



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22434. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022434 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022434
吴慧1, 徐学红1, 冯晓娟1,*( ), 米湘成1, 苏艳军1, 肖治术2, 朱朝东2, 曹垒3, 高欣4, 宋创业1, 郭良栋5, 吴东辉6, 江建平7, 沈浩8, 马克平1
), 米湘成1, 苏艳军1, 肖治术2, 朱朝东2, 曹垒3, 高欣4, 宋创业1, 郭良栋5, 吴东辉6, 江建平7, 沈浩8, 马克平1
收稿日期:2022-07-29
接受日期:2022-10-06
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-10-13
通讯作者:
冯晓娟
作者简介:* E-mail: xfeng@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Hui Wu1, Xuehong Xu1, Xiaojuan Feng1,*( ), Xiangcheng Mi1, Yanjun Su1, Zhishu Xiao2, Chaodong Zhu2, Lei Cao3, Xin Gao4, Chuangye Song1, Liangdong Guo5, Donghui Wu6, Jianping Jiang7, Hao Shen8, Keping Ma1
), Xiangcheng Mi1, Yanjun Su1, Zhishu Xiao2, Chaodong Zhu2, Lei Cao3, Xin Gao4, Chuangye Song1, Liangdong Guo5, Donghui Wu6, Jianping Jiang7, Hao Shen8, Keping Ma1
Received:2022-07-29
Accepted:2022-10-06
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-10-13
Contact:
Xiaojuan Feng
摘要:
生物多样性强烈的时空尺度依赖性和多层次性决定了生物多样性现状与变量的分析需要在不同生态系统进行多空间尺度、全面和连续的监测。因此, 构建生物多样性研究监测网络是生物多样性保护和研究的基础工作。近年来, 对地观测组织-生物多样性观测网络(GEO BON)、亚太生物多样性监测网络(APBON)等全球、区域以及国家尺度的生物多样性监测网络蓬勃发展。中国陆续在国家尺度上建立了针对生态系统和物种的长期监测网络, 其中, 中国生物多样性监测与研究网络(China Biodiversity Observation and Research Network, Sino BON)于2013年启动建设, 在我国主要生态系统和环境梯度设置30个监测主点和60个监测辅点, 目前已建成10个专项网对动物、植物和微生物进行监测, 并建立了以数据标准与汇交、近地面遥感为核心的综合监测中心。Sino BON打造了从地下、地面到森林林冠的多尺度、多类群(功能群)以及多营养级交互为重点的监测与研究平台, 为理解生物多样性变化趋势及其驱动因素、研究生物多样性维持机制, 以及国家履行《生物多样性公约》、保护生物多样性和生物资源提供详实可靠的生物多样性变化数据。为进一步支撑国家生物多样性治理能力、深化全球多样性保护合作, 我国生物多样性监测亟需在监测技术、监测区域、数据标准、综合信息平台等方向谋求更大的发展。
吴慧, 徐学红, 冯晓娟, 米湘成, 苏艳军, 肖治术, 朱朝东, 曹垒, 高欣, 宋创业, 郭良栋, 吴东辉, 江建平, 沈浩, 马克平 (2022) 全球视角下的中国生物多样性监测进展与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22434. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022434.
Hui Wu, Xuehong Xu, Xiaojuan Feng, Xiangcheng Mi, Yanjun Su, Zhishu Xiao, Chaodong Zhu, Lei Cao, Xin Gao, Chuangye Song, Liangdong Guo, Donghui Wu, Jianping Jiang, Hao Shen, Keping Ma (2022) Progress and prospect of China biodiversity monitoring from a global perspective. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22434. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022434.
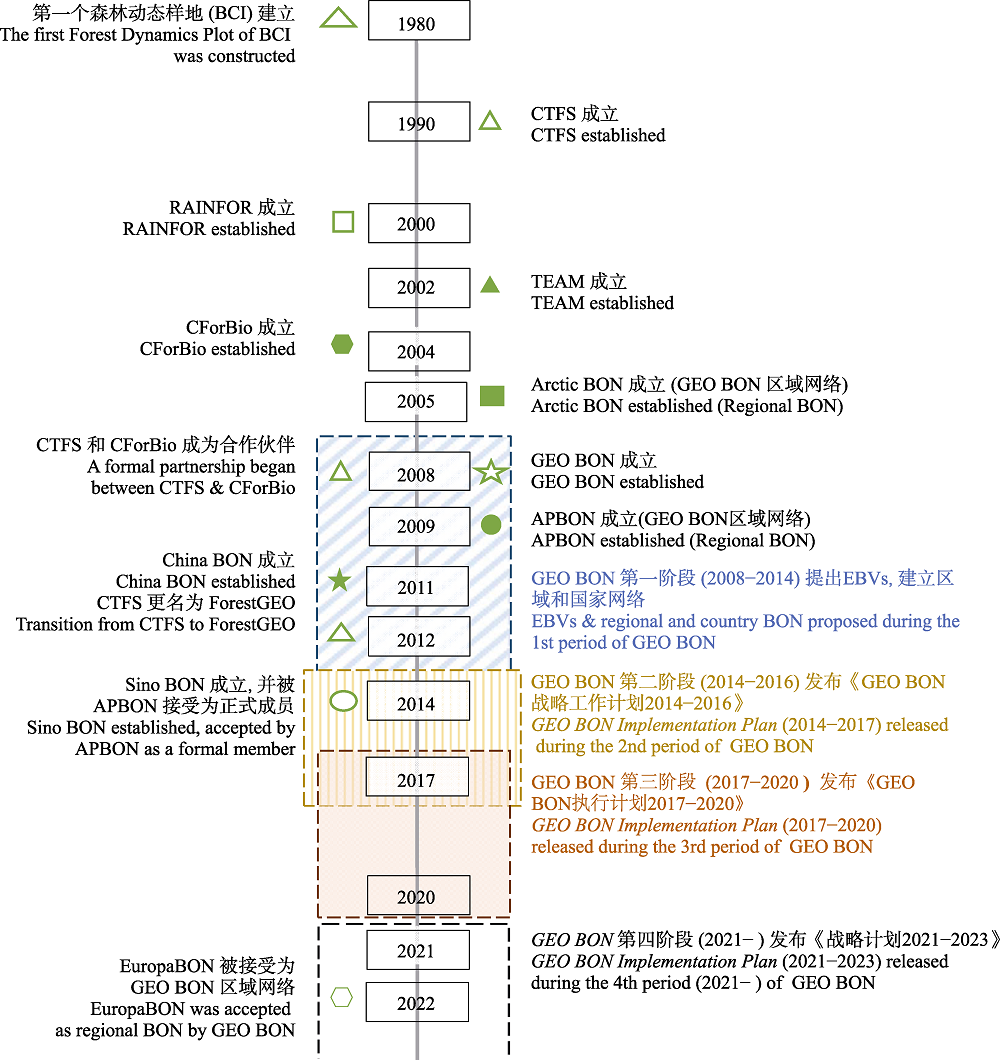
图1 全球生物多样性监测网络发展史。CTFS: 热带森林科学中心; RAINFOR: 亚马逊森林清查网络; TEAM: 热带生态评估与监测网络; CForBio: 中国森林生物多样性监测网络; ForestGEO: 全球森林监测网络; Sino BON: 中国生物多样性监测与研究网络; GEO BON: 对地观测组织-生物多样性观测网络; APBON: 亚太生物多样性监测网络; Arctic BON: 北极生物多样性观测网络; EuropaBON: 欧洲生物多样性监测网络。
Fig. 1 Timeline of history of global biodiversity monitoring network. CTFS, Center for Tropical Forest Science; RAINFOR, Amazonian Forest Inventory Network; TEAM, Tropical Ecology Assessment and Monitoring Network; CForBio, Chinese Forest Biodiversity Monitoring Network; ForestGEO, The Forest Global Earth Observatory; Sino BON, China Biodiversity Observation and Research Network; GEO BON, The Group on Earth Observations-Biodiversity Observation Network; APBON, Asia Pacific Biodiversity Observation Network; Arctic BON, Arctic Biodiversity Observation Network; EuropaBON, Europa Biodiversity Observation Network.
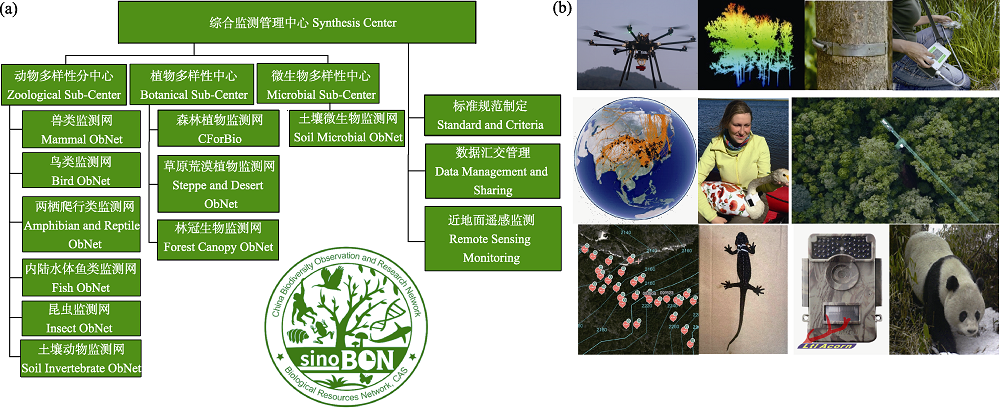
图2 Sino BON 10个专项网(a)在全国30个主点60个辅点对物种、群落和生态系统的动态变化以及多营养级之间互作进行监测, 并通过使用近地面遥感的无人机、测量树木生长的生长环、用于迁徙鸟类的卫星追踪器、用于林冠生物多样性监测的森林塔吊、用于两栖动物的无线电全频跟踪定位仪、用于哺乳动物和地栖鸟类监测的红外相机等设备打造了天-空-地一体化、长时序自动化监测的体系(b)。
Fig. 2 An illustration of how Sino BON is organized for monitoring dynamics of species and ecosystems and multiple trophic interactions through cooperation among the 10 subnetworks (a), and through the use of UAVs for near-ground remote sensing, growth rings for measuring tree growth, satellite trackers for migratory birds, forest tower cranes for canopy biodiversity monitoring, radio full-frequency tracking locators for amphibians, and infrared cameras for mammal and terrestrial bird monitoring to build a sky-ground integrated and long-term automatic monitoring system (b).
| [1] |
Ahumada JA, Silva CEF, Gajapersad K, Hallam C, Hurtado J, Martin E, McWilliam A, Mugerwa B, O’Brien T, Rovero F, Sheil D, Spironello WR, Winarni N, Andelman SJ (2011) Community structure and diversity of tropical forest mammals: Data from a global camera trap network. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366, 2703-2711.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Davies SJ, Bennett AC, Gonzalez-Akre EB, Muller-Landau HC, Joseph WS, Kassim AR (2015) CTFSForestGEO: A worldwide network monitoring forests in an era of global change. Global Change Biology, 21, 528-549. |
| [3] | Baru C, Bhandarkar M, Nambiar R, Poess M, Rabl T (2013) Setting the direction for big data benchmark standards. Selected Topics in Performance Evaluation and Benchmarking. Springer, Berlin. |
| [4] |
Beaudrot L, Ahumada JA, O’Brien T, Alvarez-Loayza P, Boekee K, Campos-Arceiz A, Eichberg D, Espinosa S, Fegraus E, Fletcher C, Gajapersad K, Hallam C, Hurtado J, Jansen PA, Kumar A, Larney E, Lima MGM, Mahony C, Martin EH, McWilliam A, Mugerwa B, Ndoundou- Hockemba M, Razafimahaimodison JC, Romero-Saltos H, Rovero F, Salvador J, Santos F, Sheil D, Spironello WR, Willig MR, Winarni NL, Zvoleff A, Andelman SJ (2016) Standardized assessment of biodiversity trends in tropical forest protected areas: The end is not in sight. PLoS Biology, 14, e1002357.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Bongers FJ, Schmid B, Bruelheide H, Bongers F, Li S, von Oheimb G, Li Y, Cheng AP, Ma KP, Liu XJ (2021) Functional diversity effects on productivity increase with age in a forest biodiversity experiment. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 1594-1603. |
| [6] | Cao L, Deng XQ, Meng FJ, Fox A (2020a) Defining flyways, discerning population trends and assessing conservation challenges of key Far East Asian Anatidae species: An introduction. Wildfowl, Special Issue 6, 1-12. |
| [7] | Cao L, Meng FJ, Zhang JJ, Deng XQ, Sawa Y, Fox AD (2020b) Moving forward: How best to use the results of waterbird monitoring and telemetry studies to safeguard the future of Far East Asian Anatidae species. Wildfowl, 6, 293-319. |
| [8] | Cao L, Meng FJ, Zhao QS (2021) Understanding effects of large-scale development on bird migration and habitats through cutting edge avian monitoring techniques. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36, 436-447. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹垒, 孟凡娟, 赵青山 (2021) 基于前沿监测技术探讨大开发对鸟类迁徙及其栖息地的影响. 中国科学院院刊, 36, 436-447.] | |
| [9] | Che J, Jiang K, Yan F, Zhang YP (2020) Amphibians and Reptiles in Tibet—Diversity and Evolutin. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [车静, 蒋珂, 颜芳, 张亚平 (2020) 西藏两栖爬行动物: 多样性与进化. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] |
Chen L, Swenson NG, Ji NN, Mi XC, Ren HB, Guo LD, Ma KP (2019) Differential soil fungus accumulation and density dependence of trees in a subtropical forest. Science, 366, 124-128.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Chen YX, Yu Y, Li C, Xiao ZS, Zhou GW, Zhang ZJ, Wang XW, Xiang ZF, Chang J, Li M (2022) Population and conservation status of a transboundary group of black snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus strykeri) between China and Myanmar. Zoological Research, 43, 523-527. |
| [12] |
Chen YW, Yu YT, Meng FJ, Deng XQ, Cao L, Fox AD (2021) Migration routes population status and important sites used by the globally threatened black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor): A synthesis of surveys and tracking studies. Avian Research, 12, 74.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Davies SJ, Abiem I, Abu Salim K, Aguilar S, Allen D, Alonso A, Anderson-Teixeira K, Andrade A, Arellano G, Ashton PS, Baker PJ, Baker ME, Baltzer JL, Basset Y, Bissiengou P, Bohlman S, Bourg NA, Brockelman WY, Bunyavejchewin S, Burslem DFRP, Cao M, Cárdenas D, Chang LW, Chang-Yang CH, Chao KJ, Chao WC, Chapman H, Chen YY, Chisholm RA, Chu CJ, Chuyong G, Clay K, Comita LS, Condit R, Cordell S, Dattaraja HS, de Oliveira AA, den Ouden J, Detto M, Dick C, Du XJ, Duque Á, Ediriweera S, Ellis EC, Obiang NLE, Esufali S, Ewango CEN, Fernando ES, Filip J, Fischer GA, Foster R, Giambelluca T, Giardina C, Gilbert GS, Gonzalez-Akre E, Gunatilleke IAUN, Gunatilleke CVS, Hao ZQ, Hau BCH, He FL, Ni HW, Howe RW, Hubbell SP, Huth A, Inman-Narahari F, Itoh A, Janík D, Jansen PA, Jiang MX, Johnson DJ, Jones FA, Kanzaki M, Kenfack D, Kiratiprayoon S, Král K, Krizel L, Lao S, Larson AJ, Li YD, Li XK, Litton CM, Liu Y, Liu SR, Lum SKY, Luskin MS, Lutz JA, Luu HT, Ma KP, Makana JR, Malhi Y, Martin A, McCarthy C, McMahon SM, McShea WJ, Memiaghe H, Mi XC, Mitre D, Mohamad M, Monks L, Muller-Landau HC, Musili PM, Myers JA, Nathalang A, Ngo KM, Norden N, Novotny V, O’Brien MJ, Orwig D, Ostertag R, Papathanassiou K, Parker GG, Pérez R, Perfecto I, Phillips RP, Pongpattananurak N, Pretzsch H, Ren HB, Reynolds G, Rodriguez LJ, Russo SE, Sack L, Sang WG, Shue J, Singh A, Song GZM, Sukumar R, Sun IF, Suresh HS, Swenson NG, Tan S, Thomas SC, Thomas D, Thompson J, Turner BL, Uowolo A, Uriarte M, Valencia R, Vandermeer J, Vicentini A, Visser M, Vrska T, Wang XG, Wang XH, Weiblen GD, Whitfeld TJS, Wolf A, Wright SJ, Xu H, Yao TL, Yap SL, Ye WH, Yu MJ, Zhang MH, Zhu DG, Zhu L, Zimmerman JK, Zuleta D (2021) ForestGEO: Understanding forest diversity and dynamics through a global observatory network. Biological Conservation, 253, 108907.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Garidi, Fan SJ, Cao L, Zhang BX, Wang YX, Zhu BG, Dong SB, Sasin A, Zhao GRLT (2022) Migration strategy of the Bohai Bay wintering population of juvenile Oriental Storks (Ciconia boyciana). Biodiversity Science, 30, 21232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[嘎日迪, 樊淑娟, 曹垒, 张贝西, 王昱熙, 朱宝光, 董树斌, Sasin A, 赵格日乐图 (2022) 东方白鹳幼鸟渤海湾越冬群体的迁徙策略. 生物多样性, 30, 21232.]
DOI |
|
| [15] |
Gu ZR, Pan SK, Lin ZZ, Hu L, Dai XY, Chang J, Xue YC, Su H, Long J, Sun MR, Ganusevich S, Sokolov V, Sokolov A, Pokrovsky I, Ji F, Bruford MW, Dixon A, Zhan XJ (2021) Climate-driven flyway changes and memory-based long- distance migration. Nature, 591, 259-264.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Guo K, Liu CC, Pan QM (2016) Methods of observing typical plant communities in the Steppe and Desert Biodiversity Observation Network, Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1220-1226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[郭柯, 刘长成, 潘庆民 (2016) 中国草原/荒漠植物多样性监测网模式植物群落监测方案. 生物多样性, 24, 1220-1226.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Guo QH, Jin SC, Li M, Yang QL Xu KX, Ju YZ, Zhang J, Xuan J, Liu J, Su YJ, Xu Q, Liu Y (2020) Application of deep learning in ecological resource research: Theories, methods, and challenges. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 50, 1354-1373. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭庆华, 金时超, 李敏, 杨秋丽, 徐可心, 巨袁臻, 张菁, 宣晶, 刘瑾, 苏艳军, 许强, 刘瑜 (2020) 深度学习在生态资源研究领域的应用: 理论、方法和挑战. 中国科学: 地球科学, 50, 1354-1373.] | |
| [18] |
Guo QH, Liu J, Li YM, Zhai QP, Wang YC, Wu FF, Hu TY, Wan HW, Liu HM, Shen WM (2016a) A near-surface remote sensing platform for biodiversity monitoring: perspectives and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1249-1266. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [郭庆华, 刘瑾, 李玉美, 翟秋萍, 王永财, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 万华伟, 刘慧明, 申文明 (2016a) 生物多样性近地面遥感监测: 应用现状与前景展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1249-1266.] | |
| [19] |
Guo QH, Wu FF, Hu TY, Chen LH, Liu J, Zhao XQ, Gao S, Pang SX (2016b) Perspectives and prospects of unmanned aerial vehicle in remote sensing monitoring of biodiversity. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1267-1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [郭庆华, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 陈琳海, 刘瑾, 赵晓倩, 高上, 庞树鑫 (2016b) 无人机在生物多样性遥感监测中的应用现状与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1267-1278.] | |
| [20] |
Guo QH, Su YJ, Hu TY, Zhao XQ, Wu FF, Li YM, Liu J, Chen LH, Xu GC, Lin GH, Zheng Y, Lin YQ, Mi XC, Lin F, Wang XG (2017) An integrated UAV-borne lidar system for 3D habitat mapping in three forest ecosystems across China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38, 2954-2972.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Hou SB, Wang K, Guo P, Chen JM, Yuan ZY, Che J (2021) Two new species and a new country record of the genus Achalinus (Reptilia: Squamata: Xenodermidae) from China. Zootaxa, 4950, 528-546.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Hu TY, Sun XL, Su YJ, Guan HC, Sun QH, Kelly M, Guo QH (2021) Development and performance evaluation of a very low-cost UAV-lidar system for forestry applications. Remote Sensing, 13, 77.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Huang YY, Chen YX, Castro-Izaguirre N, Baruffol M, Brezzi M, Lang A, Li Y, Hardtle W, von Oheimb G, Yang XF, Liu XJ, Pei KQ, Both S, Yang B, Eichenberg D, Assmann T, Bauhus J, Behrens T, Buscot F, Chen XY, Chesters D, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fang JY, Fischer M, Guo LD, Guo DL, Gutknecht JLM, He JS, He CL, Hector A, Honig L, Hu RY, Klein AM, Kuhn P, Liang Y, Li S, Michalski S, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmidt K, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Shi X, Tan MZ, Tang ZY, Trogisch S, Wang ZW, Welk E, Wirth C, Wubet T, Xiang WH, Yu MJ, Yu XD, Zhang JY, Zhang SR, Zhang NL, Zhou HZ, Zhu CD, Zhu L, Bruelheide H, Ma KP, Niklaus PA, Schmid B (2019) Impacts of species richness on productivity in a large-scale subtropical forest experiment. Science, 362, 80-83.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Jansen PA, Ahumada J, Fegraus E, O’Brien T (2014) TEAM: A standardised camera-trap survey to monitor terrestrial vertebrate communities in tropical forests. The 1st International Colloquium on Camera Trapping in Wildlife Management and Research, 263-270. |
| [25] |
Jetz W, McGowan J, Rinnan DS, Possingham HP, Visconti P, O’Donnell B, Londoño-Murcia MC (2022) Include biodiversity representation indicators in area-based conservation targets. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 6, 123-126.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Ji NN, Gao C, Sandel B, Zheng Y, Chen L, Wu BW, Li XC, Wang YL, Lu PP, Sun X, Guo LD (2019) Late Quaternary climate change explains soil fungal community composition rather than fungal richness in forest ecosystems. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 6678-6692.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Jia Q, Wang X, Zhang Y, Cao L, Fox AD (2018) Drivers of waterbird communities and their declines on Yangtze River floodplain lakes. Biological Conservation, 218, 240-246.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Jia SH, Wang XG, Yuan ZQ, Lin F, Ye J, Lin GG, Hao ZQ, Bagchi R (2020) Tree species traits affect which natural enemies drive the Janzen-Connell effect in a temperate forest. Nature Communications, 11, 286.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Jiang JP, Xie F (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity:Vertebrates. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [江建平, 谢锋 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录: 脊椎动物(第四卷)两栖动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] |
Král D, Lu YY, Bai M (2021) Airapus rakovici (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Aphodiinae: Eupariini), a new species from Fujian, China. Zootaxa, 4920, 140-144.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Li C, Xie F, Che J, Jiang JP (2017) Monitoring and research of amphibians and reptiles diversity in key areas of China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 246-254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李成, 谢锋, 车静, 江建平 (2017) 中国关键地区两栖爬行动物多样性监测与研究. 生物多样性, 25, 246-254.]
DOI |
|
| [32] |
Li HD, Tang LF, Jia CX, Holyoak M, Frund J, Huang XQ, Xiao ZS (2020a) The functional roles of species in metacommunities, as revealed by metanetwork analyses of bird-plant frugivory networks. Ecology Letters, 23, 1252-1262.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Li XY, Bleisch WV, Jiang XL (2018) Using large spatial scale camera trap data and hierarchical occupancy models to evaluate species richness and occupancy of rare and elusive wildlife communities in southwest China. Diversity and Distributions, 24, 1560-1572.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Li XY, Bleisch WV, Liu XW, Hu WQ, Jiang XL (2020a) Human disturbance and prey occupancy as predictors of carnivore richness and biomass in a Himalayan hotspot: Drivers affecting carnivores richness and biomass. Animal Conservation, 24, 64-72.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Li XY, Bleisch WV, Liu XW, Jiang XL (2020b) Camera-trap surveys reveal high diversity of mammals and pheasants in Medog, Tibet. Oryx, 55, 1-4.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Li XY, Hu WQ, Bleisch WV, Li Q, Wang HJ, Lu W, Sun J, Zhang FY, Ti B, Jiang XL (2022) Functional diversity loss and change in nocturnal behavior of mammals under anthropogenic disturbance. Conservation Biology, 36, e13839. |
| [37] |
Li XZ, Guo LD, Li JB, Yao MJ (2016) Soil microbial diversity observation in China: Current situation and future consideration. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1240-1248. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李香真, 郭良栋, 李家宝, 姚敏杰 (2016) 中国土壤微生物多样性监测的现状和思考. 生物多样性, 24, 1240-1248.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Liu HZ, Yang JX, Liu SW, Gao X, Chen YS, Zhang CG, Zhao K, Li XH, Liu W (2016) Theory and methods on fish diversity monitoring with an introduction to the inland water fish diversity observation in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1227-1233. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘焕章, 杨君兴, 刘淑伟, 高欣, 陈宇顺, 张春光, 赵凯, 李新辉, 刘伟 (2016) 鱼类多样性监测的理论方法及中国内陆水体鱼类多样性监测. 生物多样性, 24, 1227-1233.]
DOI |
|
| [39] |
Liu XQ, Su YJ, Hu TY, Yang QL, Liu BB, Deng YF, Tang H, Tang ZY, Fang JY, Guo QH (2022) Neural network guided interpolation for mapping canopy height of China’s forests by integrating GEDI and ICESat-2 data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 269, 112844.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Luo JY, Peng YQ, Xie Q (2021) First record of the cimicomorphan family Plokiophilidae (Hemiptera, Heteroptera) from China, with description of a new species of Plokiophiloides. ZooKeys, 1021, 145-157.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Ma KP (2015) Biodiversity monitoring in China: From CForBio to Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 23, 1-2. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性监测网络建设: 从CForBio到Sino BON. 生物多样性, 23, 1-2.]
DOI |
|
| [42] |
Meng FJ, Wang X, Batbayar N, Natsagdorj T, Davaasuren B, Damba I, Cao L, Fox AD (2020) Consistent habitat preference underpins the geographically divergent autumn migration of individual Mongolian common shelducks Tadorna tadorna. Current Zoology, 66, 355-362.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Meng FJ, Li HB, Wang X, Fang L, Li XH, Cao L, Fox AD (2019) Size matters: Wintering ducks stay longer and use fewer habitats on largest Chinese lakes. Avian Research, 10, 27.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Mi XC, Guo J, Hao ZQ, Xie ZQ, Guo K, Ma KP (2016) Chinese forest biodiversity monitoring: Scientific foundations and strategic planning. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1203-1219. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[米湘成, 郭静, 郝占庆, 谢宗强, 郭柯, 马克平 (2016) 中国森林生物多样性监测: 科学基础与执行计划. 生物多样性, 24, 1203-1219.]
DOI |
|
| [45] | Mi XC, Feng G, Hu YB, Zhang J, Chen L, Corlett RT, Hughes AC, Pimm S, Schmid B, Shi SH, Svenning JC, Ma KP (2021) The global significance of biodiversity science in China: An overview. National Science Review, 8, nwab032. |
| [46] |
Miao BG, Peng YQ, Yang DR, Guénard B, Liu C (2022) Diversity begets diversity: Low resource heterogeneity reduces the diversity of nut-nesting ants in rubber plantations. Insect Science, 29, 932-941.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Navarro LM, Fernández N, Guerra C, Guralnick R, Kissling WD, Londoño MC, Muller-Karger F, Turak E, Balvanera P, Costello MJ, Delavaud A, El Serafy G, Ferrier S, Geijzendorffer I, Geller GN, Jetz W, Kim ES, Kim H, Pereira HM (2017) Monitoring biodiversity change through effective global coordination. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 29, 158-169.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Pan KW, Zhang L, Shao YH, Fu SL (2016) Thematic monitoring network of soil fauna diversity in China: Exploring the mystery of soils. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1234-1239. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[潘开文, 张林, 邵元虎, 傅声雷 (2016) 中国土壤动物多样性监测: 探知土壤中的奥秘. 生物多样性, 24, 1234-1239.]
DOI |
|
| [49] |
Pereira H, Junker J, Fernández N, Maes J, Beja P, Bonn A, Breeze T, Brotóns L, Bruelheide H, Buchhorn M, Capinha C, Chow CFY, Dietrich K, Dornelas M, Dubois G, Fernandez M, Frenzel M, Friberg N, Fritz S, Georgieva I, Gobin A, Guerra C, Haande S, Herrando S, Jandt U, Kissling WD, Kühn I, Langer C, Liquete C, Solheim AL, Martí D, Martin JGC, Masur A, McCallum I, Mjelde M, Moe J, Moersberger H, Morán-Ordóñez A, Moreira F, Musche M, Navarro L, Orgiazzi A, Patchett R, Penev L, Pino J, Popova G, Potts S, Ramon A, Sandin L, Santana J, Sapundzhieva A, See L, Shamoun‐Baranes J, Smets B, Stoev P, Tedersoo L, Tiimann L, Valdez J, Vallecillo S, van Grunsven RV, Van De Kerchove R, Villero D, Visconti P, Weinhold C, Zuleger A Europa Biodiversity Observation Network: Integrating data streams to support policy. doi: 10.3897/arphapreprints.e81207.
DOI |
| [50] |
Rochette AJ, Akpona JDT, Akpona HA, Akouehou GS, Kwezi BM, Djagoun CAMS, Habonimana B, Idohou R, Legba IS, Nzigidahera B, Matilo AO, Taleb MS, Bamoninga BT, Ivory S, de Bisthoven LJ, Vanhove MPM (2019) Developing policy-relevant biodiversity indicators: Lessons learnt from case studies in Africa. Environmental Research Letters, 14, 035002.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Rovero F, Ahumada J (2017) The Tropical Ecology, Assessment and Monitoring (TEAM) Network: An early warning system for tropical rain forests. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 914-923.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Scholes RJ, Mace GM, Turner W, Geller GN, Jurgens N, Larigauderie A, Muchoney D, Walther BA, Mooney HA (2008) Toward a global biodiversity observing system. Science, 321, 1044-1045.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Scholes RJ, Walters M, Turak E, Saarenmaa H, Heip CH, Tuama ÉÓ, Faith DP, Mooney HA, Ferrier S, Jongman RH, Harrison IJ, Yahara T, Pereira HM, Larigauderie A, Geller G (2012) Building a global observing system for biodiversity. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 4, 139-146.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Shen CC, Xiong JB, Zhang HY, Feng YZ, Lin XG, Li XY, Liang WJ, Chu HY (2013) Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 57, 204-211.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Shen CC, Liang WJ, Shi Y, Lin XG, Zhang HY, Wu X, Xie G, Chain P, Grogan P, Chu HY (2014) Contrasting elevational diversity patterns between eukaryotic soil microbes and plants. Ecology, 95, 3190-3202.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Shen H, Cai JN, Li MJ, Chen Q, Ye WH, Wang ZF, Lian JY, Song L (2017) On Chinese forest canopy biodiversity monitoring. Biodiversity Science, 25, 229-236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[沈浩, 蔡佳宁, 李萌姣, 陈青, 叶万辉, 王峥峰, 练琚愉, 宋亮 (2017) 中国森林冠层生物多样性监测. 生物多样性, 25, 229-236.]
DOI |
|
| [57] | Shi SC, Hou YM, Song ZB, Jiang JP, Wang B (2021) A new leaf litter toad of Leptobrachella Smith 1925 (Anura Megophryidae) from Sichuan Province, China with supplementary description of L. oshanensis. Asian Herpetological Research, 12, 143-166. |
| [58] | Shu GC, Liu P, Zhao T, Li C, Hou YM, Zhao CL, Wang J, Shu XX, Chang J, Jiang JP, Xie F (2021) Disordered translocation is hastening local extinction of the Chinese giant salamander. Asian Herpetological Research, 12, 271-279. |
| [59] |
Wang BJ, Fang S, Wang YY, Guo QH, Hu TY, Mi XC, Lin LX, Jin GZ, Coomes DA, Yuan ZQ, Ye J, Wang XG, Lin F, Hao ZQ (2022) The shift from energy to water limitation in local canopy height from temperate to tropical forests in China. Forests, 13, 639.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Wang MQ, Anttonen P, Bruelheide H, Chen JT, Chesters D, Durka W, Guo PF, Härdtle W, Li Y, Ma KP, Michalski SG, Schmid B, Schuldt A, von Oheimb G, Wu CS, Zhang NL, Zhou QS, Zhu CD (2019) Multiple components of plant diversity loss determine herbivore phylogenetic diversity in a subtropical forest experiment. Journal of Ecology, 107, 2697-2712.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Wang MQ, Li Y, Chesters D, Bruelheide H, Ma KP, Guo PF, Zhou QS, Staab M, Zhu CD, Schuldt A (2020) Host functional and phylogenetic composition rather than host diversity structure plant-herbivore networks. Molecular Ecology, 29, 2747-2762.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Wang MQ, Yan C, Luo AR, Li Y, Chesters D, Qiao HJ, Chen JT, Zhou QS, Ma KP, Bruelheide H, Schuldt A, Zhang ZB, Zhu CD (2022) Phylogenetic relatedness functional traits and spatial scale determine herbivore co-occurrence in a subtropical forest. Ecological Monographs, 92, e01492. |
| [63] |
Wang X, Cao L, Bysykatova I, Xu ZG, Rozenfeld S, Jeong W, Vangeluwe D, Zhao YL, Xie TH, Yi KP, Fox AD (2018) The Far East taiga forest: Unrecognized inhospitable terrain for migrating Arctic-nesting waterbirds? PeerJ, 6, e4353.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Wang X, Cao L, Fox AD, Fuller R, Griffin L, Mitchell C, Zhao YL, Moon OK, Cabot D, Xu ZG, Batbayar N, Kölzsch A, van der Jeugd HP, Madsen J, Chen LD, Nathan R (2019) Stochastic simulations reveal few green wave surfing populations among spring migrating herbivorous waterfowl. Nature Communications, 10, 2187.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Takeuchi Y, Muraoka H, Yamakita T, Kano Y, Nagai S, Bunthang T, Costello MJ, Darnaedi D, Diway B, Ganyai T, Grudpan C, Hughes A, Ishii R, Lim PT, Ma KP, Muslim AM, Nakano SI, Nakaoka M, Nakashizuka T, Onuma M, Park CH, Pungga RS, Saito Y, Shakya MM, Sulaiman MK, Sumi MY, Thach P, Trisurat Y, Xu XH, Yamano H, Yao TL, Kim ES, Vergara S, Yahara T (2021) The Asia-Pacific Biodiversity Observation Network: 10-year achievements and new strategies to 2030. Ecological Research, 36, 232-257.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Turner W (2014) Sensing biodiversity. Science, 346, 301-302.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Xi JR, Deng XQ, Zhao G, Batbayar N, Damba I, Zhao QS, Cui SB, Jiang C, Chen YW, Yu YT, Cao L, Fox AD (2021) Migration routes behavior and protection status of Eurasian Spoonbills (Platalea leucorodia) wintering in China. Avian Research, 12, 70.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Xiao ZS, Li XY, Xiang ZF, Li M, Jiang XL, Zhang LB (2017) Overview of the Mammal Diversity Observation Network of Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 25, 237-245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[肖治术, 李学友, 向左甫, 李明, 蒋学龙, 张礼标 (2017) 中国兽类多样性监测网的建设规划与进展. 生物多样性, 25, 237-245.]
DOI |
|
| [69] | Yahara T, Ma KP, Darnaedi D, Miyashita T, Takenaka A, Tachida H, Nakashizuka T, Kim ES, Takamura N, Nakano SI, Shirayama Y, Yamamoto H, Vergara SG (2014) Developing a regional network of biodiversity observation in the Asia-Pacific region: Achievements and challenges of AP BON. Integrative Observations and Assessments, pp. 3-28. Springer, Tokyo. |
| [70] |
Yan F, Lü JC, Zhang BL, Yuan ZY, Zhao HP, Huang S, Gang W, Mi X, Zou DH, Xu W, Chen S, Wang J, Xie F, Wu MY, Xiao HB, Liang ZQ, Jin JQ, Wu SF, Xu CS, Tapley B, Turvey ST, Papenfuss TJ, Cunningham AA, Murphy RW, Zhang YP, Che J (2018) The Chinese giant salamander exemplifies the hidden extinction of cryptic species. Current Biology, 28, R1-R3.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Yang XF, Yan C, Zhao QJ, Holyoak M, Fortuna MA, Bascompted J, Jansene PA, Zhang ZB (2018) Ecological succession drives the structural change of seed-rodent interaction networks in fragmented forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 419, 42-50. |
| [72] |
Yi L, Dong YK, Miao BG, Peng YQ (2021) Diversity of butterfly communities in Gaoligong region of Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 29, 950-959. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[易浪, 董亚坤, 苗白鸽, 彭艳琼 (2021) 云南高黎贡山地区蝴蝶群落多样性. 生物多样性, 29, 950-959.]
DOI |
|
| [73] |
Yi XX, Wang NN, Ren HB, Yu JP, Hu TY, Su YJ, Mi XC, Guo QH, Ma KP (2022) From canopy complementarity to asymmetric competition: The negative relationship between structural diversity and productivity during succession. Journal of Ecology, 110, 457-465.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Yu H, Wang X, Cao L, Zhang L, Jia Q, Lee H, Xu ZG, Liu GH, Xu WB, Hu BH, Fox AD (2017) Are declining populations of wild geese in China ‘prisoners’ of their natural habitats? Current Biology, 27, R376-R377.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Zhang MH, Shi SC, Li C, Yan P, Wang P, Ding L, Du J, Plenković-Moraj A, Jiang JP, Shi JS (2022) Exploring cryptic biodiversity in a world heritage site: A new pitviper (Squamata Viperidae Crotalinae) from Jiuzhaigou, Aba, Sichuan, China. ZooKeys, 1114, 59-76.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Zheng Y, Chen L, Ji NN, Wang YL, Gao C, Jin SS, Hu HW, Huang Z, He JZ, Guo LD, Powell JR (2021) Assembly processes lead to divergent soil fungal communities within and among 12 forest ecosystems along a latitudinal gradient. New Phytologist, 231, 1183-1194.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn