



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 24423. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024423 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024423
• Original Papers:Biosafety and Nature Conservation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guo Yutong1, Li Sucui2, Wang Zhi3, Xie Yan4, Yang Xue5, Zhou Guangjin2, You Chunhe5, Zhu Saning2, Gao Jixi2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-21
Accepted:2024-12-27
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-02-27
Contact:
*E-mail: gjx@nies.org
Supported by:Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423.
| 植物 Plants | 动物 Animals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数 Number of species | 相对保护率 Relative protection rate (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 相对保护率 Relative protection rate (%) | |
| 极危 CR | 51 | 39.23 | 69 | 76.66 |
| 濒危 EN | 115 | 48.11 | 81 | 86.17 |
| 易危 VU | 154 | 63.63 | 112 | 90.32 |
| 特有种 Endemic species | 193 | 48.86 | 94 | 85.45 |
| 总物种数 Total number of species | 549 | 71.95 | 540 | 85.58 |
Table 1 The number and relative protected rate of national key protected endangered plant species in nature reserves in China
| 植物 Plants | 动物 Animals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数 Number of species | 相对保护率 Relative protection rate (%) | 物种数 Number of species | 相对保护率 Relative protection rate (%) | |
| 极危 CR | 51 | 39.23 | 69 | 76.66 |
| 濒危 EN | 115 | 48.11 | 81 | 86.17 |
| 易危 VU | 154 | 63.63 | 112 | 90.32 |
| 特有种 Endemic species | 193 | 48.86 | 94 | 85.45 |
| 总物种数 Total number of species | 549 | 71.95 | 540 | 85.58 |
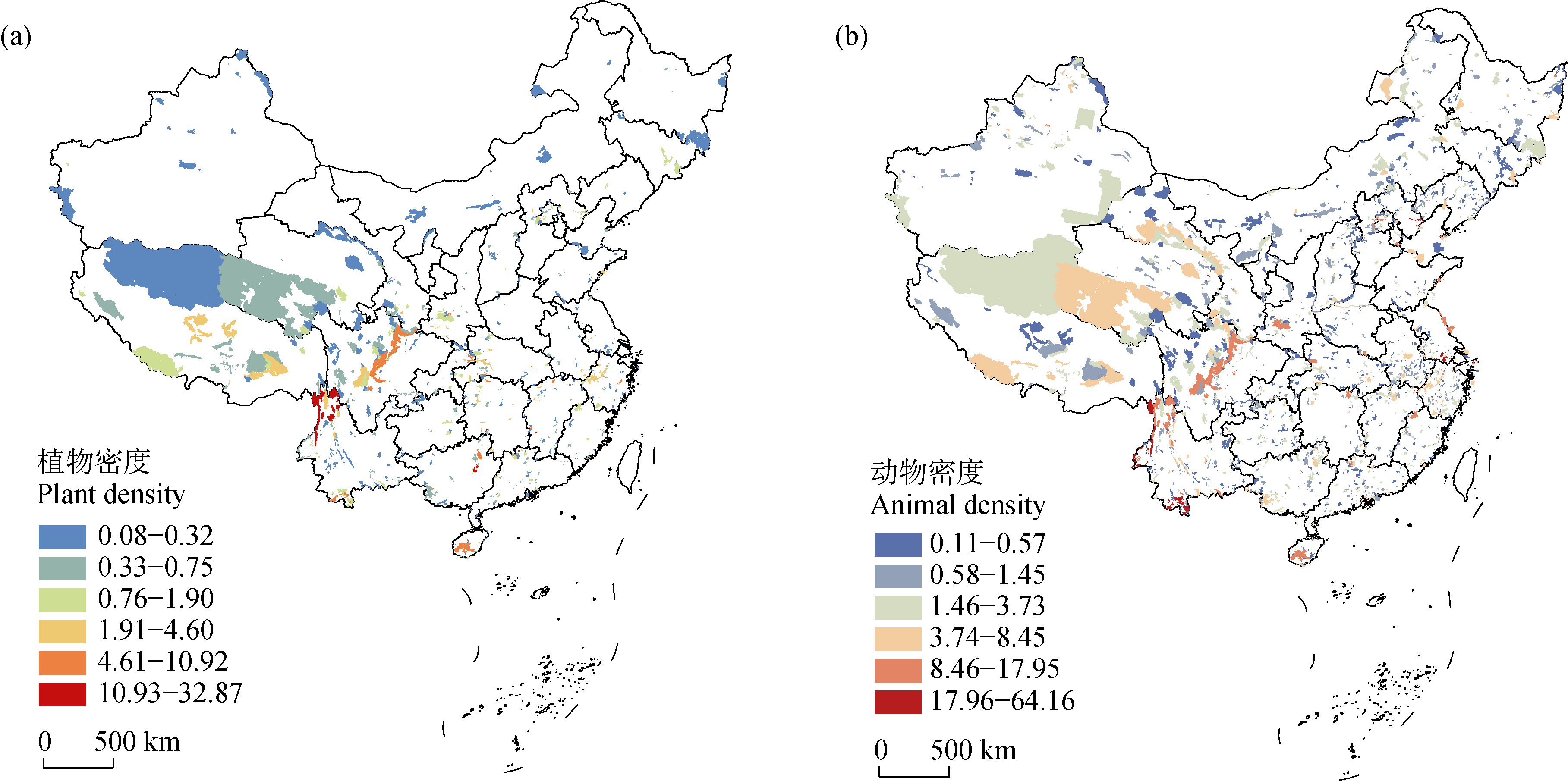
Fig. 3 Density distribution map of national key protected wild plants (a) and animals (b) in China’s nature reserves. Data for Taiwan Province, Hong Kong and Macau special administrative regions are not included in the figure.
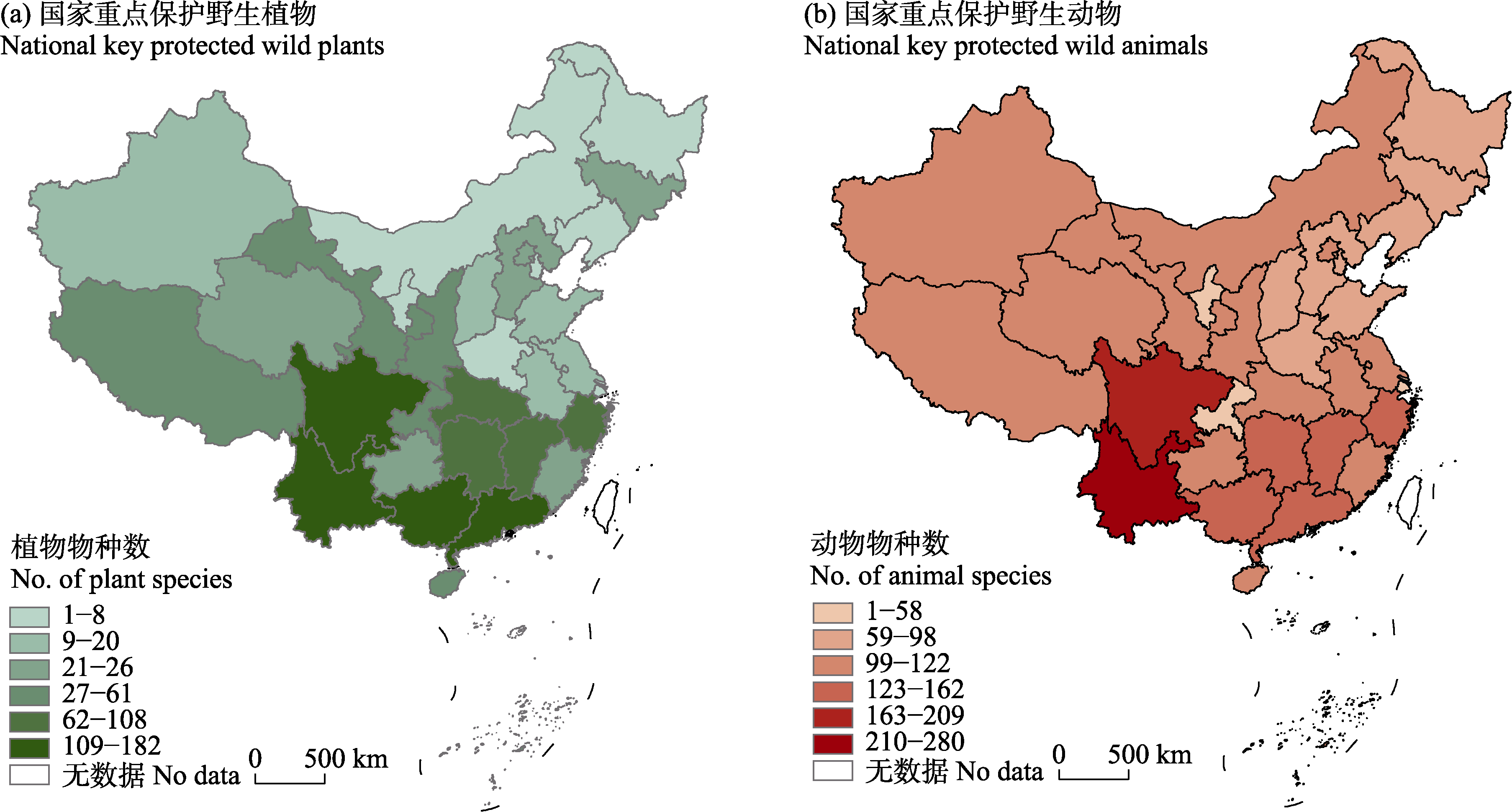
Fig. 4 Provincial distribution of national key protected wildlife in nature reserves. Data for Taiwan Province, Hong Kong and Macau special administrative regions are not included in the figure.
| [1] | Cao L, Liang F, Zou H, Lai XW(2012) Study on the diversity of rare and endangered plants in Guanshan Natural Reserve of Jiangxi Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40, 1696-1698, 1711. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹岚, 梁芳, 邹红, 赖学文 (2012) 江西官山国家级自然保护区珍稀植物多样性研究. 安徽农业科学, 40, 1696-1698, 1711.] | |
| [2] | Huang XW, Lin CT, Ji LQ(2020) The persistent multi-dimensional biases of biodiversity digital accessible knowledge of birds in China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 29, 3287-3311. |
| [3] | Jiang MK, Wang Z, Qin WH, He ZH(2006) Effectiveness of national priority wildlife protection in nature reserves. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 22(4), 35-38, 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋明康, 王智, 秦卫华, 贺昭和 (2006) 我国自然保护区内国家重点保护物种保护成效评价. 生态与农村环境学报, 22(4), 35-38, 102.] | |
| [4] | Lei JC, Xu HG, Wu J, Guan QW, Ding H, Cui P(2015) Advance in predicting the suitable habitat of species under future climate change. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 34, 794-800. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 雷军成, 徐海根, 吴军, 关庆伟, 丁晖, 崔鹏 (2015) 气候变化情景下物种适宜生境预测研究进展. 四川动物, 34, 794-800.] | |
| [5] | Li JH, Zhang SW, Yang XB, Li DH, Qi CL, Huang Y, Zhang X, Hao JW, Liang CQ, Zhu ZC, Jiang YX, Wang CY, He YQ(2024) Composition and floristic characteristics of national key protected wild plants distributed in Hainan Province, China. Guihaia, 44, 2021-2032. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李婧涵, 张顺卫, 杨小波, 李东海, 戚春林, 黄耀, 张翔, 郝杰威, 梁彩群, 朱子丞, 江悦馨, 王重阳, 何亦绮 (2024) 海南省分布的国家重点保护野生植物组成及区系特征. 广西植物, 44, 2021-2032.] | |
| [6] | Ma JZ, Rong K, Cheng K(2012) Research and practice on biodiversity in situ conservation in China: Progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 20, 551-558. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 马建章, 戎可, 程鲲 (2012) 中国生物多样性就地保护的研究与实践. 生物多样性, 20, 551-558.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Mao CZ, Zhang Y, Li JY, Zhu ZB, Lü XY, Wang CB, Bu YQ, Yang YN(2023) Pilot monitoring research of conservation rate of key species. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 15(4), 6-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛成责, 张咏, 李继影, 朱泽斌, 吕学研, 王晨波, 卜亚谦, 杨雅楠 (2023) 重点生物物种保护率试点监测研究. 环境监控与预警, 15(4), 6-13.] | |
| [8] | Qian H, Deng T, Beck J, Sun H, Xiao C, Jin Y, Ma KP(2018) Incomplete species lists derived from global and regional specimen-record databases affect macroecological analyses: A case study on the vascular plants of China. Journal of Biogeography, 45, 2718-2729. |
| [9] | UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2021) Making Peace with Nature. (accessed on 2024-10-15) https://www.unep.org/resources/making-peace-nature. |
| [10] | Wang LN, He SW, Zhao RR, Feng HN(2021) List of state key protected wildlife in Foping National Nature Reserve. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, 49(6), 28-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王兰宁, 何少文, 赵荣荣, 冯花妮 (2021) 陕西佛坪国家级自然保护区国家重点保护野生动物名录. 陕西林业科技, 49(6), 28-32.] | |
| [11] | Wang W, Li JS(2021) In-situ conservation of biodiversity in China: Advances and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 29, 133-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伟, 李俊生 (2021) 中国生物多样性就地保护成效与展望. 生物多样性, 29, 133-149.] | |
| [12] | Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB(2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 (2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [13] | Wei XZ, Pu YH, Shi HW, Xiao ZQ, Jiang MX(2024) Geographic distribution and research progresses of National Key Protected Wild Plants in Hubei Province. Guihaia, 44, 2000-2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏新增, 蒲云海, 史红文, 肖之强, 江明喜 (2024) 湖北省国家重点保护野生植物分布与研究进展. 广西植物, 44, 2000-2009.] | |
| [14] | Xia X, Zhang HN, Guo C, Qian ZD, Gao J, Xu WG, Zhou DQ, Jiang MK(2018) Evaluation of in-situ conservation of mammals in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3712-3717. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 夏欣, 张昊楠, 郭辰, 钱者东, 高军, 徐网谷, 周大庆, 蒋明康 (2018) 我国哺乳动物就地保护状况评估. 生态学报, 38, 3712-3717.] | |
| [15] | Xu CG, Wei GY, Dang GL, Huang YF, Nong Y, Hu RC(2024) Investigation and diversity analysis of medicinal plant resources in Nandan County of Guangxi. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 47, 308-312. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐传贵, 韦贵元, 党桂兰, 黄云峰, 农友, 胡仁传 (2024) 广西南丹县药用植物资源调查与多样性研究. 中药材, 47, 308-312.] | |
| [16] | Xu WH, Zhao L, Han M, Ouyang ZY(2023) Assessment of species conservation status by national park planning. National Park, 1, 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐卫华, 赵磊, 韩梅, 欧阳志云 (2023) 国家公园空间布局物种保护状况评估. 国家公园(中英文), 1, 11-16.] | |
| [17] | Yan LJ, Yang WK, Lin GJ, Dong P(2013) Impact of global warming on forest ecosystem. Tropical Geography, 33, 621-627. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 严力蛟, 杨伟康, 林国俊, 董萍 (2013) 气候变暖对森林生态系统的影响. 热带地理, 33, 621-627.] | |
| [18] | Yuan H, Zhang YB, Qin HN, Liu Y, Yu M(2009) The in situ conservation of state key protected wild plants in national nature reserves in China. Biodiversity Science, 17, 280-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 苑虎, 张殷波, 覃海宁, 刘燕, 喻梅 (2009) 中国国家重点保护野生植物的就地保护现状. 生物多样性, 17, 280-287.]
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Zhou SL, Xu C, Dong WP, Cheng T(2015) Application of DNA barcoding to conservation of highly valued, rare and endangered species. Biodiversity Science, 23, 288-290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 周世良, 徐超, 董文攀, 程涛 (2015) DNA条形码技术在珍稀濒危物种保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 23, 288-290.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Zhou YD, Chen SC, Hu GW, Mwachala G, Yan X, Wang QF(2018) Species richness and phylogenetic diversity of seed plants across vegetation zones of Mount Kenya, East Africa. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 8930-8939.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [15] | Wu Hui, Yu Le, Du Zhenrong, Zhao Qiang, Qi Wenchao, Cao Yue, Wang Jinzhou, Shen Xiaoli, Sun Yao, Ma Keping. Rapid assessment of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework implementation progress based on remote sensing monitoring: Pathway and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24526-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()