



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1291-1297. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019255 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019255
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jian Zhang,Lu Dong,Yanyun Zhang( )
)
Received:2019-08-16
Accepted:2019-11-20
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-01-14
Contact:
Zhang Yanyun
Jian Zhang, Lu Dong, Yanyun Zhang. Population genetic structure of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) from Inexpressible Island, Antarctica, using SNP markers[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1291-1297.
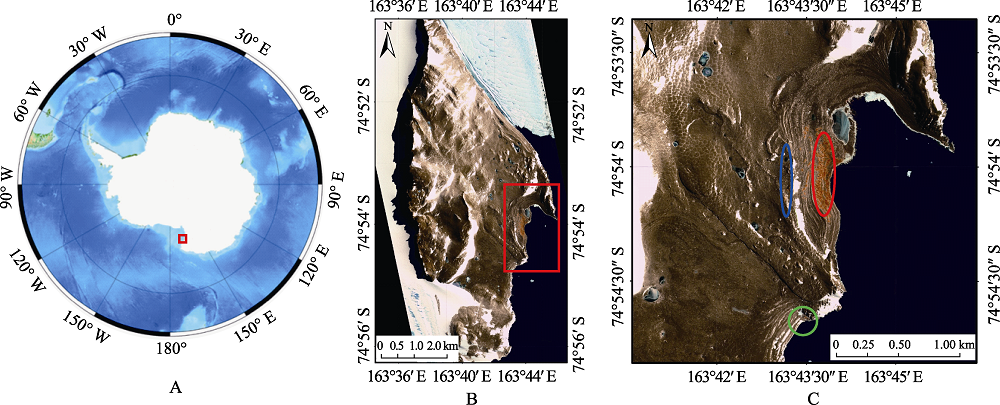
Fig. 1 Sampling sites of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) in Inexpressible Island. (A) Map of Antarctic (Red rectangle: Inexpressible Island). (B) Map of Inexpressible Island (Red rectangle: the proposed Antarctic Specially Protected Area). (C) Sampling areas in Inexpressible Island. Blue circle, high altitude area in Seaview Bay; red circle, low altitude area in Seaview Bay; green circle, South Bay.
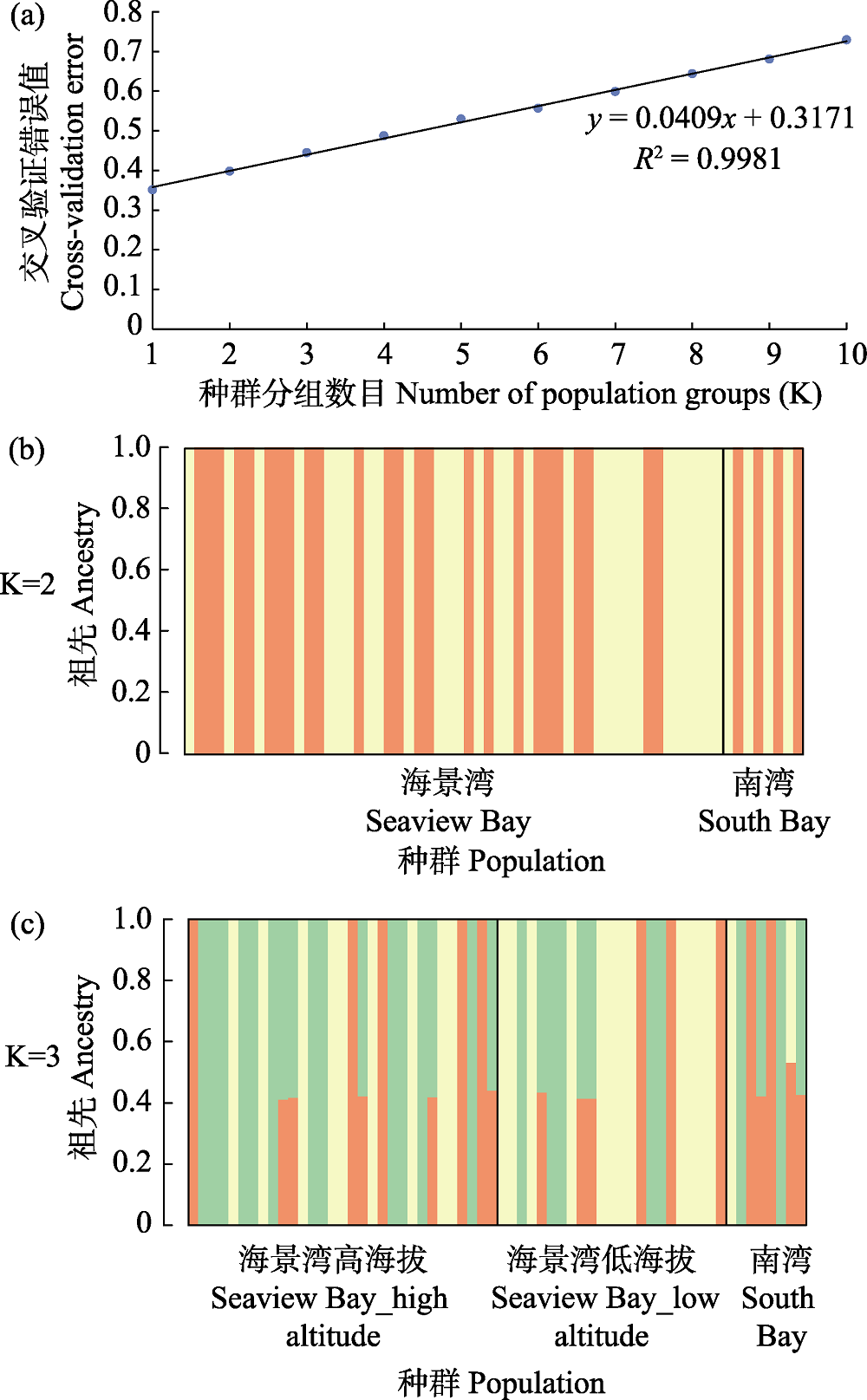
Fig. 2 Based on 110,451 SNPs, the population genetic structure of Adélie penguins was constructed by maximum likelihood method. (a) Distribution of cross-validation errors; (b) K = 2 and (c) K = 3, each vertical bar represents an individual, and the colours show the proportion of ancestry assigned to each of the clusters.
| [1] | Ainley DG, LeResche RE, Sladen WJL ( 1983) Breeding Biology of the Adélie Penguin. University of California Press, Oakland. |
| [2] | Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K ( 2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Research, 19, 1655-1664. |
| [3] | Baroni C, Hall BL ( 2004) A new Holocene relative sea-level curve for Terra Nova Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Journal of Quaternary Science, 19, 377-396. |
| [4] | Baroni C, Orombelli G ( 1991) Holocene raised beaches at Terra Nova Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Quaternary Research, 36, 157-177. |
| [5] | Borowicz A, McDowall P, Youngflesh C, Sayre-McCord T, Clucas G, Herman R, Forrest S, Rider M, Schwaller M, Hart T, Jenouvrier S, Polito MJ, Singh H, Lynch HJ ( 2018) Multi-modal survey of Adélie penguin mega-colonies reveals the Danger Islands as a seabird hotspot. Scientific Reports, 8, 9. |
| [6] | Bromwich DH, Kurtz DD ( 1984) Katabatic wind forcing of the Terra Nova Bay polynya. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 89, 3561-3572. |
| [7] | Clucas GV, Younger JL, Kao D, Emmerson L, Southwell C, Wienecke B, Rogers AD, Bost CA, Miller GD, Polito MJ, Lelliott P, Handley J, Crofts S, Phillips RA, Dunn MJ, Miller KJ, Hart T ( 2018) Comparative population genomics reveals key barriers to dispersal in Southern Ocean penguins. Molecular Ecology, 27, 4680-4697. |
| [8] | Clucas GV, Younger JL, Kao D, Rogers AD, Handley J, Miller GD, Jouventin P, Nolan P, Gharbi K, Miller KJ, Hart T ( 2016) Dispersal in the sub-Antarctic: King penguins show remarkably little population genetic differentiation across their range. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 16, 211. |
| [9] | Croxall JP, Prince PA ( 1979) Antarctic seabird and seal monitoring studies. Polar Record, 19, 573-595. |
| [10] | Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST ( 2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics, 27, 2156-2158. |
| [11] | Emslie SD, Coats L, Licht K ( 2007) A 45,000 yr record of Adélie penguins and climate change in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Geology, 35, 61-64. |
| [12] | Freed D, Aldana R, Weber JA, Edwards JS ( 2017) The Sentieon Genomics Tools—A fast and accurate solution to variant calling from next-generation sequence data. bioRxiv, 115717. |
| [13] | Funk WC, McKay JK, Hohenlohe PA, Allendorf FW ( 2012) Harnessing genomics for delineating conservation units. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27, 489-496. |
| [14] | Gorman KB, Talbot SL, Sonsthagen SA, Sage GK, Gravely MC, Fraser WR, Williams TD ( 2017) Population genetic structure and gene flow of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) breeding throughout the western Antarctic Peninsula. Antarctic Science, 29, 499-510. |
| [15] | Li H, Durbin R ( 2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics, 26, 589-595. |
| [16] | Lischer HEL, Excoffier L ( 2012) PGDSpider: An automated data conversion tool for connecting population genetics and genomics programs. Bioinformatics, 28, 298-299. |
| [17] | Lorenzini S, Baroni C, Fallick AE, Baneschi I, Salvatore MC, Zanchetta G, Dallai L ( 2010) Stable isotopes reveal Holocene changes in the diet of Adélie penguins in Northern Victoria Land (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Oecologia, 164, 911-919. |
| [18] | Lynch HJ, LaRue MA ( 2016) First global census of the Adélie penguin. Auk, 133, 236. |
| [19] | Lyver POB, Barron M, Barton KJ, Ainley DG, Pollard A, Gordon S, McNeill S, Ballard G, Wilson PR ( 2014) Trends in the breeding population of Adélie penguins in the Ross Sea, 1981-2012: A coincidence of climate and resource extraction effects. PLoS ONE, 9, e91188. |
| [20] | Manel S, Schwartz MK, Luikart G, Taberlet P ( 2003) Landscape genetics: Combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 189-197. |
| [21] | Nielsen R, Paul JS, Albrechtsen A, Song Y ( 2011) Genotype and SNP calling from next-generation sequencing data. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 443-451. |
| [22] | Palsboll PJ, Berube M, Allendorf FW ( 2007) Identification of management units using population genetic data. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22, 11-16. |
| [23] | Peakall R, Smouse PE ( 2012) GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics, 28, 2537-2539. |
| [24] | Raj A, Stephens M, Pritchard JK ( 2014) fastSTRUCTURE: Variational inference of population structure in large SNP data sets. Genetics, 197, 573-589. |
| [25] | Ritchie PA, Millar CD, Gibb GC, Baroni C, Lambert DM ( 2004) Ancient DNA enables timing of the Pleistocene origin and Holocene expansion of two Adélie penguin lineages in Antarctica. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 21, 240-248. |
| [26] | Shepherd LD, Millar CD, Ballard G, Ainley DG, Wilson PR, Haynes GD, Baroni C, Lambert DM ( 2005) Microevolution and mega-icebergs in the Antarctic. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 16717-16722. |
| [27] | Stonehouse B ( 1969) Air census of two colonies of Adélie penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) in Ross Dependency, Antarctica. Polar Record, 14, 471-475. |
| [28] | Walther GR, Post E, Convey P, Menzel A, Parmesan C, Beebee TJC, Fromentin JM, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Bairlein F ( 2002) Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature, 416, 389-395. |
| [29] | Woehler EJ, Croxall JP ( 1997) The status and trends of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic seabirds. Marine Ornithology, 25, 43-66. |
| [30] | Younger JL, Clucas GV, Kao D, Rogers AD, Gharbi K, Hart T, Miller KJ ( 2017) The challenges of detecting subtle population structure and its importance for the conservation of emperor penguins. Molecular Ecology, 26, 3883-3897. |
| [31] | Zhang C, Dong SS, Xu JY, He WM, Yang TL ( 2019) PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics, 35, 1786-1788. |
| [32] | Zhang G, Li C, Li Q, Li B, Larkin DM, Lee C, Storz JF, Antunes A, Greenwold MJ, Meredith RW ( 2014) Comparative genomics reveals insights into avian genome evolution and adaptation. Science, 346, 1311-1320. |
| [33] | Zheng XW, Levine D, Shen J, Gogarten SM, Laurie C, Weir BS ( 2012) A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics, 28, 3326-3328. |
| [1] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [2] | Xiangxiang Chen, Zhongshuai Gai, Juntuan Zhai, Jindong Xu, Peipei Jiao, Zhihua Wu, Zhijun Li. Genetic diversity and construction of core conservation units of the natural populations of Populus euphratica in Northwest China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1638-1649. |
| [3] | Erhuan Wu, Donghai Li, Xiaobo Yang, Yongling Zuo, Long Li, Peichun Zhang, Lin Chen, Lujia Tian, Chendi Li. Population structure of Cycas hainanensis and its relationship with forest canopy density [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1461-1469. |
| [4] | Denggao Xiang, Yuefei Li, Xinhui Li, Weitao Chen, Xiuhui Ma. Population structure and genetic diversity of Culter recurviceps revealed by multi-loci [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| [5] | Xiao Huang,Jiang Zhu,Lan Yao,Xunru Ai,Jin Wang,Manling Wu,Qiang Zhu,Shaolin Chen. Structure and spatial distribution pattern of a native Metasequoia glyptostroboides population in Hubei [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(4): 463-473. |
| [6] | Om Prakash Tripathi, Khongjee Rangdajied Reynald. Effect of forest fragment size on tree diversity and population structure of humid subtropical forest of Meghalaya, India [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(2): 208-214. |
| [7] | Hongtuo Fu, Hui Qiao, Jianhua Yao, Yongsheng Gong, Yan Wu, Sufei Jiang, Yiwei Xiong. Genetic diversity in five Macrobrachium hainanense populations using SRAP markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(2): 145-149. |
| [8] | Hua Tian, Ming Kang, Li Li, Xiaohong Yao, Hongwen Huang. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Castanea mollissima inferred from nuclear SSR markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 296-302. |
| [9] | Yinghui Ling, Yuejiao Cheng, Yanping Wang, Weijun Guan, Jianlin Han, Baoling Fu, Qianjun Zhao, Xiaohong He, Yabin Pu, Yuehui Ma. Genetic diversity of 23 Chinese indigenous horse breeds revealed by microsatellite markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 240-247. |
| [10] | Shixun Huang, Hong Chen, Wenxiu Tang, Wenhua Luo, Yan Wang. Biological and ecological characteristics ofHopea chinensis, a plant endemic to Guangxi [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(1): 15-23. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()