



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 23167. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023167 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023167
收稿日期:2023-05-25
接受日期:2023-08-23
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-06
通讯作者:
*E-mail: xu_zhu@xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2023-05-25
Accepted:2023-08-23
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-06
Contact:
*E-mail: xu_zhu@xjtu.edu.cn
摘要:
《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》(简称《昆蒙框架》)的落实是新阶段全球生物多样性治理的重中之重。本文基于相关文献资料查阅, 引入协同治理模型(Starting conditions-Facilitative leadership-Institutional design-Collaborative process, SFIC模型), 旨在以一种整体性、系统性思路考察《昆蒙框架》落实面临的挑战, 并分析总结应对策略, 以期为《昆蒙框架》落实提供一定参考。首先, 根据《昆蒙框架》落实对全球协同的客观需要, 以及现有研究整体性分析思路缺乏的情况, 引出本文使用的SFIC模型并说明适用性。然后, 根据SFIC模型运行的要素, 结合现实情况, 分析了《昆蒙框架》落实面临的发展中国家与发达国家治理基础、合作关系、参与动机、信息沟通、信任建立、资金筹措、后续协商、制度设计、主体领导等方面的挑战。最后依照SFIC模型, 从推动资源调动和发展中国家能力建设、促进三方援助合作、加强信息沟通共享、强化信任建设、发掘资金潜力、推进协商谈判、寻求制度约束性与激励性的平衡点、提高制度公正合理性、加强联合国责任机构领导力、发挥大国示范担当作用等方面提出了应对策略。
朱旭, 李嘉奇 (2023) 全球协同落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的挑战与出路: 基于SFIC模型的分析. 生物多样性, 31, 23167. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023167.
Xu Zhu, Jiaqi Li (2023) Global collaborative implementation of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: An analysis of challenge and solutions based on the SFIC model. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23167. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023167.
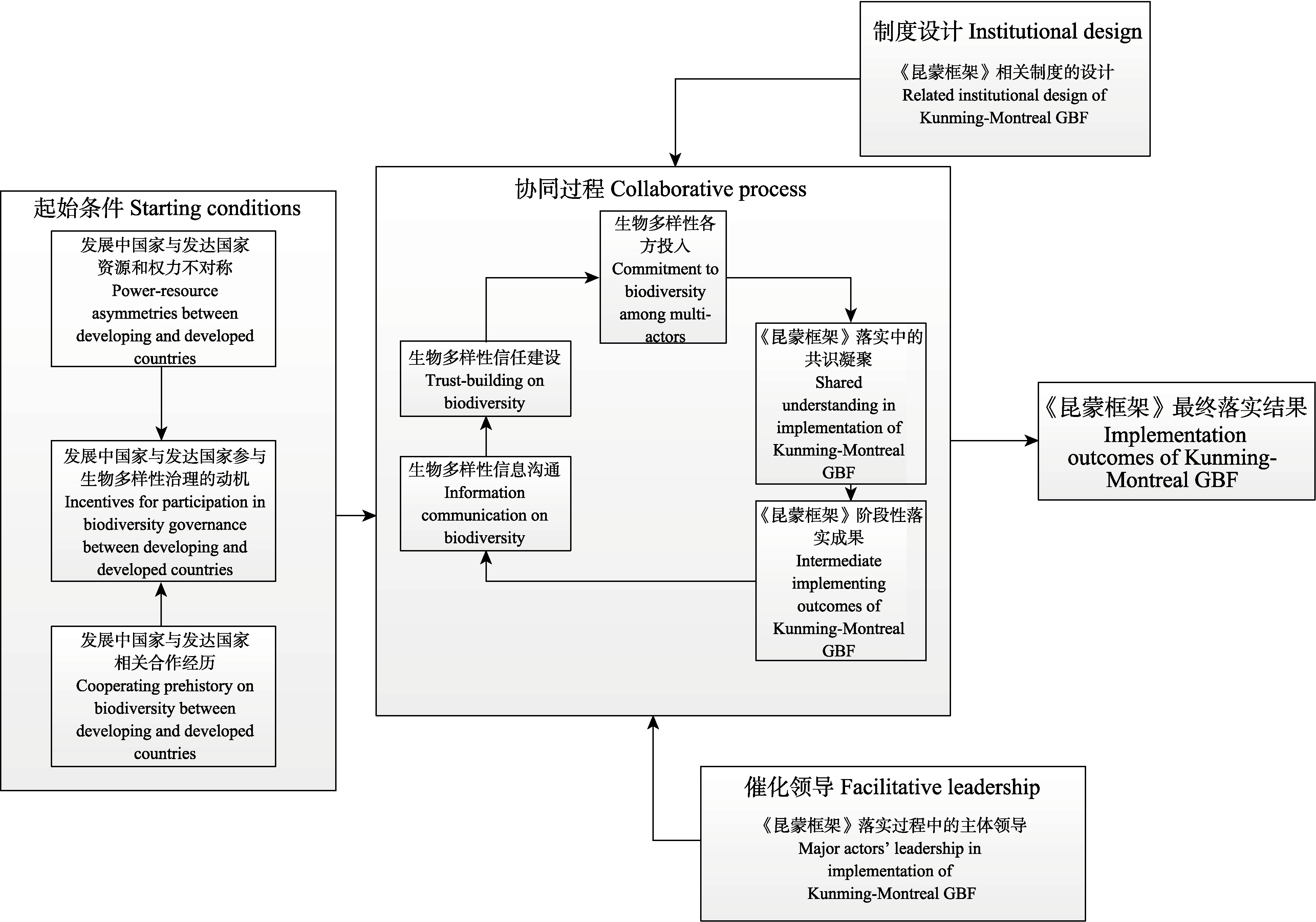
图1 协同落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的协同治理(SFIC)模型
Fig. 1 Starting conditions-Facilitative leadership-Institutional design-Collaborative process (SFIC) model on collaborative implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF)
| [1] |
Ansell C, Gash A (2008) Collaborative governance in theory and practice. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 18, 543-571.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Dong L (2017) How does the UNEP utilize incremental strengthening? Journal of China University of Geosciences (Social Sciences Edition), 17(1), 100-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 董亮 (2017) 联合国环境规划署如何渐进强化. 中国地质大学学报(社会科学版), 17(1), 100-109.] | |
| [3] | IISD International Institute for Sustainable Development (2021) Summary of the UN Biodiversity Conference (Part One), 11-15 October 2021. https://enb.iisd.org/UN-Biodive-rsity-Conference-CBD-COP15/summary. (accessed on 2023-03-10) |
| [4] | Jin GH (2023) Japan and ASEAN cooperation on biodiversity: History, characteristics, prospect and enlightenment. Yuejiang Academic Journal, 15(1), 161-170, 175. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 靳冠辉 (2023) 日本与东盟生物多样性合作: 历程、特征、前景与启示. 阅江学刊, 15(1), 161-170, 175.] | |
| [5] |
Li YX, Li YY, Zhang YXY, Liu WH (2023) The progress and prospect of the financial arrangements under the Convention on Biological Diversity. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23077. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李亦欣, 李圆圆, 张杨心怡, 刘文慧 (2023) 《生物多样性公约》资金问题最新进展及展望. 生物多样性, 31, 23077.]
DOI |
|
| [6] | Lian YM (2023) Failures of European-American approach to global species conservation strategies: Manifestations, causes and responses. Pacific Journal, 31(6), 80-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 连佑敏 (2023) 欧美式全球物种保护策略的失灵: 表现、成因及应对. 太平洋学报, 31(6), 80-94.] | |
| [7] |
Ma KP (2023) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: An important global agenda for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23133. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[ 马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》是重要的全球生物多样性保护议程. 生物多样性, 31, 23133.]
DOI |
|
| [8] | Mao WZ (2018) Power and Responsibility during the Rise of Great Powers. Nanjing University Press, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 毛维准 (2018) 大国崛起中的权力与责任. 南京大学出版社, 南京.] | |
| [9] |
Tengö M, Brondizio ES, Elmqvist T, Malmer P, Spierenburg M (2014) Connecting diverse knowledge systems for enhanced ecosystem governance: The multiple evidence base approach. AMBIO, 43, 579-591.
PMID |
| [10] | Trankmann B (2023) Biodiversity Crisis must be Urgently Addressed. https://www.undp.org/china/blog/biodiversity-crisis-must-be-urgently-addressed(accessed on 2023-07-21) |
| [11] |
Turnhout E, Neves K, De Lijster E, (2014) ‘Measurementality’ in biodiversity governance: Knowledge, transparency, and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). Environment and Planning A, 46, 581-597.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Wang Q, Liu YY, Niu H (2023) Comparison and game analysis of regulatory models of cross-border data flow in Europe and America. Journal of Intelligence, 42(3), 174-180, 173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王倩, 刘杨钺, 牛昊 (2023) 欧美跨境数据流动规制模式对比及博弈分析. 情报杂志, 42(3), 174-180, 173.] | |
| [13] | Wang QH (2023) Implementation dilemma and reform path for the Convention on Biological Diversity. Local Legislation Journal, 8(1), 78-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王倩慧 (2023) 《生物多样性公约》的履行困境与改革路径. 地方立法研究, 8(1), 78-91.] | |
| [14] | Wang SD (2021) Dilemma, motivations and prospects of upgrading global biodiversity governance. Yuejiang Academic Journal, 13(5), 15-28, 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王思丹 (2021) 全球生物多样性治理升级: 困境、动能与前景. 阅江学刊, 13(5), 15-28, 120.] | |
| [15] |
Whitehorn PR, Navarro LM, Schröter M, Fernandez M, Rotllan-Puig X, Marques A (2019) Mainstreaming biodiversity: A review of national strategies. Biological Conservation, 235, 157-163.
DOI |
| [16] | Wu ZC, Li JX (2020) China’s perspective on global trust deficit governance. CASS Journal of Political Science, 155(6), 24-36, 125-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴志成, 李佳轩 (2020) 全球信任赤字治理的中国视角. 政治学研究, 155(6), 24-36, 125-126.] | |
| [17] |
Xu J, Wang JZ (2023) Analysis of the main elements and implications of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 徐靖, 王金洲 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》主要内容及其影响. 生物多样性, 31, 23020.]
DOI |
|
| [18] |
Zhang DN, Wang L, Lu XQ, Wang CY, Liu Y (2023) Convention on Biological Diversity and its protocols: Negotiation, challenges and recommendations on the “capacity-building and development”. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22588. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 章嫡妮, 王蕾, 卢晓强, 王长永, 刘燕 (2023) 《生物多样性公约》及其议定书下“能力建设与发展”议题的磋商、挑战及政策建议. 生物多样性, 31, 22588.] | |
| [19] | Zhang HY, Qi Y, Liu HY (2023) China’s biodiversity conservation actions and prospects under the Kunming- Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. World Environ- ment, (2), 19-22. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张惠远, 齐月, 刘海燕 (2023) “昆蒙框架”下的中国生物多样性保护行动与展望. 世界环境, (2), 19-22.] | |
| [20] | Zhang LR, Luo M, Zhu ZX, Sun YQ, Jin SC, Yang CY, Meng R, Zhang LJ (2023) Analysis on the implementation path of biodiversity mainstreaming in China under the guidance of “Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework”. Guihaia, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/detail/45.1134.Q.20230711.0858.002.htm. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张丽荣, 罗明, 朱振肖, 孙雨芹, 金世超, 杨崇曜, 孟锐, 张丽佳 (2023) “昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架”指引下我国生物多样性主流化实施路径探析. 广西植物, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/detail/45.1134.Q.20230711.0858.002.htm.] | |
| [21] | Zhu AL, Weins NW, Chen RS (2023) Wealthy Nations Prioritised Unrealistic Targets over a Global Biodiversity Fund. https://www.eco-business.com/news/wealthy-nations-prioritised-unrealistic-targets-over-a-global-biodiversity-fund/. (accessed on 2023-07-21) |
| [22] | Zhu X (2023) China’s concept on global governance: Conceptual basis, constituting elements and practice principles. International Studies, 215(3), 1-25, 122-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱旭 (2023) 中国的全球治理观: 立论基础、内在逻辑与实践原则. 国际问题研究, 215(3), 1-25, 122-123.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [3] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [4] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [5] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [6] | 武慧, 俞乐, 杜贞容, 赵强, 戚文超, 曹越, 王金洲, 申小莉, 孙尧, 马克平. 基于遥感监测的《昆蒙框架》执行进展快速评估: 路径与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24526-. |
| [7] | 郭旋, 何思源, 闵庆文. 农业部门履行《生物多样性公约》的思路与途径——来自重要农业文化遗产管理的启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24527-. |
| [8] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [9] | 苏红巧, 余得光, 牟昆仑. 国家公园与国土空间规划和用途管制制度衔接路径探讨[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24570-. |
| [10] | 王晓倩, 邓毅. 与《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》衔接的中国OECMs关键问题与推进策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24569-. |
| [11] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [12] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [13] | 姜雪原, 徐嘉忆, 盛学敏, 朱源. 《中国生物多样性保护战略与行动计划(2023‒2030年)》与《昆蒙框架》的协同与差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24575-. |
| [14] | 田瑜, 李俊生. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》“3030”目标的内涵及实现路径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24086-. |
| [15] | 刘海鸥, 杜乐山, 刘文慧, 李子圆, 潘丽波, 刘蕾. 全球生物多样性框架基金管理政策分析与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23334-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
