



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 581-588. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08015 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.08015
收稿日期:2011-01-20
接受日期:2011-06-13
出版日期:2011-09-20
发布日期:2011-10-08
通讯作者:
康慕谊
基金资助:
Kaixiong Xing, Muyi Kang*( ), Qiang Wang, Jin Duan, Cheng Dai
), Qiang Wang, Jin Duan, Cheng Dai
Received:2011-01-20
Accepted:2011-06-13
Online:2011-09-20
Published:2011-10-08
Contact:
Muyi Kang
摘要:
植物物种丰富度随山地海拔梯度的变化格局是生物多样性研究的热点之一。基于种-面积关系的任何模型对群落物种数目所作估计, 其精度都依赖于样本的代表性、抽样尺度以及所涉及的分类群。作者以秦岭南坡森林群落样方实测的乔木种数据为例, 借鉴群落最小面积(minimum area, MA)的概念及其确定方式, 利用稀疏法(rarefaction)确定了能够反映研究区物种丰富度的最小表现样方数(minimum plot number), 利用3种分组方式将样方总体数据按海拔带分为不同的亚组计算各亚组的物种丰富度, 分析物种丰富度随海拔梯度的分布格局。结果表明: (1)在样方总体内计算任意数目的样方亚组的物种数时, 稀疏法可以整合整个研究区的物种组成特点, 避免单个样方数据对物种数估算的误差影响; 以最小表现样方数为基础来确定物种丰富度, 体现了物种数与样方数(所占面积)的非线性关系, 从而保证了计算结果的物种丰富度有充分的代表性。(2)秦岭南坡森林群落乔木物种的丰富度在中海拔范围(1,400-1,900 m)达到最大(≥80种), 而乔木物种密度分布的最大值出现在海拔1,890 m处(=9.5种/km2), 与以往研究结论基本一致。(3)等样方数高度带滑动分组方法结合物种密度计算分析, 不仅样方分组较详尽, 而且减少了各样方组间的微小差异, 是运用稀疏法考察区域物种丰富度时相对理想的样方分组方法。
邢开雄, 康慕谊, 王强, 段锦, 戴诚 (2011) 运用稀疏法分析物种丰富度的海拔梯度分布格局: 以样方实测乔木种数据为例. 生物多样性, 19, 581-588. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08015.
Kaixiong Xing, Muyi Kang, Qiang Wang, Jin Duan, Cheng Dai (2011) Rarefaction approach to analyzing distribution patterns of species richness along altitudinal gradients: a case study with arborous species data. Biodiversity Science, 19, 581-588. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.08015.
| 拟合模型 Model | E(Sobs(n))与样方数拟合曲线Formula of E(Sobs(n))against plot number | R2 | 拟合显著性 Significance | 拟合F值 F-value | 相对偏差绝对值的平均值 Average absolute relative deviation | 剩余标准差 Residual standard error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logarithm函数 | y = 35.187 ln(x) -28.614 | 0.976 | P<0.001 | 5504.7 | 0.0579 | 4.3115 |
| Arrhenius模型 | y = 15.062 x0.4855 | 0.966 | P<0.001 | 3790.4 | 0.0628 | 4.8430 |
表1 最小表现样方数模型曲线拟合结果
Table 1 Comparison between two fitting models for determining the minimum plot number (MPN)
| 拟合模型 Model | E(Sobs(n))与样方数拟合曲线Formula of E(Sobs(n))against plot number | R2 | 拟合显著性 Significance | 拟合F值 F-value | 相对偏差绝对值的平均值 Average absolute relative deviation | 剩余标准差 Residual standard error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logarithm函数 | y = 35.187 ln(x) -28.614 | 0.976 | P<0.001 | 5504.7 | 0.0579 | 4.3115 |
| Arrhenius模型 | y = 15.062 x0.4855 | 0.966 | P<0.001 | 3790.4 | 0.0628 | 4.8430 |
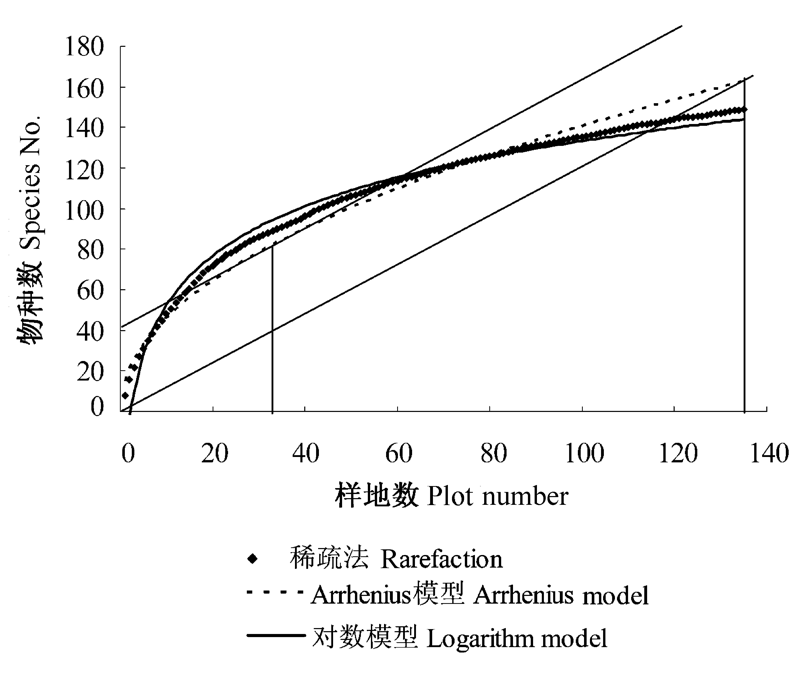
图2 利用对数模型和Arrhenius模型对E(Sobs(n))进行拟合, 并确定最小表现样方数
Fig. 2 Fitting curves of E(Sobs(n)) with Logarithm model and Arrhenius model for determination of the minimum plot number (MPN)
| 序号 Code | 等面积滑动分组 Equal-area intervals | 等海拔滑动分组 Equal-altitude intervals | 等样方数滑动分组 Equal-plot number intervals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 804-1,132 | 804-1,400 | 804-1,050 |
| 2 | 981-1,290 | 901-1,500 | 894-1,230 |
| 3 | 1,064-1,380 | 1,001-1,600 | 966-1,246 |
| 4 | 1,119-1,450 | 1,101-1,700 | 992-1,330 |
| 5 | 1,170-1,520 | 1,201-1,800 | 1020-1,332 |
| 6 | 1,223-1,600 | 1,301-1,900 | 1109-1,390 |
| 7 | 1,283-1,700 | 1,401-2,000 | 1,150-1,426 |
| 8 | 1,338-1,800 | 1,501-2,100 | 1,230-1,467 |
| 9 | 1,383-1,900 | 1,601-2,200 | 1,242-1,530 |
| 10 | 1,443-2,100 | 1,701-2,300 | 1,283-1,605 |
| 11 | 1,478-2,379 | 1,801-2,379 | 1,313-1,658 |
| 12 | 1,381-1,696 | ||
| 13 | 1,406-1,760 | ||
| 14 | 1,453-1,800 | ||
| 15 | 1,521-1,820 | ||
| 16 | 1,586-1,891 | ||
| 17 | 1,656-1,935 | ||
| 18 | 1,694-2,006 | ||
| 19 | 1,753-2,082 | ||
| 20 | 1,800-2,192 | ||
| 21 | 1,815-2,379 |
表2 三种滑动分组方式下各样方亚组的海拔起止范围(m)
Table 2 Altitudinal ranges of plot subgroups divided with moving average methods by three different partitioning approaches based on MPN
| 序号 Code | 等面积滑动分组 Equal-area intervals | 等海拔滑动分组 Equal-altitude intervals | 等样方数滑动分组 Equal-plot number intervals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 804-1,132 | 804-1,400 | 804-1,050 |
| 2 | 981-1,290 | 901-1,500 | 894-1,230 |
| 3 | 1,064-1,380 | 1,001-1,600 | 966-1,246 |
| 4 | 1,119-1,450 | 1,101-1,700 | 992-1,330 |
| 5 | 1,170-1,520 | 1,201-1,800 | 1020-1,332 |
| 6 | 1,223-1,600 | 1,301-1,900 | 1109-1,390 |
| 7 | 1,283-1,700 | 1,401-2,000 | 1,150-1,426 |
| 8 | 1,338-1,800 | 1,501-2,100 | 1,230-1,467 |
| 9 | 1,383-1,900 | 1,601-2,200 | 1,242-1,530 |
| 10 | 1,443-2,100 | 1,701-2,300 | 1,283-1,605 |
| 11 | 1,478-2,379 | 1,801-2,379 | 1,313-1,658 |
| 12 | 1,381-1,696 | ||
| 13 | 1,406-1,760 | ||
| 14 | 1,453-1,800 | ||
| 15 | 1,521-1,820 | ||
| 16 | 1,586-1,891 | ||
| 17 | 1,656-1,935 | ||
| 18 | 1,694-2,006 | ||
| 19 | 1,753-2,082 | ||
| 20 | 1,800-2,192 | ||
| 21 | 1,815-2,379 |
| [1] | Arrhenius O (1921) Species and area. Journal of Ecology, 9,95-99. |
| [2] | Bachman S, Baker WJ, Brummitt N, Dransfield J, Moat J (2004) Elevational gradients area and tropical island diversity: an example from the palms of New Guinea. Ecography, 27,299-310. |
| [3] | Baltanas A (1992) On the use of some methods for the estimation of species richness. Oikos, 65,484-492. |
| [4] | Burnett MR, August PV, Brown JH Jr, Killingbeck KT (1998) The influence of geomorphological heterogeneity on biodiversity. I. A patch-scale perspective. Conservation Biology, 12,363-370. |
| [5] | Buys MH, Maritz JS, Broucher C, Van Der Walt JJA (1994) A model for species area relationships in plant communities. Journal of Vegetation Science, 5,63-66. |
| [6] | Carpenter C (2005) The environmental control of plant species density on a Himalayan elevation gradient. Journal of Biogeography, 32,999-1018. |
| [7] |
Clark PJ, Evans FC (1955) On some aspects of spatial pattern in biological populations. Science, 121,397-398.
URL PMID |
| [8] |
Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15,70-76.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Fang JY (方精云) (2004) Exploring altitudinal patterns of plant diversity of China’s mountains. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12,1-4. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | González-Espinosa M, Rey-Benayas JM, Ramirez-Marcial N, Huston MA, Golicher D (2004) Tree diversity in the northern neotropics: regional patterns in highly diverse Chiapas, Mexico. Ecography, 27,741-756. |
| [11] | Grytnes JA, Beaman JH (2006) Elevational species richness patterns for vascular plants on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Journal of Biogeography, 33,1838-1849. |
| [12] |
Grytnes JA, Vetaas OR (2002) Species richness and altitude: a comparison between Null Models and interpolated plant species richness along the Himalayan altitudinal gradient, Nepal. The American Naturalist, 159,294-304.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | He F, Legend P (1996) On species-area relationship. The American Naturalist, 148,719-737. |
| [14] |
Hurlbert SH (1971) The nonconcept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology, 52,577-586.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] | Kang MY (康慕谊) (1997) Several characteristics of forest vegetation type in Xunhe River basin, south face of Qinling Mountain. In:Resources, Environment and Urban Studies (资源环境城市研究). Northwestern University Press, Xi’an. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | Kang MY (康慕谊), Zhu Y (朱源) (2007) Discussion and analysis on the geo-ecological boundary in Qinling range. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 27,2774-2784. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Liu CR (刘灿然), Ma KP (马克平), Yu SL (于顺利), Wang W (王巍) (1999) Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing China—the fitting and assessment of species-area curves. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 23,490-500. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Liu CR (刘灿然), Ma KP (马克平) (1997) Measurement of biotic community diversity. V. Methods for estimating the number of species in a community. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 17,601-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Ke WS (柯文山), Zhong ZC (钟章成), Wang HP (王惠平) (1998) Study on species diversity of Gordonia acuminata communities on Jinyun Mountain . Bulletin of Botanical Research (木本植物研究), 18,472-477. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | O’Brien EM, Field R, Whittaker RJ (2000) Climatic gradients in woody plant (tree and shrub) diversity: water-energy dynamics, residual variation, and topography. Oikos, 89,588-600. |
| [21] | O’Brien EM (1993) Climatic gradients in woody plant species richness: towards an explanation based on an analysis of southern Africa’s woody flora. Journal of Biogeography, 20,181-198. |
| [22] | Qian H (1998) Large-scale biogeographic patterns of vascular plant richness in North America: an analysis at the general level. Journal of Biogeography, 25,829-836. |
| [23] | Sánchez-González A, López-Mata L (2005) Plant species richness and diversity along an altitudinal gradient in the Sierra Nevada, Mexico. Diversity and Distributions, 11,567-575. |
| [24] | Shen ZH (沈泽昊), Zhang XS (张新时), Jin YX (金义兴) (2001) A vertical gradient analysis of the flora of Dalaoling Mountain in the Three Gorges region, China. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 39,260-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Smith RL (1990) Ecology and Field Biology,4th edn. Harper Collins Publishers, New York. |
| [26] | Solow AR, Roberts DL (2006) Museum collections, species distributions, and rarefaction. Diversity and Distributions, 12,423-424. |
| [27] | Thomas K, Anna MH, Thomas W (2004) Rarefaction method for assessing plant species diversity on a regional scale. Ecography, 27,532-544. |
| [28] | Wang GH (王国宏) (2002) Species diversity of plant communities along an altitudinal gradient in the middle section of northern slopes of Qilian Mountains, Zhangye, Gansu, China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 10,7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Wang ZH (王志恒), Chen AP (陈安平), Piao SL (朴世龙), Fang JY (方精云) (2004) Pattern of species richness along an altitudinal gradient on Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12,82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Whittaker RJ, Nogués-Bravo D, Araújo MB (2007) Geographical gradients of species richness: a test of the water-energy conjecture of Hawkins et al. (2003) using European data for five taxa. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16,76-89. |
| [31] | Wu JH (武吉华), Zhang S (张绅), Jiang Y (江源), Kang MY (康慕谊), Qiu Y (邱扬) (2004) Phytogeography (植物地理学), pp.180-181. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [32] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1980) Vegetation of China (中国植被), pp.254-262. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [33] | Xiong GM (熊高明), Xie ZQ (谢宗强), Lai JS (赖江山), Shen GZ (申国珍), Zhao CM (赵常明) (2007) Vegetation and plant species richness on six pre-islands, the Three Gorges Reservoir. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,533-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Zhang DC (张大才), Sun H (孙航) (2008) Distribution of specimens and species richness of seed plants above timber line in the Hengduan Mountains, southwest China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,381-388. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Zhang JT (张金屯) (2004) Quantitative Ecology (数量生态学), pp.52-53. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | Zhu Y (朱源), Jiang Y (江源), Liu QR (刘全儒), Xiong M (熊敏), Kang MY (康慕谊) (2007) Altitudinal pattern of vascular plant species richness based on equal-area belts in Mt. Helan. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15,408-418. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [3] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [4] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [5] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [6] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [7] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [8] | 杨科, 丁城志, 陈小勇, 丁刘勇, 黄敏睿, 陈晋南, 陶捐. 怒江流域鱼类多样性及空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21334-. |
| [9] | 田璐嘉, 杨小波, 李东海, 李龙, 陈琳, 梁彩群, 张培春, 李晨笛. 海口和三亚两城市破碎化林地中鸟类群落多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21424-. |
| [10] | 王爱霞, 马婧婧, 龚会蝶, 范国安, 王茂, 赵红梅, 程军回. 北疆一年生早春短命植物物种丰富度分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 735-745. |
| [11] | 郑进凤, 唐蓉, 贺霜, 陈月红, 伍素, 张凯, 徐雨, 邹晓. 贵州花溪大学城破碎化林地鸟类多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 661-667. |
| [12] | 黄小波, 郎学东, 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣. 生态系统多功能性的指标选择与驱动因子: 研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1673-1686. |
| [13] | 房丽君, 张宇军, 邢小宇. 秦岭国家植物园蝴蝶群落结构与多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 965-972. |
| [14] | 李娜,丁晨晨,曹丹丹,初红军,戚英杰,李春旺,平晓鸽,孙悦华,蒋志刚. 中国阿勒泰地区鸟类物种编目、丰富度格局和区系组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 401-411. |
| [15] | 邹安龙, 马素辉, 倪晓凤, 蔡琼, 李修平, 吉成均. 模拟氮沉降对北京东灵山辽东栎群落林下植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 607-618. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()