



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 796-812. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019197 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019197
收稿日期:2019-06-17
接受日期:2019-07-11
出版日期:2019-07-20
发布日期:2019-08-21
通讯作者:
张昭臣
基金资助:
Jiaxin Kong1,2, Zhaochen Zhang1,2,*( ), Jian Zhang1,2
), Jian Zhang1,2
Received:2019-06-17
Accepted:2019-07-11
Online:2019-07-20
Published:2019-08-21
Contact:
Zhaochen Zhang
摘要:
物种分类与识别是生物多样性监测的基础, 明确物种的类别及其分布是解决几乎所有生态学问题的前提。为深入了解基于多源遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别相关研究的发展现状和存在的问题, 本文对2000年以来该领域的研究进行了总结分析, 发现: 当前大多数研究集中在欧洲和北美地区的温带或北方森林以及南非的热带稀树草原; 使用最多的遥感数据是机载高光谱数据, 而激光雷达作为补充数据, 通过单木分割及提供单木的三维垂直结构信息, 显著提高了分类精度; 支持向量机和随机森林作为应用最广的非参数分类算法, 平均分类精度达80%; 随着计算机技术及机器学习领域的不断成熟, 人工神经网络在物种识别领域得以迅速发展。基于此, 本文对目前基于遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别中在分类对象复杂性、多源遥感数据整合、植物物候与纹理特征整合和分类算法技术等方面面临的挑战进行了总结, 并建议通过整合多时相监测数据、高光谱和激光雷达数据、短波红外等特定波谱信息、采用深度学习等方法来提高分类精度。
孔嘉鑫, 张昭臣, 张健 (2019) 基于多源遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别: 研究进展与展望. 生物多样性, 27, 796-812. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019197.
Jiaxin Kong, Zhaochen Zhang, Jian Zhang (2019) Classification and identification of plant species based on multi-source remote sensing data: Research progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 27, 796-812. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019197.
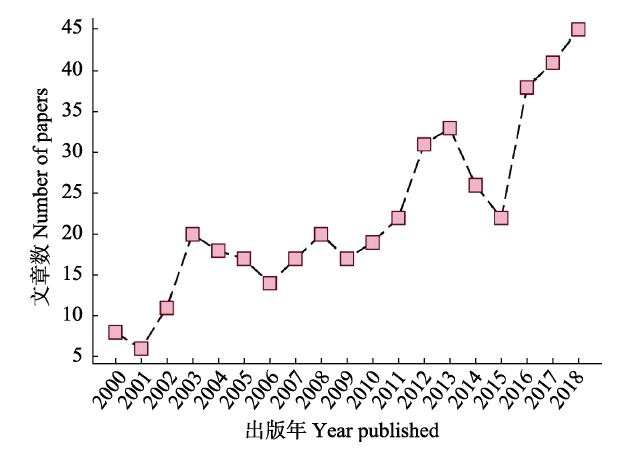
图1 2000-2018年间遥感领域3个主流期刊(International Journal of Remote Sensing、Remote Sensing of Environment和Remote Sensing)上使用多源遥感数据进行植物物种分类与识别的论文统计
Fig. 1 The papers on plant species classification and identification using different types of remote sensing data published between 2000 and 2018 in three top journals in remote sensing, including International Journal of Remote Sensing, Remote Sensing of Environment, and Remote Sensing.
| 研究对象 Research subjects | 相关案例数量 Number of case studies | 案例 Selected case studies |
|---|---|---|
| 热带/亚热带森林 Tropical/subtropical forests | 10 | |
| 热带稀树草原 Savanna | 8 | |
| 温带森林 Temperate forests | 56 | |
| 北方森林/针叶林 Boreal forest or Coniferous forest | 19 | |
| 红树林 Mangrove | 7 | |
| 草地 Grassland | 4 | |
| 城市树种 Urban tree species | 11 | |
| 入侵植物 Invasive plants | 5 |
表1 基于遥感数据进行植物物种识别的120项研究案例统计
Table 1 Statistics of 120 selected study cases of plant species identification based on remote sensing data
| 研究对象 Research subjects | 相关案例数量 Number of case studies | 案例 Selected case studies |
|---|---|---|
| 热带/亚热带森林 Tropical/subtropical forests | 10 | |
| 热带稀树草原 Savanna | 8 | |
| 温带森林 Temperate forests | 56 | |
| 北方森林/针叶林 Boreal forest or Coniferous forest | 19 | |
| 红树林 Mangrove | 7 | |
| 草地 Grassland | 4 | |
| 城市树种 Urban tree species | 11 | |
| 入侵植物 Invasive plants | 5 |
| 分类算法 Species classification algorithms | 优缺点 Advantages and disadvantages | 案例列举 Case studies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 输入数据是否需要分布假设 Does the input data need specific distribution assumption? | 是否需要训练数据 Is the training data needed? | 对各种分类问题的适用性 Applicability to different kinds of species classifications | 算法复杂性和计算成本 Algorithmic complexity and computational cost | 可操作性 Is it easy to use for ecologists? | ||
| 支持向量机 Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 随机森林 Random Forest (RF) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| 最大似然分类 Maximum Likelihood Classifiers (MLC) | 是 Yes | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 判别式分析 Discriminant Analysis (DA) | 是 Yes | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| k-最近邻分类 k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) | 否 No | 否 No | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 人工神经网络 Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) | 否 No | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较高 High | 较难 Difficult | |
| 光谱角制图 Spectral Angle Mapper (SAM) | 否 No | 否 No | 较低 Low | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 广义线性模型 Generalized Linear Model (GLM) | 是 Yes | 否 No | 较低 Low | 较高 High | 较难 Difficult | |
| 分类和回归树 Classification and regression tree (CART) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| 贝叶斯分类算法 Bayesian Classifiers | 否 No | 否 No | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
表2 常用物种分类算法的优缺点及案例
Table 2 Advantages and disadvantages of commonly used species classification algorithms and case studies
| 分类算法 Species classification algorithms | 优缺点 Advantages and disadvantages | 案例列举 Case studies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 输入数据是否需要分布假设 Does the input data need specific distribution assumption? | 是否需要训练数据 Is the training data needed? | 对各种分类问题的适用性 Applicability to different kinds of species classifications | 算法复杂性和计算成本 Algorithmic complexity and computational cost | 可操作性 Is it easy to use for ecologists? | ||
| 支持向量机 Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 随机森林 Random Forest (RF) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| 最大似然分类 Maximum Likelihood Classifiers (MLC) | 是 Yes | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 判别式分析 Discriminant Analysis (DA) | 是 Yes | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| k-最近邻分类 k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) | 否 No | 否 No | 较高 High | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 人工神经网络 Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) | 否 No | 较多 More | 较高 High | 较高 High | 较难 Difficult | |
| 光谱角制图 Spectral Angle Mapper (SAM) | 否 No | 否 No | 较低 Low | 较高 High | 容易 Easy | |
| 广义线性模型 Generalized Linear Model (GLM) | 是 Yes | 否 No | 较低 Low | 较高 High | 较难 Difficult | |
| 分类和回归树 Classification and regression tree (CART) | 否 No | 较少 Less | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
| 贝叶斯分类算法 Bayesian Classifiers | 否 No | 否 No | 较高 High | 较低 Low | 容易 Easy | |
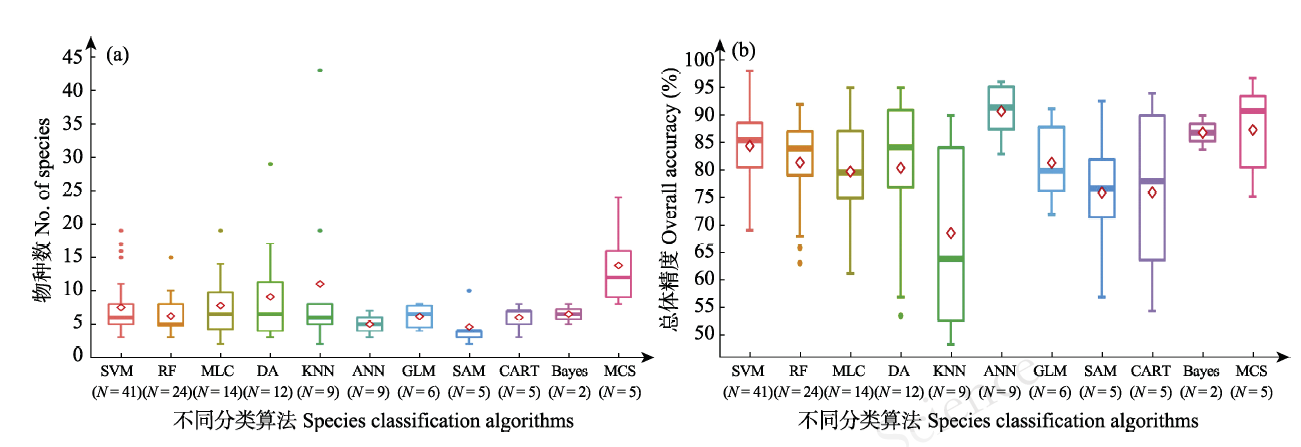
图2 常用物种分类算法的应用。(a)不同算法分类的物种数; (b)不同算法分类的总体精度。SVM: 支持向量机; RF: 随机森林; MLC: 最大似然分类; DA: 判别式分析; KNN: k-最近邻分类; ANN: 人工神经网络; GLM: 广义线性模型; SAM: 光谱角制图; CART: 分类和回归树; Bayes: 贝叶斯算法; MCS: 多分类系统。括号中N代表每种算法对应的研究案例数。
Fig. 2 Application of commonly used species classification algorithms. (a) The number of species classified by different algorithms; (b) Overall accuracy of different algorithms. SVM, Support Vector Machine; RF, Random Forest; MLC, Maximum Likelihood Classifiers; DA, Discriminant Analysis; KNN, k-Nearest Neighbor; ANN, Artificial Neural Networks; GLM, Generalized Linear Model; SAM, Spectral Angle Mapper; CART, Classification and regression tree; Bayes, Bayesian Classifiers; MCS, Multiple Classifier Systems. “N” in the brackets represents the number of study cases corresponding to each algorithm.
| [1] | Aguirre-Gutiérrez J, Seijmonsbergen AC, Duivenvoorden JF ( 2012) Optimizing land cover classification accuracy for change detection, a combined pixel-based and object-based approach in a mountainous area in Mexico. Applied Geography, 34, 29-37. |
| [2] | Alonzo M, Bookhagen B, Roberts DA ( 2014) Urban tree species mapping using hyperspectral and lidar data fusion. Remote Sensing of Environment, 148, 70-83. |
| [3] | Amiri M, Solaimani K, Miryaghoubzadeh M ( 2013) Fuzzy classification for mapping invasive species from multispectral imagery. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 41, 749-755. |
| [4] | Asner GP ( 1998) Biophysical and biochemical sources of variability in canopy reflectance. Remote Sensing of Environment, 64, 234-253. |
| [5] | Asner GP, Martin RE, Knapp DE, Tupayachi R, Anderson CB, Sinca F, Vaughn NR, Llactayo W ( 2017) Airborne laser-guided imaging spectroscopy to map forest trait diversity and guide conservation. Science, 355, 385-389. |
| [6] | Boschetti M, Boschetti L, Oliveri S, Casati L, Canova I ( 2007) Tree species mapping with airborne hyper-spectral MIVIS data, the Ticino Park study case. Journal of Remote Sensing, 28, 1251-1261. |
| [7] | Cao JJ, Leng WC, Liu K, Liu L, He Z, Zhu YH ( 2018) Object-based mangrove species classification using unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral images and digital surface models. Remote Sensing, 10, 89. |
| [8] | Ceamanos X, Waske B, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J, Fauvel M, Sveinsson JR ( 2010) A classifier ensemble based on fusion of support vector machines for classifying hyperspectral data. International Journal of Image and Data Fusion, 1, 293-307. |
| [9] | Chen XY, Yun T, Xue LF, Liu YA ( 2019) Classification of tree species using LiDAR point cloud data. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 56, 122801. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈向宇, 云挺, 薛联凤, 刘应安 ( 2019) 基于激光雷达点云数据的树种分类研究. 激光与光电子学进展, 56, 122801.] | |
| [10] | Chenari A, Erfanifard Y, Dehghani M, Pourghasemi HR ( 2017) Woodland mapping at single-tree levels using object-oriented classification of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images. In: ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-4/W4, 43-49. |
| [11] | Cheng JH, Bo YC, Zhu YX, Ji XL ( 2014) A novel method for assessing the segmentation quality of high-spatial resolution remote-sensing images. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35, 3816-3839. |
| [12] | Chi YF, Lai RW, Yu LL, Zhang ZJ, Su YQ, Ying XL ( 2017) Extracting tree species distribution with Landsat 8 OLI data. Journal of Natural Resources, 32, 1193-1203. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 池毓锋, 赖日文, 余莉莉, 张泽均, 苏艳琴, 应兴亮 ( 2017) 基于Landsat 8 OLI数据的树种类型分布提取. 自然资源学报, 32, 1193-1203.] | |
| [13] | Cho MA, Mathieu R, Asner GP, Naidoo L, van Aardt J, Ramoelo A, Debba P, Wessels K, Main R, Smit IPJ, Erasmus B ( 2012) Mapping tree species composition in South African savannas using an integrated airborne spectral and LiDAR system. Remote Sensing of Environment, 125, 214-226. |
| [14] | Clark ML, Roberts DA, Clark DB ( 2005) Hyperspectral discrimination of tropical rain forest tree species at leaf to crown scales. Remote Sensing of Environment, 96, 375-398. |
| [15] | Colgan MS, Baldeck CA, Feret JB, Asner GP ( 2012) Mapping savanna tree species at ecosystem scales using support vector machine classification and BRDF correction on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sensing, 4, 3462-3480. |
| [16] | Coops NC, Hilker T, Wulder MA, St-Onge B, Newnham G ( 2007) Estimating canopy structure of Douglas-fir forest stands from discrete-return LiDAR. Trees-Structure and Function, 21, 295-310. |
| [17] | Culvenor DS, Coops N, Preston R, Tolhurst KG ( 1999) A spatial clustering approach to automated tree crown delineation. In: International Forum on Automated High Resolution Digital Imagery for Forestry (eds Hill DA, Leckie DG), pp.67-80. Natural Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service, Pacific Forestry Centre, Victoria, Canada. |
| [18] | da Luz BR, Crowley JK ( 2007) Spectral reflectance and emissivity features of broad leaf plants: Prospects for remote sensing in the thermal infrared (8.0-14.0 μm). Remote Sensing of Environment, 109, 393-405. |
| [19] | da Luz BR, Crowley JK ( 2010) Identification of plant species by using high spatial and spectral resolution thermal infrared (8.0-13.5 μm) imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114, 404-413. |
| [20] | Dalponte M, Bruzzone L, Gianelle D ( 2008) Fusion of hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data for classification of complex forest areas. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 46, 1416-1427. |
| [21] | Dalponte M, Bruzzone L, Gianelle D ( 2012) Tree species classification in the Southern Alps based on the fusion of very high geometrical resolution multispectral/hyperspectral images and LiDAR data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 123, 258-270. |
| [22] | Dalponte M, Ørka HO, Ene LT, Gobakken T, Næsset E ( 2014) Tree crown delineation and tree species classification in boreal forests using hyperspectral and ALS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140, 306-317. |
| [23] | Dalponte M, Ørka HO, Gobakken T, Gianelle D, Næsset E ( 2013) Tree species classification in boreal forests with hyperspectral data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51, 2632-2645. |
| [24] | Dhodhi MK, Saghri JA, Ahmad I, Ul-Mustafa R ( 1999) D-ISODATA, a distributed algorithm for unsupervised classification of remotely sensed data on network of workstations. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 59, 280-301. |
| [25] | Dickinson C, Siqueira P, Clewley D, Lucas R ( 2013) Classification of forest composition using polarimetric decomposition in multiple landscapes. Remote Sensing of Environment, 131, 206-214. |
| [26] | Du PJ, Xia JS, Xue ZH, Tan K, Su HJ, Bao R ( 2016) Review of hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20, 236-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜培军, 夏俊士, 薛朝辉, 谭琨, 苏红军, 鲍蕊 ( 2016) 高光谱遥感影像分类研究进展. 遥感学报, 20, 236-256.] | |
| [27] | Dymond CC, Mladenoff DJ, Radeloff VC ( 2002) Phenological differences in Tasseled Cap indices improve deciduous forest classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 80, 460-472. |
| [28] | Engler R, Waser LT, Zimmermann NE, Schaub M, Berdos S, Ginzler C, Psomas A ( 2013) Combining ensemble modeling and remote sensing for mapping individual tree species at high spatial resolution. Forest Ecology & Management, 310, 64-73. |
| [29] | Fan X, Liu QW, Tan BX ( 2017) Classification of forest species using airborne PHI hyperspectral data. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 29(2), 110-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 樊雪, 刘清旺, 谭炳香 ( 2017) 基于机载PHI高光谱数据的森林优势树种分类研究. 国土资源遥感, 29(2), 110-116.] | |
| [30] | Fassnacht FE, Latifi H, Stereńczak K, Modzelewska A, Lefsky M, Waser LT, Straub C, Ghosh A ( 2016) Review of studies on tree species classification from remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 186, 64-87. |
| [31] | Fassnacht FE, Neumann C, Forster M, Buddenbaum H, Ghosh A, Clasen A, Joshi PK, Koch B ( 2014) Comparison of feature reduction algorithms for classifying tree species with hyperspectral data on three central European test sites. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7, 2547-2561. |
| [32] | Feng JL, Liu K, Zhu YH, Li Y, Liu L, Meng L ( 2015) Application of unmanned aerial vehicles to mangrove resources monitoring. Tropical Geography, 35, 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯家莉, 刘凯, 朱远辉, 李勇, 柳林, 蒙琳 ( 2015) 无人机遥感在红树林资源调查中的应用. 热带地理, 35, 35-42.] | |
| [33] | Féret JB, Asner GP ( 2012) Semi-supervised methods to identify individual crowns of lowland tropical canopy species using imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 4, 2457-2476. |
| [34] | Féret JB, Asner GP ( 2013) Tree species discrimination in tropical forests using airborne imaging spectroscopy. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51, 73-84. |
| [35] | Ferreira MP, Wagner FH, Aragao LEOC, Shimabukuro YE, de Souza CR ( 2019) Tree species classification in tropical forests using visible to shortwave infrared WorldView-3 images and texture analysis. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 149, 119-131. |
| [36] | Ferreira MP, Zortea M, Zanotta DC, Shimabukuro YE, de Souza CR ( 2016) Mapping tree species in tropical seasonal semi-deciduous forests with hyperspectral and multispectral data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 179, 66-78. |
| [37] | Franklin SE, Ahmed OS ( 2018) Deciduous tree species classification using object-based analysis and machine learning with unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39, 5236-5245. |
| [38] | Franklin SE, Ahmed OS, Griffin W ( 2017) Northern conifer forest species classification using multispectral data acquired from an unmanned aerial vehicle. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 83, 501-507. |
| [39] | Friedl MA, Brodley CE ( 1997) Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 61, 399-409. |
| [40] | Fu F, Wang XJ, Wang J, Wang N, Tong JH ( 2019) Tree species and age groups classification based on GF-2 Image. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 31(2), 118-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 傅锋, 王新杰, 汪锦, 王娜, 佟济宏 ( 2019) 高分二号影像树种识别及龄组划分. 国土资源遥感, 31(2), 118-124.] | |
| [41] | Gao BC, Goetz AFH ( 1990) Column atmospheric water vapor and vegetation liquid water retrievals from airborne imaging spectrometer data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95, 3549-3564. |
| [42] | Gao S, Shen X, Dai JS, Cao L ( 2018) Tree species classification in urban forests based on LiDAR point cloud segmentation and hyperspectral metrics extraction. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33, 1073-1083. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 皋厦, 申鑫, 代劲松, 曹林 ( 2018) 结合LiDAR单木分割和高光谱特征提取的城市森林树种分类. 遥感技术与应用, 33, 1073-1083.] | |
| [43] | Getzin S, Wiegand K, Schoning I ( 2012) Assessing biodiversity in forests using very high-resolution images and unmanned aerial vehicles. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 397-404. |
| [44] | Ghosh A, Fassnacht FE, Joshi PK, Koch B ( 2014) A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: Role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 26, 49-63. |
| [45] | Gini R, Passoni D, Pinto L, Sona G ( 2014) Use of unmanned aerial systems for multispectral survey and tree classification, a test in a park area of northern Italy. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 47, 251-269. |
| [46] | Gomez-Chova L, Tuia D, Moser G, Camps-Valls G ( 2015) Multimodal classification of remote sensing images: A review and future directions. Proceedings of the IEEE, 103, 1560-1584. |
| [47] | Guo QH, Liu J, Li YM, Zhai QP, Wang YC, Wu FF, Hu TY, Wan HW, Liu HM, Shen WM ( 2016) A near-surface remote sensing platform for biodiversity monitoring: Perspectives and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1249-1266. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭庆华, 刘瑾, 李玉美, 翟秋萍, 王永财, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 万华伟, 刘慧明, 申文明 ( 2016) 生物多样性近地面遥感监测: 应用现状与前景展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1249-1266.] | |
| [48] | Guo QH, Liu J, Tao SL, Xue BL, Li L, Xu GC, Li WK, Wu FF, Li YM, Chen LH, Pang SX ( 2014) Perspectives and prospects of LiDAR in forest ecosystem monitoring and modeling. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 459-478. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭庆华, 刘瑾, 陶胜利, 薛宝林, 李乐, 徐光彩, 李文楷, 吴芳芳, 李玉美, 陈琳海, 庞树鑫 ( 2014) 激光雷达在森林生态系统监测模拟中的应用现状与展望. 科学通报, 59, 459-478.] | |
| [49] | Hesketh M, Sánchez-Azofeifa GA ( 2012) The effect of seasonal spectral variation on species classification in the Panamanian tropical forest. Remote Sensing of Environment, 118, 73-82. |
| [50] | Hill RA, Wilson AK, George M, Hinsley SA ( 2010) Mapping tree species in temperate deciduous woodland using time- series multi-spectral data. Applied Vegetation Science, 13, 86-99. |
| [51] | Holmgren J, Persson A, Soderman U ( 2008) Species identification of individual trees by combining high resolution LiDAR data with multi-spectral images. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, 1537-1552. |
| [52] | Hong DY ( 2016) Biodiversity pursuits need a scientific and operative species concept. Biodiversity Science, 24, 979-999. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 洪德元 ( 2016) 生物多样性事业需要科学、可操作的物种概念. 生物多样性, 24, 979-999.] | |
| [53] | Hortal J, de Bello F, Diniz-Filho JAF, Lewinsohn TM, Lobo JM, Ladle RJ ( 2015) Seven shortfalls that beset large-scale knowledge of biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 46, 523-549. |
| [54] | Hovi A, Korhonen L, Vauhkonen J, Korpela I ( 2016) LiDAR waveform features for tree species classification and their sensitivity to tree- and acquisition related parameters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 173, 224-237. |
| [55] | Hu JB, Zhang J ( 2018) Unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing in ecology: Advances and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 20-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡健波, 张健 ( 2018) 无人机遥感在生态学中的应用进展. 生态学报, 38, 20-30.] | |
| [56] | Hughes GP ( 1968) On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 14, 55-63. |
| [57] | Hung C, Xu Z, Sukkarieh S ( 2014) Feature learning based approach for weed classification using high resolution aerial images from a digital camera mounted on a UAV. Remote Sensing, 6, 12037-12054. |
| [58] | Immitzer M, Atzberger C, Koukal T ( 2012 a) Suitability of WorldView-2 data for tree species classification with special emphasis on the four new spectral bands. Photogrammetrie Fernerkundung Geoinformation, 5, 573-588. |
| [59] | Immitzer M, Atzberger C, Koukal T ( 2012 b) Tree species classification with random forest using very high spatial resolution 8-Band WorldView-2 satellite data. Remote Sensing, 4, 2661-2693. |
| [60] | Jennings MD ( 2000) Gap analysis, concepts, methods, and recent results. Landscape Ecology, 15, 5-20. |
| [61] | Jia MM, Zhang YZ, Wang ZM, Song KS, Ren CY ( 2014) Mapping the distribution of mangrove species in the core zone of Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong, using hyperspectral data and high-resolution data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 33, 226-231. |
| [62] | Johansen K, Phinn S ( 2006) Mapping structural parameters and species composition of riparian vegetation using IKONOS and landsat ETM+ data in Australian tropical savannahs. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 72, 71-80. |
| [63] | Jones TG, Coops NC, Sharma T ( 2010) Assessing the utility of airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data for species distribution mapping in the coastal Pacific Northwest, Canada. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114, 2841-2852 |
| [64] | Kamal M, Phinn SR ( 2011) Hyperspectral data for mangrove species mapping, a comparison of pixel-based and object-based approach. Remote Sensing, 3, 2222-2242. |
| [65] | Ke YH, Quackenbush LJ, Im J ( 2010) Synergistic use of QuickBird multispectral imagery and LiDAR data for object-based forest species classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114, 1141-1154. |
| [66] | Kim S, Mcgaughey RJ, Andersen HE, Schreuder G ( 2009) Tree species differentiation using intensity data derived from leaf-on and leaf-off airborne laser scanner data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113, 1575-1586. |
| [67] | Koukal T, Atzberger C, Schneider W ( 2014) Evaluation of semi-empirical BRDF models inverted against multi-angle data from a digital airborne frame camera for enhancing forest type classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 151, 27-43. |
| [68] | Leckie DG, Ranson KJ ( 1998) Forestry applications using imaging radar. In: Principles and Applications of Imaging Radar, 3rd edn. (eds Henderson FM, Lewis AJ), pp. 435- 509. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, USA. |
| [69] | Lefsky MA, Cohen WB, Parker GG, Harding DJ ( 2002) LiDAR remote sensing for ecosystem studies. BioScience, 52, 19-30. |
| [70] | Li X, Liu K, Zhu YH, Meng L, Yu CX, Cao JJ ( 2018) Study on mangrove species classification based on ZY-3 image. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33, 360-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李想, 刘凯, 朱远辉, 蒙琳, 于晨曦, 曹晶晶 ( 2018) 基于资源三号影像的红树林物种分类研究. 遥感技术与应用, 33, 360-369.] | |
| [71] | Li XC, Bao YS, Xu XG, Jin XL, Zhang JC, Song XY ( 2013) New vegetation index fusing visible-infrared and shortwave infrared spectral feature for winter wheat LAI retrieval. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 33, 2398-2402. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李鑫川, 鲍艳松, 徐新刚, 金秀良, 张竞成, 宋晓宇 ( 2013) 融合可见光-近红外与短波红外特征的新型植被指数估算冬小麦LAI. 光谱学与光谱分析, 33, 2398-2402.] | |
| [72] | Liu LX, Coops NC, Aven NW, Pang Y ( 2017) Mapping urban tree species using integrated airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 200, 170-182. |
| [73] | Lu B, He YH ( 2017) Species classification using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-acquired high spatial resolution imagery in a heterogeneous grassland. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 128, 73-85. |
| [74] | Lu DS, Weng QH ( 2007) A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28, 823-870. |
| [75] | Lucas R, Bunting P, Paterson M, Chisholm L ( 2008) Classification of Australian forest communities using aerial photography, CASI and HyMap data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 2088-2103. |
| [76] | Madonsela S, Cho MA, Mathieu R, Mutanga O, Ramoelo A, Kaszta Z, van de Kerchove R, Wolff E ( 2017) Multi-phenology WorldView-2 imagery improves remote sensing of savannah tree species. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 58, 65-73. |
| [77] | Maghsoudi Y, Collins M, Leckie DG ( 2012) Polarimetric classification of boreal forest using nonparametric feature selection and multiple classifiers. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations & Geoinformation, 19, 139-150. |
| [78] | Malahlela OE, Cho MA, Mutanga O ( 2015) Mapping the occurrence of Chromolaena odorata (L.) in subtropical forest gaps using environmental and remote sensing data. Biological Invasion, 17, 2027-2042. |
| [79] | Mallinis G, Koutsias N, Tsakiri-Strati M, Karteris M ( 2008) Object-based classification using Quickbird imagery for delineating forest vegetation polygons in a Mediterranean test site. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 63, 237-250. |
| [80] | Mao XG, Chen WQ, Wei JY, Fan WY ( 2017) Effect and evaluation of segmentation scale on object-based forest species classification. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(12), 73-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛学刚, 陈文曲, 魏晶昱, 范文义 ( 2017) 分割尺度对面向对象树种分类的影响及评价. 林业科学, 53(12), 73-83.] | |
| [81] | Matsuki T, Yokoya N, Iwasaki A ( 2015) Hyperspectral tree species classification of Japanese complex mixed forest with the aid of LiDAR data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 8, 2177-2187. |
| [82] | Michez A, Piegay H, Jonathan L, Claessens H, Lejeune P ( 2015) Mapping of riparian invasive species with supervised classification of Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation & Geoinformation, 44, 88-94. |
| [83] | Michez A, Piegay H, Lisein J, Claessens H, Lejeune P ( 2016) Classification of riparian forest species and health condition using multi-temporal and hyperspatial imagery from unmanned aerial system. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 188, 146. |
| [84] | Miyoshi GT, Imai NN, de Moraes MVA, Tommaselli AMG, Näsi R (2017) Time series of images to improve tree species classification. In: ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-3/W3, 123-128. |
| [85] | Naidoo L, Cho MA, Mathieu R, Asner G ( 2012) Classification of savanna tree species, in the Greater Kruger National Park region, by integrating hyperspectral and LiDAR data in a Random Forest data mining environment. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 69, 167-179. |
| [86] | Onishi M, Ise T ( 2018) Automatic classification of trees using a UAV onboard camera and deep learning. arXiv, 1804. 10390. |
| [87] | Pant P, Heikkinen V, Hovi A, Korpela I, Hauta-Kasari M, Tokola T ( 2013) Evaluation of simulated bands in airborne optical sensors for tree species identification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 138, 27-37. |
| [88] | Pu RL, Landry S ( 2012) A comparative analysis of high spatial resolution IKONOS and WorldView-2 imagery for mapping urban tree species. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 516-533. |
| [89] | Puletti N, Perria R, Storchi P ( 2014) Unsupervised classification of very high remotely sensed images for grapevine rows detection. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 47, 45-54. |
| [90] | Puttonen E, Suomalainen J, Hakala T, Raikkonen E, Kaartinen H, Kaasalainen S, Litkey P ( 2010) Tree species classification from fused active hyperspectral reflectance and LIDAR measurements. Forest Ecology and Management, 260, 1843-1852. |
| [91] | Qian YR, Jia ZH, Yu J, Yang F, Duan WL ( 2011) Application of BP-ANN to classification of hyperspectral grassland in desert. Computer Engineering and Applications, 47(12), 225-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 钱育蓉, 贾振红, 于炯, 杨峰, 段文亮 ( 2011) BP-ANN在荒漠草地高光谱分类研究中的应用. 计算机工程与应用, 47(12), 225-228.]
DOI |
|
| [92] | Ranson KJ, Sun GQ ( 1994) Northern forest classification using temporal multifrequency and multipolarimetric SAR images. Remote Sensing of Environment, 47, 142-153. |
| [93] | Reitberger J, Krzystek P, Stilla U ( 2008) Analysis of full waveform LIDAR data for the classification of deciduous and coniferous trees. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, 1407-1431. |
| [94] | Riaño D, Chuvieco E, Condes S, Gonzalez-Matesanz J, Ustin SL ( 2004) Generation of crown bulk density for Pinus sylvestris L. from LiDAR. Remote Sensing of Environment, 92, 345-352. |
| [95] | Rollet R, Benie GB, Li W, Wang S, Boucher JM ( 1998) Image classification algorithm based on the RBF neural network and K-means. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19, 3003-3009. |
| [96] | Saatchi S, Buermann W, Ter Steege H, Mori S, Smith TB ( 2008) Modeling distribution of Amazonian tree species and diversity using remote sensing measurements. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 2000-2017. |
| [97] | Saatchi S, Rignot E ( 1997) Classification of boreal forest cover types using SAR images. Remote Sensing of Environment, 60, 270-281. |
| [98] | Salisbury JW ( 1986) Preliminary measurements of leaf spectral reflectance in the 8-14 μm region. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 7, 1879-1886. |
| [99] | Salisbury JW, Milton NM ( 1988) Thermal infrared (2.5- to 13.5-micrometer) directional hemispherical reflectance of leaves. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 54, 1301-1304. |
| [100] | Schneider FD, Morsdorf F, Schmid B, Petchey OL, Hueni A, Schimel DS, Schaepman ME ( 2017) Mapping functional diversity from remotely sensed morphological and physiological forest traits. Nature Communications, 8, 1441-1452. |
| [101] | Settle JJ, Briggs SA ( 1987) Fast maximum-likelihood classification of remotely sensed imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 8, 723-734. |
| [102] | Shang X, Chisholm LA ( 2014) Classification of Australian native forest species using hyperspectral remote sensing and machine-learning classification algorithms. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7, 2481-2489. |
| [103] | Skovsen S, Dyrmann M, Mortensen AK, Steen KA, Green O, Eriksen J, Gislum R, Jorgensen RN, Karstoft H ( 2017) Estimation of the botanical composition of clover-grass leys from RGB images using data simulation and fully convolutional neural networks. Sensors, 17, 2930-2947. |
| [104] | Sun C, Liu YX, Zhao SS, Zhou MX, Yang YH, Li FX ( 2016) Classification mapping and species identification of salt marshes based on a short-time interval NDVI time-series from HJ-1 optical imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 45, 27-41. |
| [105] | Suratno A, Seielstad C, Queen L ( 2009) Tree species identification in mixed coniferous forest using airborne laser scanning. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 64, 683-693. |
| [106] | Sutton SL ( 2001) Alice grows up, canopy science in transition from wonderland to reality. Plant Ecology, 153, 13-21. |
| [107] | Tang LN, Shao GF ( 2015) Drone remote sensing for forestry research and practices. Journal of Forestry Research, 26, 791-797. |
| [108] | Tang ZY, Jiang MW, Zhang J, Zhang XY ( 2018) Applications of satellite and air-borne remote sensing in biodiversity research and conservation. Biodiversity Science, 26, 807-818. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐志尧, 蒋旻炜, 张健, 张新悦 ( 2018) 航空航天遥感在物种多样性研究与保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 26, 807-818.] | |
| [109] | Tao JY, Liu LJ, Pang Y, Li DQ, Feng YY, Wang X, Ding YL, Peng Q, Xiao WH ( 2018) Automatic identification of tree species based on airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 35, 314-323. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陶江玥, 刘丽娟, 庞勇, 李登秋, 冯云云, 王雪, 丁友丽, 彭琼, 肖文惠 ( 2018) 基于机载激光雷达和高光谱数据的树种识别方法. 浙江农林大学学报, 35, 314-323.] | |
| [110] | Teng WX, Wen XR, Wang N, Shi HH ( 2019) Tree species classification and mapping using deep transfer learning with unmanned aerial vehicle high resolution image. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 56(7), 227-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 滕文秀, 温小荣, 王妮, 施慧慧 ( 2019) 基于深度迁移学习的无人机高分影像树种分类与制图. 激光与光电子学进展, 56(7), 227-286.] | |
| [111] | Trier ØD, Salberg AB, Kermit M, Rudjord Ø, Gobakken T, Naesset E, Aarsten D ( 2018) Tree species classification in Norway from airborne hyperspectral and airborne laser scanning data. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 51, 336-351. |
| [112] | Turner W ( 2014) Sensing biodiversity. Science, 346, 301-302. |
| [113] | Turner W, Spector S, Gardiner N, Fladeland M, Sterling E, Steininger M ( 2003) Remote sensing for biodiversity science and conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 306-314. |
| [114] | Ullah S, Schlerf M, Skidmore AK, Hecker C ( 2012) Identifying plant species using mid-wave infrared (2.5-6 μm) and thermal infrared (8-14 μm) emissivity spectra. Remote Sensing of Environment, 118, 95-102. |
| [115] | Urban MC ( 2015) Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science, 348, 571-573. |
| [116] | Valderrama-Landeros L, Flores-de-Santiago F, Kovacs JM, Flores-Verdugo F ( 2018) An assessment of commonly employed satellite-based remote sensors for mapping mangrove species in Mexico using an NDVI-based classification scheme. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 190, 23. |
| [117] | Voss M, Sugumaran R ( 2008) Seasonal effect on tree species classification in an urban environment using hyperspectral data, LiDAR, and an object-oriented approach. Sensors, 8, 3020-3036. |
| [118] | Wang EL, Li CJ, Zhou JP, Peng DL, Hu HT, Dong X ( 2017) Classification of Beijing afforestation species based on multi-temporal images. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 43, 710-718. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王二丽, 李存军, 周静平, 彭代亮, 胡海棠, 董熙 ( 2017) 基于多时相遥感影像的北京平原人工林树种分类. 北京工业大学学报, 43, 710-718.] | |
| [119] | Wang SH, Yang T ( 2018) Hyperspectral image dimension reduction based on manifold learning approach DLA and tree species classification. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 1, 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 汪少华, 杨婷 ( 2018) 判别流形学习算法的高光谱数据降维与树种识别. 测绘通报, 1, 55-61.] | |
| [120] | Wang T, Xu XD, Dong YL, Zhang L, Su W ( 2009) Present state and development trends of synthetic aperture radar. Ship Electronic Engineering, 29(5), 5-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王腾, 徐向东, 董云龙, 张莉, 苏伟 ( 2009) 合成孔径雷达的发展现状和趋势. 舰船电子工程, 29(5), 5-9.] | |
| [121] | Wang T, Zhang HS, Lin H, Fang CY ( 2016) Textural-spectral feature-based species classification of mangroves in Mai Po Nature Reserve from WorldView-3 imagery. Remote Sensing, 8, 24. |
| [122] | Waser LT, Ginzler C, Kuechler M, Baltsavias E, Hurni L ( 2011) Semi-automatic classification of tree species in different forest ecosystems by spectral and geometric variables derived from Airborne Digital Sensor (ADS40) and RC30 data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115, 76-85. |
| [123] | Wei JY, Mao XG, Fang BY, Bao XJ, Xu ZY ( 2016) Submeter remote sensing image recognition of trees based on Landsat 8 OLI support. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 38(11), 23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏晶昱, 毛学刚, 方本煜, 包晓建, 许振宇 ( 2016) 基于Landsat 8 OLI辅助的亚米级遥感影像树种识别. 北京林业大学学报, 38(11), 23-33.] | |
| [124] | Wright J, Lillesand TM, Kiefer RW ( 1980) Remote sensing and image interpretation. The Geographical Journal, 146, 448-449. |
| [125] | Yan L, Jiang WW ( 2016) Progress in the study of vegetation cover classification of multispectral remote sensing imagery. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 28(2), 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 闫利, 江维薇 ( 2016) 多光谱遥感影像植被覆盖分类研究进展. 国土资源遥感, 28(2), 8-13.]
DOI |
|
| [126] | Yang CH, Everitt JH, Fletcher RS, Jensen RR, Mausel PW ( 2009) Evaluating AISA+ hyperspectral imagery for mapping black mangrove along the South Texas Gulf Coast. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 75, 425-435. |
| [127] | Yang KM, Liu F, Sun YY, Wei HF, Shi GQ ( 2015) Classification algorithm of hyperspectral imagery by harmonic analysis and spectral angle mapping. Journal of Image and Graphics, 20, 836-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨可明, 刘飞, 孙阳阳, 魏华锋, 史钢强 ( 2015) 谐波分析光谱角制图高光谱影像分类. 中国图象图形学报, 20 , 836-844.] | |
| [128] | Yang XH, Rochdi N, Zhang JK, Banting J, Rolfson D, King C, Staenz K, Patterson S, Purdy B ( 2014) Mapping tree species in a boreal forest area using RapidEye and LiDAR data. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 69-71. |
| [129] | Yin LY, Qin XL, Sun GF, Zu XF, Chen XZ ( 2016) Tree species identification method based on GF-2 images. Forest Resources Management, 4, 121-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尹凌宇, 覃先林, 孙桂芬, 祖笑锋, 陈小中 ( 2016) 基于高分二号多光谱数据的树种识别方法. 林业资源管理, 4, 121-127.] | |
| [130] | Youngentob KN, Roberts DA, Held AA, Dennison PE, Jia XP, Lindenmayer DB ( 2011) Mapping two Eucalyptus subgenera using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis and continuum-removed imaging spectrometry data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 115, 1115-1128. |
| [131] | Yu LK, Yu Y, Liu XY, Du YC, Zhang H ( 2016) Tree species classification with hyperspectral image. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 44(9), 40-43, 57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于丽柯, 于颖, 柳向宇, 杜一尘, 张涵 ( 2016) 基于高光谱影像的树种分类. 东北林业大学学报, 44(9), 40-43, 57.] | |
| [132] | Yu XW, Hyyppa J, Litkey P, Kaartinen H, Vastaranta M, Holopainen M ( 2017) Single-sensor solution to tree species classification using multispectral airborne laser scanning. Remote Sensing, 9, 108. |
| [133] | Zhang CY, Qiu F ( 2012) Mapping individual tree species in an urban forest using airborne LiDAR data and hyperspectral imagery. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 78, 1079-1087. |
| [134] | Zhang J ( 2017) Biodiversity science and macroecology in the era of big data. Biodiversity Science, 25, 355-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张健 ( 2017) 大数据时代的生物多样性科学与宏生态学. 生物多样性, 25, 355-363.] | |
| [135] | Zhang JK, Rivard B, Sanchez-Azofeifa A, Castro-Esau K ( 2006) Intra- and inter-class spectral variability of tropical tree species at La Selva, Costa Rica, implications for species identification using HYDICE imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 105, 129-141. |
| [136] | Zhang YJ, Fan CK, Huang K, Liu YJ, Zu JX, Zhu JT ( 2017) Opportunities and challenges in remote sensing applications to ecosystem ecology. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 809-823. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张扬建, 范春捆, 黄珂, 刘瑶杰, 俎佳星, 朱军涛 ( 2017) 遥感在生态系统生态学上应用的机遇与挑战. 生态学杂志, 36, 809-823.] | |
| [137] | Zhao YJ, Zeng Y, Zheng ZJ, Dong WX, Zhao D, Wu BF, Zhao QJ ( 2018) Forest species diversity mapping using airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data in a subtropical forest in China. Remote Sensing of Environment, 213, 104-114. |
| [138] | Zhu HW, Basir O ( 2005) An adaptive fuzzy evidential nearest neighbor formulation for classifying remote sensing images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 43, 1874-1889. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn