



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (4): 389-398. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08014 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.08014
收稿日期:2008-01-21
接受日期:2008-06-11
出版日期:2008-07-20
发布日期:2008-07-20
通讯作者:
苗鸿
基金资助:
Jing Liu, Hong Miao*( ), Zhiyun Ouyang, Weihua Xu, Hua Zheng
), Zhiyun Ouyang, Weihua Xu, Hua Zheng
Received:2008-01-21
Accepted:2008-06-11
Online:2008-07-20
Published:2008-07-20
Contact:
Hong Miao
摘要:
目前全球各地开展了一系列评估保护区管理成效的研究工作。2005年, 国家林业局对全国634个自然保护区的管理人员发放了调查问卷, 回收有效问卷535份。本文针对其中的社区参与、社区共管和与社区的协调发展3个指标分析了国内的自然保护区社区管理效果, 并对社区管理效果的得分情况、区域特征、级别特征和影响管理效果的因素进行了分析。结果表明: 我国自然保护区的社区管理水平普遍较低, 3个指标中, 与社区的协调发展得分最高, 为1.85分, 社区参与和社区共管分别为1.15分和1.03分; 各个区域在社区管理效果方面没有显著差异(P>0.05), 华中地区的社区管理效果平均分最高, 为4.26分, 华南地区最低, 为3.73分; 国家级自然保护区的社区管理效果整体上比省级好, 二者存在显著差异(P<0.01)。通过Pearson相关分析得出, 监测与评价、人事管理、职工培训、管理计划和保护区巡护这5个指标与社区管理效果的相关程度较大。为了提高自然保护区社区管理效果, 我们建议着重从有效保护区内的自然资源、建立社区共管机制、建立生态补偿机制、国家和各省统筹拨付保护区经费以及完善职工管理制度几方面入手。
刘静, 苗鸿, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 郑华 (2008) 自然保护区社区管理效果分析. 生物多样性, 16, 389-398. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08014.
Jing Liu, Hong Miao, Zhiyun Ouyang, Weihua Xu, Hua Zheng (2008) Analyzing the effectiveness of community management in Chinese nature reserves. Biodiversity Science, 16, 389-398. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08014.
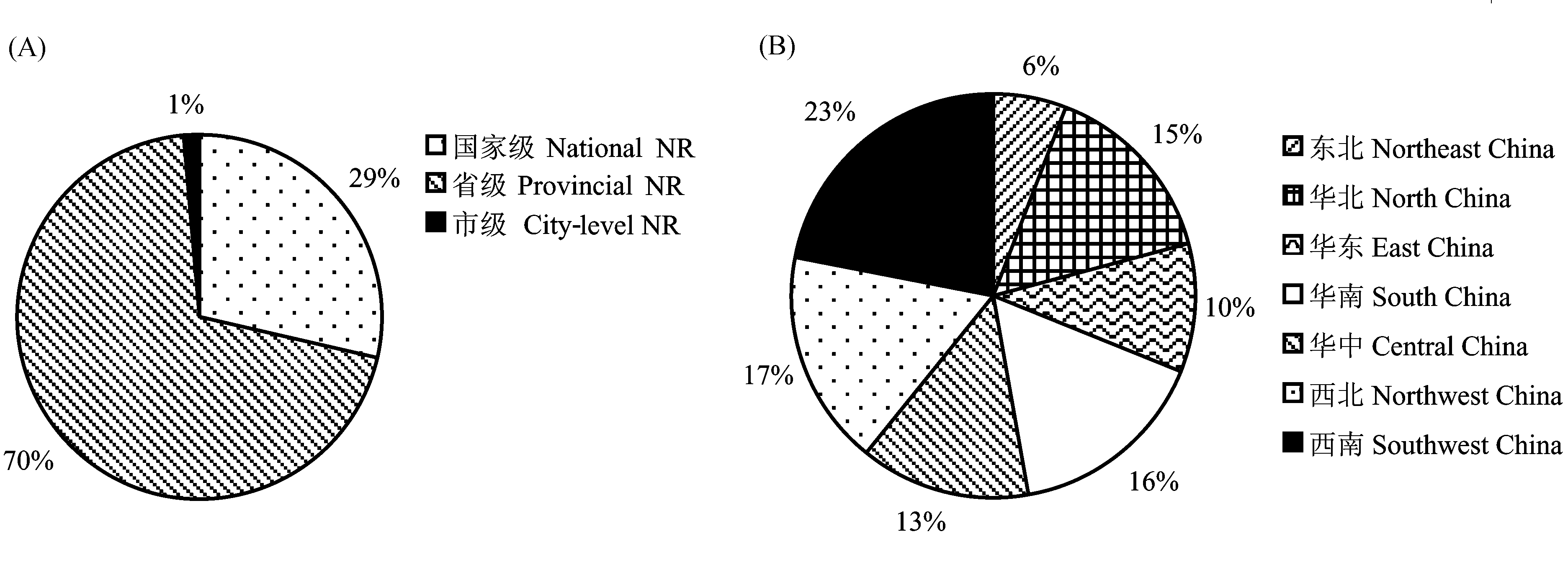
图1 本次调查所选取的自然保护区样本状况。(A)国家级、省级、市级等各级自然保护区占调查总数的百分比; (B)被调查自然保护区的区域分布。
Fig. 1 Selection characteristics of the investigated nature reserves. (A) Percentages of national, provincial and city-level nature reserves; (B) Regional distribution of the investigated nature reserves.
| 指标 Index | 评价标准 Evaluation criterion | 得分 Scores |
|---|---|---|
| 社区参与 Community participation | 保护区在制定管理决策过程中没有征求社区居民的意见 Managers don’t consult with the communities before making decisions | 0 |
| 保护区部分征求了社区居民的意见, 但社区居民没有直接参与决策 Managers consult the communities sometimes, but local people don’t participate the decision-making directly | 1 | |
| 社区居民能够参与保护区管理决策的制定 Local people can participate the decision-making | 2 | |
| 社区居民经常参与保护区管理决策的制定, 并能影响保护区的决策 Local people participate the decision-making frequently, and can have impacts on the decisions | 3 | |
| 社区共管 Community co-management | 没有开展社区共管活动 No co-management activities | 0 |
| 有共管委员会或相应的管理机构, 但活动很少 Co-management committees or relevant institutions exist, but with few activities | 1 | |
| 有共管委员会或相应的管理机构, 签订了共管协议, 不定期开展共管活动或召开协调会议 Co-management committees or relevant institutions exist, with signed co-management agreement, irregular activities and coordinating conferences | 2 | |
| 有共管委员会和相应的管理机构, 定期开展共管活动, 取得成效 Co-management committees and relevant institutions exist and get some achievements through regular activities | 3 | |
| 与社区的协调发展 Coordination with communities | 保护区的管理活动对当地社区发展有明显的负面影响 Management steps have obviously negative effects on local communities | 0 |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区发展没有不利影响, 也没有带来利益 Management steps have neither negative nor positive effects on local communities | 1 | |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区的发展有促进作用, 但是对区域经济的发展影响不大 Management steps have lots of positive effects on local communities, but few on regional economy development | 2 | |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区的发展有明显的促进作用, 促进了所在区域的发展 Management steps have lots of positive effects on both local communities and regional economy development | 3 |
表1 自然保护区社区管理效果(包括社区参与、社区共管和与社区的协调发展)评价标准
Table 1 Evaluation criterion of the effectiveness of community management, including community participation, community co-management, and coordination with communities
| 指标 Index | 评价标准 Evaluation criterion | 得分 Scores |
|---|---|---|
| 社区参与 Community participation | 保护区在制定管理决策过程中没有征求社区居民的意见 Managers don’t consult with the communities before making decisions | 0 |
| 保护区部分征求了社区居民的意见, 但社区居民没有直接参与决策 Managers consult the communities sometimes, but local people don’t participate the decision-making directly | 1 | |
| 社区居民能够参与保护区管理决策的制定 Local people can participate the decision-making | 2 | |
| 社区居民经常参与保护区管理决策的制定, 并能影响保护区的决策 Local people participate the decision-making frequently, and can have impacts on the decisions | 3 | |
| 社区共管 Community co-management | 没有开展社区共管活动 No co-management activities | 0 |
| 有共管委员会或相应的管理机构, 但活动很少 Co-management committees or relevant institutions exist, but with few activities | 1 | |
| 有共管委员会或相应的管理机构, 签订了共管协议, 不定期开展共管活动或召开协调会议 Co-management committees or relevant institutions exist, with signed co-management agreement, irregular activities and coordinating conferences | 2 | |
| 有共管委员会和相应的管理机构, 定期开展共管活动, 取得成效 Co-management committees and relevant institutions exist and get some achievements through regular activities | 3 | |
| 与社区的协调发展 Coordination with communities | 保护区的管理活动对当地社区发展有明显的负面影响 Management steps have obviously negative effects on local communities | 0 |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区发展没有不利影响, 也没有带来利益 Management steps have neither negative nor positive effects on local communities | 1 | |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区的发展有促进作用, 但是对区域经济的发展影响不大 Management steps have lots of positive effects on local communities, but few on regional economy development | 2 | |
| 保护区的管理活动对当地社区的发展有明显的促进作用, 促进了所在区域的发展 Management steps have lots of positive effects on both local communities and regional economy development | 3 |
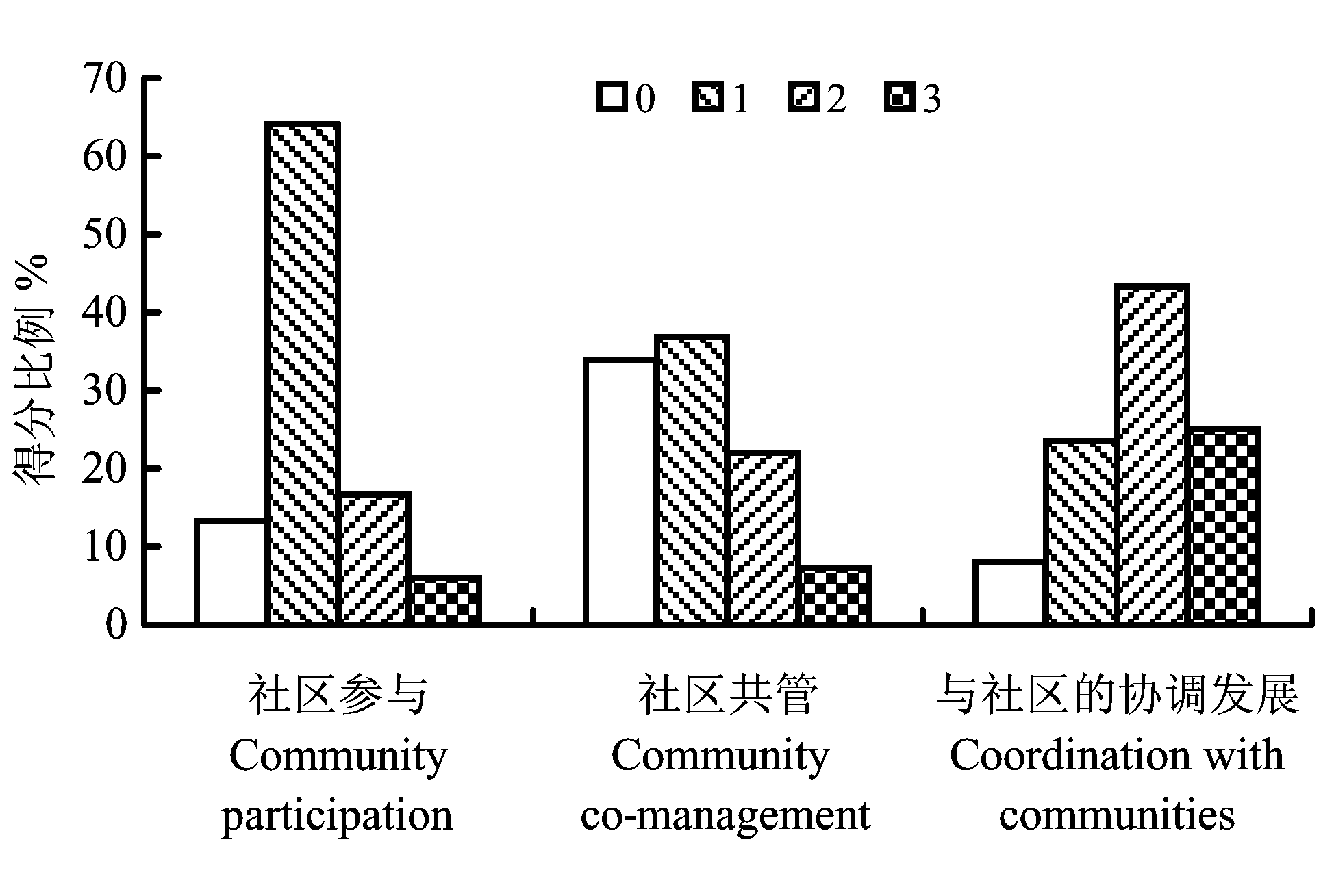
图2 社区参与、社区共管和与社区的协调发展的各分值(0-3分)的得分比例
Fig. 2 Percentage of the scores (0-3) in community participation, community co-management, and coordination with communities, respectively
| 社区参与 Community participation | 社区共管Community co-management | 与社区的协调发展Coordination with communities | 社区管理效果Community management effectiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 社区共管 Community co-management | .412** | 1 | .261** | .778** |
| 社区参与 Community participation | 1 | .412** | .270** | .718** |
| 与社区的协调发展 Coordination with communities | .270** | .261** | 1 | .710** |
| 监测与评价 Monitoring and evaluation | .337** | .433** | .287** | .481** |
| 人事管理 Personnel management | .266** | .392** | .351** | .464** |
| 职工培训 Staff training | .241** | .393** | .296** | .428** |
| 管理计划 Management plan | .277** | .358** | .283** | .419** |
| 保护区巡护 Patrolling | .280** | .350** | .287** | .418** |
| 宣传教育项目 Propaganda and education | .270** | .317** | .226** | .369** |
| 保护状况 Conservation status | .227** | .280** | .291** | .365** |
| 资源管理 Resource management | .209** | .280** | .298** | .361** |
| 设备使用和维护 Usage and maintenance of devices | .191** | .350** | .206** | .345** |
| 保护区边界 NR border | .306** | .266** | .197** | .343** |
| 保护区机构 NR institution | .176** | .303** | .241** | .333** |
| 基础设施 Infrastructure | .181** | .253** | .285** | .331** |
| 经费管理 Financial management | .130** | .286** | .273** | .322** |
| 保护对象的管理 Management of conservation objects | .221** | .232** | .253** | .320** |
| 资源监测 Resource monitoring | .239** | .326** | .139** | .319** |
| 员工数量 Staff quantity | .208** | .256** | .220** | .311** |
| 旅游管理 Tourism management | .167** | .218** | .281** | .306** |
| 保护区控制 NR controlling | .153** | .225** | .271** | .300** |
| 科研 Scientific research | .172** | .332** | .138** | .296** |
| 工资与福利 Wages and welfare | .184** | .259** | .196** | .293** |
| 总体规划 General plan | .219** | .248** | .168** | .287** |
| 事业经费 Undertaking expenditures | .122** | .305** | .157** | .272** |
| 资源调查 Resource investigation | .236** | .280** | .089(*) | .272** |
| 管理办法 Management steps | .178** | .256** | .137** | .261** |
| 公安机构建设 Construction of police agency | .059 | .198** | .071 | .155** |
| 土地/森林所有权 Land/forest rights | .057 | .112** | .126** | .138** |
| 保护区管理体制 NR management mechanism | .022 | .135** | .085(*) | .116** |
| 行政执法权 Administrative execution rights | .078 | .057 | .004 | .060 |
表2 社区管理效果影响因子相关系数表
Table 2 Correlation coefficients of the factors influencing community management effectiveness
| 社区参与 Community participation | 社区共管Community co-management | 与社区的协调发展Coordination with communities | 社区管理效果Community management effectiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 社区共管 Community co-management | .412** | 1 | .261** | .778** |
| 社区参与 Community participation | 1 | .412** | .270** | .718** |
| 与社区的协调发展 Coordination with communities | .270** | .261** | 1 | .710** |
| 监测与评价 Monitoring and evaluation | .337** | .433** | .287** | .481** |
| 人事管理 Personnel management | .266** | .392** | .351** | .464** |
| 职工培训 Staff training | .241** | .393** | .296** | .428** |
| 管理计划 Management plan | .277** | .358** | .283** | .419** |
| 保护区巡护 Patrolling | .280** | .350** | .287** | .418** |
| 宣传教育项目 Propaganda and education | .270** | .317** | .226** | .369** |
| 保护状况 Conservation status | .227** | .280** | .291** | .365** |
| 资源管理 Resource management | .209** | .280** | .298** | .361** |
| 设备使用和维护 Usage and maintenance of devices | .191** | .350** | .206** | .345** |
| 保护区边界 NR border | .306** | .266** | .197** | .343** |
| 保护区机构 NR institution | .176** | .303** | .241** | .333** |
| 基础设施 Infrastructure | .181** | .253** | .285** | .331** |
| 经费管理 Financial management | .130** | .286** | .273** | .322** |
| 保护对象的管理 Management of conservation objects | .221** | .232** | .253** | .320** |
| 资源监测 Resource monitoring | .239** | .326** | .139** | .319** |
| 员工数量 Staff quantity | .208** | .256** | .220** | .311** |
| 旅游管理 Tourism management | .167** | .218** | .281** | .306** |
| 保护区控制 NR controlling | .153** | .225** | .271** | .300** |
| 科研 Scientific research | .172** | .332** | .138** | .296** |
| 工资与福利 Wages and welfare | .184** | .259** | .196** | .293** |
| 总体规划 General plan | .219** | .248** | .168** | .287** |
| 事业经费 Undertaking expenditures | .122** | .305** | .157** | .272** |
| 资源调查 Resource investigation | .236** | .280** | .089(*) | .272** |
| 管理办法 Management steps | .178** | .256** | .137** | .261** |
| 公安机构建设 Construction of police agency | .059 | .198** | .071 | .155** |
| 土地/森林所有权 Land/forest rights | .057 | .112** | .126** | .138** |
| 保护区管理体制 NR management mechanism | .022 | .135** | .085(*) | .116** |
| 行政执法权 Administrative execution rights | .078 | .057 | .004 | .060 |
| [1] |
Castilla JC, Defeo O (2001) Latin American benthic shellfisheries: emphasis on co-management and experimental practices. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 11,1-30.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Fu XL (傅晓莉) (2005) Research on community economic development of nature reserves in western China. Future and Development (未来与发展), (5),51-53, 50. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Gao P (高平), Wen YL (温亚利) (2004) Characters, cause of poverty and its countermeasures in peripheral communities of China’s natural reserves. Research of Agricultural Modernization (农业现代化研究), 25,255-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] |
Han NY (韩念勇) (2000) A policy study on sustainable management for China’s nature reserves. Journal of Natural Resources (自然资源学报), 15,201-207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [5] | Han NY (韩念勇), Guo ZF (郭志芬) (1994) Present situation of nature reserves in China. Environmental Protection (环境保护), (11),46-47, 43. (in Chinese) |
| [6] |
Hockings M (2003) Systems for assessing the effectiveness of management in protected areas. BioScience, 53,823-832.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Hockings M, Stolton S, Dudley N (translated by Jiang MK (蒋明康), Ding H (丁晖)) (2005) Evaluating Effectiveness: A Framework for Assessing the Management of Protected Areas, pp. 12-52. China Environmental Sciences Press,Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | Huang WJ (黄文娟), Yang DD (杨道德), Zhang GZ (张国珍) (2004) A review of progress community involvement in nature reserve management in China. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology (湖南林业科技), 31(1),46-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Ishwaran N(translated by Han NY (韩念勇)) (1994) Biodiversity, nature reserves and sustainable development. China Population, Resources and Environment (中国人口、资源与环境), 4(4), 63,69-72. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Jiang LJ (姜立军), Miao H (苗鸿), Zhang J (张菊), Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云), Wang XK (王效科), Wei YC (魏彦昌) (2005) Indexes for evaluation of nature reserve management effectiveness. Rural Eco-Environment (农村生态环境), 21(1),72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Lai QK (赖庆奎), Li JQ (李建钦), Meng XY (孟祥勇) (2004) Case analysis on community co-management in the Wenshan Nature Reserve of Yunnan. Forestry and Society Journal (林业与社会), 12(3),18-23. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Li DQ, Zhou JH, Dong K, Wu B, Zhu CQ (2003) China: Management Effectiveness Assessment of Protected Areas in the Upper Yangtze Ecoregion Using WWF’s RAPPAM Methodology. http://assets.panda.org/downloads/china-casestudyfinal.pdf.() |
| [13] | Liang QH (梁启慧), He SW (何少文) (2006) Community co-management exploration involving in commercial mechanism―Project of sustainable apiculture based on conservation in and around Feping NR. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition) (陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版)), 34(Suppl.),228-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Luan XF (栾晓峰), Xie YM (谢一民), Du DC (杜德昌), Xu HF (徐宏发) (2002) The ecological and management evaluation of Chongming Dongtan Bird Nature Reserve. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Natural Science) (上海师范大学学报(自然科学版)), 31(3),73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Lv YH (吕一河), Chen LD (陈利顶), Fu BJ (傅伯杰) (2001) Biodiversity resources: utilization, conservation and management. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9,422-429. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] |
Maikhuri RK, Nautiyal S, Rao KS, Saxena KG (2001) Conservation policy-people conflicts: a case study from Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve (a World Heritage Site), India. Forest Policy and Economics, 2,355-365.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Miao H (苗鸿) (2000) Community mechanism of nature reserves in China. In:Research on Sustainable Management Policy of Nature Reserves in China (中国自然保护区可持续管理政策研究) (ed. The Chinese National Committee for the Man and the Biosphere Programme (中国人与生物圈国家委员会), pp.57-71. Scientific and Technical Document Press,Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
Nepal SK (2002) Involving indigenous people in protected area management: comparative perspectives from Nepal, Thailand, and China. Environmental Management, 30,748-763.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Newmark WD, Manyanza DN, Gamaza DGM, Sariko HI (1994) The conflict between wildlife and local people living adjacent to protected areas in Tanzania: human density as a predictor. Conservation Biology, 8,249-255.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Ouyang ZY (欧阳志云), Wang XK (王效科), Miao H (苗鸿), Han NY (韩念勇) (2002) Problems of management system of China’s nature preservation zones and their solutions. Science and Technology Review (科技导报), 22 (1),49-52. (in Chinese) |
| [21] |
Pomeroy RS, Watson LM, Parks JE, Cid GA (2005) How is your MPA doing? A methodology for evaluating the management effectiveness of marine protected areas. Ocean and Coastal Management, 48,485-502.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Su Y (苏扬) (2004) Countermeasures for improving management of natural reserves in China. Green China(绿色中国), (18),25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Wang Q (王琪), Wu L (吴磊), Lun XW (伦小文), Wang GJ (王桂君) (2005) Research on efficient management of protected areas in Jilin Province. Journal of Jilin Institute of Chemical Technology (吉林化工学院学报), 22(1),24-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Weladji RB, Tchamba MN (2003) Conflict between people and protected areas within the Benoue Wildlife Conservation Area, North Cameroon. Oryx, 37,72-79. |
| [25] |
Weladji RB, Moe SR, Vedeld P (2003) Stakeholder attitudes towards wildlife policy and the Benoue Wildlife Conservation Area, North Cameroon. Environmental Conservation, 30,334-343.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Xie ZH (谢志红), Xu YX (徐永新) (2003) Evaluation of management effectiveness of the nature reserves from Hunan Province. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology (湖南林业科技), 30(2),7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Xu JY (徐建英), Chen LD (陈利顶), Lv YH (吕一河), Fu BJ (傅伯杰) (2005) Harmonization of protected areas management and local development: methods, practices and lessons. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 24,102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Xue DY (薛达元), Zheng YW (郑允文) (1994) A study on evaluation criteria for effective management of the nature reserves in China. Rural Eco-Environment (农村生态环境), 10(2),6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Yang GM (杨光梅), Min QW (闵庆文), Li WH (李文华), Liu L (刘璐), Rong JF (荣金凤), Wu XB (吴雪宾) (2006) Herdsmen’s willingness to accept (WTA) compensation for implement of prohibiting-graze policy in Xilinguole steppe. Ecology and Environment (生态环境), 15,747-751. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Yang WZ (杨文忠), Jin L (靳莉), Zhao XD (赵晓东) (2007) Connotative evolvement of community co-management in Yunnan’s nature reserve. Problems of Forestry Economics (林业经济问题), 27,16-19, 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Zhang HM (张和民), Wang PY (王鹏彦), Zhang GQ (张贵权), Wei RP (魏荣平) (2000) Advances in conservation and research technology for captive and wild pandas of Wolong. Sichuan Journal of Zoology (四川动物), 19,35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Zhang JL (张金良), Li HF (李焕芳), Huang FG (黄方国) (2000) Community co-management: A new model for nature reserve management. Chinese Biodiversity(生物多样性), 8,347-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [3] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [4] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [5] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [6] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [7] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [8] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [9] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [10] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [11] | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪. 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [12] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [13] | 赵梦乔, 陈友, 徐正会, 王戌勃, 赵忠良, 徐文川, 何宗辉, 王文华. 云南哀牢山国家级自然保护区东坡垂直带蚂蚁物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23168-. |
| [14] | 胡远芳, 李斌强, 梁丹, 李兴权, 刘兰香, 杨家伟, 罗旭. 人为干扰对白腹锦鸡活动节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21484-. |
| [15] | 李海萍, 徐竹青, 龙志航. 大兴安岭地区重点保护和珍稀动物保护空缺分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21294-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn