



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1288-1295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016047 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016047
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
晏静1,2, 张国良1, 张瑞海1, 宋振1, 赵晓红1, 刘玉升2, 付卫东1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-02-18
接受日期:2016-04-15
出版日期:2016-11-20
发布日期:2016-12-14
通讯作者:
付卫东
基金资助:
Jing Yan1,2, Guoliang Zhang1, Ruihai Zhang1, Zhen Song1, Xiaohong Zhao1, Yusheng Liu2, Weidong Fu1,*( )
)
Received:2016-02-18
Accepted:2016-04-15
Online:2016-11-20
Published:2016-12-14
Contact:
Fu Weidong
摘要:
选择黄顶菊(Flaveria bidentis)入侵的林地、农田、荒地、沟渠等4种生境作为调查样地, 比较黄顶菊与本地植物凋落物的分解速率及凋落物分解对节肢动物群落结构的影响。于2014年10月凋落物高峰期在各样地内分别搜集黄顶菊与本地植物的凋落物, 每种凋落物称取20 g装入尼龙网分解袋中, 放入各生境。2015年的每个月将不同生境不同处理凋落袋各取回10袋, 用Tullgren法分离节肢动物。 4种生境共捕获17,466头, 隶属8纲18目, 4种生境的优势类群皆为蜱螨目和啮目。其中, 林地、农田、荒地、沟渠4种生境处理组中节肢动物数量分别为1,698头, 1,838头, 2,631头, 3,413头, 分别比对照组高18%, 53%, 22%, 11%。多数月份黄顶菊凋落物中的节肢动物丰富度及多样性指数高于同生境对照组, 并且在黄顶菊生长盛期差异显著; 黄顶菊凋落物的分解速率高于对照植物分解速率, 且各月份凋落物分解速率动态与节肢动物数量变化动态呈显著相关。黄顶菊凋落物对节肢动物的影响与人为干扰程度有关, 这种影响在人为干扰较小的荒地与沟渠生境中更为明显。综上所述, 黄顶菊凋落物的分解改变了节肢动物群落结构, 并引起节肢动物多样性的升高。
晏静, 张国良, 张瑞海, 宋振, 赵晓红, 刘玉升, 付卫东 (2016) 黄顶菊凋落物分解对节肢动物群落结构的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 1288-1295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016047.
Jing Yan, Guoliang Zhang, Ruihai Zhang, Zhen Song, Xiaohong Zhao, Yusheng Liu, Weidong Fu (2016) The effect of Flaveria bidentis litter decomposition on the structure of arthropod communities. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1288-1295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016047.
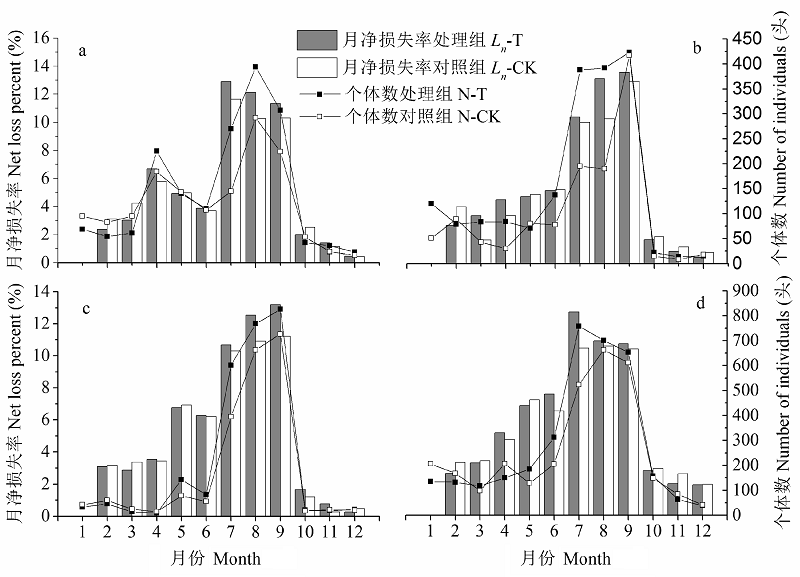
图1 4种生境凋落物月净损失率与节肢动物数量变化动态。a: 林地生境; b: 农田生境; c: 荒地生境; d: 沟渠生境。
Fig. 1 Dynamic of net loss percent of litter and the number of arthropods in four habitats. a, Forestland habitat; b, Cultivated field habitat; c, Uncultivated land habitat; d, Ditch habitat.
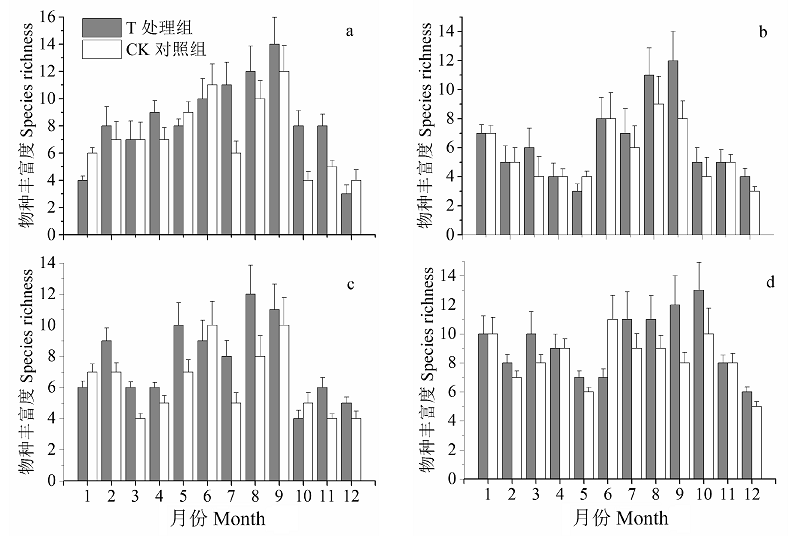
图2 4种生境节肢动物丰富度周年变化。a: 林地生境; b: 农田生境; c: 荒地生境; d: 沟渠生境。
Fig. 2 Annual variation of species richness of arthropod in four habitats. a, Forestland habitat; b, Cultivated field habitat; c, Uncultivated land habitat; d, Ditch habitat.
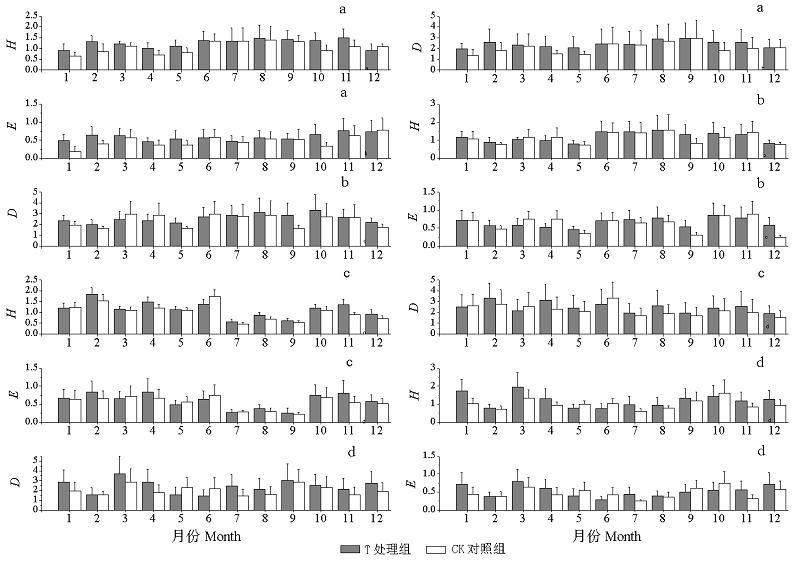
图3 4种生境节肢动物多样性。H: Shannon-Wiener多样性指数; D: Simpson多样性指数: E: Pielou均匀度指数。a: 林地生境; b: 农田生境; c: 荒地生境; d: 沟渠生境。
Fig. 3 Diversity index of arthropods in four habitats. H, Shannon-Wiener diversity index; D, Simpson-Yule index; E, Pielou evenness index. a, Forestland habitat; b, Cultivated field habitat; c, Uncultivated land habitat; d, Ditch habitat.
| 1 | Barajas-Guzmán G, Alvarez-Sánchez J (2003) The relationships between litter fauna and rates of litter decomposition in a tropical rain forest. Applied Soil Ecology, 24, 91-100. |
| 2 | Bokhorst S, Wardle DA (2013) Microclimate within litter bags of different mesh size: implications for the ‘arthropods effect’ on litter decomposition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58, 147-152. |
| 3 | Chen HL, Li YJ, Li B, Chen JK, Wu JH (2005) Impacts of exotic plant invasions on soil biodiversity and ecosystem processes. Biodiversity Science, 13, 555-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈慧丽, 李玉娟, 李博, 陈家宽, 吴纪华 (2005) 外来植物入侵对土壤生物多样性和生态系统过程的影响. 生物多样性, 13, 555-565.] | |
| 4 | Chen W, Li T, Zheng RQ, Chen P, Li T, Lu JJ, Zhang JY (2012) Effects of the invasion by Solidago canadensis L. on the community structure of soil animals. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 7072-7081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈雯, 李涛, 郑荣泉, 陈平, 李婷, 陆俊佶, 张加勇 (2012) 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对土壤动物群落结构的影响. 生态学报, 32, 7072-7081.] | |
| 5 | Cui Y, Wang SL, Yu XJ, Yan SK (2012) Effects of forest soil animals on early decomposition and nutrient release of litter. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31, 2709-2715. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔洋, 汪思龙, 于小军, 颜绍馗 (2012) 森林土壤动物对凋落物早期分解及养分释放的影响. 生态学杂志, 31, 2709-2715.] | |
| 6 | Cui ZD (1985) Function of soil animals. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 20(2), 49-52. (in Chinese) |
| [崔振东 (1985) 土壤动物的作用. 动物学杂志, 20(2), 49-52.] | |
| 7 | Darby BJ, Neher DA, Housman DC, Belnap J (2011) Few apparent short-term effects of elevated soil temperature and increased frequency of summer precipitation on the abundance and taxonomic diversity of desert soil micro- and meso-fauna. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43, 1474-1481. |
| 8 | Gao XM, Tang TG, Liang Y, Zheng TX, Sang WG, Chen YL (2004) An alert regarding biological invasion by a new exotic plant, Flaveria bidentis, and strategy for its control. Biodiversity Science, 12, 274-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高贤明, 唐廷贵, 梁宇, 郑天翔, 桑卫国, 陈艺林 (2004) 外来植物黄顶菊的入侵警报及防控对策. 生物多样性, 12, 274-279.] | |
| 9 | García-Palacios P, Maestre FT, Kattge J, Wall DH (2013) Climate and litter quality differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition across biomes. Ecology Letters, 16, 1045-1053. |
| 10 | Huangfu CH, Wang ZY, Yang DL (2009) Basic photosynthetic characteristics of exotic invasive weed Flaveria bidentis and its companion species. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 29, 781-788. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [皇甫超河, 王志勇, 杨殿林 (2009) 外来入侵种黄顶菊及其伴生植物光合特性初步研究. 西北植物学报, 29, 781-788.] | |
| 11 | Lana PC, Guiss C (1991) Influence of Spartina alterniflora on structure and temporal variability of macrobenthic associations in a tidal flat of Paranaguá Bay (southeastern Brazil). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 73, 231-244. |
| 12 | Lei YB, Xiao HF, Feng YL (2010) Impacts of alien plant invasions on biodiversity and evolutionary responses of native species. Biodiversity Science, 18, 622-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [类延宝, 肖海峰, 冯玉龙 (2010) 外来植物入侵对生物多样性的影响及本地生物的进化响应. 生物多样性, 18, 622-630.] | |
| 13 | Li HX, Sui JZ, Zhou SX (1987)Index of Insect Classification. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [李鸿兴, 隋敬之, 周士秀 (1987) 昆虫分类检索. 农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 14 | Li YH (2012) Decomposition Characteristics and Soil Fauna Community Dynamics in Mixed Eucalyptus grandis and Alnus formosana Litters. PhD dissertation, Sichuan Agricultural University, Ya’an. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李艳红 (2012) 巨桉-台湾桤木混合凋落物分解特征及其土壤动物群落动态. 博士学位论文, 四川农业大学, 雅安.] | |
| 15 | Liu N, Fu WD, Zhang GL, Liu YS, Lu AL (2014) Impacts of Flaveria bidentis invasion on ground-dwelling soil animal communities in different habitats. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 176-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘宁, 付卫东, 张国良, 刘玉升, 卢爱玲 (2014) 黄顶菊入侵对不同生境地表土壤动物群落的影响. 生态学杂志, 33, 176-183.] | |
| 16 | Liu QR (2005) Flaveria Juss. (Compositae), a newly naturalized genus in China. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 43, 178-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘全儒 (2005) 中国菊科植物一新归化属——黄菊属. 植物分类学报, 43, 178-180.] | |
| 17 | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Mark LW, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences and control. Ecological Applications, 10, 689-710. |
| 18 | Ma KP (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 1). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 162-168. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(上). 生物多样性, 2, 162-168.] | |
| 19 | Palacios-Vargas JG, Castaño-Meneses G, Gómez-Anaya JA, Martínez-Yrizar A, Mejía-Recamier BE, Martínez-Sánchez J (2007) Litter and soil arthropods diversity and density in a tropical dry forest ecosystem in Western Mexico. Biodiversity and Conservation, 16, 3703-3717. |
| 20 | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley and Sons, New York. |
| 21 | Qin Z, Zhang JE, Li QF (2009) Community structure of soil meso- fauna and micro- fauna in different habitats of urbanized region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20, 3049-3056. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦钟, 章家恩, 李庆芳 (2009) 城市化地区不同生境下中小型土壤动物群落结构特征. 应用生态学报, 20, 3049-3056.] | |
| 22 | Ren YP, Jiang S, Gu S, Wang YZ, Zheng SX (2008) Advances in Flaveria bidentis (L.) Kuntze, a new exotic plant. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 16, 390-396. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任艳萍, 江莎, 古松, 王永周, 郑书馨 (2008) 外来植物黄顶菊(Flaveria bidentis)的研究. 热带亚热带植物学报, 16, 390-396.] | |
| 23 | Schulze DJ, Walker KF (1997) Riparian eucalypts and willows and their significance for aquatic invertebrates in the River Murray, South Australia. Regulated Rivers: Research & Management, 13, 557-577. |
| 24 | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication . University of Illionis Press, Urbana. |
| 25 | Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 162, 688. |
| 26 | Tan B, Wu FZ, Yang WQ, Xia L, Yang YL, Wang A (2012) Diversity of the large soil animal communities and its response to seasonal freezing and thawing in the subalpine / alpine forests. Biodiversity Science, 20, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭波, 吴福忠, 杨万勤, 夏磊, 杨玉莲, 王奥 (2012) 川西亚高山/高山森林大型土壤动物群落多样性及其对季节性冻融的响应. 生物多样性, 20, 215-223.] | |
| 27 | Thakur MP, Berg MP, Eisenhauer N, van Langevelde F (2014) Disturbance-diversity relationships for soil fauna are explained by faunal community biomass in a salt marsh. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 78, 30-37. |
| 28 | Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH (2002) Alien invasive species in China: their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 10, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 (2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 10, 119-125.] | |
| 29 | Wood CT, Schlindwein CCD, Soares GLG, Araujo PB (2012) Feeding rates of Balloniscus sellowii (Crustacea, Isopoda, Oniscidea): the effect of leaf litter decomposition and its relation to the phenolic and flavonoid content. ZooKeys, 176, 231-245. |
| 30 | Xie JF, Quan GM, Zhang JE, Mao DJ, Xu HQ, Qin Z (2011) Effects of Ambrosia artemisiifolia invasion on the community structure of meso- and micro-fauna. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 5682-5690. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢俊芳, 全国明, 章家恩, 毛丹鹃, 徐华勤, 秦钟 (2011) 豚草入侵对中小型土壤动物群落结构特征的影响. 生态学报, 31, 5682-5690.] | |
| 31 | Yin WY (1998) Pictorical Keys of Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1998)中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 32 | Zha TG, Zhang ZQ, Sun G, Wang GM, Yun XQ, Wang YK, Liu Y (2012) Home-field advantage of litter decomposition and its soil biological driving mechanism: a review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 7991-8000. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [査同刚, 张志强, 孙阁, 王高敏, 贠小琴, 王伊琨, 刘艳 (2012) 凋落物分解主场效应及其土壤生物驱动. 生态学报, 32, 7991-8000.] | |
| 33 | Zhang GL, Fu WD, Sun YF (2013) Manual of National Comprehensive Prevention and Control Technology for the State Key Management of Alien Invasive Species. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张国良, 付卫东, 孙玉芳 (2013) 国家重点管理外来入侵物种综合防控技术手册. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 34 | Zhang GL, Fu WD, Zheng H (2014) Invasion Mechanisms and Integrated Management of Flaveria bidentis. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张国良, 付卫东, 郑浩 (2014)黄顶菊入侵机制及综合治理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 35 | Zhang GL, Fu WD, Han Y (2010) Emergency Prevention and Control Guidelines of Flaveria bidentis (L.) Kuntze. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张国良, 付卫东, 韩颖 (2010) 黄顶菊应急防控指南. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 36 | Zhang TR, Huangfu CH, Bai XM, Yang DL, Li G, Lai X, Zhao JN (2010) Effect of Flaveria bidentis invasion on soil nutrients and enzyme activities. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29, 1353-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张天瑞, 皇甫超河, 白小明, 杨殿林, 李刚, 赖欣, 赵建宁 (2010) 黄顶菊入侵对土壤养分和酶活性的影响. 生态学杂志, 29, 1353-1358.] | |
| 37 | Zhang W, Yuan S, Hu N, Lou Y, Wang S (2015) Predicting soil fauna effect on plant litter decomposition by using boosted regression trees. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 82, 81-86. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()