



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (2): 166-174. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07093 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.07093
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
徐华勤1,2, 肖润林1,*( ), 宋同清1, 罗文2, 任全2, 黄瑶1
), 宋同清1, 罗文2, 任全2, 黄瑶1
收稿日期:2007-05-26
接受日期:2007-09-19
出版日期:2008-03-20
发布日期:2008-02-20
通讯作者:
肖润林
作者简介:*E-mail:xiaorl@isa.ac.cn基金资助:
Huaqin Xu1,2, Runlin Xiao1,*( ), Tongqing Song1, Wen Luo2, Quan Ren2, Yao Huang1
), Tongqing Song1, Wen Luo2, Quan Ren2, Yao Huang1
Received:2007-05-26
Accepted:2007-09-19
Online:2008-03-20
Published:2008-02-20
Contact:
Runlin Xiao
摘要:
不同的土壤管理方式对土壤的质量有重要影响, 而土壤微生物群落功能多样性是反映土壤质量变化的重要指标之一。本研究旨在利用Biolog微孔板鉴定系统研究不同培肥措施下茶园土壤微生物群落功能多样性的变化。比较6种处理的结果发现, 与NPK肥+清耕(CK)相比, 平均吸光值(average well color development, AWCD)的变化速度(斜率)和最大值顺序为: 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草>NPK肥+稻草覆盖>饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖>饼肥+PK+清耕>NPK肥+间作三叶草>CK。可见间作三叶草与稻草覆盖不同程度地提高了微生物整体活性和丰富度, 其中饼肥+PK+间作三叶草处理处理效果最好。分析多样性指数发现, 虽然稻草覆盖与间作三叶草对土壤常见微生物种类影响并不大, 但微生物群落均匀度有所降低。对碳源利用主成分起分异作用的主要是糖类和羧酸类物质。
徐华勤, 肖润林, 宋同清, 罗文, 任全, 黄瑶 (2008) 稻草覆盖与间作三叶草对丘陵茶园土壤微生物群落功能的影响. 生物多样性, 16, 166-174. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07093.
Huaqin Xu, Runlin Xiao, Tongqing Song, Wen Luo, Quan Ren, Yao Huang (2008) Effects of mulching and intercropping on the functional diversity of soil microbial communities in tea plantations. Biodiversity Science, 16, 166-174. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07093.
图1 实验区及6种处理示意图(6种处理的代号同表1)
Fig. 1 Sketch map showing experimental area and six fertilizer treatments. Codes I–VI for six different treatments see Table 1.
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | 稻草覆盖Strawmulching | 间作三叶草 White clover intercropping | 有机肥(饼肥) Organic manure | 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素 Carbamide | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 氯化钾肥 KCl | |||||
| I | NPK+清耕 (CK) NPK fertilizer+tillage | - | - | - | 143 | 205 | 82 |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 Caky fertilizer+PK fertilizer+tillage | - | - | 1,250 | - | 90 | 62 |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 NPK fertilizer + straw mulching | 2,250 | - | - | 103 | 149 | 14.2 |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 Caky fertilizer+PK fertilizer+straw mulching | 2,250 | - | 900 | - | 68 | - |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 NPK fertilizer+intercropping with white clover | - | 0.45 | - | 143 | 205 | 82 |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 Caky fertilizer + intercropping with white clover | - | 0.45 | 1,250 | - | 90 | 62 |
表1 供试土壤的6种不同施肥处理的施肥量
Table 1 Application amount of fertilizers in the six different treatments (g/plot)
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | 稻草覆盖Strawmulching | 间作三叶草 White clover intercropping | 有机肥(饼肥) Organic manure | 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素 Carbamide | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 氯化钾肥 KCl | |||||
| I | NPK+清耕 (CK) NPK fertilizer+tillage | - | - | - | 143 | 205 | 82 |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 Caky fertilizer+PK fertilizer+tillage | - | - | 1,250 | - | 90 | 62 |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 NPK fertilizer + straw mulching | 2,250 | - | - | 103 | 149 | 14.2 |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 Caky fertilizer+PK fertilizer+straw mulching | 2,250 | - | 900 | - | 68 | - |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 NPK fertilizer+intercropping with white clover | - | 0.45 | - | 143 | 205 | 82 |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 Caky fertilizer + intercropping with white clover | - | 0.45 | 1,250 | - | 90 | 62 |
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | 全 N Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全 P Total P (g/kg) | 全 K Total K (g/kg) | 速效N Available N (mg/kg) | 有效P Available P(mg/kg) | 速效K Available K (mg/kg) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | NPK+清耕 (CK) | 0.90 (0.21) | 7.06 (0.27) | 0.63 (0.13) | 10.11 (0.37) | 18.43 (0.21) | 17.68 (0.71) | 127.98 (0.64) | 6.92 (0.31) |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 | 0.91 (0.11) | 7.67 (0.33) | 0.58 (0.19) | 10.08 (0.11) | 21.34 (1.07) | 18.22 (0.56) | 159.33 (0.96) | 7.01 (0.52) |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 | 0.98 (013) | 8.31 (0.14) | 0.51 (0.22) | 9.96 (0.35) | 24.13 (0.97) | 18.91 (0.43) | 191.70 (1.17) | 6.88 (0.97) |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 | 0.97 (0.18) | 8.05 (0.22) | 0.56 (0.17) | 9.7 (0.46) | 21.88 (1.17) | 20.89 (1.01) | 227.61 (0.97) | 6.76 (0.41) |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 | 0.95 (021) | 7.95 (0.17) | 0.57 (021) | 10.21 (0.23) | 24.69 (0.66) | 17.54 (0.44) | 83.41 (1.31) | 5.98 (0.64) |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 | 0.99 (0.14) | 8.15 (0.23) | 0.55 (0.18) | 9.89 (0.12) | 23.52 (1.32) | 16.18 (0.35) | 98.97 (0.88) | 6.30 (0.10) |
表2 不同施肥处理后土壤的养分含量(括号内为标准差)
Table 2 Nutrients of soil after fertilization treatments. Codes I-VI for six different treatments see Table 1. Standard deviation in parentheses.
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | 全 N Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全 P Total P (g/kg) | 全 K Total K (g/kg) | 速效N Available N (mg/kg) | 有效P Available P(mg/kg) | 速效K Available K (mg/kg) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | NPK+清耕 (CK) | 0.90 (0.21) | 7.06 (0.27) | 0.63 (0.13) | 10.11 (0.37) | 18.43 (0.21) | 17.68 (0.71) | 127.98 (0.64) | 6.92 (0.31) |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 | 0.91 (0.11) | 7.67 (0.33) | 0.58 (0.19) | 10.08 (0.11) | 21.34 (1.07) | 18.22 (0.56) | 159.33 (0.96) | 7.01 (0.52) |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 | 0.98 (013) | 8.31 (0.14) | 0.51 (0.22) | 9.96 (0.35) | 24.13 (0.97) | 18.91 (0.43) | 191.70 (1.17) | 6.88 (0.97) |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 | 0.97 (0.18) | 8.05 (0.22) | 0.56 (0.17) | 9.7 (0.46) | 21.88 (1.17) | 20.89 (1.01) | 227.61 (0.97) | 6.76 (0.41) |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 | 0.95 (021) | 7.95 (0.17) | 0.57 (021) | 10.21 (0.23) | 24.69 (0.66) | 17.54 (0.44) | 83.41 (1.31) | 5.98 (0.64) |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 | 0.99 (0.14) | 8.15 (0.23) | 0.55 (0.18) | 9.89 (0.12) | 23.52 (1.32) | 16.18 (0.35) | 98.97 (0.88) | 6.30 (0.10) |
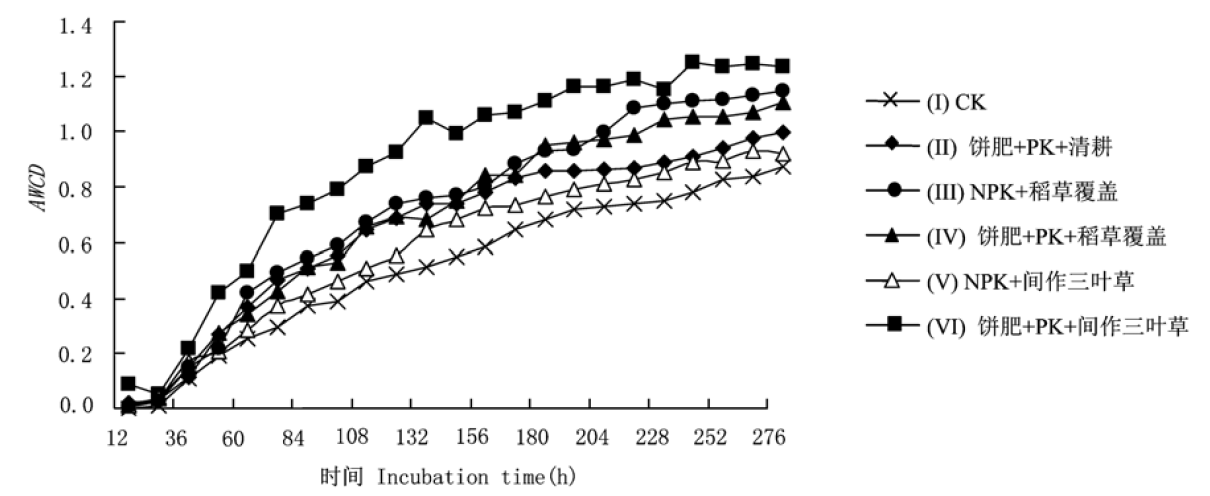
图2 供试土壤微生物培育过程中的平均吸光值(AWCD)的变化
Fig. 2 Variation in average well color development (AWCD) over time of different treatments. Codes I-VI for six different treatments see Table 1.
| 变 量 Variables | 差异源 Source | 偏差平方和 Sum of square of deviations | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方差 Mean square | F值 F | P值 P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD (饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖、饼肥+PK+清耕、饼肥+PK+间作三叶草、CK) | 组间 Among groups | 1.577 | 3 | 0.526 | 4.872 | 0.004 |
| 组内 Within groups | 9.493 | 88 | 0.108 | |||
| 总和 Total | 11.070 | 91 | ||||
| AWCD (NPK+稻草覆盖、NPK+间作三叶草、CK) | 组间 Among groups | 0.520 | 2 | 0.260 | 2.700 | 0.075 |
| 组内 Within groups | 6.357 | 66 | 0.096 | |||
| 总和 Total | 6.877 | 68 |
表3 供试土壤各处理间的平均吸光值(AWCD)的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of average well color development (AWCD) for different treatments
| 变 量 Variables | 差异源 Source | 偏差平方和 Sum of square of deviations | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方差 Mean square | F值 F | P值 P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD (饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖、饼肥+PK+清耕、饼肥+PK+间作三叶草、CK) | 组间 Among groups | 1.577 | 3 | 0.526 | 4.872 | 0.004 |
| 组内 Within groups | 9.493 | 88 | 0.108 | |||
| 总和 Total | 11.070 | 91 | ||||
| AWCD (NPK+稻草覆盖、NPK+间作三叶草、CK) | 组间 Among groups | 0.520 | 2 | 0.260 | 2.700 | 0.075 |
| 组内 Within groups | 6.357 | 66 | 0.096 | |||
| 总和 Total | 6.877 | 68 |
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | CK | 4.160±0.051 | 0.979±0.033 | 1.130±0.032 |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 | 4.483±0.026 | 0.976±0.019 | 1.130±0.042 |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 | 4.571±0.027 | 0.971±0.011 | 1.030±0.010 |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 | 4.510±0.033 | 0.981±0.071 | 1.073±0.081 |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 | 4.514±0.083 | 0.979±0.021 | 1.106±0.070 |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 | 4.533±0.037 | 0.985±0.064 | 1.039±0.043 |
表4 供试土壤微生物群落多样性指数
Table 4 Diversity indices of soil microbial communities
| 代号 Code | 处理 Treatments | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | CK | 4.160±0.051 | 0.979±0.033 | 1.130±0.032 |
| II | 饼肥+PK+清耕 | 4.483±0.026 | 0.976±0.019 | 1.130±0.042 |
| III | NPK+稻草覆盖 | 4.571±0.027 | 0.971±0.011 | 1.030±0.010 |
| IV | 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖 | 4.510±0.033 | 0.981±0.071 | 1.073±0.081 |
| V | NPK+间作三叶草 | 4.514±0.083 | 0.979±0.021 | 1.106±0.070 |
| VI | 饼肥+PK+间作三叶草 | 4.533±0.037 | 0.985±0.064 | 1.039±0.043 |
| 全 氮 Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全 磷 Total P (g/kg) | 全 钾 Total K (g/kg) | 速效N Available N (mg/kg) | 有效P Available P(mg/kg) | 速效K Available K (mg/kg) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD值 (n = 23) AWCD value | 0.658* | 0.555* | -0.520 | - 0.449 | 0.378 | -0.414 | -0.115 | -0.169 |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.757* | 0.949** | -0.889** | -0.344 | 0.885** | 0.156 | 0.192 | -0.335 |
| Simpson指数Simpson index | 0.181 | -0.084 | 0.323 | -0.280 | -0.095 | -0.331 | -0.396 | -0.499 |
| Pielou指数 Pielou index | -0.941** | -0.837** | 0.861** | 0.591* | -0.625* | -0.042 | -0.233 | 0.181 |
表5 AWCD值、多样性指数与土壤养分因子的关系(表中数据为r值)
Table 5 Relationship among soil nutrient, average well color development (AWCD), and diversity indices.
| 全 氮 Total N (g/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全 磷 Total P (g/kg) | 全 钾 Total K (g/kg) | 速效N Available N (mg/kg) | 有效P Available P(mg/kg) | 速效K Available K (mg/kg) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWCD值 (n = 23) AWCD value | 0.658* | 0.555* | -0.520 | - 0.449 | 0.378 | -0.414 | -0.115 | -0.169 |
| Shannon指数 Shannon index | 0.757* | 0.949** | -0.889** | -0.344 | 0.885** | 0.156 | 0.192 | -0.335 |
| Simpson指数Simpson index | 0.181 | -0.084 | 0.323 | -0.280 | -0.095 | -0.331 | -0.396 | -0.499 |
| Pielou指数 Pielou index | -0.941** | -0.837** | 0.861** | 0.591* | -0.625* | -0.042 | -0.233 | 0.181 |
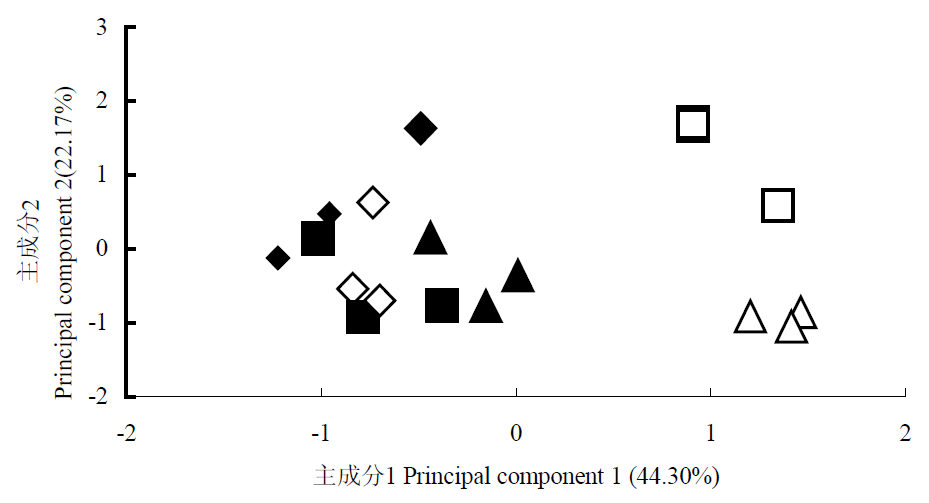
图3 6种不同处理中土壤微生物碳源利用的主成分分析 ▲ (I) CK; △ (II) 饼肥+PK+清耕;◆ (III) NPK+稻草覆盖;□ (IV) 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖;■ (V) NPK+间作三叶草;◇ (VI) 饼肥+PK+稻草覆盖
Fig. 3 Principal component analysis of carbon utilization profiles of six different treatments. Codes I-VI for six different treatments see Table 1.
| PCA1 | r | PCA2 | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| 糖类 Carbohydrates | 糖类 Carbohydrates | ||
| D-纤维二糖 D-Cellobiose | 0.609 | D-纤维二糖 D-Cellobiose | 0.614 |
| α-环状糊精 α-Cyclodextrin | 0.802 | 聚氧乙烯(20)山梨醇酐单油酸酯 Tween 80 | 0.911 |
| D-木糖 D-Xylose | 0.619 | L-天冬酰胺 L-Asparagine | 0.808 |
| 糖原 Glycogen | 0.879 | 苯乙氨 Phenylethyl-amine | 0.929 |
| α-D-乳糖 α-D-Lactose | 0.963 | 腐胺 Putrescine | 0.840 |
| D, L-α-磷酸甘油 D, L-α-Glycerol Phosphate | 0.972 | ||
| N-乙酰-D-葡糖胺 N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine | 0.943 | ||
| 羧酸类 Carboxylic Acids | 羧酸类 Carboxylic Acids | ||
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸 Glucose-1-Phosphate | 0.861 | 4-羟基-苯甲酸 4-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid | 0.847 |
| D-半乳糖醛酸 D-Galacturonic Acid | 0.797 | 甲叉丁二酸 Itaconic Acid | 0.962 |
| 2-羟基苯甲酸 2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid | 0.838 | ||
| 氨基酸类 Amino Acids | 氨基酸类 Amino Acids | ||
| L-丝氨酸 L-Serine | 0.634 | L-精氨酸 L-Arginine | 0.910 |
表6 土壤中与PCA1和PCA2相关显著的主要培养基
Table 6 Main substrates with high correlation coefficients for PC1 and PC2 in PCA of diversity patterns for each site of upper layer
| PCA1 | r | PCA2 | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| 糖类 Carbohydrates | 糖类 Carbohydrates | ||
| D-纤维二糖 D-Cellobiose | 0.609 | D-纤维二糖 D-Cellobiose | 0.614 |
| α-环状糊精 α-Cyclodextrin | 0.802 | 聚氧乙烯(20)山梨醇酐单油酸酯 Tween 80 | 0.911 |
| D-木糖 D-Xylose | 0.619 | L-天冬酰胺 L-Asparagine | 0.808 |
| 糖原 Glycogen | 0.879 | 苯乙氨 Phenylethyl-amine | 0.929 |
| α-D-乳糖 α-D-Lactose | 0.963 | 腐胺 Putrescine | 0.840 |
| D, L-α-磷酸甘油 D, L-α-Glycerol Phosphate | 0.972 | ||
| N-乙酰-D-葡糖胺 N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine | 0.943 | ||
| 羧酸类 Carboxylic Acids | 羧酸类 Carboxylic Acids | ||
| 葡萄糖-1-磷酸 Glucose-1-Phosphate | 0.861 | 4-羟基-苯甲酸 4-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid | 0.847 |
| D-半乳糖醛酸 D-Galacturonic Acid | 0.797 | 甲叉丁二酸 Itaconic Acid | 0.962 |
| 2-羟基苯甲酸 2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid | 0.838 | ||
| 氨基酸类 Amino Acids | 氨基酸类 Amino Acids | ||
| L-丝氨酸 L-Serine | 0.634 | L-精氨酸 L-Arginine | 0.910 |
| [1] | Bai Z(白震), He HB(何红波), Zhang W(张威), Xie HT(解宏图), Zhang XD(张旭东), Wang G(王鸽) (2006) PLFAs technique and its application in the study of soil microbiology. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26,2387-2394. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Bossio DA, Scow KM (1998) Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microbial Eco- logy, 35,265-278. |
| [3] | Degens BP, Schipper LA, Sparling GP, Duncan LC (2001) Is the microbial community in a soil with reduced catabolic diversity less resistant to stress or disturbance? Soil Bio- logy and Biochemistry, 33,1143-1153. |
| [4] | Dick RP (1992) A review: long-term effects of agricultural systems on soil biochemical and microbial parameters. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 40,25-36. |
| [5] | Garland JL (1996) Patterns of potential C source utilization by rhizosphere communities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 28,223-230. |
| [6] | Garland JL, Mills AL (1991) Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 57,2351-2359. |
| [7] | He ZJ(何忠俊), Hua L(华珞) (2006) Co-effects of nitrogen and zinc on the development and nutrient absorption of white clover nodules. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences (核农学报), 20,245-247. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Kaare J, Carsten SJ, Vigdis T (2001) Pesticide effects on bacterial diversity in agricultural soils-a review. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 33,443-453. |
| [9] |
Kaye JP, Hart SC (1997) Competition for nitrogen between plants and soil microorganisms. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 12,139-142.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] | Li CG(李春格), Li XM(李晓鸣), Wang JG(王敬国) (2006) Effect of soybean continuous cropping on bulk and rhizosphere soil microbial community function. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 26,1144-1150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Li FD(李阜棣), Hu ZJ(胡正嘉) (2005) Microbiology (微生物学), pp.222-223. Chinese Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Li N(黎宁), Li HX(李华兴), Zhu FJ(朱凤娇), Liu YJ(刘远金), Kuang PR(邝培锐) (2006) Relationships between soil microbial ecological characteristics and physical-chemical properties of vegetable garden soil. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 17,285-289. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Magurran AE (1988) Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement, pp.141-162. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [14] | Peng WX(彭晚霞), Song TQ(宋同清), Xiao RL(肖润林), Yang ZJ(杨知建), Li SH(李盛华), Xia YJ(夏艳珺), Tang Y(汤宇) (2005) Effects of straw mulching and intercropping white clover in tea plantation on soil moisture in subtropical hilly region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation (水土保持学报), 19,97-101, 125. |
| [15] | Shen CW(沈程文), Xiao RL(肖润林), Xu HQ(徐华勤), Xia YJ(夏艳君), Ren Q(任全), Huang Y(黄瑶) (2006) Effects of the cover and intercropping of microbial biomass of soil of tea plantations in subtropical hilly region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation (水土保持学报), 22,141-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Song TQ(宋同清), Xiao RL(肖润林), Peng WX(彭晚霞), Wang JR(王久荣), Li SH(李盛华), Liu XF(刘小飞) (2006) Effects of intercropping white clover in tea plantation on soil environment in subtropical hilly region. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 25,281-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Sugden AM (2000) Ecology: diversity and ecosystem resilience. Science, 290,233-235. |
| [18] | Teng Y(滕应), Huang CY(黄昌勇), Long J(龙健), Yao HY(姚槐应) (2003) Functional diversity of microbial community in herbage rhizosphere of reclaimed red soils. China Environmental Science (中国环境科学), 23,295-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Vanotti MB, Leclerc SA, Bundy LG (1995) Short-term effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil organinitrogen availability. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59,1350-1359. |
| [20] | Wang XL(王秀丽), Xu JM(徐建民), Yao HY(姚槐应), Xie ZM(谢正苗) (2003) Effects of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb compound contamination on soil microbial community. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (环境科学学报), 23,22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Wardle DA (1992) A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biological Review, 67,321-358. |
| [22] | Xiao RL(肖润林), Peng WX(彭晚霞), Song TQ(宋同清), Wang JR(王久荣), Xia YJ(夏艳珺), Tang Y(汤宇) (2006) Ecological regulation effects of straw mulching in tea plantation in subtropical hilly red soil region. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 25,507-511. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Xiao RL(肖润林), Wang JR(王久荣), Tang Y(汤宇), Liu YS(刘永胜), Peng WX(彭晚霞), Song TQ(宋同清) (2005) Effects of covering with outer shading screens during hot-dry season in tea plantation. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 24,251-255. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Xue D(薛冬), Yao HY(姚槐应), Huang CY(黄昌勇) (2005) Study on soil microbial properties and enzyme activities in tea gardens. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation (水土保持学报), 19,84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Yao HY(姚槐应), He ZL(何振立), Huang CY(黄昌勇) (2003) Effect of land use history on microbial diversity in red soils. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation (水土保持学报), 17,51-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Zhao X(赵璇), Wang JL(王建龙) (2006) Bioremediation of chlorophenol-contaminated soil using bioaugmentation technology and the soil microbial population dynamics. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (环境科学学报), 26,821-827. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Zheng H(郑华), Ouyang ZY(欧阳志云), Wang XK(王效科), Fang ZG(方治国), Zhao TQ(赵同谦), Miao H(苗鸿) (2004) Effects of forest restoration patterns on soil microbial communities. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 15,2019-2024. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [2] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [3] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [4] | 曹亚苏, 范敏, 彭羽, 辛嘉讯, 彭楠一. 景观格局动态对浑善达克沙地植物物种多样性和功能多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23048-. |
| [5] | 李发扬, 李滢钰, 蒋文妮, 刘曙光, 霍超, 孙巧奇, 邹红菲. 火后恢复时间影响大兴安岭寒温带森林内部与边缘鸟类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22665-. |
| [6] | 陈晓澄, 张鹏展, 康斌, 刘林山, 赵亮. 基于中国科学院西北高原生物研究所馆藏标本分析青藏高原雀形目鸟类物种和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22638-. |
| [7] | 张伟, 翟东东, 熊飞, 刘红艳, 陈元元, 王莹, 廖传松, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 邓华堂, 陈大庆. 三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| [8] | 罗彩访, 杨涛, 张秋雨, 王馨培, 沈泽昊. 滇中半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物的功能特征和功能多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23215-. |
| [9] | 姜晓燕, 高圣杰, 蒋燕, 田赟, 贾昕, 查天山. 毛乌素沙地植被不同恢复阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能多样性和系统发育多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [10] | 陈秋菊, 孙智闲, 李雪健, 张睿, 席蕊, 田晨, 王鑫, 邢迎春, 赵亚辉. 武夷山国家公园及其周边鱼类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22260-. |
| [11] | 贺佳云, 张东, 储玲, 严云志. 人为干扰对溪流鱼类功能多样性及其纵向梯度格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 927-937. |
| [12] | 黄小波, 郎学东, 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣. 生态系统多功能性的指标选择与驱动因子: 研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1673-1686. |
| [13] | 王宇彤, 牛克昌. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤环境对线虫功能多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 707-717. |
| [14] | 赵颖, 马荣, 尹永香, 张志东, 田呈明. 新疆不同来源金黄壳囊孢的多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1122-1131. |
| [15] | 雷学明, 沈芳芳, 雷学臣, 刘文飞, 段洪浪, 樊后保, 吴建平. 模拟氮沉降和灌草去除对杉木人工林地土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 962-971. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn