



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 24495. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024495 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024495
• Conservation and Governance • Next Articles
Received:2024-11-12
Accepted:2025-07-31
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
*E-mail: yinhao@bjfu.edu.cn
Supported by:Luyao Tian, Hao Yin. Research status and strategies for China’s ecological railway development based on biodiversity conservation[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(8): 24495.
| 一级策略 Primary strategy | 二级策略 Secondary strategy |
|---|---|
| 增加铁路横向连通/野生动物通道 Increasing railway lateral connectivity/wildlife passage | 在铁路之上: 建设野生动物天桥、野生动物景观桥、改良多功能天桥、树顶天桥 Over the railway: construction of wildlife overpass, landscape bridge, improved multi-functional bridge, tree-top bridge |
| 将铁路高架: 保留现状连通生境 Elevated railway: preserve the current connected habitat | |
| 在铁路之下: 建设大中型动物地下通道、小动物地下通道、鱼道、两栖动物隧道, 改良多功能地下通道、涵洞等 Under the railway: construction of large and medium-sized wildlife underpasses, small wildlife underpasses, fish lanes, amphibian tunnels, improved multi-functional underpasses, culverts, etc. | |
| 改善人工设施降低 WTC Improving artificial facilities to reduce WTC | 建设特殊设施: 设置围栏、屏障、人工震慑、带有传感器的预警系统、警示标志等 Implement specialized facilities: install fencing, barriers, artificial deterrents, sensor-based early warning systems, warning signs, etc. |
| 改善铁路基础设施: 优化排水沟、进行铁路改造及运行管理、减少人造光使用 Enhance railway infrastructure: optimize drainage systems, carry out railway renovation and operation management, and minimize artificial lighting | |
| 沿线植被管理 Vegetation management along railways | 植被规划: 近轨道处植被应降低对动物的吸引力, 提升司机的可见度; 远离轨道处植被形成异质性半自然生境 Vegetation planning: the vegetation next to the railway should minimize wildlife attraction while maintaining clear sightlines for train operators; away from the railway, vegetation should form heterogeneous semi-natural habitats |
| 制定分区植被管理计划: 只进行必要的管理活动; 避开野生动物筑巢、繁育季节 Develop a zonal vegetation management plan: carry out only necessary management activities; avoid wildlife nesting and breeding seasons | |
| 植被修复: 增加本地物种 Vegetation restoration: increase native species | |
| 生物多样性补偿 Biodiversity compensation | 生境改善 Habitat improvement |
| 营建新生境 Construction of new habitats | |
| 对特定物种进行利益补偿 Benefit compensation for specific species | |
| 定期生物多样性调查 Regular biodiversity surveys | 建设前全面评估生态影响 Comprehensive ecological impact assessment before construction |
| 施工中和施工后, 应建立基线, 定期监测野生动物相关指标 During and after construction, baselines should be established for regularly monitoring of wildlife-related indicators | |
| 预测和定期监测结合 Combining forecasting with regular monitoring | |
| 资金和政策支持 Financial and policy support | 宏观: 鼓励混合式融资方式 Macro: encourage hybrid financing |
| 微观: 鼓励生物多样性组织建设 Micro: encourage the development of biodiversity organizations |
Table 1 Ecological railway strategies based on biodiversity conservation in foreign countries
| 一级策略 Primary strategy | 二级策略 Secondary strategy |
|---|---|
| 增加铁路横向连通/野生动物通道 Increasing railway lateral connectivity/wildlife passage | 在铁路之上: 建设野生动物天桥、野生动物景观桥、改良多功能天桥、树顶天桥 Over the railway: construction of wildlife overpass, landscape bridge, improved multi-functional bridge, tree-top bridge |
| 将铁路高架: 保留现状连通生境 Elevated railway: preserve the current connected habitat | |
| 在铁路之下: 建设大中型动物地下通道、小动物地下通道、鱼道、两栖动物隧道, 改良多功能地下通道、涵洞等 Under the railway: construction of large and medium-sized wildlife underpasses, small wildlife underpasses, fish lanes, amphibian tunnels, improved multi-functional underpasses, culverts, etc. | |
| 改善人工设施降低 WTC Improving artificial facilities to reduce WTC | 建设特殊设施: 设置围栏、屏障、人工震慑、带有传感器的预警系统、警示标志等 Implement specialized facilities: install fencing, barriers, artificial deterrents, sensor-based early warning systems, warning signs, etc. |
| 改善铁路基础设施: 优化排水沟、进行铁路改造及运行管理、减少人造光使用 Enhance railway infrastructure: optimize drainage systems, carry out railway renovation and operation management, and minimize artificial lighting | |
| 沿线植被管理 Vegetation management along railways | 植被规划: 近轨道处植被应降低对动物的吸引力, 提升司机的可见度; 远离轨道处植被形成异质性半自然生境 Vegetation planning: the vegetation next to the railway should minimize wildlife attraction while maintaining clear sightlines for train operators; away from the railway, vegetation should form heterogeneous semi-natural habitats |
| 制定分区植被管理计划: 只进行必要的管理活动; 避开野生动物筑巢、繁育季节 Develop a zonal vegetation management plan: carry out only necessary management activities; avoid wildlife nesting and breeding seasons | |
| 植被修复: 增加本地物种 Vegetation restoration: increase native species | |
| 生物多样性补偿 Biodiversity compensation | 生境改善 Habitat improvement |
| 营建新生境 Construction of new habitats | |
| 对特定物种进行利益补偿 Benefit compensation for specific species | |
| 定期生物多样性调查 Regular biodiversity surveys | 建设前全面评估生态影响 Comprehensive ecological impact assessment before construction |
| 施工中和施工后, 应建立基线, 定期监测野生动物相关指标 During and after construction, baselines should be established for regularly monitoring of wildlife-related indicators | |
| 预测和定期监测结合 Combining forecasting with regular monitoring | |
| 资金和政策支持 Financial and policy support | 宏观: 鼓励混合式融资方式 Macro: encourage hybrid financing |
| 微观: 鼓励生物多样性组织建设 Micro: encourage the development of biodiversity organizations |
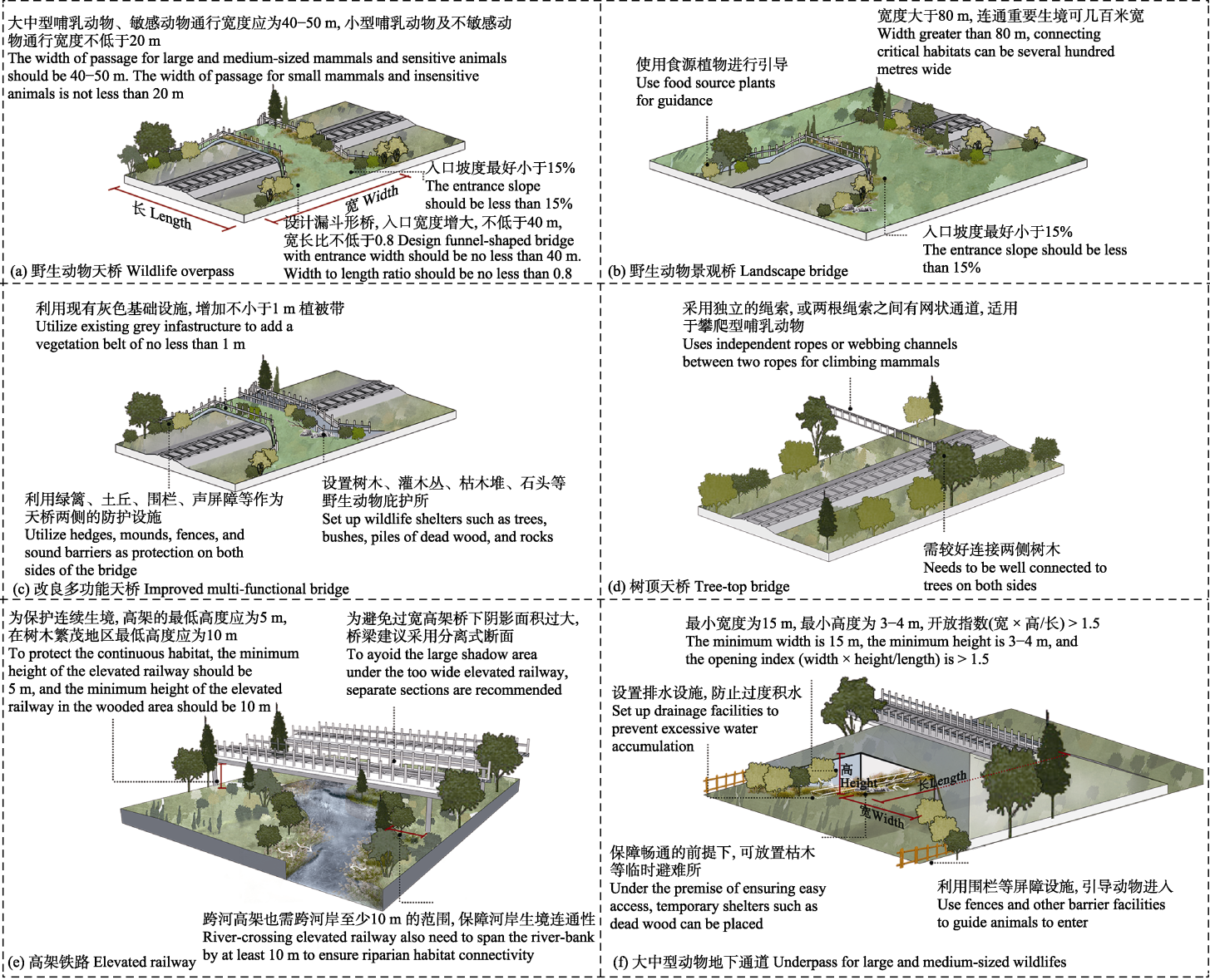
Fig. 1 Schematic of railway lateral connectivity/wildlife passage. (a) Wildlife overpass; (b) Landscape bridge; (c) Improved multi-functional bridge; (d) Tree-top bridge; (e) Elevated railway; (f) Underpass for large and medium-sized wildlife.
| 人工设施 Artificial facilities | 设计要点 Key points of design |
|---|---|
| 围栏及屏障 Fences and barriers | 高度取决于动物类型, 马鹿等不低于2.2 m, 狍等不低于1.5 m; 加大埋深, 保障稳固; 栏杆网格间距需考虑小型动物逃脱; 出入口采用开敞式、引导式设计; 需与动物通道结合; 透明屏障周边减少植物种植、采取防鸟撞措施; 仅在WTC高发地点设置; 为困在铁轨内的野生动物设置逃生通道 The height depends on the wildlife species, such as red deer, not less than 2.2 m, roe deer, not less than 1.5 m; Increase the depth of burial to ensure stability; Railing grid spacing should consider small wildlife escape; The entrance and exit are open and guided; Need to bind to wildlife passage; Reduce plant planting around transparent barriers and take bird collision prevention measures; Set only at WTC high incidence locations; Set up escape routes for wildlife trapped inside the tracks |
| 人工威慑 Artificial deterrents | 基于光学、声学或嗅觉装置, 如超声波装置、嗅觉驱避剂 Based on optical, acoustic or olfactory devices, such as ultrasonic devices, olfactory repellents |
| 带有传感器的预警系统Sensor-based early warning systems | 如利用热传感器, 触发警报装置 Such as the use of thermal sensors, trigger alarm devices |
| 警示标志 Warning signs | 只在风险较高的地点和时间段内放置, 结合闪光灯等引起司机注意 Only place in high-risk locations and time periods, combined with flashing lights, etc., to attract the driver’s attention |
| 优化排水沟 Optimizing drainage systems | 设置下水道逃生坡道 Set up drain escape ramps |
| 铁路改造与运行管理 Carrying out railway renovation and operation management | 尽量采用土质路面; 采取季节性、时段性防碰撞措施, 如在动物迁徙期铁路段封闭或限速 Try to use soil pavement; Adopting seasonal and timely collision avoidance measures, such as closures or speed limits on railway sections during wildlife migration periods. |
| 人造光 Artificial light | 使用钠灯, 防止昆虫碰撞 Use sodium lamps to prevent insect collisions |
Table 2 Content and design key points of improving related artificial facilities, based on Seiler et al (2016), Carvalho et al (2017), and Biodiversity Infrastructure (2020)
| 人工设施 Artificial facilities | 设计要点 Key points of design |
|---|---|
| 围栏及屏障 Fences and barriers | 高度取决于动物类型, 马鹿等不低于2.2 m, 狍等不低于1.5 m; 加大埋深, 保障稳固; 栏杆网格间距需考虑小型动物逃脱; 出入口采用开敞式、引导式设计; 需与动物通道结合; 透明屏障周边减少植物种植、采取防鸟撞措施; 仅在WTC高发地点设置; 为困在铁轨内的野生动物设置逃生通道 The height depends on the wildlife species, such as red deer, not less than 2.2 m, roe deer, not less than 1.5 m; Increase the depth of burial to ensure stability; Railing grid spacing should consider small wildlife escape; The entrance and exit are open and guided; Need to bind to wildlife passage; Reduce plant planting around transparent barriers and take bird collision prevention measures; Set only at WTC high incidence locations; Set up escape routes for wildlife trapped inside the tracks |
| 人工威慑 Artificial deterrents | 基于光学、声学或嗅觉装置, 如超声波装置、嗅觉驱避剂 Based on optical, acoustic or olfactory devices, such as ultrasonic devices, olfactory repellents |
| 带有传感器的预警系统Sensor-based early warning systems | 如利用热传感器, 触发警报装置 Such as the use of thermal sensors, trigger alarm devices |
| 警示标志 Warning signs | 只在风险较高的地点和时间段内放置, 结合闪光灯等引起司机注意 Only place in high-risk locations and time periods, combined with flashing lights, etc., to attract the driver’s attention |
| 优化排水沟 Optimizing drainage systems | 设置下水道逃生坡道 Set up drain escape ramps |
| 铁路改造与运行管理 Carrying out railway renovation and operation management | 尽量采用土质路面; 采取季节性、时段性防碰撞措施, 如在动物迁徙期铁路段封闭或限速 Try to use soil pavement; Adopting seasonal and timely collision avoidance measures, such as closures or speed limits on railway sections during wildlife migration periods. |
| 人造光 Artificial light | 使用钠灯, 防止昆虫碰撞 Use sodium lamps to prevent insect collisions |
| [1] | Akbar KF, Hale WHG, Headley AD, Ashraf I (2010) Evaluation of conservation status of roadside verges and their vegetation in North England. Polish Journal of Ecology, 58, 459-467. |
| [2] | Ament R, Clevenger A, van der Ree R (2023) Addressing ecological connectivity in the development of roads, railways and canals. IUCN WCPA Technical Report Series No. 5. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [3] | Andreassen HP, Gundersen H, Storaas T (2005) The effect of scent-marking, forest clearing, and supplemental feeding on moose-train collisions. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 69, 1125-1132. |
| [4] |
Auffret AG, Cousins SAO (2013) Humans as long-distance dispersers of rural plant communities. PLoS ONE, 8, e62763.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Babińska-Werka J, Krauze-Gryz D, Wasilewski M, Jasińska K (2015) Effectiveness of an acoustic wildlife warning device using natural calls to reduce the risk of train collisions with animals. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 38, 6-14.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Barrientos R, Ascensão F, Beja P, Pereira HM, Borda-de-Água L (2019) Railway ecology vs. road ecology: Similarities and differences. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 65, 12.
DOI |
| [7] | Barrientos R, Borda-de-Água L (2017) Railways as barriers for wildlife:Current knowledge. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.43-64. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [8] | Bartoszek J, Greenwald KR (2009) A population divided: Railroad tracks as barriers to gene flow in an isolated population of marbled salamanders (Ambystoma opacum). Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 4, 191-197. |
| [9] |
Bennett AF (1990) Habitat corridors and the conservation of small mammals in a fragmented forest environment. Landscape Ecology, 4, 109-122.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Biodiversity Infrastructure (2020) Best Practices to Benefit Biodiversity and Achieve Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructure. https://www.biodiversityinfrastructure.org/autthors-partners/ . (accessed on 2025-02-08) |
| [11] |
Blackwood L, Renaud FG (2022) Barriers and tools for implementing nature-based solutions for rail climate change adaptation. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 113, 103529.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM (2017) Railway Ecology. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [13] | Budzik KA, Budzik KM (2014) A preliminary report of amphibian mortality patterns on railways. Acta Herpetologica, 9, 103-107. |
| [14] | Cao GH, Wang Y, Yang YG, Guan L, Zhou HP, Zhang Q, Tao SC, Kong YP (2020) Review of design and evaluation for wildlife crossing structures. Environmental Impact Assessment, 42(3), 11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹广华, 王云, 杨艳刚, 关磊, 周红萍, 张乾, 陶双成, 孔亚平 (2020) 野生动物通道设计及评价的经验与建议. 环境影响评价, 42(3), 11-14.] | |
| [15] | Carvalho F, Santos SM, Mira A, Lourenço R (2017) Methods to monitor and mitigate wildlife mortality in railways. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.23-42. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [16] |
Catalano C, Meslec M, Boileau J, Guarino R, Aurich I, Baumann N, Chartier F, Dalix P, Deramond S, Laube P, Lee AKK, Ochsner P, Pasturel M, Soret M, Moulherat S (2021) Smart sustainable cities of the new millennium: Towards design for nature. Circular Economy and Sustainability, 1, 1053-1086.
DOI |
| [17] |
Catford JA, Daehler CC, Murphy HT, Sheppard AW, Hardesty BD, Westcott DA, Rejmánek M, Bellingham PJ, Pergl J, Horvitz CC, Hulme PE (2012) The intermediate disturbance hypothesis and plant invasions: Implications for species richness and management. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 14, 231-241.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Chen ZQ, Wang KX, Ai YW, Li W, Gao HY, Fang C (2014) The effects of railway transportation on the enrichment of heavy metals in the artificial soil on railway cut slopes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 1039-1049.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Conradt L, Roper TJ, Thomas CD (2001) Dispersal behaviour of individuals in metapopulations of two British butterflies. Oikos, 95, 416-424.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Council of Europe (2000) General guidelines for the development of the Pan-European Ecological Network. Nature and Environment Series, No. 107. |
| [21] |
Cuperus R, Canters KJ, Udo de Haes HA, Friedman DS (1999) Guidelines for ecological compensation associated with highways. Biological Conservation, 90, 41-51.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Dasgupta S, Ghosh AK (2015) Elephant-railway conflict in a biodiversity hotspot: Determinants and perceptions of the conflict in northern west Bengal, India. Human Dimensions of Wildlife, 20, 81-94. |
| [23] | DeVault TL, Blackwell BF, Seamans TW, Lima SL, Fernández-Juricic E (2015) Speed kills:Ineffective avian escape responses to oncoming vehicles. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282, 20142188. |
| [24] | Dorsey B, Olsson M, Rew LJ (2015) Ecological effects of railways on wildlife. In: Handbook of Road Ecology (eds van der Ree R, Smith DJ, Grilo C), pp. 219-227. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [25] | Dorsey BP, Clevenger A, Rew LJ (2017) Relative risk and variables associated with bear and ungulate mortalities along a railroad in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.135-155. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [26] | Ernst CH, Lovich JE (2009) Turtles of the United States and Canada, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. |
| [27] |
Fenderson LE, Kovach AI, Litvaitis JA, O’Brien KM, Boland KM, Jakubas WJ (2014) A multiscale analysis of gene flow for the New England cottontail, an imperiled habitat specialist in a fragmented landscape. Ecology and Evolution, 4, 1853-1875.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Forman RT, Sperling D, Bissonette JA, Clevenger AP, Cutshall CD, Dale VH, Winter TC (2003) Road Ecology (Vol. 482). Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [29] |
Forman RTT, Alexander LE (1998) Roads and their major ecological effects. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 29, 207-231.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
García de la Morena EL, Malo JE, Hervás I, Mata C, González S, Morales R, Herranz J (2017) On-board video recording unravels bird behavior and mortality produced by high-speed trains. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 117.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Ge C, Li Z, Li J, Huang C (2011) The effects on birds of human encroachment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 16, 604-606.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Glista DJ, DeVault TL, DeWoody JA (2009) A review of mitigation measures for reducing wildlife mortality on roadways. Landscape and Urban Planning, 91, 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Godinho C, Marques JT, Salgueiro P, Catarino L, de Castro CO, Mira A, Beja P (2017) Bird collisions in a railway crossing a wetland of international importance (Sado Estuary, Portugal). In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.103-115. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [34] | Gunson K, Chruszcz B, Clevenger A (2006) What features of the landscape and highway influence ungulate vehicle collisions in the watersheds of the Central Canadian Rocky Mountains: A fine-scale perspective? In:Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Ecology and Transportation, pp. 545-556. The U.S. Federal Highway Administration and the Western Transportation Institute, May 21-25 2006. San Diego, California. |
| [35] | Han YW, Fang TS, Jiang Y, Yin LH, Wan M (2024) A study of wild boar habitat suitability in high-density urban areas and identification of potential risk areas of “human-boar conflicts”. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 22(1), 16-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩依纹, 方铁树, 蒋韵, 殷利华, 万敏 (2024) 高密度城区野猪生境适宜性与“人猪冲突”潜在风险区识别研究. 中国城市林业, 22(1), 16-24.] | |
| [36] | Hanson CE (2008) High speed train noise effects on wildlife and domestic livestock. In: Noise and Vibration Mitigation for Rail Transportation Systems: Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Railway Noise, Munich, Germany, pp. 26-32. September 4-8, 2007. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin Heidelberg. |
| [37] | Heske EJ (2015) Blood on the tracks: Track mortality and scavenging rate in urban nature preserves. Urban Naturalist, 4, 1-13. |
| [38] |
Hopwood JL (2008) The contribution of roadside grassland restorations to native bee conservation. Biological Conservation, 141, 2632-2640.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Høye TT, Dyrmann M, Kjær C, Nielsen J, Bruus M, Mielec CL, Vesterdal MS, Bjerge K, Madsen SA, Jeppesen MR, Melvad C (2022) Accurate image-based identification of macroinvertebrate specimens using deep learning-How much training data is needed? PeerJ, 10, e13837.
DOI URL |
| [40] | IEEP (2022) Guidance on the Maintenance of Landscape Connectivity Features of Major Importance for Wild Flora and Fauna. https://ieep.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/guidance_the_implementation_of_articles_3_and_10_birds_habitats_directives.pdf . (accessed on 2025-02-08) |
| [41] | IENE (2013) COST 345 Habitat Fragmentation due to Transportation Infrastructure. https://www.iene.info/content/uploads/2013/10/COST341_final_report.pdf . (accessed on 2025-02-08) |
| [42] |
Ito TY, Okada A, Buuveibaatar B, Lhagvasuren B, Takatsuki S, Tsunekawa A (2008) One-sided barrier impact of an international railroad on Mongolian gazelles. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 72, 940-943.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Jerem P, Mathews F (2021) Passing rail traffic reduces bat activity. Scientific Reports, 11, 20671.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Johnson AM (2008) Best Practices Handbook for Roadside Vegetation Management. Retrieved from the University Digital Conservancy, https://hdl.handle.net/11299/189439 . |
| [45] |
Joly P, Morand C, Cohas A (2003) Habitat fragmentation and amphibian conservation: Building a tool for assessing landscape matrix connectivity. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 326, 132-139.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Kalarus K, Bąkowski M (2015) Railway tracks can have great value for butterflies as a new alternative habitat. Italian Journal of Zoology, 82, 565-572.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Kerbiriou C, Julien JF, Monsarrat S, Lustrat P, Haquart A, Robert A (2015) Information on population trends and biological constraints from bat counts in roost cavities: A 22-year case study of a pipistrelle bats (Pipistrellus pipistrellus Schreber) hibernaculum. Wildlife Research, 42, 35.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Kerth G, Melber M (2009) Species-specific barrier effects of a motorway on the habitat use of two threatened forest-living bat species. Biological Conservation, 142, 270-279.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Kornilev YV, Price S, Dorcas M (2006) Between a rock and a hard place: Responses of eastern box turtles (Terrapene carolina) when trapped between railroad tracks. Herpetological Review, 37, 145-148. |
| [50] |
Krauss J, Bommarco R, Guardiola M, Heikkinen RK, Helm A, Kuussaari M, Lindborg R, Öckinger E, Pärtel M, Pino J, Pöyry J, Raatikainen KM, Sang AN, Stefanescu C, Teder T, Zobel M, Steffan-Dewenter I (2010) Habitat fragmentation causes immediate and time-delayed biodiversity loss at different trophic levels. Ecology Letters, 13, 597-605.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Kušta T, Keken Z, Ježek M, Kůta Z (2015) Effectiveness and costs of odor repellents in wildlife-vehicle collisions: A case study in Central Bohemia, Czech Republic. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 38, 1-5.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Lian XM, Li XX, Xu T (2012) Avoidance distances of four ungulates from roads in Kekexili and related protection suggestions. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(1), 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [连新明, 李晓晓, 徐图 (2012) 可可西里四种有蹄类动物对道路的回避距离及保护建议. 生态学杂志, 31(1), 81-86.] | |
| [53] | Limpens HJGA, Kapteyn K (1991) Bats, their behaviour and linear landscape elements. Myotis, 29, 63-71. |
| [54] |
Linden B, Cuozzo FP, Sauther ML, Jonker WC (2022) Impact of linear infrastructure on South Africa’s primate fauna: The need for mitigation. Folia Primatologica, 93, 235-253.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Liu J, Ouyang ZY, Miao H (2010) Environmental attitudes of stakeholders and their perceptions regarding protected area-community conflicts: A case study in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 91, 2254-2262.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
López I, Rodríguez J, Burón JM, García A (2009) A methodology for evaluating environmental impacts of railway freight transportation policies. Energy Policy, 37, 5393-5398.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Lucas PS, de Carvalho RG, Grilo C (2017) Railway disturbances on wildlife:Types, effects, and mitigation measures. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.81-99. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [58] | Luo JF, Zheng JM, Zhou JX, Zhang X, Cui M (2016) Analysis of the interspecific associations present in an alpine meadow community undergoing revegetation on the railway-construction affected land of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 6528-6537. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗久富, 郑景明, 周金星, 张鑫, 崔明 (2016) 青藏高原高寒草甸区铁路工程迹地植被恢复过程的种间关联性. 生态学报, 36, 6528-6537.] | |
| [59] | Maron M, Hobbs RJ, Moilanen A, Matthews JW, Christie K, Gardner TA, Keith DA, Lindenmayer DB, McAlpine CA (2012) Faustian bargains? Restoration realities in the context of biodiversity offset policies. Biological Conservation, 155, 141-148. |
| [60] |
Miao ZY, Wu T, Chen JP, Wang D, Li HQ, Lian XM (2020) Effect of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on diurnal behavioural time budgets in male Tibetan antelopes. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 40, 135-142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [苗紫燕, 吴彤, 陈佳萍, 王东, 李宏奇, 连新明 (2020) 青藏铁路对雄性藏羚行为时间分配的影响. 兽类学报, 40, 135-142.] | |
| [61] |
Morelli F, Beim M, Jerzak L, Jones D, Tryjanowski P (2014) Can roads, railways and related structures have positive effects on birds? A review. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 30, 21-31.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Moroń D, Skórka P, Lenda M, Rożej-Pabijan E, Wantuch M, Kajzer-Bonk J, Celary W, Mielczarek ŁE, Tryjanowski P (2014) Railway embankments as new habitat for pollinators in an agricultural landscape. PLoS ONE, 9, e101297.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Network Rail (2021) Biodiversity on Britain’s Railway. https://www.networkrail.co.uk/sustainability/biodiversity-on-britains-railway/ . (accessed on 2025-02-08) |
| [64] |
Penone C, Machon N, Julliard R, Le Viol I (2012) Do railway edges provide functional connectivity for plant communities in an urban context? Biological Conservation, 148, 126-133.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Pérez-Espona S, Pérez-Barbería FJ, McLeod JE, Jiggins CD, Gordon IJ, Pemberton JM (2008) Landscape features affect gene flow of Scottish Highland red deer (Cervus elaphus). Molecular Ecology, 17, 981-996.
DOI PMID |
| [66] |
Pollock SZ, Nielsen SE, St Clair CC (2017) A railway increases the abundance and accelerates the phenology of bear-attracting plants in a forested, mountain park. Ecosphere, 8, e01985.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Ridding LE, Redhead JW, Pywell RF (2015) Fate of semi-natural grassland in England between 1960 and 2013: A test of national conservation policy. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 516-525.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Rodrigue JP, Comtois C, Slack B (2016) The Geography of Transport Systems, 4th edn. Oxon OX14 4RN Press, Routledge. |
| [69] | Roy M, Baskaran N, Sukumar R (2009) The death of jumbos on railway tracks in northern West Bengal. Gajah, 31, 36-39. |
| [70] | Rytwinski T, Fahrig L (2015) The impacts of roads and traffic on terrestrial animal populations. In: Handbook of Road Ecology (eds van der Ree R, Smith DJ, Grilo C), pp. 237-246. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [71] |
Saarinen K, Valtonen A, Jantunen J, Saarnio S (2005) Butterflies and diurnal moths along road verges: Does road type affect diversity and abundance? Biological Conservation, 123, 403-412.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Santos SM, Carvalho F, Mira A (2017) Current knowledge on wildlife mortality in railways. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.11-22. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [73] | Seiler A, Olsson M (2017) Wildlife deterrent methods for railways—An experimental study. In: Railway Ecology (eds Borda-de-Água L, Barrientos R, Beja P, Pereira HM), pp.277-291. Springer Nature, Cham. |
| [74] | Seiler A, Olsson M, Rosell C, Van Der Grift EA (2016) Cost-benefit analyses for wildlife and traffic safety. SAFEROAD Technical Report 4. Conference of European Directors of Roads (CEDR), Brussels. |
| [75] | Steve F, Vaughan R, David T, David W (2020) Soils, Landscape and Woodland: How HS2 is Using Integrated Asset Information Management in a BIM Environment. https://learninglegacy.hs2.org.uk/document/soils-landscape-and-woodland-how-hs2-is-using-integrated-asset-information-management-in-a-bim-environment/ . (accessed on 2025-02-08) |
| [76] | Tian LY, Yin H (2023) Biodiversity conservation strategies for UK railways. World Forestry Research, 36(6), 97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田璐瑶, 尹豪 (2023) 英国铁路的生物多样性策略. 世界林业研究, 36(6), 97-104.] | |
| [77] |
Tikka PM, Högmander H, Koski PS (2001) Road and railway verges serve as dispersal corridors for grassland plants. Landscape Ecology, 16, 659-666.
DOI |
| [78] |
Tikka PM, Koski PS, Kivelä RA, Kuitunen MT (2000) Can grassland plant communities be preserved on road and railway verges? Applied Vegetation Science, 3, 25-32.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Townsend PA, Levey DJ (2005) An experimental test of whether habitat corridors affect pollen transfer. Ecology, 86, 466-475.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Travers E, Härdtle W, Matthies D (2021) Corridors as a tool for linking habitats—Shortcomings and perspectives for plant conservation. Journal for Nature Conservation, 60, 125974.
DOI URL |
| [81] | van der Ree R, Smith DJ, Grilo C (2015) Handbook of Road Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [82] |
Vandevelde JC, Bouhours A, Julien JF, Couvet D, Kerbiriou C (2014) Activity of European common bats along railway verges. Ecological Engineering, 64, 49-56.
DOI URL |
| [83] | Waller JS, Servheen C (2005) Effects of transportation infrastructure on grizzly bears in northwestern Montana. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 69, 985-1000. |
| [84] |
Wang Y, Guan L, Chen JD, Kong YP (2018) Influences on mammal’s frequency of use of small bridges and culverts along the Qinghai-Tibet railway, China. Ecological Research, 33, 879-887.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Wang Y, Guan L, Du LX, Qu JP, Wang MY, Han YS, Yang YG, Zhou HP, Kong YP (2021) Overlapping barrier and avoidance effects of the Qinghai-Tibet highway and railway on four typical ungulates on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 1091-1097. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [王云, 关磊, 杜丽侠, 曲家鹏, 王明月, 韩用顺, 杨艳刚, 周红萍, 孔亚平 (2021) 青藏公路和铁路对青藏高原四种典型有蹄类动物的叠加阻隔和回避影响. 生态学杂志, 40, 1091-1097.] | |
| [86] | Wang Y, Guan L, Yang YG, Chen S, Kong YP (2019) A review on impacts on linear transportation infrastructures to Asian elephant and conservation strategies. Forestry Construction, (6), 34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云, 关磊, 杨艳刚, 陈姝, 孔亚平 (2019) 交通建设对亚洲象的影响及保护对策研究综述. 林业建设, (6), 34-37.] | |
| [87] |
Wang Y, Qu J, Han Y, Du L, Wang M, Yang Y, Cao G, Tao S, Kong Y (2022) Impacts of linear transport infrastructure on terrestrial vertebrate species and conservation in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 38, e02207.
DOI URL |
| [88] | Ware HE, McClure CJW, Carlisle JD, Barber JR (2015) A phantom road experiment reveals traffic noise is an invisible source of habitat degradation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 12105-12109. |
| [89] |
Watkins RZ, Chen JQ, Pickens J, Brosofske KD (2003) Effects of forest roads on understory plants in a managed hardwood landscape. Conservation Biology, 17, 411-419.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Wehling S, Diekmann M (2009) Importance of hedgerows as habitat corridors for forest plants in agricultural landscapes. Biological Conservation, 142, 2522-2530.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Wiącek J, Polak M, Filipiuk M, Kucharczyk M, Bohatkiewicz J (2015) Do birds avoid railroads as has been found for roads? Environmental Management, 56, 643-652.
DOI PMID |
| [92] | Wrzesień M (2009) Threatened vascular plants species in railway areas of the Lublin region (eastern Poland). In: Rare, relic and endangered plants and fungi in Poland (eds Mirek Z, Nikel A), 545-553. Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences, Kraków. |
| [93] | Wrzesień M, Denisow B (2016) Distribution and abundance of bee forage flora across an agricultural landscape-railway embankments vs. road verges. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 85, 3509. |
| [94] |
Wrzesień M, Jachuła J, Denisow B (2016) Railway embankments—A refuge areas for food flora, and pollinators in agricultural landscape. Journal of Apicultural Science, 60, 97-110.
DOI URL |
| [95] | Wu LM, Yin SY (2024) The prevention and control of wild boar should also keep pace with the times. Xinhua Daily Telegraph, 2024-11-25(006). (in Chinese) |
| [吴黎明, 尹思源 (2024) 野猪泛滥“撒野”防治也要与时俱进. 新华每日电讯, 2024-11-25(006).] | |
| [96] |
Xia L, Yang QS, Li ZC, Wu YH, Feng ZJ (2007) The effect of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway on the migration of Tibetan Antelope pantholops hodgsonii in Hoh-Xil National Nature Reserve, China. Oryx, 41, 352-357.
DOI URL |
| [97] | Xia XF (2010) Discussion on crested Ibis and its habitat protection in construction of Xi’an-Chengdu Passenger Dedicated Railway. High Speed Railway Technology, 1(5), 40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏先芳 (2010) 西成客运专线建设中朱鹮及其栖息地保护探讨. 高速铁路技术, 1(5), 40-43.] | |
| [98] | Yang QS, Xia L (2008) Tibetan wildlife is getting used to the railway. Nature, 452, 810-811. |
| [99] |
Yin BF, Huai HY, Zhang YL, Zhou L, Wei WH (2006) Influence of Qinghai-Tibetan railway and highway on wild animal’s activity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 3917-3923. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [殷宝法, 淮虎银, 张镱锂, 周乐, 魏万红 (2006) 青藏铁路、公路对野生动物活动的影响. 生态学报, 26, 3917-3923.] | |
| [100] | Yin LH, Gong SN, Wan M, Shen ZH, Han YW (2025) Study on the site selection planning of wildlife corridors along the high-speed railway based on territorial space habitat restoration: Take Wuhan metropolitan area as a case. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 41(2), 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [殷利华, 巩思凝, 万敏, 沈正豪, 韩依纹 (2025) 基于国土空间生境修复的高铁沿线动物通道选址规划研究——以武汉都市圈为例. 中国园林, 41(2), 23-30.] | |
| [101] | Zhang JY, Cheng C, Wen ZX, Xia L (2021) Discussion on wild animal investigation and monitoring scheme during the railway construction period. Railway Energy Saving & Environmental Protection & Occupational Safety and Health, 11(4), 22-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张洁瑜, 程驰, 温知新, 夏霖 (2021) 铁路建设项目施工期野生动物调查监测方案探讨. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, 11(4), 22-25.] | |
| [102] | Zhao LH (2019) Study on the protective measures for Asian crested Ibis along Xi’an-Chengdu high-speed railway. Railway Standard Design, 63(3), 174-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵留辉 (2019) 西安至成都高速铁路朱鹮防护措施研究. 铁道标准设计, 63(3), 174-177.] | |
| [103] |
Zhou JX, Yang J, Peng G (2008) Constructing a green railway on the Tibet Plateau: Evaluating the effectiveness of mitigation measures. Transportation Research Part D, 13, 369-376.
DOI URL |
| [104] | Zou JH, Shao HP (2019) Analysis of noise reduction characteristic of totally-enclosed acoustic barrier for railway bridge and its effect to ecology area. China Railway, (5), 82-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邹俊辉, 邵华平 (2019) 铁路桥梁全封闭声屏障降噪特性及对生态区作用的分析. 中国铁路, (5), 82-87.] | |
| [105] |
Zuberogoitia I, del Real J, Torres JJ, Rodríguez L, Alonso M, de Alba V, Azahara C, Zabala J (2015) Testing pole barriers as feasible mitigation measure to avoid bird vehicle collisions (BVC). Ecological Engineering, 83, 144-151.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()
