



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (4): 414-419. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.414 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.414
所属专题: 传粉生物学; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
收稿日期:2010-04-22
接受日期:2010-06-26
出版日期:2010-07-20
发布日期:2010-07-20
通讯作者:
廖万金
作者简介:*E-mail: liaowj@bnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yiyi Long, Liyuan Yang, Wanjin Liao( )
)
Received:2010-04-22
Accepted:2010-06-26
Online:2010-07-20
Published:2010-07-20
Contact:
Wanjin Liao
摘要:
隐种(cryptic species)是指形态上几乎完全相同但遗传组成存在显著分化的物种。在榕树–榕小蜂一对一共生系统中, 传粉榕小蜂隐种的发现对协同进化、物种共存等重要的生态和进化理论提出了严峻的挑战。因为很难从形态上直接区分隐种, 所以, 相关研究中的一个迫切需要解决的问题就是如何快速而准确地鉴定隐种。本文采用PCR-RFLP方法分析了mtDNACOI基因片段, 对木瓜榕(Ficus auriculata)和鸡嗉果榕(F. semicordata)的传粉榕小蜂隐种进行了区分。结果表明为木瓜榕传粉的大果榕小蜂(Ceratosolen emarginatus)存在两个隐种(A和B), 分别包含1个XhoI和1个BssSI酶切位点。将两个隐种的样品按不同比例混合, 提取基因组DNA, PCR扩增mtDNA COI片段, 经XhoI和BssSI分别酶切, 均能通过酶切图谱准确检测出混合样品的隐种组成。鸡嗉果榕小蜂(C. gravelyi)两个隐种的mtDNA COI基因序列也存在较大差别, 分别包含1个BmrI和1个AvaI酶切位点, 隐种混合样品经BmrI和AvaI分别酶切的结果也能准确鉴定混合样品的物种组成。我们的结果表明基于PCR和DNA酶切技术能快速而准确地区分传粉榕小蜂的隐种。
隆沂峄, 杨丽媛, 廖万金 (2010) 利用PCR-RFLP技术鉴定传粉榕小蜂隐种混合样品的物种组成. 生物多样性, 18, 414-419. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.414.
Yiyi Long, Liyuan Yang, Wanjin Liao (2010) Identifying cryptic species in pollinating-fig wasps by PCR-RFLP on mtDNA COI gene. Biodiversity Science, 18, 414-419. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.414.
| 样品编号 Sample No. | 大果榕小蜂 C. emarginatus | 鸡嗉果榕小蜂 C. gravelyi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 隐种A头数 Number of A | 隐种B头数Number of B | 隐种A头数 Number of A | 隐种B头数 Number of B | ||
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 2 | |
| 2 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 2 | |
| 3 | 10 | 2 | 20 | 2 | |
| 4 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 10 | |
| 5 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 20 | |
| 6 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | |
| 7 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 6 | |
| 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 10 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
表1 混合样品中大果榕小蜂隐种A和隐种B的头数与鸡嗉果榕小蜂隐种A和隐种B的头数
Table 1 Composition of cryptic species (A and B) in Ceratosolen emarginatus and C. gravelyi used in this study
| 样品编号 Sample No. | 大果榕小蜂 C. emarginatus | 鸡嗉果榕小蜂 C. gravelyi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 隐种A头数 Number of A | 隐种B头数Number of B | 隐种A头数 Number of A | 隐种B头数 Number of B | ||
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 2 | |
| 2 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 2 | |
| 3 | 10 | 2 | 20 | 2 | |
| 4 | 20 | 2 | 1 | 10 | |
| 5 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 20 | |
| 6 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | |
| 7 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 6 | |
| 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 10 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
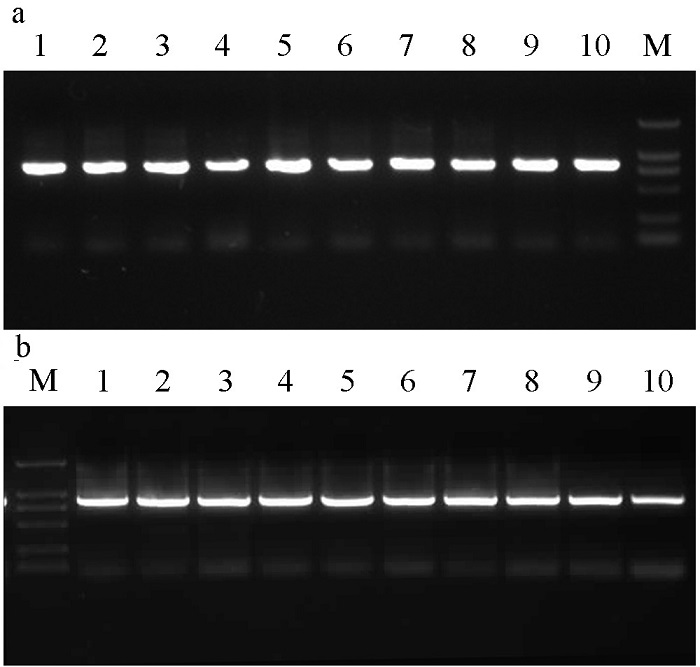
图1 大果榕小蜂(a)与鸡嗉果榕小蜂(b)COI片段PCR扩增结果。M表示DNA marker, 数字表示样品编号, 对应的隐种组成比例如表1所示。
Fig. 1 The PCR products of COI gene in Ceratosolen emarginatus (A) and C. gravelyi (B). M indicates the DNA marker, and the numbers indicate the sample number. See Table 1 for the composition of cryptic species for each sample.
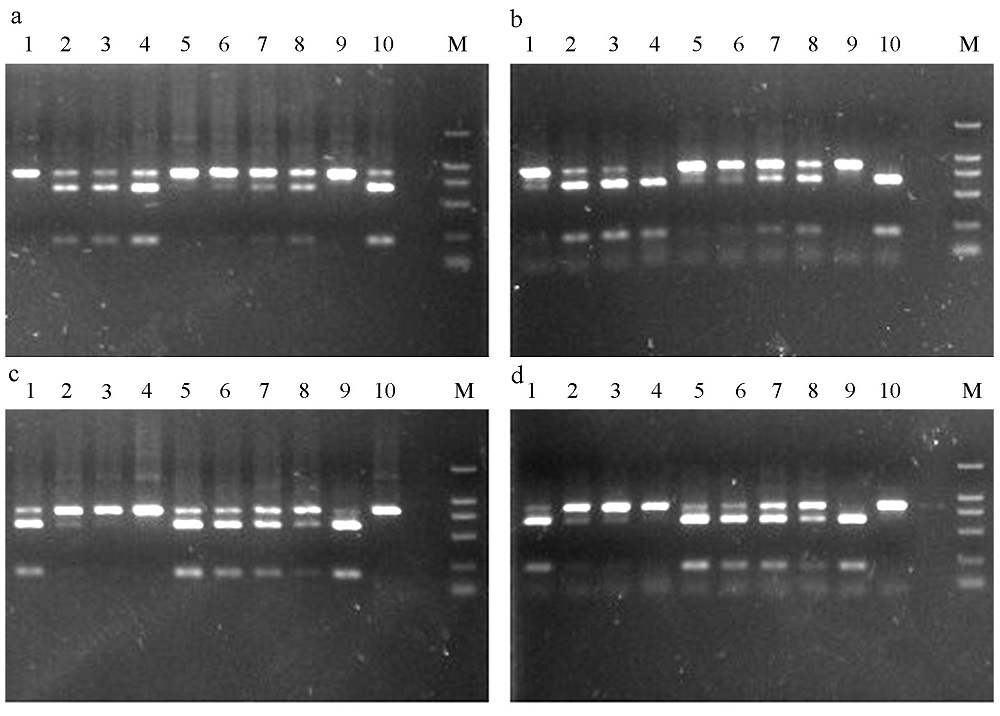
图2 大果榕小蜂混合样品经XhoI(a和b)和BssSI(c和d)酶切电泳结果。数字表示样品编号, 对应的隐种组成比例如表1所示。M表示DNA marker (DL 2000)。a和c是PCR产物经胶回收纯化后酶切图谱, b和d是PCR产物直接酶切图谱。
Fig. 2 The digested products by XhoI (a and b) and BssSI (c and d) in Ceratosolen emarginatus. a and c show the digested results of purified PCR products; b and d, unpurified. M is the DNA marker (DL 2000). 1-10 correspond to the sample numbers in Table 1.
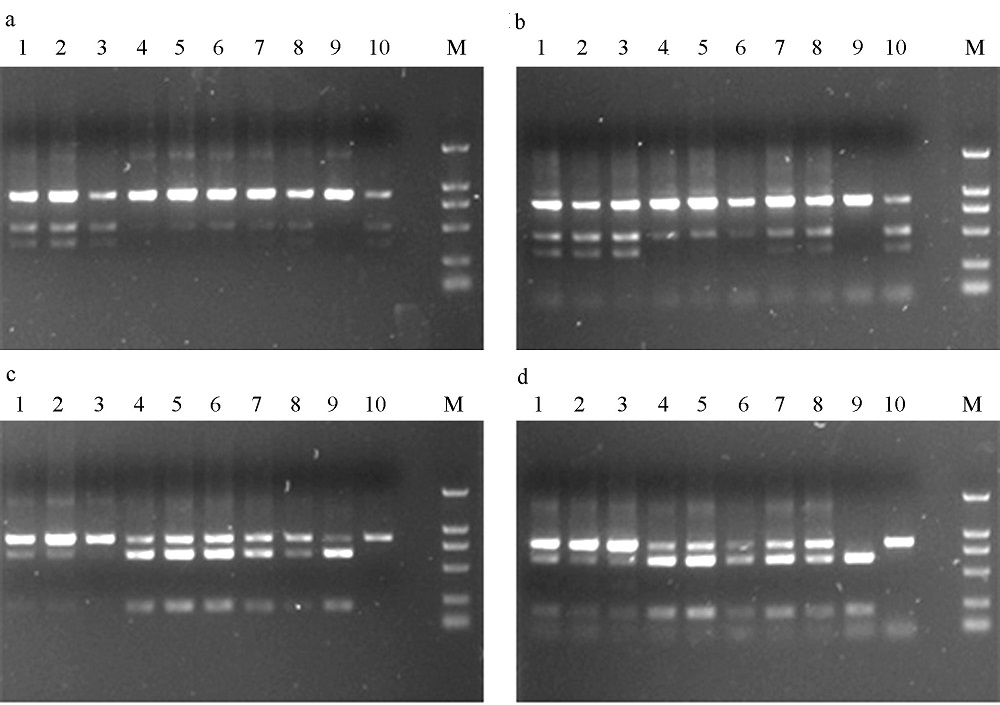
图3 鸡嗉果榕小蜂隐种混合样品经BmrI(a和b)和AvaI(c和d)酶切电泳结果。数字表示样品编号, 对应的隐种组成比例如表1所示。M表示DNA marker (DL 2000)。a和c是PCR产物经胶回收纯化后酶切图谱, b和d是PCR产物直接酶切图谱。
Fig. 3 The digested products by BmrI (a and b) and AvaI (c and d) in Ceratosolen gravelyi. a and c show the digested results of purified PCR products; b and d, unpurified. 1-10 correspond to the sample numbers in Table 1.
| [1] |
Brown GG, Gadaleta G, Pepe G, Saccone C (1986) Structural conservation and variation in the D-loop-containing region of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Molecular Biology, 192,503-511.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Chen SY, Su YH, Wu SF, Sha T, Zhang YP (2005) Mitochondrial diversity and phylogeographic structure of Chinese domestic goats. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 37,804-814.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Cook JM, Rasplus JY (2003) Mutualists with attitude: coevolving fig wasps and figs. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 18,241-248. |
| [4] |
Cook JM, Segar ST (2010) Speciation in fig wasps. Ecological Entomology, 35,54-66.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Fajardo V, Gonzalez I, Dooley J, Garret S, Brown HM, Garcia T, Martin R (2009) Application of polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and lab-on-a-chip capillary electrophoresis for the specific identification of game and domestic meats. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 89,843-847. |
| [6] |
Fajardo V, Gonzalez I, Lopez-Calleja I, Martin I, Rojas M, Hernandez PE, Garcia T, Martin R (2007) Identification of meats from red deer (Cervus elaphus), fallow deer (Dama dama), and roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) using polymerase chain reaction targeting specific sequences from the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene. Meat Science, 76,234-240.
URL PMID |
| [7] |
Haine ER, Martin J, Cook JM (2006) Deep mtDNA divergences indicate cryptic species in a fig-pollinating wasp. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6,83.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41,95-98. |
| [9] |
Karl SA, Bowen BW, Avise JC (1992) Global population genetic-structure and male-mediated gene flow in the green turtle (Chelonia mydas): RFLP analyses of anonymous nuclear loci. Genetics, 131,163-173.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Machado CA, Robbins N, Gilbert MTP, Herre EA (2005) Critical review of host specificity and its coevolutionary implications in the fig/fig-wasp mutualism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102,6558-6565. |
| [11] | Mayr E (1942) Systematics and the Origin of Species. Columbia University Press, New York. |
| [12] |
Molbo D, Machado CA, Sevenster JG, Keller L, Herre EA (2003) Cryptic species of fig-pollinating wasps: implications for the evolution of the fig-wasp mutualism, sex allocation, and precision of adaptation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100,5867-5872.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Peng YQ (彭艳琼), Yang DR (杨大荣), Zhou F (周芳), Zhang GM (张光明), Song QS (宋启示) (2003) Pollination biology of Ficus auriculata Lour. in tropical rainforest of Xishu- angbanna. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 27,111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Sharma N, Thind SS, Girish PS, Sharma D (2008) PCR-RFLP of 12S rRNA gene for meat speciation. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore, 45,353-355. |
| [15] | Simon C, Frati F, Beckenback A, Crespi B, Liu H, Flook P (1994) Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved PCR primers. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 87,651-701. |
| [16] |
Van der Kuyl AC, Kuiken CL, Dekker JT, Goudsmit J (1995) Phylogeny of African monkeys based upon mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 40,173-180.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Wang Q, Zhang X, Zhang HY, Zhang J, Chen GQ, Zhao DH, Ma HP, Liao WJ (2010) Identification of 12 animal species meat by T-RFLP on the 12S rRNA gene. Meat Science, 85,265-269.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Wang QY (王秋艳), Yang DR (杨大荣), Peng YQ (彭艳琼) (2003) Pollination behaviour and propagation of pollinator wasps on Ficus semicordata in Xishuangbanna, China. Acta Entomologica Sinica (昆虫学报), 46,27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] |
Weiblen GD (2002) How to be a fig wasp. Annual Review of Entomology, 47,299-330.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Wiebes JT (1979) Co-evolution of figs and their insect pollinators. Annual Review of Entomology, 10,1-12. |
| [21] | Zou YP (邹喻苹), Ge S (葛颂), Wang XD (王晓东) (2001) Molecular Markers in Systematic and Evolutionary Plant Biology (系统与进化植物学中的分子标记). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 谢华, 杨培, 李宗波. 鸡嗉子榕传粉榕小蜂表皮碳氢化合物的性二型及季节变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24001-. |
| [2] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [3] | 徐聪, 张飞宇, 俞道远, 孙新, 张峰. 土壤动物的分子分类预测策略评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22252-. |
| [4] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [5] | 黄建峰, 徐睿, 彭艳琼. 榕树种间杂交研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 457-467. |
| [6] | 黄建峰, 徐睿, 彭艳琼. 榕-传粉榕小蜂非一对一共生关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 295-303. |
| [7] | 曹云, 沈文静, 陈炼, 胡飞龙, 周蕾, 徐海根. Metabarcoding技术在真菌多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 932-939. |
| [8] | 王太, 张艳萍, 管丽红, 杜岩岩, 娄忠玉, 焦文龙. 甘肃省鱼类资源现状及DNA条形码在鱼类物种鉴定中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 306-313. |
| [9] | 关大伟, 李力, 姜昕, 马鸣超, 曹凤明, 周宝库, 李俊. 长期施肥对黑土大豆根瘤菌群体结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 68-78. |
| [10] | 张珰妮, 郑连明, 何劲儒, 张文静, 林元烧, 李阳. 基于线粒体COI和16S片段序列的北部湾北部水螅水母DNA条形码分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 50-60. |
| [11] | 李超伦, 王敏晓, 程方平, 孙松. DNA条形码及其在海洋浮游动物生态学研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(6): 805-814. |
| [12] | 顾海峰, 刘婷婷, 蓝东兆. 中国沿海甲藻包囊研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(6): 779-786. |
| [13] | 刘艳, 王建秀, 葛学军, 曹同. rps4作为苔藓植物候选条形码的可行性: 基于GenBank数据的分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3): 311-318. |
| [14] | 徐琳, 徐佳洁, 刘巧莉, 谢瑞美, 韦革宏. 西北部分地区苦马豆根瘤菌的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 69-75. |
| [15] | 管俊明, 彭艳琼, 杨大荣. 榕-蜂互惠关系中榕树对未传粉榕小蜂的惩罚效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(6): 626-632. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn