



Biodiv Sci ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 289-295. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019143 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019143
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xinghui Lu1,Runguo Zang2,3,*( ),Yi Ding2,3,Jihong Huang2,3,Yue Xu2,3
),Yi Ding2,3,Jihong Huang2,3,Yue Xu2,3
Received:2019-04-26
Accepted:2019-09-01
Online:2020-03-20
Published:2019-12-24
Contact:
Runguo Zang
Xinghui Lu, Runguo Zang, Yi Ding, Jihong Huang, Yue Xu. Habitat characteristics and its effects on seedling abundance of Hopea hainanensis, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(3): 289-295.
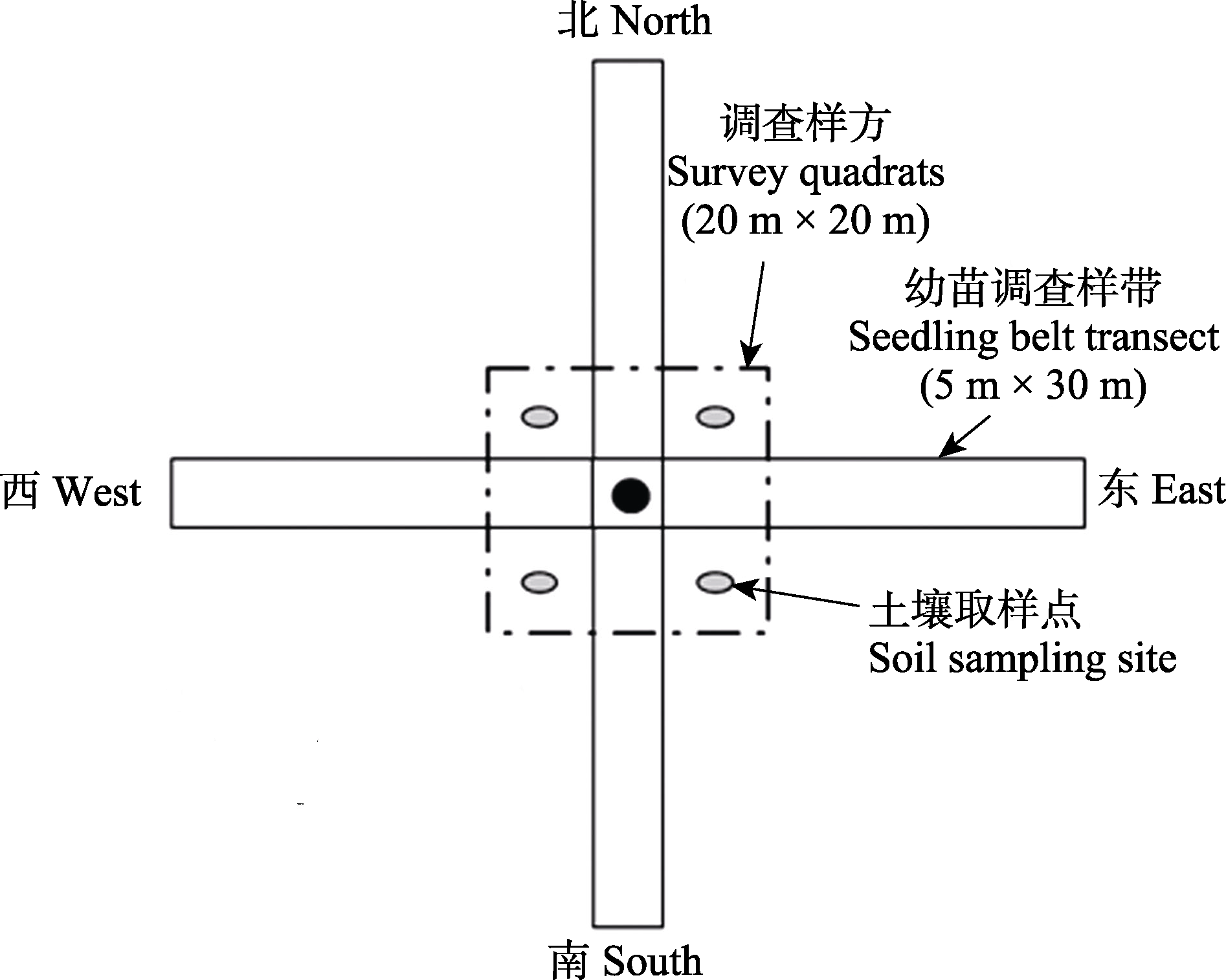
Fig. 1 Diagram for the survey quadrats of Hopea hainanensis, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations. The black dot in the center is the mother tree of Hopea hainanensis.
| 生境因子 Habitat factors | 中位数 ± 标准差 Median ± SD | 变化范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 560.9 ± 173.67 | 260-940 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 15.00 ± 10.55 | 0-40 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 12.23 ± 7.08 | 3.60-47.10 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 4.78 ± 0.57 | 3.80-5.98 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 3.75 ± 1.58 | 0.13-7.93 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 1.38 ± 0.57 | 0.30-2.49 |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 0.09-0.34 |
| 土壤有效氮 Soil available nitrogen (mg/kg) | 86.8 ± 28.03 | 15.06-140.77 |
| 土壤有效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg/kg) | 15.16 ± 7.09 | 5.74-34.26 |
| 土壤有效钾 Soil available potassium (mg/kg) | 147.88 ± 57.50 | 47.16-296.36 |
| 冠层开阔度 Canopy openness (%) | 6.94 ± 3.27 | 2.01-19.49 |
| 伴生种胸高断面积 Basal area of companion species (cm2) | 1,017.36 ± 996.31 | 226.86-3,990.67 |
| 伴生种树高 Height of companion species (m) | 23 ± 4.81 | 10.00-33.00 |
| 母株冠幅 Crown of mother tree (m) | 3.63 ± 1.05 | 1.50-6.50 |
| 母株胸径 DBH of mother tree (cm) | 20.94 ± 3.60 | 14.91-33.61 |
| 母株高度 Height of mother tree (m) | 13.51 ± 1.62 | 11.00-14.00 |
Table 1 Habitat characteristics of Hopea hainanensis, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations
| 生境因子 Habitat factors | 中位数 ± 标准差 Median ± SD | 变化范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 560.9 ± 173.67 | 260-940 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 15.00 ± 10.55 | 0-40 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content (%) | 12.23 ± 7.08 | 3.60-47.10 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 4.78 ± 0.57 | 3.80-5.98 |
| 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter (g/kg) | 3.75 ± 1.58 | 0.13-7.93 |
| 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 1.38 ± 0.57 | 0.30-2.49 |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 0.09-0.34 |
| 土壤有效氮 Soil available nitrogen (mg/kg) | 86.8 ± 28.03 | 15.06-140.77 |
| 土壤有效磷 Soil available phosphorus (mg/kg) | 15.16 ± 7.09 | 5.74-34.26 |
| 土壤有效钾 Soil available potassium (mg/kg) | 147.88 ± 57.50 | 47.16-296.36 |
| 冠层开阔度 Canopy openness (%) | 6.94 ± 3.27 | 2.01-19.49 |
| 伴生种胸高断面积 Basal area of companion species (cm2) | 1,017.36 ± 996.31 | 226.86-3,990.67 |
| 伴生种树高 Height of companion species (m) | 23 ± 4.81 | 10.00-33.00 |
| 母株冠幅 Crown of mother tree (m) | 3.63 ± 1.05 | 1.50-6.50 |
| 母株胸径 DBH of mother tree (cm) | 20.94 ± 3.60 | 14.91-33.61 |
| 母株高度 Height of mother tree (m) | 13.51 ± 1.62 | 11.00-14.00 |
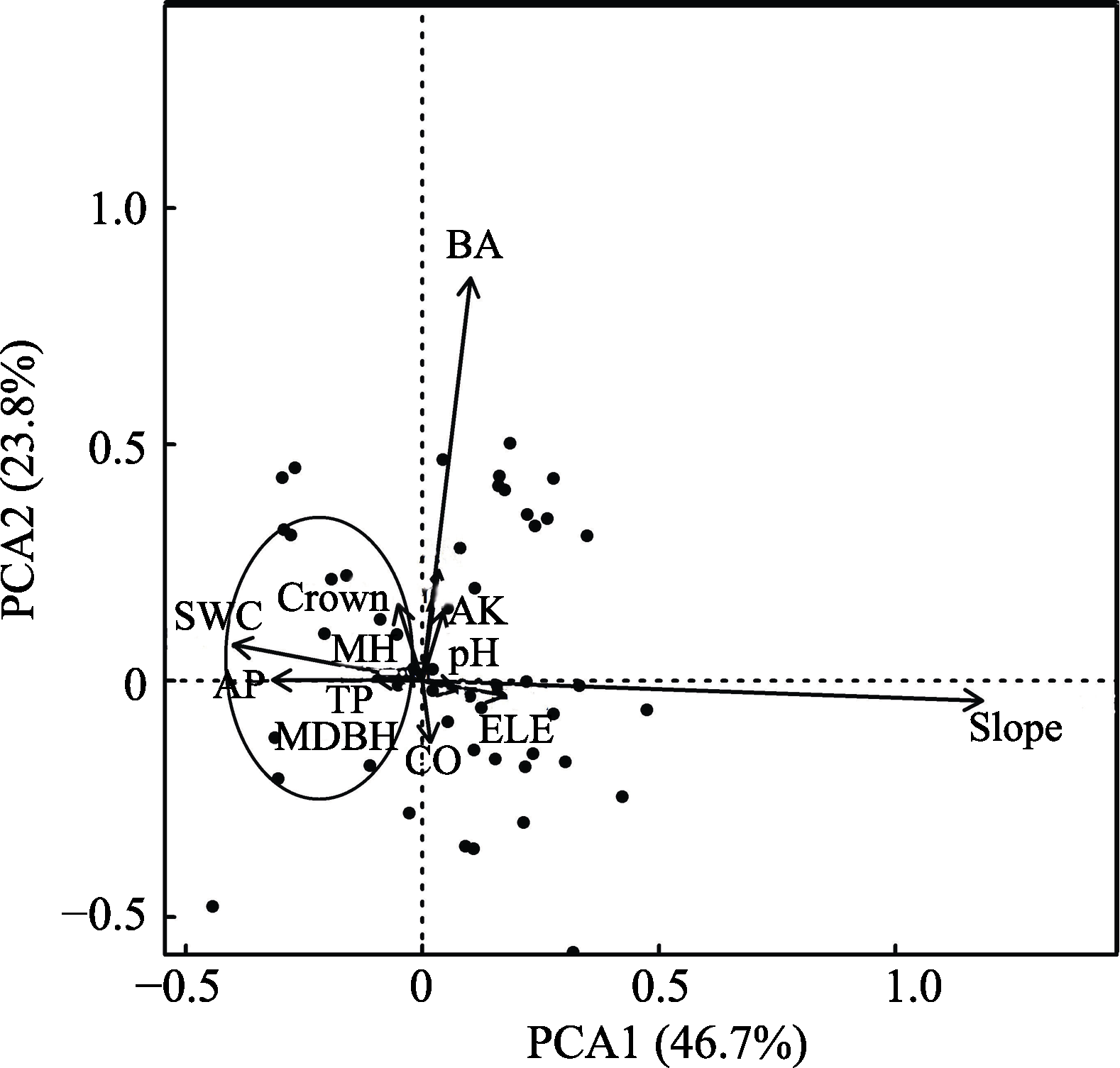
Fig. 3 Principal component analysis of habitat factors of Hopea hainanensi, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations. ELE, Elevation; SWC, Soil water content; pH, Soil pH value; TP, Soil total phosphorus; AP, Soil available phosphorus; AK, Soil available potassium; CO, Canopy openness; BA, Basal area of companion species; Crown, Crown of mother tree; MDBH, DBH of mother tree; MH, Height of mother tree.
| 生境因子 Habitat factors | PCA1 | PCA2 |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.21 | -0.03 |
| 坡度 Slope | 1.42 | -0.03 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | -0.48 | 0.11 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 0.08 | -0.02 |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus | -0.12 | 0.00 |
| 土壤有效磷 Soil available phosphorus | -0.38 | -0.00 |
| 土壤有效钾 Soil available potassium | 0.05 | 0.12 |
| 冠层开阔度 Canopy openness | 0.02 | -0.11 |
| 伴生种胸高断面积 Basal area of companion species | 0.12 | 1.05 |
| 母株冠幅 Crown of mother tree | -0.06 | 0.20 |
| 母株胸径 DBH of mother tree | -0.08 | 0.17 |
| 母株高度 Height of mother tree | -0.03 | 0.04 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.232 | 0.110 |
| 方差比例 Proportion of variance | 0.467 | 0.238 |
| 累积方差比例 Proportion of cumulative variance | 0.467 | 0.705 |
Table 2 The loadings and explained variance of environmental variables in the first two axes in principal component anlysis (PCA)
| 生境因子 Habitat factors | PCA1 | PCA2 |
|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | 0.21 | -0.03 |
| 坡度 Slope | 1.42 | -0.03 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | -0.48 | 0.11 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH value | 0.08 | -0.02 |
| 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus | -0.12 | 0.00 |
| 土壤有效磷 Soil available phosphorus | -0.38 | -0.00 |
| 土壤有效钾 Soil available potassium | 0.05 | 0.12 |
| 冠层开阔度 Canopy openness | 0.02 | -0.11 |
| 伴生种胸高断面积 Basal area of companion species | 0.12 | 1.05 |
| 母株冠幅 Crown of mother tree | -0.06 | 0.20 |
| 母株胸径 DBH of mother tree | -0.08 | 0.17 |
| 母株高度 Height of mother tree | -0.03 | 0.04 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 0.232 | 0.110 |
| 方差比例 Proportion of variance | 0.467 | 0.238 |
| 累积方差比例 Proportion of cumulative variance | 0.467 | 0.705 |
| 1 | Agricultural Chemistry Committee of Soil Science Society of China( 1983) Conventional Methods for the Agricultural Chemical Analysis of Soil. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [ 中国土壤学会农业化学专业委员会( 1983) 土壤农业化学常规分析方法. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 2 | Anderson LJ ( 2011) Aboveground-belowgroun. linkages: Biotic interactions, ecosystem processes, and global change. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 92, 222. |
| 3 | Baribault TW, Kobe RK, Finley AO ( 2012) Tropical tree growth is correlated with soil phosphorus, potassium, and calcium, though not for legumes. Ecological Monographs, 82, 189-203. |
| 4 | Chen HX, Huang CT, He F, Zheng W, Feng JP ( 2015) Review on research progress of Hopea hainanensis. Tropical Forestry, 43(4), 4-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈侯鑫, 黄川腾, 何芬, 郑伟, 冯家平 ( 2015) 坡垒研究进展综述. 热带林业, 43(4), 4-6.] | |
| 5 |
Chen L, Mi XC, Comita LS, Zhang LW, Ren HB, Ma KP ( 2010) Community-level consequences of density dependence and habitat association in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Ecology Letters, 13, 695-704.
DOI URL |
| 6 | Chen QD, Song XZ, Yang J, Wang DF ( 1982) Effects of storage temperature on Hopea hainanensis seed vigor. Tropical Forestry, 10(1), 47-50. |
| (in Chinese) [ 陈青度, 宋学之, 杨军, 王东馥 ( 1982) 不同温度贮藏对坡垒种子活力的影响. 热带林业, 10(1), 47-50.] | |
| 7 | Chen Y, Fang YS, Fang FZ, Wu ZQ, Chen XR ( 2017) Distribution characteristics of soil nutrients and microbial communities in natural forest of Hopea hainanensis. Tropical Forestry, 45(3), 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈彧, 方燕山, 方发之, 吴钟亲, 陈修仁 ( 2017) 坡垒天然林下土壤养分及微生物群落分布特征. 热带林业, 45(3), 19-22.] | |
| 8 |
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Taylor P, Alvarez-Clare S, Bustamante MMC, Chuyong G, Dobrowski SZ, Grierson P, Harms KE, Houlton BZ, Marklein A, Parton W, Porder S, Reed SC, Sierra CA, Silver WL, Tanner EVJ, Wieder WR ( 2011) Relationships among net primary productivity, nutrients and climate in tropical rain forest: A pan-tropical analysis. Ecology Letters, 14, 939-947.
DOI URL |
| 9 | Dai WJ, Zhou L, Yang M ( 2017) Research and utilization of Dipterocapaceae plants in China. World Forestry Reserch, 30(6), 46-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴文君, 周磊, 杨梅 ( 2017) 中国龙脑香科植物研究及利用现状. 世界林业研究, 30(6), 46-51.] | |
| 10 |
Ding Y, Zang RG ( 2011) Vegetation recovery dynamics of tropical lowland rain forest in Bawangling of Hainan Island, South China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 577-586. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 丁易, 臧润国 ( 2011) 海南岛霸王岭热带低地雨林植被恢复动态. 植物生态学报, 35, 577-586.]
DOI URL |
|
| 11 | Fu LK ( 1991) China Plant Red Data Book: Rare and Endangered Plants. Vol. 1. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [ 傅立国 ( 1991) 中国植物红皮书: 稀有濒危植物(第一卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 12 | Hu YJ ( 1983) Community characteristics and forest types of Dipterocarpaceae in Hainan Island. Ecological Science, 2(2), 16-24. |
| (in Chinese) [ 胡玉佳 ( 1983) 海南岛龙脑香森林的群落特征及其类型. 生态科学, 2(2), 16-24.] | |
| 13 | Hu YJ ( 1991) A study on population structure of Vatica hainanensis in Hainan Island. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 30(2), 91-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡玉佳 ( 1991) 海南岛青梅种群结构的研究. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 30(2), 91-97.] | |
| 14 | Li GY, Chen FF, Yang ZL ( 2015) Studies on seedling cultural techniques of Hopea hainanensis. Tropical Forestry, 43(4), 7-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黎国运, 陈飞飞, 杨枝林 ( 2015) 坡垒种子育苗技术研究. 热带林业, 43(4), 7-9.] | |
| 15 | Lu X, Lan QY, Yang MZ ( 2010) Research advancement of Dipterocarpaceae seeds characteristics. Seed, 29(5), 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 路信, 兰芹英, 杨明挚 ( 2010) 龙脑香科植物种子特性的研究进展. 种子, 29(5), 46-50.] | |
| 16 |
Manzané-Pinzón E, Goldstein G, Schnitzer SA ( 2018) Does soil moisture availability explain liana seedling distribution across a tropical rainfall gradient? Biotropica, 50, 215-224.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Nasto MK, Alvarez-Clare S, Lekberg Y, Sullivan BW, Townsend AR, Cleveland CC ( 2014) Interactions among nitrogen fixation and soil phosphorus acquisition strategies in lowland tropical rain forests. Ecology Letters, 17, 1282-1289.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Pinho BX, de Melo FPL, Pierce S, Lohbeck M, Tabarelli M ( 2018) Soil-mediated filtering organizes tree assemblages in regenerating tropical forests. Journal of Ecology, 106, 137-147.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Poorter L, van der Sande MT, Arets EJMM, Ascarrunz N, Enquist BJ, Finegan B, Licona JC, Martínez-Ramos M, Mazzei L, Meave JA, Muñoz R, Nytch CJ, de Oliveira AA, Pérez-García EA, Prado-Junior J, Rodríguez-Velázques J, Ruschel AR, Salgado-Negret B, Schiavini I, Swenson NG, Tenorio EA, Thompson J, Toledo M, Uriarte M, van der Hout P, Zimmerman JK, Peña-Claros M ( 2017) Biodiversity and climate determine the functioning of Neotropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, 1423-1434.
DOI URL |
| 20 | Qin JH, Yao J, Meng LJ, Chen GL, Zhao XH ( 2018) Composition of multi-year-old seedlings and their habitat interpretation in a mixed coniferous-broadleaf forest in Jiaohe, Jilin Province, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 3186-3193. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦江环, 姚杰, 孟令君, 陈桂莲, 赵秀海 ( 2018) 吉林蛟河针阔混交林多年生幼苗物种组成及其生境解释. 生态学杂志, 37, 3186-3193.] | |
| 21 | R Development Core Team ( 2011) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. . (accessed on 2019-03-02) |
| 22 | Song XZ, Chen QD, Wang DF, Yang J ( 1984) A study on the principal storage conditions of Hopea hainanensis seeds. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 20, 225-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋学之, 陈青度, 王东馥, 杨军 ( 1984) 坡垒种子主要储藏条件的研究. 林业科学, 20, 225-236.] | |
| 23 |
Spain AV, Tibbett M, Ridd M, Mclaren TI ( 2018) Phosphorus dynamics in a tropical forest soil restored after strip mining. Plant and Soil, 427, 105-123.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Tíscar PA ( 2019) Recruitment into the seedling bank of an undisturbed Mediterranean pinewood: Increasing forest resistance to changing climates. Forest Ecology and Management, 432, 591-598.
DOI URL |
| 25 | Wang W, Rao MD, Chen SW, Zhu DH, Mi XC, Zhang JT ( 2014) Effects of negative density dependence and habitat filtering on temporal variation in phylogenetic community structure of seedlings in a mid-subtropical forest. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 1844-1850. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王薇, 饶米德, 陈声文, 朱大海, 米湘成, 张金屯 ( 2014) 负密度制约和生境过滤对古田山幼苗系统发育多样性时间变化的影响. 科学通报, 59, 1844-1850.] | |
| 26 | Wen B, Lan QY, He HY ( 2002) Effects of illumination, temperature and soil moisture content on seed germination of Hopea hainanensi. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 10, 258-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 文彬, 兰芹英, 何惠英 ( 2002) 光、温度和土壤水分对坡垒种子萌发的影响. 热带亚热带植物学报, 10, 258-262.] | |
| 27 | Xu ZF, Zhu H, Liu HM, Wang H ( 1994) The changing tendency of plant species diversity in the fragmental tropical rainforest in southern Yunnan, China. Journal of Plant Resources and Environemt, 3(2), 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许再富, 朱华, 刘宏茂, 王洪 ( 1994) 滇南片段热带雨林植物物种多样性变化趋势. 植物资源与环境, 3(2), 9-15.] | |
| 28 | Yang XB, Lin Y, Liang SQ, Huang SM, Fu SX, Wang QM, Xie GG ( 1995) Study on the population structure and distribution pattern of Hopea exalata in Hainan Island. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 133, 299-303. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨小波, 林英, 梁淑群, 黄世满, 符史新, 王琼梅, 谢国干 ( 1995) 海南岛无翼坡垒种群结构与分布格局研究. 海南大学学报自然科学版, 133, 299-303.] | |
| 29 |
Zhang J, Li BH, Bai XJ, Yuan ZQ, Wang XG, Ye J, Hao ZQ ( 2009) Composition and interannual dynamics of tree seedlings in broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest in Changbai Mountain. Biodiversity Science, 17, 385-396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张健, 李步杭, 白雪娇, 原作强, 王绪高, 叶吉, 郝占庆 ( 2009) 长白山阔叶红松林乔木树种幼苗组成及其年际动态. 生物多样性, 17, 385-396.]
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()