



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 21262. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021262 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021262
收稿日期:2021-07-03
接受日期:2021-11-04
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
张燕雪丹
作者简介:*E-mail: yxdzhang@shou.edu.cn基金资助:
Yi Tang1,2, Haoran Yang1, Yanxuedan Zhang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-03
Accepted:2021-11-04
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
Yanxuedan Zhang
摘要:
珊瑚礁生态系统是《生物多样性公约》(下称《公约》)的重点保护对象。自1998年珊瑚礁出现大规模白化现象以来, 珊瑚礁养护议题一直受到《公约》缔约方大会的关注。本文通过梳理我国珊瑚礁养护管理的法律法规和相关履约措施, 结合海南、广西、广东三省的珊瑚礁资源变化状况, 评价我国在履约方面的表现并识别存在的主要差距。研究发现, 总体上我国积极采取了多种措施进行珊瑚礁的养护和管理, 活珊瑚覆盖度和种类数量有一定程度的恢复, 但仍存在相关立法分散、综合性治理方案缺乏、气候变化适应不足、跨部门协调机制不完善、海洋保护区管理有效性不足、资金缺乏且当地社区参与度低、珊瑚礁监测标准和规范简单且不统一、监测数据不足以进行有效评估、国际合作程度低、公众参与度不高等问题。建议我国结合履约要求, 与《公约》的目标和精神基本保持一致, 并考虑正在讨论的《2020后全球生物多样性保护框架》, 进一步完善珊瑚礁养护立法、行动计划和气候变化适应方案, 加强综合管理和协调机制建设, 提升海洋保护区的管理实效性, 改进珊瑚礁监测和数据采集, 提升国际合作, 进一步提高公众参与度, 从而不断提升履约能力, 构建更加完善的珊瑚礁养护体系。
唐议, 杨浩然, 张燕雪丹 (2022) 《生物多样性公约》下我国珊瑚礁养护履约进程与改善建议. 生物多样性, 30, 21262. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021262.
Yi Tang, Haoran Yang, Yanxuedan Zhang (2022) Conservation of coral reef systems under Convention on Biological Diversity: China’s performance and suggestions. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21262. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021262.
| 时间/会议 1998年第四次缔约方大会(COP4) 2000年第五次缔约方大会(COP5) 2004年第七次缔约方大会(COP7) 2010年第十次缔约方大会(COP10) 2014年第十二次缔约方大会(COP12) | 决定 第IV/5号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性的养护和可持续利用 第V/3号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性工作方案执行情况的进度报告(第IV/5号决定的执行情况) 第VII/5号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性 第X/29号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性 第X/2号决定: 2011-2020年《生物多样性战略计划》和爱知生物多样性目标 第XII/22号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性: 具有重要生态或生物意义的海洋区域 第XII/23号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性: 人为水下噪音和海洋酸化对海洋和沿海生物多样性的影响, 为实现针对珊瑚礁和密切相关的生态系统的爱知生物多样性指标10的优先行动, 以及海洋空间规划和培训倡议 |
Box 1 《生物多样性公约》缔约方大会通过的珊瑚礁养护决定
| 时间/会议 1998年第四次缔约方大会(COP4) 2000年第五次缔约方大会(COP5) 2004年第七次缔约方大会(COP7) 2010年第十次缔约方大会(COP10) 2014年第十二次缔约方大会(COP12) | 决定 第IV/5号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性的养护和可持续利用 第V/3号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性工作方案执行情况的进度报告(第IV/5号决定的执行情况) 第VII/5号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性 第X/29号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性 第X/2号决定: 2011-2020年《生物多样性战略计划》和爱知生物多样性目标 第XII/22号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性: 具有重要生态或生物意义的海洋区域 第XII/23号决定: 海洋和沿海生物多样性: 人为水下噪音和海洋酸化对海洋和沿海生物多样性的影响, 为实现针对珊瑚礁和密切相关的生态系统的爱知生物多样性指标10的优先行动, 以及海洋空间规划和培训倡议 |
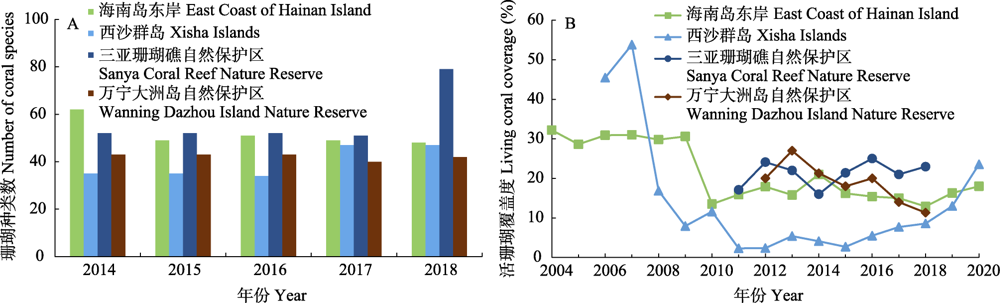
图1 2004-2020年海南省监测海域活珊瑚覆盖度① (①数据来源于海南省海洋与渔业厅、海南省生态环境厅在网上公开发布的《海南省海洋环境状况公报》。) (A)及珊瑚种类数量(B)
Fig. 1 Living coral coverage (A) and number of coral species (B) in the monitoring areas of Hainan from 2004 to 2020
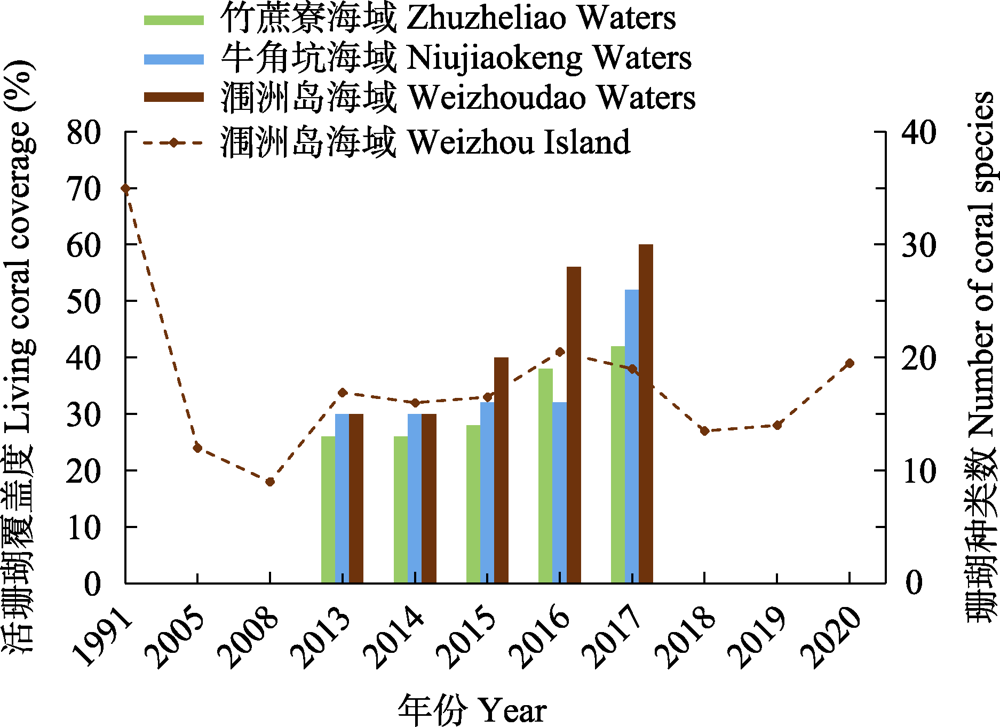
图2 1991-2020年广西壮族自治区监测海域活珊瑚覆盖度(折线图)及珊瑚种类(柱状图)①(①数据来源于广西壮族自治区海洋与渔业厅、中华人民共和国生态环境部发布的《广西壮族自治区海洋环境状况公报》《中国海洋生态环境状况公报》。)
Fig. 2 Living coral coverage (Line chart) and number of coral species (Bar chart) in the monitoring areas of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous region from 1991 to 2020
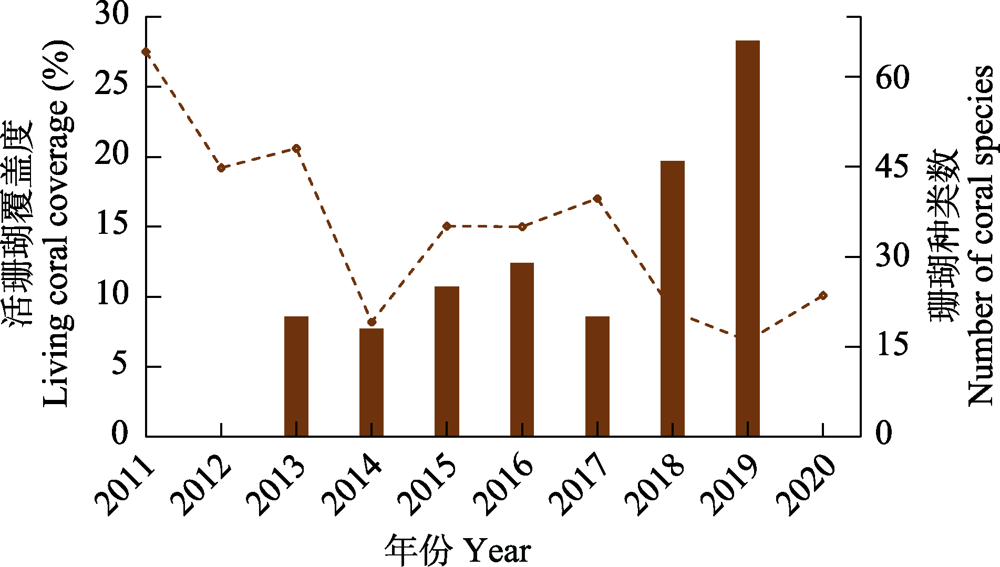
图3 2011-2020年广东省徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区监测海域活珊瑚覆盖度(折线图)及珊瑚种类(柱状图)②(②数据来源于广东省海洋与渔业局、中华人民共和国生态环境部发布的《广东省海洋环境状况公报》《中国海洋生态环境状况公报》。)
Fig. 3 Living coral coverage (Line chart) and number of coral species (Bar chart) in the monitoring areas of Xuwen Coral Reef National Nature Reserve, Guangdong from 2011 to 2020
| 国家层面《中华人民共和国海洋环境保护法》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国海岛保护法》(2010年实施) 《中华人民共和国野生动物保护法》(2018年修订)及《国家重点保护野生动物名录》(2021年实施) 《中华人民共和国防治海岸工程建设项目污染损害海洋环境管理条例》(2018年修订) 《中华人民共和国渔业法》(2013年修订) 《中华人民共和国环境保护法》(2014年修订) 《中华人民共和国水污染防治法》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国旅游法》(2018年修订) 《中华人民共和国海域使用管理法》(2002年实施) 《中华人民共和国海洋倾废管理条例》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国防治陆源污染物污染损害海洋环境管理条例》(1990年实施) 《中华人民共和国自然保护区条例》(2017年修订) 《海洋特别保护区管理办法》(2010年实施) 《海洋自然保护区管理办法》(1995年实施) 省级层面《海南省环境保护条例》(2017年修订) 《海南省环境保护条例》(2017年修订) 《海南省珊瑚礁和砗磲保护规定》(2017年实施) 《海南省自然保护区条例》(2018年修订) 《三亚市潜水活动珊瑚礁生态损失补偿办法》(2017年实施) 《广西壮族自治区环境保护条例》(2019年修订) 《广西壮族自治区海域使用管理条例》(2016年实施) 《广西壮族自治区湿地保护条例》(2015年实施) 《北海市涠洲岛生态环境保护条例》(2018年实施) 《广西壮族自治区海洋环境保护条例》(2018年修订) 《广东省环境保护条例》(2019年修订) 《广东省实施<中华人民共和国海洋环境保护法>办法》(2018年修订) 《广东省海域使用管理条例》(2007年实施) 《珠海市珊瑚资源保护管理办法》(2007年发布实施) |
Box 2 有关珊瑚礁养护的国家及省级法律法规
| 国家层面《中华人民共和国海洋环境保护法》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国海岛保护法》(2010年实施) 《中华人民共和国野生动物保护法》(2018年修订)及《国家重点保护野生动物名录》(2021年实施) 《中华人民共和国防治海岸工程建设项目污染损害海洋环境管理条例》(2018年修订) 《中华人民共和国渔业法》(2013年修订) 《中华人民共和国环境保护法》(2014年修订) 《中华人民共和国水污染防治法》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国旅游法》(2018年修订) 《中华人民共和国海域使用管理法》(2002年实施) 《中华人民共和国海洋倾废管理条例》(2017年修订) 《中华人民共和国防治陆源污染物污染损害海洋环境管理条例》(1990年实施) 《中华人民共和国自然保护区条例》(2017年修订) 《海洋特别保护区管理办法》(2010年实施) 《海洋自然保护区管理办法》(1995年实施) 省级层面《海南省环境保护条例》(2017年修订) 《海南省环境保护条例》(2017年修订) 《海南省珊瑚礁和砗磲保护规定》(2017年实施) 《海南省自然保护区条例》(2018年修订) 《三亚市潜水活动珊瑚礁生态损失补偿办法》(2017年实施) 《广西壮族自治区环境保护条例》(2019年修订) 《广西壮族自治区海域使用管理条例》(2016年实施) 《广西壮族自治区湿地保护条例》(2015年实施) 《北海市涠洲岛生态环境保护条例》(2018年实施) 《广西壮族自治区海洋环境保护条例》(2018年修订) 《广东省环境保护条例》(2019年修订) 《广东省实施<中华人民共和国海洋环境保护法>办法》(2018年修订) 《广东省海域使用管理条例》(2007年实施) 《珠海市珊瑚资源保护管理办法》(2007年发布实施) |
| [1] | Feng XJ, Yang Q, Li YQ, Ao L (2011) Survey and protection countermeasure on ecosystem of coral reef in Nansha coral reef. Journal of Logistical Engineering University, 27(4), 68-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯孝杰, 杨琴, 李永青, 敖漉 (2011) 南沙珊瑚礁生态系统的调查与保护对策. 后勤工程学院学报, 27(4), 68-71.] | |
| [2] | Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (GCRMN) (2018). Status of Coral Reefs in East Asian Seas Region: 2018. https://coralreef.nus.edu.sg/publications/Toh2018.pdf. (accessed on 2022-02-16) |
| [3] | Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (GCRMN) (2020). Status of Coral Reefs in East Asian Seas Region: 2020. http://gcrmn.net/2020-report/. (accessed on 2022-02-17) |
| [4] | Huang H, Chen Z, Huang LT (2020) China Coral Reef Status Report 2019. Coral Reef Branch, Pacific Society of China, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 黄辉, 陈竹, 黄林韬 (2020) 2019年中国珊瑚礁状况报. 中国太平洋学会珊瑚礁分会, 广州.] | |
| [5] |
Kleypas J, Allemand D, Anthony K, Baker AC, Beck MW, Hale LZ, Hilmi N, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Hughes T, Kaufman L, Kayanne H, Magnan AK, McLeod E, Mumby P, Palumbi S, Richmond RH, Rinkevich B, Steneck RS, Voolstra CR, Wachenfeld D, Gattuso J (2021) Designing a blueprint for coral reef survival. Biological Conservation, 257, 109107.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Li F, Shen C, Zhang YP, Zhou J, Peng HP, Liu L (2019) Analysis of coral species and coverage in Guangdong Xuwen Coral Reef National Nature Reserve. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 47, 304-308. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李锋, 沈城, 张艳苹, 周洁, 彭慧湃, 刘丽 (2019) 广东徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区珊瑚种类及覆盖率分析. 江苏农业科学, 47, 304-308.] | |
| [7] | Liao J (2017) The development of management and conservation in Xuwen Coral Reef National Nature Reserve. Ocean & Fishery, (6), 48-50. (in Chinese) |
| [ 廖静 (2017) 片片珊瑚花悠悠保护心--徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区“管护之路”. 海洋与渔业, (6), 48-50.] | |
| [8] |
Liu CH, Yang JB, Yin L (2021) Progress, achievements and prospects of biodiversity protection in Yunnan Province. Biodiversity Science, 29, 200-211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 刘春晖, 杨京彪, 尹仑 (2021) 云南省生物多样性保护进展、成效与前瞻. 生物多样性, 29, 200-211.] | |
| [9] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (2019) China’s Sixth National Report on the Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity. China Environment Publishing Group, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国生态环境部 (2019) 中国履行《生物多样性公约》第六次国家报告. 中国环境出版集团, 北京.] | |
| [10] |
Mo ZQ (2019) Re-legalizing China’s ecological conservation redline: The position, dilemma and path. Biodiversity Science, 27, 347-352. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 莫张勤 (2019) 生态保护红线修复机制法治化: 定位、困境及其出路. 生物多样性, 27, 347-352.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Qin TB, Yuan X (2021) China’s practice of promoting biodiversity conservation in transboundary areas. Biodiversity Science, 29, 220-230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 秦天宝, 袁昕 (2021) 推进生物多样性跨境区域保护的中国实践. 生物多样性, 29, 220-230.] | |
| [12] | Su YM, Qin YC, Zha CM (2018) A million coral project to garden the bed of the South China Sea. Cultural Geography, (7), 54-63. (in Chinese) |
| [ 苏隐墨, 秦翌晨, 查春明 (2018) “百万珊瑚计划” 把南海海底变成美丽的花园. 环球人文地理, (7), 54-63.] | |
| [13] | Wang J (2011) Thoughts on the legislation of coral reef protection in Hainan Province. Intelligence, (31), 314-315. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王婧 (2011) 海南省珊瑚礁保护的立法思考. 才智, (31), 314-315.] | |
| [14] | Wang MT, Gong WJ, Han Y, Qi D, Wang YF, Xu ST (2019) Research status and development of coral reef ecosystems in China. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (8), 13-15. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王明婷, 公维洁, 韩玉, 齐丹, 王燕芳, 许世桃 (2019) 我国珊瑚礁生态系统研究现状及发展趋势. 绿色科技, (8), 13-15.] | |
| [15] | Wang XW (2021) Research on legislative choice for marine ecological environmental damage compensation system: Analysis based on the revision of Marine Environmental Protection Law. ECUPL Journal, 24, 76-86. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王秀卫 (2021) 海洋生态环境损害赔偿制度立法进路研究--以《海洋环境保护法》修改为背景. 华东政法大学学报, 24, 76-86.] | |
| [16] | Wang YR (2014) Discussion on the status quo of the coral reefs in Hainan Province and its legislation. Modern Communication, (3), 10-11. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王玉容 (2014) 海南珊瑚礁的现状及立法保护探讨. 现代交际, (3), 10-11.] | |
| [17] |
Yang R, Peng QY, Cao Y, Zhong L, Hou SY, Zhao ZC, Huang C (2019) Transformative changes and paths toward biodiversity conservation in China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1032-1040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 杨锐, 彭钦一, 曹越, 钟乐, 侯姝彧, 赵智聪, 黄澄 (2019) 中国生物多样性保护的变革性转变及路径. 生物多样性, 27, 1032-1040.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Zeng R, Liu J, Xu Y, Yang L (2021) Discussions and adjustment suggestions on the marine ecological protection red line. Marine Environmental Science, 40, 576-581, 590. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曾容, 刘捷, 许艳, 杨璐 (2021) 海洋生态保护红线存在问题及评估调整建议. 海洋环境科学, 40, 576-581, 590.] | |
| [19] | Zhou ZG (2004) The current situation and protection countermeasures of the coral reef in Hainan. Ocean Development and Management, 21, 48-51. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周祖光 (2004) 海南珊瑚礁的现状与保护对策. 海洋开发与管理, 21, 48-51.] | |
| [20] |
Zou CX, Wang LX, Liu JH (2015) Classification and management of ecological protection redlines in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 716-724. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 邹长新, 王丽霞, 刘军会 (2015) 论生态保护红线的类型划分与管控. 生物多样性, 23, 716-724.]
DOI |
| [1] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [2] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [3] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [4] | 刘蕾, 郝志明, 杜乐山, 刘海鸥. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》视角下将性别考虑纳入中国生物多样性治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24235-. |
| [5] | 王腾, 李纯厚, 王广华, 赵金发, 石娟, 谢宏宇, 刘永, 刘玉. 西沙群岛七连屿珊瑚礁鱼类的物种组成与演替[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [6] | 刘海鸥, 杜乐山, 刘文慧, 李子圆, 潘丽波, 刘蕾. 全球生物多样性框架基金管理政策分析与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23334-. |
| [7] | 耿宜佳, 田瑜, 李俊生, 李子圆, 潘玉雪. 《生物多样性公约》框架下外来入侵物种管控的全球进展、挑战和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24275-. |
| [8] | 陈进. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》与国家植物园体系建设[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23257-. |
| [9] | 冯莉. 国际法视野下生物多样性和气候变化的协同治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23110-. |
| [10] | 耿宜佳, 李子圆, 田瑜. 《生物多样性公约》下海洋生物多样性保护的进展、挑战和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22645-. |
| [11] | 徐靖, 王金洲. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》主要内容及其影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 23020-. |
| [12] | 章嫡妮, 王蕾, 卢晓强, 王长永, 刘燕. 《生物多样性公约》及其议定书下“能力建设与发展”议题的磋商、挑战及政策建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22588-. |
| [13] | 曾岩, 何拓, 张坤, 廖菁, 朱江. 《濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约》巴拿马大会进展评述[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22687-. |
| [14] | 罗茂芳, 郭寅峰, 马克平. 简述《2020年后全球生物多样性框架》谈判进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22654-. |
| [15] | 徐靖, 王金洲, 李俊生. 商业界参与生物多样性主流化的进展、路径与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22078-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn