



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 21243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021243 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021243
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能; 有机农业
黄方倩, 王超, 刘明庆, 陈秋会, 韩笑( ), 王磊(
), 王磊( ), 席运官, 张纪兵
), 席运官, 张纪兵
收稿日期:2021-06-20
接受日期:2021-09-22
出版日期:2022-01-20
发布日期:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
韩笑,王磊
作者简介:* 共同通讯作者. E-mail: hxofrcc@126.com;wlofrcc@126.com基金资助:
Fangqian Huang, Chao Wang, Mingqing Liu, Qiuhui Chen, Xiao Han( ), Lei Wang(
), Lei Wang( ), Yunguan Xi, Jibing Zhang
), Yunguan Xi, Jibing Zhang
Received:2021-06-20
Accepted:2021-09-22
Online:2022-01-20
Published:2022-01-29
Contact:
Xiao Han,Lei Wang
摘要:
有机农业是生态环境友好的生产方式, 对农业生物多样性保护具有重要意义。个体研究的差异不利于有机农业的生态环境效益评估。本研究利用文献整合分析, 以对农田生态环境具有良好指示作用的节肢动物为研究对象, 探讨了有机种植对农田生物多样性的保护效果及影响因素。结果表明, 相比常规种植, 有机种植可使节肢动物的丰富度、多度及均匀度显著提升34.95%、64.95%及12.09%; 天敌和害虫的物种丰富度分别显著提升了22.50%和31.03%; 同时天敌的个体数量比常规显著增加了71.80%, 害虫减少了10.46%。经过3年及以上的有机种植后, 节肢动物的丰富度和多度均显著高于常规种植。常规种植化学农药施用频率可显著影响节肢动物丰富度和均匀度指数, 施药次数每增加1次, 节肢动物丰富度相比有机种植显著降低13.54%, 均匀度显著降低2.64%。有机水田对节肢动物多度的提升效果显著优于有机旱地, 为后者的4.7倍; 但二者的丰富度和均匀度没有显著差异。蔬菜和茶叶种植体系对节肢动物多样性指数的综合提升效果优于其他作物类型, 丰富度、多度和均匀度指数分别显著提升了81.46%、74.14%、18.55%和48.86%、49.06%、30.88%。鼓励常规种植减少农药施用频次, 加大有机和生态化管理措施的应用程度, 是保护农业生物多样性、实现农业绿色高质量发展的有效途径。
黄方倩, 王超, 刘明庆, 陈秋会, 韩笑, 王磊, 席运官, 张纪兵 (2022) 有机种植对农田节肢动物多样性影响的整合分析. 生物多样性, 30, 21243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021243.
Fangqian Huang, Chao Wang, Mingqing Liu, Qiuhui Chen, Xiao Han, Lei Wang, Yunguan Xi, Jibing Zhang (2022) Effects of organic planting on arthropod diversity in farmland: A meta-analysis. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21243. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021243.
| 样点分布区域(国内) Distribution of research area in China | 试验点位数量 No. of experimental sites | 样点分布区域(国外) Distribution of research area outside China | 试验点位数量 No. of experimental sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 1 | 克罗地亚 Croatia | 1 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 2 | 巴西 Brazil | 3 |
| 四川 Sichuan | 1 | 德国 Germany | 2 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 1 | 法国 France | 1 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 2 | 美国 The United States | 14 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 5 | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 2 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 4 | 瑞士 Switzerland | 5 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 2 | 西班牙 Spain | 3 |
| 福建 Fujian | 2 | 希腊 Greece | 4 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 2 | 意大利 Italy | 1 |
| 上海 Shanghai | 2 | 英国 The United Kingdom | 5 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 6 | ||
| 山东 Shandong | 2 | ||
| 河北 Hebei | 1 | ||
| 北京 Beijing | 1 |
表1 整合分析纳入的文献所涉及的研究区域分布
Table 1 The distribution of research area contained in the meta analysis
| 样点分布区域(国内) Distribution of research area in China | 试验点位数量 No. of experimental sites | 样点分布区域(国外) Distribution of research area outside China | 试验点位数量 No. of experimental sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 1 | 克罗地亚 Croatia | 1 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 2 | 巴西 Brazil | 3 |
| 四川 Sichuan | 1 | 德国 Germany | 2 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 1 | 法国 France | 1 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 2 | 美国 The United States | 14 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 5 | 葡萄牙 Portugal | 2 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 4 | 瑞士 Switzerland | 5 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 2 | 西班牙 Spain | 3 |
| 福建 Fujian | 2 | 希腊 Greece | 4 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 2 | 意大利 Italy | 1 |
| 上海 Shanghai | 2 | 英国 The United Kingdom | 5 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 6 | ||
| 山东 Shandong | 2 | ||
| 河北 Hebei | 1 | ||
| 北京 Beijing | 1 |
| 亚组类别 Categorical variable | 亚组水平 Categorical level |
|---|---|
| 有机种植年限 Years of organic planting (years) | 3-10、11-15、> 15 |
| 耕地类型 Land use | 旱地、水田 Dryland, paddy |
| 作物类型 Crop variety | 粮食、茶叶、蔬菜、水果、药材、油料作物 Grain, tea, vegetable, fruit, crude drug, oil crop |
| 常规种植年施药次数 Pesticide application frequency in conventional planting (times/year) | 1-5、6-10、11-15、> 15 |
| 功能类群 Arthropod communities | 天敌、害虫 Natural enemy, pest |
表2 影响因素的不同分组水平
Table 2 Classification of categorical variables as explanatory factors
| 亚组类别 Categorical variable | 亚组水平 Categorical level |
|---|---|
| 有机种植年限 Years of organic planting (years) | 3-10、11-15、> 15 |
| 耕地类型 Land use | 旱地、水田 Dryland, paddy |
| 作物类型 Crop variety | 粮食、茶叶、蔬菜、水果、药材、油料作物 Grain, tea, vegetable, fruit, crude drug, oil crop |
| 常规种植年施药次数 Pesticide application frequency in conventional planting (times/year) | 1-5、6-10、11-15、> 15 |
| 功能类群 Arthropod communities | 天敌、害虫 Natural enemy, pest |
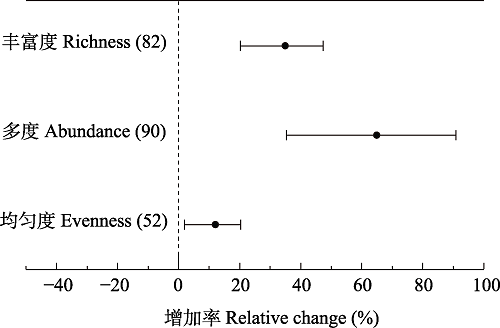
图1 有机种植相比常规种植节肢动物多样性指数的增加率。图中圆点为效应值, 即有机种植相比常规种植其节肢动物多样性指数的变化量, 误差线为效应值的95%置信区间, 括号内的数值为该效应值的样本量。若效应值的95%置信区间未跨越零轴, 则表示该效应与对照相比差异显著。
Fig. 1 The relative change of arthropod biodiversity under organic planting compared with conventional planting. The dots in the figure are the mean effect sizes, which represent the relative change of arthropod diversity under organic planting compared with conventional planting. The error lines indicate the 95% confidence interval (95% CIs) of the mean effect sizes, and the value in brackets is the sample size. Mean effect sizes were considered to be significantly different from the control if their 95% CIs did not cross the zero axis.
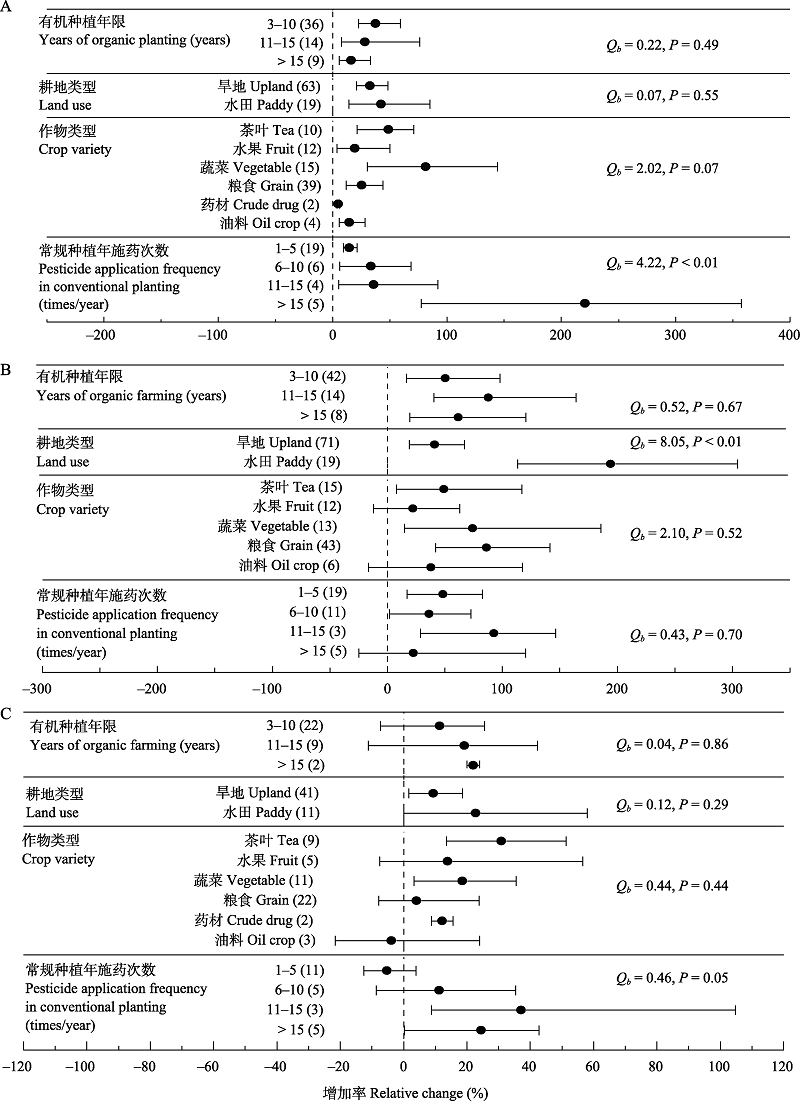
图2 有机种植相比常规种植对节肢动物丰富度(A)、多度(B)、均匀度(C)指数的增加率。图中圆点为效应值, 即有机种植相比常规种植节肢动物多样性指数的相对变化百分率, 误差线为效应值的95%置信区间, 括号内的数值为该效应值的样本量。若效应值的95%置信区间未跨越零轴, 则表示该效应与对照相比差异显著; 若亚组内不同水平的效应值95%置信区间未重叠, 则说明分类水平的差异显著。Qb (组间异质性)和P值用来描述不同水平分类因素多样性指数效应值的统计学差异。
Fig. 2 The relative change of arthropod richness (A), abundance (B), and evenness (C) under organic planting compared with conventional planting. The dots in the figure are the mean effect sizes, which represent the relative change of different diversity index (%) under organic planting compared with conventional planting. The error lines indicate the 95% confidence interval (95% CIs) of the mean effect sizes, and the value in brackets is the sample size. Mean effect sizes were considered to be significantly different from the control if their 95% CIs did not cross the zero axis, and were considered to be significantly different if their 95% CIs did not overlap. Between-group heterogeneity (Qb) and the probability (P) were used to describe statistical differences in the diversity index responses between different levels of the categorized factors.
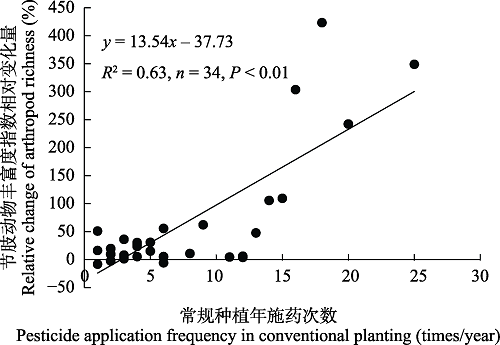
图3 有机种植相比常规种植节肢动物丰富度指数相对变化量与常规种植年施药次数的回归分析
Fig. 3 The relationship between the relative changes of arthropod richness under organic planting compared with conventional planting and the pesticide application frequency in conventional planting
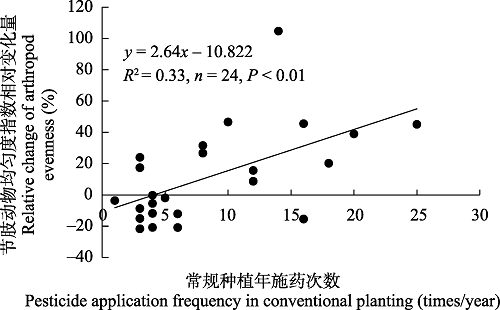
图4 有机种植相比常规种植节肢动物均匀度指数相对变化量与常规种植年施药次数的回归分析
Fig. 4 The relationship between the relative changes of arthropod evenness under organic planting compared with conventional planting and the pesticide application frequency in conventional planting
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 功能类群 Arthropod communities | 总效应值 Total effect size (%) | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval (%) | 样本量 Sample size (n) | 组间异质性 Between-group heterogeneity (Qb) | 显著性差异 Probability (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰富度 Richness | 天敌 Natural enemy | 22.50 | 13.76-33.62 | 40 | 0.81 | 0.45 |
| 害虫 Pest | 31.03 | 9.22-53.18 | 18 | |||
| 多度 Abundance | 天敌 Natural enemy | 71.80 | 45.25-105.15 | 49 | 5.82 | 0.001 |
| 害虫 Pest | -10.46 | -38.62-28.19 | 19 |
表3 节肢动物害虫和天敌功能群多样性指数对有机种植的响应
Table 3 Responses of arthropod pest and natural enemy subcommunities diversity to organic planting over conventional planting
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 功能类群 Arthropod communities | 总效应值 Total effect size (%) | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval (%) | 样本量 Sample size (n) | 组间异质性 Between-group heterogeneity (Qb) | 显著性差异 Probability (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰富度 Richness | 天敌 Natural enemy | 22.50 | 13.76-33.62 | 40 | 0.81 | 0.45 |
| 害虫 Pest | 31.03 | 9.22-53.18 | 18 | |||
| 多度 Abundance | 天敌 Natural enemy | 71.80 | 45.25-105.15 | 49 | 5.82 | 0.001 |
| 害虫 Pest | -10.46 | -38.62-28.19 | 19 |
| [1] |
Altieri MA (1999) The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 74, 19-31.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Birkhofer K, Ekroos J, Corlett EB, Smith HG (2014) Winners and losers of organic cereal farming in animal communities across central and northern europe. Biological Conservation, 175, 25-33. |
| [3] |
Bommarco R, Kleijn D, Potts SG (2013) Ecological intensification: Harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 230-238.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chen HJ, Huang ZF, Li RB, Peng ZB, Mai QF, Jiang JS (2005) Connotation, function and conservation of agriculture biological diversity. Journal of South China University of Tropical Agriculture, 11(2), 24-27. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈海坚, 黄昭奋, 黎瑞波, 彭宗波, 麦全法, 蒋菊生 (2005) 农业生物多样性的内涵与功能及其保护. 华南热带农业大学学报, 11(2), 24-27.] | |
| [5] |
Chivenge P, Vanlauwe B, Six J (2011) Does the combined application of organic and mineral nutrient sources influence maize productivity? A meta-analysis. Plant and Soil, 342, 1-30.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chu BY, Chen FJ, Ma ZH (2020) Principles of using agricultural biodiversity to control pests and crop diseases. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 57, 28-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 初炳瑶, 陈法军, 马占鸿 (2020) 农业生物多样性控制作物病虫害的方法与原理. 应用昆虫学报, 57, 28-40.] | |
| [7] |
Doles JL, Zimmerman RJ, Moore JC (2001) Soil microarthropod community structure and dynamics in organic and conventionally managed apple orchards in western Colorado, USA. Applied Soil Ecology, 18, 83-96.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Fritch RA, Sheridan H, Finn JA, McCormack S, Ó hUallacháin D (2017) Enhancing the diversity of breeding invertebrates within field margins of intensively managed grassland: Effects of alternative management practices. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 9763-9774.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Gao L, Wang L, Hu FL, Yang LR (2021) Recent progress of agro-biodiversity conservation and implications for agricultural development in China. Biodiversity Science, 29, 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 高磊, 王蕾, 胡飞龙, 杨礼荣 (2021) 农业生物多样性保护履约进展及对我国农业发展的启示. 生物多样性, 29, 177-183.]
DOI |
|
| [10] |
Han P, Niu CY, Desneux N (2014) Identification of top-down forces regulating cotton aphid population growth in transgenic Bt cotton in central China. PLoS ONE, 9, e102980.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Hedges LV, Gurevitch J, Curtis PS (1999) The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology, 80, 1150-1156.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Hou YM, Pang XF, Liang GW, You MS (2001) Effect of chemical insecticides on the diversity of arthropods in vegetable fields. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21, 1262-1268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 侯有明, 庞雄飞, 梁广文, 尤民生 (2001) 化学杀虫剂对菜田节肢动物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 21, 1262-1268.] | |
| [13] |
Kolb S, Uzman D, Leyer I, Reineke A, Entling MH (2020) Differential effects of semi-natural habitats and organic management on spiders in viticultural landscapes. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 287, 106695.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Kong J, Wang HY, Zhao BG, Ren YD, Liu YX, Chen HJ, Shan LN, Wang AC (2001) Study on ecological regulation system of the pest control in apple orchard. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21, 789-794. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孔建, 王海燕, 赵白鸽, 任应党, 刘玉霞, 陈汉杰, 单林娜, 王安超 (2001) 苹果园主要害虫生态调控体系的研究. 生态学报, 21, 789-794.] | |
| [15] |
Krauss J, Gallenberger I, Steffan-Dewenter I (2011) Decreased functional diversity and biological pest control in conventional compared to organic crop fields. PLoS ONE, 6, e19502.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Lei XD, Peng CH, Tian DL, Sun JF (2006) Meta-analysis and its application in global change. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 2587-2597. (in Chinese) |
| [ 雷相东, 彭长辉, 田大伦, 孙剑峰 (2006) 整合分析(meta-analysis)方法及其在全球变化中的应用研究. 科学通报, 51, 2587-2597.] | |
| [17] |
Letourneau DK, Armbrecht I, Rivera BS, Lerma JM, Carmona EJ, Daza MC, Escobar S, Galindo V, Gutiérrez C, López SD, Mejía JL, Rangel AMA, Rangel JH, Rivera L, Saavedra CA, Torres AM, Trujillo AR (2011) Does plant diversity benefit agroecosystems? A synthetic review. Ecological Applications, 21, 9-21.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Li Q, Chen YQ, Guo X, Chen YL (2006) Arthropod used as bio-indicator to assess the success of ecological restoration. Journal of Central South Forestry University, 26, 117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李巧, 陈又清, 郭萧, 陈彦林 (2006) 节肢动物作为生物指示物对生态恢复的评价. 中南林学院学报, 26, 117-122.] | |
| [19] |
Lichtenberg EM, Kennedy CM, Kremen C, Batáry P, Berendse F, Bommarco R, Bosque-Pérez NA, Carvalheiro LG, Snyder WE, Williams NM, Winfree R, Klatt BK, Åström S, Benjamin F, Brittain C, Chaplin-Kramer R, Clough Y, Danforth B, Diekötter T, Eigenbrode SD, Ekroos J, Elle E, Freitas BM, Fukuda Y, Gaines-Day HR, Grab H, Gratton C, Holzschuh A, Isaacs R, Isaia M, Jha S, Jonason D, Jones VP, Klein AM, Krauss J, Letourneau DK, MacFadyen S, Mallinger RE, Martin EA, Martinez E, Memmott J, Morandin L, Neame L, Otieno M, Park MG, Pfiffner L, Pocock MJO, Ponce C, Potts SG, Poveda K, Ramos M, Rosenheim JA, Rundlöf M, Sardiñas H, Saunders ME, Schon NL, Sciligo AR, Sidhu CS, Steffan-Dewenter I, Tscharntke T, Veselý M, Weisser WW, Wilson JK, Crowder DW (2017) A global synthesis of the effects of diversified farming systems on arthropod diversity within fields and across agricultural landscapes. Global Change Biology, 23, 4946-4957.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Liu YF, Zhang GR, Gu DX (2000) Effect and the acting mechanisms of the habitats and vegetational diversity on arthropod community in agroecosystem. Journal of Xiangtan Normal University (Social Science Edition), 21(6), 74-78. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘雨芳, 张古忍, 古德祥 (2000) 农田生态系统中生境与植被多样性对节肢动物群落的影响及其作用机制探讨. 湘潭师范学院学报(社会科学版), 21(6), 74-78.] | |
| [21] | Lu P, Mao NH, Liu B (2004) Core techniques and measures of plant protection in organic agriculture. China Plant Protection, 24(4), 36-39. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陆萍, 冒乃和, 刘波 (2004) 有机农业植物保护的核心技术和措施. 中国植保导刊, 24(4), 36-39.] | |
| [22] | Mao RQ, Zhang WQ, Zhang GR, Gu DX (2000) Studies on the structure of egg-parasitoid community of rice planthopper in non-rice habitat. Natural Enemies of Insects, 22, 171-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛润乾, 张文庆, 张古忍, 古德祥 (2000) 非稻田生境中稻飞虱卵寄生蜂群落结构研究. 昆虫天敌, 22, 171-176.] | |
| [23] | Marshall J, Baudry J, Burel F, Joenje W, Gerowitt B, Paoletti M, Thomas G, Kleijn D, Le Coeur D, Moonen C (2002) Field boundary habitats for wildlife, crop, and environmental protection. In: Landscape Ecology in Agroecosystems Management (ed.ed. Marshall J), pp. 219-248. CRC Press, Washington, D. C. |
| [24] |
Moreby SJ, Aebischer NJ, Southway SE, Sotherton NW (1994) A comparison of the flora and arthropod fauna of organically and conventionally grown winter wheat in southern England. Annals of Applied Biology, 125, 13-27.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Morente M, Campos M, Ruano F (2018) Evaluation of two different methods to measure the effects of the management regime on the olive-canopy arthropod community. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 259, 111-118.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Pan Y, Xi YG, Tian W, Zhou KX, Chen QH, Gao JX (2020) Research status and hotspot analysis of international organic agriculture biodiversity research based on bibliometrics. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39, 1429-1441. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘扬, 席运官, 田伟, 周可新, 陈秋会, 高吉喜 (2020) 基于文献计量的国际有机农业生物多样性研究现状与热点分析. 农业环境科学学报, 39, 1429-1441.] | |
| [27] | Peng SL, Zheng FY (1999) Introduction of MetaWin software. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 8, 295-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭少麟, 郑凤英 (1999) Meta分析及MetaWin软件. 土壤与环境, 8, 295-299.] | |
| [28] | Qian YQ, Ma KP (1994) Principles and Methods of Biodiversity Research. China Science & Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钱迎倩, 马克平 (1994) 生物多样性研究的原理与方法. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Rosenberg MS, Adams DC, Gurevitch J (2000) Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis, version 2.0. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA. |
| [30] | State Administration for Market Regulation, China Agricultural University (2019) China Organic Product Certification and Organic Industry Development (2019). China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国农业大学 (2019) 中国有机产品认证与有机产业发展(2019). 中国农业科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] | Xing SW, Zhu H, Ma RJ, Du YQ, Sun YJ, Zha GC (2017) Effects of different habitats and management on the spider communities in tea plantations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 4236-4246. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邢树文, 朱慧, 马瑞君, 杜颖青, 孙延杰, 查广才 (2017) 不同生境条件与管理方式对茶园蜘蛛群落结构及多样性的影响. 生态学报, 37, 4236-4246.] | |
| [32] | Yu XP, Hu C, Heong KL (1996) The effects of non-crop habitats on crop pests and their natural enemies. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 12(3), 130-133. (in Chinese) |
| [ 俞晓平, 胡萃, Heong KL (1996) 非作物生境对农业害虫及其天敌的影响. 中国生物防治学报, 12(3), 130-133.] | |
| [33] | Yuan W, Liu H, Zhang SX, Li WY (2010) Evaluation of communities of insect pests and natural enemies in organic rice fields of Changjiang Farm. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 26, 132-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁伟, 刘洪, 张士新, 黎伟裕 (2010) 长江农场有机稻田害虫与天敌群落评价. 上海农业学报, 26, 132-136.] | |
| [34] | Zhang QQ, Wang HS, Qin BR, Xie YL, Huang CY, Wang F, Wang KX (2014) Study on community structure and diversity of arthropods in ecological rice paddy fields. China Plant Protection, 34(4), 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张清泉, 王华生, 覃保荣, 谢义灵, 黄超燕, 王峰, 王凯学 (2014) 生态稻田节肢动物群落结构及其多样性研究. 中国植保导刊, 34(4), 19-24.] | |
| [35] | Zhang R, Zhao ZH, He DH, Wang F, Zhang ZS, Wang XP (2010) The structure and dynamics of arthropod communities in Chinese wolfberry fields under different disturbances. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 2656-2664. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张蓉, 赵紫华, 贺达汉, 王芳, 张宗山, 王新谱 (2010) 不同干扰条件下枸杞园节肢动物群落结构与动态. 生态学报, 30, 2656-2664.] | |
| [36] | Zhang YX, Tang ZH (2005) Current status of arthropod resistance development. World Pesticide, 27(4), 1-6. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张翼翾, 唐振华 (2005) 节肢动物抗药性发展的现况. 世界农药, 27(4), 1-6.] | |
| [37] | Zheng FY, Lu HF, Peng SL (2004) Non-parametric test for meta-analysis: Application of resampling tests. Ecology and Environment, 13, 616-618. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑凤英, 陆宏芳, 彭少麟 (2004) 整合分析中的非参数检验: 重复取样检验法的实例应用. 生态环境, 13, 616-618.] |
| [1] | 程建伟, 徐满厚, 窦永静, 王亚东, 王桠楠, 刘新民, 李永宏. 内蒙古典型草原马粪分解过程中节肢动物群落的季节动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24018-. |
| [2] | 牛永杰, 马全会, 朱玉, 刘海荣, 吕佳乐, 邹元春, 姜明. 氮沉降对草地昆虫多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23130-. |
| [3] | 武鹏峰, 崔淑艳, Abid Ali, 郑国. 蜘蛛飞航研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 517-530. |
| [4] | 段美春, 覃如霞, 张宏斌, 陈宝雄, 金彬, 张松泊, 任少鹏, 金树权, 朱升海, 华家宁, 刘云慧, 宇振荣. 农田节肢动物不同取样方法的综合比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 477-487. |
| [5] | 郑晓明, 杨庆文. 中国农业生物多样性保护进展概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(2): 167-176. |
| [6] | 马燕婕, 何浩鹏, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃. 转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 419-432. |
| [7] | 雷启义, 周江菊, 罗静, 张文华, 孙军, 龙春林. 贵州侗族地区香禾糯品种多样性的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 990-998. |
| [8] | 晏静, 张国良, 张瑞海, 宋振, 赵晓红, 刘玉升, 付卫东. 黄顶菊凋落物分解对节肢动物群落结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(11): 1288-1295. |
| [9] | 季洁, 张艳璇, 陈霞, 林坚贞, 孙莉. 多次释放胡瓜新小绥螨对橘园节肢动物群落多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(1): 24-31. |
| [10] | 余广彬, 杨效东. 不同演替阶段热带森林地表凋落物和土壤节肢动物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(2): 188-198. |
| [11] | 齐丹卉, 郭辉军, 崔景云, 盛才余. 云南澜沧县景迈古茶园生态系统植物多样性评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(3): 221-231. |
| [12] | 龚志莲, 郭辉军, 盛才余, 周开元. 西双版纳社区旱稻品种多样性与就地保护初探[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(4): 427-434. |
| [13] | 杨效东. 热带季节雨林凋落叶分解过程中的中小型土壤节肢动物的群落结构及动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(2): 252-261. |
| [14] | 卢宝荣, 朱有勇, 王云月. 农作物遗传多样性农家保护的现状及前景[J]. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(4): 409-415. |
| [15] | 杨效东, 唐勇, 唐建维. 热带次生林刀耕火种过程中土壤节肢动物群落结构及多样性的变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2001, 09(3): 222-227. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn