



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 574-580. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07039 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07039
艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔, 阿地力江·阿不都拉, 阿不都拉·阿巴斯*( )
)
收稿日期:2011-03-03
接受日期:2011-05-03
出版日期:2011-09-20
发布日期:2011-10-08
通讯作者:
阿不都拉·阿巴斯
基金资助:
Anwar Tumur, Adiljan Abdulla, Abdulla Abbas*( )
)
Received:2011-03-03
Accepted:2011-05-03
Online:2011-09-20
Published:2011-10-08
Contact:
Abdulla Abbas
摘要:
为了查明乌鲁木齐南部山区地生地衣群落分布格局, 作者选取了24个样点(20 m×20 m), 设置了240个50 cm×50 cm样方, 调查地生地衣的种类及盖度, 分析其分布格局及其与环境因子的关系。结果表明, 乌鲁木齐南部山区共有地生地衣17种, 隶属于2目5科10属。聚类分析和DCA排序将该地区的地生地衣分为4个主要样点组, 分别是: (1)喇叭石蕊(Cladonia pyxidata)+腐石蕊(C. cariosa)+喇叭粉石蕊(C. chlorophaea)群落, 共有7种, 总盖度为19.7%; (2)双孢散盘衣(Solorina bispora)+腐石蕊+粗皮石蕊(C. scabriuscula)群落, 共有11种, 总盖度为21.1%; (3)雪岛衣(Cetraria nivalis)+喇叭石蕊群落, 共有3种, 总盖度最小为8.05%; (4)地卷(Peltigera rufescens)+多指地卷 (P. polydactyla)群落, 共有7种, 总盖度为23.83%。CCA排序结果显示, 该地区地生地衣的分布与海拔高度、郁闭度、人为干扰和湿度有关, 其中影响最大的因素是海拔高度, 其次为郁闭度和干扰。不同海拔高度的植物群落郁闭度不同, 到达地面的光照强度也有差异, 所以不同海拔的地生地衣种类及多样性有显著性差异。
艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔, 阿地力江·阿不都拉, 阿不都拉·阿巴斯 (2011) 乌鲁木齐南部山区地生地衣群落分布格局. 生物多样性, 19, 574-580. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07039.
Anwar Tumur, Adiljan Abdulla, Abdulla Abbas (2011) Distribution of forest floor lichen communities in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi, Xinjiang, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 574-580. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07039.
| 目名和科名 Order and family | 属 Genus | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|
| 茶渍目 Lecanorales | ||
| 石蕊科 Cladoniaceae | 鹿蕊属 Cladina 石蕊属 Cladonia | 1 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris 2 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa 3 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea 4 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata 5 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula |
| 平茶渍属 Aspicilia | 6 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | |
| 膜衣科 Hymeneliaceae | 岛衣属 Cetraria | 7 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis |
| 梅衣科 Parmeliacea | 黄梅属 Xanthoparmelia | 8 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis |
| 蜈蚣衣科 Physciaceae | 大孢蜈蚣衣属 Physconia | 9 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis |
| 地卷目 Peltigerales | ||
| 地卷科 Peltigeraceae | 地卷属 Peltigera | 10 犬地卷 Peltigera canina 11 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae 12 多指地卷 P. polydactyla 13 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata 14 地卷 P. rufescens |
| 不完全地衣类 Lichenes imperfecti | 散盘衣属 Solorina 白角衣属 Siphula 地茶属 Thamnolia | 15 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora 16 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides 17 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis |
表1 乌鲁木齐南部山区地生地衣物种组成
Table 1 Species composition of floor lichens in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 目名和科名 Order and family | 属 Genus | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|
| 茶渍目 Lecanorales | ||
| 石蕊科 Cladoniaceae | 鹿蕊属 Cladina 石蕊属 Cladonia | 1 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris 2 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa 3 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea 4 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata 5 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula |
| 平茶渍属 Aspicilia | 6 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | |
| 膜衣科 Hymeneliaceae | 岛衣属 Cetraria | 7 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis |
| 梅衣科 Parmeliacea | 黄梅属 Xanthoparmelia | 8 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis |
| 蜈蚣衣科 Physciaceae | 大孢蜈蚣衣属 Physconia | 9 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis |
| 地卷目 Peltigerales | ||
| 地卷科 Peltigeraceae | 地卷属 Peltigera | 10 犬地卷 Peltigera canina 11 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae 12 多指地卷 P. polydactyla 13 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata 14 地卷 P. rufescens |
| 不完全地衣类 Lichenes imperfecti | 散盘衣属 Solorina 白角衣属 Siphula 地茶属 Thamnolia | 15 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora 16 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides 17 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis |
| 样点 Sites | 物种丰富度 Richness | Shannon-Weiner指数 Shannon-Weiner diversity index | Pielou指数 Pielou eveness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 1.54 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 6 | 1.66 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 7 | 1.77 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 7 | 1.60 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 7 | 1.74 | 0.89 |
| 6 | 6 | 1.32 | 0.74 |
| 7 | 8 | 1.88 | 0.90 |
| 8 | 9 | 1.92 | 0.87 |
| 9 | 8 | 1.29 | 0.62 |
| 10 | 8 | 1.76 | 0.84 |
| 11 | 6 | 1.36 | 0.76 |
| 12 | 5 | 1.02 | 0.64 |
| 13 | 4 | 1.22 | 0.88 |
| 14 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| 15 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| 16 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.75 |
| 17 | 3 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| 18 | 3 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| 19 | 4 | 1.29 | 0.96 |
| 20 | 5 | 1.11 | 0.69 |
| 21 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.76 |
| 22 | 5 | 0.81 | 0.50 |
| 23 | 5 | 1.31 | 0.81 |
| 24 | 6 | 0.99 | 0.55 |
表2 乌鲁木齐南部山区24个样点地生地衣多样性
Table 2 Diversity indices of floor lichen communities at 24 sites in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 样点 Sites | 物种丰富度 Richness | Shannon-Weiner指数 Shannon-Weiner diversity index | Pielou指数 Pielou eveness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 1.54 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 6 | 1.66 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 7 | 1.77 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 7 | 1.60 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 7 | 1.74 | 0.89 |
| 6 | 6 | 1.32 | 0.74 |
| 7 | 8 | 1.88 | 0.90 |
| 8 | 9 | 1.92 | 0.87 |
| 9 | 8 | 1.29 | 0.62 |
| 10 | 8 | 1.76 | 0.84 |
| 11 | 6 | 1.36 | 0.76 |
| 12 | 5 | 1.02 | 0.64 |
| 13 | 4 | 1.22 | 0.88 |
| 14 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| 15 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| 16 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.75 |
| 17 | 3 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| 18 | 3 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| 19 | 4 | 1.29 | 0.96 |
| 20 | 5 | 1.11 | 0.69 |
| 21 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.76 |
| 22 | 5 | 0.81 | 0.50 |
| 23 | 5 | 1.31 | 0.81 |
| 24 | 6 | 0.99 | 0.55 |
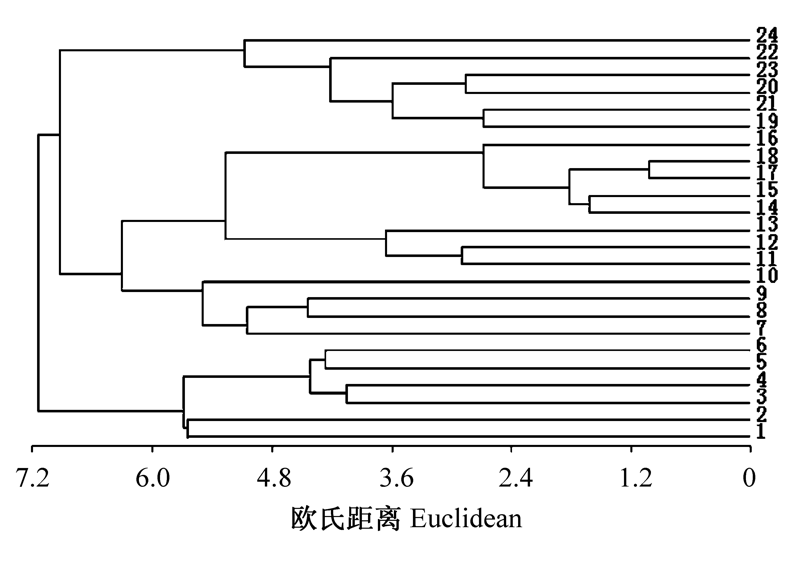
图1 乌鲁木齐南部山区地生地衣分布格局的聚类分析图。图中1-24为样点号。
Fig. 1 Cluster analysis on distribution pattern of floor lichens in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi. 1-24 indicate sampling site no.
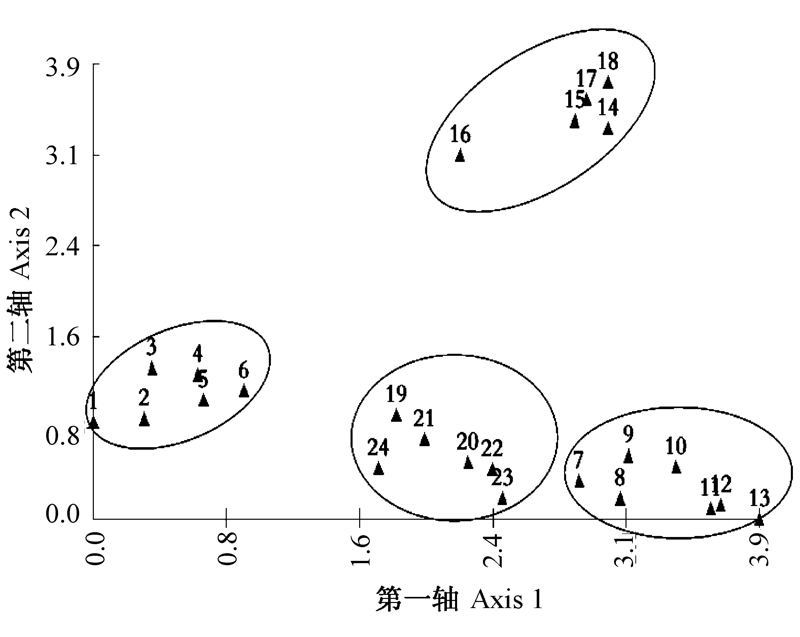
图2 乌鲁木齐南部山区地生地衣分布格局的DCA排序图。图中1-24为样点号。
Fig. 2 DCA analysis on distribution pattern of floor lichens in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi. 1-24 indicate sampling site no.
| 种类 Species | 盖度 Coverage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 群落1 | 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa | 2.95 |
| Group 1 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.04 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.19 | |
| 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea | 2.85 | |
| 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris | 2.61 | |
| 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | 3.30 | |
| 地卷 Peltigera elisabethae | 1.78 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 19.70 | |
| 群落2 | 腐石蕊 C. cariosa | 2.75 |
| Group 2 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 0.99 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.54 | |
| 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis | 1.53 | |
| 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis | 2.60 | |
| 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis | 0.02 | |
| 犬地卷 P. canina | 1.81 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 1.43 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora | 3.89 | |
| 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides | 1.05 | |
| 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis | 2.44 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 21.10 | |
| 群落3 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 2.87 |
| Group 3 | 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata | 1.77 |
| 雪岛衣 C. nivalis | 3.41 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 8.05 | |
| 群落4 | 喇叭粉石蕊 C.chlorophaea | 1.43 |
| Group 4 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.08 |
| 旱黄梅 X. camtschadalis | 3.60 | |
| 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae | 3.63 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 3.88 | |
| 地卷 P. rufescens | 4.32 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 S. bispora | 2.88 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 23.83 |
表3 4种群落中地生地衣的盖度(平均值)
Table 3 Coverage of four floor lichen communities in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 种类 Species | 盖度 Coverage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 群落1 | 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa | 2.95 |
| Group 1 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.04 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.19 | |
| 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea | 2.85 | |
| 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris | 2.61 | |
| 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | 3.30 | |
| 地卷 Peltigera elisabethae | 1.78 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 19.70 | |
| 群落2 | 腐石蕊 C. cariosa | 2.75 |
| Group 2 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 0.99 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.54 | |
| 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis | 1.53 | |
| 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis | 2.60 | |
| 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis | 0.02 | |
| 犬地卷 P. canina | 1.81 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 1.43 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora | 3.89 | |
| 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides | 1.05 | |
| 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis | 2.44 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 21.10 | |
| 群落3 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 2.87 |
| Group 3 | 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata | 1.77 |
| 雪岛衣 C. nivalis | 3.41 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 8.05 | |
| 群落4 | 喇叭粉石蕊 C.chlorophaea | 1.43 |
| Group 4 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.08 |
| 旱黄梅 X. camtschadalis | 3.60 | |
| 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae | 3.63 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 3.88 | |
| 地卷 P. rufescens | 4.32 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 S. bispora | 2.88 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 23.83 |
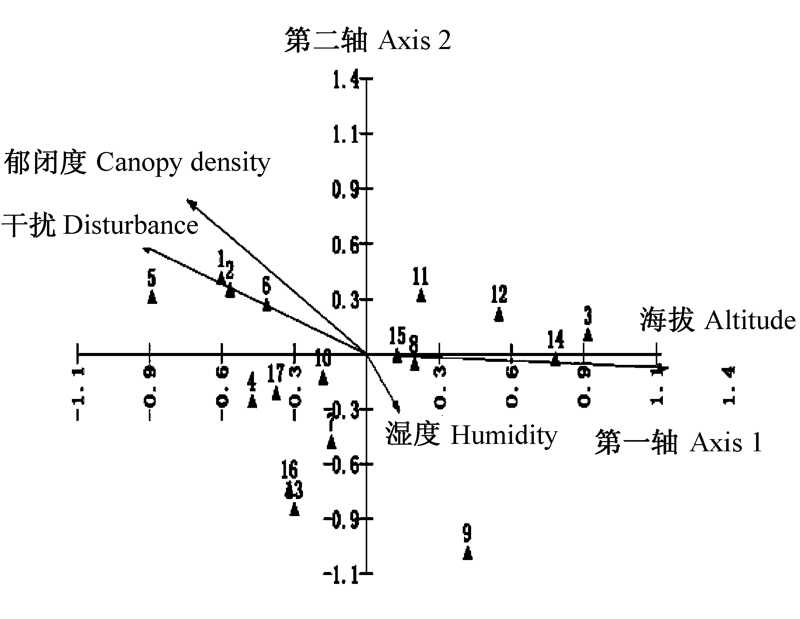
图3 乌鲁木齐南部山区17种地生地衣分布与4种环境因子关系的CCA排序图。序号所代表的地衣种见表1。
Fig. 3 CCA (Canonical Correspondence Analysis) revealing the relationships of the 17 lichen species with four environmental factors in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi. Lichen species 1-17 are listed in Table 1.
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 湿度 Humidity | 干扰 Disturbance | 海拔 Altitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 1.000 | |||
| 湿度 Humidity | 0.7183 | 1.000 | ||
| 干扰 Disturbance | -0.3517 | -0.2162 | 1.000 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.5912 | 0.7539 | 0.6326 | 1.000 |
表4 4个环境因子的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of four environmental factors
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 湿度 Humidity | 干扰 Disturbance | 海拔 Altitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 1.000 | |||
| 湿度 Humidity | 0.7183 | 1.000 | ||
| 干扰 Disturbance | -0.3517 | -0.2162 | 1.000 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.5912 | 0.7539 | 0.6326 | 1.000 |
| [1] | Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯), Wu JN (吴继农) (1998) Lichens of Xinjiang (新疆地衣). Xinjiang Science, Technology and Hygiene Publishing House, Urumqi. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Cao T (曹同), Guo SL (郭水良) (2000) A study on bryophytes diversity in the main ecosystems in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 8,50-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Cao T (曹同), Chen Y (陈怡), Yu J (于晶), Song GY (宋国元) (2004) Distribution patterns of moss species in Shanghai City. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 15,1785-1791. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Dulamsuren C, Hauck M, Mühlenberg M (2005a) Vegetation at the taiga forest-steppe borderline in the western Khentey Mountains, northern Mongolia. Annales Botanici Fennici, 42,411-426. |
| [5] | Dulamsuren C, Hauck M, Mühlenberg M (2005b) Ground vegetation in the Mongolian taiga forest-steppe ecotone does not offer evidence for the human origin of grasslands. Applied Vegetation Sciences, 8,149-154. |
| [6] | Eldridge DJ (1996) Distribution and floristics of terricolous lichens in soil crusts in arid and semi-arid New South Wales, Australia. Australia Journal of Botany, 44,581-599. |
| [7] | Eldridge DJ, Tozer ME (1997) Environmental factors relating to the distribution of terricolous bryophytes and lichens semi-arid eastern Australia. The Bryologist, 100,28-39. |
| [8] | Eldridge DJ (2001) Biological soil crusts of Australia. In: Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function and Management(eds Belnap J, Lange OL). Ecological Studies, 150,119-131. |
| [9] | Johansson P (2008) Consequences of disturbance on epiphytic lichens in boreal and near boreal forests. Biological Conservation, 141,1933-1944. |
| [10] | Loppi S, Boscagli A,De Dominicis V (2004) Ecology of soil lichens from Pliocene clay badlands of central Italy in relation to geomorphology and vascular vegetation. Catena, 55,1-15. |
| [11] | Luo GY (罗光裕) (1984) Preliminary study on the lichen species distribution and their ecological characteristics on Dailing Liangshui Forest Farm. Journal of North Eastern Forestry Institute (东北林学院学报), 12(Suppl.),84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Mason EH (1983) The Biology of Lichens, 3rd edn. Edward Arnold Publishers, London. |
| [13] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley and Sons Publishers, New York. |
| [14] | Rogers RW (1977) Lichens of hot arid and semi-arid lands. In: Lichen Ecology (ed. Seaward MRD), pp.211-252. Academic Press, London. |
| [15] | Rosentreter R, Belnap J (2001) Biological soil crusts of North America. In:Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function and Management(eds Belnap J, Lange OL). Ecological Studies 150,31-50. |
| [16] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) Mamut R (热衣木江·马木提)(2003) Preliminary study on the lichen community structure in forest ecosystem of western Tianshan Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 27,810-815. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abdulla A (阿地里江·阿不都拉) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2005) Numerical classification and species diversity of corticolous lichen communities in forest ecosystems of the Tianshan Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 29,615-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) (2006a) A preliminary study of community characteristics of corticolous lichen in forest ecosystem in Eastern Altay Mts. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 28,415-420. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) (2006b) Floor lichen diversity under different vegetation types in Two-river Source Nature Reserve in Altay Mountains, Xinjiang. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14,444-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Mamut R (热衣木江·马木提) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2009a) Study of the corticolous lichens communities structure in forest ecosystem in southern mountains of Urumqi. Chinese Bulletin of Botany (植物学报), 44,578-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2009b) Saxicolous lichen community structure and characteristics in mountainous area of southern Urumqi. Mycosystema (菌物学报), 28,178-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Wang BC (王伯荪) (1987) Plant Community Ecology (植物群落学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21,213-251. |
| [24] | Yang HX (阳含熙), Lu ZY (卢泽愚) (1981) Methodology of Quantitative Taxonomy in Plant Ecology (植物生态学的数量分类方法). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Zedda L, Gröngröft A, Schultz M, Petersen A, Mills A, Rambold G (2011) Distribution patterns of soil lichens across the principal biomes of southern Africa. Journal of Arid Environments, 75,215-220. |
| [26] | Zhang YM (张元明), Cao T (曹同), Pan BR (潘伯荣) (2002) Quantitative classification and ordination analysis on bryophyte vegetation in Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 26,10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Zhang JT (张金屯) (1995) Methodology of Vegetation Quantitative Ecology (植被数量生态学方法). Chinese Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [10] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()