



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 557-566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019021 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019021
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
张雪1,李兴安2,苏秦之1,曹棋钠1,李晨伊1,牛庆生2,*( ),郑浩1,*(
),郑浩1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-01-25
接受日期:2019-05-07
出版日期:2019-05-20
发布日期:2019-05-20
通讯作者:
牛庆生,郑浩
基金资助:
Zhang Xue1,Li Xing’an2,Su Qinzhi1,Cao Qina1,Li Chenyi1,Niu Qingsheng2,*( ),Zheng Hao1,*(
),Zheng Hao1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-25
Accepted:2019-05-07
Online:2019-05-20
Published:2019-05-20
Contact:
Niu Qingsheng,Zheng Hao
摘要:
蜜蜂和熊蜂是重要的传粉昆虫, 对农业生产及生态平衡的维持具有重要作用。近年来, 研究发现蜜蜂及熊蜂肠道内含有大量微生物, 其组成简单、特异。正常的肠道微生物群落对蜜蜂的生长、激素调节、致病菌抵抗等具有重要作用。随着高通量测序的发展, 研究者们也可快速获得传粉蜂肠道微生物组成, 这给生物多样性和物种保护及蜂类健康等的研究带来了便捷。但是由于蜜蜂和熊蜂肠道微生物群落均由特殊菌种组成, 目前的细菌16S rRNA数据库无法对其进行准确的分类, 并且部分东方蜜蜂(Apis cerana)特有的肠道微生物菌种缺乏16S rRNA序列信息。本文从来源于5个不同省份的东方蜜蜂肠道中分离得到在东方蜜蜂中普遍含有的Apibacter菌属纯菌, 获取其全长16S rRNA序列, 并对目前蜜蜂和熊蜂肠道的5个核心菌种的分类进行了综述, 对其分类和命名进行了修正。根据蜜蜂肠道微生物的明确分类, 在目前常用的SILVA细菌分类数据库基础之上对其进行了命名及分类优化, 并加入东方蜜蜂中普遍含有的Apibacter序列, 从而获得了优化数据库Bee Gut Microbiota-Database (BGM-Db)。通过1组东方蜜峰及1组西方蜜蜂(Apis mellifera)的肠道菌群高通量测序结果, 分析不同数据库的表现, 我们发现相比于SILVA和Ribosomal Database Project (RDP), BGM-Db对蜜蜂肠道16S rRNA高通量测序短序列实现了菌种级别的分类, 分辨率更高。
张雪, 李兴安, 苏秦之, 曹棋钠, 李晨伊, 牛庆生, 郑浩 (2019) 用于蜜蜂和熊蜂肠道微生物分类的细菌16S rRNA数据库优化. 生物多样性, 27, 557-566.
DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019021.
Zhang Xue, Li Xing’an, Su Qinzhi, Cao Qina, Li Chenyi, Niu Qingsheng, Zheng Hao (2019) A curated 16S rRNA reference database for the classification of honeybee and bumblebee gut microbiota. Biodiversity Science, 27, 557-566. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019021.
| 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 其他名 Other names | BGM-Db数据库聚类名 BGM-Db names | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snodgrassella | Snodgrassella alvi | Beta | Snodgrassella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Gilliamella | Gilliamella apicola | Gamma-1 | Gilliamella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Frischella | Frischella perrara | Gamma-2 | Frischella | Engel et al, 2013 |
| Schmidhempelia | ‘Candidatus Schmidhempelia bombi’ | Schmidhempelia | Martinson et al, 2014 | |
| Bartonella | Bartonella apis | Alpha-1 | Bartonella apis | Moran, 2015 |
| Commensalibacter | Commensalibacter intestini | Alpha-2.1 | Commensalibacter Alpha2.1 | Kwong et al, 2014b |
| Bombella | Bombella apis | Alpha-2.2 | Bombella Alpha2.2 | Yun et al, 2017 |
| Bombella intestini | Yun et al, 2017 | |||
| Parasaccharibacter | Parasaccharibacter apium | Moran, 2015 | ||
| Lactobacillus | Lactobacillus mellis | Firm-4 | Lactobacillus Firm-4 | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 |
| Lactobacillus mellifer | ||||
| Lactobacillus apis | Firm-5 | Lactobacillus Firm-5 | Kwong et al, 2014b | |
| Lactobacillus helsingborgensis | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 | |||
| Lactobacillus melliventris | ||||
| Lactobacillus kimbladii | ||||
| Lactobacillus kullabergensis | ||||
| Lactobacillus apinorum | ||||
| Lactobacillus kunkeei | / | Lactobacillus kunkeei | Moran, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium | Bifidobacterium asteroides | / | Bifidobacterium asteroides | Bottacini et al, 2012 |
| Bifidobacterium coryneforme | / | Bifidobacterium coryneforme/indicum | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium indicum | / | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bombi | / | Bifidobacterium bombi/commune/bohemicum | Killer et al, 2009 | |
| Bifidobacterium commune | / | Praet et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bohemicum | / | Killer et al, 2011 | ||
| Bombiscardovia | Bombiscardovia coagulans | / | Bombiscardovia | Killer et al, 2010 |
| Apibacter | Apibacter adventoris | / | Apibacter | Kwong & Moran, 2016 |
| Apibacter mensalis | / | Praet et al, 2016 |
表1 蜜蜂肠道核心菌命名校正
Table 1 List of the nomenclature of the curated bacterial species from bee gut
| 属名 Genus | 种名 Species | 其他名 Other names | BGM-Db数据库聚类名 BGM-Db names | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snodgrassella | Snodgrassella alvi | Beta | Snodgrassella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Gilliamella | Gilliamella apicola | Gamma-1 | Gilliamella | Martinson et al, 2012; Kwong & Moran, 2013 |
| Frischella | Frischella perrara | Gamma-2 | Frischella | Engel et al, 2013 |
| Schmidhempelia | ‘Candidatus Schmidhempelia bombi’ | Schmidhempelia | Martinson et al, 2014 | |
| Bartonella | Bartonella apis | Alpha-1 | Bartonella apis | Moran, 2015 |
| Commensalibacter | Commensalibacter intestini | Alpha-2.1 | Commensalibacter Alpha2.1 | Kwong et al, 2014b |
| Bombella | Bombella apis | Alpha-2.2 | Bombella Alpha2.2 | Yun et al, 2017 |
| Bombella intestini | Yun et al, 2017 | |||
| Parasaccharibacter | Parasaccharibacter apium | Moran, 2015 | ||
| Lactobacillus | Lactobacillus mellis | Firm-4 | Lactobacillus Firm-4 | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 |
| Lactobacillus mellifer | ||||
| Lactobacillus apis | Firm-5 | Lactobacillus Firm-5 | Kwong et al, 2014b | |
| Lactobacillus helsingborgensis | Olofsson et al, 2014; Moran, 2015 | |||
| Lactobacillus melliventris | ||||
| Lactobacillus kimbladii | ||||
| Lactobacillus kullabergensis | ||||
| Lactobacillus apinorum | ||||
| Lactobacillus kunkeei | / | Lactobacillus kunkeei | Moran, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium | Bifidobacterium asteroides | / | Bifidobacterium asteroides | Bottacini et al, 2012 |
| Bifidobacterium coryneforme | / | Bifidobacterium coryneforme/indicum | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | |
| Bifidobacterium indicum | / | Ellegaard et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bombi | / | Bifidobacterium bombi/commune/bohemicum | Killer et al, 2009 | |
| Bifidobacterium commune | / | Praet et al, 2015 | ||
| Bifidobacterium bohemicum | / | Killer et al, 2011 | ||
| Bombiscardovia | Bombiscardovia coagulans | / | Bombiscardovia | Killer et al, 2010 |
| Apibacter | Apibacter adventoris | / | Apibacter | Kwong & Moran, 2016 |
| Apibacter mensalis | / | Praet et al, 2016 |
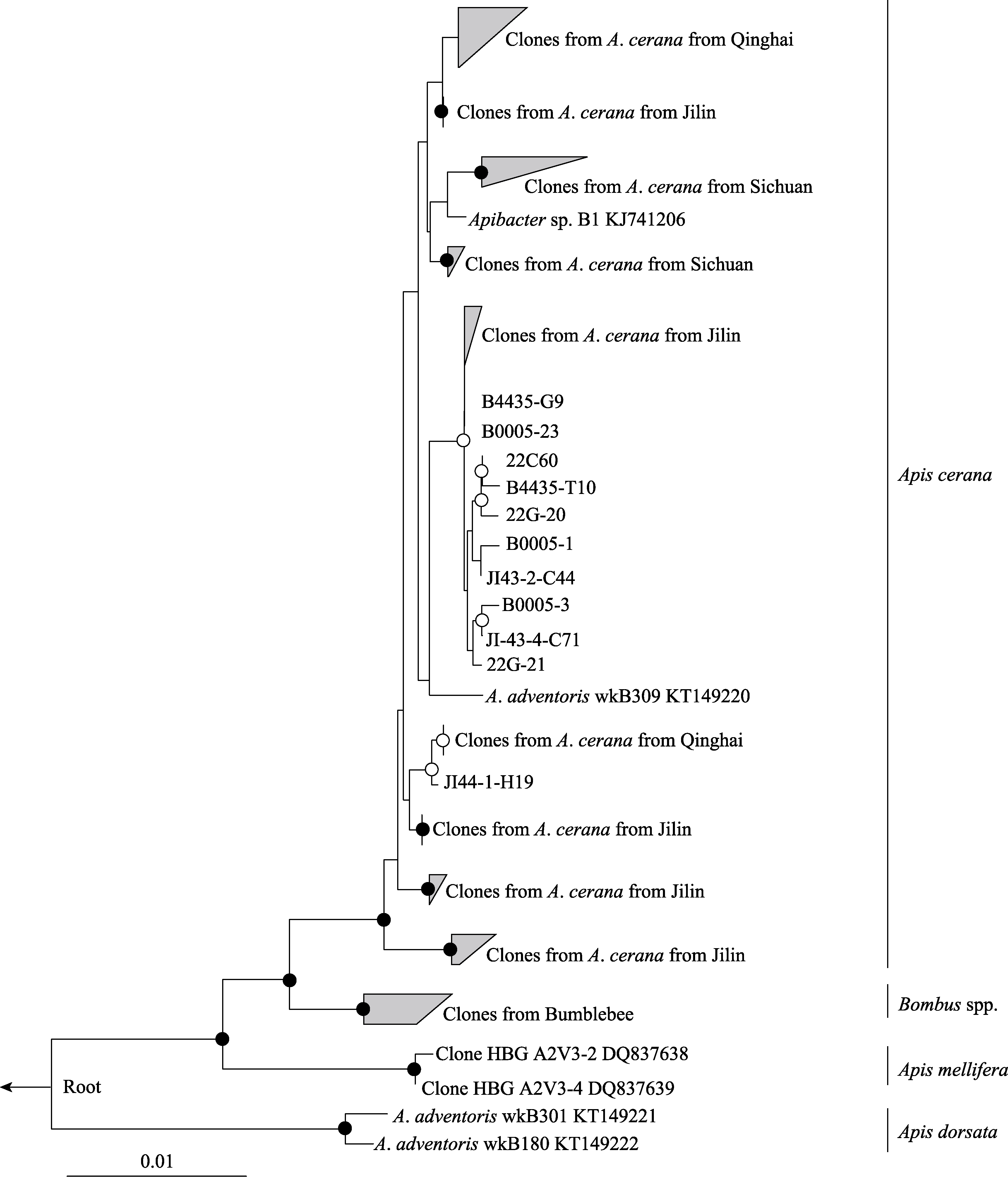
图1 基于接近全长16S rRNA序列(1,168 bp)的东方蜜蜂Apibacter菌属系统发育树。节点处白圈表示自展支持率大于75%, 黑圈表示大于95%。
Fig. 1 A maximum-likelihood tree of the Apibacter genus from A. cerana based on the near full-length 16S rRNA sequences (1,168 bp). Bootstrap values are indicated at the branching nodes (· > 95%, 〇 > 75%).
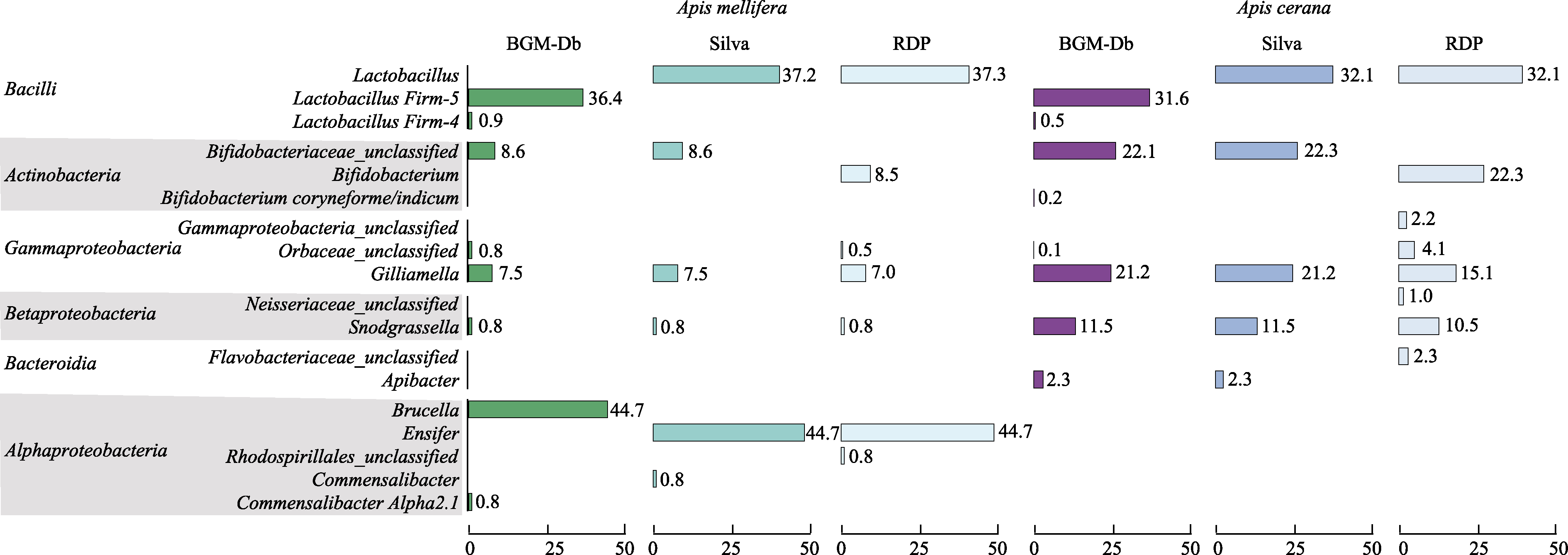
图2 利用BGM-Db、SILVA及Ribosomal Database Project (RDP)数据库对东方蜜蜂和西方蜜蜂16S rRNA测序结果分类比较
Fig. 2 Comparison of the behaviors of the BGM-Db, SILVA, and Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) databases when they are used in the classification of the gut microbiota of Apis cerana and Apis mellifera
| [1] |
Asama T, Arima TH, Gomi T, Keishi T, Tani H, Kimura Y, Tatefuji T, Hashimoto K ( 2015) Lactobacillus kunkeei YB38 from honeybee products enhances IgA production in healthy adults. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 119, 818-826.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bottacini F, Milani C, Turroni F, Sánchez B, Foroni E, Duranti S, Serafini F, Viappiani A, Strati F, Ferrarini A, Delledonne M, Henrissat B, Coutinho P, Fitzgerald GF, Margolles A, van Sinderen D, Ventura M ( 2012) Bifidobacterium asteroides PRL2011 genome analysis reveals clues for colonization of the insect gut. PLoS ONE, 7, e44229.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM ( 2014) Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D633-D642.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Corby-Harris V, Snyder L, Meador CAD, Naldo R, Mott B, Anderson KE ( 2016) Parasaccharibacter apium, gen. nov., sp. nov., improves honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) resistance to Nosema. Journal of Economic Entomology, 109, 537-543.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Corby-Harris V, Snyder LA, Schwan MR, Maes P, McFrederick QS, Anderson KE ( 2014) Origin and effect of Alpha 2.2 Acetobacteraceae in honey bee larvae and description of Parasaccharibacter apium gen. nov., sp. nov. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 7460-7472.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Cox-Foster DL, Conlan S, Holmes EC, Palacios G, Evans JD, Moran NA, Quan PL, Briese T, Hornig M, Geiser DM, Martinson V, vanEngelsdorp D, Kalkstein AL, Drysdale A, Hui J, Zhai J, Cui L, Hutchison SK, Simons JF, Egholm M, Pettis JS, Lipkin WI ( 2007) A metagenomic survey of microbes in honey bee colony collapse disorder. Science, 318, 283-287.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Ellegaard KM, Tamarit D, Javelind E, Olofsson TC, Andersson SGE, Vásquez A ( 2015) Extensive intra-phylotype diversity in Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria from the honeybee gut. BMC Genomics, 16, 284.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Engel P, Bartlett KD, Moran NA ( 2015) The bacterium Frischella perrara causes scab formation in the gut of its honeybee host. mBio, 6, e00193-15. |
| [9] | Engel P, Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2013) Frischella perrara gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gammaproteobacterium isolated from the gut of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63, 3646-3651. |
| [10] |
Engel P, Martinson VG, Moran NA ( 2012) Functional diversity within the simple gut microbiota of the honey bee. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 11002-11007.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Engel P, Stepanauskas R, Moran NA ( 2014) Hidden diversity in honey bee gut symbionts detected by single-cell genomics. PLoS Genetics, 10, e1004596.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Killer J, Kopečný J, Mrázek J, Havlík J, Koppová I, Benada O, Rada V, Kofroňová O ( 2010) Bombiscardovia coagulans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Bifidobacteriaceae isolated from the digestive tract of bumblebees. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 33, 359-366.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Killer J, Kopecny J, Mrazek J, Koppova I, Havlik J, Benada O, Kott T ( 2011) Bifidobacterium actinocoloniiforme sp. nov. and Bifidobacterium bohemicum sp. nov., from the bumblebee digestive tract. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 61, 1315-1321.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Killer J, Kopecny J, Mrazek J, Rada V, Benada O, Koppova I, Havlik J, Straka J ( 2009) Bifidobacterium bombi sp. nov., from the bumblebee digestive tract. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, 2020-2024.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kim EK, Kim SH, Nam HJ, Choi MK, Lee KA, Choi SH, Seo YY, You H, Kim B, Lee WJ ( 2012) Draft genome sequence of Commensalibacter intestini A911T, a symbiotic bacterium isolated from Drosophila melanogaster intestine. Journal of Bacteriology, 194, 1246.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Klein AM, Vaissière BE, Cane JH, Steffan-Dewenter I, Cunningham SA, Kremen C, Tscharntke T ( 2007) Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274, 303-313.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Kwong WK, Engel P, Koch H, Moran NA ( 2014 a) Genomics and host specialization of honey bee and bumble bee gut symbionts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 11509-11514.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Kwong WK, Mancenido AL, Moran NA ( 2014 b) Genome sequences of Lactobacillus sp. strains wkB8 and wkB10, members of the Firm-5 clade, from honey bee guts. Genome Announcements, 2, e01176-14. |
| [19] | Kwong WK, Medina LA, Koch H, Sing KW, Soh EJY, Ascher JS, Jaffé R, Moran NA ( 2017) Dynamic microbiome evolution in social bees. Science Advances, 3, 1-16. |
| [20] |
Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2013) Cultivation and characterization of the gut symbionts of honey bees and bumble bees: Description of Snodgrassella alvi gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Neisseriaceae of the betaproteobacteria, and Gilliamella apicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of Orbaceae fam. nov., Orbales ord. nov., a sister taxon to the order 'Enterobacteriales' of the Gammaproteobacteria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63, 2008-2018.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kwong WK, Moran NA ( 2016) Apibacter adventoris gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from honey bees. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 1323-1329.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lane DJ ( 1991) 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In: Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic (eds Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M), pp. 115-175. John Wiley and Sons, New York |
| [23] |
Li L, Praet J, Borremans W, Nunes OC, Manaia CM, Cleenwerck I, Meeus I, Smagghe G, De Vuyst L, Vandamme P ( 2015) Bombella intestini gen. nov., sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium isolated from bumble bee crop. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 65, 267-273.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Martinson VG, Danforth BN, Minckley RL, Rueppell O, Tingek S, Moran NA ( 2011) A simple and distinctive microbiota associated with honey bees and bumble bees. Molecular Ecology, 20, 619-628.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Martinson VG, Mago T, Koch H, Salzberg SL, Moran NA ( 2014) Genomic features of a bumble bee symbiont reflect its host environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 3793-3803.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Martinson VG, Moy J, Moran NA ( 2012) Establishment of characteristic gut bacteria during development of the honeybee worker. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 2830-2840.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Mikaelyan A, Köhler T, Lampert N, Rohland J, Boga H, Meuser K, Brune A ( 2015) Classifying the bacterial gut microbiota of termites and cockroaches: A curated phylogenetic reference database (DictDb). Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 38, 472-482.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Moran NA ( 2015) Genomics of the honey bee microbiome. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 10, 22-28.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Newton IL, Roeselers G ( 2012) The effect of training set on the classification of honey bee gut microbiota using the Naïve Bayesian Classifier. BMC Microbiology, 12, 221.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Olofsson TC, Alsterfjord M, Nilson B, Butler E, Vásquez A ( 2014) Lactobacillus apinorum sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellifer sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellis sp. nov., Lactobacillus melliventris sp. nov., Lactobacillus kimbladii sp. nov., Lactobacillus helsingborgensis sp. nov. and Lactobacillus kullabergensis sp. nov., isolated from the honey stomach of the honeybee Apis mellifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64, 3109-3119.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Praet J, Aerts M, Brandt ED, Meeus I, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2016) Apibacter mensalis sp. nov.: A rare member of the bumblebee gut microbiota. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 1645-1651.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Praet J, Meeus I, Cnockaert M, Aerts M, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2015) Bifidobacterium commune sp. nov. isolated from the bumble bee gut. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 107, 1307-1313.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Praet J, Parmentier A, Schmid-Hempel R, Meeus I, Smagghe G, Vandamme P ( 2018) Large-scale cultivation of the bumblebee gut microbiota reveals an underestimated bacterial species diversity capable of pathogen inhibition. Environmental Microbiology, 20, 214-227.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO ( 2007) SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, 7188-7196.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Raymann K, Shaffer Z, Moran NA ( 2017) Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biology, 15, e2001861.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Segers FH, Kešnerová L, Kosoy M, Engel P ( 2017) Genomic changes associated with the evolutionary transition of an insect gut symbiont into a blood-borne pathogen. The ISME Journal, 11, 1232-1244.
DOI |
| [37] | Steele MI, Kwong WK, Whiteley M, Moranb NA ( 2017) Diversification of type VI secretion system toxins reveals ancient antagonism among bee gut microbes. mBio, 8, e01630-17. |
| [38] |
Tarpy DR, Mattila HR, Newton ILG ( 2015) Development of the honey bee gut microbiome throughout the Queen- Rearing Process. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81, 3182-3191.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
vanEngelsdorp D, Evans JD, Saegerman C, Mullin C, Haubruge E, Nguyen BK, Frazier M, Frazier J, Cox-Foster D, Chen Y, Underwood R, Tarpy DR, Pettis JS ( 2009) Colony collapse disorder: A descriptive study. PLoS ONE, 4, e6481.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR ( 2007) Naïve Bayesian Classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5261-5267.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Yilmaz P, Parfrey LW, Yarza P, Gerken J, Pruesse E, Quast C, Schweer T, Peplies J, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO ( 2014) The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D643-D648.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Yun JH, Lee JY, Hyun DW, Jung MJ, Bae JW ( 2017) Bombella apis sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium isolated from the midgut of a honey bee. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67, 2184-2188.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Zheng H, Nishida A, Kwong WK, Koch H, Engel P, Steele MI, Moran NA ( 2016) Metabolism of toxic sugars by strains of the bee gut symbiont Gilliamella apicola. mBio, 7, e01326-16. |
| [44] |
Zheng H, Powell JE, Steele MI, Dietrich C, Moran NA ( 2017) Honeybee gut microbiota promotes host weight gain via bacterial metabolism and hormonal signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 4775-4780.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 廖雅晴, 黄泽锋, 王晓云, 张礼标, 吴毅, 余文华. 广东省翼手目物种名录更新及分子条形码数据库[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [2] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [3] | 陈静, 张丙昌, 刘燕晋, 武杰, 赵康, 明姣. 荒漠生物结皮细鞘丝藻类(Leptolyngbya-like)蓝藻多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24186-. |
| [4] | 何凯莹, 徐心慧, 张承云, 郝泽周, 肖治术, 郭莹莹. 生物声学数据档案的管理标准及管理技术进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24266-. |
| [5] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [6] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [7] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [8] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [9] | 赵雯, 王丹丹, 热依拉·木民, 黄开钏, 刘顺, 崔宝凯. 阿尔山地区兴安落叶松林土壤微生物群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [10] | 夏凡, 杨婧, 李建, 史洋, 盖立新, 黄文华, 张经纬, 杨南, 高福利, 韩莹莹, 鲍伟东. 北京地区四个豹猫亚种群肠道菌群的组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22103-. |
| [11] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [12] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [13] | 夏呈强, 李毅, 党延茹, 察倩倩, 贺晓艳, 秦启龙. 中印度洋与南海西部表层海水细菌多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21407-. |
| [14] | 陆奇丰, 黄至欢, 骆文华. 极小种群濒危植物广西火桐、丹霞梧桐的叶绿体基因组特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 586-595. |
| [15] | 王楠, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 杨盼盼, 张欣玥, 赵世伟. 宁南山区不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫群落特征:形态学鉴定与高通量测序法比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()