



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 22252. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022252 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022252
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
收稿日期:2022-05-09
接受日期:2022-08-18
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-11-25
通讯作者:
*E-mail: fzhang@njau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Cong Xu1, Feiyu Zhang1, Daoyuan Yu2, Xin Sun3, Feng Zhang1,*( )
)
Received:2022-05-09
Accepted:2022-08-18
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-11-25
Contact:
*E-mail: fzhang@njau.edu.cn
摘要:
土壤动物类群包含庞大的生物多样性, 由于传统的形态学鉴定技术很难满足该类群多样性调查和监测的巨大需求, 基于DNA等遗传物质的分子层面的鉴定技术(分子分类预测)逐渐登上舞台。然而, 分子分类预测能否在参考分子序列严重匮乏的土壤动物分类研究中实现有效鉴定、如何利用分子分类预测更为准确高效地获取土壤动物的分类信息, 是当下分子分类预测在土壤动物应用中的两大难题。为探究这两大难题, 本文基于宏条形码技术, 对5款常用的分子分类预测软件(VSEARCH、HS-BLASTN、EPA-NG、RAPPAS和APPLES; 前两款基于相似度算法, 其余基于系统发育位置算法)进行了准确性(科和属阶元)、运行速度和内存占用等性能的比较和评估。其中, 预测准确性的评估基于4类土壤动物(弹尾纲, 蜱螨亚纲, 环带纲和色矛纲)和3种分子标记(COI、16S和18S)展开。结果表明: EPA-NG在大部分场合下准确性最高, 尤其是在使用COI标记时, 准确性远高于其他工具。VSEARCH和HS-BLASTN准确性也较高, 基于16S和18S标记时, 它们的准确性和EPA-NG相当。此外, VSEARCH在所有软件中运行速度最快且内存占用最小, 这使得它在16S和18S的应用中比EPA-NG更具竞争力。RAPPAS和APPLES具有较低的假阳性, 但假阴性很高, 相对保守的算法使得它们无法将一些物种鉴定到低阶元。总体来说, 即使是在参考数据库缺少目标物种且小部分物种在分类上存在界定争议的前提下, 5款分子分类预测软件都能极为准确地将土壤动物预测至科级阶元, 因此分子分类预测在土壤动物应用中前景远大。COI标记在土壤动物科、属和种阶元上的覆盖度最广且能有效实现分子鉴定, 在目前最适合作为土壤动物尤其是土壤节肢动物的分子标记。在应用COI标记且参考数据库规模不大时, EPA-NG是分子分类预测的最佳选择; 而在应用16S、18S标记或参考数据库规模较大时, 更推荐使用VSEARCH。
徐聪, 张飞宇, 俞道远, 孙新, 张峰 (2022) 土壤动物的分子分类预测策略评估. 生物多样性, 30, 22252. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022252.
Cong Xu, Feiyu Zhang, Daoyuan Yu, Xin Sun, Feng Zhang (2022) Performance evaluation of molecular taxonomy assignment tools for soil invertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22252. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022252.
| 类群 Taxa | 分子标记 Markers | 物种数目 Species number | 属数目 Genus number | 科数目 Family number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | COI | 1,211 | 157 | 22 |
| 16S | 387 | 81 | 18 | |
| 18S | 163 | 79 | 19 | |
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | COI | 1,675 | 460 | 190 |
| 16S | 456 | 76 | 28 | |
| 18S | 635 | 459 | 220 | |
| 环带纲 Clitellata | COI | 1,297 | 255 | 39 |
| 16S | 972 | 214 | 28 | |
| 18S | 342 | 203 | 42 | |
| 色矛纲 Chromadorea | COI | 939 | 249 | 86 |
| 16S | 170 | 64 | 28 | |
| 18S | 1,042 | 430 | 135 | |
| 4个类群合并 Merged | COI | 5,122 | 1,121 | 337 |
表1 各个类群COI、16S和18S参考数据库中的物种、属和科阶元的数目
Table 1 The biodiversity showed in databases of different groups for COI, 16S and 18S
| 类群 Taxa | 分子标记 Markers | 物种数目 Species number | 属数目 Genus number | 科数目 Family number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 弹尾纲 Collembola | COI | 1,211 | 157 | 22 |
| 16S | 387 | 81 | 18 | |
| 18S | 163 | 79 | 19 | |
| 蜱螨亚纲 Acari | COI | 1,675 | 460 | 190 |
| 16S | 456 | 76 | 28 | |
| 18S | 635 | 459 | 220 | |
| 环带纲 Clitellata | COI | 1,297 | 255 | 39 |
| 16S | 972 | 214 | 28 | |
| 18S | 342 | 203 | 42 | |
| 色矛纲 Chromadorea | COI | 939 | 249 | 86 |
| 16S | 170 | 64 | 28 | |
| 18S | 1,042 | 430 | 135 | |
| 4个类群合并 Merged | COI | 5,122 | 1,121 | 337 |
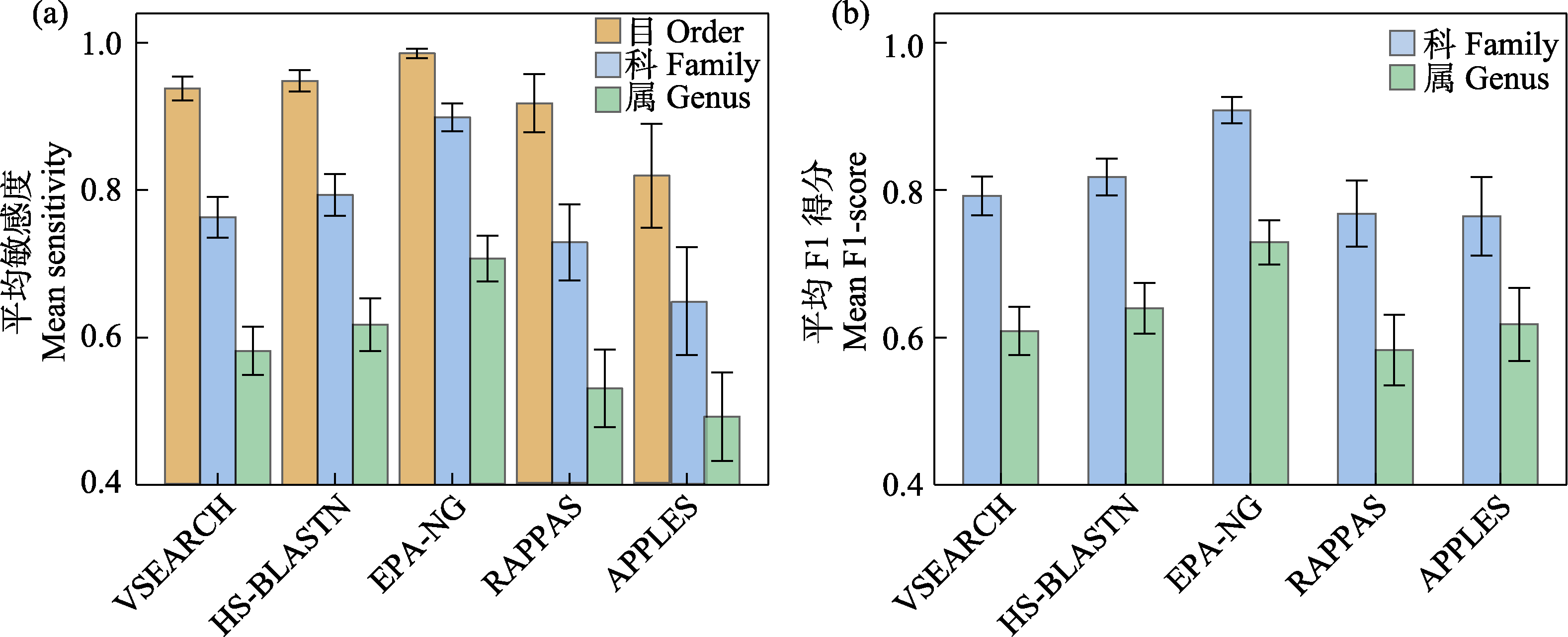
图3 5款分类预测软件在混合COI参考数据库应用中的平均敏感度(a)和平均F1分数(b)
Fig. 3 Mean sensitivity (a) and mean F1-score (b) of five taxonomic assignment tools with merged COI reference database
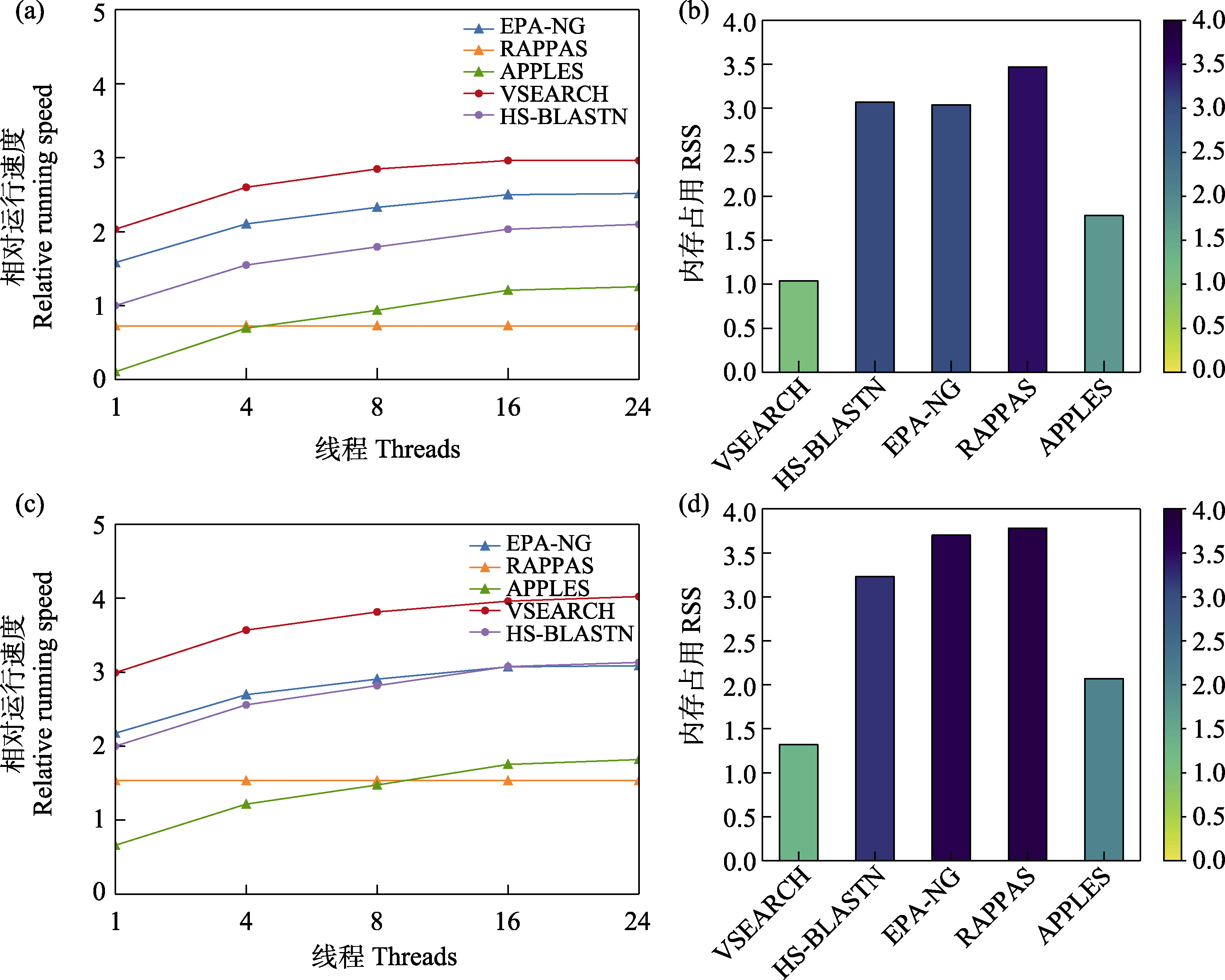
图4 5款分类预测软件在1,000量级(a, b)和5,000量级(c, d)参考数据库应用中的(相对)运行速度和内存占用
Fig. 4 Relative running speed and memory usage of five taxonomic assignment tools when applying reference databases with 1,000 sequences (a and b) and 5,000 sequences (c and d) respectively
| 分类预测软件 Tools | 推荐使用情况 Recommendation on application |
|---|---|
| EPA-NG | 以COI作为分子标记且参考数据库不大的场合 COI is used as the marker and the reference database is small |
| VSEARCH | 以16S或18S作为分子标记或者参考数据库较大的场合 16S/18S is used as the marker; the reference database includes thousands of sequences or more |
| HS-BLASTN | 同VSEARCH, 但优先级不如VSEARCH Similar to VSEARCH |
| APPLES | 仅预测较高阶元的场合 Predicting higher taxonomical hierarchy |
| RAPPAS | 目标序列间长度差异较大的场合 When sequence lengths differ greatly |
表2 5款分类预测软件的推荐使用情况
Table 2 The recommendation on application of five taxonomic assignment tools
| 分类预测软件 Tools | 推荐使用情况 Recommendation on application |
|---|---|
| EPA-NG | 以COI作为分子标记且参考数据库不大的场合 COI is used as the marker and the reference database is small |
| VSEARCH | 以16S或18S作为分子标记或者参考数据库较大的场合 16S/18S is used as the marker; the reference database includes thousands of sequences or more |
| HS-BLASTN | 同VSEARCH, 但优先级不如VSEARCH Similar to VSEARCH |
| APPLES | 仅预测较高阶元的场合 Predicting higher taxonomical hierarchy |
| RAPPAS | 目标序列间长度差异较大的场合 When sequence lengths differ greatly |
| [1] | Ahmed M, Back MA, Prior T, Karssen G, Lawson R, Adams I, Sapp M (2019) Metabarcoding of soil nematodes: The importance of taxonomic coverage and availability of reference sequences in choosing suitable marker(s). Metabarcoding and Metagenom, 3, e36408. |
| [2] |
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403-410.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Arribas P, Andújar C, Hopkins K, Shepherd M, Vogler AP (2016) Metabarcoding and mitochondrial metagenomics of endogean arthropods to unveil the mesofauna of the soil. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1071-1081.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Arribas P, Andújar C, Salces-Castellano A, Emerson BC, Vogler AP (2021) The limited spatial scale of dispersal in soil arthropods revealed with whole-community haplotype- level metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 30, 48-61.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Balaban M, Sarmashghi S, Mirarab S (2020) APPLES: Scalable distance-based phylogenetic placement with or without alignments. Systematic Biology, 69, 566-578.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Bálint M, Nowak C, Márton O, Pauls SU, Wittwer C, Aramayo JL, Schulze A, Chambert T, Cocchiararo B, Jansen M (2018) Accuracy, limitations and cost efficiency of eDNA-based community survey in tropical frogs. Molecular Ecology Resources, 18, 1415-1426.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Barbera P, Kozlov AM, Czech L, Morel B, Darriba D, Flouri T, Stamatakis A (2019) EPA-ng: Massively parallel evolutionary placement of genetic sequences. Systematic Biology, 68, 365-369.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bardgett RD,van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bazinet AL, Cummings MP (2012) A comparative evaluation of sequence classification programs. BMC Bioinformatics, 13, 92.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Berger SA, Krompass D, Stamatakis A (2011) Performance, accuracy, and web server for evolutionary placement of short sequence reads under maximum likelihood. Systematic Biology, 60, 291-302.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Berger SA, Stamatakis A (2011) Aligning short reads to reference alignments and trees. Bioinformatics, 27, 2068-2075.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Bik HM (2021) Just keep it simple? Benchmarking the accuracy of taxonomy assignment software in metabarcoding studies. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 2187-2189.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Bista I, Carvalho GR, Tang M, Walsh K, Zhou X, Hajibabaei M, Shokralla S, Seymour M, Bradley D, Liu SL, Christmas M, Creer S (2018) Performance of amplicon and shotgun sequencing for accurate biomass estimation in invertebrate community samples. Molecular Ecology Resources, 18, 1020-1034.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Bohmann K, Evans A, Gilbert MTP, Carvalho GR, Creer S, Knapp M, Yu DW,de Bruyn M (2014) Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 29, 358-367.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Brandt MI, Trouche B, Quintric L, Günther B, Wincker P, Poulain J, Arnaud-Haond S (2021) Bioinformatic pipelines combining denoising and clustering tools allow for more comprehensive prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 1904-1921.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Braukmann TWA, Ivanova NV, Prosser SWJ, Elbrecht V, Steinke D, Ratnasingham S, de Waard JR, Sones JE, Zakharov EV, Hebert PDN (2019) Metabarcoding a diverse arthropod mock community. Molecular Ecology Resources, 19, 711-727.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Cavaliere M, Angeles IB, Montresor M, Bucci C, Brocani L, Balassi E, Margiotta F, Francescangeli F, Bouchet VMP, Pawlowski J, Frontalini F (2021) Assessing the ecological quality status of the highly polluted Bagnoli area (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy) using foraminiferal eDNA metabarcoding. Science of the Total Environment, 790, 147871.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Chelkha M, Blanco-Pérez R, Bueno-Pallero FÁ, Amghar S, El Harti A, Campos-Herrera R (2020) Cutaneous excreta of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Haplotaxida: Lumbricidae) might hinder the biological control performance of entomopathogenic nematodes. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 141, 107691.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Chen Y, Ye WC, Zhang YD, Xu YS (2015) High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, 7762-7768.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Chesters D, Zheng WM, Zhu CD (2015) A DNA barcoding system integrating multigene sequence data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6, 930-937.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Chesters D, Zhu CD (2014) A protocol for species delineation of public DNA databases, applied to the Insecta. Systematic Biology, 63, 712-725.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Clarke LJ, Beard JM, Swadling KM, Deagle BE (2017) Effect of marker choice and thermal cycling protocol on zooplankton DNA metabarcoding studies. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 873-883.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Czech L, Barbera P, Stamatakis A (2020) Genesis and Gappa: Processing, analyzing and visualizing phylogenetic (placement) data. Bioinformatics, 36, 3263-3265.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Deagle BE, Jarman SN, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Taberlet P (2014) DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I marker: Not a perfect match. Biology Letters, 10, 20140562.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Decaëns T (2010) Macroecological patterns in soil communities. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 287-302.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Elbrecht V, Taberlet P, Dejean T, Valentini A, Usseglio- Polatera P, Beisel JN, Coissac E, Boyer F, Leese F (2016) Testing the potential of a ribosomal 16S marker for DNA metabarcoding of insects. PeerJ, 4, e1966. |
| [28] |
Fu SL (2007) A review and perspective on soil biodiversity research. Biodiversity Science, 15, 109-115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 傅声雷 (2007) 土壤生物多样性的研究概况与发展趋势. 生物多样性, 15, 109-115.]
DOI |
|
| [29] |
Fu SL (2018) Strengthening the research on soil fauna diversity and their ecological functions using novel technology and field experimental facility. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1031-1033. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[ 傅声雷 (2018) 利用新方法和野外实验平台加强土壤动物多样性及其生态功能的研究. 生物多样性, 26, 1031-1033.]
DOI |
|
| [30] | Gardner PP, Watson RJ, Morgan XC, Draper JL, Finn RD, Morales SE, Stott MB (2019) Identifying accurate metagenome and amplicon software via a meta-analysis of sequence to taxonomy benchmarking studies. PeerJ, 7, e6160. |
| [31] |
Gómez-Rodríguez C, Timmermans MJTN, Crampton-Platt A, Vogler AP (2017) Intraspecific genetic variation in complex assemblages from mitochondrial metagenomics: Comparison with DNA barcodes. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 248-256.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Gueuning M, Ganser D, Blaser S, Albrecht M, Knop E, Praz C, Frey JE (2019) Evaluating next-generation sequencing (NGS) methods for routine monitoring of wild bees: Metabarcoding, mitogenomics or NGS barcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 19, 847-862.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Hao JF, Zhang XH, Wang YS, Liu JL, Zhi YC, Li XJ (2017) Diversity investigation and application of DNA barcoding of Acridoidea from Baiyangdian Wetland. Biodiversity Science, 25, 409-417. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 郝金凤, 张晓红, 王昱淞, 刘金林, 智永超, 李新江 (2017) 白洋淀湿地蝗虫多样性调查及DNA条形码应用研究. 生物多样性, 25, 409-417.]
DOI |
|
| [34] |
Hardulak LA, Morinière J, Hausmann A, Hendrich L, Schmidt S, Doczkal D, Müller J, Hebert PDN, Haszprunar G (2020) DNA metabarcoding for biodiversity monitoring in a National Park: Screening for invasive and pest species. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20, 1542-1557.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S,de Waard JR (2003) Barcoding animal life:Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 270, S96-S99. |
| [36] |
Hleap JS, Littlefair JE, Steinke D, Hebert PDN, Cristescu ME (2021) Assessment of current taxonomic assignment strategies for metabarcoding eukaryotes. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 2190-2203.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Jackson JK, Battle JM, White BP, Pilgrim EM, Stein ED, Miller PE, Sweeney BW (2014) Cryptic biodiversity in streams: A comparison of macroinvertebrate communities based on morphological and DNA barcode identifications. Freshwater Science, 33, 312-324.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Ji YQ, Ashton L, Pedley SM, Edwards DP, Tang Y, Nakamura A, Kitching R, Dolman PM, Woodcock P, Edwards FA, Larsen TH, Hsu WW, Benedick S, Hamer KC, Wilcove DS, Bruce C, Wang XY, Levi T, Lott M, Emerson BC, Yu DW (2013) Reliable, verifiable and efficient monitoring of biodiversity via metabarcoding. Ecology Letters, 16, 1245-1257.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Kirse A, Bourlat SJ, Langen K, Fonseca VG (2021) Unearthing the potential of soil eDNA metabarcoding—Towards best practice advice for invertebrate biodiversity assessment. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 630560.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Lanzén A, Dahlgren TG, Bagi A, Hestetun JT (2021) Benthic eDNA metabarcoding provides accurate assessments of impact from oil extraction, and ecological insights. Ecological Indicators, 130, 108064.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Lavelle P, Decaëns T, Aubert M, Barot S, Blouin M, Bureau F, Margerie P, Mora P, Rossi JP (2006) Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. European Journal of Soil Biology, 42, S3-S15. |
| [42] |
Linard B, Swenson K, Pardi F (2019) Rapid alignment-free phylogenetic identification of metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics, 35, 3303-3312.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Liu LY, Cui HF, Tian G (2013) Application of high throughput sequencing in metagenomics. Chinese Medicinal Biotechnology, 8, 196-200. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘莉扬, 崔鸿飞, 田埂 (2013) 高通量测序技术在宏基因组学中的应用. 中国医药生物技术, 8, 196-200.] | |
| [44] |
Mathon L, Valentini A, Guérin PE, Normandeau E, Noel C, Lionnet C, Boulanger E, Thuiller W, Bernatchez L, Mouillot D, Dejean T, Manel S (2021) Benchmarking bioinformatic tools for fast and accurate eDNA metabarcoding species identification. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 2565-2579.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Murali A, Bhargava A, Wright ES (2018) IDTAXA: A novel approach for accurate taxonomic classification of microbiome sequences. Microbiome, 6, 140.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Oliverio AM, Gan HJ, Wickings K, Fierer N (2018) A DNA metabarcoding approach to characterize soil arthropod communities. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 125, 37-43.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Pan KW, Zhang L, Shao YH, Fu SL (2016) Thematic monitoring network of soil fauna diversity in China: Exploring the mystery of soils. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1234-1239. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 潘开文, 张林, 邵元虎, 傅声雷 (2016) 中国土壤动物多样性监测: 探知土壤中的奥秘. 生物多样性, 24, 1234-1239.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | Phillips HRP, Heintz-Buschart A, Eisenhauer N (2020) Putting soil invertebrate diversity on the map. Molecular Ecology, 29, 655-657. |
| [49] | Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP(2010) FastTree 2— Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE, 5, e9490. |
| [50] | Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN(2007) BOLD: The barcode of life data system (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 355-364. |
| [51] | Rodgers TW, Xu CCY, Giacalone J, Kapheim KM, Saltonstall K, Vargas M, Yu DW, Somervuo P, McMillan WO, Jansen PA (2017) Carrion fly-derived DNA metabarcoding is an effective tool for mammal surveys: Evidence from a known tropical mammal community. Molecular Ecology Resources, 17, e133-e145. |
| [52] | Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ, 4, e2584. |
| [53] |
Sales NG, Wangensteen OS, Carvalho DC, Deiner K, Præbel K, Coscia I, McDevitt AD, Mariani S (2021) Space-time dynamics in monitoring neotropical fish communities using eDNA metabarcoding. Science of the Total Environment, 754, 142096.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Shen W, Ren H (2021) TaxonKit: A practical and efficient NCBI taxonomy toolkit. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 48, 844-850.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Shi LL, Fu SL (2014) Review of soil biodiversity research: History, current status and future challenges. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 493-509. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 时雷雷, 傅声雷 (2014) 土壤生物多样性研究: 历史、现状与挑战. 科学通报, 59, 493-509.] | |
| [56] |
Stat M, Huggett MJ, Bernasconi R, DiBattista JD, Berry TE, Newman SJ, Harvey ES, Bunce M (2017) Ecosystem biomonitoring with eDNA: Metabarcoding across the tree of life in a tropical marine environment. Scientific Reports, 7, 12240.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Brochmann C, Willerslev E (2012) Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 21, 2045-2050.
DOI PMID |
| [58] |
Thakur MP, Phillips HRP, Brose U, de Vries FT, Lavelle P, Loreau M, Mathieu J, Mulder C, van der Putten WH, Rillig MC, Wardle DA, Bach EM, Bartz MLC, Bennett JM, Briones MJI, Brown G, Decaëns T, Eisenhauer N, Ferlian O, Guerra CA, König-Ries B, Orgiazzi A, Ramirez KS, Russell DJ, Rutgers M, Wall DH, Cameron EK (2020) Towards an integrative understanding of soil biodiversity. Biological Reviews, 95, 350-364.
DOI |
| [59] |
Torrell H, Cereto-Massagué A, Kazakova P, García L, Palacios H, Canela N (2021) Multiomic approach to analyze infant gut microbiota: Experimental and analytical method optimization. Biomolecules, 11, 999.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
van der Heyde M, Bunce M, Wardell-Johnson G, Fernandes K, White NE, Nevill P (2020) Testing multiple substrates for terrestrial biodiversity monitoring using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20, 732-745.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Wang WY, Srivathsan A, Foo M, Yamane SK, Meier R (2018) Sorting specimen-rich invertebrate samples with cost-effective NGS barcodes: Validating a reverse workflow for specimen processing. Molecular Ecology Resources, 18, 490-501.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Yang CX, Ji YQ, Wang XY, Yang CY, Yu DW (2013) Testing three pipelines for 18S rDNA-based metabarcoding of soil faunal diversity. Science China: Life Sciences, 56, 73-81.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Zhan LL (2013) Diversity and Influencing Factor of Meso-soil Animal Under Farm Land of Black Soil. PhD dissertation, Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 战丽莉 (2013) 农田黑土中小型土壤动物多样性特征及其影响因素. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所, 长春.] | |
| [64] | Zhang WW, Xie YW, Yang JH, Yang YN, Li D, Zhang Y, Yu HX, Zhang XW (2017) Applications and prospects of metabarcoding in environmental monitoring of phytoplankton community. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 12, 15-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张宛宛, 谢玉为, 杨江华, 杨雅楠, 李娣, 张咏, 于红霞, 张效伟 (2017) DNA宏条形码(metabarcoding)技术在浮游植物群落监测研究中的应用. 生态毒理学报, 12, 15-24.] | |
| [65] | Zhang ZD, Dong WH, Wei J, Gai YH (2012) Research progresses of soil fauna. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 28, 242-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张志丹, 董炜华, 魏健, 盖玉红 (2012) 土壤动物学研究进展. 中国农学通报, 28, 242-246.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()