



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 11-18. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08107 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.08107
收稿日期:2012-04-24
接受日期:2012-06-16
出版日期:2013-01-20
发布日期:2013-02-04
通讯作者:
李宝泉
基金资助:
1,2, Qingxi Han1, Baoquan Li1,*( )
)
Received:2012-04-24
Accepted:2012-06-16
Online:2013-01-20
Published:2013-02-04
Contact:
Li Baoquan
摘要:
为摸清辽宁獐子岛潮间带及近岸海区的大型底栖动物的分布现状和群落受扰动情况, 作者于2011年11月中旬在马牙滩潮间带和近岸海区采集大型底栖动物, 采用优势度指数、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Margalef丰富度指数、Pielou均匀度指数, Bray-Curtis相似性聚类分析、MDS标序和ABC曲线等方法, 分析该区域内大型底栖动物群落的生态学特点。结果表明, 在潮间带共鉴定大型底栖动物39种, 优势类群为多毛类、甲壳类和软体类; 优势种均为多毛类, 即小头虫(Capitella capitata)、多美沙蚕(Lycastopsis augenari)、仙居虫(Naineris laevigata)和短叶索沙蚕(Lumbrineris latreilli); 平均生物量为25.76 ± 41.08 g/m2, 以软体动物占优势; 平均栖息密度为315.11 ± 160.73 个/m2, 以多毛类占优势; 丰富度指数、均匀度指数与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数的平均值分别为1.17 ± 0.89, 0.74 ± 0.17和1.80 ± 1.09。近岸海区共鉴定大型底栖动物40种, 优势类群为多毛类、甲壳动物、软体动物和棘皮动物。优势种包括4种棘皮动物和1种多毛类, 即紫蛇尾(Ophiopholis mirabilis)、日本倍棘蛇尾(Amphioplus japonicus)、短叶索沙蚕、心形海胆(Echinocardium cordatum)和浅水萨氏真蛇尾(Ophiura sarsiivadicola)。近岸海区的平均生物量和平均栖息密度分别为218.86 ± 152.24 g/m2和700.00 ± 471.51 个/m2, 均以棘皮动物占优势。丰富度指数、均匀度指数与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数的平均值分别为1.40 ± 0.60, 0.64 ± 0.19和2.04 ± 0.78。聚类分析结果表明, 潮间带不同潮区间和近岸海区不同断面间群落差异显著。ABC曲线分析显示, 獐子岛潮间带底质环境受到中度扰动, 大型底栖动物群落结构处于不稳定状态; 近岸海区受到轻度干扰, 群落结构未发生明显变化。
王全超, 韩庆喜, 李宝泉 (2013) 辽宁獐子岛马牙滩潮间带及近岸海区大型底栖动物群落特征. 生物多样性, 21, 11-18. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08107.
,Qingxi Han,Baoquan Li (2013) Macrobenthic fauna in the intertidal and offshore areas of Zhangzi Island. Biodiversity Science, 21, 11-18. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08107.
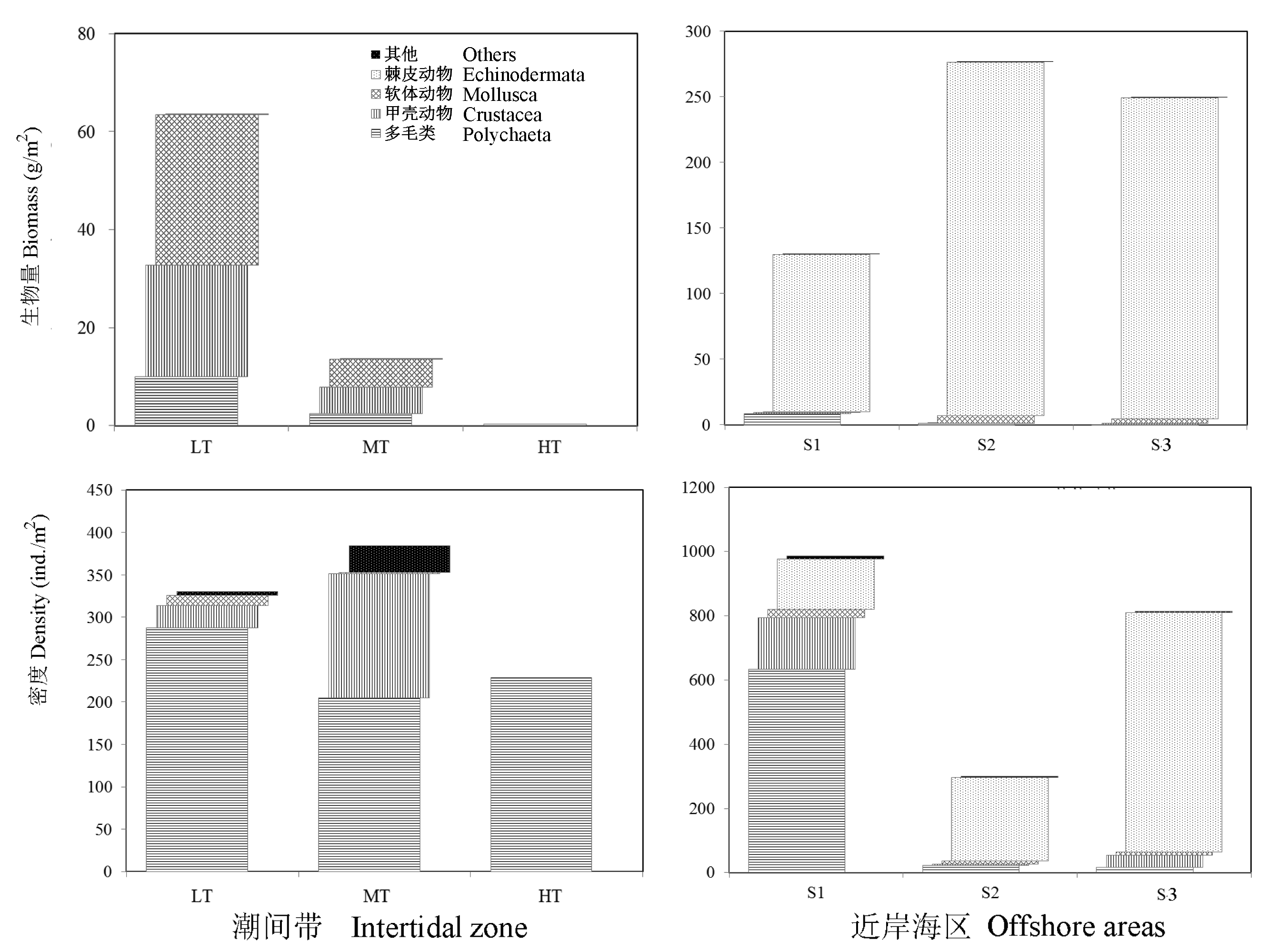
图2 獐子岛潮间带及近岸海区大型底栖动物生物量与栖息密度 (LT: 低潮区; MT: 中潮区; HT: 高潮区; S1, S2, S3, 近岸海区三个采样点)
Fig. 2 Biomass and density of macrobenthos in the intertidal zone and offshore areas of Zhangzi Island. LT, Low tidal zone; MT, Middle tidal zone; HT, High tidal zone; S1, S2, S3, three sampling sites in offshore area.
| 断面 Section | 种数 No. of species (S) | 丰富度 Richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潮间带 Intertidal zone | ||||
| LT | 13.00 ± 1.73 | 2.07 ± 0.23 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | 2.60 ± 0.36 |
| MT | 8.67 ± 4.04 | 1.27 ± 0.58 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 2.34 ± 0.59 |
| HT | 1.67 ± 0.58 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 0.70 ± 0.39 | 0.46 ± 0.49 |
| 均值 Average | 7.78 ± 5.43 | 1.17 ± 0.89 | 0.74 ± 0.17 | 1.80 ± 1.09 |
| 近岸海区 Offshore area | ||||
| S1 | 15.00 ± 2.00 | 2.04 ± 0.23 | 0.69 ± 0.06 | 2.67 ± 0.10 |
| S2 | 7.00 ± 3.00 | 1.08 ± 0.59 | 0.71 ± 0.18 | 1.99 ± 0.94 |
| S3 | 8.00 ± 2.65 | 1.08 ± 0.32 | 0.51 ± 0.26 | 1.45 ± 0.66 |
| 均值 Average | 10.00 ± 4.39 | 1.40 ± 0.60 | 0.64 ± 0.19 | 2.04 ± 0.78 |
表1 獐子岛潮间带及近岸海区各断面大型底栖动物群落多样性
Table 1 Diversity of macrobenthos at different section in the intertidal zone and offshore areas of Zhangzi Island
| 断面 Section | 种数 No. of species (S) | 丰富度 Richness index (D) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 潮间带 Intertidal zone | ||||
| LT | 13.00 ± 1.73 | 2.07 ± 0.23 | 0.71 ± 0.12 | 2.60 ± 0.36 |
| MT | 8.67 ± 4.04 | 1.27 ± 0.58 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 2.34 ± 0.59 |
| HT | 1.67 ± 0.58 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 0.70 ± 0.39 | 0.46 ± 0.49 |
| 均值 Average | 7.78 ± 5.43 | 1.17 ± 0.89 | 0.74 ± 0.17 | 1.80 ± 1.09 |
| 近岸海区 Offshore area | ||||
| S1 | 15.00 ± 2.00 | 2.04 ± 0.23 | 0.69 ± 0.06 | 2.67 ± 0.10 |
| S2 | 7.00 ± 3.00 | 1.08 ± 0.59 | 0.71 ± 0.18 | 1.99 ± 0.94 |
| S3 | 8.00 ± 2.65 | 1.08 ± 0.32 | 0.51 ± 0.26 | 1.45 ± 0.66 |
| 均值 Average | 10.00 ± 4.39 | 1.40 ± 0.60 | 0.64 ± 0.19 | 2.04 ± 0.78 |
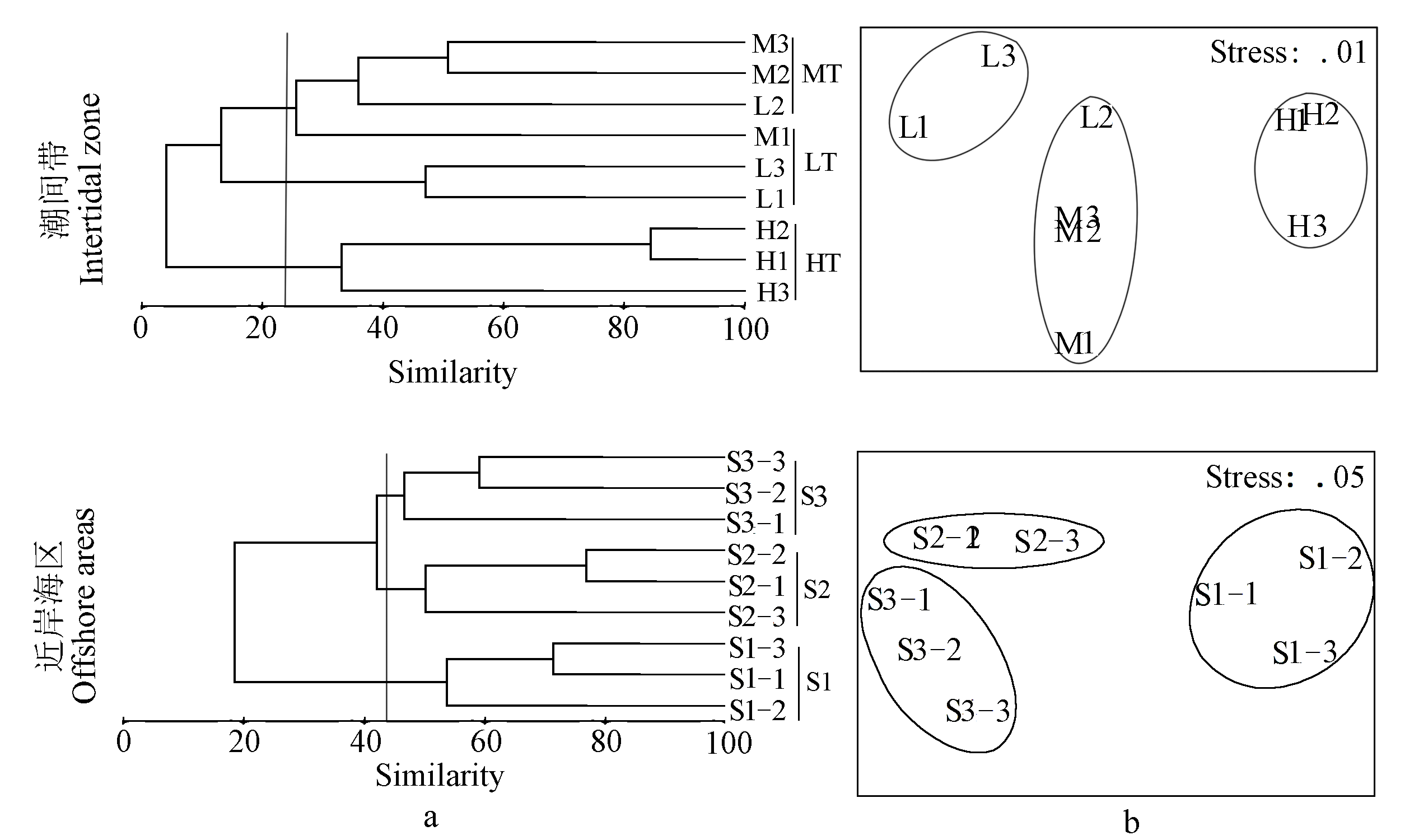
图3 獐子岛潮间带及近岸海区大型底栖动物群落的聚类分析图(a)与非度量多维标度分析图(b)(LT, 低潮区; MT, 中潮区; HT, 高潮区; S1, S2, S3, 近岸海区三个采样点)
Fig. 3 Cluster and multi-dimensional scaling on macrobenthos community in the intertidal and offshore areas of Zhangzi Island. LT, Low tidal zone; MT, Middle tidal zone; HT, High tidal zone; S1, S2, S3, three sampling sites in offshore area.
| 物种 Species | 潮间带 Intertidal zone | 近岸海区 Offshore areas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | ||||||
| 锥稚虫 Aonides oxycephala | + | + | ||||
| 花索沙蚕 Arabella iricolor | + | |||||
| 钩小蛇稚虫 Boccardiella hamata | + | |||||
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | + | |||||
| 金毛丝鳃虫 Cirratulus chrysoderma | + | |||||
| 丝鳃虫 C. cirratus | + | |||||
| 须鳃虫 Cirriformia tentaculata | + | + | ||||
| 额刺裂虫 Ehlersia cornuta | + | |||||
| 长双须虫 Eteone longa | + | |||||
| 埃氏蛰龙介 Terebella ehrenbergi | + | |||||
| 白色吻沙蚕 Glycera alba | + | |||||
| 锥唇吻沙蚕 G. onomichiensis | + | + | ||||
| 角吻沙蚕属一种 Goniada sp. | + | |||||
| 覆瓦哈鳞虫 Harmothoe imbricata | + | |||||
| 丝异须虫 Heteromastus filiforms | + | |||||
| 双唇索沙蚕 Lumbrineris cruzensis | + | |||||
| 短叶索沙蚕 L. latreilli | + | + | ||||
| 长叶索沙蚕 L. longiforlia | + | |||||
| 多美沙蚕 Lycastopsis augenari | + | |||||
| 小健足虫 Micropodarke dubia | + | |||||
| 仙居虫 Naineris laevigata | + | + | ||||
| 全刺沙蚕 Nectoneanthes oxypoda | + | |||||
| 囊叶齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys caeca | + | |||||
| 多鳃齿吻沙蚕 N. polybranchia | + | |||||
| 珠角裸沙蚕 Nicon moniloceras | + | |||||
| 蜈蚣欧努菲虫 Onuphis geophiliformis | + | |||||
| 欧文虫 Owenia fusiformis | + | |||||
| 独齿围沙蚕 Perinereis cultrifera | + | |||||
| 多齿围沙蚕 P. nuntia | + | |||||
| 乳突半突虫 Phyllodoce papillosa | + | |||||
| 树蛰虫 Pista cristata | + | |||||
| 双管阔沙蚕 Platynereis bicanaliculata | + | |||||
| 杂色伪沙蚕 Pseudonereis variegata | + | |||||
| 日本叉毛豆维虫 Schistomeringos japonica | + | |||||
| 不倒翁虫 Sternaspis scutata | + | |||||
| 多丝独毛虫 Tharyx multifilis | + | |||||
| 模裂虫属一种 Typosyllis sp. | + | |||||
| 软体动物 Mollusca | ||||||
| 泥螺 Bullacta exarata | + | |||||
| 单一丽口螺 Calliostoma unicum | + | |||||
| 灰双齿蛤 Felaniella usta | + | |||||
| 黄短口螺 Inquisitor flavidula | + | |||||
| 朝鲜花冠小月螺 Lunella coronate coreensis | + | |||||
| 异白樱蛤 Macoma incongrua | + | |||||
| 浅黄白樱蛤 M. tokyoensis | + | |||||
| 江户布目蛤 Protothaca jedoenses | + | |||||
| 菲律宾蛤 Ruditapes philippinarum | + | |||||
| 醒目云母蛤 Yoldia notabilis | + | |||||
| 甲壳动物 Crustacea | ||||||
| 窄异跳钩虾 Allorchestes angustus | + | |||||
| 双眼钩虾属一种 Ampelisca sp. | + | |||||
| 日本藻钩虾 Ampithoe japonica | + | |||||
| 强壮藻钩虾 A. valida | + | |||||
| 长尾虫属一种 Apseudes sp. | + | |||||
| 河蜾蠃蜚 Corophium acherusicum | + | |||||
| 日本褐虾 Crangon hakodatei | + | |||||
| 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | + | |||||
| 平背蜞 Gaetice depressus | + | |||||
| 日本拟钩虾 Gammaropsis japonicus | + | |||||
| 相似著名团水虱 Gnorimosphaeroma simillina | + | |||||
| 肉球近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sanguineus | + | |||||
| 施氏玻璃钩虾 Hyale schmidti | + | |||||
| 长额超刺糠虾 Hyperacanthomysis longirostris | + | |||||
| 马尔他钩虾属一种 Melita sp. | + | |||||
| 独眼钩虾属一种 Monoculode sp. | + | |||||
| 日本游泳水虱 Natatolana japonensis | + | |||||
| 大寄居蟹 Pagurus ochotensis | + | |||||
| 仿尖头钩虾属一种 Paraphoxus sp. | + | + | ||||
| 尖额钩虾属一种 Phoxocephalus sp. | + | |||||
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | ||||||
| 日本倍棘蛇尾 Amphioplus japonicus | + | |||||
| 心形海胆 Echinocardium cordatum | + | |||||
| 紫蛇尾 Ophiopholis mirabilis | + | |||||
| 浅水萨氏真蛇尾 Ophiura sarsiivadicola | + | |||||
| 其他 Others | ||||||
| 纽虫动物一种 Nemertinea 1 | + | + | ||||
附录I 獐子岛潮间带及近岸海区大型底栖动物名录
Appendix I The species checklist of macrobenthos in Zhangzi Island
| 物种 Species | 潮间带 Intertidal zone | 近岸海区 Offshore areas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多毛类 Polychaeta | ||||||
| 锥稚虫 Aonides oxycephala | + | + | ||||
| 花索沙蚕 Arabella iricolor | + | |||||
| 钩小蛇稚虫 Boccardiella hamata | + | |||||
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | + | |||||
| 金毛丝鳃虫 Cirratulus chrysoderma | + | |||||
| 丝鳃虫 C. cirratus | + | |||||
| 须鳃虫 Cirriformia tentaculata | + | + | ||||
| 额刺裂虫 Ehlersia cornuta | + | |||||
| 长双须虫 Eteone longa | + | |||||
| 埃氏蛰龙介 Terebella ehrenbergi | + | |||||
| 白色吻沙蚕 Glycera alba | + | |||||
| 锥唇吻沙蚕 G. onomichiensis | + | + | ||||
| 角吻沙蚕属一种 Goniada sp. | + | |||||
| 覆瓦哈鳞虫 Harmothoe imbricata | + | |||||
| 丝异须虫 Heteromastus filiforms | + | |||||
| 双唇索沙蚕 Lumbrineris cruzensis | + | |||||
| 短叶索沙蚕 L. latreilli | + | + | ||||
| 长叶索沙蚕 L. longiforlia | + | |||||
| 多美沙蚕 Lycastopsis augenari | + | |||||
| 小健足虫 Micropodarke dubia | + | |||||
| 仙居虫 Naineris laevigata | + | + | ||||
| 全刺沙蚕 Nectoneanthes oxypoda | + | |||||
| 囊叶齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys caeca | + | |||||
| 多鳃齿吻沙蚕 N. polybranchia | + | |||||
| 珠角裸沙蚕 Nicon moniloceras | + | |||||
| 蜈蚣欧努菲虫 Onuphis geophiliformis | + | |||||
| 欧文虫 Owenia fusiformis | + | |||||
| 独齿围沙蚕 Perinereis cultrifera | + | |||||
| 多齿围沙蚕 P. nuntia | + | |||||
| 乳突半突虫 Phyllodoce papillosa | + | |||||
| 树蛰虫 Pista cristata | + | |||||
| 双管阔沙蚕 Platynereis bicanaliculata | + | |||||
| 杂色伪沙蚕 Pseudonereis variegata | + | |||||
| 日本叉毛豆维虫 Schistomeringos japonica | + | |||||
| 不倒翁虫 Sternaspis scutata | + | |||||
| 多丝独毛虫 Tharyx multifilis | + | |||||
| 模裂虫属一种 Typosyllis sp. | + | |||||
| 软体动物 Mollusca | ||||||
| 泥螺 Bullacta exarata | + | |||||
| 单一丽口螺 Calliostoma unicum | + | |||||
| 灰双齿蛤 Felaniella usta | + | |||||
| 黄短口螺 Inquisitor flavidula | + | |||||
| 朝鲜花冠小月螺 Lunella coronate coreensis | + | |||||
| 异白樱蛤 Macoma incongrua | + | |||||
| 浅黄白樱蛤 M. tokyoensis | + | |||||
| 江户布目蛤 Protothaca jedoenses | + | |||||
| 菲律宾蛤 Ruditapes philippinarum | + | |||||
| 醒目云母蛤 Yoldia notabilis | + | |||||
| 甲壳动物 Crustacea | ||||||
| 窄异跳钩虾 Allorchestes angustus | + | |||||
| 双眼钩虾属一种 Ampelisca sp. | + | |||||
| 日本藻钩虾 Ampithoe japonica | + | |||||
| 强壮藻钩虾 A. valida | + | |||||
| 长尾虫属一种 Apseudes sp. | + | |||||
| 河蜾蠃蜚 Corophium acherusicum | + | |||||
| 日本褐虾 Crangon hakodatei | + | |||||
| 塞切尔泥钩虾 Eriopisella sechellensis | + | |||||
| 平背蜞 Gaetice depressus | + | |||||
| 日本拟钩虾 Gammaropsis japonicus | + | |||||
| 相似著名团水虱 Gnorimosphaeroma simillina | + | |||||
| 肉球近方蟹 Hemigrapsus sanguineus | + | |||||
| 施氏玻璃钩虾 Hyale schmidti | + | |||||
| 长额超刺糠虾 Hyperacanthomysis longirostris | + | |||||
| 马尔他钩虾属一种 Melita sp. | + | |||||
| 独眼钩虾属一种 Monoculode sp. | + | |||||
| 日本游泳水虱 Natatolana japonensis | + | |||||
| 大寄居蟹 Pagurus ochotensis | + | |||||
| 仿尖头钩虾属一种 Paraphoxus sp. | + | + | ||||
| 尖额钩虾属一种 Phoxocephalus sp. | + | |||||
| 棘皮动物 Echinodermata | ||||||
| 日本倍棘蛇尾 Amphioplus japonicus | + | |||||
| 心形海胆 Echinocardium cordatum | + | |||||
| 紫蛇尾 Ophiopholis mirabilis | + | |||||
| 浅水萨氏真蛇尾 Ophiura sarsiivadicola | + | |||||
| 其他 Others | ||||||
| 纽虫动物一种 Nemertinea 1 | + | + | ||||
| 1 | Cai LZ (蔡立哲), Ma L (马丽), Gao Y (高阳), Zheng TL (郑天凌), Lin P (林鹏) (2002) Analysis on assessing criterion for polluted situation using species diversity index of marine macrofauna. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 41, 641-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Cao SM (曹善茂), Zhou YB (周一兵) (2001) Species and number of benthos and evaluation about environment in the waters of Dalian coast.Journal of Dalian Fisheries University(大连水产学院学报), 16, 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Chen YQ (陈亚瞿), Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Wang YL (王云龙), Hu FX (胡方西), Hu H (胡辉), Gu GZ (谷国传) (1995) An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuarine Area. I. Biomass distribution of dominant species.Journal of Fishery Sciences of China(中国水产科学), 2, 49-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Crawford CM, Macleod CKA, Mitchell IM (2003) Effects of shellfish farming on the benthic environment.Aquaculture, 224,117-140. |
| 5 | Grall J, Glémarec M (1997) Using biotic indices to estimate macrobenthic community perturbations in the Bay of Brest. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 44, 43-53. |
| 6 | Currie DR, Small KJ (2005) Macrobenthic community responses to long-term environmental change in an east Australian sub-tropical estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 63, 315-331. |
| 7 | Herman PMJ, Middelburg JJ, van de Koppel J, Heip CHR (1999) Ecology of estuarine macrobenthos.Advances in Ecological Research, 29,195-240. |
| 8 | Huang YQ (黄雅琴), Li RG (李荣冠), Wang JJ (王建军), Zheng CX (郑成兴), Zheng FW (郑凤武), Lin JH (林俊辉), Jiang JX (江锦祥), Li SZ (李淑珠) (2010) Intertidal benthos diversity in the Meizhou Bay, Fujian Province.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 18, 156-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 9 | Hu HY (胡颢琰), Huang B (黄备), Tang JL (唐静亮), Ren SJ (任世军), Shao XW (邵秀伟) (2000) Studies on benthic ecology in coastal waters of Bohai and Yellow Seas.Donghai Marine Science(东海海洋), 18, 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | Jiao HF (焦海峰), Peng XM (彭小明), You ZJ (尤仲杰), Shi HX (施慧雄), Lou ZJ (楼志军), Liu HD (刘红丹) (2011) Species diversity of macrobenthos in the rocky intertidal zone of Yushan Island.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 511-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 11 | Li BQ (李宝泉), Li XZ (李新正), Wang HF (王洪法), Wang YQ (王永强), Wang JB (王金宝), Zhang BL (张宝琳) (2007) Characters of a macrobenthic community off the Changjiang River Estuary.Acta Zoologica Sinica(动物学报), 53, 76-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Lin GM (林更铭), Li BQ (李炳乾), Xiang P (项鹏), Yang QL (杨清良) (2009) Preliminary studies on cyclic utilization of wastewater from marine aquaculture plant.Marine Sciences(海洋科学), 33, 47-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 13 | Liu WX (刘卫霞), Yu ZS (于子山), Qu FY (曲方圆), Sui JX (隋吉星), Zhang ZN (张志南) (2009) Species composition and quantitative distribution of abundance and biomass of macrobenthos in the North Yellow Sea in winter.Periodical of Ocean University of China(中国海洋大学学报), 39, 115-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Margalef R (1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 15 | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley, New York. |
| 16 | Pinto R, Patrício J, Baeta A, Fath BD, Neto JM, Marques JC (2009) Review and evaluation of estuarine biotic indices to assess benthic condition.Ecological Indicators, 91, 1-25. |
| 17 | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois, Urbanna. |
| 18 | Tian LS (田丽斯), Li Y (李莹), Zhang M (张明), Wang HW (王宏伟) (2009) The benthic marine alga resources and seasonal changes in intertidal zone at Zhangzi Island.Fisheries Science(水产科学), 28, 142-145. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 19 | Wang HF (王洪法), Li BQ (李宝泉), Zhang BL (张宝琳), Shuai LM (帅莲梅), Li XZ (李新正) (2006) The ecological research of the macrobenthic community in intertidal zone of Hongshiya, Jiaozhou Bay.Marine Sciences(海洋科学), 30(9), 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 20 | Wang Y (王瑜), Liu LS (刘录三), Liu CQ (刘存歧), Zhu YZ (朱延忠), Xu HM (徐海明) (2010) Community structure characteristics of macrobenthos in the coastal seawaters of Bohai Bay in spring.Research of Environmental Sciences(环境科学研究), 23, 430-436. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Wang ZX (王宗兴), Fan SL (范士亮), Xu QZ (徐勤增), Wang SQ (王守强), Wei QS (韦钦胜), Zang JY (臧家业) (2010) Characteristics of macrobenthic community in spring in the coastal waters of Qingdao.Advances in Marine Science(海洋科学进展), 28, 50-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Warwick RM (1986) A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities.Marine Biology, 924, 557-562. |
| 23 | Weigelt M (1991) Short and long-term changes in the benthic community of the deeper parts of Kiel Bay (western Baltic) due to oxygen depletion and eutrophication.Meeresforsch, 33, 197-224. |
| 24 | Wu BL (吴宝铃) (1964) Subspecific differentiation and ecological characteristics of Capitella capitata (Fabricius, 1780) (Polychaeta, Capitellidae).Oceanologia et Limn- ologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 6, 260-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 25 | Yu HY (于海燕), Li XZ (李新正), Li BQ (李宝泉), Wang JB (王金宝), Wang HF (王洪法) (2006) The species diversity of macrobenthic fauna in Jiaozhou Bay.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 26, 416-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 26 | Zhang BL (张宝琳), Wang HF (王洪法), Li BQ (李宝泉), Wang YQ (王永强), Wang JB (王金宝), Li XZ (李新正) (2007) The ecology of the macrobenthic community in the intertidal zone of Xindao, Jiaozhou Bay.Marine Sciences(海洋科学), 31(1), 60-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 27 | Zhang JH (张继红), Fang JG (方建光), Jiang ZJ (蒋增杰), Wang W (王巍), Wang SH (王诗欢), Sun S (孙松) (2008) Seasonal variation of primary production and spatial-temporal distribution of chlorophyll a in mariculture area of Zhangzidao Island.Marine Fisheries Research(海洋水产研究), 29, 22-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 28 | Zhang JH (张继红), Wang W (王巍), Jiang ZJ (蒋增杰), Fang JG (方建光), Wang SH (王诗欢), Zang YC (臧有才), Xue SY (薛素艳) (2009) Distribution features of nitrogen and phosphorus in Zhangzi Island maricultural area.Progress in Fishery Sciences(渔业科学进展), 30, 88-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 29 | Zhou Y (周毅), Yang HS (杨红生), He YC (何义朝), Zhang FS (张福绥) (2002) Nitrogen and phosphorus excretion and its ecological effect by several bivalves and fouling animals.Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 33, 424-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [12] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [13] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn