



Biodiv Sci ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1227-1233. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016031 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016031
• Special Feature: Chinese Biodiversity Monitoring and Research Network (Sino BON) • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huanzhang Liu1,*( ), Junxing Yang2, Shuwei Liu2, Xin Gao1, Yushun Chen1, Chunguang Zhang3, Kai Zhao4, Xinhui Li5, Wei Liu6
), Junxing Yang2, Shuwei Liu2, Xin Gao1, Yushun Chen1, Chunguang Zhang3, Kai Zhao4, Xinhui Li5, Wei Liu6
Received:2016-11-11
Accepted:2016-11-23
Online:2016-11-20
Published:2016-12-14
Contact:
Liu Huanzhang
Huanzhang Liu, Junxing Yang, Shuwei Liu, Xin Gao, Yushun Chen, Chunguang Zhang, Kai Zhao, Xinhui Li, Wei Liu. Theory and methods on fish diversity monitoring with an introduction to the inland water fish diversity observation in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(11): 1227-1233.
| EBV 类别 EBV class | EBV举例 EBV examples | 度量与尺度 Measurement and scalability | 时间敏感性 Temporal sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 遗传组成 Genetic composition | 基因型多样性 Allelic diversity | 选定的物种(濒危或家养物种)在代表性分布区的基因型 Genotypes of selected species (e.g. endangered, domesticated) at representative locations | 世代时间 Generation time |
| 物种种群 Species populations | 丰度或分布 Abundances and distributions | 进行计数或出现与否调查, 主要针对大范围网络尺度上容易监测的 物种、生态系统服务重要的物种等 Counts or presence surveys for groups of species easy to monitor or important for ecosystem services (ES), over an extensive network of sites | 1年-10年以上 1 to >10 years |
| 物种特征 Species traits | 形态学 Phenology | 遥感监测植物叶子颜色变化的时间, 需要现场核实。在鱼类可以采用生长、繁殖等特征 Timing of leaf coloration by remote sensing (RS), with in situ validation. Growth and reproduction traits in fish. | 1年 1 year |
| 群落组成 Community composition | 分类单元多样性 Taxonomic diversity | 多个分类单元的调查以及选定区域的宏基因组研究 Consistent multitaxa surveys and metagenomics at select locations | 5年-10年以上 5 to >10 years |
| 生态系统结构 Ecosystem structure | 生境结构 Habitat structure | 全球或区域尺度的生物量或覆盖度遥感 RS of cover (or biomass) by height (or depth) globally or regionally | 1-5年 1 to 5 years |
| 生态系统功能 Ecosystem function | 营养物质保留 Nutrient retention | 选定区域的营养物输出/输入比例测量 Nutrient output/input ratios measured at select locations | 1年 1 year |
Table 1 Examples of candidate Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBV) (adopted from Pereira et al, 2013)
| EBV 类别 EBV class | EBV举例 EBV examples | 度量与尺度 Measurement and scalability | 时间敏感性 Temporal sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 遗传组成 Genetic composition | 基因型多样性 Allelic diversity | 选定的物种(濒危或家养物种)在代表性分布区的基因型 Genotypes of selected species (e.g. endangered, domesticated) at representative locations | 世代时间 Generation time |
| 物种种群 Species populations | 丰度或分布 Abundances and distributions | 进行计数或出现与否调查, 主要针对大范围网络尺度上容易监测的 物种、生态系统服务重要的物种等 Counts or presence surveys for groups of species easy to monitor or important for ecosystem services (ES), over an extensive network of sites | 1年-10年以上 1 to >10 years |
| 物种特征 Species traits | 形态学 Phenology | 遥感监测植物叶子颜色变化的时间, 需要现场核实。在鱼类可以采用生长、繁殖等特征 Timing of leaf coloration by remote sensing (RS), with in situ validation. Growth and reproduction traits in fish. | 1年 1 year |
| 群落组成 Community composition | 分类单元多样性 Taxonomic diversity | 多个分类单元的调查以及选定区域的宏基因组研究 Consistent multitaxa surveys and metagenomics at select locations | 5年-10年以上 5 to >10 years |
| 生态系统结构 Ecosystem structure | 生境结构 Habitat structure | 全球或区域尺度的生物量或覆盖度遥感 RS of cover (or biomass) by height (or depth) globally or regionally | 1-5年 1 to 5 years |
| 生态系统功能 Ecosystem function | 营养物质保留 Nutrient retention | 选定区域的营养物输出/输入比例测量 Nutrient output/input ratios measured at select locations | 1年 1 year |
| 评价指标 Metrics | 评分级别 Rating of metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| A. 物种组成与丰富度 Species richness and composition | 根据调查河流的大小或区域特征设定评价指标1-5的期望值, 大型河流鱼类物种期望值高; 中国的河流鲤科鱼类物种多。 Expectations for metrics 1-5 vary with stream size and region. Large rivers are with more species, and more cyprinids in Chinese waters | ||
| 1. 鱼类物种总数(土著物种) Total number of fish species (native fish species) | |||
| 2. 鲈类物种单元与数量(底栖物种) Number and identity of darter species (benthic species) | |||
| 3. 太阳鱼科物种单元与数量(中层鱼类) Number and identity of sunfish species (water-column species) | |||
| 4. 亚口鱼科物种单元与数量(长寿命鱼类) Number and identity of sucker species (long-lived species) | |||
| 5. 非耐受型鱼类物种单元与数量 Number and identity of intolerant species | |||
| 6. 蓝绿鳞鳃太阳鱼个体组成百分比(耐受型鱼类) Percentage of individuals as green sunfish (tolerant species) | <5 | 5-20 | >20 |
| B. 营养类型组成 Trophic composition | |||
| 7. 杂食性鱼类个体组成百分比 Percentage of individuals as omnivores | <20 | 20-45 | >45 |
| 8. 昆虫食性鲤科鱼类个体组成百分比 Percentage of individuals as insectivorous cyprinids (insectivores) | >45 | 45-20 | <20 |
| 9. 凶猛肉食性鱼类个体组成百分比(顶级捕食者) Percentage of individuals as piscivores (top carnivores) | >5 | 5-1 | <1 |
| C. 鱼类丰度与状况 Fish abundance and condition | |||
| 10. 采集到的样本个体数 Number of individuals in sample | 指标10随河流大小等因子变化 Expectations for metric 10 vary with stream size and other factors | ||
| 11. 杂交个体百分比 Percentage of individuals as hybrids | 0 | >0-1 | >1 |
| 12. 带病、肿瘤、鳍条损伤、或骨骼畸形的个体百分比 Percentage of individuals with disease, tumors, fin damage, and skeletal anomalies | 0-2 | >2-5 | >5 |
Table 2 Metrics used to assess biological integrity of fish communities based on the Index of Biotic Integrity (IBI) (from Karr, 1981, 1991 with modifications)
| 评价指标 Metrics | 评分级别 Rating of metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| A. 物种组成与丰富度 Species richness and composition | 根据调查河流的大小或区域特征设定评价指标1-5的期望值, 大型河流鱼类物种期望值高; 中国的河流鲤科鱼类物种多。 Expectations for metrics 1-5 vary with stream size and region. Large rivers are with more species, and more cyprinids in Chinese waters | ||
| 1. 鱼类物种总数(土著物种) Total number of fish species (native fish species) | |||
| 2. 鲈类物种单元与数量(底栖物种) Number and identity of darter species (benthic species) | |||
| 3. 太阳鱼科物种单元与数量(中层鱼类) Number and identity of sunfish species (water-column species) | |||
| 4. 亚口鱼科物种单元与数量(长寿命鱼类) Number and identity of sucker species (long-lived species) | |||
| 5. 非耐受型鱼类物种单元与数量 Number and identity of intolerant species | |||
| 6. 蓝绿鳞鳃太阳鱼个体组成百分比(耐受型鱼类) Percentage of individuals as green sunfish (tolerant species) | <5 | 5-20 | >20 |
| B. 营养类型组成 Trophic composition | |||
| 7. 杂食性鱼类个体组成百分比 Percentage of individuals as omnivores | <20 | 20-45 | >45 |
| 8. 昆虫食性鲤科鱼类个体组成百分比 Percentage of individuals as insectivorous cyprinids (insectivores) | >45 | 45-20 | <20 |
| 9. 凶猛肉食性鱼类个体组成百分比(顶级捕食者) Percentage of individuals as piscivores (top carnivores) | >5 | 5-1 | <1 |
| C. 鱼类丰度与状况 Fish abundance and condition | |||
| 10. 采集到的样本个体数 Number of individuals in sample | 指标10随河流大小等因子变化 Expectations for metric 10 vary with stream size and other factors | ||
| 11. 杂交个体百分比 Percentage of individuals as hybrids | 0 | >0-1 | >1 |
| 12. 带病、肿瘤、鳍条损伤、或骨骼畸形的个体百分比 Percentage of individuals with disease, tumors, fin damage, and skeletal anomalies | 0-2 | >2-5 | >5 |
| 调查方法 Survey methods | 适用水环境 Applied water body |
|---|---|
| 目测调查 Visual surveys | 小型水体或清澈的溪流 Small pools and clear streams |
| 渔获物调查 Catch returns | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 定置网等诱捕型网具 Traps | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 撒网等网具 Lift, throw and push netting | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 电鱼 Electrofishing | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 刺网 Gill netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 围网 Seine netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 拖网 Trawl netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 水声学计数 Hydroacoustic sonar counters | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 电子计数 Electronic counters | 流水水体 Running waters |
Table 3 Methods for fish surveying and applied water body (From Giles et al, 2005 with modifications)
| 调查方法 Survey methods | 适用水环境 Applied water body |
|---|---|
| 目测调查 Visual surveys | 小型水体或清澈的溪流 Small pools and clear streams |
| 渔获物调查 Catch returns | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 定置网等诱捕型网具 Traps | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 撒网等网具 Lift, throw and push netting | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 电鱼 Electrofishing | 流水或静水水体 Running and still waters |
| 刺网 Gill netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 围网 Seine netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 拖网 Trawl netting | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 水声学计数 Hydroacoustic sonar counters | 缓流或静水水体 Slow-flowing or still waters |
| 电子计数 Electronic counters | 流水水体 Running waters |
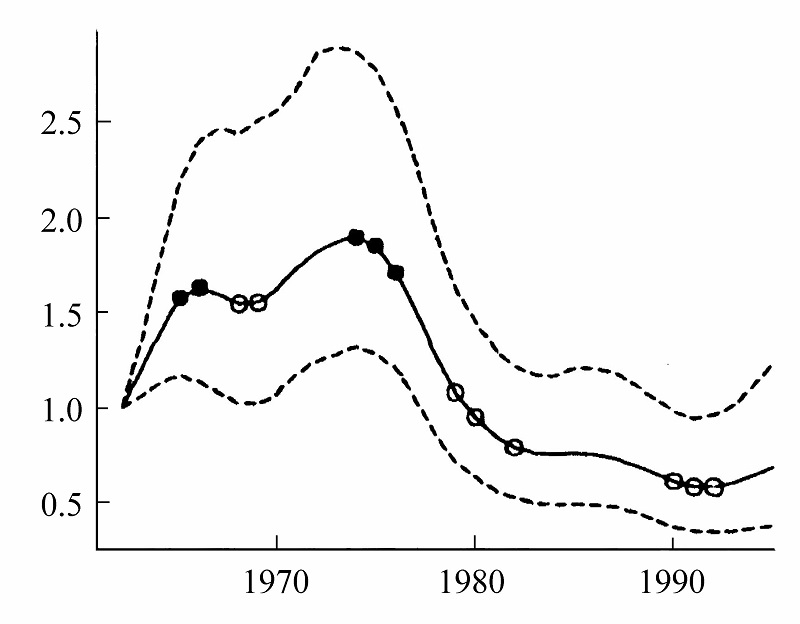
Fig. 1 Index curves from CBC data for the Bullfinch. The solid lines give the index curves from a GAM and the dashed lines represent upper and lower 95% bootstrapped confidence limits. A solid circle denotes a point at which the second derivative is significantly negative (a downturn in the index curve), and an open circle denotes a point at which the second derivative is significantly positive (an upturn in the index curve) (Fewster et al,, 2000).
| 水系 Water systems | 重要地区 Focused areas | 重点物种 Target species | 主要承担单位 Lead institutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长江 Yangtz River | 长江上游珍稀特有鱼类保护区(四川合江)、三峡库尾(重庆)、三峡大坝坝下(湖北宜昌)、中游湖泊区(江西湖口) Reserve for rare and endemic fishes of the Upper Yangtz River (Hejiang), end of the Three Gorges Reservoir (Chongqing), downstream of the Three Gorges Dam (Yichang), and floodplain of the middle Yangtz (Hukou) | 洄游性鱼类(鲟鱼类)、长江上游特有鱼类(圆口铜鱼)、长江重要经济鱼类(四大家鱼) Anadromous fish (sturgeons), endemic fishes of the Upper Yangtz River, economic species (the four major Chinese carps) | 中国科学院水生生物研究所 Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 黄河 Yellow River | 上游(巴彦淖尔)、中游(三门峡)、下游(东营) Upper reaches (Bayan Nur), middle reaches (Sanmenxia), and lower reaches (Dongying) | 马口鱼或宽鳍鱲、裂腹鱼类、鲇类 Opsariicjthys bidens or Zacco platypus, schizothroaxins, and catfishes | 中科院动物研究所 Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 黑龙江 Heilongjiang River | 上游(呼玛)、中游(萝北)、下游(抚远) Upper reaches (Huma), middle reaches (Luobei), and lower reaches (Fuyuan) | 施氏鲟或达氏鳇、鲑科鱼类 Acipenser schrenckii, Huso dauricus, salmonids | 中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所 Heilongjiang River Fisheries Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences |
| 珠江 Zhujiang River | 上游(合山)、中游(桂平)、下游(肇庆) Upper reaches (Heshan), middle reaches (Guiping), and lower reaches (Zhaoqing) | 广东鲂、野鲮亚科代表种、鳅类代表种 Megalobrama terminalis, labeonins, loaches | 中国水产科学研究院珠江水产研究所 Zhujiang River Fisheries Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences |
| 澜沧江 Lancang River | 上游(维西)、中游(大理)、下游(景洪) Upper reaches (Weixi), middle reaches (Dali), and lower reaches (Jinghong) | 裂腹鱼类、鮡类、鲃类代表种 Schizothroaxins, sisorins, barbinins | 中科院昆明动物研究所 Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 怒江 Nujiang River | 上游(贡山)、中游(六库)、下游(永德) Upper reaches (Gongshan), middle reaches (Liuku), lower reaches (Yongde) | 裂腹鱼类、鮡类、鳅类的代表种 Schizothroaxins, sisorins, loaches | 中科院昆明动物研究所 Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 塔里木河 Tarim River | 上游(阿拉尔)、中游(沙雅)、下游(尉犁) Upper reaches (Alaer), middle reaches (Shaya), and lower reaches (Yuli) | 裂腹鱼类、鳅科鱼类代表种 Schizothroaxins, loaches | 中科院西北高原生物研究所 Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 青海湖 Qinghai Lake | 湖西北岸(刚察)、湖北岸(海晏)、湖西南岸(共和) Northwest bank (Gangcha), north bank (Haiyan), and south bank (Gonghe) | 裂腹鱼类、鳅科鱼类代表种 Schizothroaxins, loaches | 中科院西北高原生物研究所 Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
Table 4 The scheme of the Sino BON–Inland Water Fish, including focused areas, targeted species (groups) and lead institutions
| 水系 Water systems | 重要地区 Focused areas | 重点物种 Target species | 主要承担单位 Lead institutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 长江 Yangtz River | 长江上游珍稀特有鱼类保护区(四川合江)、三峡库尾(重庆)、三峡大坝坝下(湖北宜昌)、中游湖泊区(江西湖口) Reserve for rare and endemic fishes of the Upper Yangtz River (Hejiang), end of the Three Gorges Reservoir (Chongqing), downstream of the Three Gorges Dam (Yichang), and floodplain of the middle Yangtz (Hukou) | 洄游性鱼类(鲟鱼类)、长江上游特有鱼类(圆口铜鱼)、长江重要经济鱼类(四大家鱼) Anadromous fish (sturgeons), endemic fishes of the Upper Yangtz River, economic species (the four major Chinese carps) | 中国科学院水生生物研究所 Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 黄河 Yellow River | 上游(巴彦淖尔)、中游(三门峡)、下游(东营) Upper reaches (Bayan Nur), middle reaches (Sanmenxia), and lower reaches (Dongying) | 马口鱼或宽鳍鱲、裂腹鱼类、鲇类 Opsariicjthys bidens or Zacco platypus, schizothroaxins, and catfishes | 中科院动物研究所 Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 黑龙江 Heilongjiang River | 上游(呼玛)、中游(萝北)、下游(抚远) Upper reaches (Huma), middle reaches (Luobei), and lower reaches (Fuyuan) | 施氏鲟或达氏鳇、鲑科鱼类 Acipenser schrenckii, Huso dauricus, salmonids | 中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所 Heilongjiang River Fisheries Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences |
| 珠江 Zhujiang River | 上游(合山)、中游(桂平)、下游(肇庆) Upper reaches (Heshan), middle reaches (Guiping), and lower reaches (Zhaoqing) | 广东鲂、野鲮亚科代表种、鳅类代表种 Megalobrama terminalis, labeonins, loaches | 中国水产科学研究院珠江水产研究所 Zhujiang River Fisheries Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences |
| 澜沧江 Lancang River | 上游(维西)、中游(大理)、下游(景洪) Upper reaches (Weixi), middle reaches (Dali), and lower reaches (Jinghong) | 裂腹鱼类、鮡类、鲃类代表种 Schizothroaxins, sisorins, barbinins | 中科院昆明动物研究所 Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 怒江 Nujiang River | 上游(贡山)、中游(六库)、下游(永德) Upper reaches (Gongshan), middle reaches (Liuku), lower reaches (Yongde) | 裂腹鱼类、鮡类、鳅类的代表种 Schizothroaxins, sisorins, loaches | 中科院昆明动物研究所 Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 塔里木河 Tarim River | 上游(阿拉尔)、中游(沙雅)、下游(尉犁) Upper reaches (Alaer), middle reaches (Shaya), and lower reaches (Yuli) | 裂腹鱼类、鳅科鱼类代表种 Schizothroaxins, loaches | 中科院西北高原生物研究所 Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 青海湖 Qinghai Lake | 湖西北岸(刚察)、湖北岸(海晏)、湖西南岸(共和) Northwest bank (Gangcha), north bank (Haiyan), and south bank (Gonghe) | 裂腹鱼类、鳅科鱼类代表种 Schizothroaxins, loaches | 中科院西北高原生物研究所 Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 监测类别 Classes | 监测方法 Methods | 监测指标 Variables |
|---|---|---|
| 重要区域鱼类资源监测(群落水平):流域内鱼类种类组成、不同分类单元和功能类群组成比例、优势种成分变化、早期资源状况、鱼类生存的水环境因子。 Fish resources monitoring in focused areas (community level): species composition, taxonomic groups and ecological functional groups, dominant species, fish early resources, and environmental abiotic factors. | 鱼类资源调查、渔获物调查、鱼类早期资源调查、水下声纳探测、水下机器人视频追踪、水环境因子调查。 Fish resource survey, fishing harvest survey, fish early resource survey, hydro acoustic survey, and environmental abiotic factor survey. | 鱼类群落特征: 鱼类名录、鱼类多样性指数、不同物种的数量组成、重量组成、优势种类、不同分类单元、功能类群的成分变化等。早期资源的种类组成与资源量。鱼类生存环境: 水温、流速、水深、河面宽度、底质特征、溶氧、pH值、透明度、电导率, 水文站的水位、径流量等。 Community level characters: species list, diversity indices, proportion of different species in numbers and biomass, dominant species, proportion of different taxonomic groups and ecological functional groups. Species composition and abundance of fish early resources. Environmental abiotic factor: water temperature, flow velocity, water depth, river width, riverbed types, dissolved oxygen, pH, transparency, conductivity, water discharge, water level of the nearby hydrographic station. |
| 重点物种鱼类生物学特征监测(物种水平):重点鱼类物种(类群)的种群动态、个体生物学特征。 Target species biological monitoring: population dynamic and biological traits. | 渔获物调查、鱼探仪、水下机器人视频追踪、声学信标。 Fishing harvest survey, sonar detection system, video monitoring with remotely operated vehicle (ROV), hydro acoustic survey. | 鱼类种群特征: 种群数量、年龄结构、性比组成、体长和体重频数分布等。鱼类个体生物学特征: 鱼类的年龄与生长、鱼类的食物组成、性腺发育、繁殖力等个体生物学特征。鱼类行为特征: 鱼类洄游时间、线路; 鱼类繁殖、摄食等行为表现。 Population level characters: population size, age structure, sexual ratio, frequency distribution of body length and body weight. Fish biological traits: age and growth, diet composition, gonad development, fecundity. Fish behavior: migration time and route, breeding and feeding behavior. |
| 重点物种遗传多样性监测:种群遗传多样性现状 Genetic diversity monitoring of target species | 线粒体DNA基因和微卫星分子标记 mtDNA and short sequence repeats (SSR) diversity analysis | 线粒体DNA基因的单倍型数目、单倍型多样性、核苷酸多样性; 微卫星标记反映的等位基因频率、杂合度与近交状态、有效种群大小等。 MtDNA haplotype numbers and diversity, nucleotide diversity, SSR genotype frequency, heterozygosity and inbreeding coefficient, effective population size. |
Table 5 Monitoring variables and methods of the Sino BON–Inland Water Fish
| 监测类别 Classes | 监测方法 Methods | 监测指标 Variables |
|---|---|---|
| 重要区域鱼类资源监测(群落水平):流域内鱼类种类组成、不同分类单元和功能类群组成比例、优势种成分变化、早期资源状况、鱼类生存的水环境因子。 Fish resources monitoring in focused areas (community level): species composition, taxonomic groups and ecological functional groups, dominant species, fish early resources, and environmental abiotic factors. | 鱼类资源调查、渔获物调查、鱼类早期资源调查、水下声纳探测、水下机器人视频追踪、水环境因子调查。 Fish resource survey, fishing harvest survey, fish early resource survey, hydro acoustic survey, and environmental abiotic factor survey. | 鱼类群落特征: 鱼类名录、鱼类多样性指数、不同物种的数量组成、重量组成、优势种类、不同分类单元、功能类群的成分变化等。早期资源的种类组成与资源量。鱼类生存环境: 水温、流速、水深、河面宽度、底质特征、溶氧、pH值、透明度、电导率, 水文站的水位、径流量等。 Community level characters: species list, diversity indices, proportion of different species in numbers and biomass, dominant species, proportion of different taxonomic groups and ecological functional groups. Species composition and abundance of fish early resources. Environmental abiotic factor: water temperature, flow velocity, water depth, river width, riverbed types, dissolved oxygen, pH, transparency, conductivity, water discharge, water level of the nearby hydrographic station. |
| 重点物种鱼类生物学特征监测(物种水平):重点鱼类物种(类群)的种群动态、个体生物学特征。 Target species biological monitoring: population dynamic and biological traits. | 渔获物调查、鱼探仪、水下机器人视频追踪、声学信标。 Fishing harvest survey, sonar detection system, video monitoring with remotely operated vehicle (ROV), hydro acoustic survey. | 鱼类种群特征: 种群数量、年龄结构、性比组成、体长和体重频数分布等。鱼类个体生物学特征: 鱼类的年龄与生长、鱼类的食物组成、性腺发育、繁殖力等个体生物学特征。鱼类行为特征: 鱼类洄游时间、线路; 鱼类繁殖、摄食等行为表现。 Population level characters: population size, age structure, sexual ratio, frequency distribution of body length and body weight. Fish biological traits: age and growth, diet composition, gonad development, fecundity. Fish behavior: migration time and route, breeding and feeding behavior. |
| 重点物种遗传多样性监测:种群遗传多样性现状 Genetic diversity monitoring of target species | 线粒体DNA基因和微卫星分子标记 mtDNA and short sequence repeats (SSR) diversity analysis | 线粒体DNA基因的单倍型数目、单倍型多样性、核苷酸多样性; 微卫星标记反映的等位基因频率、杂合度与近交状态、有效种群大小等。 MtDNA haplotype numbers and diversity, nucleotide diversity, SSR genotype frequency, heterozygosity and inbreeding coefficient, effective population size. |
| 1 | Barko VA, Herzog DP, Hrabik RA, Scheibe JS (2004) Relationship among fish assemblages and main-channel-border physical habitats in the unimpounded upper Mississippi River. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 133, 371-384. |
| 2 | Chen YY (1990) Some aspects on biological diversity of freshwater ecosystem. Bioscience Communciation, 2, 197-200. (in Chinese) |
| [陈宜瑜 (1990) 淡水生态系统中的若干生物多样性问题. 生物科学信息, 2, 197-200.] | |
| 3 | Fewster RM, Buckland ST, Siriwardena GM, Baillie SR, Wilson JD (2000) Analysis of population trends for farmland birds using generalized additive models. Ecology, 81, 1970-1984. |
| 4 | Froese R, Pauly D (2016) FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. www.fishbase.org, version (10/2016). |
| 5 | Giles N, Sands R, Fasham M (2005) Fish. In: Handbook of Biodiversity Methods: Survey, Evaluation and Monitoring (eds Hill D, Fasham M, Tucker G, Shewry M, Shaw P), pp. 368-386. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 6 | Hare SR, Mantua NJ (2000) Empirical evidence for North Pacific regime shifts in 1977 and 1989. Progress in Oceanography, 47, 103-145. |
| 7 | HJ 710.7-2014J 710.7-2014 (2014) Technical Guidelines for Biodiversity Monitoring—Inland Water Fish. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [HJ 710.7-2014 J 710.7-2014(2014) 生物多样性观测技术导则: 内陆水域鱼类. 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 8 | Karr JR (1981) Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries, 6(6), 21-27. |
| 9 | Karr JR (1991) Biological integrity: a long-neglected aspect of water resource management. Ecological Applications, 1, 66-84. |
| 10 | Killgore KJ, Hoover JJ, George SG, Lewis BR, Murphy CE, Lancaster WE (2007) Distribution, relative abundance and movements of pallid sturgeon in the free-flowing Mississippi River. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 23, 476-483. |
| 11 | Ma KP (2015) Biodiversity monitoring in China: from CForBio to Sino BON. Biodiversity Science, 23, 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性监测网络建设: 从CForBio到Sino BON. 生物多样性, 23, 1-2.] | |
| 12 | Miller DL, Hughes RM, Karr JR, Leonard PM, Moyle PB, Schrader LH, Thompson BA, Daniels RA, Fausch KD, Fitzhugh GA, Gammon JR, Halliwell DB, Angermeier PL, Orth DJ (1988) Regional applications of an index of biotic integrity for use in water resource management. Fisheries, 13(5), 12-20. |
| 13 | Miranda LE, Killgore KJ (2014) Fish depth distributions in the Lower Mississippi River. River Research and Applications, 30, 347-359. |
| 14 | Nakano SI, Yahara T, Nakashizuka T (2012) The Biodiversity Observation Network in the Asia-Pacific Region: Toward Further Development of Monitoring, Ecological Research Monographs, Springer, Tokyo. |
| 15 | Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman RHG, Scholes RJ, Bruford MW, Brummitt N, Butchart SHM, Cardoso AC, Coops NC, Dulloo E, Fith DP, Freyhof J, Gregory RD, Heip C, Höft R, Hurtt G, Jetz W, Karp DS, McGeoch MA, Obura D, Onoda Y, Pettorelli N, Reyers B, Sayre R, Scharlemann JPW, Stuart SN, Turak E, Walpole M, Wegmann M (2013) Essential biodiversity variables. Science, 339, 277-278. |
| 16 | Sarkar UK, Pathak AK, Sinha RK, Sivakumar K, Pandian AK, Pandey A, Dubey VK, Lakra WS (2012) Freshwater fish biodiversity in the River Ganga (India): changing pattern, threats and conservation perspectives. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 22, 251-272. |
| 17 | Scholes RJ, Mace GM, Turner W, Geller GN, Jürgens N, Larigauderie A, Muchoney D, Walther BA, Mooney HA (2008) Toward a Global Biodiversity Observing System. Science, 321, 1044-1045. |
| 18 | Scholes RJ, Walters M, Turak E, Saarenmaa H, Heip CH, Tuama ÉÓ, Faith DP, Mooney HA, Ferrier S, Jongman RH, Harrison IJ, Yahara T, Pereira HM, Larigauderie A, Geller G (2012) Building a global observing system for biodiversity. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 4, 139-146. |
| 19 | Steuck MJ, Yess S, Pitlo J, Van Vooren A, Rasmussen J (2010) Distribution and Relative Abundance of Upper Mississippi River Fishes. Upper Mississippi River Conservation Committee, Onalaska, Wisconsin. |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [10] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [11] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [12] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [13] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [14] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [15] | Hui Ran, Tianyou Yang, Xiaoqi Mi. The updated checklist of reptiles in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23348-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn