



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22462. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022462 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022462
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xin Jing1,*( ), Shengjing Jiang1, Huiying Liu2, Yu Li1, Jin-Sheng He1,3
), Shengjing Jiang1, Huiying Liu2, Yu Li1, Jin-Sheng He1,3
Received:2022-08-11
Accepted:2022-09-27
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-10-06
Contact:
Xin Jing
Xin Jing, Shengjing Jiang, Huiying Liu, Yu Li, Jin-Sheng He. Complex relationships and feedback mechanisms between climate change and biodiversity[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22462.
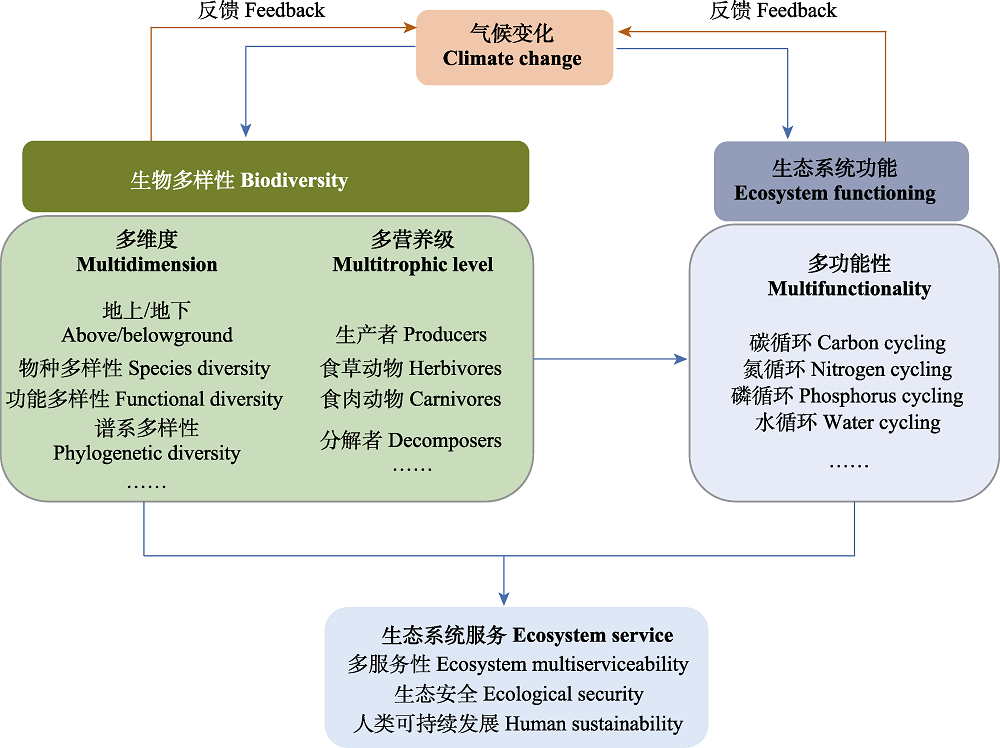
Fig. 1 Impacts of climate change on multi-dimensional, multi-trophic biodiversity, and the feedback of biodiversity to climate change. The coordinated development of human activities and biodiversity is the basis for maintaining ecosystem multiserviceability, ecological security and human sustainability.
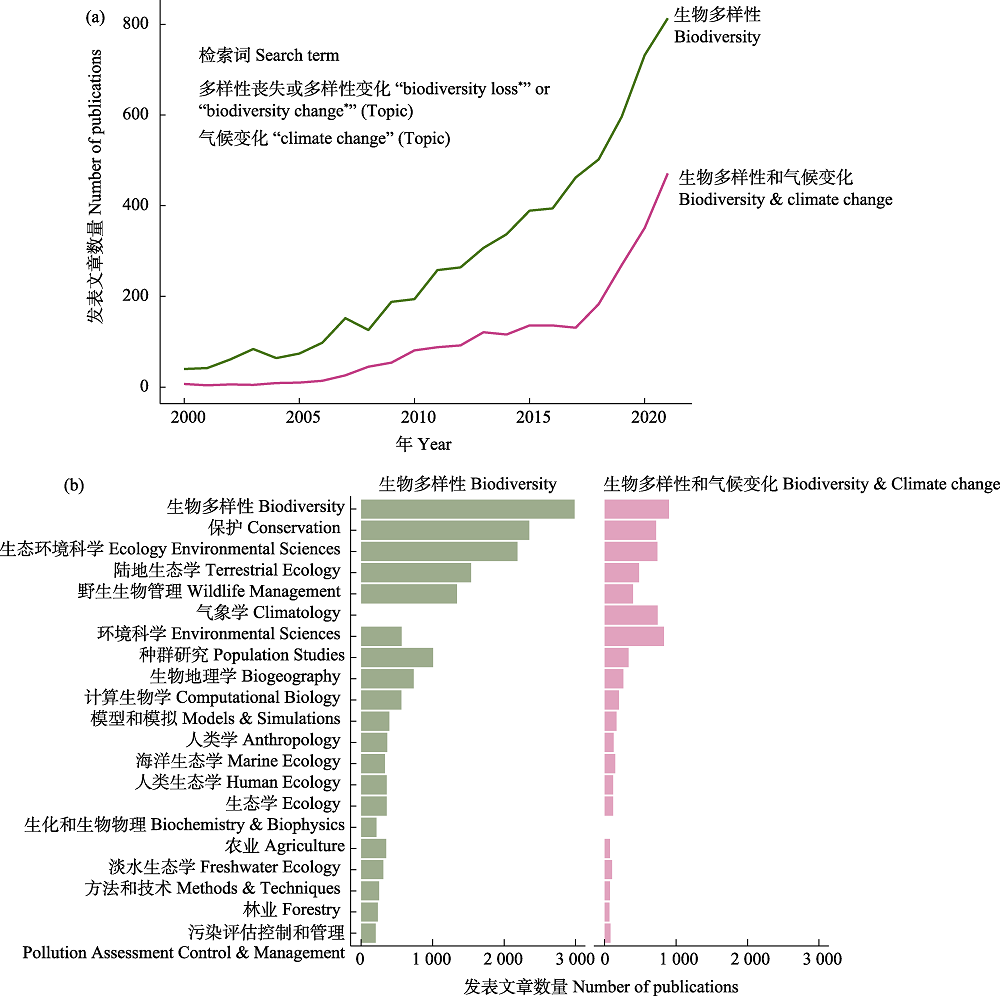
Fig. 2 Analysis of publication trends and main research areas in the field of biodiversity and climate change. (a) Publication trends in biodiversity and climate change-related articles published over the last 20 years (data sources: Web of Science, last accessed August 6, 2022). (b) Number of articles published in the main research areas of biodiversity and climate change.
| [1] |
Anderegg WR, Schwalm C, Biondi F, Camarero JJ, Koch G, Litvak M, Ogle K, Shaw JD, Shevliakova E, Williams AP, Wolf A, Ziaco E, Pacala S (2015) Pervasive drought legacies in forest ecosystems and their implications for carbon cycle models. Science, 349, 528-532.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bardgett RD (2018) Linking aboveground-belowground ecology:A short historical perspective. In: Aboveground- Belowground Community Ecology (eds Ohgushi T, Wurst S, Johnson SN), pp.1-17. Springer Nature, Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland. |
| [3] |
Bardgett RD,van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2010) Aboveground-belowground linkages: Biotic interactions, ecosystem processes, and global change. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [5] |
Bastazini VAG, Galiana N, Hillebrand H, Estiarte M, Ogaya R, Peñuelas J, Sommer U, Montoya JM, Bates A (2021) The impact of climate warming on species diversity across scales: Lessons from experimental meta-ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 1545-1554.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Bestion E, Soriano-Redondo A, Cucherousset J, Jacob S, White J, Zinger L, Fourtune L, Di Gesu L, Teyssier A, Cote J (2019) Altered trophic interactions in warming climates:Consequences for predator diet breadth and fitness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286, 20192227. |
| [7] |
Bjorkman AD, Myers-Smith IH, Elmendorf SC, Normand S, Rüger N, Beck PSA, Blach-Overgaard A, Blok D, Cornelissen JHC, Forbes BC, Georges D, Goetz SJ, Guay KC, Henry GHR, HilleRisLambers J, Hollister RD, Karger DN, Kattge J, Manning P, Prevéy JS, Rixen C, Schaepman-Strub G, Thomas HJD, Vellend M, Wilmking M, Wipf S, Carbognani M, Hermanutz L, Lévesque E, Molau U, Petraglia A, Soudzilovskaia NA, Spasojevic MJ, Tomaselli M, Vowles T, Alatalo JM, Alexander HD, Anadon-Rosell A, Angers-Blondin S, Beest MT, Berner L, Björk RG, Buchwal A, Buras A, Christie K, Cooper EJ, Dullinger S, Elberling B, Eskelinen A, Frei ER, Grau O, Grogan P, Hallinger M, Harper KA, Heijmans MMPD, Hudson J, Hülber K, Iturrate-Garcia M, Iversen CM, Jaroszynska F, Johnstone JF, Jørgensen RH, Kaarlejärvi E, Klady R, Kuleza S, Kulonen A, Lamarque LJ, Lantz T, Little CJ, Speed JDM, Michelsen A, Milbau A, Nabe-Nielsen J, Nielsen SS, Ninot JM, Oberbauer SF, Olofsson J, Onipchenko VG, Rumpf SB, Semenchuk P, Shetti R, Collier LS, Street LE, Suding KN, Tape KD, Trant A, Treier UA, Tremblay JP, Tremblay M, Venn S, Weijers S, Zamin T, Boulanger-Lapointe N, Gould WA, Hik DS, Hofgaard A, Jónsdóttir IS, Jorgenson J, Klein J, Magnusson B, Tweedie C, Wookey PA, Bahn M, Blonder B, van Bodegom PM, Bond-Lamberty B, Campetella G, Cerabolini BEL, Chapin FS III, Cornwell WK, Craine J, Dainese M, de Vries FT, Díaz S, Enquist BJ, Green W, Milla R, Niinemets Ü, Onoda Y, Ordoñez JC, Ozinga WA, Penuelas J, Poorter H, Poschlod P, Reich PB, Sandel B, Schamp B, Sheremetev S, Weiher E (2018) Plant functional trait change across a warming tundra biome. Nature, 562, 57-62.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Blanchet FG, Cazelles K, Gravel D (2020) Co-occurrence is not evidence of ecological interactions. Ecology Letters, 23, 1050-1063.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Blume-Werry G (2022) The belowground growing season. Nature Climate Change, 12, 11-12.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Bongers FJ, Schmid B, Bruelheide H, Bongers F, Li S, von Oheimb G, Li Y, Cheng AP, Ma KP, Liu XJ (2021) Functional diversity effects on productivity increase with age in a forest biodiversity experiment. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 1594-1603. |
| [11] |
Bonnet T, Morrissey MB, de Villemereuil P, Alberts SC, Arcese P, Bailey LD, Boutin S, Brekke P, Brent LJN, Camenisch G, Charmantier A, Clutton-Brock TH, Cockburn A, Coltman DW, Courtiol A, Davidian E, Evans SR, Ewen JG, Festa-Bianchet M, de Franceschi C, Gustafsson L, Höner OP, Houslay TM, Keller LF, Manser M, McAdam AG, McLean E, Nietlisbach P, Osmond HL, Pemberton JM, Postma E, Reid JM, Rutschmann A, Santure AW, Sheldon BC, Slate J, Teplitsky C, Visser ME, Wachter B, Kruuk LEB (2022) Genetic variance in fitness indicates rapid contemporary adaptive evolution in wild animals. Science, 376, 1012-1016.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Byrnes JEK, Gamfeldt L, Isbell F, Lefcheck JS, Griffin JN, Hector A, Cardinale BJ, Hooper DU, Dee LE, Duffy JE (2014) Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Challenges and solutions. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 111-124.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Chapin FS III, Díaz S (2020) Interactions between changing climate and biodiversity: Shaping humanity’s future. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 6295-6296. |
| [14] | Chen IC, Hill JK, Ohlemüller R, Roy DB, Thomas CD (2011) Rapid range shifts of species associated with high levels of climate warming. Science, 333, 1024-1026. |
| [15] | Chu HY, Feng MM, Liu X, Shi Y, Yang T, Gao GF (2020) Soil microbial biogeography: Recent advances in China and research frontiers in the world. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57, 515-529. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [褚海燕, 冯毛毛, 柳旭, 时玉, 杨腾, 高贵锋 (2020) 土壤微生物生物地理学: 国内进展与国际前沿. 土壤学报, 57, 515-529.] | |
| [16] |
Collins CG, Elmendorf SC, Smith JG, Shoemaker L, Szojka M, Swift M, Suding KN (2022) Global change re-structures alpine plant communities through interacting abiotic and biotic effects. Ecology Letters, 25, 1813-1826.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Cowie RH, Bouchet P, Fontaine B (2022) The sixth mass extinction: Fact, fiction or speculation?. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 97, 640-663.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Craven D, van der Sande MT, Meyer C, Gerstner K, Bennett JM, Giling DP, Hines J, Phillips HRP, May F, Bannar-Martin KH, Chase JM, Keil P (2020) A cross-scale assessment of productivity-diversity relationships. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 1940-1955.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Custer GF, Dini-Andreote F (2022) Embracing complexity in ecosystem response to global change. Environmental Science & Technology, 56, 9832-9834.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
de Bello F, Lavorel S, Hallett LM, Valencia E, Garnier E, Roscher C, Conti L, Galland T, Goberna M, Májeková M, Montesinos-Navarro A, Pausas JG, Verdú M, E-Vojtkó A, Götzenberger L, Lepš (2021) Functional trait effects on ecosystem stability: Assembling the jigsaw puzzle. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 36, 822-836.
DOI URL |
| [21] | De la Sota C, Ruffato-Ferreira VJ, Ruiz-García L, Alvarez S (2019) Urban green infrastructure as a strategy of climate change mitigation: A case study in northern Spain. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 40, 145-151. |
| [22] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Guerra CA, Cano-Díaz C, Egidi E, Wang JT, Eisenhauer N, Singh BK, Maestre FT (2020) The proportion of soil-borne pathogens increases with warming at the global scale. Nature Climate Change, 10, 550-554.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Des Roches S, Bell MA, Palkovacs EP (2020) Climate-driven habitat change causes evolution in Threespine Stickleback. Global Change Biology, 26, 597-606. |
| [24] |
Díaz S, Hector A, Wardle DA (2009a) Biodiversity in forest carbon sequestration initiatives: Not just a side benefit. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 1, 55-60.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Díaz S, Wardle DA, Hector A (2009b) Incorporating biodiversity in climate change mitigation initiatives. In: Biodiversity, Ecosystem Functioning, Human Wellbeing: An Ecological Economic Perspective (eds Naeem S, Bunker DE, Hector A, Loreau M, Perrings C), pp. 149-166. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [26] |
Duffy JE, Godwin CM, Cardinale BJ (2017) Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature, 549, 261-264.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Eisenhauer N, Schielzeth H, Barnes AD, Barry KE, Bonn A, Brose U, Bruelheide H, Buchmann N, Buscot F, Ebeling A, Ferlian O, Freschet GT, Giling DP, Hättenschwiler S, Hillebrand H, Hines J, Isbell F, Koller-France E, König-Ries B, de Kroon H, Meyer ST, Milcu A, Müller J, Nock CA, Petermann JS, Roscher C, Scherber C, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Schnitzer SA, Schuldt A, Tscharntke T, Türke M, van Dam NM, van der Plas F, Vogel A, Wagg C, Wardle DA, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Wirth C, Jochum M (2019) A multitrophic perspective on biodiversity-ecosystem functioning research. In: Mechanisms Underlying the Relationship Between Biodiversity and Ecosystem Function (eds Eisenhauer N, Bohan DA, Dumbrell AJ), pp. 1-54. Academic Press, London. |
| [28] |
Fang JY (2021) Ecological perspectives of carbon neutrality. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 1173-1176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[方精云 (2021) 碳中和的生态学透视. 植物生态学报, 45, 1173-1176.]
DOI |
|
| [29] |
Fei SL, Jo I, Guo QF, Wardle DA, Fang JY, Chen AP, Oswalt CM, Brockerhoff EG (2018) Impacts of climate on the biodiversity-productivity relationship in natural forests. Nature Communications, 9, 5436.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Feng XJ, Mi XC, Xiao ZS, Cao L, Wu H, Ma KP (2019) Overview of Chinese biodiversity observation network (Sino BON). Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 34, 1389-1398. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯晓娟, 米湘成, 肖治术, 曹垒, 吴慧, 马克平 (2019) 中国生物多样性监测与研究网络建设及进展. 中国科学院院刊, 34, 1389-1398.] | |
| [31] |
Feng YH, Schmid B, Loreau M, Forrester DI, Fei SL, Zhu JX, Tang ZY, Zhu JL, Hong PB, Ji CJ, Shi Y, Su HJ, Xiong XY, Xiao J, Wang SP, Fang JY (2022) Multispecies forest plantations outyield monocultures across a broad range of conditions. Science, 376, 865-868.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Forrester DI, Bauhus J (2016) A review of processes behind diversity-productivity relationships in forests. Current Forestry Reports, 2, 45-61.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Gallagher RV, Hughes L, Leishman MR (2013) Species loss and gain in communities under future climate change: Consequences for functional diversity. Ecography, 36, 531-540.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Gamfeldt L, Roger F (2017) Revisiting the biodiversity- ecosystem multifunctionality relationship. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 0168. |
| [35] |
Ganuza C, Redlich S, Uhler J, Tobisch C, Rojas-Botero S, Peters MK, Zhang J, Benjamin CS, Englmeier J, Ewald J, Fricke U, Haensel M, Kollmann J, Riebl R, Uphus L, Müller J, Steffan-Dewenter I (2022) Interactive effects of climate and land use on pollinator diversity differ among taxa and scales. Science Advances, 8, eabm9359.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Gao GF, Chu HY (2020) Techniques and methods of microbiomics and their applications. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 395-408. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[高贵锋, 褚海燕 (2020) 微生物组学的技术和方法及其应用. 植物生态学报, 44, 395-408.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | García-Palacios P, Gross N, Gaitán J, Maestre FT (2018) Climate mediates the biodiversity-ecosystem stability relationship globally. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 8400-8405. |
| [38] |
Gilman SE, Urban MC, Tewksbury J, Gilchrist GW, Holt RD (2010) A framework for community interactions under climate change. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 325-331.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Gonzalez A, Germain RM, Srivastava DS, Filotas E, Dee LE, Gravel D, Thompson PL, Isbell F, Wang S, Kéfi S, Montoya J, Zelnik YR, Loreau M (2020) Scaling-up biodiversity- ecosystem functioning research. Ecology Letters, 23, 757-776.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Grossiord C (2020) Having the right neighbors: How tree species diversity modulates drought impacts on forests. New Phytologist, 228, 42-49.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Gruner DS, Bracken MES, Berger SA, Eriksson BK, Gamfeldt L, Matthiessen B, Moorthi S, Sommer U, Hillebrand H (2017) Effects of experimental warming on biodiversity depend on ecosystem type and local species composition. Oikos, 126, 8-17.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Hawkes CV, Waring BG, Rocca JD, Kivlin SN (2017) Historical climate controls soil respiration responses to current soil moisture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 6322-6327. |
| [43] | He JS, Bu HY, Hu XW, Feng YH, Li SL, Zhu JX, Liu GH, Wang YR, Nan ZB (2020) Close-to-nature restoration of degraded alpine grasslands: Theoretical basis and technical approach. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65, 3898-3908. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺金生, 卜海燕, 胡小文, 冯彦皓, 李守丽, 朱剑霄, 刘国华, 王彦荣, 南志标 (2020) 退化高寒草地的近自然恢复: 理论基础与技术途径. 科学通报, 65, 3898-3908.] | |
| [44] | He JS, Fang JY, Ma KP, Huang JH (2003) Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity: Why is there a discrepancy in the relationship between experimental and natural ecosystems? Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 835-843. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[贺金生, 方精云, 马克平, 黄建辉 (2003) 生物多样性与生态系统生产力: 为什么野外观测和受控实验结果不一致? 植物生态学报, 27, 835-843.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Hector A, Bagchi R (2007) Biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature, 448, 188-190.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Hicks Pries CE, Castanha C, Porras RC, Torn MS (2017) The whole-soil carbon flux in response to warming. Science, 355, 1420-1423.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Hoffmann M, Hilton-Taylor C, Angulo A, Böhm M, Brooks TM, Butchart SHM, Carpenter KE, Chanson J, Collen B, Cox NA, Darwall WRT, Dulvy NK, Harrison LR, Katariya V, Pollock CM, Quader S, Richman NI, Rodrigues ASL, Tognelli MF, Vié JC, Aguiar JM, Allen DJ, Allen GR, Amori G, Ananjeva NB, Andreone F, Andrew P, Ortiz ALA, Baillie JEM, Baldi R, Bell BD, Biju SD, Bird JP, Black-Decima P, Blanc JJ, Bolaños F, Bolivar-G W, Burfield IJ, Burton JA, Capper DR, Castro F, Catullo G, Cavanagh RD, Channing AL, Chao NL, Chenery AM, Chiozza F, Clausnitzer V, Collar NJ, Collett LC, Collette BB, Cortez Fernandez CF, Craig MT, Crosby MJ, Cumberlidge N, Cuttelod A, Derocher AE, Diesmos AC, Donaldson JS, Duckworth JW, Dutson G, Dutta SK, Emslie RH, Farjon A, Fowler S, Freyhof J, Garshelis DL, Gerlach J, Gower DJ, Grant TD, Hammerson GA, Harris RB, Heaney LR, Hedges SB, Hero JM, Hughes B, Hussain SA, Javier IM, Inger RF, Ishii N, Iskandar DT, Jenkins RKB, Kaneko Y, Kottelat M, Kovacs KM, Kuzmin SL, La Marca E, Lamoreux JF, Lau MWN, Lavilla EO, Leus K, Lewison RL, Lichtenstein G, Livingstone SR, Lukoschek V, Mallon DP, McGowan PJK, McIvor A, Moehlman PD, Molur S, Alonso AM, Musick JA, Nowell K, Nussbaum RA, Olech W, Orlov NL, Papenfuss TJ, Parra-Olea G, Perrin WF, Polidoro BA, Pourkazemi M, Racey PA, Ragle JS, Ram M, Rathbun G, Reynolds RP, Rhodin AGJ, Richards SJ, Rodríguez LO, Ron SR, Rondinini C, Rylands AB, de Mitcheson YS, Sanciangco JC, Sanders KL, Santos-Barrera G, Schipper J, Self-Sullivan C, Shi YC, Shoemaker A, Short FT, Sillero-Zubiri C, Silvano DL, Smith KG, Smith AT, Snoeks J, Stattersfield AJ, Symes AJ, Taber AB, Talukdar BK, Temple HJ, Timmins R, Tobias JA, Tsytsulina K, Tweddle D, Ubeda C, Valenti SV, van Dijk PP, Veiga LM, Veloso A, Wege DC, Wilkinson M, Williamson EA, Xie F, Young BE, Akçakaya HR, Bennun L, Blackburn TM, Boitani L, Dublin HT, da Fonseca GAB, Gascon C, Lacher TE Jr, Mace GM, Mainka SA, McNeely JA, Mittermeier RA, Reid GM, Rodriguez JP, Rosenberg AA, Samways MJ, Smart J, Stein BA, Stuart SN (2010) The impact of conservation on the status of the world’s vertebrates. Science, 330, 1503-1509.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JEK, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature, 486, 105-108.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Hua FY, Bruijnzeel LA, Meli P, Martin PA, Zhang J, Nakagawa S, Miao XR, Wang WY, McEvoy C, Peña-Arancibia JL, Brancalion PHS, Smith P, Edwards DP, Balmford A (2022) The biodiversity and ecosystem service contributions and trade-offs of forest restoration approaches. Science, 376, 839-844.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Huang YY, Chen YX, Castro-Izaguirre N, Baruffol M, Brezzi M, Lang A, Li Y, Härdtle W, von Oheimb G, Yang XF, Liu XJ, Pei KQ, Both S, Yang B, Eichenberg D, Assmann T, Bauhus J, Behrens T, Buscot F, Chen XY, Chesters D, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fang JY, Fischer M, Guo LD, Guo DL, Gutknecht JLM, He JS, He CL, Hector A, Hönig L, Hu RY, Klein AM, Kühn P, Liang Y, Li S, Michalski S, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmidt K, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Shi XZ, Tan MZ, Tang ZY, Trogisch S, Wang ZW, Welk E, Wirth C, Wubet T, Xiang WH, Yu MJ, Yu XD, Zhang JY, Zhang SR, Zhang NL, Zhou HZ, Zhu CD, Zhu L, Bruelheide H, Ma KP, Niklaus PA, Schmid B (2018) Impacts of species richness on productivity in a large-scale subtropical forest experiment. Science, 362, 80-83.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Humphrey V, Zscheischler J, Ciais P, Gudmundsson L, Sitch S, Seneviratne SI (2018) Sensitivity of atmospheric CO2 growth rate to observed changes in terrestrial water storage. Nature, 560, 628-631.
DOI URL |
| [52] | IPCC (2021) Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pirani A, Connors SL, Péan C, Berger S, Caud N, Chen Y, Goldfarb L, Gomis MI, Huang M, Leitzell K, Lonnoy E, Matthews JBR, Maycock TK, Waterfield T, Yelekçi O, Yu R, Zhou B). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. |
| [53] |
Isbell F, Balvanera P, Mori AS, He JS, Bullock JM, Regmi GR, Seabloom EW, Ferrier S, Sala OE, Guerrero-Ramírez NR, Tavella J, Larkin DJ, Schmid B, Outhwaite CL, Pramual P, Borer ET, Loreau M, Omotoriogun TC, Obura DO, Anderson M, Portales-Reyes C, Kirkman K, Vergara PM, Clark AT, Komatsu KJ, Petchey OL, Weiskopf SR, Williams LJ, Collins SL, Eisenhauer N, Trisos CH, Renard D, Wright AJ, Tripathi P, Cowles J, Byrnes JEK, Reich PB, Purvis A, Sharip Z, O’Connor MI, Kazanski CE, Haddad NM, Soto EH, Dee LE, Díaz S, Zirbel CR, Avolio ML, Wang SP, Ma ZY, Liang JJ, Farah HC, Johnson JA, Miller BW, Hautier Y, Smith MD, Knops JMH, Myers BJE, Harmáčková ZV, Cortés J, Harfoot MBJ, Gonzalez A, Newbold T, Oehri J, Mazón M, Dobbs C, Palmer MS (2022) Expert perspectives on global biodiversity loss and its drivers and impacts on people. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, doi: 10.1002/fee.2536.
DOI |
| [54] |
Isbell F, Craven D, Connolly J, Loreau M, Schmid B, Beierkuhnlein C, Bezemer TM, Bonin C, Bruelheide H, de Luca E, Ebeling A, Griffin JN, Guo QF, Hautier Y, Hector A, Jentsch A, Kreyling J, Lanta V, Manning P, Meyer ST, Mori AS, Naeem S, Niklaus PA, Polley HW, Reich PB, Roscher C, Seabloom EW, Smith MD, Thakur MP, Tilman D, Tracy BF, van der Putten WH, van Ruijven J, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Wilsey B, Eisenhauer N (2015) Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes. Nature, 526, 574-577.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Jing X, He JS (2021) Relationship between biodiversity, ecosystem multifunctionality and multiserviceability: Literature overview and research advances. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 1094-1111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[井新, 贺金生 (2021) 生物多样性与生态系统多功能性和多服务性的关系: 回顾与展望. 植物生态学报, 45, 1094-1111.]
DOI |
|
| [56] |
Jing X, Muys B, Baeten L, Bruelheide H, de Wandeler H, Desie E, Hättenschwiler S, Jactel H, Jaroszewicz B, Jucker T, Kardol P, Pollastrini M, Ratcliffe S, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Selvi F, Vancampenhout K, van der Plas F, Verheyen K, Vesterdal L, Zuo J,Van Meerbeek K (2022) Climatic conditions, not above- and belowground resource availability and uptake capacity, mediate tree diversity effects on productivity and stability. Science of the Total Environment, 812, 152560.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Jing X, Prager CM, Classen AT, Maestre FT, He JS, Sanders NJ (2020) Variation in the methods leads to variation in the interpretation of biodiversity-ecosystem multifunctionality relationships. Journal of Plant Ecology, 13, 431-441.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Jing X, Sanders NJ, Shi Y, Chu HY, Classen AT, Zhao K, Chen LT, Shi Y, Jiang YX, He JS (2015) The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and belowground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nature Communications, 6, 8159.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Jones KR, Watson JEM, Possingham HP, Klein CJ (2016) Incorporating climate change into spatial conservation prioritisation: A review. Biological Conservation, 194, 121-130.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Kharouba HM, Ehrlén J, Gelman A, Bolmgren K, Allen JM, Travers SE, Wolkovich EM (2018) Global shifts in the phenological synchrony of species interactions over recent decades. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 5211-5216. |
| [61] | Komatsu KJ, Avolio ML, Lemoine NP, Isbell F, Grman E, Houseman GR, Koerner SE, Johnson DS, Wilcox KR, Alatalo JM, Anderson JP, Aerts R, Baer SG, Baldwin AH, Bates J, Beierkuhnlein C, Belote RT, Blair J, Bloor JMG, Bohlen PJ, Bork EW, Boughton EH, Bowman WD, Britton AJ, Cahill Jr JF, Chaneton E, Chiariello NR, Cheng JM, Collins SL, Cornelissen JHC, Du GZ, Eskelinen A, Firn J, Foster B, Gough L, Gross K, Hallett LM, Han XG, Harmens H, Hovenden MJ, Jagerbrand A, Jentsch A, Kern C, Klanderud K, Knapp AK, Kreyling J, Li W, Luo YQ, McCulley RL, McLaren JR, Megonigal JP, Morgan JW, Onipchenko V, Pennings SC, Prevéy JS, Price JN, Reich PB, Robinson CH, Russell FL, Sala OE, Seabloom EW, Smith MD, Soudzilovskaia NA, Souza L, Suding K, Suttle KB, Svejcar T, Tilman D, Tognetti P, Turkington R, White S, Xu ZW, Yahdjian L, Yu Q, Zhang PF, Zhang YH (2019) Global change effects on plant communities are magnified by time and the number of global change factors imposed. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 17867-17873. |
| [62] |
Lavergne S, Mouquet N, Thuiller W, Ronce O (2010) Biodiversity and climate change: Integrating evolutionary and ecological responses of species and communities. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 41, 321-350.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Soliveres S, Gross N, Torices R, Berdugo M, Maestre FT (2019) Phylogenetic, functional, and taxonomic richness have both positive and negative effects on ecosystem multifunctionality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 8419-8424. |
| [64] | Lenoir J, Bertrand R, Comte L, Bourgeaud L, Hattab T, Murienne J, Grenouillet G (2020) Species better track climate warming in the oceans than on land. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 1044-1059. |
| [65] | Li DJ, Miller JED, Harrison S (2019) Climate drives loss of phylogenetic diversity in a grassland community. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 19989-19994. |
| [66] |
Li N, Euring D, Cha JY, Lin Z, Lu MZ, Huang LJ, Kim WY (2021) Plant hormone-mediated regulation of heat tolerance in response to global climate change. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 627969.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Li ZY, Ye XZ, Wang SP (2021) Ecosystem stability and its relationship with biodiversity. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 1127-1139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李周园, 叶小洲, 王少鹏 (2021) 生态系统稳定性及其与生物多样性的关系. 植物生态学报, 45, 1127-1139.]
DOI |
|
| [68] |
Liu AR, Yang T, Xu W, Shangguan ZJ, Wang JZ, Liu HY, Shi Y, Chu HY, He JS (2018) Status, issues and prospects of belowground biodiversity on the Tibetan alpine grassland. Biodiversity Science, 26, 972-987. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘安榕, 杨腾, 徐炜, 上官子健, 王金洲, 刘慧颖, 时玉, 褚海燕, 贺金生 (2018) 青藏高原高寒草地地下生物多样性: 进展、问题与展望. 生物多样性, 26, 972-987.]
DOI |
|
| [69] |
Liu HY, Wang H, Li N, Shao JJ, Zhou XH, van Groenigen KJ, Thakur MP (2022a) Phenological mismatches between above- and belowground plant responses to climate warming. Nature Climate Change, 12, 97-102.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Liu HY, Xu CY, Allen CD, Hartmann H, Wei XH, Yakir D, Wu XC, Yu PT (2022b) Nature-based framework for sustainable afforestation in global drylands under changing climate. Global Change Biology, 28, 2202-2220.
DOI URL |
| [71] | Liu XJ, Trogisch S, He JS, Niklaus PA, Bruelheide H, Tang ZY, Erfmeier A, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Pietsch KA, Yang B, Kühn P, Scholten T, Huang YY, Wang C, Staab M, Leppert KN, Wirth C, Schmid B, Ma KP (2018) Tree species richness increases ecosystem carbon storage in subtropical forests. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285, 20181240. |
| [72] |
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature, 412, 72-76.
DOI URL |
| [73] | Luo YH, Cadotte MW, Liu J, Burgess KS, Tan SL, Ye LJ, Zou JY, Chen ZZ, Jiang XL, Li J, Xu K, Li DZ, Gao LM (2022) Multitrophic diversity and biotic associations influence subalpine forest ecosystem multifunctionality. Ecology, 103, e3745. |
| [74] | Ma KP, Zhu M, Ji LQ, Ma JC, Guo QH, Ouyang ZY, Zhu L (2018) Establishing China infrastructure for big biodiversity data. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33, 838-845. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 朱敏, 纪力强, 马俊才, 郭庆华, 欧阳志云, 朱丽 (2018) 中国生物多样性大数据平台建设. 中国科学院院刊, 33, 838-845.] | |
| [75] |
Makiola A, Holdaway RJ, Wood JR, Orwin KH, Glare TR, Dickie IA (2022) Environmental and plant community drivers of plant pathogen composition and richness. New Phytologist, 233, 496-504.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Malik AA, Martiny JBH, Brodie EL, Martiny AC, Treseder KK, Allison SD (2020) Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change. The ISME Journal, 14, 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [77] | Manning P, Loos J, Barnes AD, Batáry P, Bianchi FJJA, Buchmann N, de Deyn GB, Ebeling A, Eisenhauer N, Fischer M, Fründ J, Grass I, Isselstein J, Jochum M, Klein AM, Klingenberg EOF, Landis DA, Lepš J, Tscharntke T (2019) Transferring biodiversity-ecosystem function research to the management of ‘real-world’ ecosystems. Advances in Ecological Research, 66, 323-356. |
| [78] | Manning P, van der Plas F, Soliveres S, Allan E, Maestre FT, Mace G, Whittingham MJ, Fischer M (2018) Redefining ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 427-436. |
| [79] | Mi XC, Feng G, Zhang J, Hu YB, Zhu L, Ma KP (2021) Review on biodiversity science in China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36, 384-398. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [米湘成, 冯刚, 张健, 胡义波, 朱丽, 马克平 (2021) 中国生物多样性科学研究进展评述. 中国科学院院刊, 36, 384-398.] | |
| [80] |
Mori AS, Dee LE, Gonzalez A, Ohashi H, Cowles J, Wright AJ, Loreau M, Hautier Y, Newbold T, Reich PB, Matsui T, Takeuchi W, Okada KI, Seidl R, Isbell F (2021) Biodiversity-productivity relationships are key to nature-based climate solutions. Nature Climate Change, 11, 543-550.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Mouillot D, Loiseau N, Grenié M, Algar AC, Allegra M, Cadotte MW, Casajus N, Denelle P, Guéguen M, Maire A, Maitner B, McGill BJ, McLean M, Mouquet N, Munoz F, Thuiller W, Villéger S, Violle C, Auber A (2021) The dimensionality and structure of species trait spaces. Ecology Letters, 24, 1988-2009.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Niu SL, Wan SQ, Ma KP (2009) Acclimation and mitigation of terrestrial ecosystem and biodiversity to climate change. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 24, 421-427. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛书丽, 万师强, 马克平 (2009) 陆地生态系统及生物多样性对气候变化的适应与减缓. 中国科学院院刊, 24, 421-427.] | |
| [83] |
Niu SL, Chen WN (2020) Global change and ecosystems research progress and prospect. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 449-460. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[牛书丽, 陈卫楠 (2020) 全球变化与生态系统研究现状与展望. 植物生态学报, 44, 449-460.]
DOI |
|
| [84] | O’Connor MI, Mori AS, Gonzalez A, Dee LE, Loreau M, Avolio M, Byrnes JEK, Cheung W, Cowles J, Clark AT, Hautier Y, Hector A, Komatsu K, Newbold T, Outhwaite CL, Reich PB, Seabloom E, Williams L, Wright A, Isbell F (2021) Grand challenges in biodiversity-ecosystem functioning research in the era of science-policy platforms require explicit consideration of feedbacks. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 288, 20210783. |
| [85] |
Pardikes NA, Revilla TA, Lue CH, Thierry M, Souto-Vilarós D, Hrcek J (2022) Effects of phenological mismatch under warming are modified by community context. Global Change Biology, 28, 4013-4026.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Pereira HM, Navarro LM, Martins IS (2012) Global biodiversity change: The bad, the good, and the unknown. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 37, 25-50.
DOI |
| [87] |
Petry WK, Soule JD, Iler AM, Chicas-Mosier A, Inouye DW, Miller TEX, Mooney KA (2016) Sex-specific responses to climate change in plants alter population sex ratio and performance. Science, 353, 69-71.
DOI PMID |
| [88] |
Pettorelli N, Graham NAJ, Seddon N, Bustamante M, Lowton MJ, Sutherland WJ, Koldewey HJ, Prentice HC, Barlow J (2021) Time to integrate global climate change and biodiversity science-policy agendas. Journal of Applied Ecology, 58, 2384-2393.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Piao SL, He Y, Wang XH, Chen FH (2022) Estimation of China’s terrestrial ecosystem carbon sink: Methods, progress and prospects. Science China Earth Sciences, 65, 641-651. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [朴世龙, 何悦, 王旭辉, 陈发虎 (2022) 中国陆地生态系统碳汇估算: 方法、进展、展望. 中国科学: 地球科学, 52, 1010-1020.] | |
| [90] | Pörtner HO, Scholes RJ, Agard J, Archer E, Arneth A, Bai X, Barnes D, Burrows M, Chan L, Cheung WLW, Diamond S, Donatti C, Duarte C, Eisenhauer N, Foden W, Gasalla MA, Handa C, Hickler T, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Ichii K, Jacob U, Insarov G, Kiessling W, Leadley P, Leemans R, Levin L, Lim M, Maharaj S, Managi S, Marquet PA, McElwee P, Midgley G, Oberdorff T, Obura D, Osman Elasha B, Pandit R, Pascual U, Pires APF, Popp A, Reyes-García V, Sankaran M, Settele J, Shin Y-J, Sintayehu DW, Smith P, Steiner N, Strassburg B, Sukumar R, Trisos C, Val AL, Wu J, Aldrian E, Parmesan C, Pichs-Madruga R, Roberts DC, Rogers AD, Díaz SM, Fischer M, Hashimoto S, Lavorel S, Ning W, Ngo H (2021) Scientific outcome of the IPBES-IPCC co-sponsored workshop on biodiversity and climate change. Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), https://zenodo.org/record/5101125. (last accessed on 2022-08-06). |
| [91] |
Potts SG, Biesmeijer JC, Kremen C, Neumann P, Schweiger O, Kunin WE (2010) Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 345-353.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Pretty J, Benton TG, Bharucha ZP, Dicks LV, Flora CB, Godfray HCJ, Goulson D, Hartley S, Lampkin N, Morris C, Pierzynski G, Prasad PVV, Reganold J, Rockström J, Smith P, Thorne P, Wratten S (2018) Global assessment of agricultural system redesign for sustainable intensification. Nature Sustainability, 1, 441-446.
DOI URL |
| [93] | Qiu JX, Cardinale BJ (2020) Scaling up biodiversity- ecosystem function relationships across space and over time. Ecology, 101, e03166. |
| [94] |
Ratcliffe S, Wirth C, Jucker T, van der Plas F, Scherer- Lorenzen M, Verheyen K, Allan E, Benavides R, Bruelheide H, Ohse B, Paquette A, Ampoorter E, Bastias CC, Bauhus J, Bonal D, Bouriaud O, Bussotti F, Carnol M, Castagneyrol B, Chećko E, Dawud SM, De Wandeler H, Domisch T, Finér L, Fischer M, Fotelli M, Gessler A, Granier A, Grossiord C, Guyot V, Haase J, Hättenschwiler S, Jactel H, Jaroszewicz B, Joly FX, Kambach S, Kolb S, Koricheva J, Liebersgesell M, Milligan H, Müller S, Muys B, Nguyen D, Nock C, Pollastrini M, Purschke O, Radoglou K, Raulund-Rasmussen K, Roger F, Ruiz-Benito P, Seidl R, Selvi F, Seiferling I, Stenlid J, Valladares F, Vesterdal L, Baeten L (2017) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning relations in European forests depend on environmental context. Ecology Letters, 20, 1414-1426.
DOI PMID |
| [95] |
Rillig MC, Ryo M, Lehmann A, Aguilar-Trigueros CA, Buchert S, Wulf A, Iwasaki A, Roy J, Yang GW (2019) The role of multiple global change factors in driving soil functions and microbial biodiversity. Science, 366, 886-890.
DOI PMID |
| [96] |
Rinawati F, Stein K, Lindner A (2013) Climate change impacts on biodiversity—The setting of a lingering global crisis. Diversity, 5, 114-123.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Roslin T, Antão L, Hällfors M, Meyke E, Lo C, Tikhonov G, del Mar Delgado M, Gurarie E, Abadonova M, Abduraimov O, Adrianova O, Akimova T, Akkiev M, Ananin A, Andreeva E, Andriychuk N, Antipin M, Arzamascev K, Babina S, Babushkin M, Bakin O, Barabancova A, Basilskaja I, Belova N, Belyaeva N, Bespalova T, Bisikalova E, Bobretsov A, Bobrov V, Bobrovskyi V, Bochkareva E, Bogdanov G, Bolshakov V, Bondarchuk S, Bukharova E, Butunina A, Buyvolov Y, Buyvolova A, Bykov Y, Chakhireva E, Chashchina O, Cherenkova N, Chistjakov S, Chuhontseva S, Davydov EA, Demchenko V, Diadicheva E, Dobrolyubov A, Dostoyevskaya L, Drovnina S, Drozdova Z, Dubanaev A, Dubrovsky Y, Elsukov S, Epova L, Ermakova O, Ermakova OS, Ershkova E, Esengeldenova A, Evstigneev O, Fedchenko I, Fedotova V, Filatova T, Gashev S, Gavrilov A, Gaydysh I, Golovcov D, Goncharova N, Gorbunova E, Gordeeva T, Grishchenko V, Gromyko L, Hohryakov V, Hritankov A, Ignatenko E, Igosheva S, Ivanova U, Ivanova N, Kalinkin Y, Kaygorodova E, Kazansky F, Kiseleva D, Knorre A, Kolpashikov L, Korobov E, Korolyova H, Korotkikh N, Kosenkov G, Kossenko S, Kotlugalyamova E, Kozlovsky E, Kozsheechkin V, Kozurak A, Kozyr I, Krasnopevtseva A, Kruglikov S, Kuberskaya O, Kudryavtsev A, Kulebyakina E, Kulsha Y, Kupriyanova M, Kurbanbagamaev M, Kutenkov A, Kutenkova N, Kuyantseva N, Kuznetsov A, Larin E, Lebedev P, Litvinov K, Luzhkova N, Mahmudov A, Makovkina L, Mamontov V, Mayorova S, Megalinskaja I, Meydus A, Minin A, Mitrofanov O, Motruk M, Myslenkov A, Nasonova N, Nemtseva N, Nesterova I, Nezdoliy T, Niroda T, Novikova T, Panicheva D, Pavlov A, Pavlova K, Podolski S, Polikarpova N, Polyanskaya T, Pospelov I, Pospelova E, Prokhorov I, Prokosheva I, Puchnina L, Putrashyk I, Raiskaya J, Rozhkov Y, Rozhkova O, Rudenko M, Rybnikova I, Rykova S, Sahnevich M, Samoylov A, Sanko V, Sapelnikova I, Sazonov S, Selyunina Z, Shalaeva K, Shashkov M, Shcherbakov A, Shevchyk V, Shubin S, Shujskaja E, Sibgatullin R, Sikkila N, Sitnikova E, Sivkov A, Skok N, Skorokhodova S, Smirnova E, Sokolova G, Sopin V, Spasovski Y, Stepanov S, Stratiy V, Strekalovskaya V, Sukhov A, Suleymanova G, Sultangareeva L, Teleganova V, Teplov V, Teplova V, Tertitsa T, Timoshkin V, Tirski D, Tolmachev A, Tomilin A, Tselishcheva L, Turgunov M, Tyukh Y, Van P, Van V, Vasin A, Vasina A, Vekliuk A, Vetchinnikova L, Vinogradov V, Volodchenkov N, Voloshina I, Xoliqov T, Yablonovska-Grishchenko E, Yakovlev V, Yakovleva M, Yantser O, Yarema Y, Zahvatov A, Zakharov V, Zelenetskiy N, Zheltukhin A, Zubina T, Kurhinen J, Ovaskainen O (2021) Phenological shifts of abiotic events, producers and consumers across a continent. Nature Climate Change, 11, 241-248.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
Sala OE, Chapin FS III, Armesto JJ, Berlow E, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E, Huenneke LF, Jackson RB, Kinzig A, Leemans R, Lodge DM, Mooney HA, Oesterheld M, Poff NL, Sykes MT, Walker BH, Walker M, Wall DH (2000) Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science, 287, 1770-1774.
PMID |
| [99] |
Saladin B, Pellissier L, Graham CH, Nobis MP, Salamin N, Zimmermann NE (2020) Rapid climate change results in long-lasting spatial homogenization of phylogenetic diversity. Nature Communications, 11, 4663.
DOI PMID |
| [100] |
Scheffers BR, De Meester L, Bridge TCL, Hoffmann AA, Pandolfi JM, Corlett RT, Butchart SHM, Pearce-Kelly P, Kovacs KM, Dudgeon D, Pacifici M, Rondinini C, Foden WB, Martin TG, Mora C, Bickford D, Watson JEM (2016) The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science, 354, aaf7671.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
Schuldt A, Assmann T, Brezzi M, Buscot F, Eichenberg D, Gutknecht J, Härdtle W, He JS, Klein AM, Kühn P, Liu XJ, Ma KP, Niklaus PA, Pietsch KA, Purahong W, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Scholten T, Staab M, Tang ZY, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Wirth C, Wubet T, Zhu CD, Bruelheide H (2018) Biodiversity across trophic levels drives multifunctionality in highly diverse forests. Nature Communications, 9, 2989.
DOI PMID |
| [102] | Shen MG, Wang SP, Jiang N, Sun JP, Cao RY, Ling XF, Fang B, Zhang L, Zhang LH, Xu XY, Lv WW, Li BL, Sun QL, Meng FD, Jiang YH, Dorji T, Fu YS, Iler A, Vitasse Y, Steltzer H, Ji ZM, Zhao WW, Piao SL, Fu BJ (2022) Plant phenology changes and drivers on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3, 633-651. |
| [103] |
Shin YJ, Midgley GF, Archer ERM, Arneth A, Barnes DKA, Chan LN, Hashimoto S, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Insarov G, Leadley P, Levin LA, Ngo HT, Pandit R, Pires APF, Pörtner HO, Rogers AD, Scholes RJ, Settele J, Smith P (2022) Actions to halt biodiversity loss generally benefit the climate. Global Change Biology, 28, 2846-2874.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Smith P, Arneth A, Barnes DKA, Ichii K, Marquet PA, Popp A, Pörtner HO, Rogers AD, Scholes RJ, Strassburg B, Wu JG, Ngo H (2022) How do we best synergize climate mitigation actions to co-benefit biodiversity? Global Change Biology, 28, 2555-2577.
DOI URL |
| [105] | Song J, Wan SQ, Piao SL, Knapp AK, Classen AT, Vicca S, Ciais P, Hovenden MJ, Leuzinger S, Beier C, Kardol P, Xia JY, Liu Q, Ru JY, Zhou ZX, Luo YQ, Guo DL, Adam Langley J, Zscheischler J, Dukes JS, Tang JW, Chen JQ, Hofmockel KS, Kueppers LM, Rustad L, Liu LL, Smith MD, Templer PH, Quinn Thomas R, Norby RJ, Phillips RP, Niu SL, Fatichi S, Wang YP, Shao PS, Han HY, Wang DD, Lei LJ, Wang JL, Li XN, Zhang Q, Li XM, Su FL, Liu B, Yang F, Ma GG, Li GY, Liu YC, Liu YZ, Yang ZL, Zhang KS, Miao Y, Hu MJ, Yan C, Zhang A, Zhong MX, Hui Y, Li Y, Zheng MM (2019) A meta-analysis of 1,119 manipulative experiments on terrestrial carbon-cycling responses to global change. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3, 1309-1320. |
| [106] |
Strassburg BBN, Iribarrem A, Beyer HL, Cordeiro CL, Crouzeilles R, Jakovac CC, Braga Junqueira A, Lacerda E, Latawiec AE, Balmford A, Brooks TM, Butchart SHM, Chazdon RL, Erb KH, Brancalion P, Buchanan G, Cooper D, Díaz S, Donald PF, Kapos V, Leclère D, Miles L, Obersteiner M, Plutzar C, de M Scaramuzza CA, Scarano FR, Visconti P (2020) Global priority areas for ecosystem restoration. Nature, 586, 724-729.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Terraube J, Villers A, Poudré L, Varjonen R, Korpimäki E (2017) Increased autumn rainfall disrupts predator-prey interactions in fragmented boreal forests. Global Change Biology, 23, 1361-1373.
DOI PMID |
| [108] | Thackeray SJ, Henrys PA, Hemming D, Bell JR, Botham MS, Burthe S, Helaouet P, Johns DG, Jones ID, Leech DI, Mackay EB, Massimino D, Atkinson S, Bacon PJ, Brereton TM, Carvalho L, Clutton-Brock TH, Duck C, Edwards M, Elliott JM, Hall SJG, Harrington R, Pearce-Higgins JW, Høye TT, Kruuk LEB, Pemberton JM, Sparks TH, Thompson PM, White I, Winfield IJ, Wanless S (2016) Phenological sensitivity to climate across taxa and trophic levels. Nature, 535, 241-245. |
| [109] |
Thakur MP (2020) Climate warming and trophic mismatches in terrestrial ecosystems: The green-brown imbalance hypothesis. Biology Letters, 16, 20190770.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Thuiller W, Lavergne S, Roquet C, Boulangeat I, Lafourcade B, Araujo MB (2011) Consequences of climate change on the Tree of Life in Europe. Nature, 470, 531-534.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Tilman D, Isbell F, Cowles JM (2014) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 45, 471-493.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops J, Wedin D, Mielke T, Lehman C (2001) Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science, 294, 843-845.
PMID |
| [113] |
van der Plas F (2019) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in naturally assembled communities. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 94, 1220-1245.
DOI PMID |
| [114] |
van der Plas F, Manning P, Allan E, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Verheyen K, Wirth C, Zavala MA, Hector A, Ampoorter E, Baeten L, Barbaro L, Bauhus J, Benavides R, Benneter A, Berthold F, Bonal D, Bouriaud O, Bruelheide H, Bussotti F, Carnol M, Castagneyrol B, Charbonnier Y, Coomes D, Coppi A, Bastias CC, Muhie Dawud S, De Wandeler H, Domisch T, Finér L, Gessler A, Granier A, Grossiord C, Guyot V, Hättenschwiler S, Jactel H, Jaroszewicz B, Joly FX, Jucker T, Koricheva J, Milligan H, Müller S, Muys B, Nguyen D, Pollastrini M, Raulund-Rasmussen K, Selvi F, Stenlid J, Valladares F, Vesterdal L, Zielínski D, Fischer M (2016) Jack-of-all-trades effects drive biodiversity- ecosystem multifunctionality relationships in European forests. Nature Communications, 7, 11109.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
Vasiliev D, Greenwood S (2021) The role of climate change in pollinator decline across the Northern Hemisphere is underestimated. Science of the Total Environment, 775, 145788.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Violle C, Navas ML, Vile D, Kazakou E, Fortunel C, Hummel I, Garnier E (2007) Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos, 116, 882-892.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
Verheyen K, Vanhellemont M, Auge H, Baeten L, Baraloto C, Barsoum N, Bilodeau-Gauthier S, Bruelheide H, Castagneyrol B, Godbold D, Haase J, Hector A, Jactel H, Koricheva J, Loreau M, Mereu S, Messier C, Muys B, Nolet P, Paquette A, Parker J, Perring M, Ponette Q, Potvin C, Reich P, Smith A, Weih M, Scherer-Lorenzen M (2016) Contributions of a global network of tree diversity experiments to sustainable forest plantations. Ambio, 45, 29-41.
DOI URL |
| [118] | Visser ME, Gienapp P (2019) Evolutionary and demographic consequences of phenological mismatches. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3, 879-885. |
| [119] |
Wang QQ, Gao Y, Wang R (2021) Review on impacts of global change on food web structure. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 1064-1074. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[王晴晴, 高燕, 王嵘 (2021) 全球变化对食物网结构影响机制的研究进展. 植物生态学报, 45, 1064-1074.]
DOI |
|
| [120] | Warren R, Price J, Jenkins R (2021) Climate change and terrestrial biodiversity. In: The Impacts of Climate Change: A comprehensive Study of Physical, Biophisical, Social and Political Issues (ed. Letcher TM), pp. 85-114. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| [121] |
Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB (2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 (2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [122] | Wolf C, Levi T, Ripple WJ, Zárrate-Charry DA, Betts MG (2021) A forest loss report card for the world’s protected areas. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 520-529. |
| [123] |
Wu D, Xu C, Wang SP, Zhang L, Kortsch S (2022) Why are biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationships so elusive? Trophic interactions may amplify ecosystem function variability. Journal of Animal Ecology, doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13808.
DOI |
| [124] |
Xu W, Ma ZY, Jing X, He JS (2016) Biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Advances and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 24, 55-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐炜, 马志远, 井新, 贺金生 (2016) 生物多样性与生态系统多功能性: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 55-71.]
DOI |
|
| [125] |
Yang GW, Ryo M, Roy J, Lammel DR, Ballhausen MB, Jing X, Zhu XF, Rillig MC (2022) Multiple anthropogenic pressures eliminate the effects of soil microbial diversity on ecosystem functions in experimental microcosms. Nature Communications, 13, 4260.
DOI PMID |
| [126] | Yang YH, Shi Y, Sun WJ, Chang JF, Zhu JX, Chen LY, Wang X, Guo YP, Zhang HT, Yu LF, Zhao SQ, Xu K, Zhu JL, Shen HH, Wang YY, Peng YF, Zhao X, Wang XP, Hu HF, Chen SP, Huang M, Wen XF, Wang SP, Zhu B, Niu SL, Tang ZY, Liu LL, Fang JY (2022) Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality. Science China Life Sciences, 65, 534-574. |
| [杨元合, 石岳, 孙文娟, 常锦峰, 朱剑霄, 陈蕾伊, 王欣, 郭焱培, 张宏图, 于凌飞, 赵淑清, 徐亢, 朱江玲, 沈海花, 王媛媛, 彭云峰, 赵霞, 王襄平, 胡会峰, 陈世苹, 黄玫, 温学发, 王少鹏, 朱彪, 牛书丽, 唐志尧, 刘玲莉, 方精云 (2022) 中国及全球陆地生态系统碳源汇特征及其对碳中和的贡献. 中国科学: 生命科学, 52, 534-574.] | |
| [127] | Yu GR, Hao TX, Zhu JX (2022) Discussion on action strategies of China’s carbon peak and carbon neutrality. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 37, 423-434. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于贵瑞, 郝天象, 朱剑兴 (2022) 中国碳达峰、碳中和行动方略之探讨. 中国科学院院刊, 37, 423-434.] | |
| [128] | Yu GR, Yang M, Fu C, Wang QF, Chen Z (2021) Thinking on large-scale terrestrial ecosystem management and its theoretical fundament and practice. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 771-787. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[于贵瑞, 杨萌, 付超, 王秋凤, 陈智 (2021) 大尺度陆地生态系统管理的理论基础及其应用研究的思考. 应用生态学报, 32, 771-787.]
DOI |
|
| [129] |
Zellweger F, de Frenne P, Lenoir J, Vangansbeke P, Verheyen K, Bernhardt-Römermann M, Baeten L, Hédl R, Berki I, Brunet J, van Calster H, Chudomelová M, Decocq G, Dirnböck T, Durak T, Heinken T, Jaroszewicz B, Kopecký M, Máliš F, Macek M, Malicki M, Naaf T, Nagel TA, Ortmann-Ajkai A, Petřík P, Pielech R, Reczyńska K, Schmidt W, Standovár T, Świerkosz K, Teleki B, Vild O, Wulf M, Coomes D (2020) Forest microclimate dynamics drive plant responses to warming. Science, 368, 772-775.
DOI PMID |
| [130] | Zu KL, Wang ZH (2022) Research progress on the elevational distribution of mountain species in response to climate change. Biodiversity Science, 30, 123-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祖奎玲, 王志恒 (2022) 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 123-137.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()