, Li SP (2020) Modern coexistence theory as a framework for invasion ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1362-1375. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于文波, 黎绍鹏 (2020) 基于现代物种共存理论的入侵生态学概念框架. 生物多样性, 28, 1362-1375.] | |
| [210] |
Zhang P, Li B, Wu JH, Hu SJ (2019) Invasive plants differentially affect soil biota through litter and rhizosphere pathways: A meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 22, 200-210.
DOI PMID |
| [211] |
Zhang WX, Chen DM, Zhao CC (2007) Functions of earthworm in ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 15, 142-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张卫信, 陈迪马, 赵灿灿 (2007) 蚯蚓在生态系统中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 142-153.]
DOI |
|
| [212] | Zhang WX, Shen ZF, Song B, Ma ZH, Shao YH, Fu SL (2022) Soil food web manipulation and ecological functions: Challenges and perspectives. Science & Technology Review, 40(3), 52-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[张卫信, 申智锋, 宋博, 马子鹤, 邵元虎, 傅声雷 (2022) 土壤食物网调控及其生态功能研究的困境与思考. 科技导报, 40(3), 52-63.]
DOI |
|
| [213] |
Zhang Y, Zhang AJ, Luo RY, Pang XY (2022) Response of soil Collembola to nitrogen and phosphorus deposition: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 2585-2592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张燕, 张阿娟, 罗如熠, 庞学勇 (2022) 土壤跳虫对氮磷养分响应的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 33, 2585-2592.]
DOI |
|
| [214] | Zhang ZJ, Liu YJ, Brunel C, van Kleunen M (2020a) Evidence for Elton’s diversity-invasibility hypothesis from belowground. Ecology, 101, e03187. |
| [215] | Zhang ZJ, Liu YJ, Brunel C, van Kleunen M (2020b) Soil-microorganism-mediated invasional meltdown in plants. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 1612-1621. |
| [216] | Zhao MX, Lu XF, Zhao HX, Yang YF, Hale L, Gao Q, Liu WX, Guo JY, Li Q, Zhou JZ, Wan FH (2019) Ageratina adenophora invasions are associated with microbially mediated differences in biogeochemical cycles. Science of the Total Environment, 677, 47-56. |
| [217] | Zhao RJ, Chen T, Dong LJ, Guo H, Ma HK, Song X, Wang MG, Xue W, Yang Q (2023) Progress of plant-soil feedback in ecology studies. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 47, 1333-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[赵榕江, 陈焘, 董丽佳, 郭辉, 马海鲲, 宋旭, 王明刚, 薛伟, 杨强 (2023) 植物-土壤反馈及其在生态学中的研究进展. 植物生态学报, 47, 1333-1355.]
DOI |
|
| [218] | Zheng H, Gao DD, Zhou YQ, Zhao J (2023) Energy flow across soil food webs of different ecosystems: Food webs with complex structures support higher energy flux. Geoderma, 439, 116666. |
| [219] | Zheng YL, Feng YL, Zhang LK, Callaway RM, Valiente- Banuet A, Luo DQ, Liao ZY, Lei YB, Barclay GF, Silva-Pereyra C (2015) Integrating novel chemical weapons and evolutionarily increased competitive ability in success of a tropical invader. New Phytologist, 205, 1350-1359. |
| [220] | Zhu Y, Wang YF, Chen LD (2020) Effects of non-native tree plantations on soil microarthropods and their feeding activity on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Forest Ecology and Management, 477, 118501. |
| [1] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [2] | 莫笑梅, 张琪, 杨嘉欣, 郑国, 胡中民, 张晓珂, 梁思维, 崔淑艳. 北方典型草地土壤线虫代谢速率及能量流动对氮沉降和降水模式改变的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24341-. |
| [3] | 姚祝, 魏雪, 马金豪, 任晓, 王玉英, 胡雷, 吴鹏飞. 气候暖湿化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的短期影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23483-. |
| [4] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [5] | 殷正, 张乃莉, 张春雨, 赵秀海. 长白山不同演替阶段温带森林木本植物菌根类型对林下草本植物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23337-. |
| [6] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [7] | 沈诗韵, 潘远飞, 陈丽茹, 土艳丽, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草原产地和入侵地种群的植物-土壤反馈差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [8] | 刘金花, 李风, 田桃, 肖海峰. 土壤细菌和线虫对热带雨林优势植物凋落物特性和多样性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23276-. |
| [9] | 胡惠玲, 姚致远, 高世斌, 朱波. 紫色土线虫对长期不同施肥措施的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22189-. |
| [10] | 刘笑彤, 田艺佳, 刘汉文, 梁翠影, 姜思维, 梁文举, 张晓珂. 下辽河平原农田土壤线虫群落组成的季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22222-. |
| [11] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [12] | 肖宇珊, 杨昌娆, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 张士秀, 崔淑艳. 降水格局对北方温带草原土壤微食物网结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22208-. |
| [13] | 吴文佳, 袁也, 张静, 周丽霞, 王俊, 任海, 刘占锋. 南亚热带森林演替过程中土壤线虫群落结构变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22205-. |
| [14] | 姚海凤, 张赛超, 上官华媛, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化对土壤动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22547-. |
| [15] | 欧阳园丽, 张参参, 林小凡, 田立新, 顾菡娇, 陈伏生, 卜文圣. 中国亚热带不同菌根树种的根叶形态学性状特征与生长差异: 以江西新岗山为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 746-758. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()