



Biodiv Sci ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (5): 649-657. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13257 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13257
Special Issue: 海洋生物多样性
• Marine Biodiversity Special Feature • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xue Chen1,3, Wuchang Zhang1,*( ), Qiang Wu2, Qingshan Luan2, Tian Xiao1
), Qiang Wu2, Qingshan Luan2, Tian Xiao1
Received:2013-12-11
Accepted:2014-04-17
Online:2014-09-20
Published:2014-10-09
Contact:
Zhang Wuchang
Xue Chen, Wuchang Zhang, Qiang Wu, Qingshan Luan, Tian Xiao. Seasonal change of the community of large-sized tintinnids (Ciliophora, Tintinnida) in Laizhou Bay[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(5): 649-657.
| 中文种名 Chinese name | 拉丁文种名 Latin name | Amax | Mmax |
|---|---|---|---|
| 透明壳种类 Hyaline species | |||
| 尖底类瓮虫 | Amphorellopsis acuta | 2.81 | 8 |
| 卢氏真铃虫 | Eutintinnus lusus-undae | 2.53 | 7 |
| 巴拿马网纹虫 | Favella panamensis | 4.21 | 6 |
| 黏着壳种类 Agglutinated species | |||
| 鲁西塔尼亚类铃虫 | Codonellopsis lusitanica | 1.04 | 8 |
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 316.72 | 5 |
| 诺氏薄铃虫 | Leprotintinnus nordqvisti | 0.42 | 7 |
| 简单薄铃虫 | L. simplex | 7.67 | 7 |
| 白领细壳虫 | Stenosemella nivalis | 16.93 | 7 |
| 巴西拟铃虫 | Tintinnopsis brasiliensis | 1.04 | 3 |
| 布氏拟铃虫 | T. butschlii | 1.18 | 7 |
| 清兰拟铃虫 | T. chinglanensis | 65.85 | 7 |
| 有角拟铃虫 | T. corniger | 3.87 | 7 |
| 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 9.44 | 8 |
| 直颈拟铃虫 | T. directa | 0.53 | 7 |
| 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 3.85 | 11 |
| 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 14.21 | 4 |
| 卡拉直克拟铃虫 | T. karajacensis | 0.20 | 3 |
| 罗氏拟铃虫 | T. lohmanni | 6.15 | 7 |
| 梅氏拟铃虫 | T. mayeri | 0.11 | 4 |
| 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 29.14 | 7 |
| 圆锥拟铃虫 | T. rapa | 0.59 | 3 |
| 斯氏拟铃虫 | T. schotti | 12.43 | 9 |
| 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 13.38 | 8 |
| 未定种1 | Tintinnopsis sp.1 | 4.84 | 5 |
| 未定种2 | Tintinnopsis sp.2 | 0.39 | 6 |
| 未定种3 | Tintinnopsis sp.3 | 0.80 | 8 |
Table 1 Species list of tintinnids in Laizhou Bay from March to November
| 中文种名 Chinese name | 拉丁文种名 Latin name | Amax | Mmax |
|---|---|---|---|
| 透明壳种类 Hyaline species | |||
| 尖底类瓮虫 | Amphorellopsis acuta | 2.81 | 8 |
| 卢氏真铃虫 | Eutintinnus lusus-undae | 2.53 | 7 |
| 巴拿马网纹虫 | Favella panamensis | 4.21 | 6 |
| 黏着壳种类 Agglutinated species | |||
| 鲁西塔尼亚类铃虫 | Codonellopsis lusitanica | 1.04 | 8 |
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 316.72 | 5 |
| 诺氏薄铃虫 | Leprotintinnus nordqvisti | 0.42 | 7 |
| 简单薄铃虫 | L. simplex | 7.67 | 7 |
| 白领细壳虫 | Stenosemella nivalis | 16.93 | 7 |
| 巴西拟铃虫 | Tintinnopsis brasiliensis | 1.04 | 3 |
| 布氏拟铃虫 | T. butschlii | 1.18 | 7 |
| 清兰拟铃虫 | T. chinglanensis | 65.85 | 7 |
| 有角拟铃虫 | T. corniger | 3.87 | 7 |
| 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 9.44 | 8 |
| 直颈拟铃虫 | T. directa | 0.53 | 7 |
| 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 3.85 | 11 |
| 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 14.21 | 4 |
| 卡拉直克拟铃虫 | T. karajacensis | 0.20 | 3 |
| 罗氏拟铃虫 | T. lohmanni | 6.15 | 7 |
| 梅氏拟铃虫 | T. mayeri | 0.11 | 4 |
| 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 29.14 | 7 |
| 圆锥拟铃虫 | T. rapa | 0.59 | 3 |
| 斯氏拟铃虫 | T. schotti | 12.43 | 9 |
| 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 13.38 | 8 |
| 未定种1 | Tintinnopsis sp.1 | 4.84 | 5 |
| 未定种2 | Tintinnopsis sp.2 | 0.39 | 6 |
| 未定种3 | Tintinnopsis sp.3 | 0.80 | 8 |
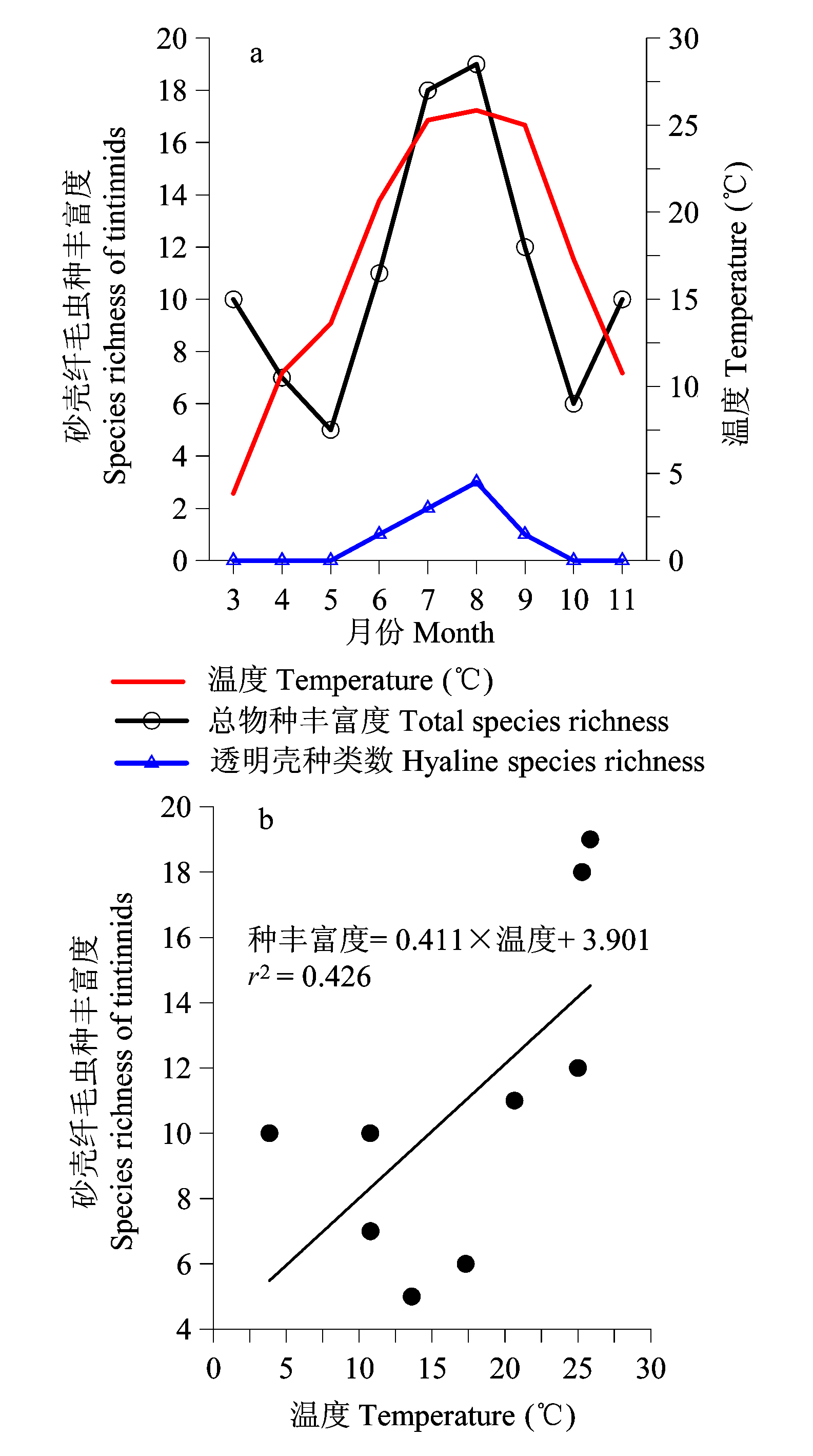
Fig. 2 Variation of species richness of tintinnids in Laizhou Bay from March to November (a), and the relationship between temperature and species richness (b).
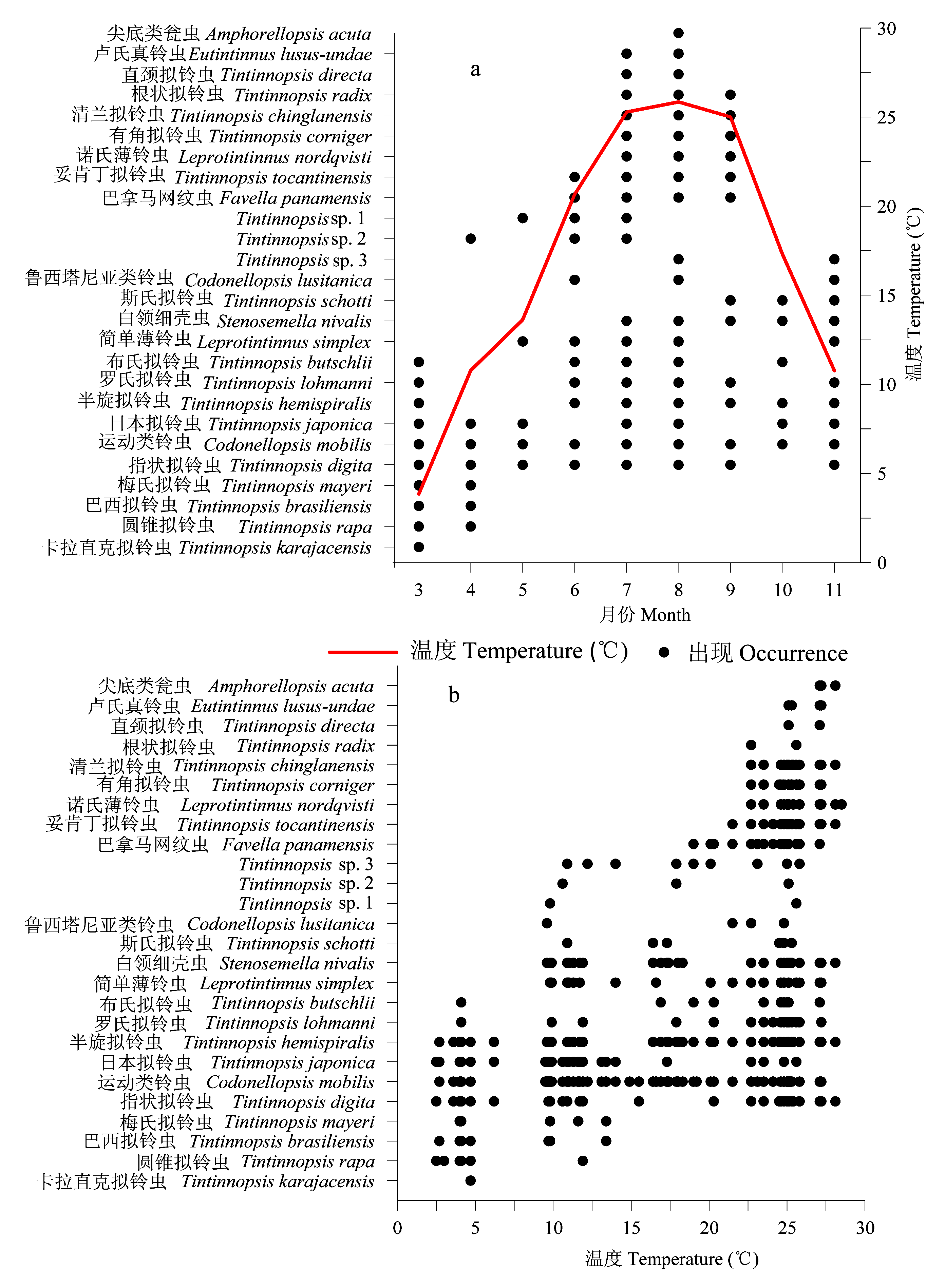
Fig. 3 Temporal variation of temperature (°C), occurrence (a) and temperature range (b) of each tintinnid species in Laizhou Bay from March to November
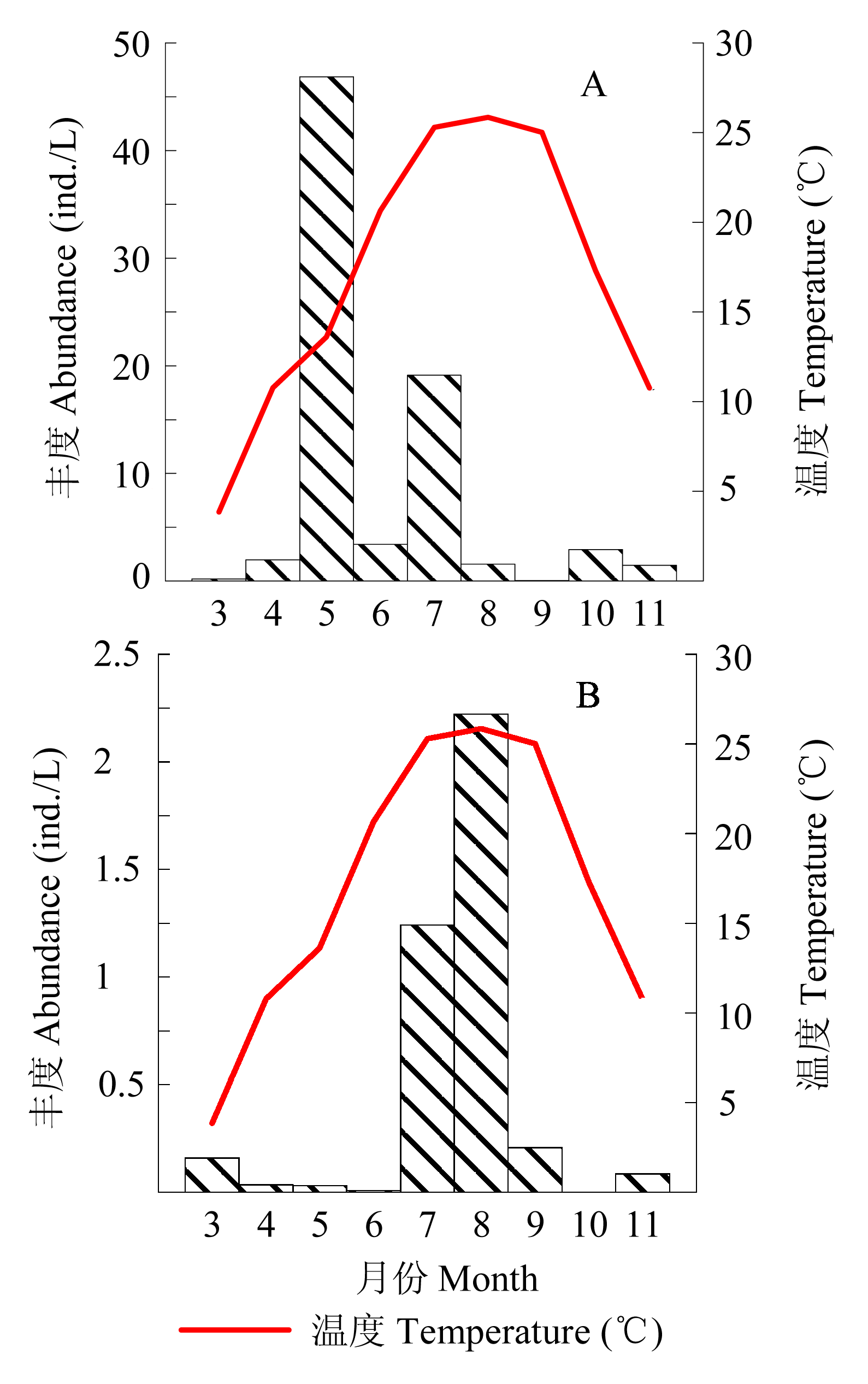
Fig. 5 Temporal variation of temperature (°C) and tintinnid abundance (ind./L) of 2 species in Laizhou Bay from March to November. A, Codonellopsis mobilis; B, Tintinnopsis digita.
| 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance | 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.293 | 8月 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.179 |
| 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.100 | 清兰拟铃虫 | T. chinglanensis | 0.129 | ||
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.065 | 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 0.095 | ||
| 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.065 | 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.077 | ||
| 巴西拟铃虫 | T. brasiliensis | 0.065 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.045 | ||
| 4月 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.637 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.044 | |
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.288 | 罗氏拟铃虫 | T. lohmanni | 0.040 | ||
| 5月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.979 | 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.031 | |
| 9月 | 斯氏拟铃虫 | T. schotti | 0.220 | ||||
| 6月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.581 | 有角拟铃虫 | T. corniger | 0.042 | |
| 巴拿马网纹虫 | F. panamensis | 0.189 | 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.033 | ||
| Tintinnopsis sp.1 | 0.049 | 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.032 | |||
| 7月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.305 | 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.024 | |
| 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.157 | 10月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.496 | |
| 清兰拟铃虫 | T.chinglanensis | 0.086 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.349 | ||
| 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.075 | 11月 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.445 | |
| 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 0.067 | 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.267 | ||
| 简单薄铃虫 | L. simplex | 0.033 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.215 | ||
| 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.030 | |||||
Table 2 The dominant species of tintinnids and their dominance in Laizhou Bay from March to November
| 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance | 优势种 Dominant species | 优势度 Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3月 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.293 | 8月 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.179 |
| 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.100 | 清兰拟铃虫 | T. chinglanensis | 0.129 | ||
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.065 | 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 0.095 | ||
| 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.065 | 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.077 | ||
| 巴西拟铃虫 | T. brasiliensis | 0.065 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.045 | ||
| 4月 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.637 | 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.044 | |
| 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.288 | 罗氏拟铃虫 | T. lohmanni | 0.040 | ||
| 5月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.979 | 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.031 | |
| 9月 | 斯氏拟铃虫 | T. schotti | 0.220 | ||||
| 6月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.581 | 有角拟铃虫 | T. corniger | 0.042 | |
| 巴拿马网纹虫 | F. panamensis | 0.189 | 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.033 | ||
| Tintinnopsis sp.1 | 0.049 | 指状拟铃虫 | T. digita | 0.032 | |||
| 7月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.305 | 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.024 | |
| 根状拟铃虫 | T. radix | 0.157 | 10月 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.496 | |
| 清兰拟铃虫 | T.chinglanensis | 0.086 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.349 | ||
| 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.075 | 11月 | 白领细壳虫 | S. nivalis | 0.445 | |
| 妥肯丁拟铃虫 | T. tocantinensis | 0.067 | 半旋拟铃虫 | T. hemispiralis | 0.267 | ||
| 简单薄铃虫 | L. simplex | 0.033 | 运动类铃虫 | C. mobilis | 0.215 | ||
| 日本拟铃虫 | T. japonica | 0.030 | |||||
| 3月 March | 4月 April | 5月 May | 6月 June | 7月 July | 8月 August | 9月 September | 10月 October | 11月 November | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种丰富度 Species richness | 10 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 18 | 19 | 12 | 6 | 10 |
| 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 0.78±0.15 | 0.62±0.18 | 0.40±0.30 | 0.59±0.19 | 0.57±0.13 | 0.72±0.08 | 0.76±0.26 | 0.55±0.18 | 0.69±0.11 |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 1.71±0.60 | 1.00±0.23 | 0.42±0.29 | 1.33±0.34 | 2.06±0.50 | 2.38±0.32 | 1.45±0.75 | 1.04±0.46 | 1.71±0.36 |
Table 3 Species richness, evenness index and diversity indices of tintinnids in Laizhou Bay from March to November
| 3月 March | 4月 April | 5月 May | 6月 June | 7月 July | 8月 August | 9月 September | 10月 October | 11月 November | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种丰富度 Species richness | 10 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 18 | 19 | 12 | 6 | 10 |
| 均匀度指数 Evenness index (J) | 0.78±0.15 | 0.62±0.18 | 0.40±0.30 | 0.59±0.19 | 0.57±0.13 | 0.72±0.08 | 0.76±0.26 | 0.55±0.18 | 0.69±0.11 |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 1.71±0.60 | 1.00±0.23 | 0.42±0.29 | 1.33±0.34 | 2.06±0.50 | 2.38±0.32 | 1.45±0.75 | 1.04±0.46 | 1.71±0.36 |
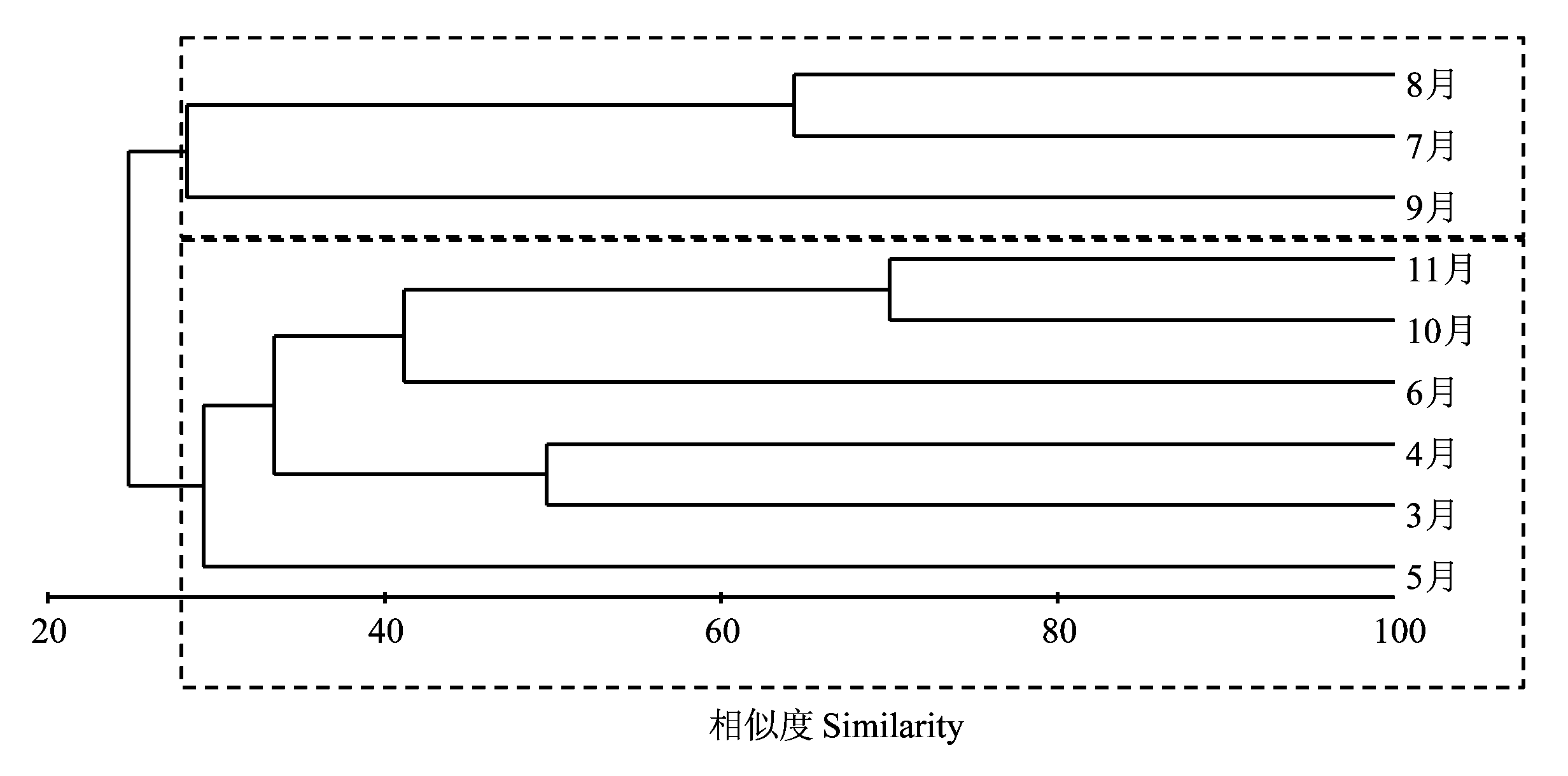
Fig. 6 Cluster analysis based on Bray-Curtis similarity matrix of average species abundance (ind./L) of 8 stations in Laizhou Bay from March to November
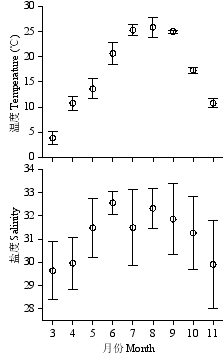
Fig. S1 Temporal variation of temperature (°C) and salinity in Laizhou Bay from March to November. Data are averages of the 8 stations with standard deviation. http://www.biodiversity-science.net/fileup/PDF/w2013-257-1.pdf
| [1] | .Abboud-Abi Saab M (1989) Distribution and ecology of tintinnids in the plankton of Lebanese coastal waters (eastern Mediterranean). Journal of Plankton Research, 11, 203-222. |
| [2] | .Abboud-Abi Saab M (2002) Annual cycle of the micro- zooplankton communities in the waters surrounding the Palm Island Nature Reserve (north Lebanon), with special attention to tintinnids. Mediterranean Marine Science, 3, 55-76. |
| [3] | .Azam F, Fenchel T, Field JG, Gray JS, Meyer-Reil LA, Thingstad F (1983) The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 10, 257-263. |
| [4] | .Bojanić N (2001) Seasonal distribution of the ciliated protozoa in Kastela Bay. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 81, 383-390. |
| [5] | .Bojanić N, Šolić M, Krstulović N, Šestanović S, Marasović I, Ninčević Ž (2005) Temporal variability in abundance and biomass of ciliates and copepods in the eutrophicated part of Kaštela Bay (Middle Adriatic Sea). Helgoland Marine Research, 59, 107-120. |
| [6] | .Dolan JR (1991) Guilds of ciliate microzooplankton in the Chesapeake Bay. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 33, 137-152. |
| [7] | .Dolan JR, Gallegos CL (2001) Estuarine diversity of tintinnids (planktonic ciliates). Journal of Plankton Research, 23, 1009-1027. |
| [8] | .Dolan JR, Montagnes DJ, Agatha S, Coats DW, Stoecker DK (2013) The Biology and Ecology of Tintinnid Ciliates: Models for Marine Plankton. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester, UK. |
| [9] | .Elliott DT, Kaufmann RS (2007) Spatial and temporal variability of mesozooplankton and tintinnid ciliates in a seasonally hypersaline estuary. Estuaries and Coasts, 30, 418-430. |
| [10] | .Gold K, Morales EA (1975) Seasonal changes in lorica sizes and the species of Tintinnida in the New York Bight. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 22, 520-528. |
| [11] | .Graziano C (1989) On the ecology of tintinnids (Ciliophora: Oligotrichida) in the North Irish Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 29, 233-245. |
| [12] | .Kamiyama T, Tsujino M (1996) Seasonal variation in the species composition of tintinnid ciliates in Hiroshima Bay, the Seto Inland Sea of Japan. Journal of Plankton Research, 18, 2313-2327. |
| [13] | .Kofoid CA, Campbell AS (1929) A Conspectus of the Marine and Fresh-water Ciliata Belonging to the Suborder Tintinnoinea: with Descriptions of New Species Principally from the Agassiz Expedition to the Eastern Tropical Pacific 1904-1905. University of California, Publications in Zoology, 34, 1-403. |
| [14] | .Kofoid CA, Campbell AS (1939) The Ciliata: the Tintinnoinea. Reports on the Scientific Results of the Expedition to the Eastern Tropical Pacific 1904-1905. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College, 84, 1473. |
| [15] | .Laval-Peuto M, Heinbokel JF, Anderson OR, Rassoulzadegan F, Sherr BF (1986) Role of micro- and nanozooplankton in marine food webs. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 7, 387-395. |
| [16] | .Leakey R, Burkill PH, Sleigh M (1993) Planktonic ciliates in Southampton Water: quantitative taxonomic studies. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United King- dom, 73, 579-594. |
| [17] | .Modigh M, Castaldo S (2002) Variability and persistence in tintinnid assemblages at a Mediterranean coastal site. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 28, 299-311. |
| [18] | .Montagnes D, Lynn D, Roff J, Taylor W (1988) The annual cycle of heterotrophic planktonic ciliates in the waters surrounding the Isles of Shoals, Gulf of Maine: an assessment of their trophic role. Marine Biology, 99, 21-30. |
| [19] | .Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13, 131-144. |
| [20] | .Pierce RW (1992) Ecology of planktonic ciliates in marine food webs. Reviews in Aquatic Sciences, 6, 139-181. |
| [21] | .Pierce RW, Turner JT (1994) Plankton studies in Buzzards Bay, Massachusetts, USA. IV. Tintinnids, 1987 to 1988. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 112, 235-240. |
| [22] | .Sanders RW (1987) Tintinnids and other microzooplankton: seasonal distributions and relationships to resources and Hydrography in a Maine estuary. Journal of Plankton Research, 9, 65-77. |
| [23] | .Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [24] | .Sitran R, Bergamasco A, Decembrini F, Guglielmo L (2007) Temporal succession of tintinnids in the northern Ionian Sea, central Mediterranean. Journal of Plankton Research, 29, 495-508. |
| [25] | .Sun J (孙军), Liu DY (刘东艳) (2003) The application of diversity indices in marine phytoplankton studies. Acta Oceanologica Sinica(海洋学报), 26, 62-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | .Urrutxurtu I, Orive E, de la Sota A (2003) Seasonal dynamics of ciliated protozoa and their potential food in an eutrophic estuary (Bay of Biscay). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 57, 1169-1182. |
| [27] | .Vaqué D, Blough H, Duarte C (1997) Dynamics of ciliate abundance, biomass and community composition in an oligotrophic coastal environment (NW Mediterranean). Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 12, 71-83. |
| [28] | .Verity PG (1987) Abundance, community composition, size distribution, and production rates of tintinnids in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 24, 671-690. |
| [29] | .Witek M (1998) Annual changes of abundance and biomass of planktonic ciliates in the Gdańsk Basin, southern Baltic. International Review of Hydrobiology, 83, 163-182. |
| [30] | .Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 4, 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | .Yu Y (于莹), Zhang WC (张武昌), Zhao N (赵楠), Sun XX (孙晓霞), Zhang CX (张翠霞), Feng MP (丰美萍), Xiao T (肖天) (2011) Annual variations in the abundance and biomass of planktonic ciliate in the Jiaozhou Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 42, 690-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | .Zhang WC (张武昌), Wang R (王荣) (2000) Microzooplank- ton and their grazing pressure on phytoplankton in Bohai Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica(海洋与湖沼), 31, 252-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | .Zhang WC (张武昌), Feng MP (丰美萍), Yu Y (于莹), Zhang CX (张翠霞), Xiao T (肖天) (2012) An Illustrated Guide to Contemporary Tintinnids in the World (砂壳纤毛虫图谱). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [3] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [4] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [5] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [6] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [7] | Li Hualiang, Zhang Mingjun, Zhang Xibin, Tan Rong, Li Shichuan, Feng Erhui, Lin Xueyun, Chen Min, Yan enbo, Zeng Zhigao. Composition and influencing factors of the amphibian community in Hainan Dongzhaigang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [8] | Wang Fengqiong, Zhang Xinyi, Wang Xinting, Jiang Chao, Hou Yali, Bao Daorina. Point pattern analysis of Leymus chinensis population in primary L. chinensis community in the steppe ecosystem [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24271-. |
| [9] | Yuan Liu, Jianqing Du, Liyuan Ma, Gang Yang, Jianqing Tian. Diversity and distribution of methanogen communities in the riparian wetlands of the Nam Co basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24247-. |
| [10] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [11] | Yuqi Zhang, Jun Wen, Yin Zhang, Shengzhi Li. Assessing the common welfare in the Giant Panda National Park: From the perspective of stakeholders [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [12] | Rongfei Su, Ruishan Chen, Linlin Yu, Jingbin Wu, Yan Kang. Biodiversity in community habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai based on camera trapping [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| [13] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [14] | Jianwei Cheng, Manhou Xu, Yongjing Dou, Yadong Wang, Yanan Wang, Xinmin Liu, Frank Yonghong Li. Seasonal dynamics of arthropod communities during horse dung decomposition in Inner Mongolian grasslands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24018-. |
| [15] | Mengyao Zheng, Yuan Li, Xuerong Wang, Yue Zhang, Tong Jia. Soil protozoa community assembly mechanism in different vegetation types of Luya Mountain [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()