



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 608-614. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017039 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017039
Special Issue: 传粉生物学; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yukun Wei*( ), Yanbo Huang, Guibin Li
), Yanbo Huang, Guibin Li
Received:2017-05-27
Accepted:2017-06-21
Online:2017-06-20
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Wei Yukun
Yukun Wei, Yanbo Huang, Guibin Li. Reproductive isolation in sympatric Salvia species sharing a sole pollinator[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(6): 608-614.
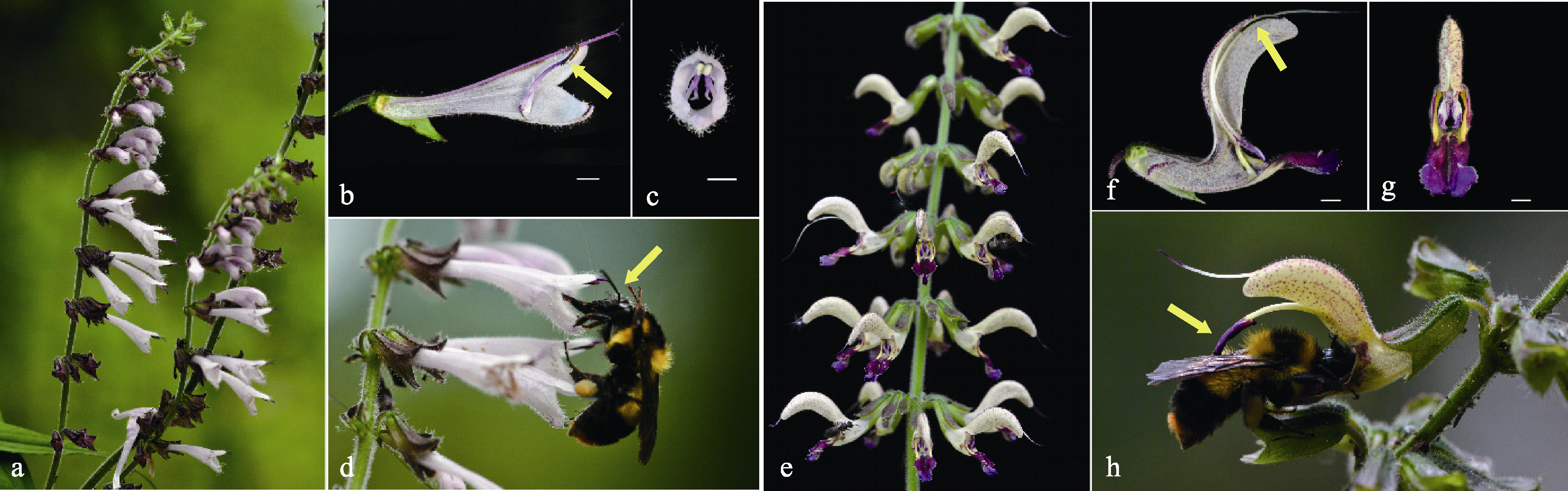

Fig. 1 Comparison of inflorescences, flower structures, and insect pollinations of Salvia liguliloba and S. bowleyana (Bar = 2 mm). (a) Inflorescences of S. liguliloba; (b) Flower lateral dissection of S. liguliloba (the arrow indicates anther); (c) A front view of S. liguliloba flower; (d) Bombus trifasciatus is visiting flowers and pollinating S. liguliloba (the arrow indicates pollen placement sites on bumblebee); (e) Inflorescences of S. bowleyana; (f) Flower lateral dissection of S. bowleyana (the arrow indicates anther); (g) A front view of S. bowleyana flower; (h) Bombus trifasciatus is visiting flowers and pollinating S. bowleyana (the arrow indicates pollen placement sites on bumblebee).
| 花冠长 Corolla length | 花冠宽 Corolla width | 花冠高 Corolla height | 冠筒长 Tube length | 冠口高 Entrance height | 冠筒口高 Tube entrance height | 冠筒口宽 Tube entrance width | 花丝长 Filament length | 药隔长 Connective length | 雌蕊长 Pistil length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 23.7 ± 0.74a | 5.31 ± 0.34a | 7.30 ± 0.67b | 19.5 ± 0.8a | 4.87 ± 0.61b | 4.87 ± 0.61a | 4.41 ± 0.52a | 2.39 ± 0.14b | 5.19 ± 0.33b | 23.7 ± 0.43b |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 22.8 ± 1.10b | 4.47 ± 0.26b | 16.6 ± 0.94a | 12.4 ± 0.76b | 11.2 ± 0.80a | 4.47 ± 0.28a | 3.21 ± 0.23b | 4.30 ± 0.26a | 14.3 ± 0.68a | 26.1 ± 1.85a |
| P | 0.0407 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0585 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0011 |
Table 1 Comparison of flower structures between Salvia liguliloba and S. bowleyana (mean ± SD)
| 花冠长 Corolla length | 花冠宽 Corolla width | 花冠高 Corolla height | 冠筒长 Tube length | 冠口高 Entrance height | 冠筒口高 Tube entrance height | 冠筒口宽 Tube entrance width | 花丝长 Filament length | 药隔长 Connective length | 雌蕊长 Pistil length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 23.7 ± 0.74a | 5.31 ± 0.34a | 7.30 ± 0.67b | 19.5 ± 0.8a | 4.87 ± 0.61b | 4.87 ± 0.61a | 4.41 ± 0.52a | 2.39 ± 0.14b | 5.19 ± 0.33b | 23.7 ± 0.43b |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 22.8 ± 1.10b | 4.47 ± 0.26b | 16.6 ± 0.94a | 12.4 ± 0.76b | 11.2 ± 0.80a | 4.47 ± 0.28a | 3.21 ± 0.23b | 4.30 ± 0.26a | 14.3 ± 0.68a | 26.1 ± 1.85a |
| P | 0.0407 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0585 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0011 |
| 单株花序总数 No. of infloresce- nce in individual plant | 假圆锥花序 分枝数 No. of branch in a false panicle | 假总状花序的 轮伞花序数 No. of verticillaster in a false raceme | 轮伞花序小 花总数 No. of flower in a verticillaster | 轮伞花序同时 开放小花数 No. of flowering in a verticillaster | 单株总花数 Total no. of flower in individual plant | 单株总开花数 Total no. of flowering in individual plant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 2.0±2.1a (n = 35) | 2.0±1.9b (n = 39) | 9.3±2.4a (n = 83) | 5.6±1.1b (n = 93) | 1.4±1.7b (n = 234) | 262±299b (n = 26) | 21±30a (n = 36) |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 2.2±0.45a (n = 5) | 5.8±3.0a (n = 11) | 9.5±1.9a (n = 40) | 9.8±1.9a (n = 160) | 1.8±1.0a (n = 160) | 891±472a (n = 5) | 48±56a (n = 16) |
| P | 0.681 | 0.0020 | 0.7166 | 0.000 | 0.0053 | 0.0005 | 0.089 |
Table 2 Comparisons of flowering and inflorescence between Salvia liguliloba and S. bowleyana (mean ± SD)
| 单株花序总数 No. of infloresce- nce in individual plant | 假圆锥花序 分枝数 No. of branch in a false panicle | 假总状花序的 轮伞花序数 No. of verticillaster in a false raceme | 轮伞花序小 花总数 No. of flower in a verticillaster | 轮伞花序同时 开放小花数 No. of flowering in a verticillaster | 单株总花数 Total no. of flower in individual plant | 单株总开花数 Total no. of flowering in individual plant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 2.0±2.1a (n = 35) | 2.0±1.9b (n = 39) | 9.3±2.4a (n = 83) | 5.6±1.1b (n = 93) | 1.4±1.7b (n = 234) | 262±299b (n = 26) | 21±30a (n = 36) |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 2.2±0.45a (n = 5) | 5.8±3.0a (n = 11) | 9.5±1.9a (n = 40) | 9.8±1.9a (n = 160) | 1.8±1.0a (n = 160) | 891±472a (n = 5) | 48±56a (n = 16) |
| P | 0.681 | 0.0020 | 0.7166 | 0.000 | 0.0053 | 0.0005 | 0.089 |
| 相对频次 Relative frequency | 单花访问时间 Visit time per flower (s) | 活跃度 Activity rate | 访花频率 Visitation rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 0.14 ± 0.017 b (n = 3) | 2.01 ± 0.85 a (n = 30) | 9.71 ± 3.15 b (n = 7) | 1.36 ± 0.17 b (n = 3) |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 0.86 ± 0.017 a (n = 3) | 1.80 ± 0.63 a (n = 30) | 16.2 ± 3.4 a (n = 52) | 13.9 ± 0.28 a (n = 3) |
| P | 0.000 | 0.2758 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Table 3 Comparisons of flower visiting behavior of Bombus trifasciatus between Salvia liguliloba and S. bowleyana (mean ± SD)
| 相对频次 Relative frequency | 单花访问时间 Visit time per flower (s) | 活跃度 Activity rate | 访花频率 Visitation rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 舌瓣鼠尾草 S. liguliloba | 0.14 ± 0.017 b (n = 3) | 2.01 ± 0.85 a (n = 30) | 9.71 ± 3.15 b (n = 7) | 1.36 ± 0.17 b (n = 3) |
| 南丹参 S. bowleyana | 0.86 ± 0.017 a (n = 3) | 1.80 ± 0.63 a (n = 30) | 16.2 ± 3.4 a (n = 52) | 13.9 ± 0.28 a (n = 3) |
| P | 0.000 | 0.2758 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
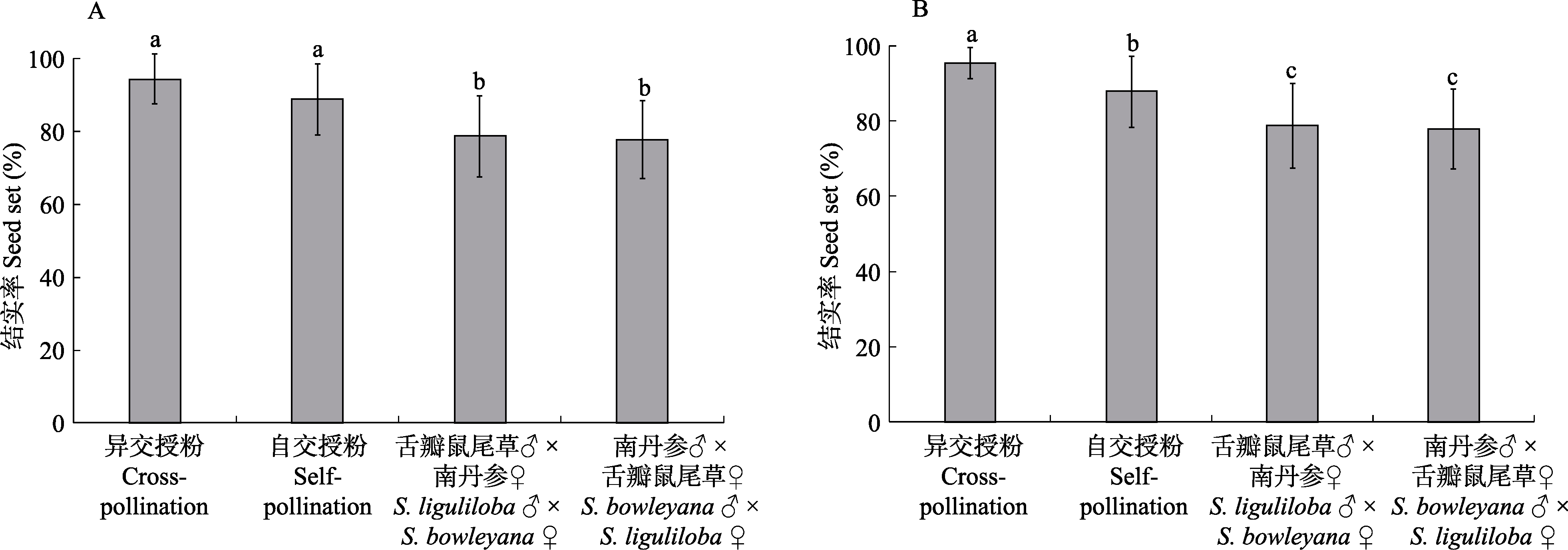
Fig. 2 Comparisons of cross-pollination, self-pollination, and hybridization of Salvia liguliloba and S. bowleyana. (A) and (B) show S. liguliloba and S. bowleyana, respectively. Different letters indicate significant difference at the level of P < 0.05 by t-test.
| [1] | Baack E, Melo MC, Rieseberg LH, Ortiz-Barrientos D (2015) The origins of reproductive isolation in plants. New Phytologist, 207, 968-984. |
| [2] | Claßen-Bockhoff R, Speck T, Tweraser E, Wester P, Thimm S, Reith M (2004) The staminal lever mechanism in Salvia L. (Lamiaceae): a key innovation for adaptive radiation? Organisms Diversity & Evolution, 4, 189-205. |
| [3] | Claßen-Bockhoff R, Wester P, Tweraser E (2003) The staminal lever mechanism in Salvia L. (Lamiaceae): a review. Plant Biology, 5, 33-41. |
| [4] | Epling C (1947) Natural hybridization of Salvia apiana and S. mellifera. Evolution, 1, 69-78. |
| [5] | Hopkins R (2013) Reinforcement in plants. New Phytologist, 197, 1095-1103. |
| [6] | Huang S, Shi X (2013) Floral isolation in Pedicularis: how do congeners with shared pollinators minimize reproductive interference? New Phytologist, 199, 858-865. |
| [7] | Huang YB, Wei YK, Ge BJ, Wang Q (2014) Research progress in pollination biology of genus Salvia (Lamiaceae) and their pollination mechanisms in East Asia (China). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 2282-2289. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄艳波, 魏宇昆, 葛斌杰, 王琦 (2014) 鼠尾草属东亚分支的传粉模式. 生态学报, 34, 2282-2289.] | |
| [8] | Huang YB, Wei YK, Wang Q, Xiao YE, Ye XY (2015) Floral morphology and pollination mechanism of Salvia liguliloba, a narrow endemic species with degraded lever-like stamens. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 753-761. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄艳波, 魏宇昆, 王琦, 肖月娥, 叶喜阳 (2015) 舌瓣鼠尾草退化杠杆雄蕊的相关花部特征及传粉机制. 植物生态学报, 39, 753-761.] | |
| [9] | Huang Z, Liu H, Huang S (2015) Interspecific pollen transfer between two coflowering species was minimized by bumblebee fidelity and differential pollen placement on the bumblebee body. Journal of Plant Ecology, 8, 109-115. |
| [10] | Kipling R, Warren J (2013) How generalists coexist: the role of floral phenotype and spatial factors in the pollination systems of two Ranunculus species. Journal of Plant Ecology, 7, 480-489. |
| [11] | Ma YP, Xie WJ, Sun WB, Marczewski T (2016a) Strong reproductive isolation despite occasional hybridization between a widely distributed and a narrow endemic Rhododendron species. Scientific Reports, 6, 19146. |
| [12] | Ma YP, Zhou RC, Milne R (2016b) Pollinator-mediated isolation may be an underestimated factor in promoting homoploid hybrid speciation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1183. |
| [13] | Melo MC, Grealy A, Brittain B, Walter GM, Ortiz-Barrientos D (2014) Strong extrinsic reproductive isolation between parapatric populations of an Australian groundsel. New Phytologist, 203, 323-334. |
| [14] | Meyn O, Emboden WA (1987) Parameters and consequences of introgression in Salvia apiana × S. mellifera (Lamiaceae). Systematic Botany, 12, 390-399. |
| [15] | Pauw A (2013) Can pollination niches facilitate plant coexistence? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 30-37. |
| [16] | Pedron M, Buzatto CR, Singer RB, Batista JAN, Moser A (2012) Pollination biology of four sympatric species of Habenaria (Orchidaceae: Orchidinae) from southern Brazil. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 170, 141-156. |
| [17] | Ruchisansakun S, Tangtorwongsakul P, Cozien RJ, Smets EF, Niet TVD (2016) Floral specialization for different pollinators and divergent use of the same pollinator among co-occuring Impatiens species (Balsaminaceae) from Southeast Asia. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 181, 651-666. |
| [18] | Wei YK, Wang Q, Huang YB (2015) Species diversity and distribution of Salvia (Lamiaceae). Biodiversity Science, 23, 3-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏宇昆, 王琦, 黄艳波 (2015) 唇形科鼠尾草属的物种多样性与分布. 生物多样性, 23, 3-10.] | |
| [19] | Wester P, Claßen-Bockhoff R (2007) Floral diversity and pollen transfer mechanisms in bird-pollinated Salvia species. Annals of Botany, 100, 401-421. |
| [20] | Widmer A, Lexer C, Cozzolino S (2009) Evolution of reproductive isolation in plants. Heredity, 102, 31-38. |
| [21] | Yang FC (1992) Comprehensive Investigation Report on Natural Resource of Tianmu Mountain Nature Reserve. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [杨逢春 (1992) 天目山自然保护区自然资源综合考察报告. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [10] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [11] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [12] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [13] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [14] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [15] | Hui Ran, Tianyou Yang, Xiaoqi Mi. The updated checklist of reptiles in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23348-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn