



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 888-895. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016079 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016079
张静1,4, 李渊2, 宋娜1, 林龙山2, 高天翔3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-03-22
接受日期:2016-05-13
出版日期:2016-08-20
发布日期:2016-09-02
通讯作者:
高天翔
基金资助:
Jing Zhang1,4, Yuan Li2, Na Song1, Longshan Lin2, Tianxiang Gao3,*( )
)
Received:2016-03-22
Accepted:2016-05-13
Online:2016-08-20
Published:2016-09-02
Contact:
Gao Tianxiang
摘要:
利用DNA条形码技术对中国沿海分布的6种棱鳀属(Thryssa)鱼类样品进行了物种鉴定, 并每种取5尾用于探讨该属系统发育关系。结果显示: 棱鳀属鱼类的主要形态鉴别特征为上颌骨伸达位置和第一鳃耙的下鳃耙数量。在525 bp的目的片段上有175个变异位点, 其中简约信息位点172个, 单一信息位点3个, 无插入缺失现象, 转换数为182, 颠换数为57。A+T含量明显高于G+C含量, 并且表现出明显的反G偏倚。结合GenBank中相关的同源序列进行比较发现, 所有序列明显分为10个组群, 表明已提交的棱鳀属鱼类COI基因序列中仍存在一定的问题。从各组群间的遗传距离和氨基酸遗传差异水平可以看出, 10个组群应为不同的有效种, 但是否存在隐存种还有待于进一步确定。从NJ树上可以看出, 长颌棱鳀(T. setirostris)是最先分化出的物种, 保持着最原始的特征, 而中颌棱鳀(T. mystax)与黄吻棱鳀(T. vitrirostris)聚类到一起, 二者间存在共享单倍型。棱鳀属鱼类最早分化于中新世早期。在今后的研究中仍需要结合更多的分子标记对中颌棱鳀和黄吻棱鳀的分类地位作进一步的探讨。
张静, 李渊, 宋娜, 林龙山, 高天翔 (2016) 我国沿海棱鳀属鱼类的物种鉴定与系统发育. 生物多样性, 24, 888-895. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016079.
Jing Zhang, Yuan Li, Na Song, Longshan Lin, Tianxiang Gao (2016) Species identification and phylogenetic relationship of Thryssa species in the coastal waters of China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 888-895. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016079.
| 种名 Species | 本研究 This study | 引用序列号 Accession no. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地点 Sampling sites | 采样时间 Sampling time | 编号 Number | ||
| 赤鼻棱鳀 T. kammalensis | 福建省晋江市 Jinjiang, Fujian | 2014.3 | CB1-CB5 | EF607590-607596, JN813096, JQ738607-738609, KF951618, KP260469, KP260453 |
| 中颌棱鳀 T. mystax | 山东省东营市 Dongying, Shandong | 2009.10 | ZH1-ZH5 | ——— |
| 杜氏棱鳀 T. dussumieri | 福建省漳州市 Zhangzhou, Fujian | 2013.5 | DS1-DS5 | JX983287-983289 |
| 长颌棱鳀 T. setirostris | 福建省泉州市 Quanzhou, Fujian | 2013.5 | CH1-CH5 | EF607597-607599, EU541324, JF494684-494688 |
| 汉氏棱鳀 T. hamiltonii | 福建省晋江市 Jinjiang, Fujian | 2013.11 | HS1-HS5 | EF607588, EF607589, JQ681498, EU148567-148570 |
| 黄吻棱鳀 T. vitrirostris | 广东省江门市 Jiangmen, Guangdong | 2013.3 | HW1-HW5 | JF494689-494693 |
表1 研究所用棱鳀属鱼类样品和相关序列信息
Table 1 Information of Thryssa samples and sequences in this study
| 种名 Species | 本研究 This study | 引用序列号 Accession no. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地点 Sampling sites | 采样时间 Sampling time | 编号 Number | ||
| 赤鼻棱鳀 T. kammalensis | 福建省晋江市 Jinjiang, Fujian | 2014.3 | CB1-CB5 | EF607590-607596, JN813096, JQ738607-738609, KF951618, KP260469, KP260453 |
| 中颌棱鳀 T. mystax | 山东省东营市 Dongying, Shandong | 2009.10 | ZH1-ZH5 | ——— |
| 杜氏棱鳀 T. dussumieri | 福建省漳州市 Zhangzhou, Fujian | 2013.5 | DS1-DS5 | JX983287-983289 |
| 长颌棱鳀 T. setirostris | 福建省泉州市 Quanzhou, Fujian | 2013.5 | CH1-CH5 | EF607597-607599, EU541324, JF494684-494688 |
| 汉氏棱鳀 T. hamiltonii | 福建省晋江市 Jinjiang, Fujian | 2013.11 | HS1-HS5 | EF607588, EF607589, JQ681498, EU148567-148570 |
| 黄吻棱鳀 T. vitrirostris | 广东省江门市 Jiangmen, Guangdong | 2013.3 | HW1-HW5 | JF494689-494693 |
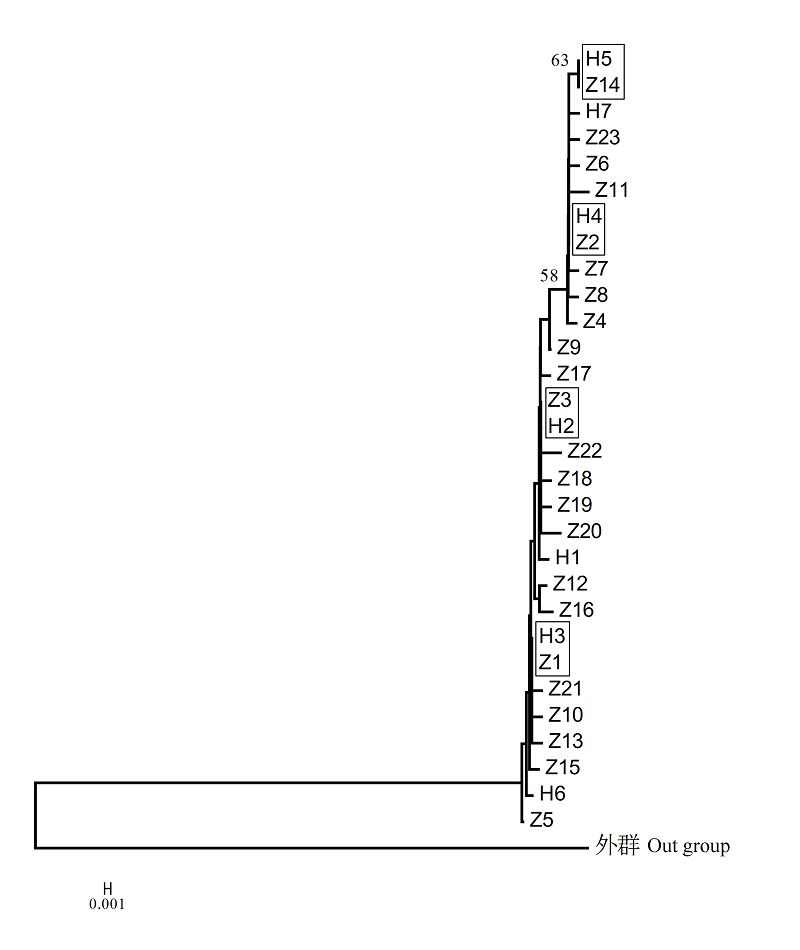
图1 基于单倍型构建黄吻棱鳀和中颌棱鳀的邻接系统发育树(方框内为共享单倍型)
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of Thryssa vitrirostris and T. mystax based on all haplotypes. Shared haplotypes are in the box.
| 种类 Species | 碱基组成 Nucleotide composition (%) | 单倍型数量 Number of haplotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T(U) | C | A | G | ||
| 赤鼻棱鳀 T. kammalensis | 31.6 | 25.3 | 25.5 | 17.5 | 1 |
| 中颌棱鳀 T. mystax | 30.3 | 26.1 | 26.1 | 17.5 | 2 |
| 杜氏棱鳀 T. dussumieri | 28.4 | 26.2 | 26.6 | 18.8 | 2 |
| 长颌棱鳀 T. setirostris | 28.8 | 27.1 | 25.3 | 18.9 | 2 |
| 汉氏棱鳀 T. hamiltonii | 30.3 | 25.1 | 25.0 | 19.6 | 2 |
| 黄吻棱鳀 T. vitrirostris | 30.3 | 26.1 | 26.1 | 17.5 | 3 |
| 平均 Average | 29.9 | 26.1 | 25.5 | 18.5 | - |
表3 6种棱鳀属鱼类线粒体COI片段的碱基组成及单倍型数量
Table 3 Base composition and number of haplotypes of mitochondrial COI gene segment in six Thryssa species
| 种类 Species | 碱基组成 Nucleotide composition (%) | 单倍型数量 Number of haplotypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T(U) | C | A | G | ||
| 赤鼻棱鳀 T. kammalensis | 31.6 | 25.3 | 25.5 | 17.5 | 1 |
| 中颌棱鳀 T. mystax | 30.3 | 26.1 | 26.1 | 17.5 | 2 |
| 杜氏棱鳀 T. dussumieri | 28.4 | 26.2 | 26.6 | 18.8 | 2 |
| 长颌棱鳀 T. setirostris | 28.8 | 27.1 | 25.3 | 18.9 | 2 |
| 汉氏棱鳀 T. hamiltonii | 30.3 | 25.1 | 25.0 | 19.6 | 2 |
| 黄吻棱鳀 T. vitrirostris | 30.3 | 26.1 | 26.1 | 17.5 | 3 |
| 平均 Average | 29.9 | 26.1 | 25.5 | 18.5 | - |
| 组群1 Group 1 | 组群2 Group 2 | 组群3 Group 3 | 组群4 Group 4 | 组群5 Group 5 | 组群6 Group 6 | 组群7 Group 7 | 组群8 Group 8 | 组群9 Group 9 | 组群10 Group 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群1 Group 1 | 0.001 | 2.83 | 2.75 | 13.58 | 15.75 | 15.25 | 15.33 | 15.08 | 13.92 | 14.50 |
| 组群2 Group 2 | 0.034 | 0.001 | 4.00 | 14.42 | 15.17 | 14.00 | 14.42 | 15.00 | 15.33 | 15.83 |
| 组群3 Group 3 | 0.033 | 0.048 | - | 13.58 | 14.50 | 14.92 | 16.75 | 16.17 | 14.83 | 15.50 |
| 组群4 Group 4 | 0.163 | 0.173 | 0.163 | 0.004 | 15.50 | 16.08 | 17.33 | 14.75 | 16.25 | 16.33 |
| 组群5 Group 5 | 0.189 | 0.182 | 0.174 | 0.186 | 0.002 | 16.83 | 17.83 | 15.83 | 15.42 | 17.00 |
| 组群6 Group 6 | 0.183 | 0.168 | 0.179 | 0.193 | 0.202 | 0.001 | 12.25 | 15.50 | 15.50 | 16.33 |
| 组群7 Group 7 | 0.184 | 0.173 | 0.201 | 0.208 | 0.214 | 0.147 | 0.003 | 14.25 | 15.92 | 16.17 |
| 组群8 Group 8 | 0.181 | 0.180 | 0.194 | 0.177 | 0.190 | 0.186 | 0.171 | 0.003 | 17.42 | 16.08 |
| 组群9 Group 9 | 0.167 | 0.184 | 0.178 | 0.195 | 0.185 | 0.186 | 0.191 | 0.209 | - | 13.67 |
| 组群10 Group 10 | 0.174 | 0.190 | 0.186 | 0.196 | 0.204 | 0.196 | 0.194 | 0.193 | 0.164 | 0.001 |
表4 基于COI基因序列10个组群的组内、组间的遗传距离和分化时间(百万年)
Table 4 Genetic distances within and among groups, the divergence dates between ten groups based on COI gene
| 组群1 Group 1 | 组群2 Group 2 | 组群3 Group 3 | 组群4 Group 4 | 组群5 Group 5 | 组群6 Group 6 | 组群7 Group 7 | 组群8 Group 8 | 组群9 Group 9 | 组群10 Group 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群1 Group 1 | 0.001 | 2.83 | 2.75 | 13.58 | 15.75 | 15.25 | 15.33 | 15.08 | 13.92 | 14.50 |
| 组群2 Group 2 | 0.034 | 0.001 | 4.00 | 14.42 | 15.17 | 14.00 | 14.42 | 15.00 | 15.33 | 15.83 |
| 组群3 Group 3 | 0.033 | 0.048 | - | 13.58 | 14.50 | 14.92 | 16.75 | 16.17 | 14.83 | 15.50 |
| 组群4 Group 4 | 0.163 | 0.173 | 0.163 | 0.004 | 15.50 | 16.08 | 17.33 | 14.75 | 16.25 | 16.33 |
| 组群5 Group 5 | 0.189 | 0.182 | 0.174 | 0.186 | 0.002 | 16.83 | 17.83 | 15.83 | 15.42 | 17.00 |
| 组群6 Group 6 | 0.183 | 0.168 | 0.179 | 0.193 | 0.202 | 0.001 | 12.25 | 15.50 | 15.50 | 16.33 |
| 组群7 Group 7 | 0.184 | 0.173 | 0.201 | 0.208 | 0.214 | 0.147 | 0.003 | 14.25 | 15.92 | 16.17 |
| 组群8 Group 8 | 0.181 | 0.180 | 0.194 | 0.177 | 0.190 | 0.186 | 0.171 | 0.003 | 17.42 | 16.08 |
| 组群9 Group 9 | 0.167 | 0.184 | 0.178 | 0.195 | 0.185 | 0.186 | 0.191 | 0.209 | - | 13.67 |
| 组群10 Group 10 | 0.174 | 0.190 | 0.186 | 0.196 | 0.204 | 0.196 | 0.194 | 0.193 | 0.164 | 0.001 |
| [1] | Bermingham E, McCafferty SS, Martin AP (1997) Fish biogeography and molecular clocks: perspectives from the Panamanian Isthmus. In: Molecular Systematics of Fishes (eds Kocher TD, Stepier CA), pp. 113-126. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [2] | Bloom DD, Lovejoy NR (2012) Molecular phylogenetics reveals a pattern of biome conservatism in New World anchovies (family Engraulidae). Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 25, 701-715. |
| [3] | Chen WT, Ma XH, Shen YJ, Mao YT, He SP (2015) The fish diversity in the upper reaches of the Salween River, Nujiang River, revealed by DNA barcoding. Scientific Reports, Doi: 10.1038/srep17437. |
| [4] | Gao TX, Ji DP, Xiao YS, Xue TQ, Yanagimoto T, Setoguma T (2011) Description and DNA barcoding of a new Sillago species, Sillago sinica (Perciformes: Sillaginidae), from coastal waters of China. Zoological Studies, 50, 254-263. |
| [5] | Guo XW, Tang QS (2000) Consumption and ecological conversion efficiency of Thrissa kammalensis. Journal of Fisheries of China, 24, 422-427. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭学武, 唐启升 (2000) 赤鼻棱鳀的摄食与生态转换效率. 水产学报, 24, 422-427.] | |
| [6] | Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321. |
| [7] | Hyde JR, Vetter RD (2007) The origin, evolution, and diversification of rockfishes of the genus Sebastes (Cuvier). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 44, 790-811. |
| [8] | Jia XP, Li YZ, Li CH, Qiu YS, Gan JL (2004) Environment and Fishery Resources in the Exclusive Economic Zone and the Continental Shelf of South China Sea, pp. 339-542. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [贾晓平, 李永振, 李纯厚, 邱永松, 甘居利 (2004) 南海专属经济区和大陆架渔业生态环境与渔业资源, 339-542. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Ko HL, Wang YT, Chiu TS, Lee MA, Leu MY, Chang KZ, Chen WY, Shao KT (2012) Evaluating the accuracy of morphological identification of larval fishes by applying DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE, 8, e53451. |
| [10] | Krück NC, Tibbetts IR, Ward RD, Johnson JW, Loh WKW, Ovenden JR (2013) Multi-gene barcoding to discriminate sibling species within a morphologically difficult fish genus (Sillago). Fisheries Research, 143, 39-46. |
| [11] | Lavoué S, Miya M, Nishida M (2010) Mitochondrial phylogenomics of anchovies (family Engraulidae) and recurrent origins of pronounced miniaturization in the order Clupeiformes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 480-485. |
| [12] | Li ZY, Jin XS, Zhuang ZM, Su YQ, Tang QS (2007) Food competition of Engraulis japonicus and Thryssa kammalensis from the southern Yellow Sea in spring. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 14, 630-636. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李忠义, 金显仕, 庄志猛, 苏永全, 唐启升 (2007) 南黄海春季鳀和赤鼻棱鳀的食物竞争. 中国水产科学, 14, 630-636.] | |
| [13] | Li Y, Song N, Khan FS, Yanagimoto T, Gao TX (2013) New evidence of morphological characters and DNA barcoding of Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen, 1788). Journal of Fisheries of China, 37, 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李渊, 宋娜, Khan FS, 柳本卓, 高天翔 (2013) 银鲳形态特征与DNA条形码研究. 水产学报, 37, 1-9.] | |
| [14] | Li Y, Zhang LY, Song PQ, Zhong ZH, Zhang R, Gao TX, Lin LS (2014) A new record of Sillago species in Fujian coastal waters—Sillago sinica (Gao and Xue, 2011). Journal of Applied Oceanography, 33, 546-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李渊, 张丽艳, 宋普庆, 钟指挥, 张然, 高天翔, 林龙山 (2014) 福建省沿海鱚属(Sillago)鱼类新记录种——中国鱚(Sillago sinica Gao and Xue, 2011). 应用海洋学学报, 33, 546-552.] | |
| [15] | Ma CY, Ma LB, Ni Y, Shen AL, Zhang Y, Zhang FY, Zhao YL (2010) Phylogenetic relationship of Thryssa inferred from morphologic characteristic and mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene sequences. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 17, 471-476. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马春艳, 马凌波, 倪勇, 沈盎绿, 张永, 张凤英, 赵云龙 (2010) 基于形态特征和线粒体16S rRNA基因序列探讨棱鳀属的系统进化. 中国水产科学, 17, 471-476.] | |
| [16] | Shen YJ, Guan LH, Wang DQ, Gan XN (2016a) DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecology and Evolution, Doi:10.1002/ece3.2060. |
| [17] | Shen YJ, Kang JL, Chen WT, He SP (2016b) DNA barcoding for the identification of common economic aquatic products in Central China and its application for the supervision of the market trade. Food Control, 61, 79-91. |
| [18] | Summerer M, Hanel R, Sturmbauer C (2001) Mitochondrial phylogeny and biogeographic affinities of sea breams of the genus Diplodus (Sparidae). Journal of Fish Biology, 59, 1638-1652. |
| [19] | Sun DR, Chen Z (2013) Fish Retrieval of South China Sea (Volume I), pp. 120-123. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [孙典荣, 陈铮 (2013) 南海鱼类检索 (上册), 120-123. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert PDN (2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360, 1847-1857. |
| [21] | Whitehead PJP, Nelson GJ, Wongratana F (1988) FAO Species Catalogue, Vol. 7: Clupeoid Fishes of the World (suborder Clupeoidei): an Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of the Herrings, Sardines, Pilchards, Sprats, Shads, Anchovies and Wolf-herrings (Part 2): Enggraulidae, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, pp. 305-579. |
| [22] | Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhang ZH, Gao TX (2013) DNA barcodes of eight species in genus Sebastes. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 48, 45-50. |
| [23] | Zhang JB, Hanner R (2012) Molecular approach to the identification of fish in the South China Sea. PLoS ONE, 7, e30621. |
| [24] | Zhang SY (2001) Fauna Sinica: Osteichthyes, Acipenseriformes, Elopiforms, Clupeiformes, Gonorhynchiformes, pp. 137-147. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张世义 (2001) 中国动物志∙硬骨鱼纲: 鲟形目、海鲢目、鲱形目、鼠鱚目, 137-147. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Zhou MY, Chen X, Yang SY (2015) Identification of several fish eggs and larvae by DNA barcoding in Xiamen Water. Marine Environmental Science, 34, 120-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周美玉, 陈骁, 杨圣云 (2015) 采用DNA条形码技术对厦门海域鱼卵、仔稚鱼种类的鉴定. 海洋环境科学, 34, 120-125.] | |
| [26] | Zhu YD. Wu HL, Jin XB, Meng QW, Liu J, Lian ZS, Shen GY, Huang ST, Chen HX, Zhang QY, Li WD, Wu XH (1984) Fish of Fujian (Vol. I), pp. 140-153. Fujian Science and Technology Publishing House, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [朱元鼎, 伍汉霖, 金鑫波, 孟庆闻, 刘基, 连珍水, 沈根媛, 黄少涛, 陈焕新, 张其永, 李婉端, 吴秀鸿 (1984) 福建鱼类志 (上卷), 140-153. 福建科学技术出版社, 福州.] |
| [1] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [2] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [3] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [4] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [5] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [6] | 佟一杰, 张萌娜, 万霞, 杨星科, 白明. 全球锹甲的几何形态学数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1159-1164. |
| [7] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [8] | 王楠, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 杨盼盼, 张欣玥, 赵世伟. 宁南山区不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫群落特征:形态学鉴定与高通量测序法比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| [9] | 王伟, 刘阳. 植物生命之树重建的现状、问题和对策建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 176-188. |
| [10] | 胡芮, 王儒晓, 杜诗雨, 李萌, 邢雨辉, 潘达, 徐海根, 孙红英. 扬州宝应湖底栖大型无脊椎动物的生物多样性及其变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569. |
| [11] | 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙. |
| [12] | 刘山林. DNA条形码参考数据集构建和序列分析相关的新兴技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| [13] | 陈作艺, 许晓静, 朱素英, 翟梦怡, 李扬. 中国沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群的多样性组成及地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 149-158. |
| [14] | 侯勤曦, 慈秀芹, 刘志芳, 徐武美, 李捷. 基于DNA条形码评估西双版纳国家级自然保护区对樟科植物进化历史的保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 217-228. |
| [15] | 刘青青, 董志军. 基于线粒体COI基因分析钩手水母的群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1204-1211. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn