



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 400-408. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018256 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018256
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yifeng Hu1, Wenhua Yu1, Yang Yue1, Zhenglanyi Huang1, Yuchun Li2, Yi Wu1,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-21
Accepted:2018-12-31
Online:2019-04-20
Published:2019-06-05
Contact:
Yi Wu
Yifeng Hu, Wenhua Yu, Yang Yue, Zhenglanyi Huang, Yuchun Li, Yi Wu. Species diversity and potential distribution of Chiroptera on Hainan Island, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 400-408.
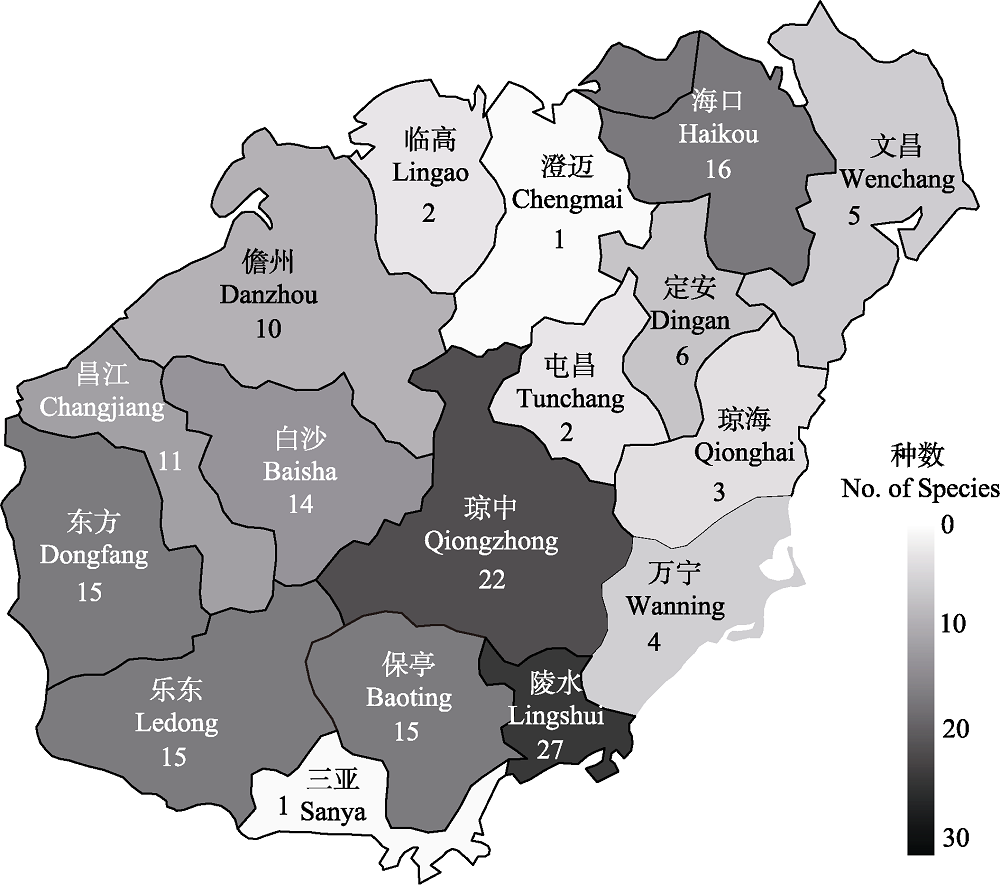
Fig. 2 The distribution of bat species in different city of Hainan Island. The darker colors show areas with higher bat biodiversity, figures represent the number of species.
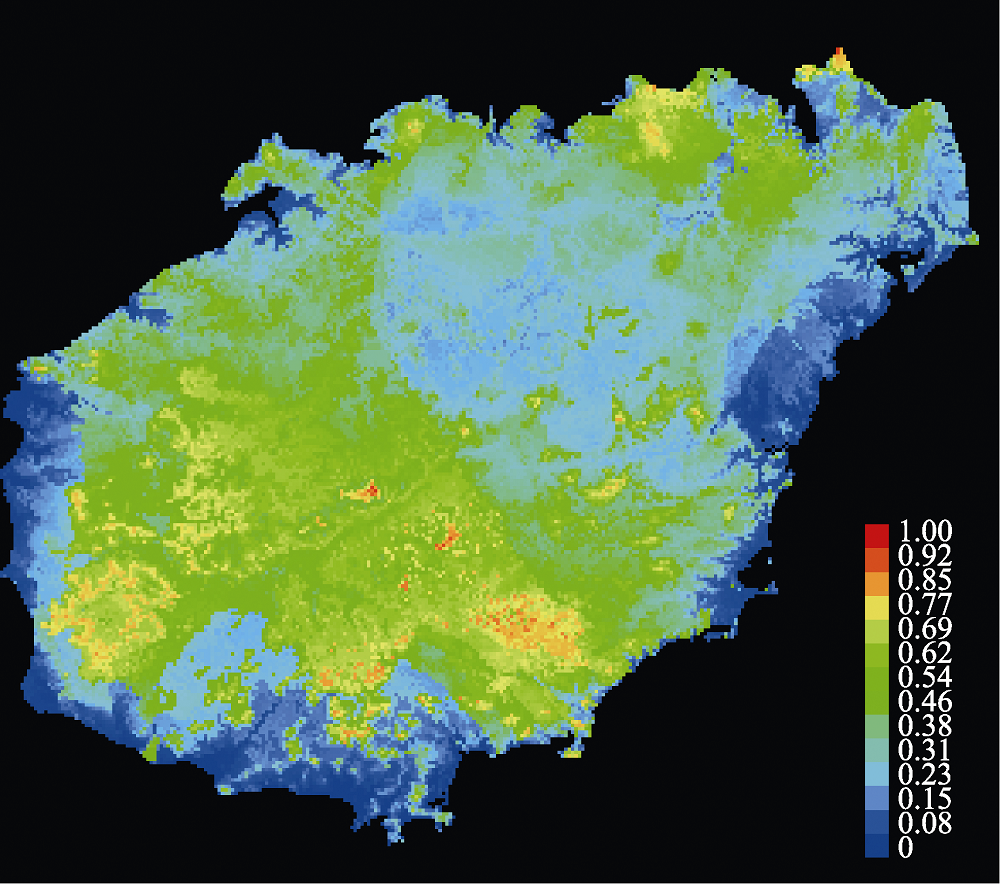
Fig. 4 Suitable habitat distribution of bats in Hainan Island. The species existing probability range from 0 to 1. Warmer colors show areas with higher predicted probability, red is the highest, dark blue is the lowest.
| [1] |
Buckley LB, Davies TJ, Ackerly DD, Kraft NJB, Harrison SP, Anacker BL, Cornell HV, Damschen EI, Grytnes JA, Hawkins BA, McCain CM, Stephens PR, Wiens JJ (2010) Phylogeny, niche conservatism and the latitudinal diversity gradient in mammals. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 2131-2138.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T (2006) Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 19, 531-545.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Che XF, Zhang JH, Huang HJ, Liu SJ, Zhang MJ (2014) Climate regionalization in Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 34(6), 60-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 车秀芬, 张京红, 黄海静, 刘少军, 张明洁 (2014) 海南岛气候区划研究. 热带农业科学, 34(6), 60-65.] | |
| [4] | Cui SP, Luo X, Li CW, Hu HJ, Jiang ZG (2018) Predicting the potential distribution of white-lipped deer using the MaxEnt model. Biodiversity Science, 26, 171-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 崔绍朋, 罗晓, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 蒋志刚 (2018) 基于MaxEnt模型预测白唇鹿的潜在分布区. 生物多样性, 26, 171-176.] | |
| [5] |
Daszak P (2010) Bats, in black and white. Science, 329, 634-635.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Drummond MJ, McCarthy JJ, Sinha M, Spratt HM, Volpi E, Esser KA, Rasmussen BB (2011) Aging and microRNA expression in human skeletal muscle: A microarray and bioinformatics analysis. Physiological Genomics, 43, 595-603.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792-1797.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Francis CM, Eger JL (2012) A review of tube-nosed bats (Murina) from Laos with a description of two new species. Acta Chiropterologica, 14, 15-38.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Gao SH, Huang ZM, Zhang TQ, Lin X (1988) Climate of Hainan Island. China Meteorological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 高素华, 黄增明, 张统钦, 林熙 (1988) 海南岛气候. 气象出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] |
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Hu YF, Li F, Wu Y, Li YC, Yu WH (2018) New record of Harpiocephalus harpia in Hainan Province. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 38(3), 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡宜峰, 黎舫, 吴毅, 李玉春, 余文华 (2018) 海南省蝙蝠新记录——毛翼管鼻蝠. 浙江林业科技, 38(3), 85-88.] | |
| [12] | Jiang HS, Song XJ, Liao WB, Li TH, Wu Y, Jin JH, Zou FS, Dong SY, Yi ZS, Zhou GY, Song B, Ke MH (2006) The Biodiversity and Its Conservation of Diaoluo Mountain, Hainan, China. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 江海声, 宋晓军, 廖文波, 李泰辉, 吴毅, 金建华, 邹发生, 董仕勇, 易祖盛, 周光益, 宋斌, 柯铭辉 (2006) 海南吊罗山生物多样性及其保护. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [13] | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.] | |
| [14] | Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY (2017) China’s mammal diversity (2nd edition). Biodiversity Science, 24, 886-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 (2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性 (第2版). 生物多样性, 25, 886-895.] | |
| [15] | Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Feng ZJ, Li LL (2015) China’s Mammal Diversity and Geographic Distribution. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 冯祚建, 李立立 (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性及地理分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] |
Johnson JB, Edwards JW, Ford WM, Gates JE (2009) Roost tree selection by northern myotis (Myotis septentrionalis) maternity colonies following prescribed fire in a Central Appalachian Mountains hardwood forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 258, 233-242.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li DW, Yin F, Zeng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang XW (2010) Cluster analysis on the distribution patterns of Chiroptera in Hainan Island. Journal of Biology, 27(2), 16-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李德伟, 尹锋, 曾玉, 张园, 张信文 (2010) 海南岛翼手类地理分布格局的聚类分析. 生物学杂志, 27(2), 16-20.] | |
| [18] | Li YC, Meng YH, Zhang LC, Ye Q (2005) Analysis of environmental factors on geographical distribution of Chinese Chiroptera. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 51, 413-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李玉春, 蒙以航, 张利存, 叶青 (2005) 中国翼手目地理分布的环境因子影响分析. 动物学报, 51, 413-422.] | |
| [19] | Li YC, Chen Z, Long YR, Zhou F, Zhong YR (2006a) Species diversity of Chiroptera in Ma’anling volcano area, Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 41(3), 106-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李玉春, 陈忠, 龙育儒, 周锋, 钟友仁 (2006a) 海南岛马鞍岭火山口地区翼手目物种多样性. 动物学杂志, 41(3), 106-109.] | |
| [20] | Li YC, Wu Y, Chen Z (2006b) A new record of Rickett’s big-footed bat Myotis ricketti in Hainan Island of China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 26, 211-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李玉春, 吴毅, 陈忠 (2006b) 海南岛发现大足鼠耳蝠分布新纪录. 兽类学报, 26, 211-212.] | |
| [21] | Liu SY, Wu Y (2019) Handbook of the Mammals of China. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘少英, 吴毅 (2019) 中国兽类图鉴. 海峡书局出版社, 福州.] | |
| [22] | Liu ZX, Zhang YX, Zhang JS, Zhang LB (2014) Murina eleryi discovered in Hunan Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 49, 132-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘志霄, 张佑祥, 张劲硕, 张礼标 (2014) 湖南省发现艾氏管鼻蝠. 动物学杂志, 49, 132-135.] | |
| [23] |
Maine JJ, Boyles JG (2015) Bats initiate vital agroecological interactions in corn. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 12438-12443.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Manel S, Williams HC, Ormerod SJ (2001) Evaluating presence-absence models in ecology: The need to account for prevalence. Journal of Applied Ecology, 38, 921-931. |
| [25] |
Olival KJ, Hosseini PR, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Ross N, Bogich TL, Daszak P (2017) Host and viral traits predict zoonotic spillover from mammals. Nature, 546, 646-650.
DOI |
| [26] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Posada D, Crandall KL (1998) ModelTest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817-818.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Russo D, Jones G, Migliozzi A (2002) Habitat selection by the Mediterranean horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus euryale (Chiroptera: Rhinolophidae) in a rural area of southern Italy and implications for conservation. Biological Conservation, 107, 71-81.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The Neighbor-Joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406-425. |
| [30] | Shaw TH, Wang S, Lu CK, Chang LK (1966) A survey of the mammals of Hainan Island, China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 3, 260-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 寿振黄, 汪松, 陆长坤, 张鑾光 (1966) 海南岛的兽类调查. 动物分类学报, 3, 260-276.] | |
| [31] | Shi HT (2001) Retrieval of Terrestrial Vertebrates in Hainan. Hainan Publishing House, Haikou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 史海涛 (2001) 海南陆栖脊椎动物检索. 海南出版社, 海口.] | |
| [32] | Shi HT, Zhao EM, Wang LJ, Bi H, Lü SQ, Liu HN, Wang JC, Zhao H, Hong ML (2011) Amphibians and Reptiles of Hainan. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 史海涛, 赵尔宓, 王力军, 毕华, 吕顺清, 刘惠宁, 汪继超, 赵蕙, 洪美玲 (2011) 海南两栖爬行动物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Simmons NB (2005) Order Chiroptera // Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Maryland. |
| [34] | Wang YX (2003) A Complete Checklist of Mammal Species and Subspecies in China: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王应祥 (2003) 中国哺乳动物物种与亚种分类名录与分布大全. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] |
Williams-Guillén K, Prefecto I, Vandermeer J (2008) Bats limit insects in a neotropical agroforestry system. Science, 320, 70.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Wong S, Lau S, Woo P, Yuen KY (2010) Bats as a continuing source of emerging infections in humans. Reviews in Medical Virology, 17(2), 67-91. |
| [37] | Wu XY, Dong SK, Liu SL, Liu QR, Han YH, Zhang XL, Su XK, Zhao HD, Feng J (2018) Identifying priority areas for grassland endangered plant species in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on the MaxEnt model. Biodiversity Science, 26, 138-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 武晓宇, 董世魁, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 韩雨晖, 张晓蕾, 苏旭坤, 赵海迪, 冯憬 (2018) 基于MaxEnt模型的三江源区草地濒危保护植物热点区识别. 生物多样性, 26, 138-148.] | |
| [38] | Wu Y, Jiang HS, Peng HY, Li SN, Wang WY (2003) Study on the species biodiversity of mammals in Diaoluoshan Mountain. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2, 505-511. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴毅, 江海声, 彭洪元, 李仕宁, 王文毅 (2003) 吊罗山保护区哺乳动物多样性初步研究. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 2, 505-511.] | |
| [39] |
Wu Y, Li YC, Lin LK, Harada M, Chen Z, Motokawa M (2012) New records of Kerivoula titania (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from Hainan Island and Taiwan. Mammal Study, 37, 69-72.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wu Y, Motokawa M, Li YC, Harada M, Chen Z, Yu WH (2010) Karyotype of Harrison’s tube nosed bat Murina harrisoni (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae: Murininae) based on the second specimen recorded from Hainan Island, China. Mammal Study, 35, 277-279.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Xu LH, Liu ZH, Yu SM (1983) Birds and Beasts in Hainan Island, China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐龙辉, 刘振河, 余斯绵 (1983) 海南岛的鸟兽. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Xu ZX, Yu WH, Wu Y, Li F, Chen BC, Harada M, Motokawa M, Gong YN, Li YC (2014) Preliminary study on population genetic structure and taxonomy of Elery’s tube-nosed bat (Murina eleryi). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 34, 270-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐忠鲜, 余文华, 吴毅, 李锋, 陈柏承, 原田正史, 本川雅治, 龚粤宁, 李玉春 (2014) 艾氏管鼻蝠种群遗传结构初步研究及其分类探讨. 兽类学报, 34, 270-277.] | |
| [43] | Yan JA (2008) Study on Evolution History of Hainan Island’s Ecological Environment. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 颜家安 (2008) 海南岛生态环境变迁研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [44] | Yang QS, Xia L, Feng ZJ, Ma Y, Quan GQ, Wu Y (2007) A guide to the measurement of mammal skull V, Insectivora and Chiroptera. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 42(2), 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨奇森, 夏霖, 冯祚建, 马勇, 全国强, 吴毅 (2007) 兽类头骨测量标准V, 食虫目、翼手目. 动物学杂志, 42(2), 56-62.] | |
| [45] | Yu WH, Wu Y, Li YC, Jiang HS, Chen Z (2008) A new record of greater bamboo bat Tylonycteris robustula of Hainan Island. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 7, 30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余文华, 吴毅, 李玉春, 江海声, 陈忠 (2008) 海南岛发现褐扁颅蝠(Tylonycteris robustula)分布新纪录. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 7, 30-33.] | |
| [46] |
Yu WH, Li F, Csorba G, Xu ZX, Wang XY, Guo WJ, Li YC, Wu Y (2018) A revision of Kerivoula hardwickii and occurrence of K. furva (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) in China. Zootaxa, 4461, 45-56.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Zhang CJ, Wu Y (2006) Habitat selection of environment, ecological function and protection of cave bat. Bulletin of Biology, 41(5), 4-6. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张成菊, 吴毅 (2006) 洞穴型蝙蝠的栖息环境选择、生态作用及保护. 生物学通报, 41(5), 4-6.] | |
| [48] | Zhang LB, Zhu GJ, Yu DM, Ye JP, Zhang W, Hong TY, Tan M (2008) New record of Tylonycteris robustula (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) from Hainan, Guizhou, and Sichuan Province. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 28, 316-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张礼标, 朱光剑, 于冬梅, 叶建平, 张伟, 洪体玉, 谭敏 (2008) 海南、贵州和四川三省翼手类新纪录——褐扁颅蝠. 兽类学报, 28, 316-320.] | |
| [49] | Zhang RZ (1999) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 (1999) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [50] | Zhu BL, Zhu GJ, Li DW, Hong TY, Zhang XW (2008) A preliminary survey on species diversity of Chiroptera in Hainan Island. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 21, 75-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱斌良, 朱光剑, 李德伟, 洪体玉, 张信文 (2008) 海南岛翼手目物种多样性的初步调查. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 21, 75-81.] | |
| [51] | Zhu GJ, Li DW, Ye JP, Hong TY, Zhang LB (2008 a) New record of Ia io in Hainan Island, its echolocation pulses and ND1 analysis. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43, 69-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱光剑, 李德伟, 叶建平, 洪体玉, 张礼标 (2008 a) 南蝠海南岛分布新纪录、回声定位信号和ND1分析. 动物学杂志, 43, 69-75.] | |
| [52] | Zhu GJ, Han NJ, Hong TY, Tan M, Yu DM, Zhang LB (2008 b) Echolocation call, roost and ND1 sequence analysis of new record of Nyctalus plancyi (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) on Hainan Island. Zoological Research, 29, 447-451. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱光剑, 韩乃坚, 洪体玉, 谭敏, 于冬梅, 张礼标 (2008 b) 海南属种新纪录——中华山蝠的回声定位信号、栖息地及序列分析. 动物学研究, 29, 447-451.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Yaqing Liao, Zefeng Huang, Xiaoyun Wang, Libiao Zhang, Yi Wu, Wenhua Yu. An updated checklist of Chiroptera in Guangdong Province and a molecular barcode database [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24584-. |
| [4] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn