



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (6): 631-637. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.2010.631 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.2010.631
所属专题: 外来物种入侵:机制、影响与防控; 生物入侵
廖成章1,2,*( ), 唐小平1, 程小玲1, 李博2, 骆亦其2
), 唐小平1, 程小玲1, 李博2, 骆亦其2
收稿日期:2010-03-07
接受日期:2010-06-22
出版日期:2010-11-20
发布日期:2011-01-31
通讯作者:
廖成章
作者简介:*E-mail: 031023079@fudan.edu.cn基金资助:
Chengzhang Liao1,2,*( ), Xiaoping Tang1, Xiaoling Cheng1, Bo Li2, Yiqi Luo2
), Xiaoping Tang1, Xiaoling Cheng1, Bo Li2, Yiqi Luo2
Received:2010-03-07
Accepted:2010-06-22
Online:2010-11-20
Published:2011-01-31
Contact:
Chengzhang Liao
摘要:
土壤氮含量是限制植物生长的重要因素, 所以入侵植物要入侵成功必须突破土壤氮限制的瓶颈。近年来, 外来种互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)在中国海岸带盐沼中快速取代土著种芦苇(Phragmites australis), 引起了多方面的生态学后果。为了解互花米草与本地种芦苇空中凋落物的氮含量是否存在差异及产生这种差异的机制, 2003年11月至2004年4月, 作者在长江口九段沙湿地对互花米草与芦苇空中凋落物氮含量(单位面积凋落物的总氮量, N g/m2)进行了测定, 结果表明互花米草的氮含量比芦苇高。在空中分解过程中, 互花米草茎(包括叶鞘与秆)凋落物的氮含量显著上升, 但芦苇茎凋落物的氮含量显著降低。2006年1月, 又对中国海岸带6个地点的盐沼中互花米草的凋落物进行取样和氮浓度测定, 发现互花米草空中叶鞘与秆的老凋落物(2004年冬季产生)的氮浓度均显著高于其新产生的凋落物(2005年冬季产生), 表明在空中分解过程中, 互花米草叶鞘与秆凋落物氮含量增加具有普遍性。进一步的温室受控实验结果表明, 互花米草凋落物氮含量增加可能是由腐生固氮微生物引起的。以上结果表明,互花米草取代芦苇后, 改变了空中凋落物的氮动态, 增加了生态系统中氮的输入, 可能有利于互花米草的快速扩张。
廖成章, 唐小平, 程小玲, 李博, 骆亦其 (2010) 外来种互花米草和土著种芦苇空中凋落物氮动态的比较研究. 生物多样性, 18, 631-637. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.2010.631.
Chengzhang Liao, Xiaoping Tang, Xiaoling Cheng, Bo Li, Yiqi Luo (2010) Nitrogen dynamics of aerial litter of exotic Spartina alterniflora and native Phragmites australis. Biodiversity Science, 18, 631-637. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.2010.631.
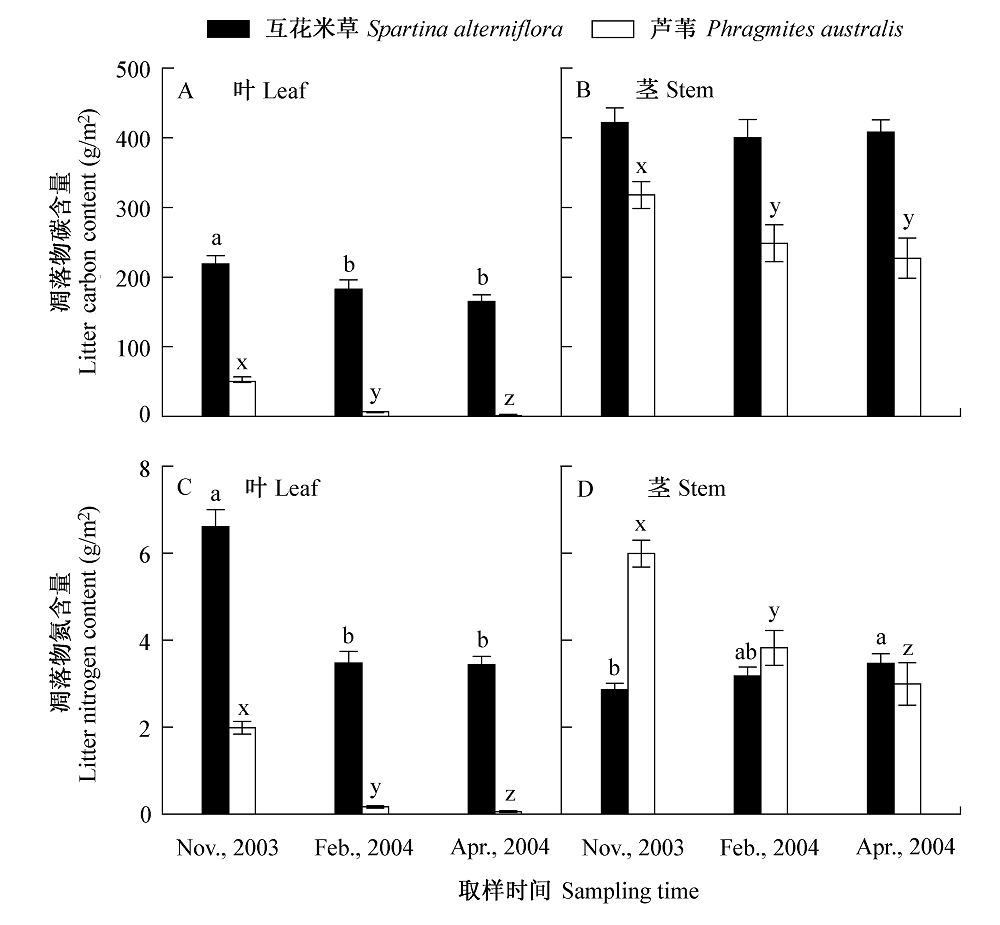
图1 长江口九段沙湿地外来种互花米草与土著种芦苇空中叶(A, C)与茎(B, D)凋落物碳、氮含量(平均值±标准误, n = 12)的动态变化。同一物种不同字母表示不同取样间差异显著; 除2004年2、4月两次取样的茎凋落物氮含量之外, 互花米草与芦苇两物种之间碳、氮含量差异极显著。
Fig. 1 Changes of carbon and nitrogen contents in aerial leaf litter (A and C), and aerial stem and sheath litter (B and D) for exotic Spartina alterniflora and native Phragmites australis in Jiuduansha wetlands of the Yangtze Estuary. Vertical bars represent mean ± 1 SE (n = 12). Different letters indicate significant differences for litter C and N contents from different sampling times within the same species. There were statistical differences in C and N contents between Spartina and Phragmites litters except for the N content in stem and sheath litter in February and April of 2004.
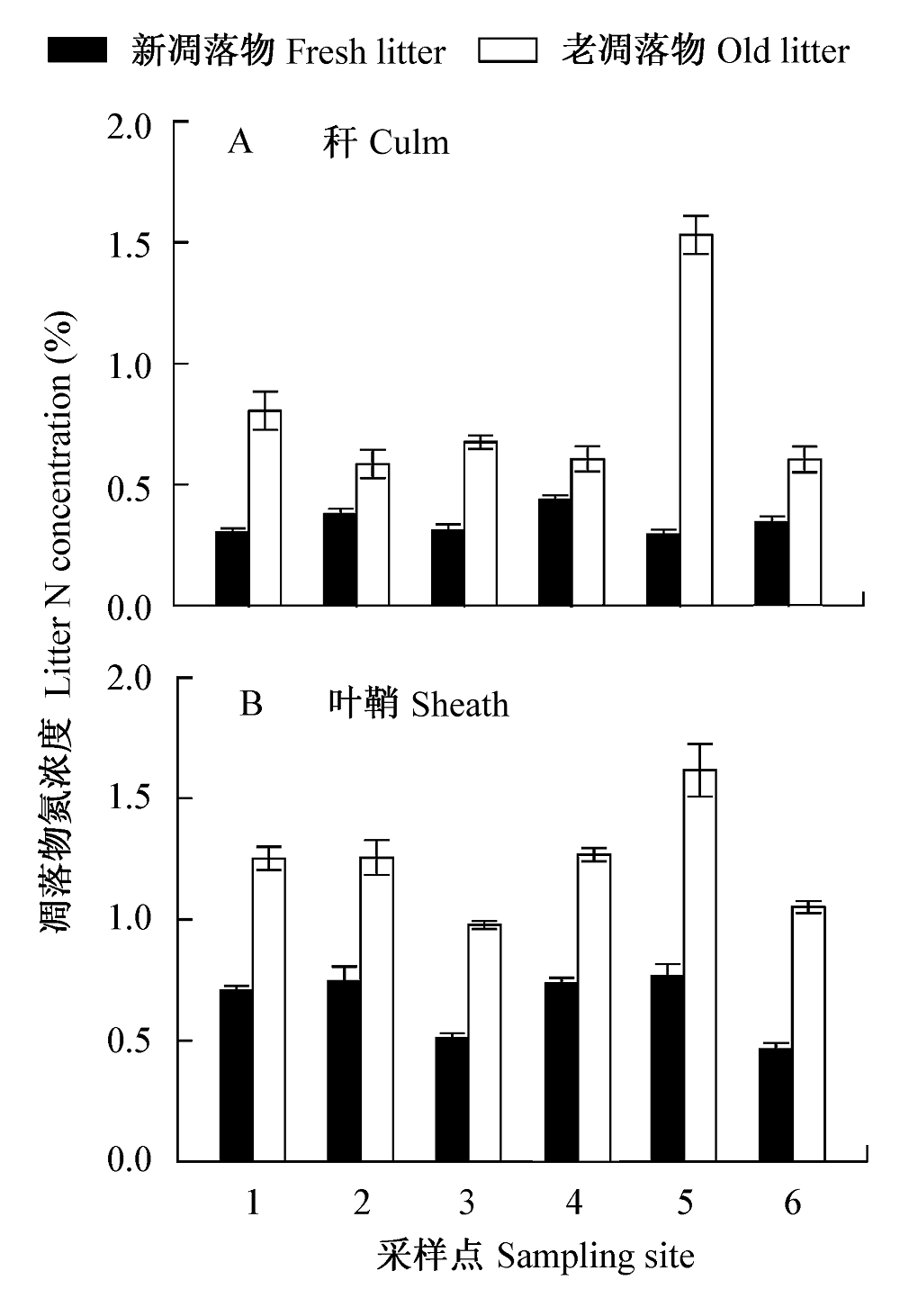
图2 中国东海岸5个盐沼湿地及复旦大学实验基地同质园内外来种互花米草秆(A)和叶鞘凋落物(B)氮浓度差异(平均值±标准误, n = 10)。6个地点的新、老凋落物氮浓度差异均极显著。1: 江苏大丰; 2: 上海崇明; 3:长江口九段沙; 4: 福建漳州; 5: 上海南汇; 6: 复旦大学。
Fig. 2 Comparison of nitrogen concentrations of culm (A) and sheath litter (B) between new (produced in 2005) and old aerial litter (produced in 2004) of exotic Spartina alterniflora sampled from the East Coast of China in January of 2006. There were significant differences in N concentration between new and old aerial litter across the six sites. Vertical bars represent mean ± 1 SE (n = 10). 1, Dafeng city of Jiangsu; 2, Chongming County of Shanghai; 3, Jiuduan Islands of Shanghai; 4, Zhangzhou City of Fujian; 5, Nanhui District of Shanghai; 6, Fudan University.
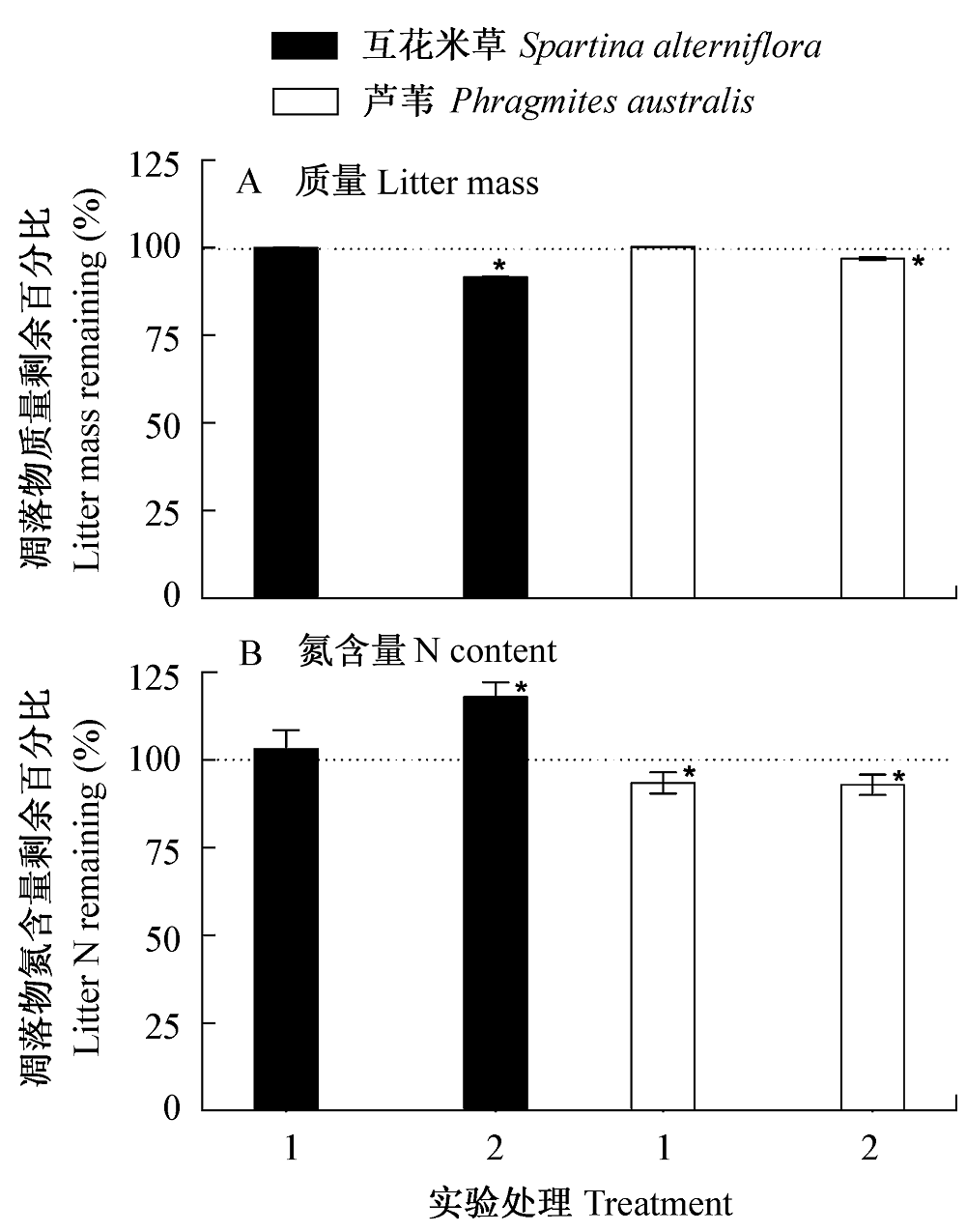
图3 外来种互花米草和土著种芦苇秆凋落物在温室分解45 d后质量(A)和氮含量(B)(占初始值的百分比, 平均值±标准误, n = 10)。实验处理1: 瓶内干燥、瓶口密封; 2: 瓶内加水、瓶口加盖; *表示凋落物质量或氮含量变化显著。
Fig. 3 Percent changes in stem litter mass (A) and N content (B) of exotic Spartina and native Phragmites stem litter under two treatments during glasshouse decomposition over a period of 45 days. Vertical bars represent mean ± 1 SE (n = 10). In treatment 1, the bottles were desiccated and sealed, whereas in Treatment 2, the bottles were watered and covered (not sealed). Asterisks indicate significant changes of litter mass and N content after 45-day decomposition for each species.
| [1] | Berg B, McClaugherty L (2003) Plant Litter Decomposition, Humus Formation, Carbon Sequestration. Springer, New York. |
| [2] | Bowden WB (1986) Nitrification, nitrate reduction, and nitrogen immobilization in a tidal fresh-water marsh sediment. Ecology, 67, 88-99. |
| [3] | Chen JK (陈家宽)(2003) Comprehensive Surveys on Shanghai Jiuduansha Wetland Nature Reserve, the Yangtze River Estuary (上海九段沙湿地自然保护区科学考察集). Science Press. Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Christian JM, Wilson SD (1999) Long-term ecosystem impacts of an introduced grass in the northern Great Plains. Ecology, 80, 2397-2407. |
| [5] | Crooks JA (2002) Characterizing ecosystem-level consequences of biological invasions: the role of ecosystem engineers. Oikos, 97, 153-166. |
| [6] | Currin CA, Paerl HW (1998) Epiphytic nitrogen fixation associated with standing dead shoots of smooth cordgrass, Spartina alterniflora. Estuaries, 21, 108-117. |
| [7] | Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems, 6, 503-523. |
| [8] | Gallagher JL, Reimold RJ, Linthurst RA, Pfeiffer WJ (1980) Aerial production, mortality, and mineral accumulation-export dynamics in Spartina alterniflora and Juncus roemerianus plant stands in a Georgia salt-marsh. Ecology, 61, 303-312. |
| [9] |
Gordon DR (1998) Effects of invasive, non-indigenous plant species on ecosystem processes: lessons from Florida. Ecological Applications, 8, 975-989.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hanson RB (1977) Nitrogen-fixation (acetylene-reduction) in a salt-marsh amended with sewage sludge and organic-carbon and nitrogen-compounds. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 33, 846-852.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Hobbie SE (2000) Interactions between litter lignin and soil nitrogen availability during leaf litter decomposition in a Hawaiian Montane forest. Ecosystems, 3, 484-494. |
| [12] |
Knops JMH, Bradley KL, Wedin DA (2002) Mechanisms of plant species impacts on ecosystem nitrogen cycling. Ecology Letters, 5, 454-466.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Kuehn KA, Steiner D, Gessner MO (2004) Diel mineralization patterns of standing-dead plant litter: implications for CO2 flux from wetlands. Ecology, 85, 2504-2518. |
| [14] | Liao CZ (2007) The Effects of Invasive Alien Plants on Ecosystem Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles: A Case Study of Spartina alterniflora Invasion in the Yangtze Estuary and A Meta-analysis. PhD dissertation. Fudan University, Shanghai, China. |
| [15] |
Liao CZ, Luo YQ, Jiang LF, Zhou XH, Wu XW, Fang CM, Chen JK, Li B (2007) Invasion of Spartina alterniflora enhanced ecosystem carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecosystems, 10, 1351-1361.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Liao CZ, Luo YQ, Fang CM, Chen JK, Li B (2008a) Litter pool sizes, decomposition, and nitrogen dynamics in Spartina alterniflora-invaded and native coastal marshlands of the Yangtze Estuary. Oecologia, 156, 589-600.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Liao CZ, Peng RH, Luo YQ, Zhou XH, Wu XW, Fang CM, Chen JK, Li B (2008b) Altered ecosystem carbon and nitrogen cycles by plant invasion: a meta-analysis. New Phytologist, 177, 706-714. |
| [18] | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecological Applications, 10, 689-710. |
| [19] | Melillo JM, Aber JD, Muratore JF (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology, 63, 621-626. |
| [20] | Newell SY (1993) Decomposition of shoots of a saltmarsh grass: methodology and dynamics of microbial assemblages. Advances in Microbial Ecology, 13, 301-326. |
| [21] | Patriquin DG, Denike D (1978) In situ acetylene-reduction assays of nitrogenase activity associated with emergent halophyte Spartina alterniflora Loisel. methodological problems. Aquatic Botany, 4, 211-226. |
| [22] | Pimentel D, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2005) Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecological Economics, 52, 273-288. |
| [23] | Poon MOK, Hyde KD (1998) Biodiversity of intertidal estuarine fungi on Phragmites at Mai Po marshes, Hong Kong. Botanica Marina, 41, 141-155. |
| [24] |
Rice DL, Tenore KR (1981) Dynamics of carbon and nitrogen during the decomposition of detritus derived from estuarine macrophytes. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 13, 681-690.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Schlesinger WH (1985) Decomposition of chaparral shrub foliage. Ecology, 66, 1353-1359. |
| [26] | Schubauer JP, Hopkinson CS (1984) Aboveground and belowground emergent macrophyte production and turnover in a coastal marsh ecosystem, Georgia. Limnology and Oceanography, 29, 1052-1065. |
| [27] |
Seabloom EW, Williams JW, Slayback D, Stoms DM, Viers JH, Dobson AP (2006) Human impacts, plant invasion, and imperiled, plant species in California. Ecological Applications, 16, 1338-1350.
URL PMID |
| [28] | Seliskar DM, Gallagher JL, Burdick DM, Mutz LA (2002) The regulation of ecosystem functions by ecotypic variation in the dominant plant: a Spartina alterniflora salt-marsh case study. Journal of Ecology, 90, 1-11. |
| [29] | Teal JM, Valiela I, Berlo D (1979) Nitrogen fixation by rhizosphere and free-living bacteria in salt-marsh sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 24, 126-132. |
| [30] | Vitousek PM, Walker LR (1989) Biological invasion by Myrica faya in Hawai’i: plant demography, nitrogen fixation, ecosystem effects. Ecological Monographs, 59, 247-265. |
| [31] | Wang Q (王卿), An SQ (安树青), Ma ZJ (马志军), Zhao B (赵斌), Chen JK (陈家宽), Li B (李博)(2006) Invasive Spartina alterniflora: biology, ecology and management. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 44, 559-588. (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [32] | Weber E, Li B (2008) Plant invasions in China: what is to be expected in the wake of economic development? BioScience, 58, 437-444. |
| [33] | Wilcove DS, Rothstein D, Dubow J, Phillips A, Losos E (1998) Quantifying threats to imperiled species in the United States. BioScience, 48, 607-615. |
| [34] | Xu HG, Ding H, Li MY, Qiang S, Guo JY, Han ZM, Huang ZG, Sun HY, He SP, Wu HR, Wan FH (2006) The distribution and economic losses of alien species invasion to China. Biological Invasions, 8, 1495-1500. |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 沈诗韵, 潘远飞, 陈丽茹, 土艳丽, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草原产地和入侵地种群的植物-土壤反馈差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [3] | 邓铭先, 黄河燕, 沈诗韵, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 斯确多吉, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草在青藏高原对模拟增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1198-1205. |
| [4] | 陈旭, 王国严, 彭培好, 李景吉, 石松林, 张廷斌. 四川攀西地区云南松群落物种多样性和谱系多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 865-874. |
| [5] | 黄河燕, 朱政财, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 周永洪, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对模拟全天增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 419-427. |
| [6] | 孙思邈, 陈吉欣, 冯炜炜, 张昶, 黄凯, 管铭, 孙建坤, 刘明超, 冯玉龙. 植物氮形态利用策略及对外来植物入侵性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 72-80. |
| [7] | 于良瑞, 朱政财, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对同基因型邻体根系的表型可塑性: 入侵地和原产地的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 651-657. |
| [8] | 朱珣之, 李强, 李扬苹, 韩洪波, 马克平. 紫茎泽兰入侵对土壤细菌的群落组成和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(5): 665-672. |
| [9] | 马丁, 鞠瑞亭, 李博. 土著昆虫素毒蛾对入侵植物互花米草地理种群的选择性[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 101-108. |
| [10] | 赵彩云, 柳晓燕, 白加德, 吕凤春, 李俊生. 广西北海西村港互花米草对红树林湿地大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 630-639. |
| [11] | 王思凯, 盛强, 储忝江, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华. 植物入侵对食物网的影响及其途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(3): 249-259. |
| [12] | 许湘琴, 王莹莹, 陆强, 林植华, 陈慧丽. 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对杭州湾地区土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(5): 519-527. |
| [13] | 张亦默, 王卿, 卢蒙, 贾昕, 耿宇鹏, 李博. 中国东部沿海互花米草种群生活史特征的纬度变异与可塑性[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(5): 462-469. |
| [14] | 高慧, 彭筱葳, 李博, 吴千红, 董慧琴. 互花米草入侵九段沙河口湿地对当地昆虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(5): 400-409. |
| [15] | 李贺鹏, 张利权, 王东辉. 上海地区外来种互花米草的分布现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(2): 114-120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn