



Biodiv Sci ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 3-11. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.09077 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.09077
Special Issue: 生物入侵
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinping Wang1,2, Lijia Dong1,2, Weiguo Sang1,*( )
)
Received:2011-05-09
Accepted:2011-10-21
Online:2012-01-20
Published:2012-02-14
Contact:
Weiguo Sang
Jinping Wang, Lijia Dong, Weiguo Sang. Effects of different nitrogen regimes on competition betweenAmbrosia artemisiifolia, an invasive species, and two native species, Artemisia annua and Artemisia mongolica[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 3-11.
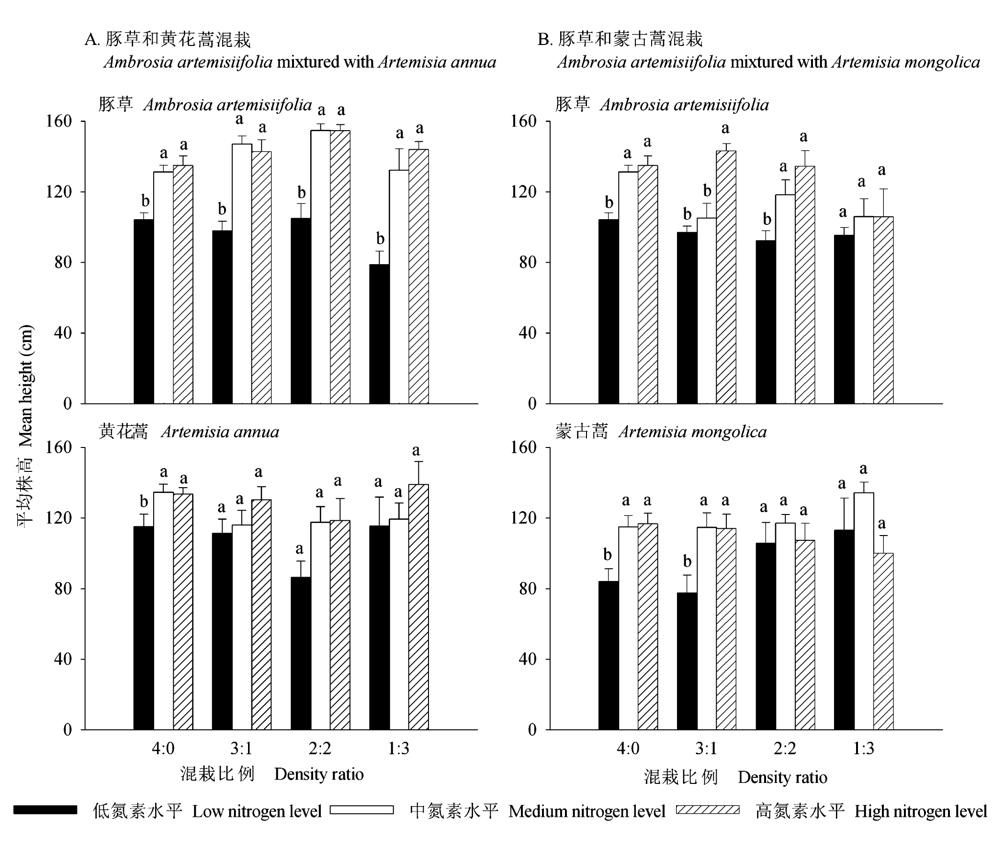
Fig. 1 Mean height of Ambrosia artemisiifolia,Artemisia annuaandArtemisia mongolica under different N regimes. Vertical bars represent means ± SE. Different small letters indicate significant differences among different N regimes in the same density ratio (LSD test: P<0.05, n = 5).
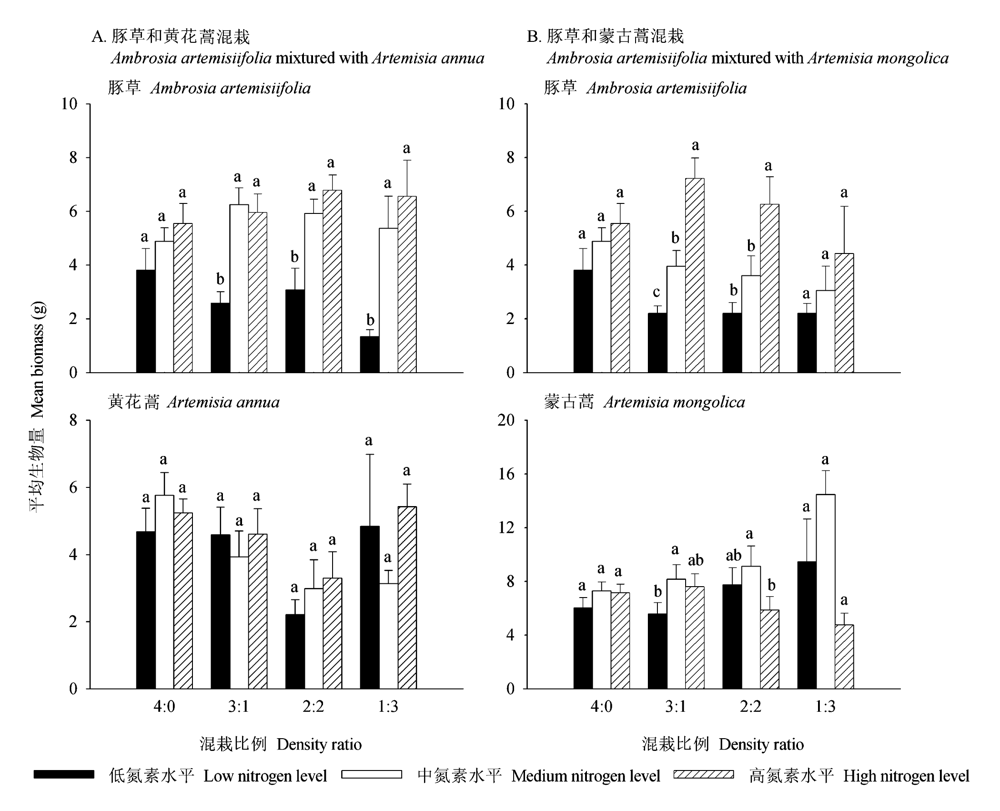
Fig. 2 Mean biomass of Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Artemisia annuaandArtemisia mongolica under different N regimes. Vertical bars represent means ± SE. Different small letters indicate significant differences among different N regimes in the same density ratio (LSD test: P< 0.05,n = 5).
| 竞争指标 Indices | 氮素水平 N levels | 混栽比例 Density ratio (Na:Nb/c) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3:1 | 2:2 | 1:3 | ||||
| 豚草和黄花蒿混栽 Ambrosia artemisiifoliamixtured with Artemisia annua | 豚草的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | 0.25±0.09* | 0.03±0.51 | 0.56±0.33* | |
| Relative competition intensity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | -0.27±0.14 | -0.20±0.10 | -0.08±0.23 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.08±0.10 | -0.31±0.18 | -0.18±0.23 | |||
| 黄花蒿的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | -0.04±0.32 | 0.61±0.07* | 0.36±0.53 | ||
| Relative competition intensity of Artemisia annua | 中氮 Medium | 0.43±0.11* | 0.43±0.18 | 0.25±0.23 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.04±0.12 | 0.36±0.13 | 0.12±0.05 | |||
| 豚草的竞争攻击力系数 | 低氮 Low | -0.15±0.20 | 0.29±0.26 | -0.46±0.32 | ||
| Aggressivity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | 0.35±0.09* | 0.32±0.13 | 0.17±0.22 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.02±0.09 | 0.34±0.14 | 0.15±0.13 | |||
| 豚草和蒙古蒿混栽 Ambrosia artemisiifoliamixtured with Artemisia mongolica | 豚草的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | 0.26±0.16 | 0.24±0.20 | 0.28±0.19 | |
| Relative competition intensity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | 0.19±0.04* | 0.28±0.14 | 0.36±0.21 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.26±0.10 | -0.16±0.17 | 0.14±0.35 | |||
| 蒙古蒿的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | -0.63±0.46 | -0.27±0.25 | 0.06±0.13 | ||
| Relative competition intensity of Artemisia mongolica. | 中氮 Medium | -1.03±0.25* | -0.28±0.13 | -0.18±0.18 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.30±0.11 | -0.07±0.12 | 0.19±0.14 | |||
| 豚草的竞争攻击力系数 | 低氮 Low | -0.45±0.26 | -0.25±0.20 | -0.11±0.11 | ||
| Aggressivity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | -0.61±0.13* | -0.28±0.12 | -0.27±0.15 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.28±0.11 | 0.18±0.15 | -0.11±0.23 | |||
Table 1 Competition indices of Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Artemisia annua and Artemisia mongolica under different N regimes
| 竞争指标 Indices | 氮素水平 N levels | 混栽比例 Density ratio (Na:Nb/c) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3:1 | 2:2 | 1:3 | ||||
| 豚草和黄花蒿混栽 Ambrosia artemisiifoliamixtured with Artemisia annua | 豚草的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | 0.25±0.09* | 0.03±0.51 | 0.56±0.33* | |
| Relative competition intensity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | -0.27±0.14 | -0.20±0.10 | -0.08±0.23 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.08±0.10 | -0.31±0.18 | -0.18±0.23 | |||
| 黄花蒿的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | -0.04±0.32 | 0.61±0.07* | 0.36±0.53 | ||
| Relative competition intensity of Artemisia annua | 中氮 Medium | 0.43±0.11* | 0.43±0.18 | 0.25±0.23 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.04±0.12 | 0.36±0.13 | 0.12±0.05 | |||
| 豚草的竞争攻击力系数 | 低氮 Low | -0.15±0.20 | 0.29±0.26 | -0.46±0.32 | ||
| Aggressivity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | 0.35±0.09* | 0.32±0.13 | 0.17±0.22 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.02±0.09 | 0.34±0.14 | 0.15±0.13 | |||
| 豚草和蒙古蒿混栽 Ambrosia artemisiifoliamixtured with Artemisia mongolica | 豚草的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | 0.26±0.16 | 0.24±0.20 | 0.28±0.19 | |
| Relative competition intensity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | 0.19±0.04* | 0.28±0.14 | 0.36±0.21 | ||
| 高氮 High | -0.26±0.10 | -0.16±0.17 | 0.14±0.35 | |||
| 蒙古蒿的相对竞争强度 | 低氮 Low | -0.63±0.46 | -0.27±0.25 | 0.06±0.13 | ||
| Relative competition intensity of Artemisia mongolica. | 中氮 Medium | -1.03±0.25* | -0.28±0.13 | -0.18±0.18 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.30±0.11 | -0.07±0.12 | 0.19±0.14 | |||
| 豚草的竞争攻击力系数 | 低氮 Low | -0.45±0.26 | -0.25±0.20 | -0.11±0.11 | ||
| Aggressivity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 中氮 Medium | -0.61±0.13* | -0.28±0.12 | -0.27±0.15 | ||
| 高氮 High | 0.28±0.11 | 0.18±0.15 | -0.11±0.23 | |||
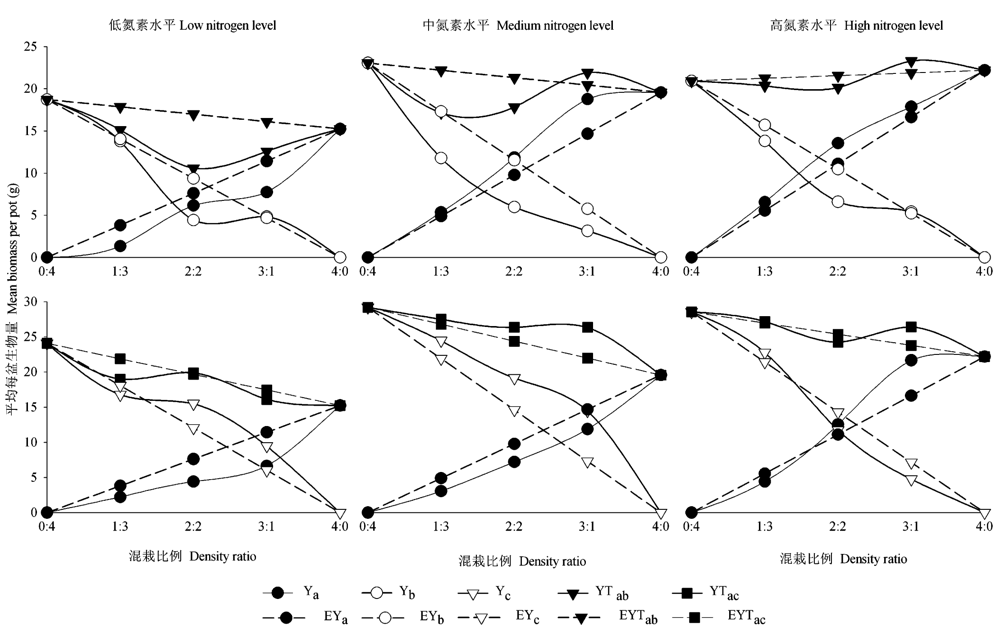
Fig. 3 Replacement diagrams under different N regimes. Ya, Yb, Yc represent the biomass of Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Artemisia annuaandArtemisia mongolica, and YTab, YTac represent the total biomass per pot. EYa, EYb, EYc represent the biomass of Ambrosia artemisiifolia, Artemisia annuaorArtemisia mongolica, and EYTab, EYTac represent the total biomass per pot by virtue of the density ratio according to monoculture. The expected biomass is obtained when inter- and intra- specific competition are equal.
| [1] | Alpert P, Bone E, Holzapfel C (2000) Invasiveness, invasibility and the role of environmental stress in the spread of non-native plants. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 3,52-66. |
| [2] | Bobbink J (1987) Increasing dominance of Brachypodium pinnatum (L.) Beauv. in chalk grasslands: a threat to a species-rich ecosystem. Biological Conservation, 40,301-314. |
| [3] | Brooks ML (2003) Effects of increased soil nitrogen on the dominance of alien annual plants in the Mojave Desert. Journal of Applied Ecology, 40,344-353. |
| [4] | Burke M, Grime J (1996) An experimental study of plant community invasibility. Ecology, 77,776-790. |
| [5] |
Callaway RM, Aschehoug ET (2000) Invasive plants versus their new and old neighbors: a mechanism for exotic invasion. Science, 290,521.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Cassidy TM, Fownes JH, Harrington RA (2004) Nitrogen limits an invasive perennial shrub in forest understory. Biological Invasions, 6,113-121. |
| [7] | Chapin FS, Vitousek PM, Van Cleve K (1986) The nature of nutrient limitation in plant communities. The American Naturalist, 127,48-58. |
| [8] | Chen H, Chen LJ, Albright TP (2007) Predicting the potential distribution of invasive exotic species using GIS and information-theoretic approaches: A case of ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) distribution in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52,1223-1230. |
| [9] |
Clot B, Schneiter D, Tercier P, Gehrig R, Annie G, Thibaudon M (2002) Ambrosia pollen in Switzerland: local production or transport? Allergie et Immunologie, 34,126-128.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Corbin JD, D'Antonio CM (2004) Competition between native perennial and exotic annual grasses: implications for an historical invasion. Ecology, 85,1273-1283. |
| [11] | Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: a general theory of invasibility. Journal of Ecology, 88,528-534. |
| [12] |
Dukes JS, Mooney HA (1999) Does global change increase the success of biological invaders? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 14,135-139.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems, 6,503-523. |
| [14] |
Fichtner K, Schulze ED (1992) The effect of nitrogen nutrition on growth and biomass partitioning of annual plants originating from habitats of different nitrogen availability. Oecologia, 92,236-241.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Fogarty G, Facelli JM (1999) Growth and competition of Cytisus scoparius, an invasive shrub, and Australian native shrubs. Plant Ecology, 144,27-35. |
| [16] | Fumanal B, Girod C, Fried G, Bretagnolle F, Chauvel B (2008) Can the large ecological amplitude of Ambrosia artemisiifolia explain its invasive success in France? Weed Research, 48,349-359. |
| [17] |
Funk JL, Vitousek PM (2007) Resource-use efficiency and plant invasion in low-resource systems. Nature, 446,1079-1081.
URL PMID |
| [18] |
Genton B, Shykoff J, Giraud T (2005) High genetic diversity in French invasive populations of common ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifolia, as a result of multiple sources of introduction. Molecular Ecology, 14,4275-4285.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | Gibson D (1999) Designs for greenhouse studies of interactions between plants. Journal of Ecology, 87,1-16. |
| [20] | Grace JB (1995) On the measurement of plant competition intensity. Ecology, 76,305-308. |
| [21] |
Hager HA (2004) Competitive effect versus competitive response of invasive and native wetland plant species. Oecologia, 139,140-149.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Hobbs RJ, Gulmon S, Hobbs V, Mooney H (1988) Effects of fertiliser addition and subsequent gopher disturbance on a serpentine annual grassland community. Oecologia, 75,291-295.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | Holland EA, Dentener FJ, Braswell BH, Sulzman JM (1999) Contemporary and pre-industrial global reactive nitrogen budgets. Biogeochemistry, 46,7-43. |
| [24] | Huenneke LF, Hamburg SP, Koide R, Mooney HA, Vitousek PM (1990) Effects of soil resources on plant invasion and community structure in Californian serpentine grassland. Ecology, 71,478-491. |
| [25] | Jolliffe PA (2000) The replacement series. Journal of Ecology, 88,371-385. |
| [26] | Kolb A, Alpert P, Enters D, Holzapfel C (2002) Patterns of invasion within a grassland community. Journal of Ecology, 90,871-881. |
| [27] | Lake JC, Leishman MR (2004) Invasion success of exotic plants in natural ecosystems: the role of disturbance, plant attributes and freedom from herbivores. Biological Conservation, 117,215-226. |
| [28] | Leishman MR, Thomson VP (2005) Experimental evidence for the effects of additional water, nutrients and physical disturbance on invasive plants in low fertility Hawkesbury Sandstone soils, Sydney, Australia. Journal of Ecology, 93,38-49. |
| [29] | Levine JM, Vila M, Antonio C, Dukes JS, Grigulis K, Lavorel S (2003) Mechanisms underlying the impacts of exotic plant invasions. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 270,775. |
| [30] | Liu XJ, Ju XT, Zhang Y, He CE, Kopsch J, Zhang FS (2006) Nitrogen deposition in agroecosystems in the Beijing area. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 113,370-377. |
| [31] | Lu JZ (陆建忠), Qiu W (裘伟), Chen JK (陈家宽), Li B (李博) (2005) Impact of invasive species on soil properties: Canadian goldenrod ( Solidago canadensis) as a case study. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 13,347-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | MacDonald AM, Kotanen PM (2010) Leaf damage has weak effects on growth and fecundity of common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia). Botany, 88,158-164. |
| [33] | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecological Applications, 10,689-710. |
| [34] |
Maron JL, Connors PG (1996) A native nitrogen-fixing shrub facilitates weed invasion. Oecologia, 105,302-312.
URL PMID |
| [35] | McGilchrist C, Trenbath B (1971) A revised analysis of plant competition experiments. Biometrics, 27,659-671. |
| [36] | Patracchini C, Vidotto F, Ferrero A (2011) Common ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia) growth as affected by plant density and clipping. Weed Technology, 25,268-276. |
| [37] | Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience, 50,53-65. |
| [38] | Prinzing A, Durka W, Klotz S, Brandl R (2002) Which species become aliens? Evolutionary Ecology Research, 4,385-405. |
| [39] | Rejmanek M, Richardson DM (1996) What attributes make some plant species more invasive? Ecology, 77,1655-1661. |
| [40] | Shea K, Chesson P (2002) Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17,170-176. |
| [41] | Sher AA, Hyatt LA (1999) The disturbed resource-flux invasion matrix: a new framework for patterns of plant invasion. Biological Invasions, 1,107-114. |
| [42] |
Suding KN, LeJeune KD, Seastedt TR (2004) Competitive impacts and responses of an invasive weed: dependencies on nitrogen and phosphorus availability. Oecologia, 141,526-535.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | Vitousek PM, D'antonio CM, Loope LL, Rejmanek M, Westbrooks R (1997) Introduced species: a significant component of human-caused global change. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 21,1-16. |
| [44] | Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Westbrooks R (1996) Biological invasions as global environmental change. The American Scientist, 84,468-478. |
| [45] | Wang K (王坤), Yang J (杨继), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2010) Comparison of morphological traits between alligator weed and two congeners under different water and nutrient conditions. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 18, 615-621. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Wang ML (王满莲), Feng YL (冯玉龙) (2005) Effects of soil nitrogen levels on morphology, biomass allocation and photosynthesis in Ageratina adenophora and Chromoleana odorata. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 29,697-705. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] |
Wayne P, Foster S, Connolly J, Bazzaz F, Epstein P (2002) Production of allergenic pollen by ragweed ( Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) is increased in CO2-enriched atmospheres. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, 88,279-282.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] |
Wedin DA, Tilman D (1996) Influence of nitrogen loading and species composition on the carbon balance of grasslands. Science, 274,1720.
DOI URL PMID |
| [49] | Weigelt A, Jolliffe P (2003) Indices of plant competition. Journal of Ecology, 91,707-720. |
| [1] | Haobin Zhang, Lu Xiao, Yanjie Liu. Effects of artificial light at night on the diversity and growth of invasive alien and native plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | Xianglin Yang, Caiyun Zhao, Junsheng Li, Fangfang Chong, Wenjin Li. Invasive plant species lead to a more clustered community phylogenetic structure: An analysis of herbaceous plants in Guangxi’s national nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [3] | Congcong Du, Xueyu Feng, Zhilin Chen. The reducing of climate niche differences in the bridgehead effect promotes the invasion of Solenopsis invicta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [4] | Linjun He, Wenjing Yang, Yuhao Shi, Kezhemo Ashuo, Yu Fan, Guoyan Wang, Jingji Li, Songlin Shi, Guihua Yi, Peihao Peng. Effects of plant community phylogeny and functional diversity on Ageratina adenophora invasion under fire disturbance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [5] | Xuejiao Yuan, Yuanyuan Zhang, Yanliang Zhang, Luyi Hu, Weiguo Sang, Zheng Yang, Qi Chen. Investigating the prediction ability of the species distribution model fitted with the historical distribution records of Chromolaena odorata [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [6] | Lixia Han, Yongjian Wang, Xuan Liu. Comparisons between non-native species invasion and native species range expansion [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [7] | Yu Xiao, Yuran Li, Hexiang Duan, Zhengtao Ren, Shengbi Feng, Zhicheng Jiang, Jiahua Li, Pin Zhang, Jinming Hu, Yupeng Geng. Invasion status and control measures for alien plants within the Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [8] | Jiajia Pu, Pingjun Yang, Yang Dai, Kexin Tao, Lei Gao, Yuzhou Du, Jun Cao, Xiaoping Yu, Qianqian Yang. Species identification and population genetic structure of non-native apple snails (Ampullariidea: Pomacea) in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [9] | Shiyun Shen, Yuanfei Pan, Liru Chen, Yanli Tu, Xiaoyun Pan. Plant-soil feedbacks differ between native and introduced populations of Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [10] | Minhao Chen, Chao Zhang, Jiadong Wang, Zhenjie Zhan, Junzhi Chen, Xiaofeng Luan. Distribution and niche overlap of American mink and Eurasian otter in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22289-. |
| [11] | Bo Wei, Linshan Liu, Changjun Gu, Haibin Yu, Yili Zhang, Binghua Zhang, Bohao Cui, Dianqing Gong, Yanli Tu. The climate niche is stable and the distribution area of Ageratina adenophora is predicted to expand in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 21443-. |
| [12] | Bo Yang, Qinwen Lin, Qiang Zhu, Long Ma, Xiaowei Li. Species cataloging of vascular plants in Ningxia, northwestern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 22039-. |
| [13] | Xiaohong Chen, Haojie Chen, Yazhu Wang, Shuli Xiao, Xiaoqin Heng, Anjiu Zhao. Intraspecific and interspecific competition of the endangered plant Michelia wilsonii [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22003-. |
| [14] | Yanjie Liu, Wei Huang, Qiang Yang, Yu-Long Zheng, Shao-Peng Li, Hao Wu, Ruiting Ju, Yan Sun, Jianqing Ding. Research advances of plant invasion ecology over the past 10 years [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22438-. |
| [15] | Mingxian Deng, Heyan Huang, Shiyun Shen, Jihua Wu, Qiong La, Tsechoe Dorji, Xiaoyun Pan. Phenotypic plasticity of Alternanthera philoxeroides in response to simulated daily warming in the Tibet Plateau in introduced vs. native populations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1198-1205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()