



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 1461-1469. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021150 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021150
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Erhuan Wu1, Donghai Li2,*( ), Xiaobo Yang2,*(
), Xiaobo Yang2,*( ), Yongling Zuo2, Long Li2, Peichun Zhang2, Lin Chen2, Lujia Tian2, Chendi Li2
), Yongling Zuo2, Long Li2, Peichun Zhang2, Lin Chen2, Lujia Tian2, Chendi Li2
Received:2021-04-22
Accepted:2021-09-02
Online:2021-11-20
Published:2021-11-23
Contact:
Donghai Li,Xiaobo Yang
Erhuan Wu, Donghai Li, Xiaobo Yang, Yongling Zuo, Long Li, Peichun Zhang, Lin Chen, Lujia Tian, Chendi Li. Population structure of Cycas hainanensis and its relationship with forest canopy density[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1461-1469.
| 样方 Quadrat | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 森林郁闭度 Forest canopy density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 517.3 | 10.0° | 0.64 |
| B | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 519.1 | 12.2° | 0.51 |
| C | 109°5′ E | 19°16′ N | 512.3 | 14.4° | 0.47 |
| D | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 510.2 | 14.4° | 0.29 |
| E | 109°5′ E | 19°16′ N | 504.8 | 10.0° | 0.59 |
| F | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 503.6 | 13.8° | 0.59 |
Table 1 Physical characteristic of survey quadrat of Cycas hainanensis in the Baomeiling Nature Reserve of Changjiang County
| 样方 Quadrat | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 森林郁闭度 Forest canopy density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 517.3 | 10.0° | 0.64 |
| B | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 519.1 | 12.2° | 0.51 |
| C | 109°5′ E | 19°16′ N | 512.3 | 14.4° | 0.47 |
| D | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 510.2 | 14.4° | 0.29 |
| E | 109°5′ E | 19°16′ N | 504.8 | 10.0° | 0.59 |
| F | 109°6′ E | 19°16′ N | 503.6 | 13.8° | 0.59 |
| 层次 Layer | 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 频度 Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 枝花李榄 Linociera ramiflora | 0.006 | 0.27 |
| 黄牛木 Cratoxylum cochinchinense | 0.027 | 0.82 | |
| 破布叶 Microcos paniculata | 0.015 | 0.55 | |
| 厚皮树 Lannea coromandelica | 0.012 | 0.60 | |
| 细基丸 Polyalthia cerasoides | 0.010 | 0.53 | |
| 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 0.017 | 0.37 | |
| 牛矢果 Osmanthus matsumuranus | 0.012 | 0.45 | |
| 粉背琼楠 Beilschmiedia glauca | 0.013 | 0.50 | |
| 枫香 Liquidambar formosana | 0.001 | 0.13 | |
| 乌墨 Syzygium cumini | 0.001 | 0.12 | |
| 翻白叶 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 0.002 | 0.13 | |
| 马占相思 Acacia mangium | 0.002 | 0.10 | |
| 香合欢 Albizia odoratissima | 0.001 | 0.13 | |
| 倒吊笔 Wrightia pubescens | 0.007 | 0.38 | |
| 灌木层 Shrub | 海南苏铁 Cycas hainanensis | 0.140 | 0.97 |
| 银柴 Aporosa dioica | 0.026 | 0.83 | |
| 猪肚木 Canthium horridum | 0.028 | 0.77 | |
| 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | 0.016 | 0.60 | |
| 粉背琼楠 Beilschmiedia glauca | 0.008 | 0.38 | |
| 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | 0.009 | 0.35 | |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 0.012 | 0.58 | |
| 海金沙 Lygodium japonicum | 0.00067 | 0.033 | |
| 草本层 Herb | 草豆蔻 Alpinia hainanensis | 0.00017 | 0.033 |
Table 2 Abundance and frequency of main species in tree layer, shrub layer, and herb layer
| 层次 Layer | 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 频度 Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree | 枝花李榄 Linociera ramiflora | 0.006 | 0.27 |
| 黄牛木 Cratoxylum cochinchinense | 0.027 | 0.82 | |
| 破布叶 Microcos paniculata | 0.015 | 0.55 | |
| 厚皮树 Lannea coromandelica | 0.012 | 0.60 | |
| 细基丸 Polyalthia cerasoides | 0.010 | 0.53 | |
| 岭南山竹子 Garcinia oblongifolia | 0.017 | 0.37 | |
| 牛矢果 Osmanthus matsumuranus | 0.012 | 0.45 | |
| 粉背琼楠 Beilschmiedia glauca | 0.013 | 0.50 | |
| 枫香 Liquidambar formosana | 0.001 | 0.13 | |
| 乌墨 Syzygium cumini | 0.001 | 0.12 | |
| 翻白叶 Pterospermum heterophyllum | 0.002 | 0.13 | |
| 马占相思 Acacia mangium | 0.002 | 0.10 | |
| 香合欢 Albizia odoratissima | 0.001 | 0.13 | |
| 倒吊笔 Wrightia pubescens | 0.007 | 0.38 | |
| 灌木层 Shrub | 海南苏铁 Cycas hainanensis | 0.140 | 0.97 |
| 银柴 Aporosa dioica | 0.026 | 0.83 | |
| 猪肚木 Canthium horridum | 0.028 | 0.77 | |
| 山石榴 Catunaregam spinosa | 0.016 | 0.60 | |
| 粉背琼楠 Beilschmiedia glauca | 0.008 | 0.38 | |
| 潺槁木姜子 Litsea glutinosa | 0.009 | 0.35 | |
| 九节 Psychotria asiatica | 0.012 | 0.58 | |
| 海金沙 Lygodium japonicum | 0.00067 | 0.033 | |
| 草本层 Herb | 草豆蔻 Alpinia hainanensis | 0.00017 | 0.033 |
| 样方 Quadrat | Simpson多样性指数 Simpson’s diversity index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon diversity index | Pielou均匀度 指数 Pielou evenness index | 物种丰富度 Species richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.949 | 3.410 | 0.811 | 9.699 |
| B | 0.951 | 3.360 | 0.831 | 8.252 |
| C | 0.947 | 3.310 | 0.841 | 7.383 |
| D | 0.960 | 3.610 | 0.865 | 9.410 |
| E | 0.949 | 3.400 | 0.841 | 8.252 |
| F | 0.952 | 3.500 | 0.823 | 10.133 |
Table 3 Community species diversity index
| 样方 Quadrat | Simpson多样性指数 Simpson’s diversity index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon diversity index | Pielou均匀度 指数 Pielou evenness index | 物种丰富度 Species richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.949 | 3.410 | 0.811 | 9.699 |
| B | 0.951 | 3.360 | 0.831 | 8.252 |
| C | 0.947 | 3.310 | 0.841 | 7.383 |
| D | 0.960 | 3.610 | 0.865 | 9.410 |
| E | 0.949 | 3.400 | 0.841 | 8.252 |
| F | 0.952 | 3.500 | 0.823 | 10.133 |
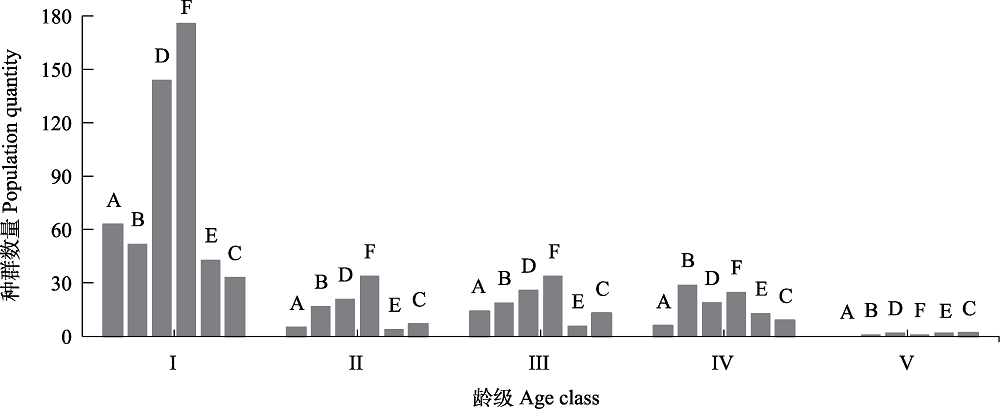
Fig. 1 Age structure of Cycas hainanensis population in different quadrat in the Baomeiling Provincial Nature Reserve of Changjiang County, Hainan Province. Details of quadrat A, B, C, D, E, F see Table 1.
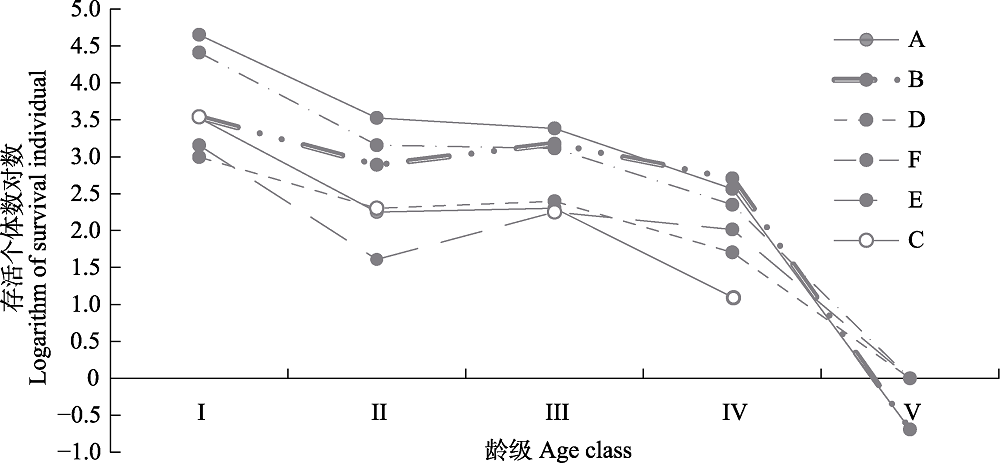
Fig. 2 Survival curve of Cycas hainanensis population in different quadrat in the Baomeiling Provincial Nature Reserve of Changjiang County, Hainan Province. Details of quadrat A, B, C, D, E, F see Table 1.
| 样方 Quadrat | 郁闭度Forest canopy density | 方差Variance | 方差均值比 Average variance ratio (DI) | t | 负二项参数Negative binomial parameters (k) | 丛生指数Cluster index (I) | 平均拥挤指数Average crowding index (m*) | 聚集指数Patchiness index (Pai) | 扩散型指数Type diffusion index (I&) | 格林指数Green index (GI) | Cassie 指标 Cassie index(CA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.64 | 31.12 | 3.58 | 5.48 | 4.62 | 2.58 | 11.28 | 1.30 | 1.27 | 2.38 | 0.22 |
| B | 0.51 | 192.1 | 16.14 | 32.2 | 1.75 | 15.14 | 27.04 | 2.27 | 2.15 | 19.9 | 0.57 |
| C | 0.47 | 11.38 | 1.78 | 1.65 | 10.29 | 0.78 | 7.18 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 0.44 | 0.10 |
| D | 0.29 | 134.7 | 26.38 | 11.5 | 5.10 | 15.38 | 26.48 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 12.5 | 0.20 |
| E | 0.59 | 17.43 | 2.53 | 3.25 | 6.01 | 1.53 | 8.43 | 1.22 | 1.20 | 1.06 | 0.17 |
| F | 0.59 | 311.8 | 11.55 | 22.4 | 3.55 | 10.55 | 37.57 | 1.40 | 1.35 | 31.5 | 0.28 |
Table 4 Spatial distribution pattern of Cycas hainanensis population in the Baomeiling Provincial Nature Reserve of Changjiang County, Hainan Province. Details of quadrat A, B, C, D, E, F see Table 1.
| 样方 Quadrat | 郁闭度Forest canopy density | 方差Variance | 方差均值比 Average variance ratio (DI) | t | 负二项参数Negative binomial parameters (k) | 丛生指数Cluster index (I) | 平均拥挤指数Average crowding index (m*) | 聚集指数Patchiness index (Pai) | 扩散型指数Type diffusion index (I&) | 格林指数Green index (GI) | Cassie 指标 Cassie index(CA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.64 | 31.12 | 3.58 | 5.48 | 4.62 | 2.58 | 11.28 | 1.30 | 1.27 | 2.38 | 0.22 |
| B | 0.51 | 192.1 | 16.14 | 32.2 | 1.75 | 15.14 | 27.04 | 2.27 | 2.15 | 19.9 | 0.57 |
| C | 0.47 | 11.38 | 1.78 | 1.65 | 10.29 | 0.78 | 7.18 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 0.44 | 0.10 |
| D | 0.29 | 134.7 | 26.38 | 11.5 | 5.10 | 15.38 | 26.48 | 1.26 | 1.23 | 12.5 | 0.20 |
| E | 0.59 | 17.43 | 2.53 | 3.25 | 6.01 | 1.53 | 8.43 | 1.22 | 1.20 | 1.06 | 0.17 |
| F | 0.59 | 311.8 | 11.55 | 22.4 | 3.55 | 10.55 | 37.57 | 1.40 | 1.35 | 31.5 | 0.28 |
| 龄级 Age class | 透光率 Light transmittance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88.89% | 66.67% | 58.33% | 36.11% | 21.53% | |
| I | 2 | 7 | 33 | 94 | 8 |
| II | 3 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 0 |
| 总计 Total | 5 | 9 | 49 | 98 | 8 |
Table 5 Density (inds./100 m2) of Cycas hainanensis population at different age classes under different light transmittance
| 龄级 Age class | 透光率 Light transmittance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88.89% | 66.67% | 58.33% | 36.11% | 21.53% | |
| I | 2 | 7 | 33 | 94 | 8 |
| II | 3 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 0 |
| 总计 Total | 5 | 9 | 49 | 98 | 8 |
| [1] |
Bell DM, Bradford JB, Lauenroth WK (2014) Early indicators of change: Divergent climate envelopes between tree life stages imply range shifts in the Western United States. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 168-180.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Cao Y, Xue QQ, Qi JY, Liu CY, Wang L, Men LN, Zhang ZW (2019) Effects of light transmittance on the community composition of soil macrofauna in artificial Hippophae rhamnoides plantation. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 47, 2159-2162, 2201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹悦, 薛琪琪, 祁靖宇, 柳春雨, 王磊, 门丽娜, 张志伟 (2019) 林内透光率对人工沙棘林大型土壤动物群落组成的影响. 山西农业科学, 47, 2159-2162, 2201.] | |
| [3] | Chen JR (2004) “Panda” in the plant --Cycads. Forest & Humankind, (12), 4-6. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈家瑞 (2004) 植物界的大熊猫--苏铁. 森林与人类, (12), 4-6.] | |
| [4] | Hill KD (2008) The genus Cycas (Cycadaceae) in China. Telopea, 12, 71-118. |
| [5] | Hu QP, Guo ZH, Li CY, Ma LY (2008) Leaf morphology and photosynthetic characteristics of seedlings of a deciduous and an evergreen broad-leaved species under different light regimes in subtropical forests. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 3262-3270. |
| [6] |
Huang HM, Dong R, He DN, Xiang YR, Zhang XJ, Chen J, Tao JP (2018) Effects of temporal and spatial variation of canopy structures and light conditions on population characteristics of Fargesia decurvata. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 2129-2138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI PMID |
|
[ 黄慧敏, 董蓉, 何丹妮, 向运蓉, 张小晶, 陈娟, 陶建平 (2018) 冠层结构和光环境的时空变化对紫耳箭竹种群特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 29, 2129-2138.]
PMID |
|
| [7] | Huang YF, Liao SB, Chen Y, Luo SX, Liu DW, Cai G, Sun B (2013) Population characteristics and conservation of Cycas fairylakea. Forest Research, 26, 668-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄应锋, 廖绍波, 陈勇, 罗水兴, 刘东蔚, 蔡刚, 孙冰 (2013) 深圳梅林仙湖苏铁的种群特征与保护研究. 林业科学研究, 26, 668-672.] | |
| [8] | Li J, Lin JY, He YH, Jiang Y, Liang RL (2016) Population structure and distribution pattern of Cycas bifida in Chongzuo of Guangxi. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 43(12), 25-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李娟, 林建勇, 何应会, 蒋燚, 梁瑞龙 (2016) 广西崇左叉叶苏铁种群结构与分布格局研究. 广东农业科学, 43(12), 25-29. ] | |
| [9] | Li XW, Chen SL (2008) Effect of shading on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaves of Fritillaria cirrhosa. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 3438-3446. |
| [10] | Li YL, Zhang L, Yang XB, Li DH, Zhang K, Wu TT (2017) Study on spatial distribution and population dynamics of wild tea in Hainan Island. Forestry Resource Management, 46(2), 81-87, 138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李苑菱, 张丽, 杨小波, 李东海, 张凯, 吴庭天 (2017) 海南岛野生茶树空间分布及种群动态研究. 林业资源管理, 46(2), 81-87, 138.] | |
| [11] | Li YN, Zhang BL, Qin SY, Li SY, Huang XR (2008) Review of research and application of forest canopy closure and its measuring methods. World Forestry Research, 21(1), 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李永宁, 张宾兰, 秦淑英, 李帅英, 黄选瑞 (2008) 郁闭度及其测定方法研究与应用. 世界林业研究, 21(1), 40-46.] | |
| [12] | Liu B, Zhang CC, Wang JS, Li ZM, Ouyang YL, Chen W, Chen FS, Bu WS (2020) Characteristic of species diversity in stands of different restoration models in Jiulian Mountain, Jiangxi Province. Forest Research, 33(4), 42-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘斌, 张参参, 汪金松, 李张敏, 欧阳园丽, 陈维, 陈伏生, 卜文圣 (2020) 江西九连山不同恢复模式林分的物种多样性特征. 林业科学研究, 33(4), 42-52.] | |
| [13] | Luo WH, Tang WX, Huang SX, Liang HL, Zhao B (2014) Ex situ conservation of Cycas debaoensis: A rare and endangered plant. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 31, 812-816. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 骆文华, 唐文秀, 黄仕训, 梁惠凌, 赵博 (2014) 珍稀濒危植物德保苏铁迁地保护研究. 浙江农林大学学报, 31, 812-816. ] | |
| [14] |
Mestre L, Toro-Manríquez M, Soler R, Huertas-Herrera A, Martínez-Pastur G, Lencinas MV (2017) The influence of canopy-layer composition on understory plant diversity in southern temperate forests. Forest Ecosystems, 4, 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Normand S, Zimmermann NE, Schurr FM, Lischke H (2014) Demography as the basis for understanding and predicting range dynamics. Ecography, 37, 1149-1154.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Rozendaal DMA, Hurtado VH, Poorter L (2006) Plasticity in leaf traits of 38 tropical tree species in response to light; relationships with light demand and adult stature. Functional Ecology, 20, 207-216.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Ru WM, Zhang GP, Bi RC, Zhang F, Zhang JT (2007) Population structure and pattern of endangered Ulmus lamellosa in Shanxi. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 13, 14-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 茹文明, 张桂萍, 毕润成, 张锋, 张金屯 (2007) 濒危植物脱皮榆种群结构与分布格局研究. 应用与环境生物学报, 13, 14-17.] | |
| [18] | Song P, Hong W, Wu CZ, Feng L, Fan HL, Zhu H, Lin YM, Zhang Q (2005) Population structure and its dynamics of rare and endangered plant Alsophila spinulosa. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 16, 413-418. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋萍, 洪伟, 吴承祯, 封磊, 范海兰, 朱慧, 林勇明, 张琼 (2005) 珍稀濒危植物桫椤种群结构与动态研究. 应用生态学报, 16, 413-418.] | |
| [19] | Sun XL, Shi SZ, Zhao XY, Xu YY, Hong XJ (2017) Present situation and protection countermeasures of wild and endangered plants in minimal population in Hainan Province. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (18), 11-13, 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙湘来, 石绍章, 赵小迎, 许洋瑜, 洪小江 (2017) 海南省极小种群野生濒危植物现状与保护对策. 绿色科技, (18), 11-13, 38.] | |
| [20] | Tang YJ, Liao JP (2001) Studies on comparative anatomy of the pinnae of six species of Cycas. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 18, 615-622, 604. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐源江, 廖景平 (2001) 六种苏铁属植物的羽片比较解剖学研究. 植物学通报, 18, 615-622, 604.] | |
| [21] | Xie CP, Wu CK, Fu G, Lai SF, Fang Y, Wang HC (2019) Population structure characteristics and dynamics of Cycas hainanensis in Wuzhi Mountains, Hainan Province. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 39(1), 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢春平, 吴昌魁, 付桂, 赖水发, 方彦, 王华晨 (2019) 五指山地区海南苏铁种群结构特征与动态. 中南林业科技大学学报, 39(1), 77-85.] | |
| [22] | Xie ZQ, Chen WL, Liu ZY, Jiang MX, Huang HD (1999) Spatial distribution pattern of Cathaya argyrophylla population. Acta Botanica Sinica, 48, 3-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢宗强, 陈伟烈, 刘正宇, 江明喜, 黄汉东 (1999) 银杉种群的空间分布格局. 植物学报, 48, 3-5.] | |
| [23] | Xue JH (2006) Forest Ecology. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 薛建辉 (2006) 森林生态学. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] | Xu F, Guo WH, Xu WH, Wang RQ (2010) Effects of light intensity on growth and photosynthesis of seedlings of Quercus acutissima and Robinia pseudoacacia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 3098-3107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐飞, 郭卫华, 徐伟红, 王仁卿 (2010) 不同光环境对麻栎和刺槐幼苗生长和光合特征的影响. 生态学报, 30, 3098-3107.] | |
| [25] | Yang XB (2015) The Colored Illustrated Flora of Hainan Province (Vol. 2). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨小波 (2015) 海南植物图志(第2卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] |
Zhang J, Shang guan TL, Duan YH, Guo W, Liu WH, Guo DG (2014) Age structure and dynamics of Quercus wutaishanica population in Lingkong Mountain of Shanxi Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 3125-3130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
|
[ 张婕, 上官铁梁, 段毅豪, 郭微, 刘卫华, 郭东罡 (2014) 灵空山辽东栎种群年龄结构与动态. 应用生态学报, 25, 3125-3130.]
PMID |
|
| [27] | Zhao RB, Yang XB, Li DH, Qi CL, Li JB (2018) Study on geographical distribution and distribution characteristics of cyatheaceae in Hainan Island. Forestry Resource Management, 47(2), 65-73, 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵瑞白, 杨小波, 李东海, 戚春林, 李剑碧 (2018) 海南岛桫椤科植物地理分布和分布特征研究. 林业资源管理, 47(2), 65-73, 97.] | |
| [28] | Zheng YR (1997) The applicability of various methods in analysis of Picea mongolica population spatial distribution pattern. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 21, 480-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑元润 (1997) 不同方法在沙地云杉种群分布格局分析中的适用性研究. 植物生态学报, 21, 480-484. ] | |
| [29] | Zhou JL, Zheng SZ, Yang C (1992) Plant Ecology. Higher Education Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周纪伦, 郑师章, 杨持 (1992) 植物种群生态学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | Di Lin, Shuanglin Chen, Que Du, Wenlong Song, Gu Rao, Shuzhen Yan. Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [9] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [10] | Jingci Meng, Guodong Wang, Guanglan Cao, Nanlin Hu, Meiling Zhao, Yantong Zhao, Zhenshan Xue, Bo Liu, Wenhua Piao, Ming Jiang. Patterns and drivers of plant species richness in Phragmites australis marshes in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [11] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [12] | Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu. Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [13] | Jiayi Feng, Juyu Lian, Yujun Feng, Dongxu Zhang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye. Effects of vertical stratification on community structure and functions in a subtropical, evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [14] | Xingyu Wang, Jinghui Meng, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [15] | Qingqing Du, Siyuan Ren, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, Yan Zhu. Factors affecting the productivity of sapling and adult trees in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn