



Biodiv Sci ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 389-398. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015243 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015243
Special Issue: 中国西南干旱河谷的植物多样性; 生物入侵
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue Xu1, Peng Li1, Ye Liu2, Wanjun Zhang3, Siyu Qin4, Zehao Shen1,*( )
)
Received:2015-09-14
Accepted:2015-09-14
Online:2016-04-20
Published:2016-05-11
Contact:
Shen Zehao
Yue Xu, Peng Li, Ye Liu, Wanjun Zhang, Siyu Qin, Zehao Shen. Spatial patterns and determinants of species richness of alien and native plants in the Nujiang River valley[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(4): 389-398.
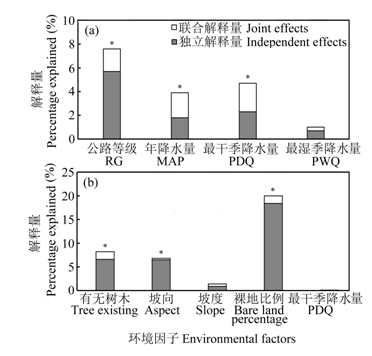
Fig. 3 Independent and joint contributions of environmental variables accounting for the spatial pattern of invasive and native species richness in Nujiang River valley, based on hierarchical variation partitioning model. * indicates that influence is significant at the 0.05 level. RG, Road grade; MAP, Mean annual precipitation; PDQ, Precipitation of driest quarter; PWQ, Precipitation of wettest quarter.
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第一主成分 PCA1 | 第二主成分 PCA2 | 第三主成分 PCA3 | 第四主成分 PCA4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 公路等级 Road grade | 0.108 | -0.028 | -0.056 | 0.021 |
| 与公路距离 Distance to roads | -0.029 | 0.129 | -0.153 | -0.487 |
| 样方内是否存在乔木 Presence or absence of trees | 0.029 | -0.006 | -0.046 | -0.113 |
| 坡形 Shape | -0.019 | 0.011 | -0.007 | 0.024 |
| 坡位 Position | 0.099 | -0.151 | 0.086 | -0.461 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.039 | -0.062 | 0.050 | -0.581 |
| 裸地比例 Bare land percentage | -0.148 | -0.087 | 0.077 | 0.420 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | -0.351 | -0.082 | -0.033 | -0.048 |
| 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | -0.349 | -0.112 | -0.032 | -0.042 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | -0.353 | -0.022 | -0.029 | -0.054 |
| 年潜在蒸散 Potential evapotranspiration | -0.351 | -0.082 | -0.032 | -0.048 |
| 年降水 Mean annual precipitation | -0.179 | 0.507 | -0.162 | 0.002 |
| 最干季降水 Precipitation of driest quarter | -0.185 | 0.415 | 0.376 | -0.008 |
| 最湿季降水 Precipitation of wettest quarter | -0.116 | 0.323 | -0.611 | 0.019 |
| 年实际蒸散 Actural evapotranspiration | -0.351 | 0.059 | -0.049 | -0.045 |
| 水分亏缺 Water deficit | 0.311 | 0.275 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality | 0.103 | 0.507 | 0.038 | -0.052 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | 0.164 | -0.211 | -0.637 | 0.055 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 8.288 | 2.662 | 1.578 | 1.203 |
| 解释百分比 Percentage explained (%) | 48.600 | 15.600 | 9.300 | 7.100 |
Table 1 Principal component analysis (PCA) of environmental factors. Entries are factor loadings, eigenvalues and percentage of variation explained for the four principal components. Large component loadings among four principal components were bolded.
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第一主成分 PCA1 | 第二主成分 PCA2 | 第三主成分 PCA3 | 第四主成分 PCA4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 公路等级 Road grade | 0.108 | -0.028 | -0.056 | 0.021 |
| 与公路距离 Distance to roads | -0.029 | 0.129 | -0.153 | -0.487 |
| 样方内是否存在乔木 Presence or absence of trees | 0.029 | -0.006 | -0.046 | -0.113 |
| 坡形 Shape | -0.019 | 0.011 | -0.007 | 0.024 |
| 坡位 Position | 0.099 | -0.151 | 0.086 | -0.461 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.039 | -0.062 | 0.050 | -0.581 |
| 裸地比例 Bare land percentage | -0.148 | -0.087 | 0.077 | 0.420 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | -0.351 | -0.082 | -0.033 | -0.048 |
| 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | -0.349 | -0.112 | -0.032 | -0.042 |
| 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | -0.353 | -0.022 | -0.029 | -0.054 |
| 年潜在蒸散 Potential evapotranspiration | -0.351 | -0.082 | -0.032 | -0.048 |
| 年降水 Mean annual precipitation | -0.179 | 0.507 | -0.162 | 0.002 |
| 最干季降水 Precipitation of driest quarter | -0.185 | 0.415 | 0.376 | -0.008 |
| 最湿季降水 Precipitation of wettest quarter | -0.116 | 0.323 | -0.611 | 0.019 |
| 年实际蒸散 Actural evapotranspiration | -0.351 | 0.059 | -0.049 | -0.045 |
| 水分亏缺 Water deficit | 0.311 | 0.275 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality | 0.103 | 0.507 | 0.038 | -0.052 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | 0.164 | -0.211 | -0.637 | 0.055 |
| 特征值 Eigenvalue | 8.288 | 2.662 | 1.578 | 1.203 |
| 解释百分比 Percentage explained (%) | 48.600 | 15.600 | 9.300 | 7.100 |
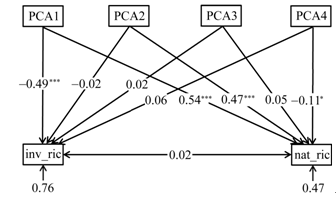
Fig. 5 A structural equation model showing the multivariate effects on invasive plant richness (inv_ric) by native plant richness (nat_ric) and four principal components (PCA1, PCA2, PCA3, PCA4) of environmental factors. The direction of arrows shows the causal relationships, numbers are standardized path coefficients, accompanied by positive (+) or negative (-) illustrations. The proportion of variation explained by the model is indicated by the number near each textbox. Asterisks imply the level of significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
| 1 | Baker HG (1974) The evolution of weeds. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 5, 1-24. |
| 2 | Baruch Z, Fernandez DS (1993) Water relations of native and introduced C4 grasses in a neotropical savanna. Oecologia, 96, 179-185. |
| 3 | Brooks ML, D’Antonio CM, Richardson DM, Grace JB, Keeley JE, DiTomaso JM, Hobbs RJ, Pellant M, Pyke D (2004) Effects of invasive alien plants on fire regimes. BioScience, 54, 677-688. |
| 4 | Brutsaert WH (1982) Evaporation in the atmosphere: theory, history and application. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht. |
| 5 | Bulleri F, Bruno JF, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2008) Beyond competition: incorporating positive interactions between species to predict ecosystem invasibility. PLoS Biology, 6, 1136-1140. |
| 6 | Christian CE (2001) Consequences of a biological invasion reveal the importance of mutualism for plant communities. Nature, 413, 635-639. |
| 7 | Daehler CC (2005) Upper-montane plant invasions in the Hawaiian Islands: patterns and opportunities. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 7, 203-216. |
| 8 | Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: a general theory of invasibility. Journal of Ecology, 88, 528-534. |
| 9 | Deutschewitz K, Lausch A, Kühn I, Klotz S (2003) Native and alien plant species in relation to spatial heterogeneity on a regional scale in Germany. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 299-311. |
| 10 | Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems, 6, 503-523. |
| 11 | Ehrenfeld JG (2010) Ecosystem consequences of biological invasions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 41, 59-80. |
| 12 | Elton CS (1958) The Ecology of Invasions by Animals and Plants. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| 13 | Fang JY, Lechowicz MJ (2006) Climatic limits for the present distribution of beech (Fagus L.) species in the world. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1804-1819. |
| 14 | Fang JY, Song YC, Liu HY, Piao SL (2002) Vegetation-climate relationship and its application in the division of vegetation zone in China. Acta Botanica Sinica, 44, 1105-1122. |
| 15 | Fargione J, Brown CS, Tilman D (2003) Community assembly and invasion: an experimental test of neutral versus niche processes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 8916-8920. |
| 16 | Funk J, Zachary V (2010) Physiological responses to short-term water and light stress in native and invasive plant species in southern California. Biological Invasions, 12, 1685-1694. |
| 17 | Gerhardt F, Collinge SK (2007) Abiotic constraints eclipse biotic resistance in determining invasibility along experimental vernal pool gradients. Ecological Applications, 17, 922-933. |
| 18 | Giorgis MA, Tecco PA, Cingolani AM, Renison D, Marcora P, Paiaro V (2011) Factors associated with woody alien species distribution in a newly invaded mountain system of central Argentina. Biological Invasions, 13, 1423-1434. |
| 19 | Grotkopp E, Rejmánek M, Rost TL (2002) Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine (Pinus) species. The American Naturalist, 159, 396-419. |
| 20 | Halpern SL, Underwood N (2006) Approaches for testing herbivore effects on plant population dynamics. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 922-929. |
| 21 | Hamilton JG, Holzapfel C, Mahall BE (1999) Coexistence and interference between a native perennial grass and non-native annual grasses in California. Oecologia, 121, 518-526. |
| 22 | Hansen MJ, Clevenger AP (2005) The influence of disturbance and habitat on the presence of non-native plant species along transport corridors. Biological Conservation, 125, 249-259. |
| 23 | Harrison S (1999) Native and alien species diversity at the local and regional scales in a grazed California grassland. Oecologia, 121, 99-106. |
| 24 | Hawkins BA, Field R, Cornell HV, Currie DJ, Guégan JF, Kaufman DM, Kerr MJ, Mittelbach GG, Oberdorff T, O’Brien EM, Porter RE, Turner JRG (2003) Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology, 84, 3105-3117. |
| 25 | Hu FG, Duan CF, Liu GH (2007) Exotic invasive weeds in farmland of dry-hot valley in Yunnan Nujiang region. Weed Sciences, (4), 20-23.(in Chinese) |
| [胡发广, 段春芳, 刘光华 (2007) 云南怒江干热河谷农田外来入侵杂草的调查. 杂草科学, (4), 20-23.] | |
| 26 | Hulme PE, Pyšek P, Jarošík V, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Vila M (2013) Bias and error in understanding plant invasion impacts. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 212-218. |
| 27 | Kennedy TA, Naeem S, Howe KM, Knops JMH, Tilman D, Reich P (2002) Biodiversity as a barrier to ecological invasion. Nature, 417, 636-638. |
| 28 | Kissling WD, Lord JM, Schnittler M (2006) Agamospermous seed production of the invasive tussock grass Nardus stricta L. (Poaceae) in New Zealand: evidence from pollination experiments. Flora, 201, 144-151. |
| 29 | Kueffer C, P Pyšek, Richardson DM (2013) Integrative invasion science: model systems, multi-site studies, focused meta-analysis and invasion syndromes. New Phytologist, 200, 615-633. |
| 30 | Lembrechts JJ, Milbau A, Nijs I (2014) Alien roadside species more easily invade alpine than lowland plant communities in a subarctic mountain ecosystem. PloS ONE, 9, e89664. |
| 31 | Levine JM (2000) Species diversity and biological invasions: relating local process to community pattern. Science, 288, 852-854. |
| 32 | Levine JM, D’Antonio CM (1999) Elton revisited: a review of evidence linking diversity and invasibility. Oikos, 1999, 15-26. |
| 33 | Li H, Bai Y, Yang SH, Zhu X, Zhao K (2009) Prediction of vegetations dynamic changes in central Nujiang watershed based on Markov process mode. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28, 371-376.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晖, 白杨, 杨树华, 朱雪, 赵凯 (2009) 基于马尔柯夫模型的怒江流域中段植被动态变化预测. 生态学杂志, 28, 371-376.] | |
| 34 | Liu J, Dong M, Miao SL, Li ZY, Song MH, Wang RQ (2006) Invasive alien plants in China: role of clonality and geographical origin. Biological Invasions, 8, 1461-1470. |
| 35 | Liu Y (2015) Plant diversity and biogeography of the arid valleys in Southwest China. PhD dissertation, Peking University, Beijing.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晔 (2015) 中国西南干旱河谷的植物多样性地理格局. 博士学位论文, 北京大学, 北京.] | |
| 36 | Liu Y, Shen LF, Wang T, Fang R, Jiang R, Shen ZH (2013) Invasive pattern and influential factors of Eupatorium adenophorum along the highway in three parallel rivers region in northwestern Yunnan. Highway Traffic Science and Technology, 5, 284-288.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晔, 沈利峰, 王韬, 房锐, 姜睿, 沈泽昊 (2013) 滇西北三江并流地区公路沿线紫茎泽兰的入侵格局及影响因素. 公路交通科技, 5, 284-288.] | |
| 37 | Lomolino MV (2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: historical and prospective views. Global Ecological Biogeogrophy, 10, 3-13. |
| 38 | Lozon JD, MacIssac HJ (1997) Biological invasions: are they dependent on disturbance? Environmental Reviews, 5, 131-144. |
| 39 | Lu P, Sang WG, Ma KP (2005) Progress and prospects in research of exotic invasive species, Eupatorium adenophorum. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29, 1029-1037.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [鲁萍, 桑卫国, 马克平 (2005) 外来入侵种紫茎泽兰研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 29, 1029-1037.] | |
| 40 | Lu ZJ, Ma KP (2004) The influence of topographical factors on the invasion of the alien species, Eupatorium adenophorum. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica , 28, 761-767.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢志军, 马克平 (2004) 地形因素对外来入侵种紫茎泽兰的影响. 植物生态学报, 28, 761-767.] | |
| 41 | Lu ZJ, Ma KP (2005) Scale dependent relationships between native plant diversity and the invasion of croftonweed (Eupatorium adenophorum) in Southwest China. Weed Science, 53, 600-604. |
| 42 | Nally RM (2002) Multiple regression and inference in ecology and conservation biology: further comments on identifying important predictor variables. Biodiversity and Conservation, 11, 1397-1401. |
| 43 | Marini L, Battisti A, Bona E, Federici G, Martini F, Pautasso M, Hulme PE (2012) Alien and native plant life-forms respond differently to human and climate pressures. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 534-544. |
| 44 | Matzek V (2011) Superior performance and nutrient-use efficiency of invasive plants over non-invasive congeners in a resource-limited environment. Biological Invasions, 13, 3005-3014. |
| 45 | Mooney HA, Hobbs RJ (2000) Invasive Species in a Changing World. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| 46 | Palmer MW, Maurer TA (1997) Does diversity beget diversity? A case study of crops and weeds. Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 235-240. |
| 47 | Parendes LA, Jones JA (2000) Role of light availability and dispersal in exotic plant invasion along roads and streams in the H. J. Andrews experimental forest, Oregon. Conservation Biology, 14, 64-75. |
| 48 | Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience, 50, 53-65. |
| 49 | Pokorny ML, Sheley RL, Zabinski CA, Engel RE, Svejcar TJ, Borkowski JJ (2005) Plant functional group diversity as a mechanism for invasion resistance. Restoration Ecology, 13, 448-459. |
| 50 | Rahbek C (1995) The elevational gradient of species richness: a uniform pattern? Ecography, 18, 200-205. |
| 51 | Rudgers JA, Mattingly WB, Koslow JM (2005) Mutualistic fungus promotes plant invasion into diverse communities. Oecologia, 144, 463-471. |
| 52 | Souza L, Bunn WA, Simberloff D, Lawton RM, Sanders NJ (2011) Biotic and abiotic influences on native and exotic richness relationship across spatial scales: favourable environments for native species are highly invasible. Functional Ecology, 25, 1106-1112. |
| 53 | Spence LA, Dickie IA, Coomes DA (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculum potential: a mechanism promoting positive diversity-invasibility relationships in mountain beech forests in New Zealand? Mycorrhiza, 21, 309-314. |
| 54 | Stephenson NJ (1990) Climatic control of vegetation distribution: the role of the water balance. The American Naturalist, 135, 649-670. |
| 55 | Stevens GC (1992) The elevational gradient in altitudinal range: an extension of Rapoport’s latitudinal rule to altitude. The American Naturalist, 140, 893-911. |
| 56 | Thornthwaite CW, Hare FK (1955) Climatic classification in forestry. Unasylva, 9, 51-59. |
| 57 | Toledo M, Poorter L, Pena-Claros M, Alarcon A, Balcazar J, Leano C, Licona JC, Llanque O, Vroomans V, Zuidema P, Bongers F (2011) Climate is a stronger driver of tree and forest growth rates than soil and disturbance. Journal of Ecology, 99, 254-264. |
| 58 | van Kleunen MV, Weber E, Fischer M (2010) A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species. Ecology Letters, 13, 235-245. |
| 59 | Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: a meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702-708. |
| 60 | Wang DN (2012) Prevention and control situation and the countermeasures of exotic invasive species Mikania micrantha. Yunnan Agricultural Science and Technology, Suppl.1, 235-236.(in Chinese) |
| [王大能 (2012) 西盟县外来入侵有害生物薇甘菊防控现状及对策. , 云南农业科技, 235-236.] | |
| 61 | Watkins RZ, Chen JQ, Pickens J, Brosofske KD (2003) Effects of forest roads on understory plants in a managed hardwood landscape. Conservation Biology, 17, 411-419. |
| 62 | Yunnan Province Three Parallel Rivers Administration Bureau (2010) An overview of the world natural heritage “Three Parallel Rivers” and the protection progress. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 26(5), 52-55.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [云南省三江并流管理局 (2010) 世界自然遗产地——“三江并流”的概况及其保护工作的进展 . 中国园林,26(5), 52-55.] | |
| 63 | Zeiter M, Stampfli A (2012) Positive diversity-invasibility relationship in species-rich semi-natural grassland at the neighbourhood scale. Annals of Botany, 110, 1385-1393. |
| 64 | Zheng L, Feng YL (2005) The effects of ecophysiological traits on carbon gain in invasive plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2782-2787.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑丽, 冯玉龙 (2005) 入侵植物的生理生态特性对碳积累的影响. 生态学报, 25, 2782-2787.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()