



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 799-806. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015218 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015218
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianmin Chu1, Yifu Li2, Lei Zhang1, Bin Li1, Mingyuan Gao1, Xiaoqian Tang1, Jianwei Ni1, Xinqiao Xu1,*( )
)
Received:2016-11-22
Accepted:2017-02-17
Online:2017-08-20
Published:2017-08-31
Contact:
Xu Xinqiao
Jianmin Chu, Yifu Li, Lei Zhang, Bin Li, Mingyuan Gao, Xiaoqian Tang, Jianwei Ni, Xinqiao Xu. Potential distribution range and conservation strategies for the endangered species Amygdalus pedunculata[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(8): 799-806.
| 数据代码 Code | 环境因子 Environmental variables |
|---|---|
| BIO2 | 平均温度日较差 Mean diurnal temperature range |
| BIO3 | 等温性 Isothermality |
| BIO5 | 最热月最高温度 Max. temperature of the warmest month |
| BIO6 | 最冷月最低温度 Min. temperature of the coldest month |
| BIO7 | 平均温度年较差 Temperature annual range |
| BIO13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month |
| BIO14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month |
| BIO15 | 降水量季节性 Precipitation seasonality |
Table 1 Environmental variables used in the distribution modeling of Amygdalus pedunculata
| 数据代码 Code | 环境因子 Environmental variables |
|---|---|
| BIO2 | 平均温度日较差 Mean diurnal temperature range |
| BIO3 | 等温性 Isothermality |
| BIO5 | 最热月最高温度 Max. temperature of the warmest month |
| BIO6 | 最冷月最低温度 Min. temperature of the coldest month |
| BIO7 | 平均温度年较差 Temperature annual range |
| BIO13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month |
| BIO14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month |
| BIO15 | 降水量季节性 Precipitation seasonality |
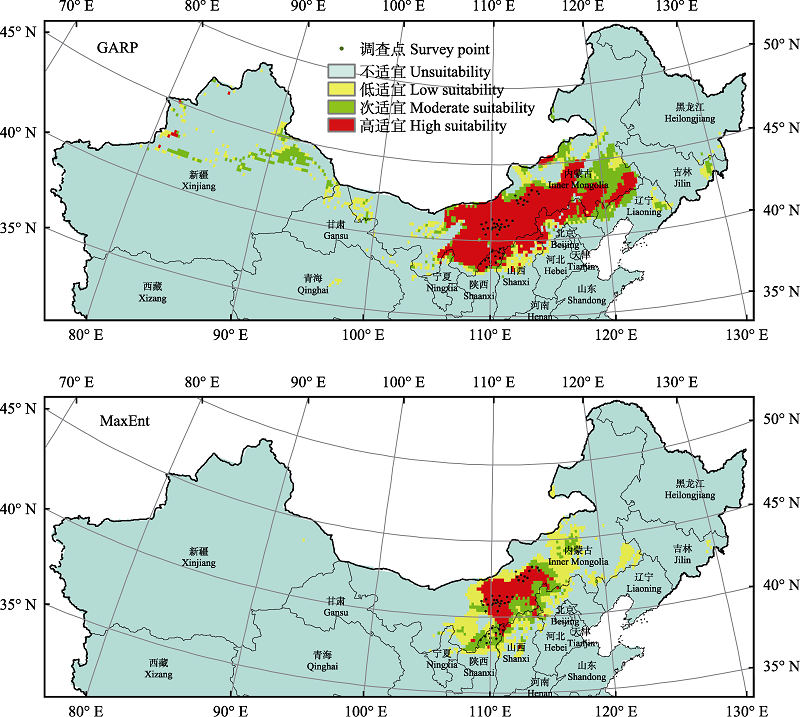
Fig. 1 Potential distributions of Amygdalus pedunculata predicted by genetic algorithm for rule-set prediction (GARP) model and maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model
| 模型类型 Model type | Kappa | 真实技巧统计法 True skill statistic (TSS) | 总体精度 Overall accuracy | 受试者工作特征曲线下面积 Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaxEnt | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.14 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.002 |
| GARP | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.01 |
Table 2 Predictive accuracy of genetic algorithm for rule-set prediction (GARP) model and maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model
| 模型类型 Model type | Kappa | 真实技巧统计法 True skill statistic (TSS) | 总体精度 Overall accuracy | 受试者工作特征曲线下面积 Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaxEnt | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.14 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.002 |
| GARP | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.01 |
| 预测面积 Prediction area (×10,000 km2) | ||
|---|---|---|
| MaxEnt | GARP | |
| 高适宜区 High suitability area | 11.9373 | 48.2647 |
| 次适宜区 Moderate suitability area | 12.1625 | 24.2406 |
| 低适宜区 Low suitability area | 26.0358 | 18.4617 |
| 总计 Total | 50.1356 | 90.9670 |
Table 3 Comparison of prediction area between the GARP model and the MaxEnt model
| 预测面积 Prediction area (×10,000 km2) | ||
|---|---|---|
| MaxEnt | GARP | |
| 高适宜区 High suitability area | 11.9373 | 48.2647 |
| 次适宜区 Moderate suitability area | 12.1625 | 24.2406 |
| 低适宜区 Low suitability area | 26.0358 | 18.4617 |
| 总计 Total | 50.1356 | 90.9670 |
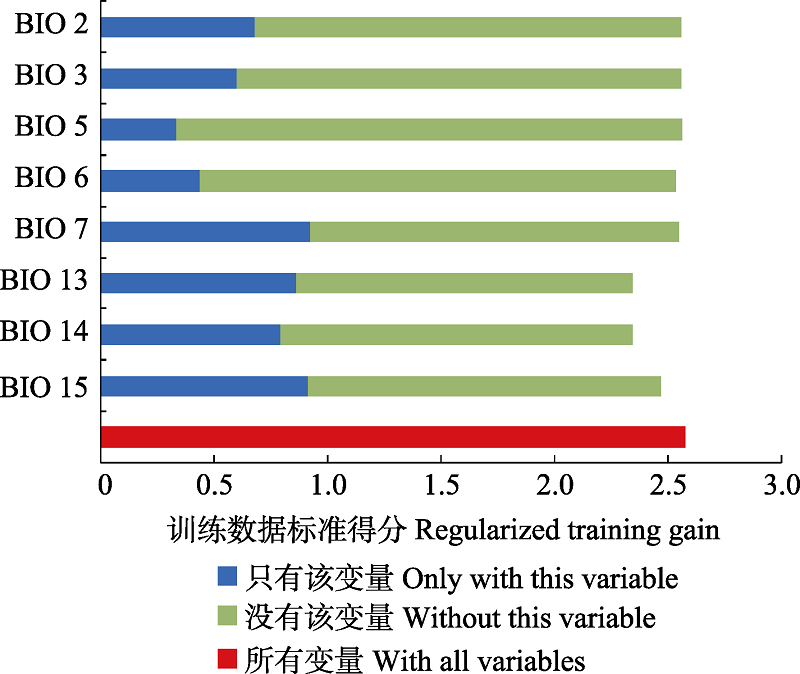
Fig. 2 Importance of environmental factors estimated by MaxEnt model. Blue bars indicate the importance of the variable of interest. Green bars indicate the importance of all variables without the variable of interest. The longer the bar, the more important the variables. The abbreviations of climatic variables are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | Allouche O, Tsoar A, Kadmon R (2006) Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: prevalence, Kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 1223-1232. |
| [2] | Calenge C (2006) The package “adehabitat” for the R software: a tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecological Modelling, 197, 516-519. |
| [3] | Chu JM, Xu XQ, Zhang YL (2013) Production and properties of biodiesel produced from Amygdalus pedunculata Pall. Bioresource Technology, 134, 374-376. |
| [4] | Fu LG, Jin JM (1991) China Plant Red Data Book, Vol. 1: Rare and Endangered Plants. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [傅立国, 金鉴明 (1991) 中国植物红皮书: 稀有濒危植物(第一册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Graham B (2001) Neutral macroecology. Science, 293, 2413-2418. |
| [6] | Guisan A, Thuiller W (2005) Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models. Ecology Letters, 8, 993-1009. |
| [7] | Guo CH, Luo M, Ma YH, Ma XW (2005) Advances of characteristic research of threatened long carpopodium almond. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 33(12), 125-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭春会, 罗梦, 马玉华, 马小卫 (2005) 沙地濒危植物长柄扁桃特性研究进展. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 33(12), 125-129.] | |
| [8] | Hampe A (2004) Bioclimate envelope models: what they detect and what they hide. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 13, 469-471. |
| [9] | Hao YQ, Zhao XF (2011) Distinguishing early-acting inbreeding depression from late-acting ovarian self-incompatibility. Biodiversity Science, 19,106-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郝祎祺, 赵鑫峰 (2011) 被子植物早期近交衰退与晚期自交不亲和. 生物多样性, 19, 106-112.] | |
| [10] | Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978. |
| [11] | Ji ZL, Qian AD (1981) Investigation of the resources of Amygdalus pedunculata Pall. and Prunus mongolica Maxim. from the natural distribution in China. China Fruits, (2), 38-40. (in Chinese) |
| [姬钟亮, 钱安东 (1981) 长柄扁桃和蒙古扁桃在我国自然分布区的调查. 中国果树, (2), 38-40.] | |
| [12] | Lei GH, Liu LT, Han C, Shen YH, Huo YM (2009) Analysis of tocopherol content in endangered long carpopodium almond nutlet. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39, 777-779. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [雷根虎, 刘丽婷, 韩超, 申烨华, 霍艳敏 (2009) 沙地濒危植物长柄扁桃仁中维生素E含量分析. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 777-779.] | |
| [13] | Li C, Li GP, Chen Q, Bai B, Shen YH, Zhang YL (2010) Fatty acid composition analysis of the seed oil of Amygdalus pedunculata Pall. China Oils and Fats, 35(4), 77-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李聪, 李国平, 陈俏, 白斌, 申烨华, 张应龙 (2010) 长柄扁桃油脂肪酸成分分析. 中国油脂, 35(4), 77-79.] | |
| [14] | Li QY, Wang XP (2013) Elevational pattern of species richness in the Three Gorges region of the Yangtze River: effect of climate, geometric constraints, area and topographical heterogeneity. Biodiversity Science, 21, 141-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李巧燕, 王襄平 (2013) 长江三峡库区物种多样性的垂直分布格局: 气候、几何限制、面积及地形异质性的影响. 生物多样性, 21, 141-152.] | |
| [15] | Lu Q, Wang JH, Chu JM (2012) Desert Plants in China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [卢琦, 王继和, 褚建民(2012) 中国荒漠植物图鉴. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Ma Y, Ma RC (2004) Identification of genetic relationship of almond by AFLP. Journal of Fruit Science, 21, 552-555. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马艳, 马荣才 (2004) 扁桃种质资源的AFLP分析. 果树学报, 21, 552-555.] | |
| [17] | McCune B, Grace J (2002) Analysis of Ecological Communities. Mjm Software Design, Glenden Beach, OR. |
| [18] | Moilanen A (2005) Reserve selection using nonlinear species distribution models. The American Naturalist, 165, 695-706. |
| [19] | Monserud RA, Leemans R (1992) Comparing global vegetation maps with the Kappa statistic. Ecological Modelling, 62, 275-293. |
| [20] | Özkan K, Mert A, Şentürk Ö (2011) Estimation of potential distribution of non-wood trading species richness using classification and regression tree technique: A case study from the Lakes District, Turkey. 2nd International Non- Wood Forest Products Symposium, Isparta, Turkey. |
| [21] | Phillips SJ, Miroslav K, Schapire RE (2004) A maximum entropy approach to species distribution modeling. Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, 95, 655-662. |
| [22] | Qiao HJ, Hu JH, Huang JH (2013) Theoretical basis, future directions, and challenges for ecological niche models. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 43, 915-927. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [乔慧捷, 胡军华, 黄继红 (2013) 生态位模型的理论基础、发展方向与挑战. 中国科学: 生命科学, 43, 915-927.] | |
| [23] | Qiao HJ, Soberón J, Peterson AT (2015) No silver bullets in correlative ecological niche modeling: insights from testing among many potential algorithms for niche estimation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution,6, 1126-1136. |
| [24] | Saupe EE, Qiao HJ, Hendricks JR, Portell RW, Hunter SJ, Soberón J, Lieberman BS (2015) Niche breadth and geographic range size as determinants of species survival on geological time scales. Global Ecology & Biogeography, 24, 1159-1169. |
| [25] | Stockwell D, Peters D (1999) The GARP modeling system: problems and solutions to automated spatial prediction. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 13, 143-158. |
| [26] | Su GX (1997) Germplasm resources of almonds in China. China Seeds, 2, 6-8. |
| (in Chinese) [苏贵兴 (1987) 我国的扁桃种质资源. 作物品种资源, 2, 6-8.] | |
| [27] | van Proosdij ASJ, Sosef MSM, Wieringa JJ, Raes N (2015) Minimum required number of specimen records to develop accurate species distribution models. Ecography, 39, 542-552. |
| [28] | Wu B, Su ZZ, Chen ZX (2007) A revised potential extent of desertification in China. Journal of Desert Research, 27,911-917. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴波, 苏志珠, 陈仲新 (2007) 中国荒漠化潜在发生范围的修订. 中国沙漠, 27, 911-917.] | |
| [29] | Xu XQ, Chu JM (2013) Analysis on development potential and countermeasures of Amygdalus pedunculata industry. Forest Resources Management, 1, 22-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许新桥, 褚建民 (2013) 长柄扁桃产业发展潜势分析及问题对策研究. 林业资源管理, 1, 22-25.] | |
| [30] | Xu XT, Yang Y, Wang LS (2008) Geographic distribution and potential distribution estimation of Pseudotaxus chienii. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32,1134-1145. |
| [徐晓婷, 杨永, 王利松 (2008) 白豆杉的地理分布及潜在分布区估计. 植物生态学报, 32, 1134-1145.] | |
| [31] | Xu ZL, Peng HH, Peng SZ (2015) The development and evaluation of species distribution models. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 557-567. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [许仲林, 彭焕华, 彭守章 (2015) 物种分布模型的发展及评价方法. 生态学报, 35, 557-567.] | |
| [32] | Zhang DY, Jiang XH (1999) Progress in studies of genetic diversity and conservation biology of endangered plant species. Chinese Biodiversity, 7, 31-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张大勇, 姜新华 (1999) 遗传多样性与濒危植物保护生物学研究进展. 生物多样性, 7, 31-37.] | |
| [33] | Zhang L, Liu SR, Sun PS, Wang TL (2011) Comparative evaluation of the effects of climate change on the potential distribution of Pinus massoniana. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1091-1105. |
| [张雷, 刘世荣, 孙鹏森, 王同立 (2011) 气候变化对马尾松潜在分布影响预估的多模型比较. 植物生态学报, 35, 1091-1105.] | |
| [34] | Zhang P, Shen YH, Wang XL, Hou RT (2007) Determination of amygdalin in Amygdalus pedunculata Pall by high performance liquid chromatography. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 26(10), 80-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张萍, 申烨华, 王晓玲, 侯睿婷 (2007) 高效液相色谱法测定长柄扁桃仁中的苦杏仁甙. 分析实验室, 26(10), 80-83.] | |
| [35] | Zhang WJ, Chen JK (2003) Advances in study of the distribution area of species. Biodiversity Science, 11, 364-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张文驹, 陈家宽 (2003) 物种分布区研究进展. 生物多样性, 11, 364-369.] | |
| [36] | Zhang YB, Ma KP (2008) Geographic distribution patterns and status assessment of threatened plants in China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17, 1783-1798. |
| [37] | Zhao YZ (1992) Atlas of Endangered Rare Plants in Inner Mongolia. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵一之 (1992) 内蒙古珍稀濒危植物图谱. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Zhu GP, Liu GQ, Bu WJ, Gao YB (2013) Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 21, 90-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱耿平, 刘国卿,卜文俊, 高玉葆 (2013) 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 21, 90-98. ] | |
| [39] | Zuo WY, Lao N, Geng YY, Ma KP (2007) Predicting species’ potential distribution—SVM compared with GARP. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 31, 711-719. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [左闻韵, 劳逆, 耿玉英, 马克平 (2007) 预测物种潜在分布区——比较SVM与GARP. 植物生态学报, 31, 711-719.] |
| [1] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [2] | Motong Li, Tuo He, Wei Li, Jing Liao, Yan Zeng. Regulating international trade in wild fauna and flora: An analysis of CITES terminology [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [3] | Fu Mengdi, Zhu Yanpeng, Ren Yueheng, Li Shuang, Qin Le, Xie Zhengjun, Wang Qingchun, Zhang Libo. Research on the optimization of wildlife passage spatial layout in Xinjiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24346-. |
| [4] | Tuo He, Yan Zeng, Yafang Yin, Kun Zhang, Liangchen Yuan, Hui Dong, Zhihua Zhou. Consolidating the scientific foundation for global wild plant conservation and sustainable trade—Comments on the 27th Meeting of the Plants Committee of CITES [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24390-. |
| [5] | Wei Liu, Ruge Wang, Tianqiao Fan, Nayiman Abudulijiang, Xinhang Song, Shuping Xiao, Ning Guo, Lingying Shuai. Habitat suitability for the Aviceda leuphotes in Mingxi County, Fujian Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [6] | Jinfeng Chen, Xinjing Wu, Hai Lin, Guofa Cui. A comparative analysis of the List of State Key Protected Wild Animals and other wildlife protection lists [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22639-. |
| [7] | Qiongyue Zhang, Zhuodi Deng, Xuebin Hu, Zhifeng Ding, Rongbo Xiao, Chen Xiu, Zhenghao Wu, Guang Wang, Donghui Han, Yuke Zhang, Jianchao Liang, Huijian Hu. The impact of urbanization on regional bird distribution and habitat connectivity in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [8] | Yanyan Liu, Chang Liu, Xiaoxin Wei. Current status of taxonomy, systematics and conservation of the white pines in China and adjacent regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21344-. |
| [9] | Jirong Teng, Xingming Liu, Liwen He, Junliang Wang, Jian Huang, Jie Feng, Fang Wang, Yue Weng. The spatio-temporal impact of domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) on giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in Baishuijiang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21204-. |
| [10] | Chen Zhang, Wei Ma, Chen Chen, Muyang Wang, Wenxuan Xu, Weikang Yang. Changes of habitat pattern for goitered gazelle in the Xinjiang Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve under the influence of major projects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21176-. |
| [11] | Xing Ma, Hao Wang, Wei Yu, Yong Du, Jianchao Liang, Huijian Hu, Shengrong Qiu, Lu Liu. Analysis on the hotspot and conservation gaps of bird biodiversity in Guangdong Province based on MaxEnt model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(8): 1097-1107. |
| [12] | Run Zhou, Xiuqin Ci, Jianhua Xiao, Guanlong Cao, Jie Li. Effects and conservation assessment of climate change on the dominant group—The genusCinnamomum of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 697-711. |
| [13] | Yuhan Shi, Zongxin Ren, Weijia Wang, Xin Xu, Jie Liu, Yanhui Zhao, Hong Wang. Predicting the spatial distribution of three Astragalusspecies and their pollinating bumblebees in the Sino-Himalayas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [14] | Jiang Zhigang. China’s key protected species lists, their criteria and management [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 698-703. |
| [15] | Hongfei Zhuang, Yinbo Zhang, Wei Wang, Yueheng Ren, Fangzheng Liu, Jinhong Du, Yue Zhou. Optimized hot spot analysis for probability of species distribution under different spatial scales based on MaxEnt model: Manglietia insignis case [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(9): 931-940. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn