



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22533. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022533 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022533
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Helu Zhang1,2, Meihong Zhao1,2, Shichun Sun2,3, Xiaoshou Liu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-18
Accepted:2022-11-28
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-23
Contact:
* E-mail: Helu Zhang, Meihong Zhao, Shichun Sun, Xiaoshou Liu. Diversity and community characteristics of free-living nematodes in plateau salt lakes in Nagqu City, Tibet[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22533.
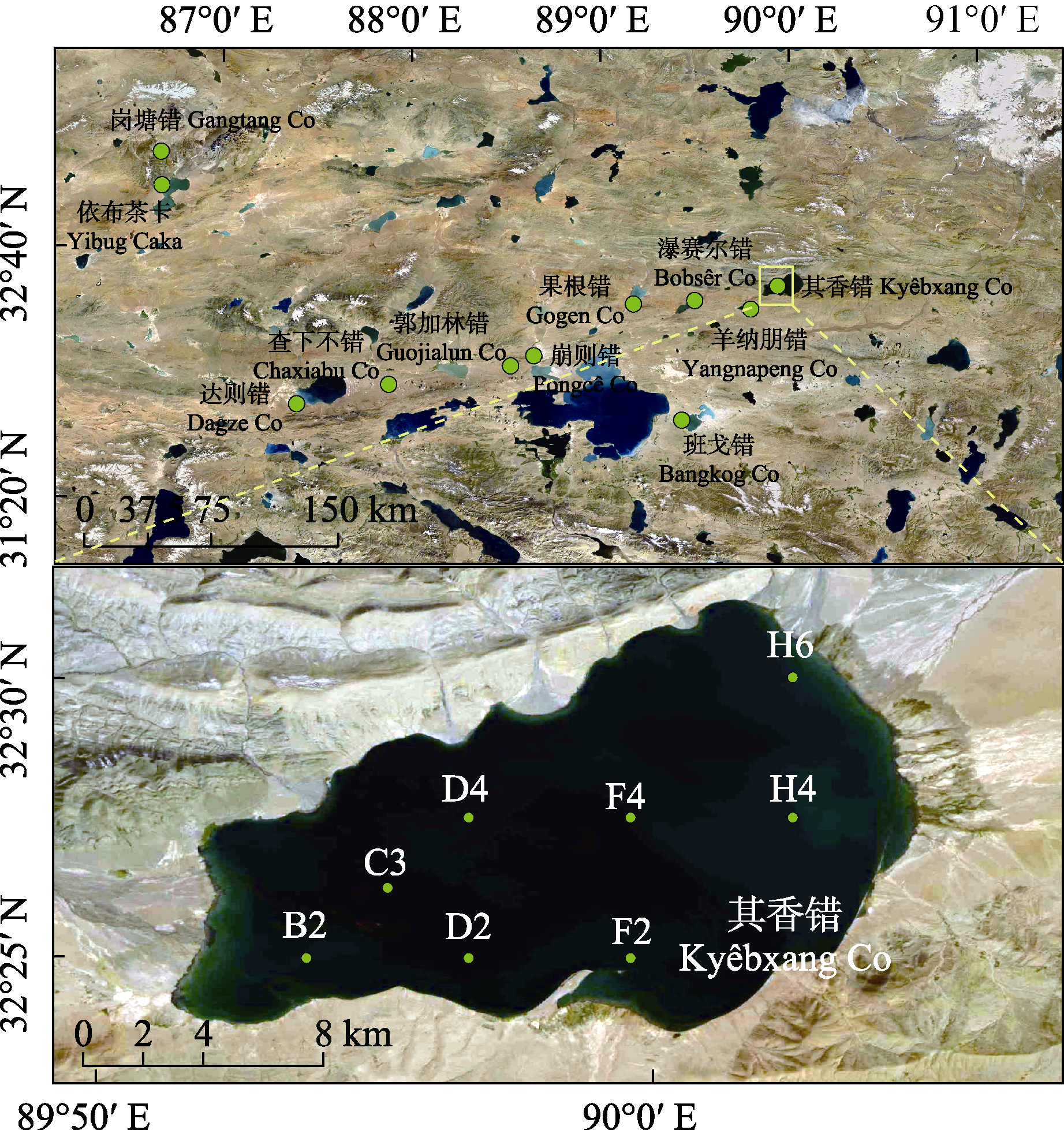
Fig. 1 Map of the sampling sites in plateau salt lakes in Nagqu City, Tibet. The picture above is all salt lakes and the picture below is Kyêbxang Co.
| 湖泊 Lakes | 东经 Longitude (E) | 北纬 Latitude (N) | 沉积物类型 Type of sediment | 温度 (T, ℃) | 盐度 (Sal) | pH | 中值粒径 (Md, mm) | 含水量 (W, %) | 有机质 含量 (OM, %) | 叶绿素a 含量 (Chl-a, μg/g) | 溶解氧 含量 (DO, mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 崩则错 Pongcê Co (BZC) | 88°38′ | 32°04′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 20.60 | 0.64 | 8.90 | 1.180 | 15.8 | 3.4 | 0.060 | 6.81 |
| 查下不错 Chaxiabu Co (CXBC) | 87°52′ | 31°55′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 19.18 | 2.89 | 8.96 | 0.250 | 23.6 | 0.3 | 0.160 | 6.42 |
| 果根错 Gogen Co (GGC) | 89°10′ | 32°21′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 12.74 | 4.67 | 8.98 | 0.300 | 13.6 | 1.6 | 0.669 | 7.26 |
| 瀑赛尔错 Bobsêr Co (PSEC) | 89°29′ | 32°22′ | 砂质砾 Sandy gravel | 13.53 | 4.70 | 9.00 | 0.650 | 16.0 | 0.5 | 1.659 | 6.62 |
| 郭加林错 Guojialun Co (GJLC) | 88°31′ | 32°01′ | 砾质砂 Gravelly sand | 16.14 | 10.20 | 8.94 | 0.190 | 15.2 | 0.4 | 0.049 | 5.38 |
| 达则错 Dagze Co (DZC) | 87°23′ | 31°49′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 18.86 | 11.82 | 8.19 | 0.180 | 21.3 | 1.5 | 0.391 | 6.62 |
| 羊纳朋错 Yangnapeng Co (YNPC) | 89°47′ | 32°19′ | 砾质砂 Gravelly sand | 18.55 | 32.31 | 9.03 | 0.360 | 14.6 | 0.9 | 1.600 | 3.58 |
| 班戈错 Bangkog Co (BGC) | 89°25′ | 31°44′ | 含砾泥质砂 Gravelly muddy sand | 14.40 | 44.25 | 9.24 | 0.200 | 36.4 | 1.9 | 2.527 | 7.20 |
| 岗塘错 Gangtang Co (GTC) | 86°39′ | 33°10′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 13.78 | 45.52 | 8.85 | 0.340 | 17.0 | 1.0 | 0.111 | 3.73 |
| 依布茶卡 Yibug Caka (YBCK) | 86°40′ | 32°59′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 16.32 | 49.85 | 8.76 | 0.206 | 58.3 | 12.6 | 1.619 | 5.36 |
| 其香错 Kyêbxang Co (QXC) | 89°59′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.20 | 44.35 | 9.03 | 0.190 | 49.1 | 5.0 | 0.570 | 5.45 |
| H6 | 90°02′ | 32°30′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.54 | 41.22 | 9.00 | 0.229 | 40.7 | 2.8 | 0.706 | 4.62 |
| B2 | 89°53′ | 32°24′ | 砂 Sand | 14.04 | 41.23 | 8.95 | 0.221 | 46.3 | 2.9 | 0.612 | 5.45 |
| H4 | 90°02′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.78 | 41.31 | 9.04 | 0.161 | 44.1 | 1.9 | 0.887 | 4.74 |
| C3 | 89°55′ | 32°26′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 13.70 | 42.33 | 9.11 | 0.182 | 46.4 | 3.6 | 0.557 | 7.60 |
| F2 | 89°59′ | 32°24′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 13.72 | 42.98 | 9.10 | 0.183 | 53.0 | 4.5 | 0.344 | 4.85 |
| D2 | 89°56′ | 32°24′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.09 | 44.73 | 9.00 | 0.184 | 51.5 | 7.8 | 0.474 | 5.09 |
| F4 | 89°59′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.16 | 49.20 | 9.11 | 0.160 | 60.6 | 8.6 | 0.599 | 6.46 |
| D4 | 89°56′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.56 | 51.81 | 8.89 | 0.229 | 49.6 | 7.2 | 0.401 | 4.78 |
Table 1 Environmental variables of the sampling lakes in Nagqu City, Tibet (Station H6-D4 belongs to Kyêbxang Co)
| 湖泊 Lakes | 东经 Longitude (E) | 北纬 Latitude (N) | 沉积物类型 Type of sediment | 温度 (T, ℃) | 盐度 (Sal) | pH | 中值粒径 (Md, mm) | 含水量 (W, %) | 有机质 含量 (OM, %) | 叶绿素a 含量 (Chl-a, μg/g) | 溶解氧 含量 (DO, mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 崩则错 Pongcê Co (BZC) | 88°38′ | 32°04′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 20.60 | 0.64 | 8.90 | 1.180 | 15.8 | 3.4 | 0.060 | 6.81 |
| 查下不错 Chaxiabu Co (CXBC) | 87°52′ | 31°55′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 19.18 | 2.89 | 8.96 | 0.250 | 23.6 | 0.3 | 0.160 | 6.42 |
| 果根错 Gogen Co (GGC) | 89°10′ | 32°21′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 12.74 | 4.67 | 8.98 | 0.300 | 13.6 | 1.6 | 0.669 | 7.26 |
| 瀑赛尔错 Bobsêr Co (PSEC) | 89°29′ | 32°22′ | 砂质砾 Sandy gravel | 13.53 | 4.70 | 9.00 | 0.650 | 16.0 | 0.5 | 1.659 | 6.62 |
| 郭加林错 Guojialun Co (GJLC) | 88°31′ | 32°01′ | 砾质砂 Gravelly sand | 16.14 | 10.20 | 8.94 | 0.190 | 15.2 | 0.4 | 0.049 | 5.38 |
| 达则错 Dagze Co (DZC) | 87°23′ | 31°49′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 18.86 | 11.82 | 8.19 | 0.180 | 21.3 | 1.5 | 0.391 | 6.62 |
| 羊纳朋错 Yangnapeng Co (YNPC) | 89°47′ | 32°19′ | 砾质砂 Gravelly sand | 18.55 | 32.31 | 9.03 | 0.360 | 14.6 | 0.9 | 1.600 | 3.58 |
| 班戈错 Bangkog Co (BGC) | 89°25′ | 31°44′ | 含砾泥质砂 Gravelly muddy sand | 14.40 | 44.25 | 9.24 | 0.200 | 36.4 | 1.9 | 2.527 | 7.20 |
| 岗塘错 Gangtang Co (GTC) | 86°39′ | 33°10′ | 含砾砂 Gravelly sand | 13.78 | 45.52 | 8.85 | 0.340 | 17.0 | 1.0 | 0.111 | 3.73 |
| 依布茶卡 Yibug Caka (YBCK) | 86°40′ | 32°59′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 16.32 | 49.85 | 8.76 | 0.206 | 58.3 | 12.6 | 1.619 | 5.36 |
| 其香错 Kyêbxang Co (QXC) | 89°59′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.20 | 44.35 | 9.03 | 0.190 | 49.1 | 5.0 | 0.570 | 5.45 |
| H6 | 90°02′ | 32°30′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.54 | 41.22 | 9.00 | 0.229 | 40.7 | 2.8 | 0.706 | 4.62 |
| B2 | 89°53′ | 32°24′ | 砂 Sand | 14.04 | 41.23 | 8.95 | 0.221 | 46.3 | 2.9 | 0.612 | 5.45 |
| H4 | 90°02′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.78 | 41.31 | 9.04 | 0.161 | 44.1 | 1.9 | 0.887 | 4.74 |
| C3 | 89°55′ | 32°26′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 13.70 | 42.33 | 9.11 | 0.182 | 46.4 | 3.6 | 0.557 | 7.60 |
| F2 | 89°59′ | 32°24′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 13.72 | 42.98 | 9.10 | 0.183 | 53.0 | 4.5 | 0.344 | 4.85 |
| D2 | 89°56′ | 32°24′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.09 | 44.73 | 9.00 | 0.184 | 51.5 | 7.8 | 0.474 | 5.09 |
| F4 | 89°59′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.16 | 49.20 | 9.11 | 0.160 | 60.6 | 8.6 | 0.599 | 6.46 |
| D4 | 89°56′ | 32°27′ | 粉砂质砂 Chalky sand | 14.56 | 51.81 | 8.89 | 0.229 | 49.6 | 7.2 | 0.401 | 4.78 |
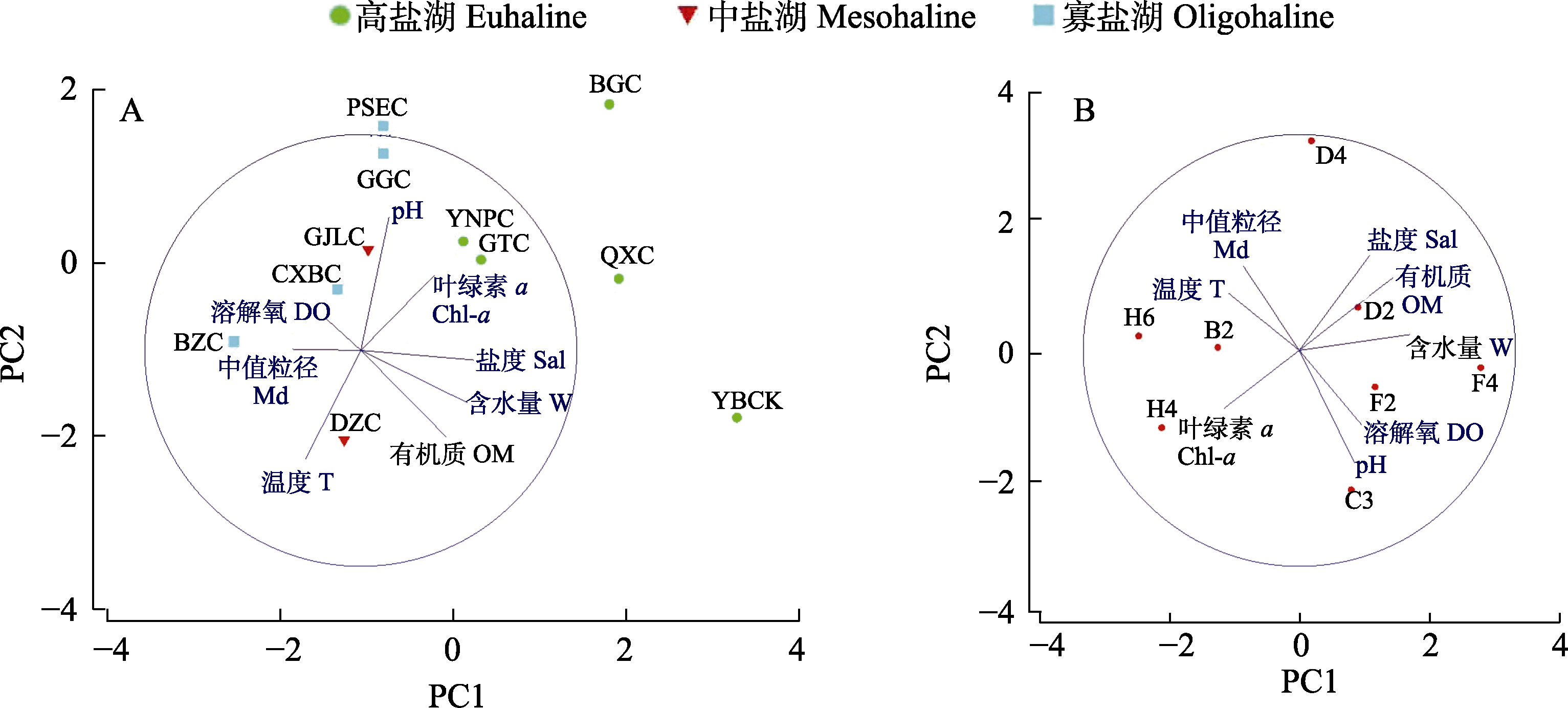
Fig. 2 Principal component analysis (PCA) results of environmental factors of all salt lakes (A) and Kyêbxang Co (B) in Nagqu City, Tibet. Abbreviation meanings are shown in Table 1.
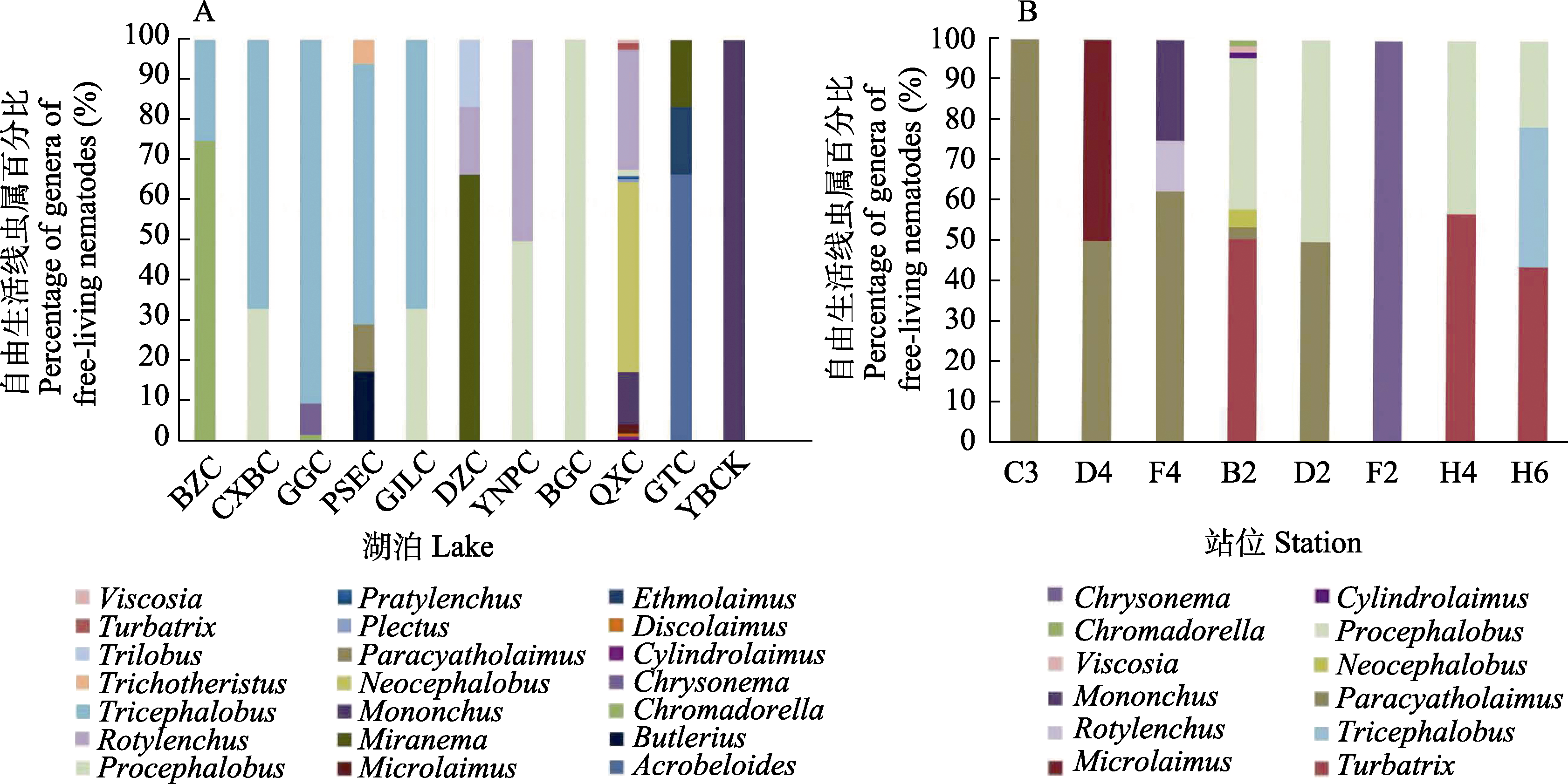
Fig. 4 Percentage of genera of free-living nematodes of all salt lakes (A) and Kyêbxang Co (B) in Nagqu City, Tibet. Abbreviation meanings are shown in Table 1.
| 湖泊 Lakes | 物种数 No. of species (S) | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (d) | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J') | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index (1 - λ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 崩则错 Pongcê Co | 2 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.59 | 0.81 |
| 查下不错 Chaxiabu Co | 2 | - | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.92 |
| 果根错 Gogen Co | 3 | 0.79 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.53 |
| 瀑赛尔错 Bobsêr Co | 4 | 2.10 | 0.73 | 0.35 | 1.45 |
| 郭加林错 Guojialun Co | 2 | 2.60 | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.92 |
| 达则错 Dagze Co | 3 | 5.20 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 1.25 |
| 羊纳朋错 Yangnapeng Co | 2 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 |
| 班戈错 Bangkog Co | 1 | - | - | - | 0.00 |
| 其香错 Kyêbxang Co | 12 | 3.61 | 0.57 | 1.04 | 2.05 |
| 岗塘错 Gangtang Co | 3 | 5.20 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 1.25 |
| 依布茶卡 Yibug Caka | 1 | 0.00 | - | - | 0.00 |
Table 2 Biodiversity indices of free-living nematode communities of plateau salt lakes in Nagqu City, Tibet
| 湖泊 Lakes | 物种数 No. of species (S) | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (d) | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (J') | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index (1 - λ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 崩则错 Pongcê Co | 2 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 0.59 | 0.81 |
| 查下不错 Chaxiabu Co | 2 | - | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.92 |
| 果根错 Gogen Co | 3 | 0.79 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.53 |
| 瀑赛尔错 Bobsêr Co | 4 | 2.10 | 0.73 | 0.35 | 1.45 |
| 郭加林错 Guojialun Co | 2 | 2.60 | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.92 |
| 达则错 Dagze Co | 3 | 5.20 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 1.25 |
| 羊纳朋错 Yangnapeng Co | 2 | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 |
| 班戈错 Bangkog Co | 1 | - | - | - | 0.00 |
| 其香错 Kyêbxang Co | 12 | 3.61 | 0.57 | 1.04 | 2.05 |
| 岗塘错 Gangtang Co | 3 | 5.20 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 1.25 |
| 依布茶卡 Yibug Caka | 1 | 0.00 | - | - | 0.00 |
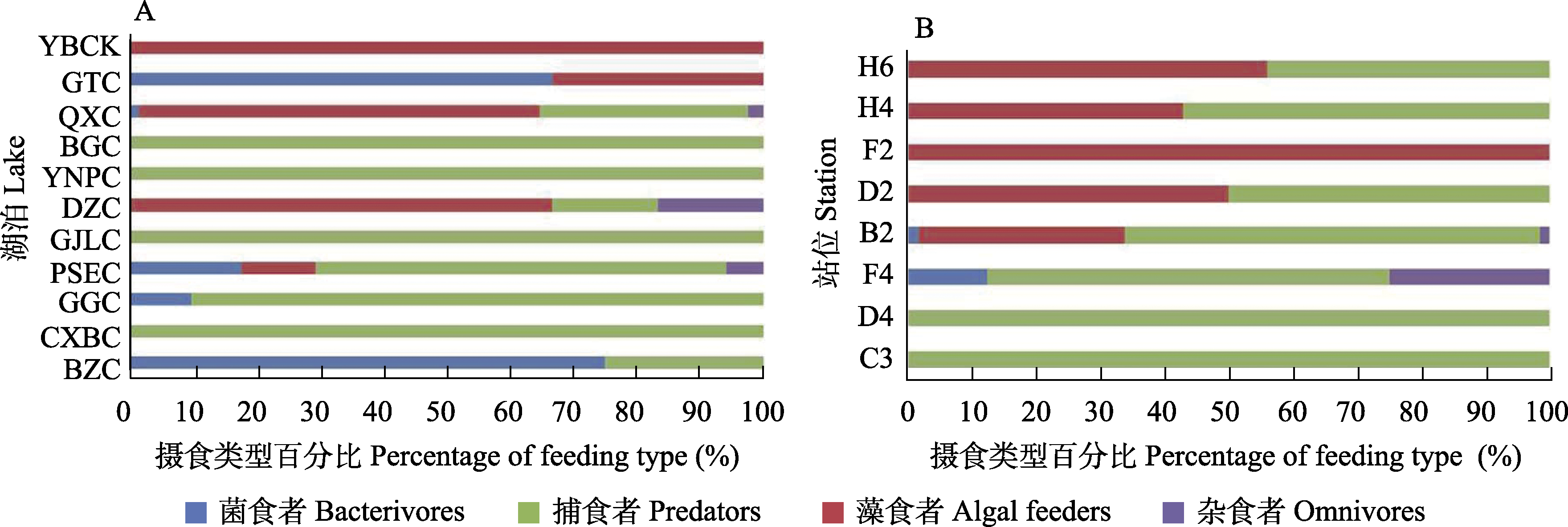
Fig. 5 Percentage of four feeding types of free-living nematodes of all salt lakes (A) and Kyêbxang Co (B) in Nagqu City, Tibet. Abbreviation meanings are shown in Table 1.
| [1] | An BS, Cheng GD (2014) Dynamic analysis of the ecological footprint and carrying capacity of Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 1002-1009. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [安宝晟, 程国栋 (2014) 西藏生态足迹与承载力动态分析. 生态学报, 34, 1002-1009.] | |
| [2] | Bassler-Veit B, Barut IF, Meric E, Avsar N, Nazik A, Kapan-Yeşilyurt S, Yildiz A (2013) Distribution of microflora, meiofauna, and macrofauna assemblages in the hypersaline environment of Northeastern Aegean Sea coasts. Journal of Coastal Research, 29, 883-898. |
| [3] |
Bianchelli S, Pusceddu A, Buschi E, Danovaro R (2016) Trophic status and meiofauna biodiversity in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Insights for the assessment of good environmental status. Marine Environmental Research, 113, 18-30.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Brock MA, Hammer UT (1987) Saline lake ecosystems of the world. Journal of Ecology, 75, 580-580.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Chen LJ, Yang F, Wu SX, Liu XF, Jia QX (2013) Characteristics of community structures of phytoplankton in the salt lakes in Naqu region, Tibet. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 22, 577-585. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈立婧, 杨菲, 吴淑贤, 刘喜方, 贾沁贤 (2013) 西藏那曲地区盐湖浮游植物群落结构的特征. 上海海洋大学学报, 22, 577-585.] | |
| [6] | Dai YZ, Tang SY, Zhang JB (2000) The distribution of zoobenthos species and bio-assessment of water quality in Dongting Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20, 277-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴友芝, 唐受印, 张建波 (2000) 洞庭湖底栖动物种类分布及水质生物学评价. 生态学报, 20, 277-282.] | |
| [7] |
Hakenkamp CC, Morin A (2000) The importance of meiofauna to lotic ecosystem functioning. Freshwater Biology, 44, 165-175.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Higgins RP, Thiel H (1988) Introduction to the Study of Meiofauna. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington. |
| [9] | Hua E, Cui CY, Xu HL, Liu XS (2020) Study on the community characteristics of marine nematodes in Futian Mangrove Reserve, Shenzhen. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 50(9), 46-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [华尔, 崔春燕, 徐华林, 刘晓收 (2020) 深圳福田红树林保护区自由生活海洋线虫群落特征研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 50(9), 46-63.] | |
| [10] | Huo YZ, Zhao W, Zhang YS, Zheng MP, Jia QX, Wang HL, Lü GJ (2005) Plankton community diversity of saline lakes in Xilinguole, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Lake Sciences, 17, 243-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [霍元子, 赵文, 张永生, 郑绵平, 贾沁贤, 王海雷, 吕光俊 (2005) 内蒙古锡林郭勒盟盐湖浮游生物的群落特征. 湖泊科学, 17, 243-250.] | |
| [11] |
Immerzeel WW, van Beek LPH, Bierkens MFP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science, 328, 1382-1385.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Jesús-Navarrete A, Legorreta TÁ (2022) Biological traits analysis of free-living nematodes as indicators of environmental quality at Lake Bacalar, Mexico. Limnology, 23, 355-364.
DOI |
| [13] | Jia QX, Liu XF, Wang HP, Liu SS, Luo YH, Chen LJ, Zheng MP (2017) Bio-ecological resources of saline lakes in Tibet and their economic prospect. Science & Technology Review, 35(12), 19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾沁贤, 刘喜方, 王洪平, 刘沙沙, 罗玉虎, 陈立婧, 郑绵平 (2017) 西藏盐湖生物与生态资源及其开发利用. 科技导报, 35(12), 19-26.] | |
| [14] | La B, Bian D, Dunyu DJ, Yang M, Zhang WH, Baima RZ (2021) Change of Qixiangco Lake area and its reasons in Nagqu City from 1988 to 2018. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 37(5), 72-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [拉巴, 边多, 顿玉多吉, 央美, 张伟华, 白玛仁增 (2021) 1988-2018年那曲市其香错水域面积变化及原因分析. 气象与环境学报, 37(5), 72-77.] | |
| [15] | Li JJ, Huang Y (2009) Studies on the meiofauna community in Weishan Lake. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 22(4), 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李金金, 黄勇 (2009) 微山湖小型底栖生物群落结构的初步研究. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 22(4), 51-54.] | |
| [16] | Mao SQ, Lin X, Luo Y, Zhu YF, Yan XJ (2016) Community structure of meiofauna and its correlation with environmental factors in Xiangshan Bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 1442-1452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毛硕乾, 林霞, 罗杨, 朱艺峰, 严小军 (2016) 象山港小型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的相关性. 生态学报, 36, 1442-1452.] | |
| [17] |
Marco C, Angela B, Paola GDM, Tiziana DL (2021) An overview of studies on meiofaunal traits of the littoral zone of lakes. Water, 13, 473-473.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Margalef DR (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systematics, 3, 36-71. |
| [19] | Mu FH, Zhang T, Li J, Hua E (2020) Spatiotemporal distribution of meiofauna and its influencing factors at the Dadeji Beach, Xiamen. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 50(9), 34-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [慕芳红, 张婷, 李佳, 华尔 (2020) 厦门大德记沙滩小型底栖动物的时空分布及影响因素. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 50(9), 34-45.] | |
| [20] |
Pandiya-rajan RS, Anitha G, Ramu K, Ranga-Rao V, Ramanamurthy MV (2022) Influence of salinity on the meiofaunal distribution in a hypersaline lake along the southeast coast of India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194, 1-12.
DOI |
| [21] | Pielou EC (1977) Mathematical Ecology. John Wiley and Sons, New York. |
| [22] |
Ristau K, Spann N, Traunspurger W (2015) Species and trait compositions of freshwater nematodes as indicative descriptors of lake eutrophication. Ecological Indicators, 53, 196-205.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Schratzberger M, Somerfield PJ (2020) Effects of widespread human disturbances in the marine environment suggest a new agenda for meiofauna research is needed. Science of the Total Environment, 728, 138435.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois. |
| [25] | Shen JR, Song DX (1963) Notes on copepoda collected from Shigatze and Fyangtse regions in Tibet, China. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 15, 79-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈嘉瑞, 宋大祥 (1963) 中国西藏日喀则和江孜地区桡足类的研究. 动物学报, 15, 79-97.] | |
| [26] | Shen JR, Song DX (1964) A preliminary study of cladocera from Tibet, China. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 16, 61-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈嘉瑞, 宋大祥 (1964) 西藏枝角类的初步研究. 动物学报, 16, 61-69.] | |
| [27] | Shen JR, Song DX (1965) The planktonic crustaceans of northwestern Tibet. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 17, 298-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈嘉瑞, 宋大祥 (1965) 西藏西北部的浮游甲壳动物. 动物学报, 17, 298-308.] | |
| [28] |
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688.
DOI |
| [29] | Sinh NV, Phuong N, Quang NX (2014) The distribution of meiofauna community related to salinity gradient in the Ham Luong estuary, Mekong River. Tap Chi Sinh Hoc, 35, 417-423. |
| [30] |
Takashi ITO (1959) The Venice system for the classification of marine waters according to salinity: Symposium on the classification of brackish waters, Venice, 8-14 April 1958. Japanese Journal of Limnology (Rikusuigaku Zasshi), 20, 119-120.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Tan WJ, Zeng JL, Li CL, Rao YY, Chen XW, Cai LZ (2017) Characteristic analysis of benthic meiofauna communites in Futian mangrove area of the Shenzhen Bay. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science Edition), 56, 859-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭文娟, 曾佳丽, 李晨岚, 饶义勇, 陈昕韡, 蔡立哲 (2017) 深圳湾福田红树林区小型底栖动物群落特征分析. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 56, 859-865.] | |
| [32] |
Tom M, Magda V (1997) Observations on the feeding ecology of estuarine nematodes. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 77, 211-227.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Urban-Malinga B, Hedtkamp SIC, Beusekom JEEV, Wiktor J, Węsławski JM (2006) Comparison of nematode communities in Baltic and North Sea sublittoral, permeable sandsDiversity and environmental control. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 70, 224-238.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Williams WD (1981) Inland salt lakes: An introduction. Hydrobiologia, 81, 1-14. |
| [35] |
Williams WD (1991) Chinese and Mongolian saline lakes: A limnological overview. Hydrobiologia, 210, 39-66.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Wu JH, Liang YL (1999) A comparative study of benthic nematodes in two Chinese lakes with contrasting sources of primary production. Hydrobiologia, 411, 31-37.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Xiao H (2020) Current situation and control measure tourism pollution control in Chaka salt lakes. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (4), 72-73, 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖慧 (2020) 茶卡盐湖旅游污染治理现状及防治对策. 绿色科技, (4), 72-73, 76.] | |
| [38] |
Xu MQ, Cao H, Jia QX, Gao YR, Chen SG (2002) Preliminary study of plankton community diversity of the Gahai Salt Lake in the Qaidam Basin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 10, 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[许木启, 曹宏, 贾沁贤, 高玉荣, 陈声贵 (2002) 青藏高原柴达木盆地尕海盐湖浮游生物群落多样性特征的初步研究. 生物多样性, 10, 38-43.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Yan FG, Wang HJ, Wang HZ, Zhang TL, Li W (2010) Community characteristics of meiofauna in an algae-dominated shallow lake, with a discussion on the ecological role. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 34, 634-638. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫福桂, 王海军, 王洪铸, 张堂林, 李为 (2010) 藻型浅水湖泊小型底栖动物的群落特征及生态地位探讨. 水生生物学报, 34, 634-638.] | |
| [40] | Yang KH, Yao FF, Dong D, Dong W, Luo JC (2017) Spatiotemporal monitoring of lake area dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 19, 972-982. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[杨珂含, 姚方方, 董迪, 董文, 骆剑承 (2017) 青藏高原湖泊面积动态监测. 地球信息科学学报, 19, 972-982.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Yang SX (1989) The origin and distribution of salt lakes in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Journal of Lake Sciences, (1), 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨绍修 (1989) 青藏高原盐湖的形成与分布. 湖泊科学, (1), 28-36.] | |
| [42] |
Yeates GW, Bongers T, de Goede RG, Freckman DW, Georgieva SS (1993) Feeding habits in soil nematode families and generaAn outline for soil ecologists. Journal of Nematology, 25, 315-331.
PMID |
| [43] |
Zhang GQ, Luo W, Chen WF, Zheng GX (2019) A robust but variable lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Science Bulletin, 64, 1306-1309.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Zhang ZN, Qian GZ (1990) A study on sampling methods for meiofauna. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (4), 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张志南, 钱国珍 (1990) 小型底栖生物取样方法的研究. 海洋湖沼通报, (4), 37-42.] | |
| [45] | Zhang ZN, Zhou H, Hua E, Mu FH, Liu XS, Yu ZS (2017) Meiofauna study for the forty years in China—Progress and prospect. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 48, 657-671. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张志南, 周红, 华尔, 慕芳红, 刘晓收, 于子山 (2017) 中国小型底栖生物研究的40年——进展与展望. 海洋与湖沼, 48, 657-671.] | |
| [46] | Zhao MH, Liu XS (2021) Taxa composition and distribution patterns of meiofauna in the intertidal zones of Shandong Peninsula. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 34(5), 100-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵美红, 刘晓收 (2021) 山东半岛沿岸潮间带小型底栖动物类群组成与分布格局. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 34(5), 100-110.] | |
| [47] | Zheng MP, Qi W (2006) Saline resources and its development in China. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, (5), 45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑绵平, 齐文 (2006) 我国盐湖资源及其开发利用. 矿产保护与利用, (5), 45-50.] | |
| [48] | Zheng XY (1988) Tibetan Salt Lakes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑喜玉 (1988) 西藏盐湖. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn