



Biodiv Sci ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 574-580. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07039 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07039
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anwar Tumur, Adiljan Abdulla, Abdulla Abbas*( )
)
Received:2011-03-03
Accepted:2011-05-03
Online:2011-09-20
Published:2011-10-08
Contact:
Abdulla Abbas
Anwar Tumur, Adiljan Abdulla, Abdulla Abbas. Distribution of forest floor lichen communities in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi, Xinjiang, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2011, 19(5): 574-580.
| 目名和科名 Order and family | 属 Genus | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|
| 茶渍目 Lecanorales | ||
| 石蕊科 Cladoniaceae | 鹿蕊属 Cladina 石蕊属 Cladonia | 1 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris 2 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa 3 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea 4 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata 5 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula |
| 平茶渍属 Aspicilia | 6 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | |
| 膜衣科 Hymeneliaceae | 岛衣属 Cetraria | 7 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis |
| 梅衣科 Parmeliacea | 黄梅属 Xanthoparmelia | 8 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis |
| 蜈蚣衣科 Physciaceae | 大孢蜈蚣衣属 Physconia | 9 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis |
| 地卷目 Peltigerales | ||
| 地卷科 Peltigeraceae | 地卷属 Peltigera | 10 犬地卷 Peltigera canina 11 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae 12 多指地卷 P. polydactyla 13 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata 14 地卷 P. rufescens |
| 不完全地衣类 Lichenes imperfecti | 散盘衣属 Solorina 白角衣属 Siphula 地茶属 Thamnolia | 15 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora 16 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides 17 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis |
Table 1 Species composition of floor lichens in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 目名和科名 Order and family | 属 Genus | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|
| 茶渍目 Lecanorales | ||
| 石蕊科 Cladoniaceae | 鹿蕊属 Cladina 石蕊属 Cladonia | 1 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris 2 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa 3 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea 4 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata 5 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula |
| 平茶渍属 Aspicilia | 6 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | |
| 膜衣科 Hymeneliaceae | 岛衣属 Cetraria | 7 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis |
| 梅衣科 Parmeliacea | 黄梅属 Xanthoparmelia | 8 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis |
| 蜈蚣衣科 Physciaceae | 大孢蜈蚣衣属 Physconia | 9 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis |
| 地卷目 Peltigerales | ||
| 地卷科 Peltigeraceae | 地卷属 Peltigera | 10 犬地卷 Peltigera canina 11 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae 12 多指地卷 P. polydactyla 13 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata 14 地卷 P. rufescens |
| 不完全地衣类 Lichenes imperfecti | 散盘衣属 Solorina 白角衣属 Siphula 地茶属 Thamnolia | 15 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora 16 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides 17 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis |
| 样点 Sites | 物种丰富度 Richness | Shannon-Weiner指数 Shannon-Weiner diversity index | Pielou指数 Pielou eveness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 1.54 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 6 | 1.66 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 7 | 1.77 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 7 | 1.60 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 7 | 1.74 | 0.89 |
| 6 | 6 | 1.32 | 0.74 |
| 7 | 8 | 1.88 | 0.90 |
| 8 | 9 | 1.92 | 0.87 |
| 9 | 8 | 1.29 | 0.62 |
| 10 | 8 | 1.76 | 0.84 |
| 11 | 6 | 1.36 | 0.76 |
| 12 | 5 | 1.02 | 0.64 |
| 13 | 4 | 1.22 | 0.88 |
| 14 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| 15 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| 16 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.75 |
| 17 | 3 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| 18 | 3 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| 19 | 4 | 1.29 | 0.96 |
| 20 | 5 | 1.11 | 0.69 |
| 21 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.76 |
| 22 | 5 | 0.81 | 0.50 |
| 23 | 5 | 1.31 | 0.81 |
| 24 | 6 | 0.99 | 0.55 |
Table 2 Diversity indices of floor lichen communities at 24 sites in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 样点 Sites | 物种丰富度 Richness | Shannon-Weiner指数 Shannon-Weiner diversity index | Pielou指数 Pielou eveness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 1.54 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 6 | 1.66 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 7 | 1.77 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 7 | 1.60 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 7 | 1.74 | 0.89 |
| 6 | 6 | 1.32 | 0.74 |
| 7 | 8 | 1.88 | 0.90 |
| 8 | 9 | 1.92 | 0.87 |
| 9 | 8 | 1.29 | 0.62 |
| 10 | 8 | 1.76 | 0.84 |
| 11 | 6 | 1.36 | 0.76 |
| 12 | 5 | 1.02 | 0.64 |
| 13 | 4 | 1.22 | 0.88 |
| 14 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| 15 | 3 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| 16 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.75 |
| 17 | 3 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| 18 | 3 | 0.61 | 0.56 |
| 19 | 4 | 1.29 | 0.96 |
| 20 | 5 | 1.11 | 0.69 |
| 21 | 4 | 1.04 | 0.76 |
| 22 | 5 | 0.81 | 0.50 |
| 23 | 5 | 1.31 | 0.81 |
| 24 | 6 | 0.99 | 0.55 |
| 种类 Species | 盖度 Coverage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 群落1 | 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa | 2.95 |
| Group 1 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.04 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.19 | |
| 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea | 2.85 | |
| 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris | 2.61 | |
| 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | 3.30 | |
| 地卷 Peltigera elisabethae | 1.78 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 19.70 | |
| 群落2 | 腐石蕊 C. cariosa | 2.75 |
| Group 2 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 0.99 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.54 | |
| 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis | 1.53 | |
| 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis | 2.60 | |
| 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis | 0.02 | |
| 犬地卷 P. canina | 1.81 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 1.43 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora | 3.89 | |
| 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides | 1.05 | |
| 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis | 2.44 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 21.10 | |
| 群落3 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 2.87 |
| Group 3 | 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata | 1.77 |
| 雪岛衣 C. nivalis | 3.41 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 8.05 | |
| 群落4 | 喇叭粉石蕊 C.chlorophaea | 1.43 |
| Group 4 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.08 |
| 旱黄梅 X. camtschadalis | 3.60 | |
| 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae | 3.63 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 3.88 | |
| 地卷 P. rufescens | 4.32 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 S. bispora | 2.88 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 23.83 |
Table 3 Coverage of four floor lichen communities in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi
| 种类 Species | 盖度 Coverage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 群落1 | 腐石蕊 Cladonia cariosa | 2.95 |
| Group 1 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.04 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.19 | |
| 喇叭粉石蕊 C. chlorophaea | 2.85 | |
| 雀鹿蕊 Cladina stellaris | 2.61 | |
| 窝点平茶渍 Aspicilia lacunosa | 3.30 | |
| 地卷 Peltigera elisabethae | 1.78 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 19.70 | |
| 群落2 | 腐石蕊 C. cariosa | 2.75 |
| Group 2 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 0.99 |
| 粗皮石蕊 C. scabriuscula | 2.54 | |
| 雪岛衣 Cetraria nivalis | 1.53 | |
| 旱黄梅 Xanthoparmelia camtschadalis | 2.60 | |
| 甘肃大孢蜈蚣衣 Physconia kansuensis | 0.02 | |
| 犬地卷 P. canina | 1.81 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 1.43 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 Solorina bispora | 3.89 | |
| 翅白角衣 Siphula pteruloides | 1.05 | |
| 雪地茶 Thamnolia subuliformis | 2.44 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 21.10 | |
| 群落3 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 2.87 |
| Group 3 | 裂芽地卷 P. praetextata | 1.77 |
| 雪岛衣 C. nivalis | 3.41 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 8.05 | |
| 群落4 | 喇叭粉石蕊 C.chlorophaea | 1.43 |
| Group 4 | 喇叭石蕊 C. pyxidata | 4.08 |
| 旱黄梅 X. camtschadalis | 3.60 | |
| 平盘软地卷 P. elisabethae | 3.63 | |
| 多指地卷 P. polydactyla | 3.88 | |
| 地卷 P. rufescens | 4.32 | |
| 双孢散盘衣 S. bispora | 2.88 | |
| 小计 Subtotal | 23.83 |
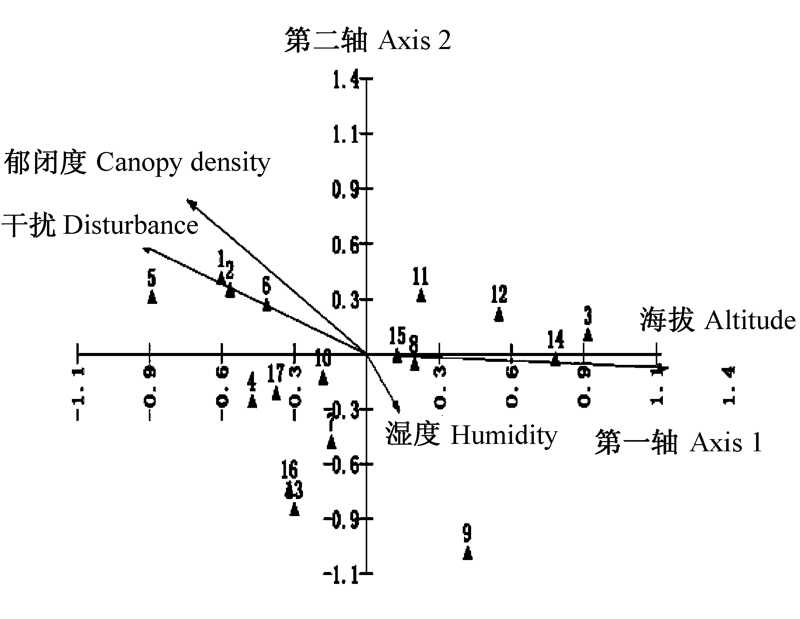
Fig. 3 CCA (Canonical Correspondence Analysis) revealing the relationships of the 17 lichen species with four environmental factors in the mountainous area of southern Urumqi. Lichen species 1-17 are listed in Table 1.
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 湿度 Humidity | 干扰 Disturbance | 海拔 Altitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 1.000 | |||
| 湿度 Humidity | 0.7183 | 1.000 | ||
| 干扰 Disturbance | -0.3517 | -0.2162 | 1.000 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.5912 | 0.7539 | 0.6326 | 1.000 |
Table 4 Correlation analysis of four environmental factors
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 湿度 Humidity | 干扰 Disturbance | 海拔 Altitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 郁闭度 Canopy density | 1.000 | |||
| 湿度 Humidity | 0.7183 | 1.000 | ||
| 干扰 Disturbance | -0.3517 | -0.2162 | 1.000 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.5912 | 0.7539 | 0.6326 | 1.000 |
| [1] | Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯), Wu JN (吴继农) (1998) Lichens of Xinjiang (新疆地衣). Xinjiang Science, Technology and Hygiene Publishing House, Urumqi. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Cao T (曹同), Guo SL (郭水良) (2000) A study on bryophytes diversity in the main ecosystems in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 8,50-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Cao T (曹同), Chen Y (陈怡), Yu J (于晶), Song GY (宋国元) (2004) Distribution patterns of moss species in Shanghai City. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 15,1785-1791. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Dulamsuren C, Hauck M, Mühlenberg M (2005a) Vegetation at the taiga forest-steppe borderline in the western Khentey Mountains, northern Mongolia. Annales Botanici Fennici, 42,411-426. |
| [5] | Dulamsuren C, Hauck M, Mühlenberg M (2005b) Ground vegetation in the Mongolian taiga forest-steppe ecotone does not offer evidence for the human origin of grasslands. Applied Vegetation Sciences, 8,149-154. |
| [6] | Eldridge DJ (1996) Distribution and floristics of terricolous lichens in soil crusts in arid and semi-arid New South Wales, Australia. Australia Journal of Botany, 44,581-599. |
| [7] | Eldridge DJ, Tozer ME (1997) Environmental factors relating to the distribution of terricolous bryophytes and lichens semi-arid eastern Australia. The Bryologist, 100,28-39. |
| [8] | Eldridge DJ (2001) Biological soil crusts of Australia. In: Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function and Management(eds Belnap J, Lange OL). Ecological Studies, 150,119-131. |
| [9] | Johansson P (2008) Consequences of disturbance on epiphytic lichens in boreal and near boreal forests. Biological Conservation, 141,1933-1944. |
| [10] | Loppi S, Boscagli A,De Dominicis V (2004) Ecology of soil lichens from Pliocene clay badlands of central Italy in relation to geomorphology and vascular vegetation. Catena, 55,1-15. |
| [11] | Luo GY (罗光裕) (1984) Preliminary study on the lichen species distribution and their ecological characteristics on Dailing Liangshui Forest Farm. Journal of North Eastern Forestry Institute (东北林学院学报), 12(Suppl.),84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Mason EH (1983) The Biology of Lichens, 3rd edn. Edward Arnold Publishers, London. |
| [13] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley and Sons Publishers, New York. |
| [14] | Rogers RW (1977) Lichens of hot arid and semi-arid lands. In: Lichen Ecology (ed. Seaward MRD), pp.211-252. Academic Press, London. |
| [15] | Rosentreter R, Belnap J (2001) Biological soil crusts of North America. In:Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function and Management(eds Belnap J, Lange OL). Ecological Studies 150,31-50. |
| [16] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) Mamut R (热衣木江·马木提)(2003) Preliminary study on the lichen community structure in forest ecosystem of western Tianshan Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 27,810-815. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abdulla A (阿地里江·阿不都拉) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2005) Numerical classification and species diversity of corticolous lichen communities in forest ecosystems of the Tianshan Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 29,615-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) (2006a) A preliminary study of community characteristics of corticolous lichen in forest ecosystem in Eastern Altay Mts. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 28,415-420. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯) (2006b) Floor lichen diversity under different vegetation types in Two-river Source Nature Reserve in Altay Mountains, Xinjiang. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14,444-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Mamut R (热衣木江·马木提) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2009a) Study of the corticolous lichens communities structure in forest ecosystem in southern mountains of Urumqi. Chinese Bulletin of Botany (植物学报), 44,578-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Tumur A (艾尼瓦尔·吐米尔) Abbas A (阿不都拉·阿巴斯)(2009b) Saxicolous lichen community structure and characteristics in mountainous area of southern Urumqi. Mycosystema (菌物学报), 28,178-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Wang BC (王伯荪) (1987) Plant Community Ecology (植物群落学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21,213-251. |
| [24] | Yang HX (阳含熙), Lu ZY (卢泽愚) (1981) Methodology of Quantitative Taxonomy in Plant Ecology (植物生态学的数量分类方法). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Zedda L, Gröngröft A, Schultz M, Petersen A, Mills A, Rambold G (2011) Distribution patterns of soil lichens across the principal biomes of southern Africa. Journal of Arid Environments, 75,215-220. |
| [26] | Zhang YM (张元明), Cao T (曹同), Pan BR (潘伯荣) (2002) Quantitative classification and ordination analysis on bryophyte vegetation in Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 26,10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Zhang JT (张金屯) (1995) Methodology of Vegetation Quantitative Ecology (植被数量生态学方法). Chinese Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [10] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [11] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [12] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [13] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [14] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [15] | Hui Ran, Tianyou Yang, Xiaoqi Mi. The updated checklist of reptiles in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23348-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()