



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 24532. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024532 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024532
• Special Feature: How the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework Becomes a Mainstream Work Objective in the China’s System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liu Li1,2, Zang Mingyue1,2, Ma Yue1,2, Wan Yaqiong1,2, Hu Feilong1,2, Lu Xiaoqiang1,2, Liu Yan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-01
Accepted:2025-03-05
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-05
Contact:
*E-mail: liuyan@nies.org
Supported by:Liu Li, Zang Mingyue, Ma Yue, Wan Yaqiong, Hu Feilong, Lu Xiaoqiang, Liu Yan. Measures, progress and prospects of central-local cooperation in the implementation of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24532.
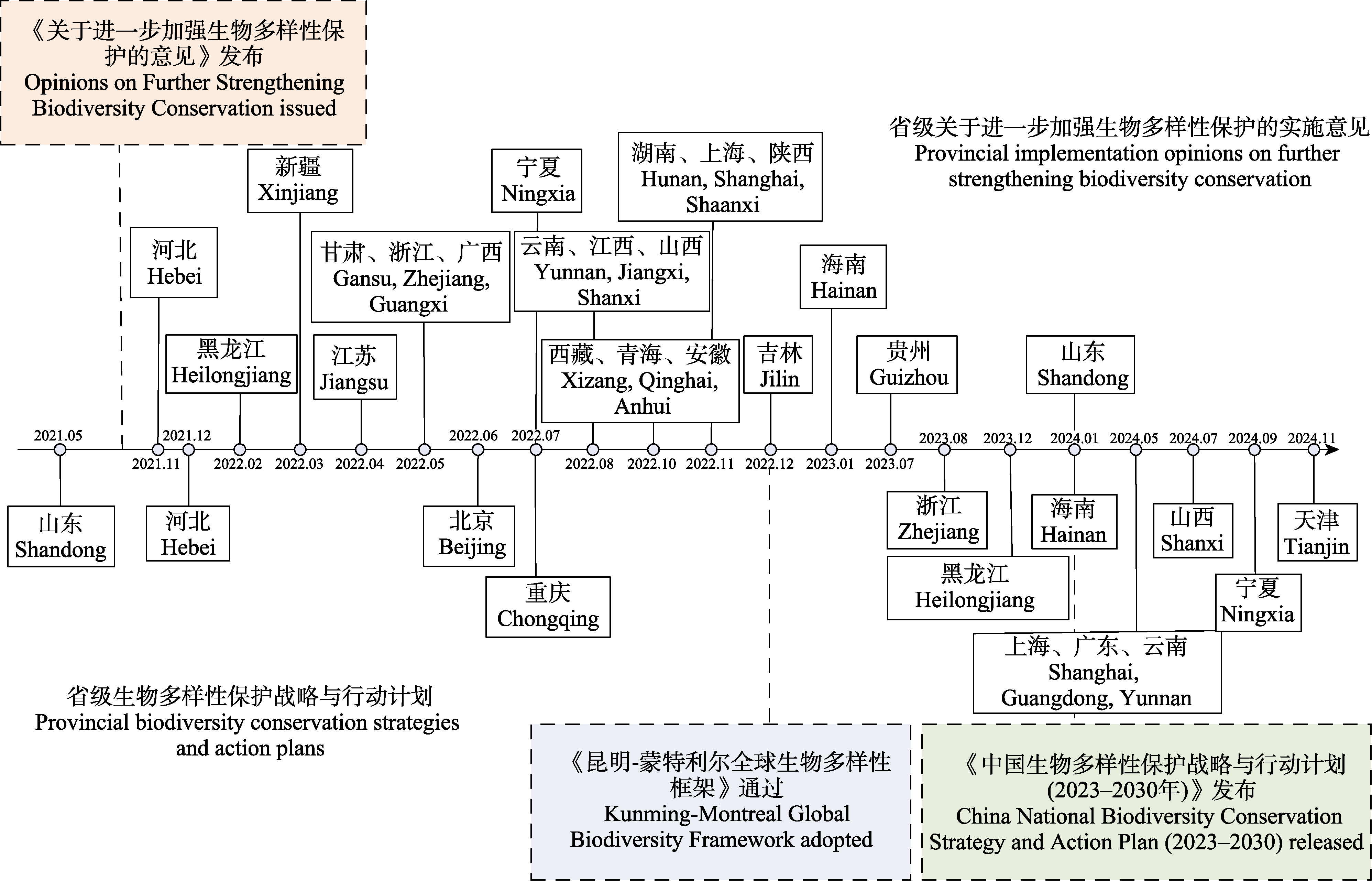
Fig. 1 Provincial implementation opinions on further strengthening biodiversity conservation and biodiversity conservation strategies and action plans released
| [1] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2008) CBD/COP/DEC/IX/28: Promoting Engagement of Cities and Local Authorities. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-09/cop-09-dec-28-en.pdf. |
| [2] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2010) CBD/COP/DEC/X/22: Plan of Action on Subnational Governments, Cities and Other Local Authorities for Biodiversity. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-10/cop-10-dec-22-en.pdf/. |
| [3] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2022a) CBD/COP/DEC/15/4: Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-15/cop-15-dec-04-en.pdf. |
| [4] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2022b) CBD/COP/DEC/15/6: Mechanisms for Planning, Monitoring, Reporting and Review. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-15/cop-15-dec-06-en.pdf. |
| [5] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2022c) CBD/COP/DEC/15/12: Engagement with Subnational Governments, Cities and Other Local Authorities to Enhance Implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-15/cop-15-dec-12-en.pdf. |
| [6] |
Cui CY, Hou YL, Wang TY, Wen YL(2022) Biodiversity conservation supported by finance: Global practice and policy enlightenment. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 崔楚云, 侯一蕾, 王天一, 温亚利 (2022) 金融支持生物多样性保护: 全球实践及政策启示. 生物多样性, 30, 22326.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Deutz A, Heal GM, Niu R, Swanson E, Townshend T, Zhu L, Delmar A, Meghji A, Sethi SA, Tobin-de la Puente J (2020) Financing Nature: Closing the Global Biodiversity Financing Gap. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://www.paulsoninstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/FINANCING-NATURE_Full-Report_Final-with-endorsements_101420.pdf. |
| [8] | He J, Xie J, Liu GH(2017) Analysis and outlook on the economic policies in biodiversity conservation. Environment and Sustainable Development, 42(6), 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何军, 谢婧, 刘桂环 (2017) 生物多样性保护经济政策分析及展望. 环境与可持续发展, 42(6), 20-25.] | |
| [9] |
Hu XH, Zhang L, Zhou YW, He WH(2020) Present situation and analysis of standards for coastal wetland ecological restoration in China. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(6), 131-139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 胡雪红, 张立, 周炎武, 何伟宏 (2020) 我国滨海湿地生态修复领域规范的现状与分析. 热带海洋学报, 39(6), 131-139.]
DOI |
|
| [10] | Huang FX, Wang YS(2001) Difficulties and counter-measuers for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 9, 399-406. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄富祥, 王跃思 (2001) 试论生物多样性保护理论与实践面临的困难及现实出路. 生物多样性, 9, 399-406.] | |
| [11] | IISD (International Institute for Sustainable Development) (2022) Summary Report on the 4th Meeting of the Open-ended Working Group on the Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework. (accessed on 2025-01-21) https://enb.iisd.org/fourth-meeting-working-group-post-2020-global-biodiversity-framework-summary. |
| [12] | IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services) (2019) Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. (accessed on 2025-01-20) https://www.ipbes.net/global-assessment. |
| [13] | Li XQ, Dong ZF, Ge CZ, Li XL(2022) Study on innovative policy for financing biodiversity. Environmental Protection, 50(8), 28-31. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李晓琼, 董战峰, 葛察忠, 李晓亮 (2022) 生物多样性保护的金融政策创新研究. 环境保护, 50(8), 28-31.] | |
| [14] |
Li YX, Li YY, Zhang YXY, Liu WH(2023) The progress and prospect of the financial arrangements under the Convention on Biological Diversity. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23077. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李亦欣, 李圆圆, 张杨心怡, 刘文慧 (2023) 《生物多样性公约》资金问题最新进展及展望. 生物多样性, 31, 23077.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | Liu S, Li P, Feng ZZ(2019) Eco-restoration research progress and strategy about wind-break and sand-fixation forest in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolitan Region. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38, 267-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘硕, 李品, 冯兆忠 (2019) 京津冀防风固沙植被生态修复研究进展与对策. 生态学杂志, 38, 267-274.] | |
| [16] | Luo MF, Yang M, Ma KP(2023) Core targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Framework and recommendations for conservation action in China. Guihaia, 43, 1350-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗茂芳, 杨明, 马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》核心目标与我国的保护行动建议. 广西植物, 43, 1350-1355.] | |
| [17] |
Ma KP(2023) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: An important global agenda for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23133. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[ 马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》是重要的全球生物多样性保护议程. 生物多样性, 31, 23133.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Meng R, Zhang LR, Xue DY(2021) China’s synergy of biodiversity conservation and poverty alleviation. Journal of Minzu University of China (Natural Sciences Edition), 30(4), 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孟锐, 张丽荣, 薛达元 (2021) 中国生物多样性保护与减贫协调增效. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 30(4), 39-44.] | |
| [19] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2019) China’s Sixth National Report on the Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 生态环境部 (2019) 中国履行《生物多样性公约》第六次国家报告. 中国环境出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Qin TB(2022) On the paradigm shift of legal regulation of biodiversity conservation. Frontiers, (4), 42-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦天宝 (2022) 论生物多样性保护法律规制的范式转变. 人民论坛 · 学术前沿 (4), 42-51.] | |
| [21] | Ren H, Guo ZH(2021) Progress and prospect of biodiversity conservation in China. Ecological Science, 40, 247-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任海, 郭兆晖 (2021) 中国生物多样性保护的进展及展望. 生态科学, 40, 247-252.] | |
| [22] | SCBD (Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity) (2020) Global Biodiversity Outlook 5. (accessed on 2025-01-17) https://www.cbd.int/gbo/gbo5/publication/gbo-5-en.pdf. |
| [23] | Sha T, Li Q, Meng ZJ, Fu ML, Liu JW, Zhong LN(2022) Blue Book of Ecological Development: Report on the Development of Ecotourism in China (2022-2023). Social Sciences Academic Press (China), Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 沙涛, 李群, 孟志军, 傅梦麟, 刘基伟, 钟栎娜 (2022) 生态发展蓝皮书: 中国生态旅游发展报告(2022-2023). 社会科学文献出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] | UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2021) Making Peace with Nature: A Scientific Blueprint to Tackle the Climate, Biodiversity and Pollution Emergencies. (accessed on 2025-01-17) https://www.unep.org/resources/making-peace-nature. |
| [25] | Wang Q, Gao HJ(2019) Current situation, problems and future direction for governance of black and odorous water bodies in Chinese cities. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 13, 507-510. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王谦, 高红杰 (2019) 我国城市黑臭水体治理现状、问题及未来方向. 环境工程学报, 13, 507-510.] | |
| [26] |
Wang Y, Zhang FC, Nan X, Li HT, Liu HO(2022) Financial issues of the Convention on Biological Diversity and its reference for China’s CBD implementation. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22401. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王也, 张风春, 南希, 李宏涛, 刘海鸥 (2022) 《生物多样性公约》资金问题分析及对我国履约的启示. 生物多样性, 30, 22401.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Wei FW, Ping XG, Hu YB, Nie YG, Zeng Y, Huang GP(2021) Main achievements, challenges, and recommendations of biodiversity conservation in China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36, 375-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 平晓鸽, 胡义波, 聂永刚, 曾岩, 黄广平 (2021) 中国生物多样性保护取得的主要成绩、面临的挑战与对策建议. 中国科学院院刊, 36, 375-383.] | |
| [28] | WWF (World Wildlife Fund) (2024) Living Planet Report 2024—A System in Peril. (accessed on 2025-01-17) https://wwflpr.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/2024-lpr-executive-summary.pdf. |
| [29] |
Xu J, Wang JZ, Li JS(2022) Progress, pathways and suggestions on business engagement in biodiversity mainstreaming. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22078. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 徐靖, 王金洲, 李俊生 (2022) 商业界参与生物多样性主流化的进展、路径与建议. 生物多样性, 30, 22078.] | |
| [30] |
Yang R, Peng QY, Cao Y, Zhong L, Hou SY, Zhao ZC, Huang C(2019) Transformative changes and paths toward biodiversity conservation in China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1032-1040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 杨锐, 彭钦一, 曹越, 钟乐, 侯姝彧, 赵智聪, 黄澄 (2019) 中国生物多样性保护的变革性转变及路径. 生物多样性, 27, 1032-1040.]
DOI |
|
| [31] | Zhang LR, Luo M, Zhu ZX, Sun YQ, Jin SC, Yang CY, Meng R, Zhang LJ(2023) Implementation path of biodiversity mainstreaming in China under the guidance of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. Guihaia, 43, 1356-1365. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张丽荣, 罗明, 朱振肖, 孙雨芹, 金世超, 杨崇曜, 孟锐, 张丽佳 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》指引下中国生物多样性主流化实施路径探析. 广西植物, 43, 1356-1365.] | |
| [32] | Zhang Y, Liu BH, Liu L, Yang C(2021) Integrated treatment of eutrophic water in the river course with hard river banks: A case study of Chaisang River. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15, 3875-3882. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张怡, 刘本洪, 刘蕾, 杨春 (2021) 硬质河岸和水体富营养化河道的综合治理技术: 以柴桑河为例. 环境工程学报, 15, 3875-3882.] | |
| [33] |
Zhao FW, Li YS, Chen H(2024) Reflections on biodiversity legislation in China’s new era. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24027. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 赵富伟, 李颖硕, 陈慧 (2024) 新时期我国生物多样性法制建设思考. 生物多样性, 32, 24027.]
DOI |
|
| [34] |
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Ding LM(2024) Implications of the rhino bond for China green bond market and Kunming Biodiversity Fund. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24363. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 赵阳, 王也, 丁黎明 (2024) “犀牛债券”对我国绿色债券和昆明生物多样性基金的启示. 生物多样性, 32, 24363.]
DOI |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()