



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 149-158. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018261 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018261
收稿日期:2018-09-28
接受日期:2019-01-27
出版日期:2019-02-20
发布日期:2019-04-16
通讯作者:
李扬
基金资助:
Chen Zuoyi1,2,Xu Xiaojing1,Zhu Suying1,Zhai Mengyi1,Li Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-28
Accepted:2019-01-27
Online:2019-02-20
Published:2019-04-16
Contact:
Li Yang
摘要:
洛氏角毛藻复合群(Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex)指具有与洛氏角毛藻相似形态学特征的物种集合, 它们广泛分布于全球近岸水域。近年国际上关于该复合群的分类学研究取得新进展, 而我国相关研究仍较为滞后。为了弄清我国沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群的物种多样性, 明确物种信息, 厘清种间界限, 为相关研究提供准确的物种鉴定依据, 本研究陆续在中国沿海建立了该复合群的332个单克隆培养株系, 利用光学显微镜、扫描电镜和透射电镜进行了较为详尽的形态学研究, 基于核糖体大亚基编码基因D1-D3区序列, 构建了分子系统学关系。结果表明其形态聚类与分子系统学结论相一致, 显示我国洛氏角毛藻复合群具有较高的物种多样性, 共鉴定到5个物种, 分别是并基角毛藻(C. decipiens)、优美角毛藻(C. elegans)、平孢角毛藻(C. laevisporus)、曼纳角毛藻(C. mannaii)和稀树角毛藻(C. pauciramosus)。研究表明传统认知的光镜下特征, 如群体特征、角毛走势等易变化, 其分类学价值需谨慎应用。角毛的超微结构, 如角毛孔纹的形状、大小、密度等是有效的种间区别特征, 休眠孢子亦是重要的物种识别依据。并基角毛藻和平孢角毛藻在我国沿岸的分布范围最为广泛, 而稀树角毛藻的分布较为有限。
陈作艺, 许晓静, 朱素英, 翟梦怡, 李扬 (2019) 中国沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群的多样性组成及地理分布. 生物多样性, 27, 149-158. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018261.
Chen Zuoyi, Xu Xiaojing, Zhu Suying, Zhai Mengyi, Li Yang (2019) Species diversity and geographical distribution of the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex along the coast of China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 149-158. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018261.
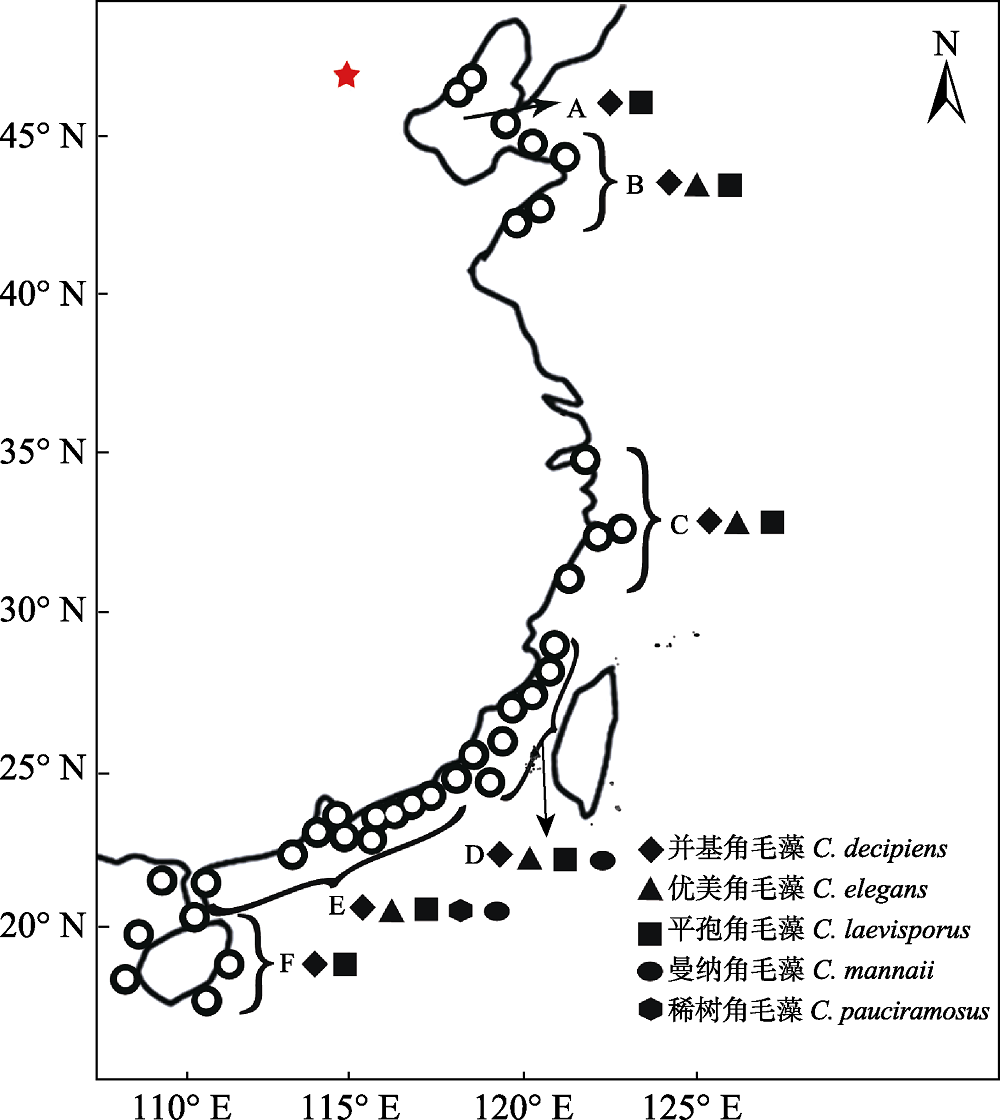
图1 采样站位及中国沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群物种地理分布图。〇: 采样站位; A: 渤海; B: 山东半岛; C: 浙江沿岸; D: 台湾海峡; E: 广东沿岸; F: 环海南岛。
Fig. 1 Sampling sites and geographical distribution of the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex along the coast of China. 〇, Sampling sites; A, Bohai Sea; B, Shandong coast; C, Zhejiang coast; D, Taiwan Strait; E, Guangdong coast; F, Hainan coast.
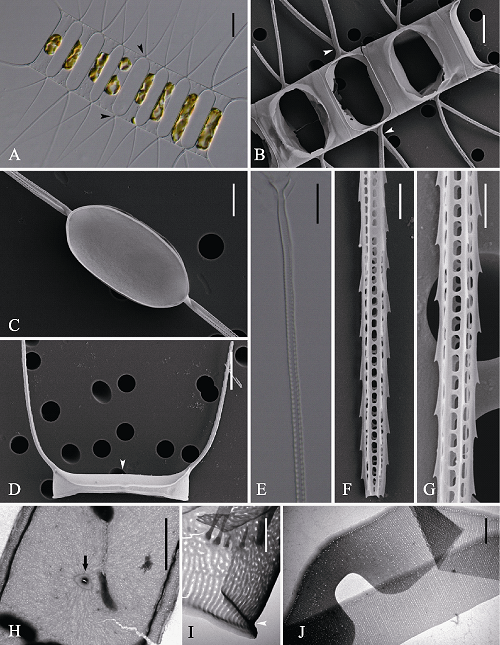
图2 并基角毛藻的光学显微镜(LM) (A, E)、扫描电镜(SEM) (B-D, F, G)和透射电镜(TEM) (H-J)示意图。A-B: 细胞链宽环面观, 分别显示链中角毛无并行融合(A, 箭头)及有并行融合(B, 箭头); C: 壳面观; D: 链端壳面, 示U型端角毛及唇形突(箭头); E-G: 角毛结构; H: 链端壳面, 示唇形突(箭型); I: 壳套; J: 环带。标尺 = 20 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, E), 6 μm (C), 5 μm (H), 2 μm (F, G, J), 1 μm (I)。
Fig. 2 Morphology of Chaetoceros decipiens under light microscopy (LM) (A, E), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (B-D, F, G) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (H-J). A-B, Broad girdle views showing fusing sibling setae base present (B, arrowheads) and not (A, arrowheads); C, Internal view of intercalary valve; D, Terminal valve with rimoportula (arrowhead) and U-shaped terminal setae; E-G, Structure of setae; H, Terminal valve with rimoportula (arrow); I, Mantle; J, Girdle bands. Scale bars, 20 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, E), 6 μm (C), 5 μm (H), 2 μm (F, G, J), 1 μm (I).
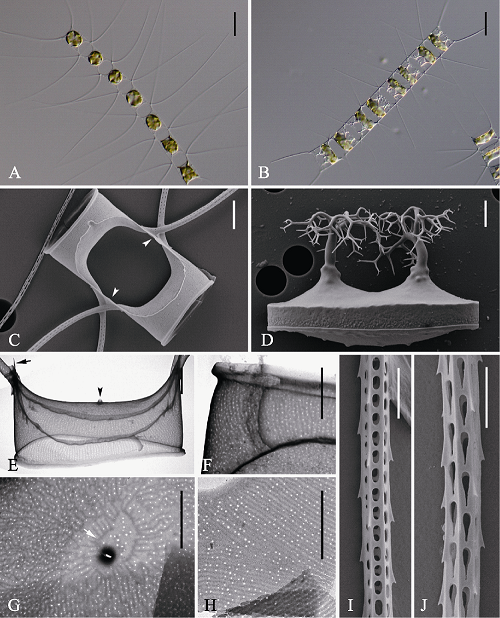
图3 优美角毛藻的光学显微镜(LM) (A-B)、扫描电镜(SEM) (C-D, I-J)和透射电镜(TEM) (E-H)示意图。A: 链状群体; B: 休眠孢子位于母细胞链中; C: 链中壳面, 示硅质翼(箭头); D: 释放的成熟休眠孢子; E: 端壳面, 示唇形突(箭头)和硅质脊(箭型); F: 壳套; G: 链端壳面, 示中央环纹(箭型); H: 环带; I-J: 角毛结构. 标尺 = 20 μm (A, B), 6 μm (D), 4 μm (C), 2 μm (E, F, G, H, I, J)。
Fig. 3 Morphology of Chaetoceros elegans under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-D, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (E-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica ear-like structures (arrowhead); D, Released resting spore. E, Terminal valve with external process of rimoportula (arrowhead) and fringe (arrow); F, Parallel rows of poroids on the mantle; G, Central annulus (arrow) on terminal valve; H, Girdle bands; I and J, Seta structure. Scale bars, 20 μm (A, B), 6 μm (D), 4 μm (C), 2 μm (E, F, G, H, I, J).
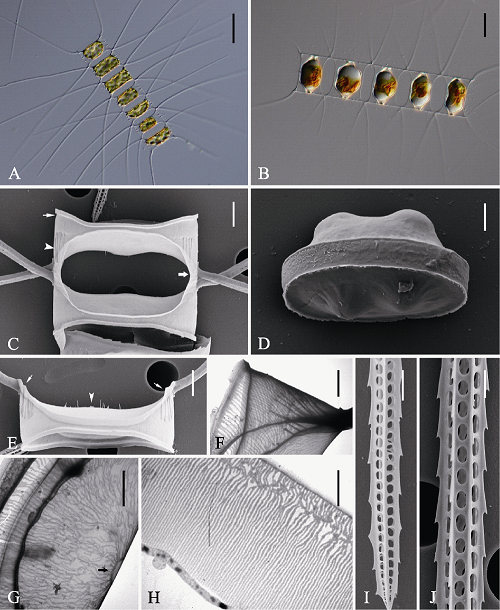
图4 平孢角毛藻的光学显微镜(LM) (A-B)、扫描电镜(SEM) (C-E, I-J)和透射电镜(TEM) (F-H)示意图。A: 链状群体; B: 休眠孢子位于母细胞链中; C: 链中壳面, 示硅质翼(宽箭型), 硅质脊(箭头)及壳套基部凹槽(窄箭型); D: 释放的成熟休眠孢子; E: 链端壳面, 示唇形突(箭头)及硅质肋纹(箭型); F: 壳套; G: 链中壳面, 示中央环纹(箭型); H: 环带; I, J: 角毛结构。标尺 = 50 μm (A), 20 μm (B), 4 μm (C, E), 2 μm (D, F, G, H, I, J)。
Fig. 4 Morphology of Chaetoceros laevisporus under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-E, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (F-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica wings (broad arrow), silica ridges (arrowhead) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrow); D, A released resting spore; E, Terminal valve with central processes (arrowhead) and silica rib (arrows); F, Mantle; G, Intercalary valve with central annulus (arrow); H, Girdle bands; I and J, Setae structure. Scale bars, 50 μm (A), 20 μm (B), 4 μm (C, E), 2 μm (D, F, G, H, I, J).
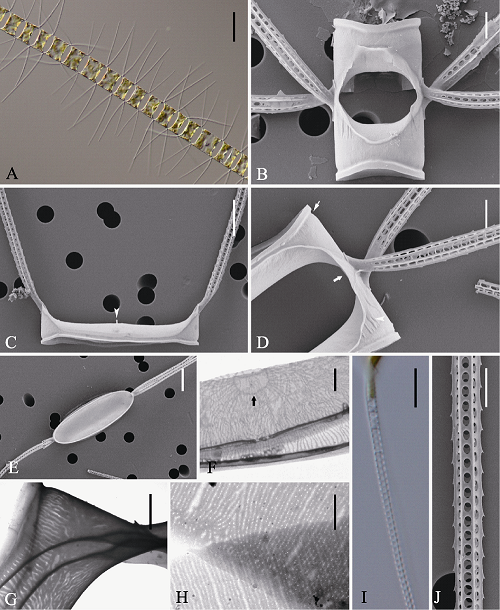
图5 曼纳角毛藻的光学显微镜(LM) (A, I)、扫描电镜(SEM) (B-E, J)和透射电镜(TEM) (F-H)示意图。A: 链状群体; B: 链中壳面; C: 端壳面, 示唇形突(箭头); D: 链中壳面, 示重叠硅质翼(宽箭型), 硅质脊(箭头)及壳套基部凹槽(窄箭型); E-F: 链中壳面, 示中央环纹(F, 箭型); G: 壳套; H: 环带; I, J: 角毛结构。标尺 = 50 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, I), 5 μm (F), 4 μm (C, E, J), 2 μm (G, H)。
Fig. 5 Morphology of Chaetoceros mannaii under light microscopy (LM) (A, I), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (B-E, J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (F-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Sibling intercalary valves showing aperture; C, Terminal valve view with external process of rimoportula (arrowhead); D, Intercalary cells with overlapping silica wings (broad arrow), silica ridges (arrowhead) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrow); E, F, Internal view of an intercalary valves, showing central annulus (F, arrow); G, Mantle; H, Girdle bands; I and J: Setae structure. Scale bars, 50 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, I), 5 μm (F), 4 μm (C, E, J), 2 μm (G, H).
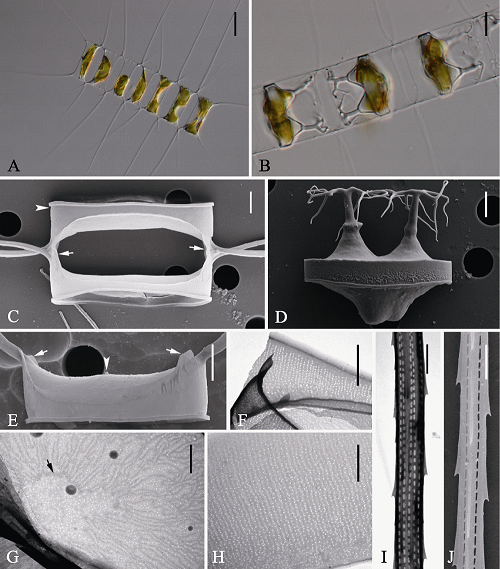
图6 稀树角毛藻的光学显微镜(LM) (A-B)、扫描电镜(SEM) (C-D, I-J)和透射电镜(TEM) (E-H)示意图。A: 链状群体; B: 休眠孢子位于母细胞链中; C: 链中壳面, 示重叠硅质翼(箭型)及壳套基部凹槽(箭头); D: 释放的成熟休眠孢子; E: 链端壳面, 示中央唇形突(箭头)和硅质肋纹(箭型); F: 壳套; G: 链中壳面, 示中央环纹(箭型); H: 环带; I-J: 角毛结构。标尺 = 20 μm (A), 10 μm (D), 4 μm (C, D, E), 2 μm (F), 1 μm (G, H, I, J)。
Fig. 6 Morphology of Chaetoceros pauciramosus under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-D, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (E-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica ear-like structures (arrows) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrowhead); D, Released resting spore; E, Terminal valve with short external tubes of rimoportulae (arrowhead) and silica rib (arrows); F, Mantle; G, Intercalary valve, showing central annulus (arrow); H, Girdle bands; I and J, Seta structure. Scale bars, 20 μm (A), 10 μm (D), 4 μm (C, D, E), 2 μm (F), 1 μm (G, H, I, J).
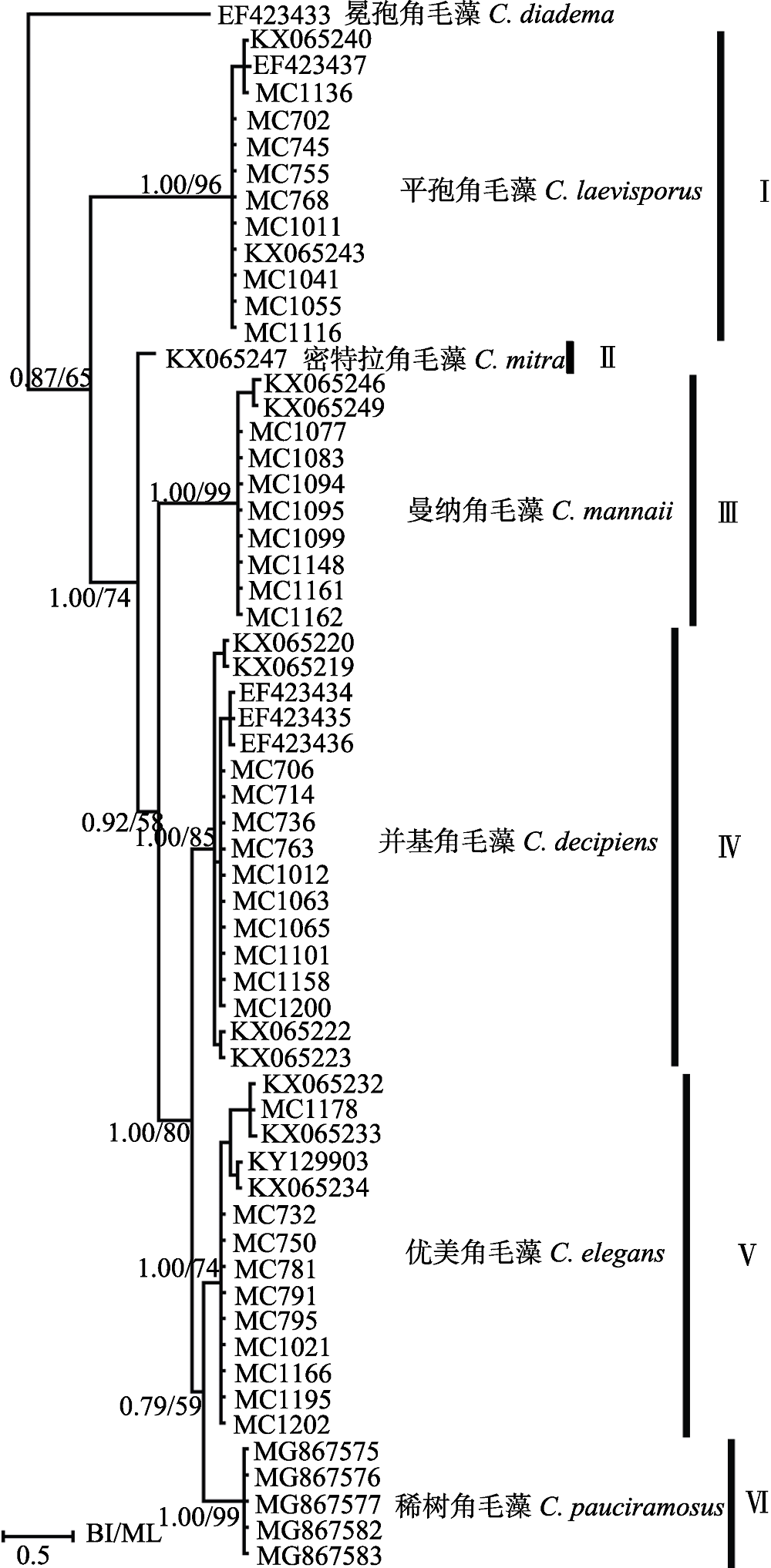
图7 基于核糖体大亚基部分序列的最大似然树。分支上的置信值分别显示贝叶斯分析和最大似然分析。
Fig. 7 Molecular phylogenetic tree inferred from LSU rDNA, with Chaetoceros diadema as outgroup. Supporting values on each nodule are from Bayesian and Maximum Likelihood analysis.
| 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 0.081 (52) | ||||
| 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 0.105 (69) | 0.047 (33) | |||
| 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 0.089 (58) | 0.028 (20) | 0.057 (38) | ||
| 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 0.083 (53) | 0.036 (25) | 0.067 (44) | 0.027 (17) | |
| 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 0.092 (60) | 0.040 (26) | 0.059 (39) | 0.028 (18) | 0.028 (21) |
表1 洛氏角毛藻复合群中各个物种之间的遗传距离(括号内为碱基差异数)
Table 1 Genetic distance among allied taxa within the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex (data in the brackets are numbers of different base pairs)
| 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 0.081 (52) | ||||
| 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 0.105 (69) | 0.047 (33) | |||
| 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 0.089 (58) | 0.028 (20) | 0.057 (38) | ||
| 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 0.083 (53) | 0.036 (25) | 0.067 (44) | 0.027 (17) | |
| 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 0.092 (60) | 0.040 (26) | 0.059 (39) | 0.028 (18) | 0.028 (21) |
| 特征 Character | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 洛氏角毛藻 C. lorenzianus type material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 角毛孔纹形状 Seta poroid shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 水滴状 Drop-shaped | 椭圆形 Oval | 椭圆形 Oval | 细长形 Elongated | 圆形或椭圆形 Round or oval | 圆形 Oval |
| 角毛孔纹大小 Seta poroid size (μm) | 0.3-0.6 (0.4 ± 0.1) | 0.3-1.6 (0.7 ± 0.3) | 0.3-0.9 (0.6 ± 0.1) | 0.8-1.5 (1.1 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.6 (0.3 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) | Nd Nd |
| 角毛孔纹密度 Seta poroid number in 10 μm | 14-25 (20.2 ± 3.6) | 6-27 (18.7 ± 5.0) | 11-17 (14.1 ± 1.9) | 6-10 (7.9 ± 1.0) | 18-44 (31.7 ± 5.4) | 30-56 (39.8 ± 7.4) | 5-9 (7.2 ± 1.7) |
| Brunel 型 Brunel group | I I | I I | I I | I I | I I | II II | I I |
| 角毛基部并行融合Fusion of seta bases | 有或无 Present/absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 短或无 Short/absent | 无 Absent | 有 Present |
| 休眠孢子 Resting spore | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 壳面平滑 Smooth | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支? Two branching processes? |
| 窗孔形状 Aperture shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 圆形或四边形 Rounded or quadrangular | 椭圆形 Oval | 六边形 Hexagonal | 六边形或花生形 Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 六边形或花生形Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 圆形或六边形 Oval or hexagonal |
| 角毛基部 Basal part of setae | 无 Lacking | 有且明显 Distinct | 无 Lacking | 短 Short | 短 Short | 无 Lacking | 无 Lacking |
| 壳面及壳套孔纹 Poroids on valve face and mantle | 有 Yes | 有 Yes | 无 No | 无 No | 有 Yes | 无 No | nd nd |
表2 洛氏角毛藻复合群相似物种之间的形态学比较
Table 2 Morphological comparison among allied taxa within Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex
| 特征 Character | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 洛氏角毛藻 C. lorenzianus type material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 角毛孔纹形状 Seta poroid shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 水滴状 Drop-shaped | 椭圆形 Oval | 椭圆形 Oval | 细长形 Elongated | 圆形或椭圆形 Round or oval | 圆形 Oval |
| 角毛孔纹大小 Seta poroid size (μm) | 0.3-0.6 (0.4 ± 0.1) | 0.3-1.6 (0.7 ± 0.3) | 0.3-0.9 (0.6 ± 0.1) | 0.8-1.5 (1.1 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.6 (0.3 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) | Nd Nd |
| 角毛孔纹密度 Seta poroid number in 10 μm | 14-25 (20.2 ± 3.6) | 6-27 (18.7 ± 5.0) | 11-17 (14.1 ± 1.9) | 6-10 (7.9 ± 1.0) | 18-44 (31.7 ± 5.4) | 30-56 (39.8 ± 7.4) | 5-9 (7.2 ± 1.7) |
| Brunel 型 Brunel group | I I | I I | I I | I I | I I | II II | I I |
| 角毛基部并行融合Fusion of seta bases | 有或无 Present/absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 短或无 Short/absent | 无 Absent | 有 Present |
| 休眠孢子 Resting spore | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 壳面平滑 Smooth | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支? Two branching processes? |
| 窗孔形状 Aperture shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 圆形或四边形 Rounded or quadrangular | 椭圆形 Oval | 六边形 Hexagonal | 六边形或花生形 Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 六边形或花生形Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 圆形或六边形 Oval or hexagonal |
| 角毛基部 Basal part of setae | 无 Lacking | 有且明显 Distinct | 无 Lacking | 短 Short | 短 Short | 无 Lacking | 无 Lacking |
| 壳面及壳套孔纹 Poroids on valve face and mantle | 有 Yes | 有 Yes | 无 No | 无 No | 有 Yes | 无 No | nd nd |
| [1] |
Chen ZY, Li Y ( 2017) Preliminary study on some taxonomic puzzles of Chaetoceros decipiens Cleve. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41, 914-922. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 陈作艺, 李扬 ( 2017) 并基角毛藻若干分类学疑问的初步探讨. 水生生物学报, 41, 914-922.]
DOI URL |
|
| [2] |
Chen ZY, Lundholm N, Moestrup Ø, Kownacka J, Li Y ( 2018) Chaetoceros pauciramosus sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae), a widely distributed brackish water species in the C. lorenzianus complex. Protist, 169, 615-631.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chin TG, Chen JH, Huang KG ( 1965) Marine Planktonic Diatoms from China Sea, p. 115. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 金德祥, 陈金环, 黄凯歌 ( 1965) 中国海洋浮游硅藻类, 见115页. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [4] | Chin TG ( 1951) A list of Chinese diatoms from 1847 to 1946. Amoy Fishries Bulletin, 5, 145-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金德祥 ( 1951) 中国硅藻目录. 厦门水产学报, 5, 145-230.] | |
| [5] | Chu SP, Kuo YC ( 1957) Studies on the genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg from the fishing ground of the mackerel, Pneumatophorus japonicus (Houttuyn), off the Shantung coastal from Chefoo to Weihai. Part I. A systematic study. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1, 27-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱树屏, 郭玉洁 ( 1957) 烟台、威海鲐鱼渔场及其附近海区角毛硅藻属的研究. I. 分类的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 1, 27-87.] | |
| [6] | Chu SP, Kuo YC ( 1958) Studies on the genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg from the fishing ground of the mackerel, Pneumatophorus japonicus (Houttuyn), off the Shanung coast from Chefoo to Weihai. Part II. An ecological study. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1, 167-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱树屏, 郭玉洁 ( 1958) 烟台、威海鲐鱼渔场及其附近海区角毛硅藻属的研究. II. 生态的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 1, 167-179.] | |
| [7] | Evensen DL, Hasle GR ( 1975) The morphology of some Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae) species as seen in the electron microscopes. Nova Hedwigia, 53, 152-174. |
| [8] | Grunow A ( 1863) About some new and insufficiently known species and genera of diatoms. Negotiations of the Imperial Royal Zoological-Botanical Society in Vienna, 13, 137-162. |
| [9] | Guo YJ ( 1963) The nature of Chaetoceros flora of the Yellow Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 5, 322-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭玉洁 ( 1963) 黃海角毛藻属(Genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg)区系的性质. 海洋与湖沼, 5, 322-332.] | |
| [10] | Guo YJ, Qian SB ( 2003) Flora Algarum Marinarum Sinicarum, Tomus V. Bacillariophyta, No.1 Centricae, pp. 345-346. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郭玉洁, 钱树本 ( 2003) 中国海藻志 (第5卷): 硅藻门 (第一册), 中心纲. 345-346页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | Hall TA ( 1999) BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Window 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95-98. |
| [12] | Hasle GR, Syvertsen EE ( 1997) Marine diatoms. In: Identifying Marine Phytoplankton (ed. Tomas CR), pp. 5-387. Academic Press, London. |
| [13] |
Hernández-Becerril DU ( 1996) A morphological study of Chaetoceros species (Bacillariophyta) from the plankton of the Pacific Ocean of Mexico. Bulletin of the Natural History Museum (Botany series), 26, 1-73.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Jensen KG, Moestrup ? ( 1998) The genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae) in inner Danish coastal waters. Nordic Journal of Botany, 18, 88.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kooistra WHCF, Sarno D, Hernández-Becerril DU, Assmy P, Prisco CD, Montresor M ( 2010) Comparative molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses of taxa in the Chaetocerataceae (Bacillariophyta). Phycologia, 49, 471-500.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kownacka J, Edler L, Gromisz S, ?otocka M, Olenina I, Ostrowska M, Piwosz K ( 2013) Non-indigenous species Chaetoceros cf. lorenzianus Grunow 1863— A new, predominant component of autumn phytoplankton in the southern Baltic Sea. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 119, 101-111.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li Y, Boonprakob A, Gaonkar CC, Kooistra WHCF, Lange CB, Hernández-Becerril DU, Chen ZY, Moestrup ?, Lundholm N ( 2017) Diversity in the globally distributed diatom genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae): Three new species from warm-temperate waters. PLoS ONE, 12, 1-38. |
| [18] |
Lin GM, Yang QL ( 2007) Species diversity and the distribution of micro-phytoplankton in the Taiwan Strait. Biodiversity Science, 15, 31-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 林更铭, 杨清良 ( 2007) 台湾海峡小型浮游植物的物种多样性和分布特征. 生物多样性, 15, 31-45.]
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
Lundholm N, Daugbjerg N, Moestrup ? ( 2002) Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo- nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA. European Journal of Phycology, 37, 115-134.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T ( 2010) Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, pp.1-8.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Nylander JAA ( 2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden. |
| [22] | Okamura K ( 1911) Some littoral diatoms of Japan. Report Imperial Fisheries Institute Tokyo Japan. 7, 3-18. |
| [23] | Rines JEB, Hargraves PE ( 1988) The Chaetoceros Ehrenberg (Bacillariophyceae) flora of Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, USA. Bible Phycology, 79, 5-196. |
| [24] |
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A ( 2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539-542.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Round FE, Crawford RM, Mann DG ( 1990) The Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera, p. 747. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [26] | Wang Y, Nie R, Li Y, Lü SH ( 2010) Species diversity and geographical distribution of Chaetoceros in Guangdong coast waters. Advance in Marine Science, 28, 342-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王艳, 聂瑞, 李扬, 吕颂辉 ( 2010) 广东沿海角毛藻(Chaetoceros)的种类多样性及其地理分布. 海洋科学进展, 28, 342-352.] | |
| [27] |
Xue B, Sun J, Li TT ( 2016) Phytoplankton community structure of northern South China Sea in summer of 2014. Haiyang Xuebao, 8, 54-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 薛冰, 孙军, 李婷婷 ( 2016) 2014年夏季南海北部浮游植物群落结构.海洋学报, 8, 54-65.]
DOI URL |
|
| [28] | Yang Y, Sun J, Guan XY, Zhai WD, Guo SJ ( 2016) Seasonal variation of net-phytoplankton community in Bohai Sea. Marine Science Bulletin, 35, 121-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨阳, 孙军, 关翔宇, 翟惟东, 郭术津 ( 2016) 渤海网采浮游植物群集的季节变化. 海洋通报, 35, 121-131.] | |
| [29] | Zhai MY, Zhu SY, Chen ZY, Li Y ( 2017) Preliminary study on the species diversity of Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex from Guangdong coastal waters. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41, 1282-1290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 翟梦怡, 朱素英, 陈作艺, 李扬 ( 2017) 广东沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群物种多样性的探究. 水生生物学报, 41, 1282-1290.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn