



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 50-60. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014089 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014089
张珰妮3, 郑连明1,2,3,*( ), 何劲儒3, 张文静1,3, 林元烧1,3, 李阳3
), 何劲儒3, 张文静1,3, 林元烧1,3, 李阳3
收稿日期:2014-05-09
接受日期:2014-11-19
出版日期:2015-01-20
发布日期:2015-05-04
通讯作者:
郑连明
作者简介:E-mail: zhlm@xmu.edu.cn基金资助:
Dangni Zhang3, Lianming Zheng1,2,3,*( ), Jinru He3, Wenjing Zhang1,3, Yuanshao Lin1,3, Yang Li3
), Jinru He3, Wenjing Zhang1,3, Yuanshao Lin1,3, Yang Li3
Received:2014-05-09
Accepted:2014-11-19
Online:2015-01-20
Published:2015-05-04
Contact:
Lianming Zheng
摘要:
水螅水母类是浮游动物群落的重要组成部分, 在近岸海洋生态系统物质循环和能量流动中扮演着重要角色。水螅水母类形态结构简单, 但其物种的准确鉴定一直是分类工作中的难点。DNA条形码极大地促进了水螅水母物种的快速、准确鉴定。本研究扩增了北部湾北部28种水螅水母的线粒体COI和16S序列, 分别为92条和116条; 比较了2个基因片段的种内、种间K2P (Kimura 2-parameter)遗传距离; 构建了基于这2个基因片段的系统发育邻接树(neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree); 并结合矢量分析构建了Klee-diagram图。结果显示: COI序列的种内遗传距离为0.008±0.005(0-0.033), 种间遗传距离为0.298±0.128 (0.092-0.597); 16S序列的种内遗传距离为0.006± 0.010(0-0.047), 种间遗传距离为0.394±0.195(0.068-0.898)。2个基因序列在所调查种类中, 种内遗传差异均小于种间遗传差异, 存在明显的条形码间隔(barcoding gap)。基于2个基因片段的NJ树均显示, 单种所有个体都位于同一独立分枝。研究结果表明, 以COI和16S作为DNA条形码均能对北部湾北部常见水螅水母类进行物种鉴定。
张珰妮, 郑连明, 何劲儒, 张文静, 林元烧, 李阳 (2015) 基于线粒体COI和16S片段序列的北部湾北部水螅水母DNA条形码分析. 生物多样性, 23, 50-60. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014089.
Dangni Zhang, Lianming Zheng, Jinru He, Wenjing Zhang, Yuanshao Lin, Yang Li (2015) DNA barcoding of hydromedusae in northern Beibu Gulf for species identification. Biodiversity Science, 23, 50-60. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014089.
| 分类组别 Taxonomy group | COI | 16S | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数值 N | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 S.D. | 计数值 N | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 S.D. | |
| 种内遗传距离 Intra-species | 194 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 320 | 0.000 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 0.010 |
| 种间遗传距离 Inter-species | 3,992 | 0.092 | 0.597 | 0.298 | 0.128 | 6,350 | 0.068 | 0.898 | 0.394 | 0.195 |
| 各属遗传距离 Intra-genus | 370 | 0.092 | 0.215 | 0.171 | 0.032 | 316 | 0.068 | 0.225 | 0.157 | 0.044 |
| 多管水母属 Aequorea | 41 | 0.126 | 0.160 | 0.148 | 0.016 | 75 | 0.085 | 0.127 | 0.109 | 0.014 |
| 和平水母属 Eirene | 323 | 0.092 | 0.215 | 0.173 | 0.032 | 220 | 0.068 | 0.225 | 0.174 | 0.036 |
| 真瘤水母属 Eutima | 6 | 0.203 | 0.212 | 0.208 | 0.003 | 15 | 0.184 | 0.189 | 0.187 | 0.002 |
| 玛拉水母属 Malagazzia | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.000 |
| 各科遗传距离 Intra-family | 230 | 0.127 | 0.351 | 0.189 | 0.037 | 473 | 0.111 | 0.386 | 0.258 | 0.091 |
| 多管水母科 Aequoreidae | 12 | 0.127 | 0.159 | 0.145 | 0.010 | 16 | 0.111 | 0.125 | 0.117 | 0.005 |
| 双生水母科 Diphyidae | 9 | 0.347 | 0.351 | 0.349 | 0.002 | 169 | 0.360 | 0.386 | 0.373 | 0.007 |
| 和平水母科 Eirenidae | 206 | 0.155 | 0.233 | 0.185 | 0.017 | 277 | 0.114 | 0.261 | 0.200 | 0.035 |
| 触丝水母科 Lovenellidae | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 0.202 | 0.205 | 0.203 | 0.001 |
| 玛拉水母科 Malagazziidae | 3 | 0.175 | 0.177 | 0.175 | 0.001 | 5 | 0.121 | 0.132 | 0.128 | 0.006 |
| 各目遗传距离 Intra-order | 940 | 0.105 | 0.566 | 0.199 | 0.075 | 1,847 | 0.086 | 0.775 | 0.211 | 0.096 |
| 花水母目 Anthoathecata | 12 | 0.178 | 0.211 | 0.204 | 0.009 | 35 | 0.222 | 0.289 | 0.260 | 0.017 |
| 软水母目 Leptothecata | 878 | 0.105 | 0.566 | 0.185 | 0.046 | 1,747 | 0.086 | 0.327 | 0.194 | 0.032 |
| 管水母目 Siphonophorae | 50 | 0.446 | 0.499 | 0.483 | 0.014 | 65 | 0.366 | 0.775 | 0.659 | 0.148 |
| 各亚纲遗传距离 Intra-subclass | 1,425 | 0.150 | 0.596 | 0.349 | 0.143 | 3,160 | 0.185 | 0.756 | 0.486 | 0.144 |
| 软水母亚纲 Hydroidolina | 1,395 | 0.150 | 0.596 | 0.348 | 0.144 | 3,154 | 0.185 | 0.672 | 0.486 | 0.144 |
| 硬水母亚纲 Trachylinae | 30 | 0.407 | 0.418 | 0.413 | 0.004 | 6 | 0.728 | 0.756 | 0.741 | 0.010 |
| 水螅虫纲遗传距离 Intra-class (Hydrozoa) | 1,027 | 0.207 | 0.597 | 0.371 | 0.076 | 554 | 0.295 | 0.898 | 0.570 | 0.170 |
表1 各分类阶元遗传距离统计
Table 1 Genetic distance on different taxonomic levels
| 分类组别 Taxonomy group | COI | 16S | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 计数值 N | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 S.D. | 计数值 N | 最小值 Min | 最大值 Max | 平均值 Mean | 标准差 S.D. | |
| 种内遗传距离 Intra-species | 194 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 320 | 0.000 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 0.010 |
| 种间遗传距离 Inter-species | 3,992 | 0.092 | 0.597 | 0.298 | 0.128 | 6,350 | 0.068 | 0.898 | 0.394 | 0.195 |
| 各属遗传距离 Intra-genus | 370 | 0.092 | 0.215 | 0.171 | 0.032 | 316 | 0.068 | 0.225 | 0.157 | 0.044 |
| 多管水母属 Aequorea | 41 | 0.126 | 0.160 | 0.148 | 0.016 | 75 | 0.085 | 0.127 | 0.109 | 0.014 |
| 和平水母属 Eirene | 323 | 0.092 | 0.215 | 0.173 | 0.032 | 220 | 0.068 | 0.225 | 0.174 | 0.036 |
| 真瘤水母属 Eutima | 6 | 0.203 | 0.212 | 0.208 | 0.003 | 15 | 0.184 | 0.189 | 0.187 | 0.002 |
| 玛拉水母属 Malagazzia | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.000 |
| 各科遗传距离 Intra-family | 230 | 0.127 | 0.351 | 0.189 | 0.037 | 473 | 0.111 | 0.386 | 0.258 | 0.091 |
| 多管水母科 Aequoreidae | 12 | 0.127 | 0.159 | 0.145 | 0.010 | 16 | 0.111 | 0.125 | 0.117 | 0.005 |
| 双生水母科 Diphyidae | 9 | 0.347 | 0.351 | 0.349 | 0.002 | 169 | 0.360 | 0.386 | 0.373 | 0.007 |
| 和平水母科 Eirenidae | 206 | 0.155 | 0.233 | 0.185 | 0.017 | 277 | 0.114 | 0.261 | 0.200 | 0.035 |
| 触丝水母科 Lovenellidae | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | 0.202 | 0.205 | 0.203 | 0.001 |
| 玛拉水母科 Malagazziidae | 3 | 0.175 | 0.177 | 0.175 | 0.001 | 5 | 0.121 | 0.132 | 0.128 | 0.006 |
| 各目遗传距离 Intra-order | 940 | 0.105 | 0.566 | 0.199 | 0.075 | 1,847 | 0.086 | 0.775 | 0.211 | 0.096 |
| 花水母目 Anthoathecata | 12 | 0.178 | 0.211 | 0.204 | 0.009 | 35 | 0.222 | 0.289 | 0.260 | 0.017 |
| 软水母目 Leptothecata | 878 | 0.105 | 0.566 | 0.185 | 0.046 | 1,747 | 0.086 | 0.327 | 0.194 | 0.032 |
| 管水母目 Siphonophorae | 50 | 0.446 | 0.499 | 0.483 | 0.014 | 65 | 0.366 | 0.775 | 0.659 | 0.148 |
| 各亚纲遗传距离 Intra-subclass | 1,425 | 0.150 | 0.596 | 0.349 | 0.143 | 3,160 | 0.185 | 0.756 | 0.486 | 0.144 |
| 软水母亚纲 Hydroidolina | 1,395 | 0.150 | 0.596 | 0.348 | 0.144 | 3,154 | 0.185 | 0.672 | 0.486 | 0.144 |
| 硬水母亚纲 Trachylinae | 30 | 0.407 | 0.418 | 0.413 | 0.004 | 6 | 0.728 | 0.756 | 0.741 | 0.010 |
| 水螅虫纲遗传距离 Intra-class (Hydrozoa) | 1,027 | 0.207 | 0.597 | 0.371 | 0.076 | 554 | 0.295 | 0.898 | 0.570 | 0.170 |
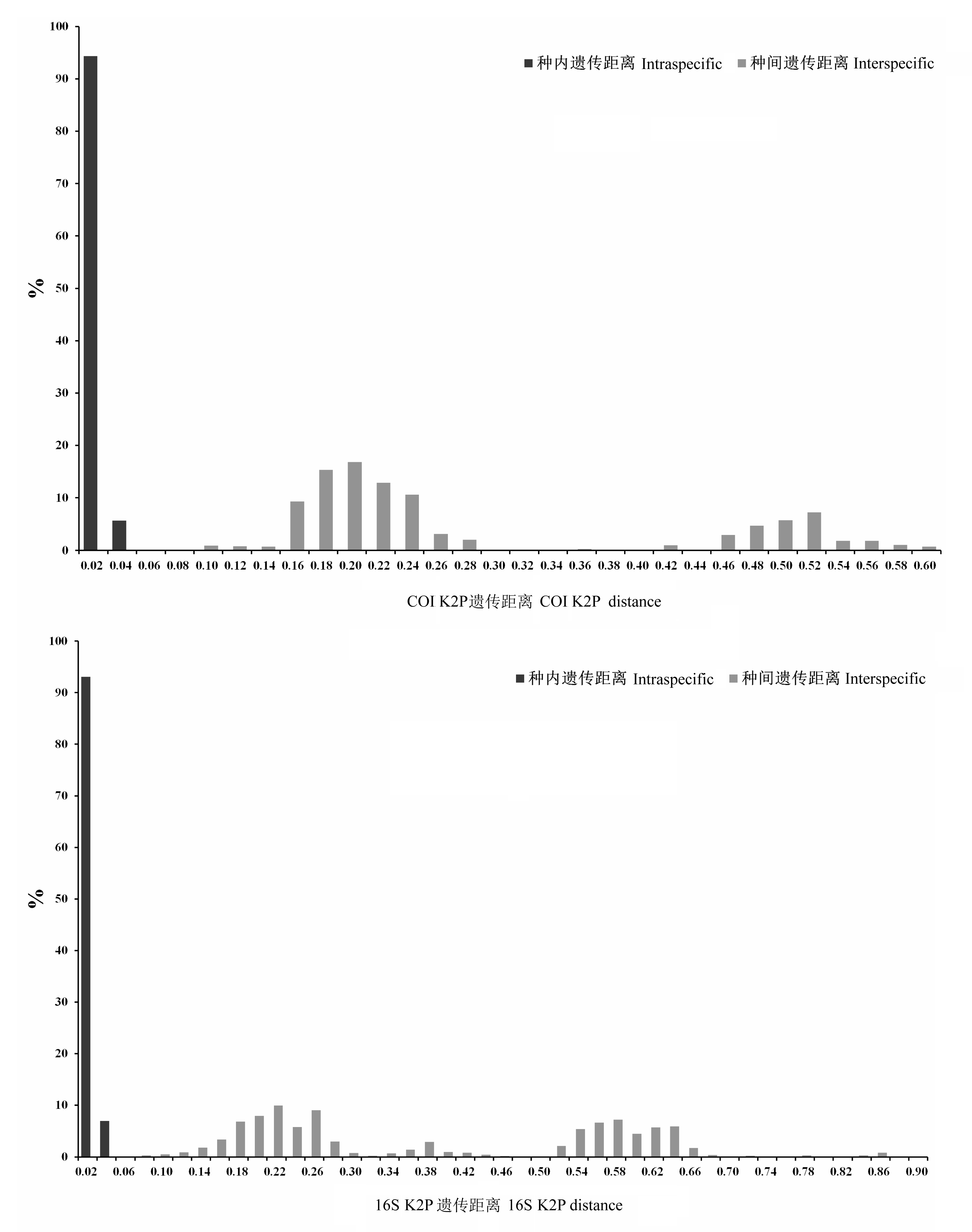
图2 COI、16S种内种间遗传差异(K2P遗传距离)分布图
Fig. 2 Distribution of the intraspecific and interspecific genetic variabilities (Kimura-2-parameter distance) of COI and 16S
| 1 |
Bucklin A, Steinke D, Blanco-Bercial L ( 2011) DNA barcoding of marine metazoa. Annual Review of Marine Science, 3, 471-508.
DOI URL PMID |
| 2 | Cheng FP ( 程方平), Wang MX ( 王敏晓), Wang YT ( 王彦涛), Zhang F ( 张芳), Li CL ( 李超伦), Sun S ( 孙松 ) ( 2012) DNA barcoding of common medusozoa in northern China based on mtCOI sequence. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 43, 451-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 |
Cheng F, Wang M, Sun S, Li C, Zhang Y ( 2013) DNA barcoding of Antarctic marine zooplankton for species identification and recognition. Advances in Polar Science, 24, 119-127.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Collins AG, Bentlage B, Lindner A, Lindsaya D, Haddocka SHD, Jarmsa G, Norenburga JL, Jankowskia T, Cartwrighta P ( 2008) Phylogenetics of Trachylina (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa) with new insights on the evolution of some problematic taxa. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 88, 1673-1685.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Del-Prado R, Cubas P, Lumbsch HT, Divakar PK, Blanco O, de Paz GA, Molina MC, Crespo A ( 2010) Genetic distances within and among species in monophyletic lineages of Parmeliceae (Ascomycota) as a tool for taxon delimitation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 125-133.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 |
Ender A, Schierwater B ( 2003) Placozoa are not derived cnidarians: evidence from molecular morphology. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 20, 130-134.
DOI URL PMID |
| 7 |
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R ( 1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294-299.
URL PMID |
| 8 |
Govindarajan AF, Boero F, Halanych KM ( 2006) Phylogenetic analysis with multiple markers indicates repeated loss of the adult medusa stage in Campanulariidae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 38, 820-834.
DOI URL PMID |
| 9 |
Govindarajan AF, Halanych KM, Cunningham CW ( 2005) Mitochondrial evolution and phylogeography in the hydrozoan Obelia geniculata(Cnidaria). Marine Biology, 146, 213-222.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Hajibabaei M, Janzen DH, Burns JM, Hallwachs W, Hebert PDN ( 2006) DNA barcodes distinguish species of tropical Lepidoptera. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 968-971.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Hebert PDN, Gregory TR ( 2005) The promise of DNA barcoding for taxonomy. Systematic Biology, 54, 852-859.
DOI URL PMID |
| 12 |
Hebert PDN, Penton EH, Burns JM, Janzen DH, Hallwachs W, Affiliations A ( 2004a) Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 14812-14817.
DOI URL |
| 13 | Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S, Waard JR ( 2003) Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit I divergences among closely related species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 270, S96-S99. |
| 14 | Hebert PDN, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM ( 2004b) Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biology, 2, 1657-1663. |
| 15 |
Hellberg ME ( 2006) No variation and low synonymous substitution rates in coral mtDNA despite high nuclear variation. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6, 1-8.
DOI URL PMID |
| 16 |
Huang D, Meier R, Todd PA, Chou LM ( 2008) Slow mitochondrial COI sequence evolution at the base of the metazoan tree and its implications for DNA barcoding. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 66, 167-174.
DOI URL PMID |
| 17 | Huang JQ ( 黄加祺), Li SP ( 李尚平), Zhong QP ( 钟秋平), Zhang CX ( 张晨晓), Zhang YJ ( 张艳军 ) ( 2010) One new species of genus Eucheilota in Guangxi Coast, China. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) ( 厦门大学学报自然科学版), 49, 428-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 |
Jennifer EP ( 2012) Jellyfish and ctenophore blooms coincide with human proliferations and environmental perturbations. Annual Review of Marine Science, 4, 209-235.
DOI URL PMID |
| 19 |
Kimura M ( 1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 16, 111-120.
DOI URL PMID |
| 20 | Köhler F ( 2007) From DNA taxonomy to barcoding: how a vague idea evolved into a biosystematic tool. Mitteilungen aus dem Museum für Naturkunde Berlin Zoologische Reihe, 83, 44-51. |
| 21 |
Laakmann S, Holst S ( 2013) Emphasizing the diversity of North Sea hydromedusae by combined morphological and molecular methods. Journal of Plankton Research, 36, 64-76.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG ( 2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23, 2947-2948.
DOI URL PMID |
| 23 |
Leclère L, Schuchert P, Cruaud C, Couloux A, Manuel M ( 2009) Molecular phylogenetics of Thecata (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria) reveals long-term maintenance of life history traits despite high frequency of recent character changes. Systematic Biology, 58, 509-526.
DOI URL PMID |
| 24 | Li SP ( 李尚平), Zhong QP ( 钟秋平), Zhang CX ( 张晨晓), Huang JQ ( 黄加祺), Zhang YJ ( 张艳军 ) ( 2010) Two new species of the genus Hydractinia in Guangxi Coast, China (Cnidaria, Anthomedusae, Hydractiniidae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica (动物分类学报), 35, 853-856. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 25 |
McFadden CS, Benayahu Y, Pante E, Thoma JN, Nevarez PA, France SC ( 2011) Limitations of mitochondrial gene barcoding in Octocorallia. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 19-31.
DOI URL PMID |
| 26 | McFadden CS, Tullis I, Hutchinson MB, Winner K ( 2000) Rates of evolution of cnidarian mitochondrial genes. American Zoologist, 40, 1124. |
| 27 | Meyer CP, Paulay G ( 2005) DNA barcoding: error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biology, 3, 2229-2238. |
| 28 |
Miglietta MP, Schuchert P, Cunningham CW ( 2009) Reconciling genealogical and morphological species in a worldwide study of the family Hydractiniidae (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa). Zoologica Scripta, 38, 403-430.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Miranda LS, Collins AG, Marques AC ( 2010) Molecules clarify a Cnidarian life cycle—the “Hydrozoan” Microhydrula limopsicola is an early life stage of the Staurozoan Haliclystus antarcticus. PLoS ONE, 5, e10182.
DOI URL PMID |
| 30 |
Moura CJ, Cunha MR, Porteiro FM, Rogers AD ( 2011 a) Polyphyly and cryptic diversity in the hydrozoan families Lafoeidae and Hebellidae (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Invertebrate Systematics, 25, 454-470.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Moura CJ, Cunha MR, Porteiro FM, Rogers AD ( 2011 b) The use of the DNA barcode gene 16S mRNA for the clarification of taxonomic problems within the family Sertulariidae (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa). Zoologica Scripta, 40, 520-537.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Moura CJ, Cunha MR, Porteiro FM, Rogers AD ( 2012) A molecular phylogenetic appraisal of the systematics of the Aglaopheniidae (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa, Leptothecata) from the north-east Atlantic and west Mediterranean. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 164, 717-727.
DOI URL |
| 33 | Moura CJ, Harris DJ, Cunha MR, Rogers AD ( 2008) DNA barcoding reveals cryptic diversity in marine hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) from coastal and deep-sea environments. Zoologica Scripta, 37, 93-108. |
| 34 |
Ortman BD, Bucklin A, Pagès F, Youngbluth M ( 2010) DNA barcoding the Medusozoa using mtCOI. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57, 2148-2156.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Pitt KA, Welsh DT, Condon RH ( 2009) Influence of jellyfish blooms on carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycling and plankton production. Hydrobiologia, 616, 133-149.
DOI URL |
| 36 | Pontin DR, Cruickshank RH ( 2012) Molecular phylogenetics of the genus Physalia(Cnidaria: Siphonophora) in New Zealand coastal waters reveals cryptic diversity. Hydrobiologia, 686, 91-105. |
| 37 |
Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN ( 2007) BOLD: the barcode of life data system (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 355-364.
DOI URL PMID |
| 38 |
Schuchert P ( 2005) Species boundaries in the hydrozoan genus Coryne. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 36, 194-199.
DOI URL PMID |
| 39 |
Schuchert P ( 2006) The European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Capitata Part 1. Revue Suisse de Zoologie, 113, 325-410.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Schuchert P ( 2007) The European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Filifera Part 2. Revue Suisse de Zoologie, 114, 195-396.
DOI URL |
| 41 |
Schuchert P ( 2008 a) The European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Filifera Part 3. Revue Suisse de Zoologie, 115, 221-302.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Schuchert P ( 2008 b) The European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Filifera Part 4. Revue Suisse de Zoologie, 115, 677-757.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Schuchert P ( 2009) The European athecate hydroids and their medusae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria): Filifera Part 5. Revue Suisse de Zoologie, 116, 441-507.
DOI URL |
| 44 |
Schuchert P, Reiswig HM ( 2006) Brinckmannia hexactinellidophila, n. gen., n. sp.: a hydroid living in tissues of glass sponges of the reefs, fjords, and seamounts of Pacific Canada and Alaska. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 84, 564-572.
DOI URL |
| 45 |
Shearer TL, van Oppen MJH, Romano SL, Wörheide G ( 2002) Slow mitochondrial DNA sequence evolution in the Anthozoa (Cnidaria). Molecular Ecology, 11, 2475-2487.
DOI URL PMID |
| 46 |
Sinniger F, Reimer JD, Pawlowski J ( 2008) Potential of DNA sequences to identify zoanthids (Cnidaria: Zoantharia). Zoological Science, 25, 1253-1260.
DOI URL PMID |
| 47 |
Sirovich L, Stoeckle MY, Zhang Y ( 2009) A scalable method for analysis and display of DNA sequences. PLoS ONE, 4, e7051.
DOI URL PMID |
| 48 |
Sirovich L, Stoeckle MY, Zhang Y ( 2010) Structural analysis of biodiversity. PLoS ONE, 5, e9266.
DOI URL PMID |
| 49 |
Stampar SN, Maronna MM, Vermeij MJA, Silveira FLD, Morandini AC ( 2012) Evolutionary diversification of banded tube-dwelling anemones (Cnidaria; Ceriantharia; Isarachnanthus) in the Atlantic Ocean. PLoS ONE, 7, e41091.
DOI URL PMID |
| 50 |
Sun Y, Li Q, Kong L, Zheng X ( 2012) DNA barcoding of Caenogastropoda along coast of China based on the COI gene. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12, 209-218.
DOI URL PMID |
| 51 |
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S ( 2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731-2739.
DOI URL PMID |
| 52 |
Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert PDN ( 2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 360, 1847-1857.
DOI URL |
| 53 | Xu ZZ ( 许振祖), Huang JQ ( 黄加祺), Guo DH ( 郭东晖 ) ( 2008) Six new species of Anthomedusae (Hydrozoa, Hydroidomedusae) from the Beibu Gulf, China. In: Symposium on Oceanography of Beibu Gulf I (北部湾海洋科学研究论文集(第1辑)) (eds Hu JY (胡建宇), Yang SY (杨圣云)), pp. 209-221. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 54 |
Zemlak TS, Ward RD, Connell AD, Holmes BH, Hebert PD ( 2009) DNA barcoding reveals overlooked marine fishes. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 237-242.
DOI URL PMID |
| 55 | Zheng LM, Lin YS, Li SJ, Cao WQ, Xu ZZ, Huang JQ ( 2009) Aequorea taiwanensis n. sp. (Hydrozoa, Leptomedusae) and mtCOI sequence analysis for the genus Aequorea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28, 109-115. |
| 56 |
Zhou KL, Zheng LM, He JR, Lin YS, Cao WQ, Zhang WJ ( 2013) Detection of a new Clytia species (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa: Campanulariidae) with DNA barcoding and life cycle analyses. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 93, 2075-2088.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [2] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [3] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [4] | 徐聪, 张飞宇, 俞道远, 孙新, 张峰. 土壤动物的分子分类预测策略评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22252-. |
| [5] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [6] | 张梦华, 张宪春. 中国薄叶卷柏复合群的物种划分[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1607-1619. |
| [7] | 陈向向, 盖中帅, 翟军团, 徐劲东, 焦培培, 吴智华, 李志军. 中国西北地区天然胡杨群体遗传多样性及核心保护单元的构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1638-1649. |
| [8] | 李媛媛, 刘超男, 王嵘, 罗水兴, 农寿千, 王静雯, 陈小勇. 分子标记在濒危物种保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 367-375. |
| [9] | 胡芮, 王儒晓, 杜诗雨, 李萌, 邢雨辉, 潘达, 徐海根, 孙红英. 扬州宝应湖底栖大型无脊椎动物的生物多样性及其变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569. |
| [10] | 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙. |
| [11] | 刘山林. DNA条形码参考数据集构建和序列分析相关的新兴技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| [12] | 张亚红, 贾会霞, 王志彬, 孙佩, 曹德美, 胡建军. 滇杨种群遗传多样性与遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 355-365. |
| [13] | 赵颖, 马荣, 尹永香, 张志东, 田呈明. 新疆不同来源金黄壳囊孢的多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1122-1131. |
| [14] | 侯勤曦, 慈秀芹, 刘志芳, 徐武美, 李捷. 基于DNA条形码评估西双版纳国家级自然保护区对樟科植物进化历史的保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 217-228. |
| [15] | 刘青青, 董志军. 基于线粒体COI基因分析钩手水母的群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1204-1211. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()