



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 143-150. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08286 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08286
收稿日期:2008-11-06
接受日期:2009-03-05
出版日期:2009-03-20
发布日期:2009-03-20
通讯作者:
杨金权
作者简介:* E-mail: jqyang@shou.edu.cn基金资助:
Xuelan Yan, Wenqiao Tang, Jinquan Yang**( )
)
Received:2008-11-06
Accepted:2009-03-05
Online:2009-03-20
Published:2009-03-20
Contact:
Jinquan Yang*
摘要:
为了解中国东南部沿海凤鲚(Coilia mystus)的种群遗传多样性和遗传结构, 本文分析了长江口(CJ)、钱塘江口(QT)、闽江口(MJ)和九龙江口(JL)4个凤鲚地理群体的mtDNA控制区561 bp片段的序列变异。65尾样本共检测到28个单元型。4个群体总的单元型多样性和核苷酸多样性均较高(h = 0.9433 ± 0.0168, π = 0.0317 ± 0.0158), 但单个群体的核苷酸多样性水平却很低, 其中以CJ最高(π = 0.0080 ± 0.0046), MJ最低(π = 0.0015 ± 0.0013)。MJ与JL群体之间以及CJ与QT群体之间的平均K2P遗传距离很小, 分别为0.3%和0.8%; 而CJ、QT分别与MJ、JL群体之间的遗传距离均较大, 达到了6%。采用最大似然法(ML)、最大简约法(MP)和邻接法(NJ)分别构建的单元型间的系统发育树揭示, 4个凤鲚群体构成CJ-QT 和MJ-JL 2个支系, 且具有极高的支持率。单元型的网络分析也显示这两个支系间有高达28步的突变次数。AMOVA分析显示大部分的遗传变异来自这两支系群体间(90.77%), 表明凤鲚群体间存在着显著的地理分化。种群分化指数和基因流分析也表明, 支系间群体有着明显的遗传分化(FST > 0.9, Nm < 0.03)。所有分析结果支持所研究的凤鲚标本属于两个不同的地理种群, 且种群的分化至少已达到亚种水平。采用BEAST和TRACER软件得到凤鲚两个亚种的最近共同祖先约在0.34-0.46百万年前, 处于更新世晚期, 推测可能是第四纪晚期的气候旋回和海平面的升降导致了凤鲚的种群分化。
阎雪岚, 唐文乔, 杨金权 (2009) 基于线粒体控制区的序列变异分析中国东南部沿海凤鲚种群遗传结构. 生物多样性, 17, 143-150. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08286.
Xuelan Yan, Wenqiao Tang, Jinquan Yang* (2009) Population genetic structure of tapertail anchovy (Coilia mystus) in coastal waters of southeast China based on mtDNA control region sequences. Biodiversity Science, 17, 143-150. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08286.
| 采集地 Location | 样本数Sample size | 单元型数 Haplotype number | 单元型 Haplotype | 单元型多样性Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 Minjiang River (MJ) | 17 | 6 | H1(1)、H2(1)、H4(2)、H5(1)、H7(1)、H8(11) | 0.5882 ± 0.1348 | 0.0015 ± 0.0013 |
| 九龙江 Jiulong River (JL) | 16 | 7 | H1(1)、H3(1)、H6(1)、H8(10)、H9(1)、H10(1)、H11(1) | 0.6250 ± 0.1390 | 0.0037 ± 0.0024 |
| 长江 Yangtze River (CJ) | 18 | 11 | H12(4)、H13(1)、H14(1)、H15(1)、H19(3)、H20(1)、H21(1)、H22(1)、H23(3)、H25(1)、 H27(1) | 0.9216 ± 0.0417 | 0.0080 ± 0.0046 |
| 钱塘江 Qiantang River (QT) | 14 | 10 | H14(1)、H16(1)、H17(1)、H18(1)、H19(3)、H22(2)、H23(2)、H24(1)、H26(1)、H28(1) | 0.9451 ± 0.0451 | 0.0077 ± 0.0046 |
| 总计 Total | 65 | 28 | 0.9433 ± 0.0168 | 0.0317 ± 0.0158 |
表1 凤鲚的样本信息、28个单元型(H1-H28)的分布频率及群体mtDNA的遗传多样性
Table 1 Sample information, distribution frequency of 28 haplotypes (H1-H28), haplotype diversity (h) and nucleotide diversity (π) of Coilia mystus
| 采集地 Location | 样本数Sample size | 单元型数 Haplotype number | 单元型 Haplotype | 单元型多样性Haplotype diversity (h) | 核苷酸多样性 Nucleotide diversity (π) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 Minjiang River (MJ) | 17 | 6 | H1(1)、H2(1)、H4(2)、H5(1)、H7(1)、H8(11) | 0.5882 ± 0.1348 | 0.0015 ± 0.0013 |
| 九龙江 Jiulong River (JL) | 16 | 7 | H1(1)、H3(1)、H6(1)、H8(10)、H9(1)、H10(1)、H11(1) | 0.6250 ± 0.1390 | 0.0037 ± 0.0024 |
| 长江 Yangtze River (CJ) | 18 | 11 | H12(4)、H13(1)、H14(1)、H15(1)、H19(3)、H20(1)、H21(1)、H22(1)、H23(3)、H25(1)、 H27(1) | 0.9216 ± 0.0417 | 0.0080 ± 0.0046 |
| 钱塘江 Qiantang River (QT) | 14 | 10 | H14(1)、H16(1)、H17(1)、H18(1)、H19(3)、H22(2)、H23(2)、H24(1)、H26(1)、H28(1) | 0.9451 ± 0.0451 | 0.0077 ± 0.0046 |
| 总计 Total | 65 | 28 | 0.9433 ± 0.0168 | 0.0317 ± 0.0158 |
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 0.002 | |||
| 九龙江 JL | 0.003 | 0.004 | ||
| 长江 CJ | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.007 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
表2 凤鲚样本群体内与群体间的K2P遗传距离
Table 2 The average K2P distance between and within Coilia mystus populations
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 0.002 | |||
| 九龙江 JL | 0.003 | 0.004 | ||
| 长江 CJ | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.007 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
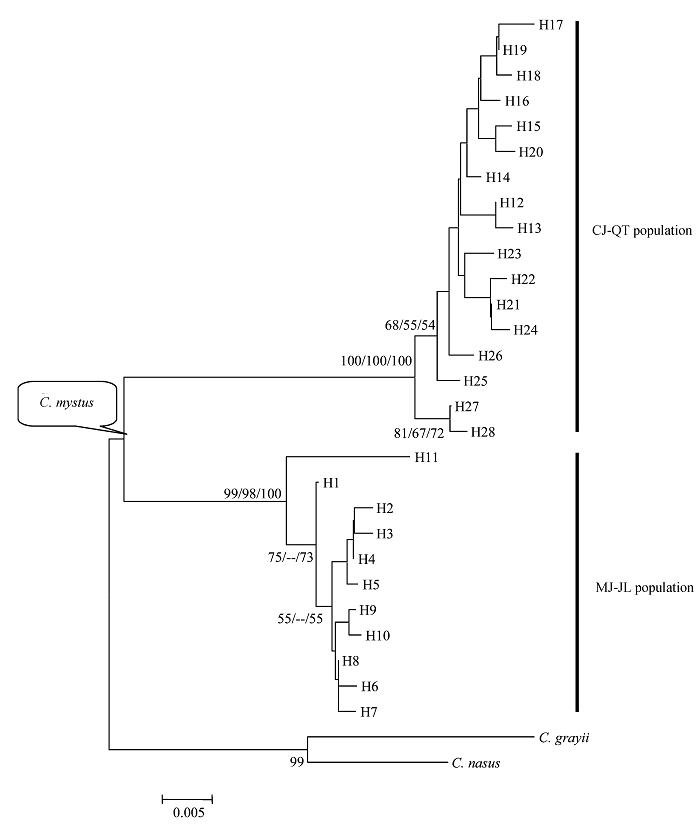
图1 基于线粒体控制区序列构建的四个凤鲚群体的系统发育树。节点处的数值为bootstrap检验的支持率(仅显示支持率大于50%)、左为邻接树、中间为ML树、右为MP树(仅显示Ti/Tv为 2:1的加权树, 树长=137, CI = 0.8248, HI = 0.1752))。
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic trees of four Coilia mystus populations resulted from mtDNA control region sequence. Numbers at nodes are percent recovery in bootstrap analysis. Given for bootstrap values greater than 50% (Neighbor-joining left, maximum likelihood middle, maximum parsimony right (only shows Ti/Tv 2:1weighted; tree length = 137, CI = 0.8248 and HI = 0.1752)).
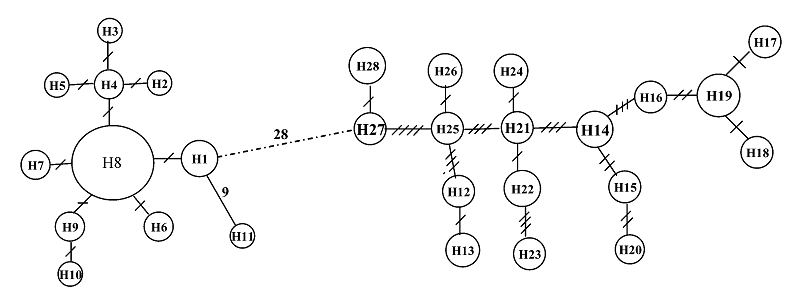
图2 4个凤鲚群体控制区序列单元型间的网络亲缘关系图。圆圈内字符为单元型编号, 连接两个圆圈线段上的斜线数表示变异步数。
Fig. 2 Minimum spanning networks showing genetic relationship among control region haplotypes for the four Coilia mystus populations. The characters within circles are haplotype codes. Slashes on the lines joining haplotypes denote number of observed mutations.
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异分量 Variance components | 变异百分比 Percentage of variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Among groups | 1 | 14.59231 | 90.77 |
| 组内种群间 Among populations within group | 2 | 0.03239 | 0.20 |
| 种群内 Within population | 61 | 1.45064 | 9.02 |
| 总计 Total | 64 | 16.07535 |
表3 凤鲚群体65个样本mtDNA 561 bp控制区序列片段的分子变异分析
Table 3 AMOVA of 561 bp mtDNA control region sequences for 65 individuals of Coilia mystus
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | 变异分量 Variance components | 变异百分比 Percentage of variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 组间 Among groups | 1 | 14.59231 | 90.77 |
| 组内种群间 Among populations within group | 2 | 0.03239 | 0.20 |
| 种群内 Within population | 61 | 1.45064 | 9.02 |
| 总计 Total | 64 | 16.07535 |
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 82.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 九龙江 JL | 0.0030 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 长江 CJ | 0.9245 | 0.9060 | 19.91 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.9183 | 0.8998 | 0.0120 |
表4 凤鲚群体间分化指数FST(对角线下)和基因流(Nm) (对角线上)
Table 4 Matrix of pairwise FST (below diagonal) and Nm (above diagonal) between four populations of Coilia mystus
| 种群 Population | 闽江 MJ | 九龙江 JL | 长江 CJ | 钱塘江 QT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 闽江 MJ | 82.96 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 九龙江 JL | 0.0030 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 长江 CJ | 0.9245 | 0.9060 | 19.91 | |
| 钱塘江 QT | 0.9183 | 0.8998 | 0.0120 |
| [1] | Avise JC (2000) Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species, pp. 9-32. Harvard University Press, London. |
| [2] | Bekessy SA, Ennos RA, Burgman MA, Newton AC, Ades PK (2003) Neutral DNA markers fail to detect genetic divergence in an ecologically important trait. Biological Conservation, 110, 267-275. |
| [3] |
Bowen BW, Grant WS (1997) Phylogeography of the sardines (Sardinops spp.): assessing biogeographic models and population histories in temperate upwelling zones. Evolution, 51, 1601-1610.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Cheng QQ (程起群), Ma CY (马春艳), Miu T (缪烔), Lu X (陆星), Sha ZX (沙珍霞) (2007) Genetic diversity in two wild populations of tapertail anchovy Coilia mystus via 12S ribosomal segment sequences of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University (大连水产学院学报), 22, 387-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Cheng QQ (程起群), Ma CY (马春艳), Zhuang P (庄平), Sha ZX (沙珍霞), Lu X (陆星), Miu T (缪烔) (2008) Genetic structure and evolution characters in three populations of Coilia mystus based on cytochrome b gene segment sequence of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 32, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] |
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7, 214.
URL PMID |
| [7] |
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics Online, 1, 47-50.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [9] | Galtier N, Gouy M, Gautier C (1996) SEAVIEW and PHYLO_WIN: two graphic tools for sequence alignment and molecular phylogeny. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 12, 543-548. |
| [10] | Grant WS, Bowen BW (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426. |
| [11] | Liu JX, Gao TX, Zhuang ZM, Jin XS, Yokogawa K, Zhang YP (2006) Late Pleistocene divergence and subsequent population expansion of two closely related fish species, Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) and Australian anchovy (E. australis). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40, 712-723. |
| [12] | Liu WB (刘文斌) (1995) Biochemical and morphological comparison and interspecific relationships of four species of the genus Coilia in China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 26, 558-565. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Ni Y (倪勇) (1999) Fishery resources conservation for Coilia mystus in the Changjiang estuary. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 6(5), 75-77. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818. |
| [15] | Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.4. http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer. |
| [16] | Randi E, Lucchini V (1998) Organization and evolution of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the avian genus Alectoris. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 47, 149-162. |
| [17] | Rozas J, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics, 19, 2496-2497. |
| [18] | Shi WG (施炜纲), Wang B (王博) (2002) Status quo of tapertail anchovy resource in the estuaries of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 26, 648-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and other Methods) (version 4.0). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA. |
| [20] | Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599. |
| [21] | Tang QY, Liu HZ, Mayden R, Xiong BX (2006) Comparison of evolutionary rates in the mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene and control region and their implications for phylogeny of the Cobitoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 39, 347-357. |
| [22] | Tang WQ (唐文乔), Hu XL (胡雪莲), Yang JQ (杨金权) (2007) Species validities of Coilia brachygnathus and C. nasus taihuensis based on sequence variations of complete mtDNA control region. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 15, 224-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | van Tienderen PH, de Haan AA, van der Linden CG, Vosman B (2002) Biodiversity assessment using markers for ecologically important trait. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 577-582. |
| [25] |
Verheyen E, Salzburger W, Snoeks J, Meyer A (2003) Origin of the superflock of cichlid fishes from lake Victoria, East Africa. Science, 300, 325-329.
URL PMID |
| [26] | Vrijenhoek RC (1994) Genetic diversity and fitness in small populations. In: Conservation Genetics (eds Loeschcke V, Tomiuk J, Jian SK), pp. 37-53, Birkhäuser-Verlag, Basel. |
| [27] | Whitehead PJP, Nelson GJ, Wongratana T (1988) FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid Fishes of the World (Suborder Clupeoidei). Part 2: Engraulididae. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/2), 305-579. |
| [28] | Yang JQ (杨金权), Hu XL (胡雪莲), Tang WQ (唐文乔), Lin HD (林弘都) (2008) mtDNA control region sequence variation and genetic diversity of Coilia nasus in Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 43(1), 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Yu ZN, Kong XY, Guo TH, Jiang YY, Zhuang ZM, Jin XS (2005) Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation of Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Fisheries Science, 71, 299-307. |
| [30] | Yuan CM (袁传宓), Lin JB (林金榜), Qin AL (秦安舲), Liu RH (刘仁华) (1976) Historical and present taxonomic status about the genus Coilia in China. Journal of Nanjing University Mathematical Biquarterly (南京大学学报数学半年刊), (2), 1-12. (in Chinese) |
| [31] | Zhang SY (张世义) (2001) Fauna Sinica (Osteichthyes): Acipenseriformes, Elopiformes, Clupeiformes, Gonorhynch- iformes (中国动物志(硬骨鱼纲): 鲟形目, 海鲢目, 鲱形目, 鼠鳝目), pp. 148-154. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [32] | Zhang YP, Ge S (2007) Molecular evolution study in China: progress and future promise. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Science, 362, 973-986. |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [8] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [11] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [12] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [13] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [14] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [15] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn