



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 24143. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024143 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024143
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dekui He*( )(
)( ), Jinnan Chen(
), Jinnan Chen( ), Liuyong Ding(
), Liuyong Ding( ), Yiyang Xu, Junhao Huang, Xiaoyun Sui(
), Yiyang Xu, Junhao Huang, Xiaoyun Sui( )
)
Received:2024-04-12
Accepted:2024-07-03
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-08-11
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Dekui He, Jinnan Chen, Liuyong Ding, Yiyang Xu, Junhao Huang, Xiaoyun Sui. The status and distribution pattern of fish diversity in the Yarlung Tsangpo River[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24143.
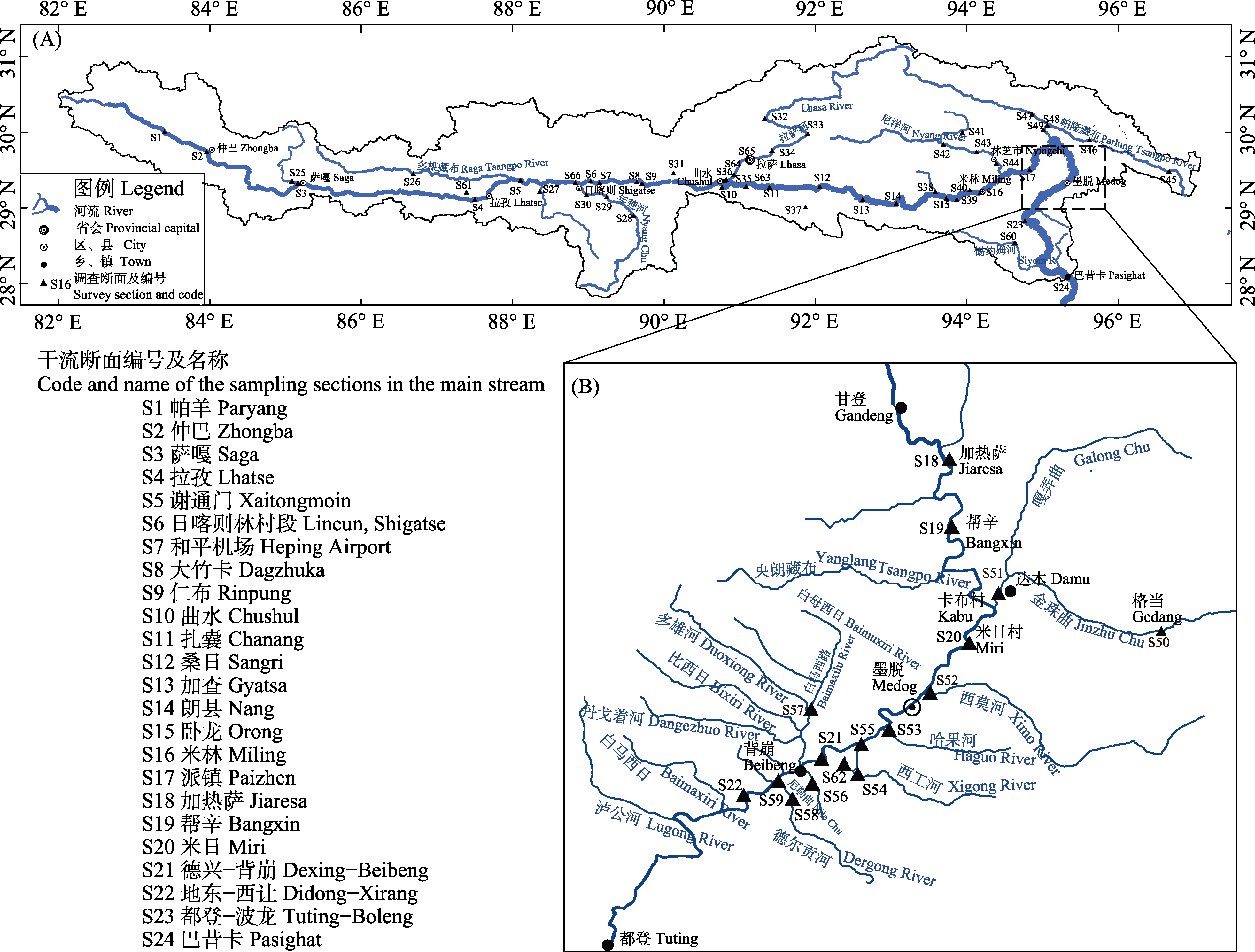
Fig. 1 The map of the Yarlung Tsangpo River system and investigation sections in this study. (A) Main river and investigation sections; (B) Enlarged view of the lower Yarlung Tsangbo River.
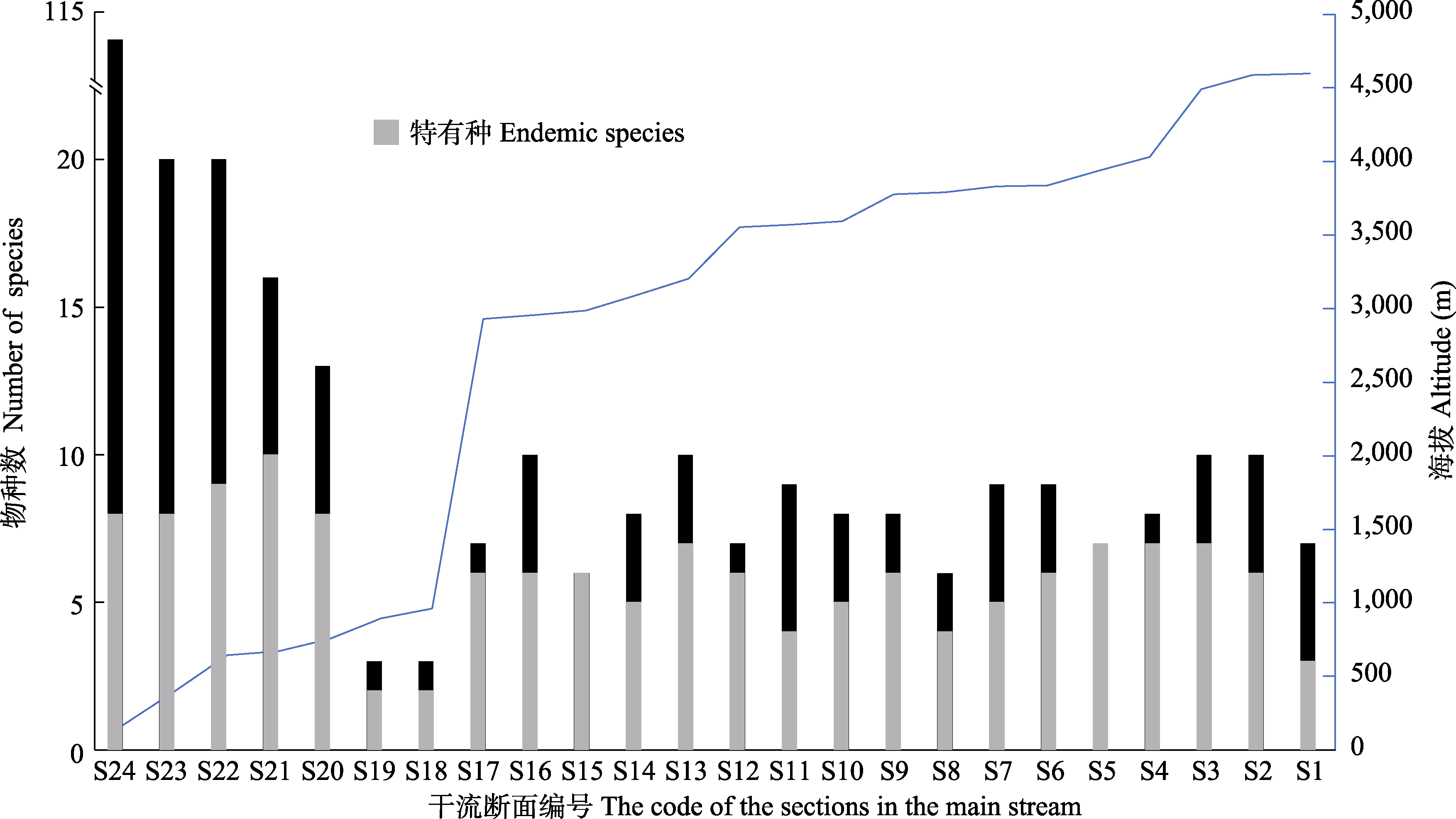
Fig. 2 Variations in endemic species and species richness along altitude (line) in the main stream of the Yarlung Tsangpo River survey sections (locations). Section codes (S) correspond to those in Appendix 1.
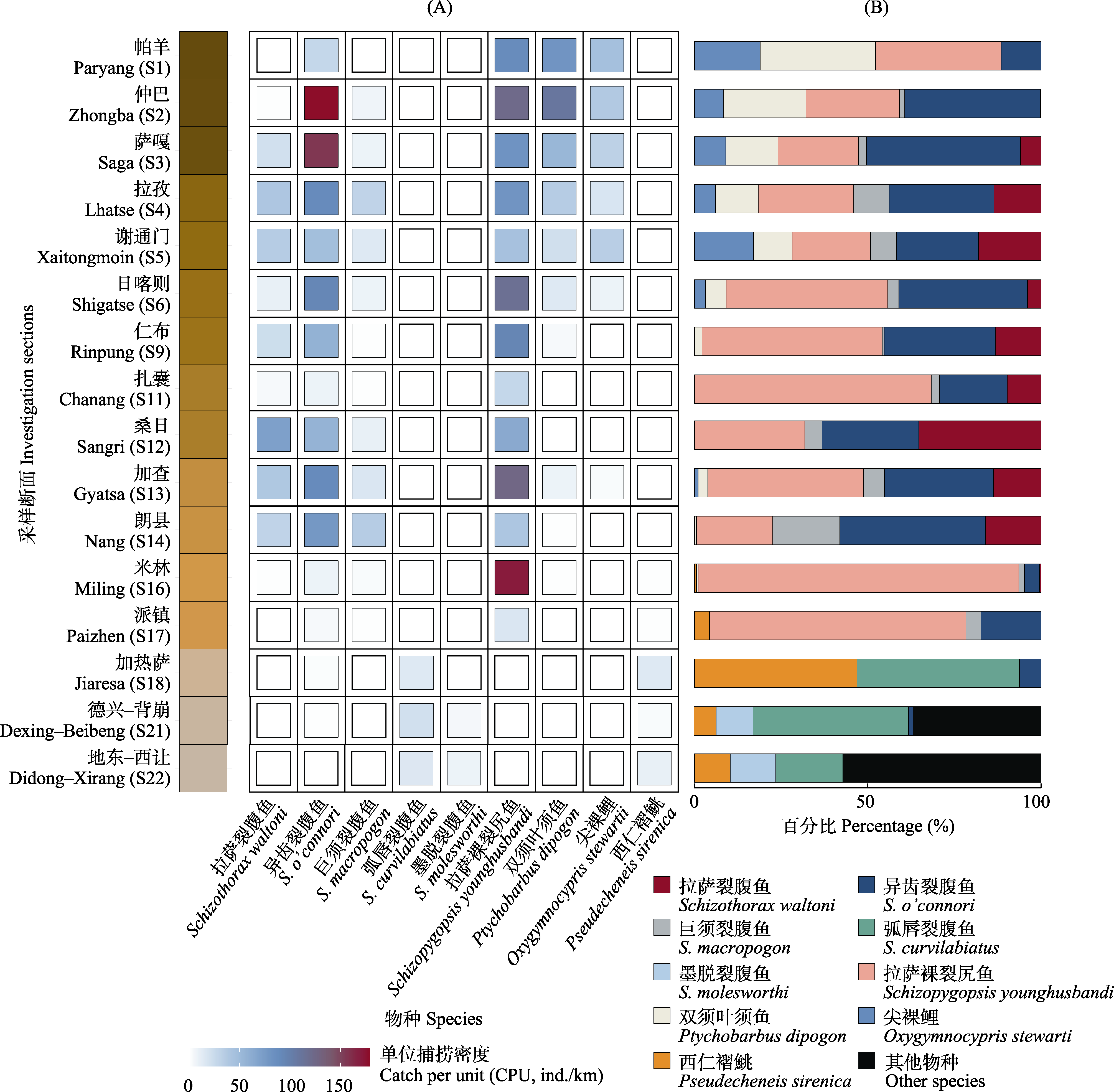
Fig. 3 The catch per unit (CPU, individuals per kilometer) of the commercial fish species in different sections catches (A), and the percentage of representative fish species in catches (B) by gill net in the Yarlung Tsangpo River mainstream. Locality codes (S) correspond to those in Appendix 1.
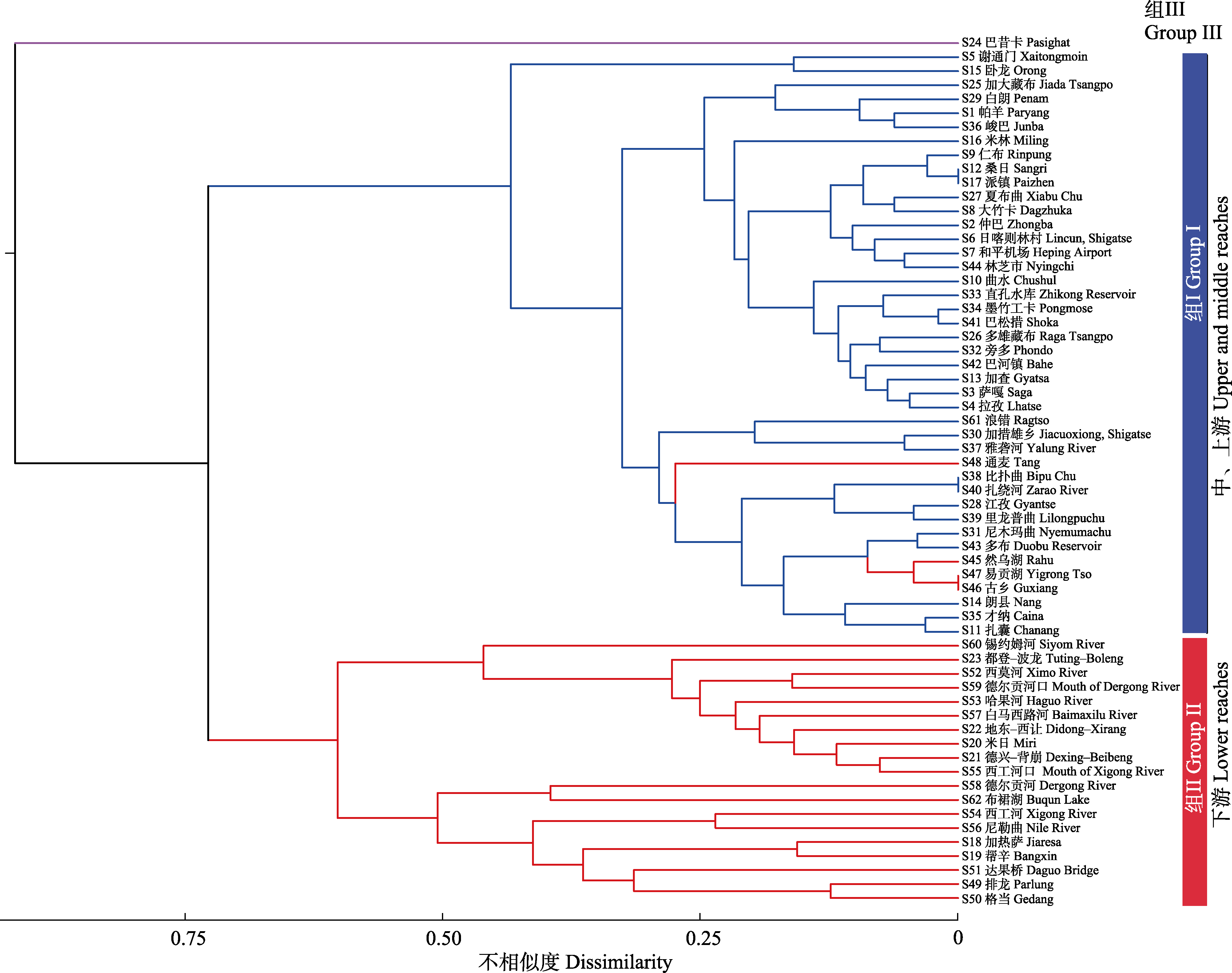
Fig. 4 The dendrograms of unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic means (UPGMA) clustering based on Taxoβdissim metrics of taxonomy relationship among sections (excluding four wetland locations) in the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin. The red lines indicate that the sections locate in the lower reaches of the river, blue indicate the upper and middle ones, and the purple indicates the Pasighat section. Section codes (S) correspond to those in Appendix 1.
| 物种 Species | 调查时期 Investigation period | 分布范围 Distribution | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001−2005 | 2006−2010 | 2011−2015 | 2016−2020 | 2021−2023 | 中游 Middle reaches | 下游 Lower reaches | |||||||
| 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | |||||||||||||
| 鳅科 Cobitidae | |||||||||||||
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | |||||||||||||
| 达里湖高原鳅 Triplophysa dalaica# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 硬刺高原鳅 Triplophysa scleroptera# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲤科 Cyprinidae | |||||||||||||
| 鲫 Carassius auratus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 银鲫 Carassius gibelio# | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 双须叶须鱼 Ptychobarbus dipogon*# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 巨须裂腹鱼 Schizothorax macropogon*# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 齐口裂腹鱼 Schizothorax prenanti# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 拉萨裂腹鱼 Schizothorax waltoni*# | + | ||||||||||||
| 鲴科 Xenocyprididae | |||||||||||||
| 草鱼 Ctenopharyngodon idella# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 鲢 Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鳙 Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 鲂 Megalobrama skolkovii# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 丁鱥科 Tincidae | |||||||||||||
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 鮈科 Gobionidae | |||||||||||||
| 棒花鱼 Abbottina rivularis# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 雅罗鱼科 Leuciscidae | |||||||||||||
| 大吻鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | |||||||||||||
| 鲇科 Siluridae | |||||||||||||
| 鲇 Silurus asotus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鮰科 Ictaluridae | |||||||||||||
| 云斑鮰 Ameiurus nebulosus# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲑形目 Salmoniformes | |||||||||||||
| 鲑科 Salmonidae | |||||||||||||
| 褐鳟 Salmo trutta# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鰕虎鱼目 Gobiiformes | |||||||||||||
| 沙塘鳢科 Odontobutidae | |||||||||||||
| 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 葛氏鲈塘鳢 Perccottus glenii | + | ||||||||||||
| 鰕虎鱼科 Gobiidae | |||||||||||||
| 波氏吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius cliffordpopei# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 合鳃鱼目 Synbranchiformes | |||||||||||||
| 合鳃科 Synbranchidae | |||||||||||||
| 黄鳝 Monopterus albus | + | + | |||||||||||
| 攀鲈目 Anabantiformes | |||||||||||||
| 鳢科 Channidae | |||||||||||||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鳉形目 Cyprinodontiformes | |||||||||||||
| 胎鳉科 Poeciliidae | |||||||||||||
| 西部食蚊鱼 Gambusia affinis# | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 颌针鱼目 Beloniformes | |||||||||||||
| 异鳉科 Adrianichthyidae | |||||||||||||
| 青鳉 Oryzias sinensis# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 合计 Total | 30 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 25 | 9 | |||||
Table 1 The information of the non-native fish species in the Yarlung Tsangpo River
| 物种 Species | 调查时期 Investigation period | 分布范围 Distribution | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001−2005 | 2006−2010 | 2011−2015 | 2016−2020 | 2021−2023 | 中游 Middle reaches | 下游 Lower reaches | |||||||
| 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | |||||||||||||
| 鳅科 Cobitidae | |||||||||||||
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | |||||||||||||
| 达里湖高原鳅 Triplophysa dalaica# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 硬刺高原鳅 Triplophysa scleroptera# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲤科 Cyprinidae | |||||||||||||
| 鲫 Carassius auratus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 银鲫 Carassius gibelio# | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 双须叶须鱼 Ptychobarbus dipogon*# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 巨须裂腹鱼 Schizothorax macropogon*# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 齐口裂腹鱼 Schizothorax prenanti# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 拉萨裂腹鱼 Schizothorax waltoni*# | + | ||||||||||||
| 鲴科 Xenocyprididae | |||||||||||||
| 草鱼 Ctenopharyngodon idella# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 鲢 Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鳙 Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 鲂 Megalobrama skolkovii# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 丁鱥科 Tincidae | |||||||||||||
| 丁鱥 Tinca tinca# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 鮈科 Gobionidae | |||||||||||||
| 棒花鱼 Abbottina rivularis# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 雅罗鱼科 Leuciscidae | |||||||||||||
| 大吻鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | |||||||||||||
| 鲇科 Siluridae | |||||||||||||
| 鲇 Silurus asotus# | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 大口鲇 Silurus meridionalis# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鮰科 Ictaluridae | |||||||||||||
| 云斑鮰 Ameiurus nebulosus# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲑形目 Salmoniformes | |||||||||||||
| 鲑科 Salmonidae | |||||||||||||
| 褐鳟 Salmo trutta# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鰕虎鱼目 Gobiiformes | |||||||||||||
| 沙塘鳢科 Odontobutidae | |||||||||||||
| 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis# | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 葛氏鲈塘鳢 Perccottus glenii | + | ||||||||||||
| 鰕虎鱼科 Gobiidae | |||||||||||||
| 波氏吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius cliffordpopei# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 合鳃鱼目 Synbranchiformes | |||||||||||||
| 合鳃科 Synbranchidae | |||||||||||||
| 黄鳝 Monopterus albus | + | + | |||||||||||
| 攀鲈目 Anabantiformes | |||||||||||||
| 鳢科 Channidae | |||||||||||||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus# | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鳉形目 Cyprinodontiformes | |||||||||||||
| 胎鳉科 Poeciliidae | |||||||||||||
| 西部食蚊鱼 Gambusia affinis# | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 颌针鱼目 Beloniformes | |||||||||||||
| 异鳉科 Adrianichthyidae | |||||||||||||
| 青鳉 Oryzias sinensis# | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 合计 Total | 30 | 9 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 25 | 9 | |||||
| [1] | Agostinho AA, Gomes LC, Veríssimo SK, Okada E (2004) Flood regime, dam regulation and fish in the Upper Paraná River: Effects on assemblage attributes reproduction and recruitment. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 14, 11-19. |
| [2] | Bagra K, Kadu K, Nebeshwar-Sharma K, Laskar BA, Sarkar UK, Das DN (2009) Ichthyological survey and review of the checklist of fish fauna of “Arunachal Pradesh”. Check List, 5, 330-350. |
| [3] | Bănărescu P (1991) Zoogeography of Fresh Waters (Vol. 2): Distribution and Dispersal of Freshwater Animals in North America and Eurasia. AULA-Verlag, Wiesbaden. |
| [4] | Baselga A, Orme CDL (2012) Betapart: An R package for the study of beta diversity. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 808-812. |
| [5] | Bhatt JP, Manish K, Pandit MK (2012) Elevational gradients in fish diversity in the Himalaya: Water discharge is the key driver of distribution patterns. PLoS ONE, 7, e46237. |
| [6] | Chaudhuri BL (1913) Zoological results of the Abor Expedition, 1911-12. XVIII. Fish. Records of the Indian Museum (Calcutta), 8, 243-257. |
| [7] | Chen F, Chen YF (2010) Investigation and protection strategies of fishes of Lhasa River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 34, 278-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈锋, 陈毅峰 (2010) 拉萨河鱼类调查及保护. 水生生物学报, 34, 278-285.] | |
| [8] | Chen YX, Tan HM, Lin PC, Zhang C, Wang L, He DK (2024) Taxonomic revision of the Sisoridae (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes) fishes of the lower Yarlung Tsangpo River, with descriptions of three new species and one new record in China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 48, 920-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈咏霞, 谭慧敏, 林鹏程, 张驰, 王琳, 何德奎 (2024) 雅鲁藏布江下游鮡科鱼类分类整理及三新种和中国一新纪录种. 水生生物学报, 48, 920-949.] | |
| [9] | Chen YY (1998) The Fishes of the Hengduan Mountains Region. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈宜瑜 (1998) 横断山区鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Chen YY, Chen YF, Liu HZ (1996) Studies on the position of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Region in zoogeographic divisions and its eastern demarcation line. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 20, 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈宜瑜, 陈毅峰, 刘焕章 (1996) 青藏高原动物地理区的地位和东部界线问题. 水生生物学报, 20, 97-103.] | |
| [11] | Chu XL, Zheng BS, Dai DY (1999) Fauna Sinica·Osteichthyes·Siluriformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [褚新洛, 郑葆珊, 戴定远 (1999) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲇形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | Darshan AD, Abujam S, Das DN (2019) Biodiversity of Fishes in “Arunachal” Himalaya: Systematics, Classification, and Taxonomic Identification. Academic Press, London. |
| [13] | Das BK, Boruah P, Kar D (2017) Icthyofaunal diversity of Siang River in “Arunachal Pradesh”. Proceedings of the Zoological Society, 70, 52-60. |
| [14] | Deng J, Dong DH, Zhang HX, Jiang W, Zhao H, Kong F, Xu TQ, Wang QJ (2020) Investigation and diversity analysis of fish resources in the Dogxung Zangbo Basin of the Yalu Tsangpo River. Genomics and Applied Biology, 39, 3468-3474. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓捷, 董滇红, 张红星, 姜维, 赵虎, 孔飞, 许涛清, 王启军 (2020) 雅鲁藏布江多雄藏布流域鱼类资源调查与多样性分析. 基因组学与应用生物学, 39, 3468-3474.] | |
| [15] | Ding HP, Qin JH, Lin SQ, Gesang D, Zhang ZM, Xie CX (2014) Exotic fishes in Chabalang Wetland of Lhasa. Journal of Hydroecology, 35(2), 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁慧萍, 覃剑晖, 林少卿, 格桑达娃, 张志明, 谢从新 (2014) 拉萨市茶巴朗湿地的外来鱼类. 水生态学杂志, 35(2), 49-55.] | |
| [16] |
Ding HP, Zhang ZM, Xie CX, Huo B (2022) Effects of fish invasion on aquatic ecosystem of the Yarlung Zangbo River and the prevention and control strategies. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41, 2440-2448. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [丁慧萍, 张志明, 谢从新, 霍斌 (2022) 鱼类入侵对雅鲁藏布江水域生态系统的影响及其防治对策. 生态学杂志, 41, 2440-2448.] | |
| [17] | Fan LQ, Liu HP, Lin J, Pu Q (2016) Non-native fishes: Distribution and assemblage structure in the Lhasa River basin, Tibet, China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 40, 958-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [范丽卿, 刘海平, 林进, 普穷 (2016) 拉萨河流域外来鱼类的分布、群落结构及其与环境的关系. 水生生物学报, 40, 958-967.] | |
| [18] | Fricke R, Eschmeyer WN, Van der Laan R (2024) Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp. (accessed on 2021-04-08) |
| [19] | Gong Z, Freyhof J, Wang J, Liu M, Liu F, Lin PC, Jiang YL, Liu HZ (2018a) Two new species of Garra (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) from the lower Yarlung Tsangpo River drainage in southeastern Tibet, China. Zootaxa, 4532, 367-384. |
| [20] | Gong Z, Lin PC, Liu F, Liu HZ (2018b) Exostoma tibetana, a new glyptosternine catfish from the lower Yarlung Tsangpo River drainage in southeastern Tibet, China (Siluriformes: Sisoridae). Zootaxa, 4527, 392-402. |
| [21] | Gong Z, Liu YC, Feng HZ, Zhu TS (2024) Fish diversity evaluation and community assembly process analysis in the Yarlung Tsangpo River based on multi-faceted indices. Journal of Lake Sciences, 36, 213-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [巩政, 刘艳超, 冯慧喆, 朱天顺 (2024) 基于多维度指数的雅鲁藏布江鱼类多样性评价及群落构建过程分析. 湖泊科学, 36, 213-222.] | |
| [22] | Guan ZH, Chen CY (1984) River and Lake in Tibet. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [关志华, 陈传友 (1984) 西藏河流与湖泊. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [23] | Gurumayum SD, Kosygin L, Tamang L (2016) Ichthyofaunal diversity of “Arunachal Pradesh”: A part of Himalaya biodiversity hotspot. International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 4, 337-346. |
| [24] | Gurumayum SD, Nath KP, Kosygin L (2020) Conservation status and endemicity of type fish species discovered from “Arunachal Pradesh”. Bulletin of “Arunachal” Forest Research, 35(1/2), 1-14. |
| [25] | He DK, Chen YF (2009) Phylogeography of Schizothorax o’connori (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Tibet. Hydrobiologia, 635, 251-262. |
| [26] | He DK, Sui XY, Sun HY, Tao J, Ding CZ, Chen YF, Chen YY (2020) Diversity, pattern and ecological drivers of freshwater fish in China and adjacent areas. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 30, 387-404. |
| [27] |
Holt BG, Lessard JP, Borregaard MK, Fritz SA, Araújo MB, Dimitrov D, Fabre PH, Graham CH, Graves GR, Jønsson KA, Nogués-Bravo D, Wang ZH, Whittaker RJ, Fjeldså J, Rahbek C (2013) An update of Wallace’s zoogeographic regions of the world. Science, 339, 74-78.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Ji F, Li L (2017) Atlas of Fishes of Xizang Plateau. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [纪锋, 李雷 (2017) 西藏鱼类图集. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Jin X, Ma B (2020) Fishes and Resources in the Lower Reaches of the Yalung Zangbo River of the Xizang Plateau. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [金星, 马波 (2020) 西藏雅鲁藏布江下游鱼类及其资源. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Johnson PT, Olden JD, Vander Zanden MJ (2008) Dam invaders: Impoundments facilitate biological invasions into freshwaters. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 6, 357-363. |
| [31] | Kundu S, Chandra K, Tyagi K, Pakrashi A, Kumar V (2019) DNA barcoding of freshwater fishes from Brahmaputra River in Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 4, 2411-2419. |
| [32] | Legendre P, Legendre L (2012) Numerical Ecology, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. |
| [33] | Li L, Ma B, Jin X, Jin HY, Wu S, Chen ZX, Cheng L, Wang NM, Hao QR (2022) Structural and diversity characteristics of fish communities in the Motuo reach of the Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 29, 1326-1336. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李雷, 马波, 金星, 金洪宇, 吴松, 陈忠祥, 程磊, 王念民, 郝其睿 (2022) 西藏雅鲁藏布江大峡谷墨脱江段鱼类群落结构及多样性的空间分布特征. 中国水产科学, 29, 1326-1336.] | |
| [34] | Li L, Wu S, Wang NM, Qin DL, Tang SZ, Jin HY, Zhu TB, Jin X, Ma B (2021) Community structure of fishery resources from the Sangri to Jiacha reach of middle Yarlung Zangbo River of Tibet, China. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 34(1), 40-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李雷, 吴松, 王念民, 覃东立, 汤施展, 金洪宇, 朱挺兵, 金星, 马波 (2021) 雅鲁藏布江中游桑日至加查江段渔业资源群落结构特征. 水产学杂志, 34(1), 40-45.] | |
| [35] | Li XX, Mu T, Wang ZW, Qian JS, Zhu R (2024) First record of the genus Schizothorax in rivers of the Central Himalayas in China. Journal of Fish Biology, 104, 497-504. |
| [36] | Linder HP (2001) Plant diversity and endemism in sub-Saharan tropical Africa. Journal of Biogeography, 28, 169-182. |
| [37] | Liu F, Li MZ, Wang J, Gong Z, Liu M, Liu HZ, Lin PC (2021) Species composition and longitudinal patterns of fish assemblages in the middle and lower Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecological Indicators, 125, 107542. |
| [38] | Liu HP, Mou ZB, Cai B, Li BH, Zhang BB, Zhou JS, Zhang C, Pan YZ, Chen MQ (2018) Coupling supply-side structural reform and technological innovation boosting the fishery resource conservation process in Tibet. Journal of Lake Sciences, 30, 266-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘海平, 牟振波, 蔡斌, 李宝海, 张忭忭, 周建设, 张驰, 潘瑛子, 陈美群 (2018) 供给侧改革与科技创新耦合助推西藏渔业资源养护. 湖泊科学, 30, 266-278.] | |
| [39] | Liu KM, Zheng Z, Gong DJ (2017) Elevational patterns of species richness and their underlying mechanism. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 541-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘开明, 郑智, 龚大洁 (2017) 物种丰富度的垂直分布格局及其形成机制. 生态学杂志, 36, 541-554.] | |
| [40] | Oksanen J, Simpson GL, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E,..., Hannigan G, Hill MO, Lahti L, McGlinn D, Ouellette M-H, Cunha ER, Smith T, Stier A, Ter Braak CJF, Weedon J (2022) vegan: Community ecology package version 2.6-2. CRAN. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. (accessed on 2023-05-10) |
| [41] |
Perrigo A, Hoorn C, Antonelli A (2020) Why mountains matter for biodiversity. Journal of Biogeography, 47, 315-325.
DOI |
| [42] | Pubu, Lhagdor, Bsang, Tsering (2010) Study on species diversity of vertebrates in the National Reserve of Lhalu Wetland, Lhasa. Journal of Tibet University, 25(3), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [普布, 拉多, 巴桑, 次仁 (2010) 西藏拉萨拉鲁湿地国家级自然保护区脊椎动物物种多样性研究. 西藏大学学报(自然科学版), 25(3), 1-7.] | |
| [43] | Qian JS, Lin SQ, Wang X, Wang HS (2023) First record of the non-native fish Rhinogobius cliffordpopei (Nichols, 1925) (Gobiiformes: Gobiidae) in Tibet, China. BioInvasions Records, 12, 1139-1146. |
| [44] | Sá-Oliveira JC, Hawes JE, Isaac-Nahum VJ, Peres CA (2015) Upstream and downstream responses of fish assemblages to an eastern Amazonian hydroelectric dam. Freshwater Biology, 60, 2037-2050. |
| [45] | Sinha B, Tamang L (2015) Ichthyofauna of “East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh”. Records of Zoological Survey of India, 115(Part-3), 241-253. |
| [46] | Sun HY, He DK, Sui XY, Chen YF (2020) Predicting impacts of future climate change and hydropower development towards habitats of native and non-native fishes. Science of the Total Environment, 707, 135419. |
| [47] | Talwar P, Jhingran A (1992) Inland Fishes of India and Adjacent Countries, Vols. 1-2. Oxford & IBH Publishing Company, New Delhi. |
| [48] | Tao J, Ding CZ, Chen JN, Ding LY, Brosse S, Heino J, Hermoso V, Wu RD, Wang ZW, Hu JX, Che RX, Jin XW, Ji SH, He DK (2023) Boosting freshwater fish conservation with high-resolution distribution mapping across a large territory. Conservation Biology, 37, e14036. |
| [49] | van der Laan R, Fricke R, Eschmeyer WN (2024) Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Classification. http://www.calacademy.org/scientists/catalog-of-fishes-classification/. (accessed on 2024-04-08) |
| [50] | Vishwanath W, Darshan A (2007) Two new catfish species of the genus Pseudecheneis Blyth (Teleostei: Siluriformes) from northeastern India. Zoos’ Print Journal, 22, 2627-2631. |
| [51] | Wang M, Huang J, Chen Y, He D (2024) Triplophysa shannanensis, a new species of Tibetan stone loach (Nemacheilidae) from the Yarlung Tsangpo-Brahmaputra River, Tibet. Journal of Ichthyology, 64, 177-201. |
| [52] | Wang ZW, Zhu R, Li XX, Qian JS, Sui XY (2023) First record of the non-native western mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis (Baird & Girard, 1853), in the Eastern Himalayas, China. BioInvasions Records, 12, 298-305. |
| [53] | Wu YF, Wu CZ (1992) The Fishes of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [武云飞, 吴翠珍 (1992) 青藏高原鱼类. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [54] | Xie CX, Huo B, Wei KJ, Ma BS, Qin JH (2019) Biology and Resource Conservation of Schizothoracinae Fishes in the Middle Reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [谢从新, 霍斌, 魏开建, 马宝珊, 覃剑晖 (2019) 雅鲁藏布江中游裂腹鱼类生物学与资源保护. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [55] | Yang HY, Huang DM (2011) A preliminary investigation on fish fauna and resources of the upper and middle Yalu Tsangpo River. Journal of Huazhong Normal University (Natural Sciences), 45, 629-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨汉运, 黄道明 (2011) 雅鲁藏布江中上游鱼类区系和资源状况初步调查. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 45, 629-633.] | |
| [56] | Yang YC, Li BY, Yin ZS (1983) Tibetan Landforms. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨逸畴, 李炳元, 尹泽生 (1983) 西藏地貌. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Yue PQ (2000) Fauna Sinica·Osteichthyes·Cyprinifomes (Vol. 3). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [乐佩琦 (2000) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(下). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [58] | Zhang CG, Cai B, Xu TQ (1995) Fish and Fishery in Tibet. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 蔡斌, 许涛清 (1995) 西藏鱼类及其资源. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [59] | Zhang E, Cao WX (2021) China’s Biodiversity Red List·Vertebrates (Vol. 5):Freshwater Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [张鹗, 曹文宣 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第五卷): 淡水鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [60] | Zhu R, Sui XY, Sun HH, Jia YT, Feng X, Chen YF (2022) Community structure and its changes of non-native fish from Lhalu Wetland and Chabalang Wetland in Tibet Autonomous Region. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 46, 1761-1769. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱仁, 隋晓云, 孙欢欢, 贾银涛, 冯秀, 陈毅峰 (2022) 西藏拉鲁湿地和茶巴朗湿地外来鱼类群落结构及变动趋势. 水生生物学报, 46, 1761-1769.] | |
| [61] | Zhu R, Sun H, Ji S, Li X, Jia Y, Sui X (2023) First wild record of tench, Tinca tinca (Linnaeus, 1758) in Tibet, China. BioInvasions Records, 12, 292-297. |
| [62] | Zhu SQ (1989) The Loaches of the Subfamily Nemacheilinae in China (Cypriniformes: Cobitidae). Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanjing, (in Chinese) |
| [朱松泉(1989) 中国条鳅志. 江苏科学技术出版社, 南京.] | |
| [63] | Zhu TB, Chen L, Yang DG, Ma B, Li L (2017) Distribution and habitat character of Schizothoracinae fishes in the middle Yarlung Zangbo River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 2817-2823. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱挺兵, 陈亮, 杨德国, 马波, 李雷 (2017) 雅鲁藏布江中游裂腹鱼类的分布及栖息地特征. 生态学杂志, 36, 2817-2823.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [10] | Xuan Zhou, Shengfang Zhang, Ning Liu, Yujie Lu, Sizhu Zheng, Xiaojun Yang, Yuanyuan Lu, Meike Liu, Ming Bai. Revision of the systematic status and update of Latin-English-Chinese catalogue of storage beetles [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24238-. |
| [11] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [12] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [13] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [14] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [15] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()