



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 24010. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024010 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024010
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qi Wu1, Xiaoqing Zhang2, Yuting Yang1, Yibo Zhou1, Yi Ma3, Daming Xu4,*( ), Xingfeng Si5,6, Jian Wang1,6,*(
), Xingfeng Si5,6, Jian Wang1,6,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-11
Accepted:2024-03-14
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-05-06
Contact:
* E-mail: Qi Wu, Xiaoqing Zhang, Yuting Yang, Yibo Zhou, Yi Ma, Daming Xu, Xingfeng Si, Jian Wang. Spatio-temporal changes in biodiversity of epiphyllous liverworts in Qingyuan Area of Qianjiangyuan-Baishanzu National Park, Zhejiang Province[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 24010.
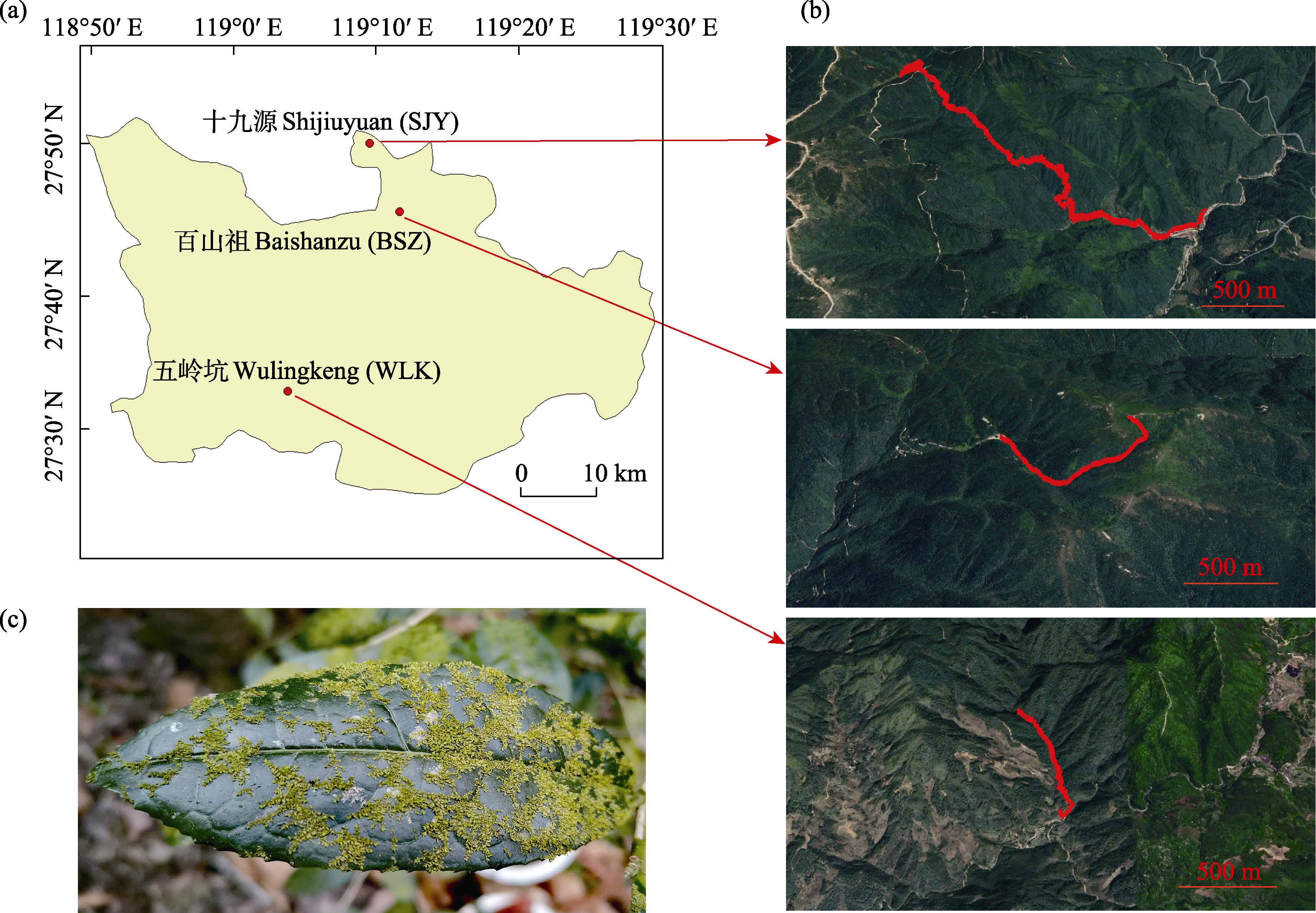
Fig. 1 Map of sites (a), sampling lines (b) and habitats (c) of epiphyllous liverworts in Qingyuan Area of Qianjiangyuan-Baishanzu National Park, Zhejiang Province
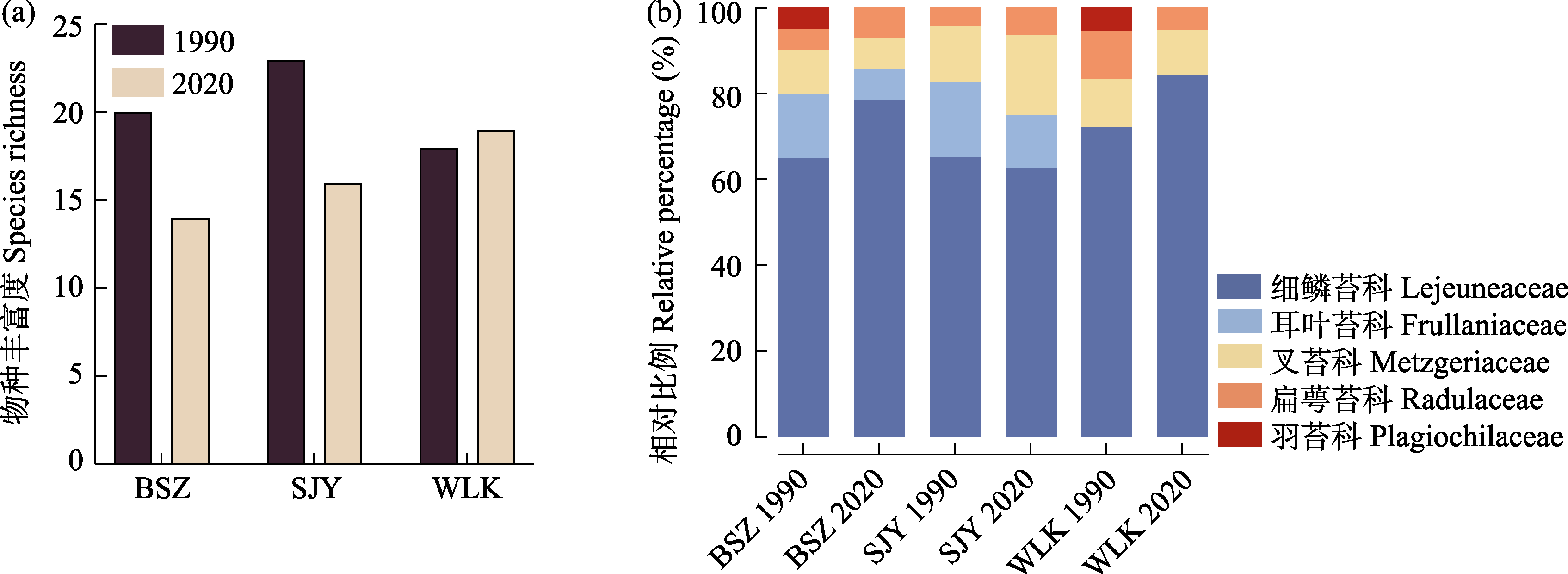
Fig. 2 Changes in species number (a) and relative proportion (b) of epiphyllous liverworts in Baishanzu (BSZ), Shijiuyuan (SJY) and Wulingkeng (WLK) between 1990 and 2020
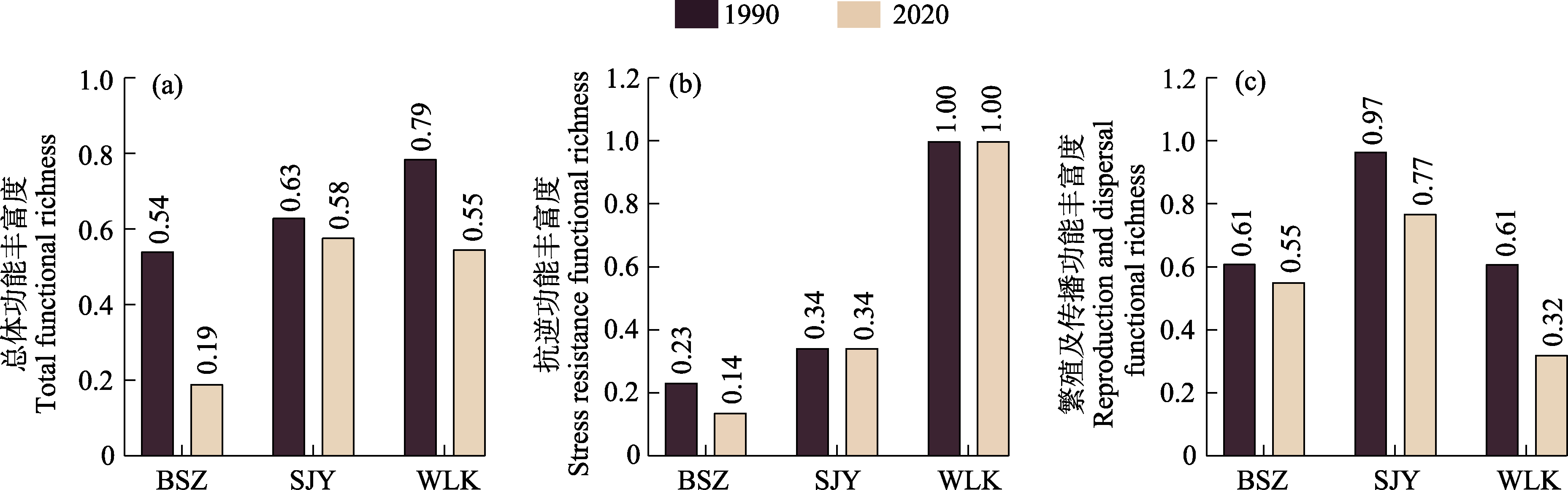
Fig. 3 Changes in total functional richness (a), stress resistance functional richness (b) and reproduction and dispersal functional richness (c) of epiphyllous liverworts in Baishanzu (BSZ), Shijiuyuan (SJY) and Wulingkeng (WLK) between 1990 and 2020
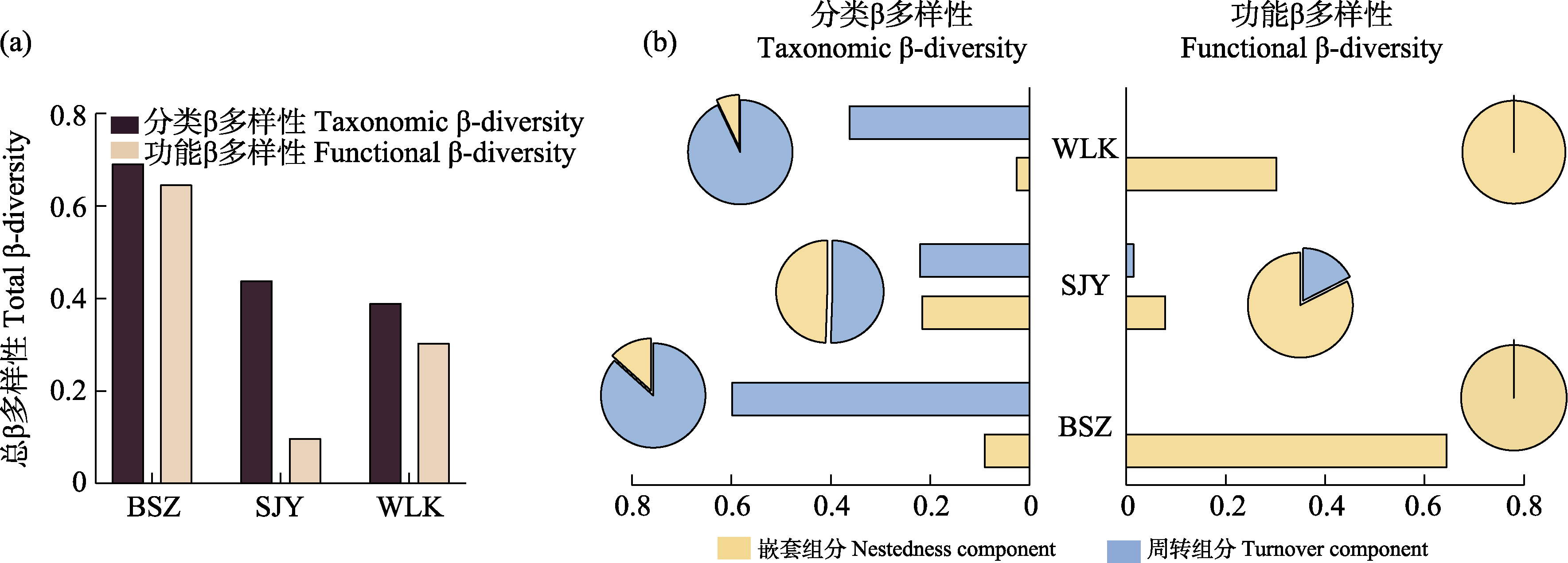
Fig. 4 Taxonomic β-diversity and functional β-diversity (a) and their decomposition (b) of epiphyllous liverworts in Baishanzu (BSZ), Shijiuyuan (SJY), and Wulingkeng (WLK) during 30 years (1990-2020)
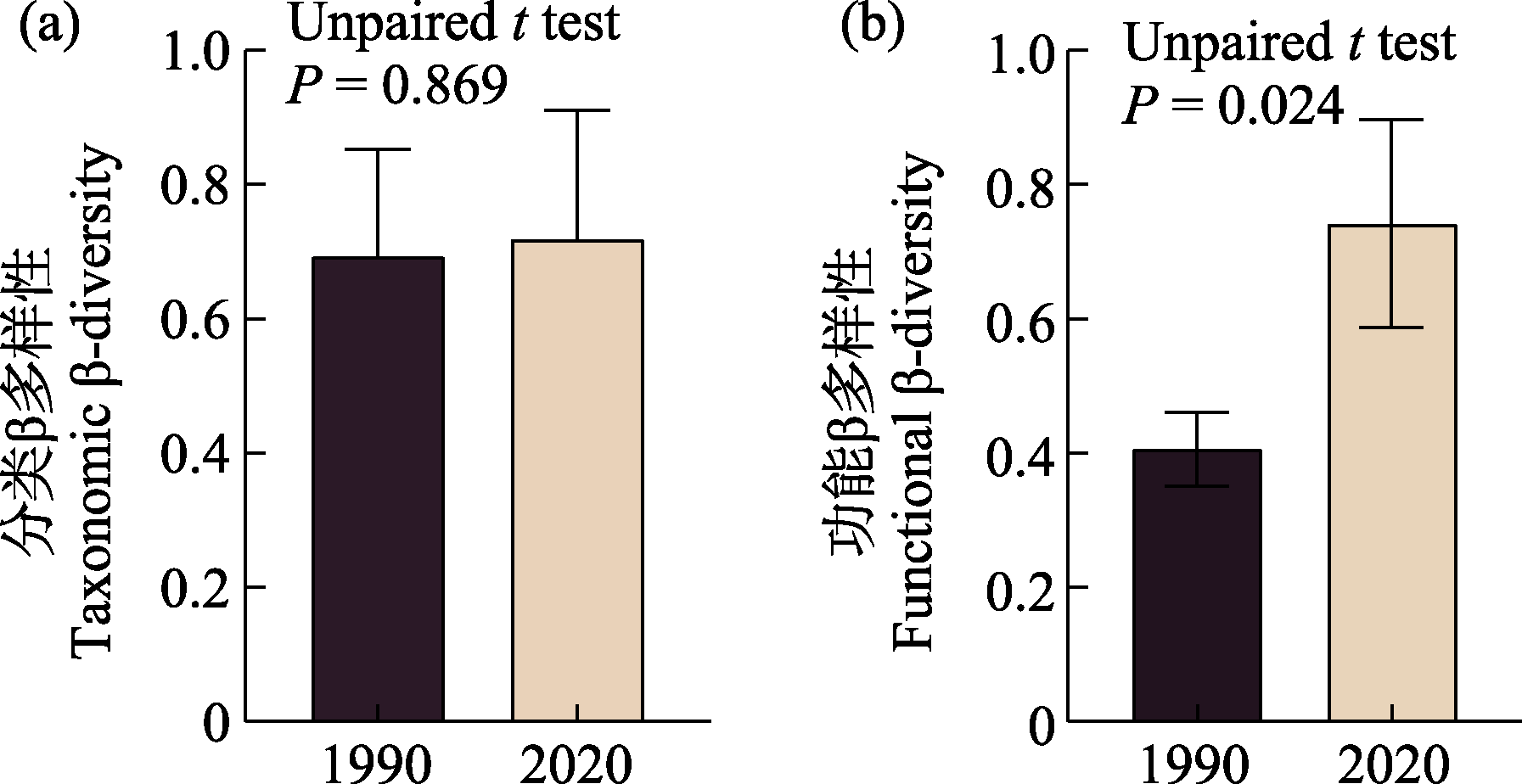
Fig. 5 Changes of taxonomic (a) and functional (b) β-diversity of epiphyllous liverworts between Baishanzu, Shijiuyuan and Wulingkeng between 1990 and 2020 (mean ± SD)
| [1] | Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143. |
| [2] | Baselga A (2012) The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1223-1232. |
| [3] |
Brown JH, Morgan Ernest SK, Parody JM, Haskell JP (2001) Regulation of diversity: Maintenance of species richness in changing environments. Oecologia, 126, 321-332.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Chen DL, Chen XR, Ye ZL, Liang WQ, Zhang HJ, Pu JB (2018) Investigation on wild macrofungus resources in Baishanzu National Nature Reserve. Edible Fungi of China, 37(3), 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈德良, 陈小荣, 叶珍林, 梁卫青, 张宏建, 浦锦宝 (2018) 百山祖国家级自然保护区野生大型真菌资源调查. 中国食用, 37(3), 7-11.] | |
| [5] | Chen X, Dai Z, Xing SC, Wang J (2022) Effective of in-situ conservation of epiphyllous liverworts in Qingyuan County, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 39, 166-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈星, 戴尊, 邢诗晨, 王健 (2022) 浙江省庆元县叶附生苔的就地保护成效. 浙江农林大学学报, 39, 166-172.] | |
| [6] |
Dai Z, Chen X, Zhang JH, Zhu MJ, Song K, Xing SC, Tu SW, Zou L, Lei ZP, Li HQ, Wang J (2022) Species diversity of epiphyllous liverworts and host plants in the Wuyanling National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21229. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[戴尊, 陈星, 张建行, 朱毛洁, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 涂淑雯, 邹璐, 雷祖培, 李宏庆, 王健 (2022) 浙江乌岩岭国家级自然保护区叶附生苔类及附主植物多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 21229.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Dornelas MA, Chase JM, Gotelli NJ, Magurran AE, McGill BJ, Antão LH, Blowes SA, Daskalova GN, Leung B, Martins IS, Moyes F, Myers-Smith IH, Thomas CD, Vellend M (2023) Looking back on biodiversity change: Lessons for the road ahead. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 378, 20220199. |
| [8] | Jiang YB, Shao XM (2016) Diversity and distribution pattern of epiphyllous liverworts and its ecological determinants. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 523-532. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[姜炎彬, 邵小明 (2016) 叶附生苔植物物种多样性分布格局及生态成因. 植物生态学报, 40, 523-532.]
DOI |
|
| [9] |
Jiang YB, Wang TJ, Wu YP, Hu RG, Huang K, Shao XM (2018) Past distribution of epiphyllous liverworts in China: The usability of historical data. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 7436-7450.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Korhonen JJ, Soininen J, Hillebrand H (2010) A quantitative analysis of temporal turnover in aquatic species assemblages across ecosystems. Ecology, 91, 508-517.
PMID |
| [11] |
Kraichak E (2012) Asexual propagules as an adaptive trait for epiphylly in tropical leafy liverworts (Lejeuneaceae). American Journal of Botany, 99, 1436-1444.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Leclerc C, Courchamp F, Bellard C (2020) Future climate change vulnerability of endemic island mammals. Nature Communications, 11, 4943.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Lennon JJ, Koleff P, Greenwood JJD, Gaston KJ (2001) The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 966-979. |
| [14] | Leroy F, Reif J, Storch D, Keil P (2023) How has bird biodiversity changed over time? A review across spatio-temporal scales. Basic and Applied Ecology, 69, 26-38. |
| [15] | Lewthwaite JMM, Mooers AØ (2022) Geographical homogenization but little net change in the local richness of Canadian butterflies. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 31, 266-279. |
| [16] | McKinney ML, Lockwood JL (1999) Biotic homogenization: A few winners replacing many losers in the next mass extinction. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14, 450-453. |
| [17] | Mouillot D, Graham NAJ, Villéger S, Mason NWH, Bellwood DR (2013) A functional approach reveals community responses to disturbances. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 167-177. |
| [18] | Mountain Research Initiative EDW Working Group(2015) Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nature Climate Change, 5, 424-430. |
| [19] |
Pereira HM, Navarro LM, Santos Martins I (2012) Global biodiversity change: The bad, the good, and the unknown. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 37, 25-50.
DOI |
| [20] | Pócs T (1996) Epiphyllous liverworts diversity at worldwide level and its threat and conservation. Anales Del Instituto De Biología Serie Botánica, 67, 109-127. |
| [21] | Shin YJ, Midgley GF, Archer ERM, Arneth A, Barnes DKA, Chan LN, Hashimoto S, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Insarov G, Leadley P, Levin LA, Ngo HT, Pandit R, Pires APF, Pörtner HO, Rogers AD, Scholes RJ, Settele J, Smith P (2022) Actions to halt biodiversity loss generally benefit the climate. Global Change Biology, 28, 2846-2874. |
| [22] | Shuai FM, Li XH, Chen FC, Li YF, Yang JP, Li J, Wu Z (2017) Functional diversity of freshwater fishes and methods of measurement. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 5228-5237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [帅方敏, 李新辉, 陈方灿, 李跃飞, 杨计平, 李捷, 武智 (2017) 淡水鱼类功能多样性及其研究方法. 生态学报, 37, 5228-5237.] | |
| [23] | Schuster RM (1983) New Manual of Bryology, Vol. 1. The Hattori Botanical Laboratory, Nichinan. |
| [24] |
Si XF, Baselga A, Leprieur F, Song X, Ding P (2016) Selective extinction drives taxonomic and functional alpha and beta diversities in island bird assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 85, 409-418.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Si XF, Zhao YH, Chen CW, Ren P, Zeng D, Wu LB, Ding P (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解:方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 67-80. |
| [27] |
Söderström L, Hagborg A, von Konrat M, Bartholomew-Began S, Bell D, Briscoe L, Brown E, Cargill DC, Costa DP, Crandall-Stotler BJ, Cooper ED, Dauphin G, Engel JJ, Feldberg K, Glenny D, Gradstein SR, He XL, Heinrichs J, Hentschel J, Ilkiu-Borges AL, Katagiri T, Konstantinova NA, Larraín J, Long DG, Nebel M, Pócs T, Puche F, Reiner-Drehwald E, Renner MAM, Sass-Gyarmati A, Schäfer-Verwimp A, Segarra-Moragues JG, Stotler RE, Sukkharak P, Thiers BM, Uribe J, Váňa J, Villarreal JC, Wigginton M, Zhang L, Zhu RL (2016) World checklist of hornworts and liverworts. PhytoKeys, 59, 1-828.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Sonnleitner M, Dullinger S, Wanek W, Zechmeister H (2009) Microclimatic patterns correlate with the distribution of epiphyllous bryophytes in a tropical lowland rain forest in Costa Rica. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 25, 321-330. |
| [29] | Tang X, Gradstein SR, Sun LW, Zhu MJ, Shi RP, Wei QQ, Chen YQ, Zhou XX, Wang J (2018) A contribution to the knowledge of epiphyllous bryophytes in Tianmushan National Nature Reserve (Zhejiang, China), with remarks on climate warming and nature conservation. Lindbergia, 41, 01103. |
| [30] | Villéger S, Grenouillet G, Brosse S (2013) Decomposing functional β-diversity reveals that low functional β-diversity is driven by low functional turnover in European fish assemblages. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 671-681. |
| [31] |
Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Wang LS, Jia Y, Zhang XC, Qin HN (2018) Species Catalogue of China (Vol.1): Plants, A Synoptic Checklist (I). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王利松, 贾渝, 张宪春, 覃海宁 (2018) 中国生物物种名录(第一卷): 植物总名录(上卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Winter M, Schweiger O, Klotz S, Nentwig W, Andriopoulos P, Arianoutsou M, Basnou C, Delipetrou P, Didžiulis V, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Lambdon PW, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Roy DB, Kühn I (2009) Plant extinctions and introductions lead to phylogenetic and taxonomic homogenization of the European flora. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 21721-21725. |
| [34] | Wu PC, Li DK, Gao CH (1987) Preliminary measurment on some ecological factors of the epiphyllous liverworts in Mt. Wuyi. Acta Botanica Sinica, 29, 449-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴鹏程, 李登科, 高彩华 (1987) 福建武夷山叶附生苔类植物着生生境因素的初步测定. 植物学报, 29, 449-452.] | |
| [35] | Wu YS, Cai HM, Wu JL, Wu M (2022) Investigation and utilization value evaluation of Rhododendron resources in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province. Special Economic Animals and Plants, 25, 116-118. (in Chinese) |
| [吴义松, 蔡焕满, 吴家连, 吴敏 (2022) 浙江百山祖杜鹃花属植物资源调查及其利用价值评价. 特种经济动植物, 25, 116-118.] | |
| [36] |
Yao X, Chen X, Dai Z, Song K, Xing SC, Cao HY, Zou L, Wang J (2023) Importance of collection strategy on detection probability and species diversity of epiphyllous liverworts. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22685. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健 (2023) 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性. 生物多样性, 31, 22685.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | Zhou LY, Wang ZS, Chen SN, Yao ZG, Xu WX, Wei N, An SQ (2009) Advances in researches on ecological epiphylls. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33, 993-1002. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[周灵燕, 王中生, 陈姝凝, 姚志刚, 徐卫祥, 魏娜, 安树青 (2009) 叶附生生物生态学研究进展. 植物生态学报, 33, 993-1002.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Zhu RL, Ma XY, Cao C, Cao ZY (2022) Advances in research on bryophyte diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅 (2022) 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22378.] | |
| [39] | Zhu RL, So ML (2001) Epiphyllous Liverworts of China. Nova Hedwigia Beiheft, 121, 1-418. |
| [40] | Zhu RL, Hu RL, Zhang GZ (1994) Epiphyllous liverworts from Baishanzu Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province, China. Hikobia, 11, 543-547. |
| [41] | Zhu RL, Zhang GZ, Mao XR (1992) Resources of epiphyllous liverworts in Baishanzu Nature Reserve of Zhejiang Province. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 1(3), 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱瑞良, 章刚正, 毛小荣 (1992) 浙江百山祖自然保护区叶附生苔资源. 植物资源与环境, 1(3), 19-23.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()