



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 149-158. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018261 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018261
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen Zuoyi1,2,Xu Xiaojing1,Zhu Suying1,Zhai Mengyi1,Li Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-28
Accepted:2019-01-27
Online:2019-02-20
Published:2019-04-16
Contact:
Li Yang
Chen Zuoyi, Xu Xiaojing, Zhu Suying, Zhai Mengyi, Li Yang. Species diversity and geographical distribution of the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex along the coast of China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(2): 149-158.
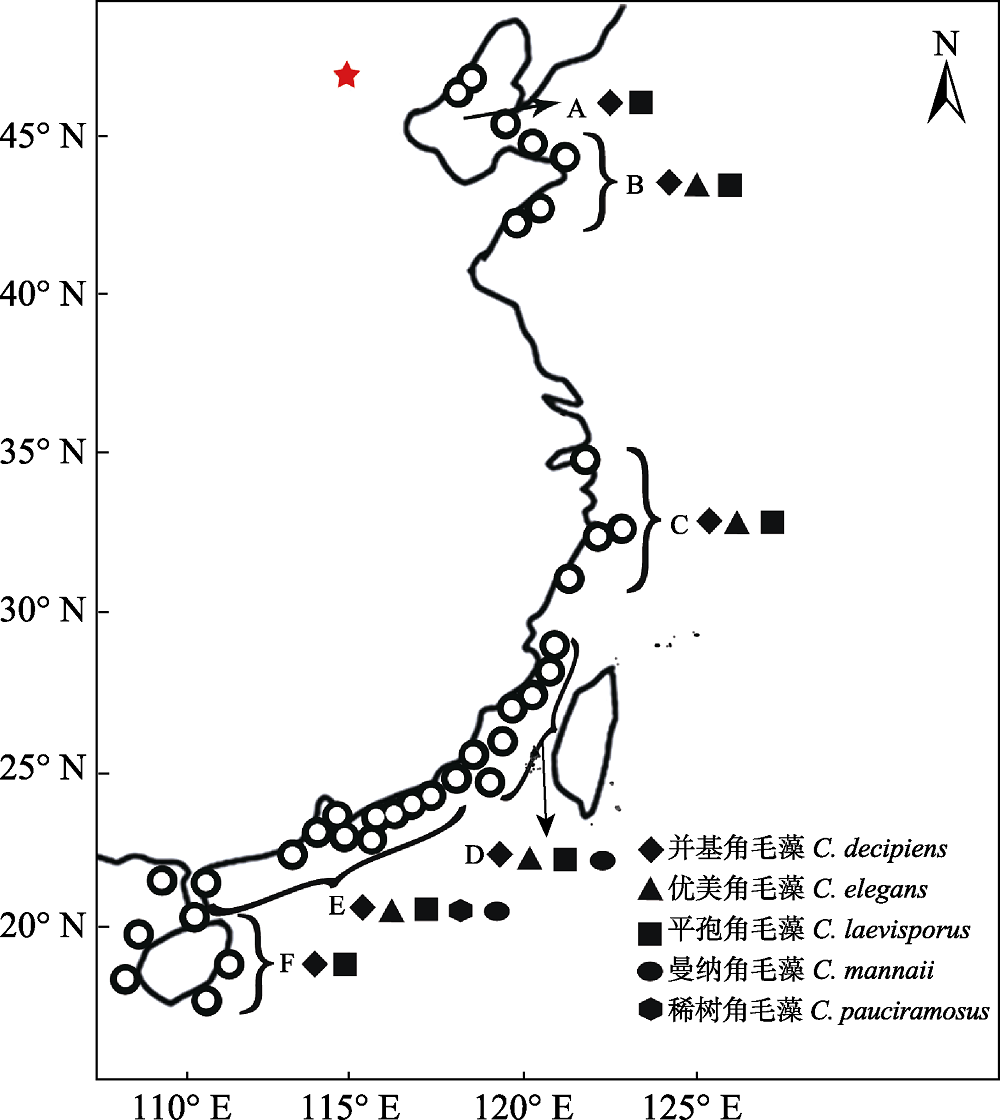
Fig. 1 Sampling sites and geographical distribution of the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex along the coast of China. 〇, Sampling sites; A, Bohai Sea; B, Shandong coast; C, Zhejiang coast; D, Taiwan Strait; E, Guangdong coast; F, Hainan coast.
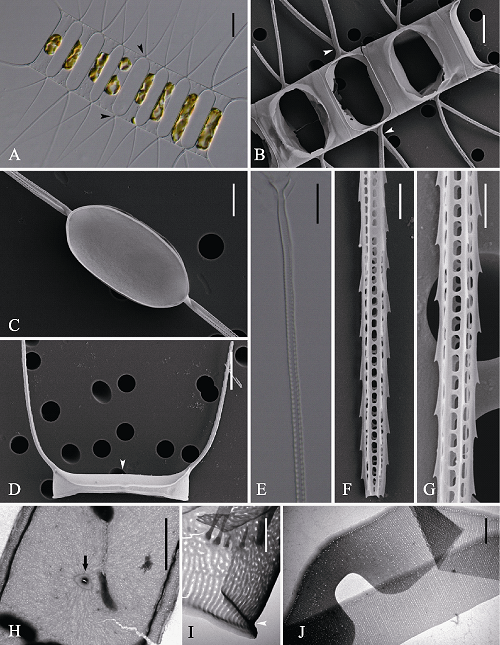
Fig. 2 Morphology of Chaetoceros decipiens under light microscopy (LM) (A, E), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (B-D, F, G) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (H-J). A-B, Broad girdle views showing fusing sibling setae base present (B, arrowheads) and not (A, arrowheads); C, Internal view of intercalary valve; D, Terminal valve with rimoportula (arrowhead) and U-shaped terminal setae; E-G, Structure of setae; H, Terminal valve with rimoportula (arrow); I, Mantle; J, Girdle bands. Scale bars, 20 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, E), 6 μm (C), 5 μm (H), 2 μm (F, G, J), 1 μm (I).
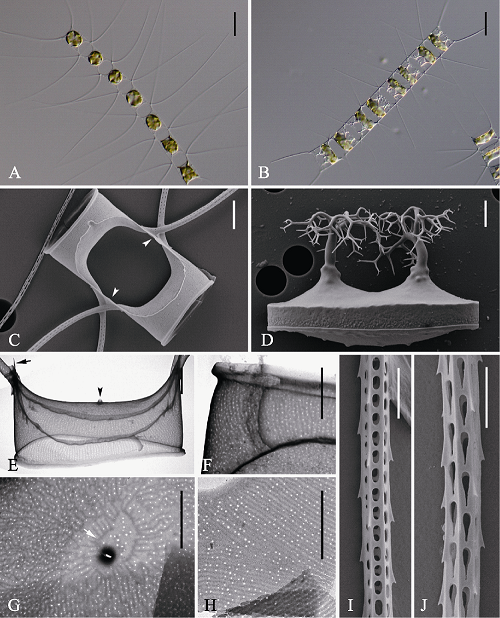
Fig. 3 Morphology of Chaetoceros elegans under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-D, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (E-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica ear-like structures (arrowhead); D, Released resting spore. E, Terminal valve with external process of rimoportula (arrowhead) and fringe (arrow); F, Parallel rows of poroids on the mantle; G, Central annulus (arrow) on terminal valve; H, Girdle bands; I and J, Seta structure. Scale bars, 20 μm (A, B), 6 μm (D), 4 μm (C), 2 μm (E, F, G, H, I, J).
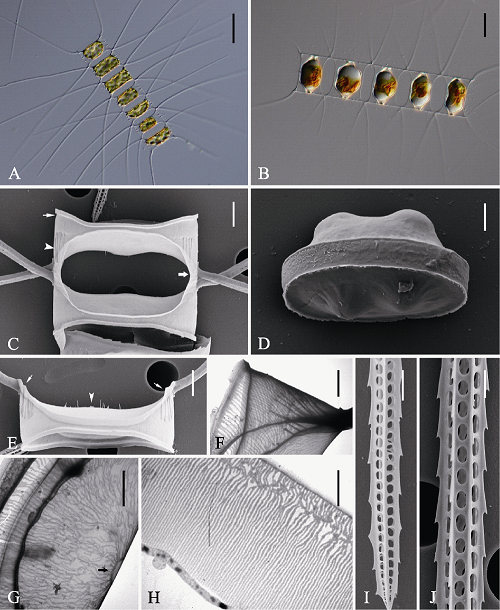
Fig. 4 Morphology of Chaetoceros laevisporus under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-E, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (F-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica wings (broad arrow), silica ridges (arrowhead) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrow); D, A released resting spore; E, Terminal valve with central processes (arrowhead) and silica rib (arrows); F, Mantle; G, Intercalary valve with central annulus (arrow); H, Girdle bands; I and J, Setae structure. Scale bars, 50 μm (A), 20 μm (B), 4 μm (C, E), 2 μm (D, F, G, H, I, J).
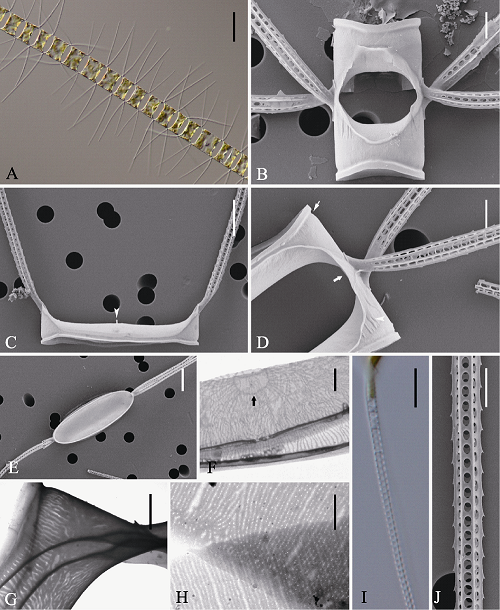
Fig. 5 Morphology of Chaetoceros mannaii under light microscopy (LM) (A, I), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (B-E, J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (F-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Sibling intercalary valves showing aperture; C, Terminal valve view with external process of rimoportula (arrowhead); D, Intercalary cells with overlapping silica wings (broad arrow), silica ridges (arrowhead) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrow); E, F, Internal view of an intercalary valves, showing central annulus (F, arrow); G, Mantle; H, Girdle bands; I and J: Setae structure. Scale bars, 50 μm (A), 10 μm (B, D, I), 5 μm (F), 4 μm (C, E, J), 2 μm (G, H).
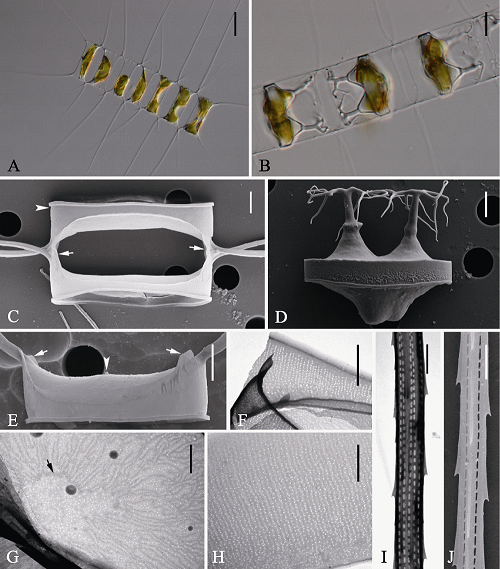
Fig. 6 Morphology of Chaetoceros pauciramosus under light microscopy (LM) (A-B), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (C-D, I-J) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (E-H). A, Chain in broad girdle view; B, Resting spores within the mother cells of a chain; C, Sibling intercalary valves showing overlapping silica ear-like structures (arrows) and furrow above the basal ring of mantle (arrowhead); D, Released resting spore; E, Terminal valve with short external tubes of rimoportulae (arrowhead) and silica rib (arrows); F, Mantle; G, Intercalary valve, showing central annulus (arrow); H, Girdle bands; I and J, Seta structure. Scale bars, 20 μm (A), 10 μm (D), 4 μm (C, D, E), 2 μm (F), 1 μm (G, H, I, J).
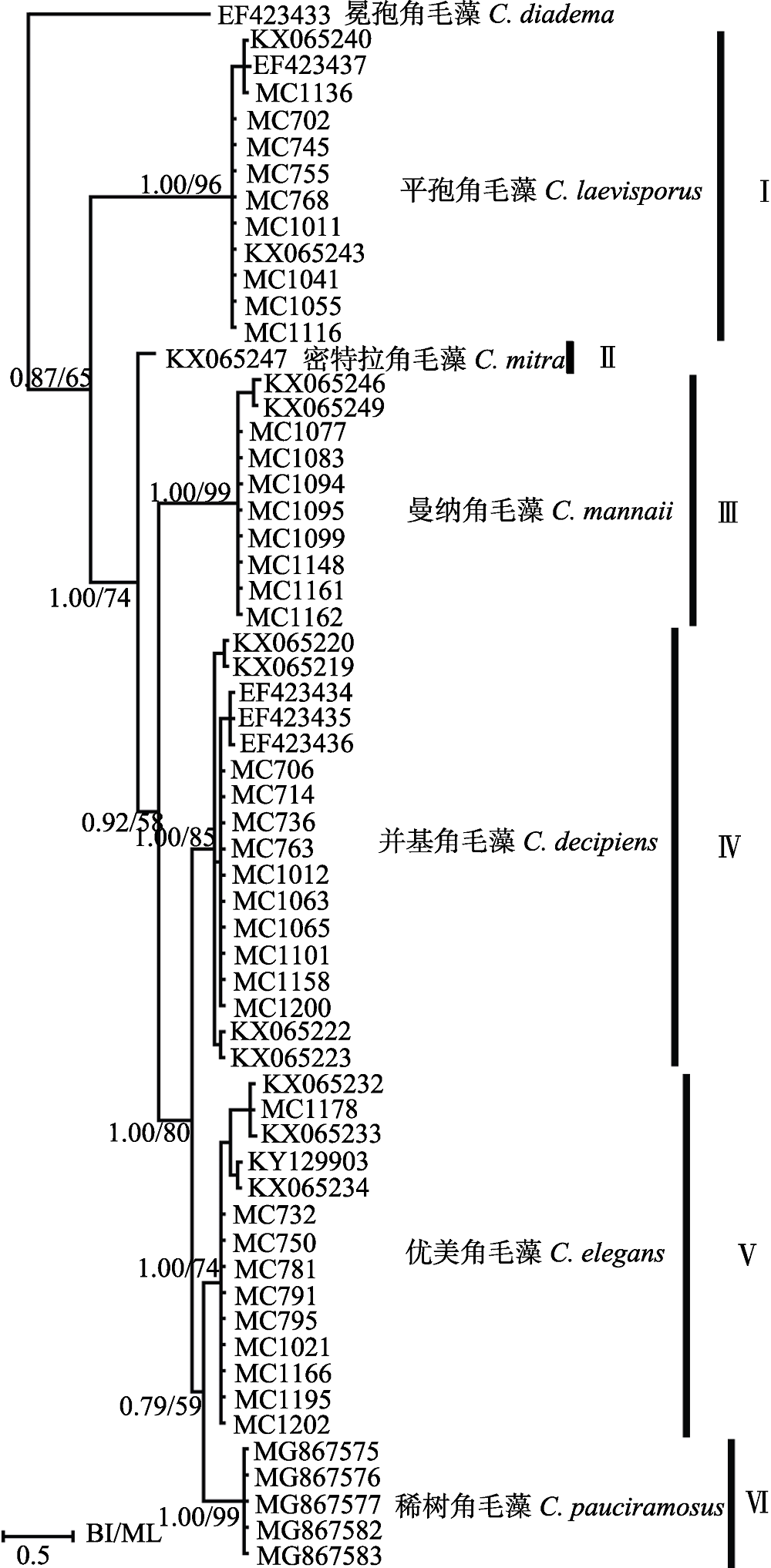
Fig. 7 Molecular phylogenetic tree inferred from LSU rDNA, with Chaetoceros diadema as outgroup. Supporting values on each nodule are from Bayesian and Maximum Likelihood analysis.
| 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 0.081 (52) | ||||
| 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 0.105 (69) | 0.047 (33) | |||
| 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 0.089 (58) | 0.028 (20) | 0.057 (38) | ||
| 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 0.083 (53) | 0.036 (25) | 0.067 (44) | 0.027 (17) | |
| 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 0.092 (60) | 0.040 (26) | 0.059 (39) | 0.028 (18) | 0.028 (21) |
Table 1 Genetic distance among allied taxa within the Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex (data in the brackets are numbers of different base pairs)
| 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 0.081 (52) | ||||
| 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 0.105 (69) | 0.047 (33) | |||
| 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 0.089 (58) | 0.028 (20) | 0.057 (38) | ||
| 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 0.083 (53) | 0.036 (25) | 0.067 (44) | 0.027 (17) | |
| 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 0.092 (60) | 0.040 (26) | 0.059 (39) | 0.028 (18) | 0.028 (21) |
| 特征 Character | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 洛氏角毛藻 C. lorenzianus type material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 角毛孔纹形状 Seta poroid shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 水滴状 Drop-shaped | 椭圆形 Oval | 椭圆形 Oval | 细长形 Elongated | 圆形或椭圆形 Round or oval | 圆形 Oval |
| 角毛孔纹大小 Seta poroid size (μm) | 0.3-0.6 (0.4 ± 0.1) | 0.3-1.6 (0.7 ± 0.3) | 0.3-0.9 (0.6 ± 0.1) | 0.8-1.5 (1.1 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.6 (0.3 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) | Nd Nd |
| 角毛孔纹密度 Seta poroid number in 10 μm | 14-25 (20.2 ± 3.6) | 6-27 (18.7 ± 5.0) | 11-17 (14.1 ± 1.9) | 6-10 (7.9 ± 1.0) | 18-44 (31.7 ± 5.4) | 30-56 (39.8 ± 7.4) | 5-9 (7.2 ± 1.7) |
| Brunel 型 Brunel group | I I | I I | I I | I I | I I | II II | I I |
| 角毛基部并行融合Fusion of seta bases | 有或无 Present/absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 短或无 Short/absent | 无 Absent | 有 Present |
| 休眠孢子 Resting spore | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 壳面平滑 Smooth | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支? Two branching processes? |
| 窗孔形状 Aperture shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 圆形或四边形 Rounded or quadrangular | 椭圆形 Oval | 六边形 Hexagonal | 六边形或花生形 Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 六边形或花生形Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 圆形或六边形 Oval or hexagonal |
| 角毛基部 Basal part of setae | 无 Lacking | 有且明显 Distinct | 无 Lacking | 短 Short | 短 Short | 无 Lacking | 无 Lacking |
| 壳面及壳套孔纹 Poroids on valve face and mantle | 有 Yes | 有 Yes | 无 No | 无 No | 有 Yes | 无 No | nd nd |
Table 2 Morphological comparison among allied taxa within Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex
| 特征 Character | 并基角毛藻 C. decipiens | 优美角毛藻 C. elegans | 平孢角毛藻 C. laevisporus | 曼纳角毛藻 C. mannaii | 稀树角毛藻 C. pauciramosus | 密特拉角毛藻 C. mitra | 洛氏角毛藻 C. lorenzianus type material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 角毛孔纹形状 Seta poroid shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 水滴状 Drop-shaped | 椭圆形 Oval | 椭圆形 Oval | 细长形 Elongated | 圆形或椭圆形 Round or oval | 圆形 Oval |
| 角毛孔纹大小 Seta poroid size (μm) | 0.3-0.6 (0.4 ± 0.1) | 0.3-1.6 (0.7 ± 0.3) | 0.3-0.9 (0.6 ± 0.1) | 0.8-1.5 (1.1 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.6 (0.3 ± 0.1) | 0.1-0.3 (0.2 ± 0.1) | Nd Nd |
| 角毛孔纹密度 Seta poroid number in 10 μm | 14-25 (20.2 ± 3.6) | 6-27 (18.7 ± 5.0) | 11-17 (14.1 ± 1.9) | 6-10 (7.9 ± 1.0) | 18-44 (31.7 ± 5.4) | 30-56 (39.8 ± 7.4) | 5-9 (7.2 ± 1.7) |
| Brunel 型 Brunel group | I I | I I | I I | I I | I I | II II | I I |
| 角毛基部并行融合Fusion of seta bases | 有或无 Present/absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 无 Absent | 短或无 Short/absent | 无 Absent | 有 Present |
| 休眠孢子 Resting spore | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 壳面平滑 Smooth | 未发现 Unknown | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支 Two branching processes | 有二叉分支? Two branching processes? |
| 窗孔形状 Aperture shape | 椭圆形 Oval | 圆形或四边形 Rounded or quadrangular | 椭圆形 Oval | 六边形 Hexagonal | 六边形或花生形 Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 六边形或花生形Hexagonal or peanut shaped | 圆形或六边形 Oval or hexagonal |
| 角毛基部 Basal part of setae | 无 Lacking | 有且明显 Distinct | 无 Lacking | 短 Short | 短 Short | 无 Lacking | 无 Lacking |
| 壳面及壳套孔纹 Poroids on valve face and mantle | 有 Yes | 有 Yes | 无 No | 无 No | 有 Yes | 无 No | nd nd |
| [1] |
Chen ZY, Li Y ( 2017) Preliminary study on some taxonomic puzzles of Chaetoceros decipiens Cleve. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41, 914-922. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 陈作艺, 李扬 ( 2017) 并基角毛藻若干分类学疑问的初步探讨. 水生生物学报, 41, 914-922.]
DOI URL |
|
| [2] |
Chen ZY, Lundholm N, Moestrup Ø, Kownacka J, Li Y ( 2018) Chaetoceros pauciramosus sp. nov. (Bacillariophyceae), a widely distributed brackish water species in the C. lorenzianus complex. Protist, 169, 615-631.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chin TG, Chen JH, Huang KG ( 1965) Marine Planktonic Diatoms from China Sea, p. 115. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 金德祥, 陈金环, 黄凯歌 ( 1965) 中国海洋浮游硅藻类, 见115页. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [4] | Chin TG ( 1951) A list of Chinese diatoms from 1847 to 1946. Amoy Fishries Bulletin, 5, 145-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金德祥 ( 1951) 中国硅藻目录. 厦门水产学报, 5, 145-230.] | |
| [5] | Chu SP, Kuo YC ( 1957) Studies on the genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg from the fishing ground of the mackerel, Pneumatophorus japonicus (Houttuyn), off the Shantung coastal from Chefoo to Weihai. Part I. A systematic study. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1, 27-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱树屏, 郭玉洁 ( 1957) 烟台、威海鲐鱼渔场及其附近海区角毛硅藻属的研究. I. 分类的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 1, 27-87.] | |
| [6] | Chu SP, Kuo YC ( 1958) Studies on the genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg from the fishing ground of the mackerel, Pneumatophorus japonicus (Houttuyn), off the Shanung coast from Chefoo to Weihai. Part II. An ecological study. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1, 167-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱树屏, 郭玉洁 ( 1958) 烟台、威海鲐鱼渔场及其附近海区角毛硅藻属的研究. II. 生态的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 1, 167-179.] | |
| [7] | Evensen DL, Hasle GR ( 1975) The morphology of some Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae) species as seen in the electron microscopes. Nova Hedwigia, 53, 152-174. |
| [8] | Grunow A ( 1863) About some new and insufficiently known species and genera of diatoms. Negotiations of the Imperial Royal Zoological-Botanical Society in Vienna, 13, 137-162. |
| [9] | Guo YJ ( 1963) The nature of Chaetoceros flora of the Yellow Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 5, 322-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭玉洁 ( 1963) 黃海角毛藻属(Genus Chaetoceros Ehrenberg)区系的性质. 海洋与湖沼, 5, 322-332.] | |
| [10] | Guo YJ, Qian SB ( 2003) Flora Algarum Marinarum Sinicarum, Tomus V. Bacillariophyta, No.1 Centricae, pp. 345-346. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郭玉洁, 钱树本 ( 2003) 中国海藻志 (第5卷): 硅藻门 (第一册), 中心纲. 345-346页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | Hall TA ( 1999) BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Window 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95-98. |
| [12] | Hasle GR, Syvertsen EE ( 1997) Marine diatoms. In: Identifying Marine Phytoplankton (ed. Tomas CR), pp. 5-387. Academic Press, London. |
| [13] |
Hernández-Becerril DU ( 1996) A morphological study of Chaetoceros species (Bacillariophyta) from the plankton of the Pacific Ocean of Mexico. Bulletin of the Natural History Museum (Botany series), 26, 1-73.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Jensen KG, Moestrup ? ( 1998) The genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae) in inner Danish coastal waters. Nordic Journal of Botany, 18, 88.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kooistra WHCF, Sarno D, Hernández-Becerril DU, Assmy P, Prisco CD, Montresor M ( 2010) Comparative molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses of taxa in the Chaetocerataceae (Bacillariophyta). Phycologia, 49, 471-500.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kownacka J, Edler L, Gromisz S, ?otocka M, Olenina I, Ostrowska M, Piwosz K ( 2013) Non-indigenous species Chaetoceros cf. lorenzianus Grunow 1863— A new, predominant component of autumn phytoplankton in the southern Baltic Sea. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 119, 101-111.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li Y, Boonprakob A, Gaonkar CC, Kooistra WHCF, Lange CB, Hernández-Becerril DU, Chen ZY, Moestrup ?, Lundholm N ( 2017) Diversity in the globally distributed diatom genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae): Three new species from warm-temperate waters. PLoS ONE, 12, 1-38. |
| [18] |
Lin GM, Yang QL ( 2007) Species diversity and the distribution of micro-phytoplankton in the Taiwan Strait. Biodiversity Science, 15, 31-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 林更铭, 杨清良 ( 2007) 台湾海峡小型浮游植物的物种多样性和分布特征. 生物多样性, 15, 31-45.]
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
Lundholm N, Daugbjerg N, Moestrup ? ( 2002) Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo- nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA. European Journal of Phycology, 37, 115-134.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T ( 2010) Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, pp.1-8.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Nylander JAA ( 2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden. |
| [22] | Okamura K ( 1911) Some littoral diatoms of Japan. Report Imperial Fisheries Institute Tokyo Japan. 7, 3-18. |
| [23] | Rines JEB, Hargraves PE ( 1988) The Chaetoceros Ehrenberg (Bacillariophyceae) flora of Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, USA. Bible Phycology, 79, 5-196. |
| [24] |
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A ( 2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539-542.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Round FE, Crawford RM, Mann DG ( 1990) The Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera, p. 747. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [26] | Wang Y, Nie R, Li Y, Lü SH ( 2010) Species diversity and geographical distribution of Chaetoceros in Guangdong coast waters. Advance in Marine Science, 28, 342-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王艳, 聂瑞, 李扬, 吕颂辉 ( 2010) 广东沿海角毛藻(Chaetoceros)的种类多样性及其地理分布. 海洋科学进展, 28, 342-352.] | |
| [27] |
Xue B, Sun J, Li TT ( 2016) Phytoplankton community structure of northern South China Sea in summer of 2014. Haiyang Xuebao, 8, 54-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 薛冰, 孙军, 李婷婷 ( 2016) 2014年夏季南海北部浮游植物群落结构.海洋学报, 8, 54-65.]
DOI URL |
|
| [28] | Yang Y, Sun J, Guan XY, Zhai WD, Guo SJ ( 2016) Seasonal variation of net-phytoplankton community in Bohai Sea. Marine Science Bulletin, 35, 121-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨阳, 孙军, 关翔宇, 翟惟东, 郭术津 ( 2016) 渤海网采浮游植物群集的季节变化. 海洋通报, 35, 121-131.] | |
| [29] | Zhai MY, Zhu SY, Chen ZY, Li Y ( 2017) Preliminary study on the species diversity of Chaetoceros lorenzianus complex from Guangdong coastal waters. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41, 1282-1290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 翟梦怡, 朱素英, 陈作艺, 李扬 ( 2017) 广东沿海洛氏角毛藻复合群物种多样性的探究. 水生生物学报, 41, 1282-1290.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Hong Deyuan. A brief discussion on methodology in taxonomy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [7] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn