



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1073-1086. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021001 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021001
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhenbin Jiao1,2, Yibo Luo1,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-02
Accepted:2021-03-22
Online:2021-08-20
Published:2021-05-28
Contact:
Yibo Luo
Zhenbin Jiao, Yibo Luo. Effects of environmental and genetic factors on phenotypic traits and species classification of Dendrobium huoshanense[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(8): 1073-1086.
| 野生型 Wild type | F1代 F1 generation | F2代 F2 generation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 林间 Woodland | 温室 Greenhouse | 林间 Woodland | 温室 Greenhouse | |||
| 假鳞茎数量 Number of pseudobulbs | 93 | 202 | 355 | 221 | 500 | |
| 假鳞茎茎长 Pseudobulb length (cm) | 1.84 ± 0.85A | 5.53 ± 2.59BE | 5.80 ± 2.65BCE | 4.92 ± 2.28BD | 5.77 ± 2.83BCE | |
| 假鳞茎直径 Pseudobulb diameter (cm) | 0.45 ± 0.07A | 0.70 ± 0.12B | 0.69 ± 0.13B | 0.58 ± 0.13C | 0.59 ± 0.13C | |
| 假鳞茎茎长直径比 Length/diameter ratio of pseudobulb | 4.17 ± 2.03A | 7.98 ± 3.70B | 8.64 ± 4.24B | 9.13 ± 5.07BC | 10.16 ± 5.55C | |
| 假鳞茎节长 Internode length of pseudobulb (cm) | 0.65 ± 0.18A | 1.14 ± 0.32BE | 1.26 ± 0.36CE | 1.18 ± 0.30BcDE | 1.20 ± 0.39BCDE | |
| 假鳞茎节数 Number of pseudobulb internodes | 3.67 ± 0.81A | 6.02 ± 1.46BE | 5.75 ± 1.28Bce | 5.48 ± 1.40C | 6.05 ± 1.62BDE | |
| 花朵数量 Number of flowers | 2 | 26 | 107 | 31 | 151 | |
| 中萼片长 Dorsal sepal length (cm) | 1.35 ± 0.07A | 1.41 ± 0.16AB | 1.29 ± 0.19AC | 1.51 ± 0.26ABD | 1.44 ± 0.23ABD | |
| 中萼片宽 Dorsal sepal width (cm) | 0.60 ± 0AE | 0.68 ± 0.09Be | 0.66 ± 0.11BC | 0.66 ± 0.10aBCDE | 0.61 ± 0.09AbDE | |
| 中萼片长宽比 Length/width ratio of dorsal sepal | 2.25 ± 0.11A | 2.11 ± 0.34AB | 2.02 ± 0.34ABC | 2.29 ± 0.38ABD | 2.39 ± 0.44AD | |
| 花瓣长 Petal length (cm) | 1.40 ± 0A | 1.37 ± 0.15AB | 1.28 ± 0.21BC | 1.47 ± 0.24ABD | 1.42 ± 0.22ABD | |
| 花瓣宽 Petal width (cm) | 0.80 ± 0A | 0.80 ± 0.11A | 0.77 ± 0.14A | 0.76 ± 0.13AD | 0.68 ± 0.13d | |
| 花瓣长宽比 Length/width ratio of petal | 1.75 ± 0A | 1.74 ± 0.28AB | 1.71 ± 0.30ABC | 1.99 ± 0.41aBcD | 2.13 ± 0.39D | |
| 花梗长 Pedicel length (cm) | 2.15 ± 0.07A | 1.93 ± 0.46A | 2.11 ± 0.44A | 2.07 ± 0.43A | 2.17 ± 0.51A | |
Table 1 Differences in phenotypic traits of pseudobulbs and flowers among Dendrobium huoshanense in wild-type, F1 and F2 generations of D. huoshanense under different environments
| 野生型 Wild type | F1代 F1 generation | F2代 F2 generation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 林间 Woodland | 温室 Greenhouse | 林间 Woodland | 温室 Greenhouse | |||
| 假鳞茎数量 Number of pseudobulbs | 93 | 202 | 355 | 221 | 500 | |
| 假鳞茎茎长 Pseudobulb length (cm) | 1.84 ± 0.85A | 5.53 ± 2.59BE | 5.80 ± 2.65BCE | 4.92 ± 2.28BD | 5.77 ± 2.83BCE | |
| 假鳞茎直径 Pseudobulb diameter (cm) | 0.45 ± 0.07A | 0.70 ± 0.12B | 0.69 ± 0.13B | 0.58 ± 0.13C | 0.59 ± 0.13C | |
| 假鳞茎茎长直径比 Length/diameter ratio of pseudobulb | 4.17 ± 2.03A | 7.98 ± 3.70B | 8.64 ± 4.24B | 9.13 ± 5.07BC | 10.16 ± 5.55C | |
| 假鳞茎节长 Internode length of pseudobulb (cm) | 0.65 ± 0.18A | 1.14 ± 0.32BE | 1.26 ± 0.36CE | 1.18 ± 0.30BcDE | 1.20 ± 0.39BCDE | |
| 假鳞茎节数 Number of pseudobulb internodes | 3.67 ± 0.81A | 6.02 ± 1.46BE | 5.75 ± 1.28Bce | 5.48 ± 1.40C | 6.05 ± 1.62BDE | |
| 花朵数量 Number of flowers | 2 | 26 | 107 | 31 | 151 | |
| 中萼片长 Dorsal sepal length (cm) | 1.35 ± 0.07A | 1.41 ± 0.16AB | 1.29 ± 0.19AC | 1.51 ± 0.26ABD | 1.44 ± 0.23ABD | |
| 中萼片宽 Dorsal sepal width (cm) | 0.60 ± 0AE | 0.68 ± 0.09Be | 0.66 ± 0.11BC | 0.66 ± 0.10aBCDE | 0.61 ± 0.09AbDE | |
| 中萼片长宽比 Length/width ratio of dorsal sepal | 2.25 ± 0.11A | 2.11 ± 0.34AB | 2.02 ± 0.34ABC | 2.29 ± 0.38ABD | 2.39 ± 0.44AD | |
| 花瓣长 Petal length (cm) | 1.40 ± 0A | 1.37 ± 0.15AB | 1.28 ± 0.21BC | 1.47 ± 0.24ABD | 1.42 ± 0.22ABD | |
| 花瓣宽 Petal width (cm) | 0.80 ± 0A | 0.80 ± 0.11A | 0.77 ± 0.14A | 0.76 ± 0.13AD | 0.68 ± 0.13d | |
| 花瓣长宽比 Length/width ratio of petal | 1.75 ± 0A | 1.74 ± 0.28AB | 1.71 ± 0.30ABC | 1.99 ± 0.41aBcD | 2.13 ± 0.39D | |
| 花梗长 Pedicel length (cm) | 2.15 ± 0.07A | 1.93 ± 0.46A | 2.11 ± 0.44A | 2.07 ± 0.43A | 2.17 ± 0.51A | |
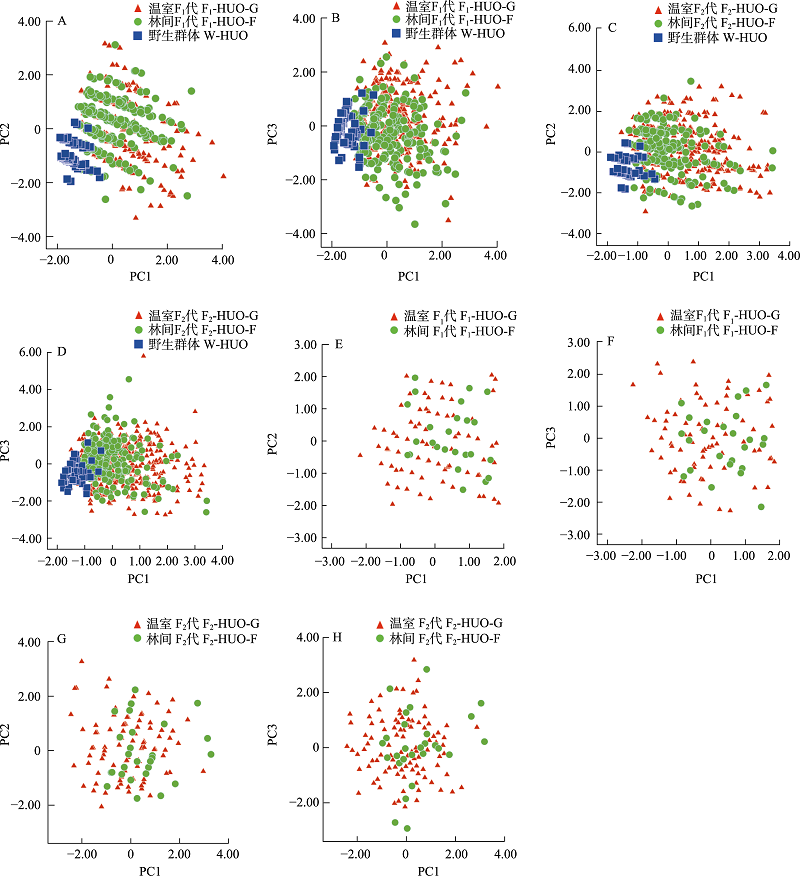
Fig. 1 Principal component analysis of pseudobulbs and flowers of Dendrobium huoshanense in different environmental conditions. A-B, PCA of pseudobulbs in wild-type (W-HUO), F1 generation under woodland (F1-HUO-F) and greenhouse (F1-HUO-G); C-D, PCA of pseudobulbs in F2 generation under woodland (F2-HUO-F) and greenhouse (F2-HUO-G); E-F, PCA of flowers in F1 generation under woodland (F1-HUO-F) and greenhouse (F1-HUO-G); G-H, PCA of flowers in F2 generation under woodland (F2-HUO-F) and greenhouse (F2-HUO-G).
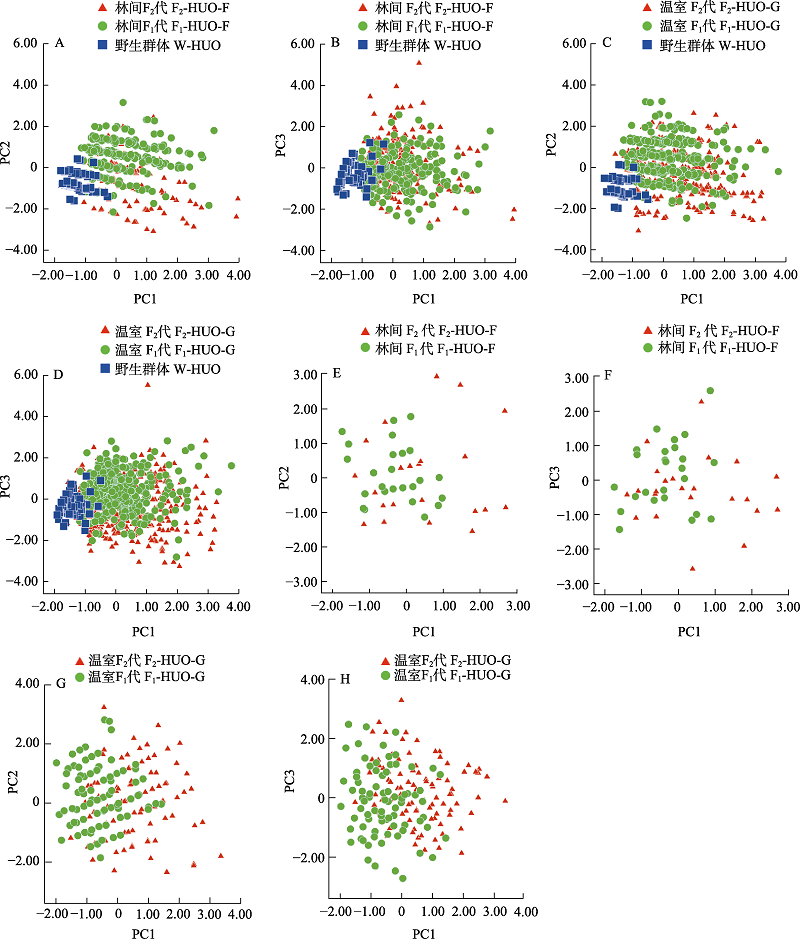
Fig. 2 Principal component analysis of pseudobulbs and flowers of Dendrobium huoshanense in different generations. A?B, PCA of pseudobulbs inwild-type (W-HUO), F1 (F1-HUO-F) and F2 generations (F2-HUO-F) under woodland; C?D, PCA of pseudobulbs in D. huoshanense in wild-type (W-HUO), F1 (F1-HUO-G) and F2 generations (F2-HUO-G) under greenhouse; E?F, PCA of flowers in F1 (F1-HUO-F) and F2 generations (F2-HUO-F) under woodland; G?H, PCA of flowers in F1 (F1-HUO-G) and F2 generations (F2-HUO-G) under greenhouse.
| 霍山石斛 D. huoshanense | 河南石斛 D. henanense | 细茎石斛 D. moniliforme | 铁皮石斛 D. catenatum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | F1 generation | F2 generation | ||||
| 假鳞茎数量 No. of pseudobulbs | 93 | 557 | 721 | 98 | 217 | 414 |
| 假鳞茎茎长 Pseudobulb length (cm) | 1.84 ± 0.85A | 5.70 ± 2.63B | 5.51 ± 2.70B | 8.76 ± 2.12C | 18.54 ± 5.87E | 14.97 ± 8.26D |
| 假鳞茎直径 Pseudobulb diameter (cm) | 0.45 ± 0.07A | 0.70 ± 0.13B | 0.59 ± 0.13C | 0.43 ± 0.06AD | 0.39 ± 0.09F | 0.53 ± 0.11E |
| 假鳞茎茎长直径比 Length/diameter ratio of pseudobulb | 4.17 ± 2.03A | 8.40 ± 4.06B | 9.84 ± 5.42C | 20.75 ± 5.90D | 48.99 ± 16.88F | 30.16 ± 19.40E |
| 假鳞茎节长 Internode length of pseudobulb (cm) | 0.65 ± 0.18A | 1.21 ± 0.35B | 1.19 ± 0.36B | 1.52 ± 0.32C | 2.38 ± 0.55D | 1.65 ± 0.57c |
| 假鳞茎节数 No. of pseudobulb internodes | 3.67 ± 0.81A | 5.85 ± 1.35B | 5.87 ± 1.58B | 8.45 ± 1.44C | 10.42 ± 2.30d | 11.17 ± 3.21D |
| 花朵数量 Number of flowers | 2 | 132 | 181 | 5 | 138 | 235 |
| 中萼片长 Dorsal sepal length (cm) | 1.35 ± 0.07A | 1.32 ± 0.19AB | 1.45 ± 0.23AC | 1.62 ± 0.15ABCD | 1.47 ± 0.27ACD | 1.77 ± 0.23ADE |
| 中萼片宽 Dorsal sepal width (cm) | 0.60 ± 0A | 0.66 ± 0.11B | 0.62 ± 0.09abC | 0.70 ± 0.09ABCD | 0.51 ± 0.08DF | 0.63 ± 0.07bCDE |
| 中萼片长宽比 Length/width ratio of dorsal sepal | 2.25 ± 0.11A | 2.03 ± 0.34AB | 2.37 ± 0.43AC | 2.35 ± 0.31ABCD | 2.90 ± 0.45ADE | 2.83 ± 0.40ADE |
| 花瓣长 Petal length (cm) | 1.40 ± 0A | 1.30 ± 0.20B | 1.43 ± 0.22ACF | 1.52 ± 0.07AbCDF | 1.49 ± 0.24DF | 1.67 ± 0.20DE |
| 花瓣宽 Petal width (cm) | 0.80 ± 0A | 0.77 ± 0.14AB | 0.69 ± 0.13C | 0.82 ± 0.04ABcD | 0.52 ± 0.09F | 0.56 ± 0.07E |
| 花瓣长宽比 Length/width ratio of petal | 1.75 ± 0A | 1.72 ± 0.29AB | 2.11 ± 0.40C | 1.86 ± 0.16ABCD | 2.92 ± 0.47E | 3.01 ± 0.46E |
Table 2 Differences in phenotypic traits of pseudobulbs and flowers among Dendrobium huoshanense and related species
| 霍山石斛 D. huoshanense | 河南石斛 D. henanense | 细茎石斛 D. moniliforme | 铁皮石斛 D. catenatum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | F1 generation | F2 generation | ||||
| 假鳞茎数量 No. of pseudobulbs | 93 | 557 | 721 | 98 | 217 | 414 |
| 假鳞茎茎长 Pseudobulb length (cm) | 1.84 ± 0.85A | 5.70 ± 2.63B | 5.51 ± 2.70B | 8.76 ± 2.12C | 18.54 ± 5.87E | 14.97 ± 8.26D |
| 假鳞茎直径 Pseudobulb diameter (cm) | 0.45 ± 0.07A | 0.70 ± 0.13B | 0.59 ± 0.13C | 0.43 ± 0.06AD | 0.39 ± 0.09F | 0.53 ± 0.11E |
| 假鳞茎茎长直径比 Length/diameter ratio of pseudobulb | 4.17 ± 2.03A | 8.40 ± 4.06B | 9.84 ± 5.42C | 20.75 ± 5.90D | 48.99 ± 16.88F | 30.16 ± 19.40E |
| 假鳞茎节长 Internode length of pseudobulb (cm) | 0.65 ± 0.18A | 1.21 ± 0.35B | 1.19 ± 0.36B | 1.52 ± 0.32C | 2.38 ± 0.55D | 1.65 ± 0.57c |
| 假鳞茎节数 No. of pseudobulb internodes | 3.67 ± 0.81A | 5.85 ± 1.35B | 5.87 ± 1.58B | 8.45 ± 1.44C | 10.42 ± 2.30d | 11.17 ± 3.21D |
| 花朵数量 Number of flowers | 2 | 132 | 181 | 5 | 138 | 235 |
| 中萼片长 Dorsal sepal length (cm) | 1.35 ± 0.07A | 1.32 ± 0.19AB | 1.45 ± 0.23AC | 1.62 ± 0.15ABCD | 1.47 ± 0.27ACD | 1.77 ± 0.23ADE |
| 中萼片宽 Dorsal sepal width (cm) | 0.60 ± 0A | 0.66 ± 0.11B | 0.62 ± 0.09abC | 0.70 ± 0.09ABCD | 0.51 ± 0.08DF | 0.63 ± 0.07bCDE |
| 中萼片长宽比 Length/width ratio of dorsal sepal | 2.25 ± 0.11A | 2.03 ± 0.34AB | 2.37 ± 0.43AC | 2.35 ± 0.31ABCD | 2.90 ± 0.45ADE | 2.83 ± 0.40ADE |
| 花瓣长 Petal length (cm) | 1.40 ± 0A | 1.30 ± 0.20B | 1.43 ± 0.22ACF | 1.52 ± 0.07AbCDF | 1.49 ± 0.24DF | 1.67 ± 0.20DE |
| 花瓣宽 Petal width (cm) | 0.80 ± 0A | 0.77 ± 0.14AB | 0.69 ± 0.13C | 0.82 ± 0.04ABcD | 0.52 ± 0.09F | 0.56 ± 0.07E |
| 花瓣长宽比 Length/width ratio of petal | 1.75 ± 0A | 1.72 ± 0.29AB | 2.11 ± 0.40C | 1.86 ± 0.16ABCD | 2.92 ± 0.47E | 3.01 ± 0.46E |
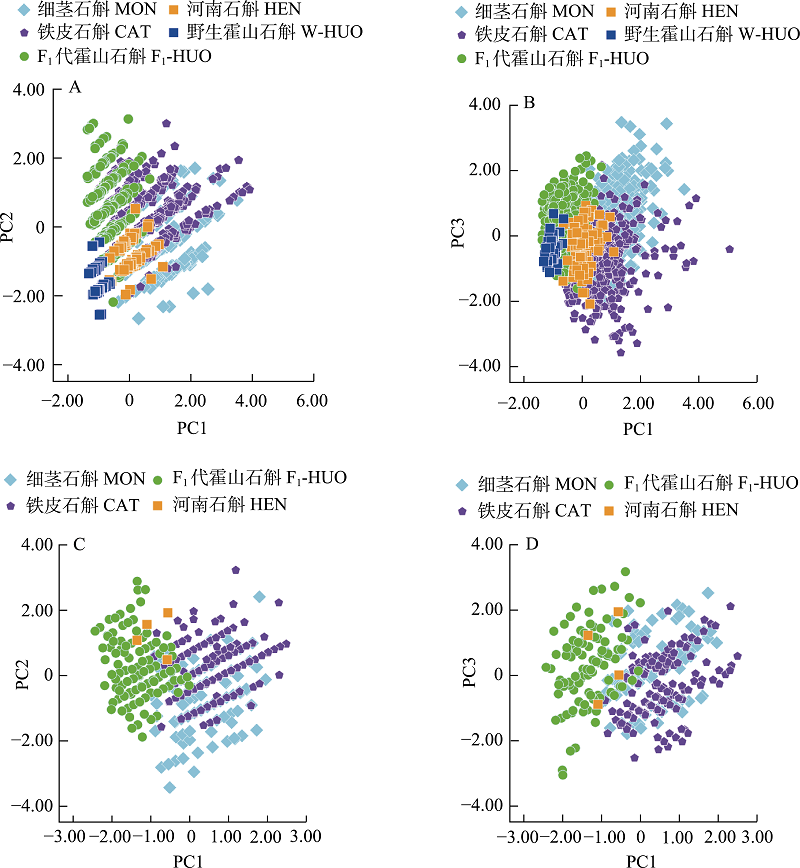
Fig. 3 Principal component analysis (PCA) of phenotypic traits of pseudobulbs and flowers in Dendrobium huoshanense in wild-type (W-HUO), F1 generation of D. huoshanense (F1-HUO), D. henanense (HEN), D. moniliforme (MON) and D. catenatum (CAT). A?B, PCA of pseudobulbs in D. huoshanense and related species; C?D, PCA of flowers in D. huoshanense and related species.
| [1] |
Adams PB (2011) Systematics of Dendrobiinae (Orchidaceae), with special reference to Australian taxa. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 166, 105-126.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Anderson JT, Inouye DW, McKinney AM, Colautti RI, Mitchell-Olds T (2012) Phenotypic plasticity and adaptive evolution contribute to advancing flowering phenology in response to climate change. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 3843-3852. |
| [3] |
Bashline L, Lei L, Li SD, Gu Y (2014) Cell wall, cytoskeleton, and cell expansion in higher plants. Molecular Plant, 7, 586-600.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Cribb P, Govaerts R (2005) Just how many orchids are there? In: Proceedings of the 18th World Orchid Conference (eds Raynal-Roques A, Roguenant A, Prat D). Naturalia Publications, Turriers. |
| [5] | Fan ZF, Xu HC, Yu RY (1992) A study on the species group age structure ofLarix gmelini population and its relation to disturbance in the north Daxinganling Mountains. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 28(1),2-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范兆飞, 徐化成, 于汝元 (1992) 大兴安岭北部兴安落叶松种群年龄结构及其与自然干扰关系的研究. 林业科学, 28(1),2-11.] | |
| [6] |
Fang W, Liu ED (2012) The development of classical plant taxonomy and iFlora. Plant Diversity and Resources, 34, 532-538. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 方伟, 刘恩德 (2012) 经典植物分类学的发展与iFlora. 植物分类与资源学报, 34, 532-538.] | |
| [7] |
Fox RJ, Donelson JM, Schunter C, Ravasi T, Gaitán-Espitia JD (2019) Beyond buying time: The role of plasticity in phenotypic adaptation to rapid environmental change. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374, 20180174.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
García-Verdugo C, Fay MF, Granado-Yela C, De Casas RR, Balaguer L, Besnard G, Vargas P (2009) Genetic diversity and differentiation processes in the ploidy series ofOlea europaea L.: A multiscale approach from subspecies to insular populations. Molecular Ecology, 18, 454-467.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
García-Verdugo C, Méndez M, Velázquez-Rosas N, Balaguer L (2010) Contrasting patterns of morphological and physiological differentiation across insular environments: Phenotypic variation and heritability of light-related traits inOlea europaea. Oecologia, 164, 647-655.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Ge S (2017) What determines species diversity? Chinese Science Bulletin, 62, 2033-2041. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 葛颂 (2017) 什么决定了物种的多样性? 科学通报, 62, 2033-2041.] | |
| [11] |
Gienapp P, Teplitsky C, Alho JS, Mills JA, Merilä J (2008) Climate change and evolution: Disentangling environmental and genetic responses. Molecular Ecology, 17, 167-178.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Guo HQ, Li L, Aluru M, Aluru S, Yin YH (2013) Mechanisms and networks for brassinosteroid regulated gene expression. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 16, 545-553.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Harder LD, Johnson SD (2009) Darwin's beautiful contrivances: Evolutionary and functional evidence for floral adaptation. New Phytologist, 183, 530-545.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Herrera CM, Castellanos MC, Medrano M (2006) Geographical context of floral evolution:Towards an improved research programme in floral diversification. In: Ecology and Evolution of Flowers (eds Harder LD, Barrett SCH), pp.278-294. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [15] |
Hong DY (2016) Biodiversity pursuits need a scientific and operative species concept. Biodiversity Science, 24, 979-999. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 洪德元 (2016) 生物多样性事业需要科学、可操作的物种概念. 生物多样性, 24, 979-999.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Huang DB, Wang SG, Zhang BC, Shangguan KK, Shi YY, Zhang DM, Liu XL, Wu K, Xu ZP, Fu XD, Zhou YH (2015) A gibberellin-mediated DELLA-NAC signaling cascade regulates cellulose synthesis in rice. The Plant Cell, 27, 1681-1696. |
| [17] |
Jin XH, Chen SC, Luo YB (2009) Taxonomic revision ofDendrobium moniliforme complex (Orchidaceae). Scientia Horticulturae, 120, 143-145.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Kater MM, Dreni L, Colombo L (2006) Functional conservation of MADS-box factors controlling floral organ identity in rice andArabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 3433-3444.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kong HZ (2016) Biodiversity undertakings call for extensive discussion on species concept and the criteria for species delimitation. Biodiversity Science, 24, 977-978. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
| [ 孔宏智 (2016) 生物多样性事业呼唤对物种概念和物种划分标准的深度讨论. 生物多样性, 24, 977-978.] | |
| [20] |
Leimar O (2009) Environmental and genetic cues in the evolution of phenotypic polymorphism. Evolutionary Ecology, 23, 125-135.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Li L, Liu T, Liu B, Liu ZQ, Si LM, Zhang R (2010) Phenotypic variation and covariation among natural populations ofArabidopsis thaliana in North Xinjiang. Biodiversity Science, 18, 497-508. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李磊, 刘彤, 刘斌, 刘忠权, 司朗明, 张荣 (2010) 新疆北部拟南芥自然居群表型变异与协变. 生物多样性, 18, 497-508.]
DOI |
|
| [22] |
Liao ZG, Yu H, Duan JB, Yuan K, Yu CJ, Meng XB, Kou LQ, Chen MJ, Jing YH, Liu GF, Smith SM, Li JY (2019) SLR1 inhibits MOC1 degradation to coordinate tiller number and plant height in rice. Nature Communications, 10, 2738.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Liu JQ (2016) “The integrative species concept” and “species on the speciation way”. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1004-1008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 刘建全 (2016) “整合物种概念”和“分化路上的物种”. 生物多样性, 24, 1004-1008.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Liu LC, Du GG, Si WJ, Wang F, Luo HJ, Zhou ZJ (2015) Phenotypic variation and covariation in natural populations of the exotic weedGaura parviflora in different habitat. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(7),41-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘龙昌, 杜改改, 司卫杰, 王菲, 罗海军, 周正军 (2015) 不同生境小花山桃草自然种群表型变异与协变. 草业学报, 24(7),41-51.] | |
| [25] | Ma KP (1993) On the concept of biodiversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 1, 20-22. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平 (1993) 试论生物多样性的概念. 生物多样性, 1, 20-22.] | |
| [26] |
Marowa P, Ding AM, Kong YZ (2016) Expansins: Roles in plant growth and potential applications in crop improvement. Plant Cell Reports, 35, 949-965.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Mitchell-Olds T, Willis JH, Goldstein DB (2007) Which evolutionary processes influence natural genetic variation for phenotypic traits? Nature Reviews Genetics, 8, 845-856. |
| [28] |
Montalvo AM, Ellstrand NC (2000) Transplantation of the subshrubLotus scoparius: Testing the home-site advantage hypothesis. Conservation Biology, 14, 1034-1045.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Morris MW, Stern WL, Judd WS (1996) Vegetative anatomy and systematics of subtribe Dendrobiinae (Orchidaceae). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 120, 89-144.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Ng TB, Liu JY, Wong JH, Ye XJ, Wing Sze SC, Tong Y, Zhang KY (2012) Review of research onDendrobium, a prized folk medicine. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1795-1803.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Pande PK, Dhiman RC (2011) Performance and variability patterns in wood properties and growth traits in the parents, F1 and F2 generation hybrid clones ofPopulus deltoides. Journal of Forestry Research, 22, 379-385.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Pelaz S, Ditta GS, Baumann E, Wisman E, Yanofsky MF (2000) B and C floral organ identity functions requireSEPALLATA MADS-box genes. Nature, 405, 200-203.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Pigliucci M, Murren CJ, Schlichting CD (2006) Phenotypic plasticity and evolution by genetic assimilation. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 209, 2362-2367.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Pintado A, Valladares F, Sancho LG (1997) Exploring phenotypic plasticity in the lichenRamalina capitata: Morphology, water relations and chlorophyll content in north- and south-facing populations. Annals of Botany, 80, 345-353.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Pridgeon AM, Cribb PJ, Chase MW, Rasmussen FN (2014) Genera Orchidacearum. Vol. 6: Epidendroideae (Part three). Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [36] | Rasmussen HN (1995) Terrestrial Orchids:From Seed to Mycotrophic Plant. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [37] |
Rutter MT, Fenster CB (2007) Testing for adaptation to climate inArabidopsis thaliana: A calibrated common garden approach. Annals of Botany, 99, 529-536.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Schenck D, Christian M, Jones A, Lüthen H (2010) Rapid auxin-induced cell expansion and gene expression: A four-decade-old question revisited. Plant Physiology, 152, 1183-1185.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Schlichting CD, Levin DA (1984) Phenotypic plasticity of annual phlox: Tests of some hypotheses. American Journal of Botany, 71, 252-260.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Siefert A, Fridley JD, Ritchie ME (2014) Community functional responses to soil and climate at multiple spatial scales: When does intraspecific variation matter? PLoS ONE, 9, e111189.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Simpson GG (1951) The species concept. Evolution, 5, 285-298.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Sletvold N, Grindeland JM, Ågren J (2010) Pollinator-mediated selection on floral display, spur length and flowering phenology in the deceptive orchidDactylorhiza lapponica. New Phytologist, 188, 385-392.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge. |
| [44] |
Soto-Cerda BJ, Diederichsen A, Ragupathy R, Cloutier S (2013) Genetic characterization of a core collection of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) suitable for association mapping studies and evidence of divergent selection between fiber and linseed types. BMC Plant Biology, 13, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Sultan SE (2000) Phenotypic plasticity for plant development, function and life history. Trends in Plant Science, 5, 537-542.
PMID |
| [46] |
Tamhane AC (1981) Randomized response techniques for multiple sensitive attributes. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 76, 916-923.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y (2005) A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant,dwarf11, with reduced seed length. The Plant Cell, 17, 776-790.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Tsi ZH (1980) A preliminary study of the orchid genusDendrobium SW China. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 18, 427-449. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吉占和 (1980) 中国石斛属的初步研究. 植物分类学报, 18, 427-449.] | |
| [49] |
Valladares F, Sanchez-Gomez D, Zavala MA (2006) Quantitative estimation of phenotypic plasticity: Bridging the gap between the evolutionary concept and its ecological applications. Journal of Ecology, 94, 1103-1116.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
van der Knaap E, Kim JH, Kende H (2000) A novel gibberellin-induced gene from rice and its potential regulatory role in stem growth. Plant Physiology, 122, 695-704.
PMID |
| [51] |
Wang B, Smith SM, Li JY (2018) Genetic regulation of shoot architecture. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 69, 437-468.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Wang S, Zhou DW (2017) Research on phenotypic plasticity in plants: An overview of history, current status, and development trends. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 8161-8169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王姝, 周道玮 (2017) 植物表型可塑性研究进展. 生态学报, 37, 8161-8169.] | |
| [53] |
Wang ZY, Bai MY, Oh E, Zhu JY (2012) Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annual Review of Genetics, 46, 701-724.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Weber CR, Moorthy BR (1952) Heritable and nonheritable relationships and variability of oil content and agronomic characters in the F2 generation of soybean crosses. Agronomy Journal, 44, 202-209.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Wood HP (2006) The Dendrobiums. ARG Gantner Verlag, Ruggell. |
| [56] |
Xiang XG, Mi XC, Zhou HL, Li JW, Chung SW, Li DZ, Huang WC, Jin WT, Li ZY, Huang LQ, Jin XH (2016) Biogeographical diversification of mainland AsianDendrobium (Orchidaceae) and its implications for the historical dynamics of evergreen broad-leaved forests. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 1310-1323.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Xiang XG, Schuiteman A, Li DZ, Huang WC, Chung SW, Li JW, Zhou HL, Jin WT, Lai YJ, Li ZY, Jin XH (2013) Molecular systematics ofDendrobium (Orchidaceae, Dendrobieae) from mainland Asia based on plastid and nuclear sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 69, 950-960.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Xiang YZ, Huang CH, Hu Y, Wen J, Li SS, Yi TS, Chen HY, Xiang J, Ma H (2017) Evolution of Rosaceae fruit types based on nuclear phylogeny in the context of geological times and genome duplication. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 262-281.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Xing Y, Zhao X, Dong KH, Shi WW (2008) A study on morphological variation of different populations of Lespedeza davurica. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 17(4),26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邢毅, 赵祥, 董宽虎, 史威威 (2008) 不同居群达乌里胡枝子形态变异研究. 草业学报, 17(4),26-31.] | |
| [60] | Xu Q (2015) Molecular Phylogeny of Dendrobium and Genome-wide Analysis of NBS Genes in D. catenatum. PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐晴 (2015) 石斛属的系统发育和铁皮石斛NBS基因的分析. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [61] |
Yang QE (2016) Comments on species-level taxonomy of plants in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1024-1030. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 杨亲二 (2016) 我国植物种级水平分类学研究刍议. 生物多样性, 24, 1024-1030.]
DOI |
|
| [62] | Yukawa T, Uehara K (1996) Vegetative diversification and radiation in subtribe Dendrobiinae (Orchidaceae): Evidence from chloroplast DNA phylogeny and anatomical characters. Plant Systematics & Evolution, 201, 1-14. |
| [63] | Zhu GH, Tsi ZH, Wood JJ, Wood HP (2009) Orchidaceae. In: Flora of China, Vol. 25 (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY), pp. 382-383. Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [64] |
Zhu QH, Ge S (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among A-genome species of the genusOryza revealed by intron sequences of four nuclear genes. New Phytologist, 167, 249-265.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Song Yuanhao, Gong Lü, Li Ben, Hu Yang, Li Xiuzhen. Impacts of different pond-to-wetland restoration methods on macrofauna in the Liao River Estuary, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [2] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [3] | Yali Zhang, Bingchang Zhang, Kang Zhao, Kaikai Li, Yanjin Liu. Variation of bacterial communities and their driving factors in different types of biological soil crusts in Mu Us sandy land [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [4] | Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Tao Yang, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Qiuyu Zhang, Hongqiang Zhang, Xu Zhang, Xiaokun Ou, Zehao Shen. Spatial variation and determinants of woody plant species diversity in a semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [5] | Ting Wang, Lizhi Zhou. The spatial-temporal patterns of bird diversity and its determinants in the small wetlands in Hefei City [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [6] | Wenkai Xue, Huadanshang Meng, Yanhong Wang, Pan Zhu, Ji De, Xiaofang Guo. Relationship between culturable filamentous fungal diversity and environmental factors in Nam Co Lake [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [7] | Jing Huang, Mei Sun, Wenfeng Yu, Jianyong Wu, Huaizhen Tian. Trade of native orchids on Chinese online platforms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(4): 21233-. |
| [8] | Moxu Wu, Mingtai An, Li Tian, Feng Liu. Effects of environmental factors on quantitative characteristics of woody plant sexual system in Maolan karst forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| [9] | Yuhan Shi, Zongxin Ren, Weijia Wang, Xin Xu, Jie Liu, Yanhui Zhao, Hong Wang. Predicting the spatial distribution of three Astragalusspecies and their pollinating bumblebees in the Sino-Himalayas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [10] | Xinghui Lu, Runguo Zang, Yi Ding, Jihong Huang, Yue Xu. Habitat characteristics and its effects on seedling abundance of Hopea hainanensis, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(3): 289-295. |
| [11] | Qiuhong Feng, Dengfeng Li, Tao Yu, Junqing Li, Wenbao Ma, Lei Zhang. Phenotypic fruit and seed variations of Acer catalpifolium, a Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(3): 314-322. |
| [12] | Rijin Jiang,Linlin Zhang,Kaida Xu,Pengfei Li,Yi Xiao,Ziwei Fan. Characteristics and diversity of nekton functional groups in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1330-1338. |
| [13] | Xiuqin Yin, Yan Tao, Haixia Wang, Chen Ma, Xinchang Kou, Huan Xu, Dong Cui. Forest soil fauna ecology in Northeast China: Review and prospect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(10): 1083-1090. |
| [14] | Yaqiong Song, Zhilong Liu, Sophie Willian, Jiangyun Gao. Characteristics of the orchid trade at public markets and implications for conservation in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(5): 531-539. |
| [15] | Fang Sheng, Shuying Chen, Jia Tian, Peng Li, Xue Qin, Shuping Luo, Jiang Li. Genetic diversity of Crataegus songorica in Xinjiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(5): 518-530. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn